Progress and Gaps in Research on Urban Green Space Morphology: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Regional Distribution of Studies
3.2. Frequency of Publications
3.3. Main Source Publications
3.4. Knowledge Frame and Research Category
3.5. Research Frontiers
3.5.1. Urban Green Space Planning
3.5.2. Urban Green Space Pattern and Urban Landscape Pattern
3.5.3. Strategies, Planning Management and Solutions for Sustainable Development of Urban Green Space
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swanwick, C.; Dunnett, N.; Woolley, H. Nature, role and value of green space in towns and cities: An overview. Built Environ. 2003, 29, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, M. Visualizing a field of research: A methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How to Use Cite Space. Available online: https://leanpub.com/howtousecitespace (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Turner, T. Greenways, blueways, skyways and other ways to a better London. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1995, 33, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.; Chen, S.S. Comprehensive greenspace planning based on landscape ecology principles in compact Nanjing city, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 65, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.R.; Manabe, T.; Ito, K.; Fujita, N.; Imanishi, A.; Hashimoto, D.; Iwasaki, A. Integrating ecological and cultural values toward conservation and utilization of shrine/temple forests as urban green space in Japanese cities. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 6, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.D.D.; Byrne, J. Informal urban greenspace: A typology and trilingual systematic review of its role for urban residents and trends in the literature. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, F.; Hu, Y.; James, P.; Xu, F.; Yu, L. Assessing growth scenarios for their landscape ecological security impact using the SLEUTH urban growth model. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2016, 142, 05015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosada, A.; Walerzak, M.; Urbański, P. Historical city parks in the wedge-ring system of urban green space in Poznań. Teka Kom. Urban. Archit. 2016, 44, 299–317. [Google Scholar]
- Tulisi, A. Urban green network design defining green network from an urban planning perspective. TeMA J. Land Use Mobil. Environ. 2017, 10, 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Badach, J.; Raszeja, E. Developing a framework for the implementation of landscape and greenspace indicators in sustainable urban planning. Waterfront landscape management: Case studies in Gdańsk, Poznań and Bristol. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Nakagoshi, N. Spatial-temporal gradient analysis of urban green spaces in Jinan, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Nakagoshi, N.; Yin, H.; Kikuchi, A. Spatial gradient analysis of urban green spaces combined with landscape metrics in Jinan city of China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2005, 15, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.-C. Spatial–temporal dynamics of urban green space in response to rapid urbanization and greening policies. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhao, X.L.; Du, H.Y.; Yang, D.Y.; Cai, Y.L. Analysis on landscape pattern of urban green space in Shanghai. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2017, 18, 788–801. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Da, L. Spatial characteristics of urban green space: A case study of Shanghai, China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 1799–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, W.; He, W. Planning of green space ecological network in urban areas: An example of Nanchang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12889–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Planning an ecological network of Xiamen Island (China) using landscape metrics and network analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serret, H.; Raymond, R.; Foltête, J.-C.; Clergeau, P.; Simon, L.; Machon, N. Potential contributions of green spaces at business sites to the ecological network in an urban agglomeration: The case of the Ile-de-France region, France. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 131, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, O.M.R. The green areas of San Juan, Puerto Rico. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; He, P. MSPA-based urban green infrastructure planning and management approach for urban sustainability: Case study of Longgang in China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2015, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J.S. A MSPA-based approach of urban green space system planning. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518, 5972–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, R.; Mahiny, A.S.; Khorasani, N. Assessment of changes in urban green spaces of Mashad city using satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2009, 11, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhu, J.; Gan, M. Dynamics of hierarchical urban green space patches and implications for management policy. Sensors 2017, 17, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.M.; Vu, T.T. A landscape ecological perspective of the impacts of urbanization on urban green spaces in the Klang Valley. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 85, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Xu, G.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B. Analyzing the impacts of urban expansion on green fragmentation using constraint gradient analysis. Prof. Geogr. 2017, 69, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Xie, S.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Yu, C. Urban green space fragmentation and urbanization: A spatiotemporal perspective. Forests 2019, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Han, L. Understanding the dynamic of greenspace in the urbanized area of Beijing based on high resolution satellite images. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Qian, Y.; Li, W.; Han, L. Quantifying and characterizing the dynamics of urban greenspace at the patch level: A new approach using object-based image analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Li, W.; Han, L. The rapid but “invisible” changes in urban greenspace: A comparative study of nine Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T. A review study of landscape metrics support to sustainable development of urban green spaces. In Proceedings of the 47th International Federation of Landscape Architects (IFLA) World Congress, Suzhou, China, 28–30 May 2010; Meng, Z.Z., Chen, X., Eds.; London Science Publishing Ltd.: London, UK, 2010; pp. 414–417. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Jim, C.; Tao, Y.; Shi, T. Landscape ecological assessment of green space fragmentation in Hong Kong. Urban For. Urban Green. 2011, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jim, C.; Wang, H. Assessing the landscape and ecological quality of urban green spaces in a compact city. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 121, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Q. Assessing urban green space distribution in a compact megacity by landscape metrics. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2017, 25, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolch, J.R.; Byrne, J.; Newell, J.P. Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: The challenge of making cities ‘just green enough’. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondermann, M. Planning culture as a system of meaning: A study using the example of cooperative green urban development in Düsseldorf, Germany. Spat. Res. Plan. 2017, 75, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Frantzeskaki, N. Seven lessons for planning nature-based solutions in cities. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; Armitage, R.P.; James, P. Appraisal of social-ecological innovation as an adaptive response by stakeholders to local conditions: Mapping stakeholder involvement in horticulture orientated green space management. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 18, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, M.; Armitage, R.P.; James, P. Social-ecological innovation: Adaptive responses to urban environmental conditions. Urban Ecosyst. 2016, 19, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, N.; Mahmoudi, D.; Simpson, M.; Santos, J.P. Socio-spatial differentiation in the Sustainable City: A mixed-methods assessment of residential gardens in metropolitan Portland, Oregon, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.Y.; Wang, J.; Sia, A. Perspectives on five decades of the urban greening of Singapore. Cities 2013, 32, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, C.; Dedekorkut-Howes, A.; Byrne, J. Factors shaping urban greenspace provision: A systematic review of the literature. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 178, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, I.; Soga, M.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Land sparing is crucial for urban ecosystem services. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 13, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Sustainable urban greening strategies for compact cities in developing and developed economies. Urban Ecosyst. 2013, 16, 741–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.; Chan, M.W. Urban greenspace delivery in Hong Kong: Spatial-institutional limitations and solutions. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 18, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgström, S.T.; Elmqvist, T.; Angelstam, P.; Alfsen-Norodom, C. Scale mismatches in management of urban landscapes. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmqvist, T.; Colding, J.; Barthel, S.; Borgström, S.; Duit, A.; Lundberg, J.; Andersson, E.; Ahrné, K.; Ernstson, H.; Folke, C.; et al. The dynamics of social-ecological systems in urban landscapes—Stockholm and the national urban park, Sweden. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1023, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middle, I.; Dzidic, P.; Buckley, A.; Bennett, D.; Tye, M.; Jones, R. Integrating community gardens into public parks: An innovative approach for providing ecosystem services in urban areas. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolini, F.; Massetti, L.; Sanesi, G.; Pearlmutter, D. Knowledge transfer between stakeholders in the field of urban forestry and green infrastructure: Results of a European survey. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artmann, M.; Inostroza, L.; Fan, P. Urban sprawl, compact urban development and green cities. How much do we know, how much do we agree? Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jim, C.; Tao, Y. Challenges and strategies for greening the compact city of Hong Kong. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2012, 138, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltynowski, M.; Kronenberg, J.; Bergier, T.; Kabisch, N.; Łaszkiewicz, E.; Strohbach, M.W. Challenges of urban green space management in the face of using inadequate data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 31, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Cirella, G.T. Modern compact cities: How much greenery do we need? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Jiang, P. Assessing Impacts of urban form on landscape structure of urban green spaces in China using Landsat images based on google earth engine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, J.; Hu, Y. Influence of three types of boundary on the level of greenspace in cities. Procedia Eng. 2017, 198, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-S.; Chen, T.-L. Decision making on allocating urban green spaces based upon spatially-varying relationships between urban green spaces and urban compaction degree. Sustainability 2015, 7, 13399–13415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-S.; Chen, T.-L. Explore energy consumption feature of urban spatial pattern and open green space. DEStech Trans. Environ. Energy Earth Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, K.; Kumar, P.; Pathan, S.; Sharma, K. Urban Neighborhood Green Index—A measure of green spaces in urban areas. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Jancso, T.; Vatseva, R. An effective Building Neighborhood Green Index model for measuring urban green space. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecká, M.; Szatmári, D.; Rosina, K. Analysis of urban green spaces based on Sentinel-2A: Case studies from Slovakia. Land 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, I.; Mathey, J.; Rößler, S.; Bräuer, A.; Goldberg, V. Urban vegetation structure types as a methodological approach for identifying ecosystem services—Application to the analysis of micro-climatic effects. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 42, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribadi, D.O.; Xu, C. Optimizing ecosystem services of urban green spaces based on integer programming approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Smart Cities, Automation & Intelligent Computing Systems (ICON-SONICS), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 8–10 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Hayek, U.W.; Neuenschwander, N.; Halatsch, J.; Regamey, A.R. Procedural modeling of urban green space pattern designs taking into account ecological parameters. In ECAADE 2010: Future Cities, Proceedings of the 28th Conference on Education in Computer Aided Architectural Design in Europe, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–18 September 2010; Schmitt, G., Hovestad, L., VanGool, L., Bosche, F., Burkhard, R., Coleman, S., Halatsch, J., Hansmeyer, M., Konsorski Lang, S., Kunze, A., et al., Eds.; ECAADE-Education & Research Computer Aided Architectural Design Europe: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; pp. 339–347. [Google Scholar]
- Neuenschwander, N.; Hayek, U.W.; Regamey, A.G. Integrating an urban green space typology into procedural 3D visualization for collaborative planning. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 48, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Qiu, J.X.; Breuste, J.; Friedman, C.R.; Zhou, W.Q.; Wang, X.K. Variations of urban greenness across urban structural units in Beijing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2013, 12, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tao, L.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Ye, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y. Spatial pattern of urban green spaces in a long-term compact urbanization process—A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Z.; Ali, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, X.; Li, R. Mapping the changes in urban greenness based on localized spatial association analysis under temporal context using MODIS Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleit, S.; Ennos, R.; Golding, Y. Modeling the environmental impacts of urban land use and land cover change—A study in Merseyside, UK. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 71, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikuzani, Y.U.; Kouagou, R.S.; Maréchal, J.; Ilunga, E.I.W.; Malaisse, F.; Bogaert, J.; Kankumbi, F.M. Changes in the spatial pattern and ecological functionalities of green spaces in Lubumbashi (the Democratic Republic of Congo) in relation with the degree of urbanization. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2018, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. A spatio-temporal study of fringe belts and urban green spaces in Birmingham, UK. Urban Morphol. 2019, 23, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehand, J.W.R. Green space in urban morphology: A historico-geographical approach. Urban Morphol. 2019, 23, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
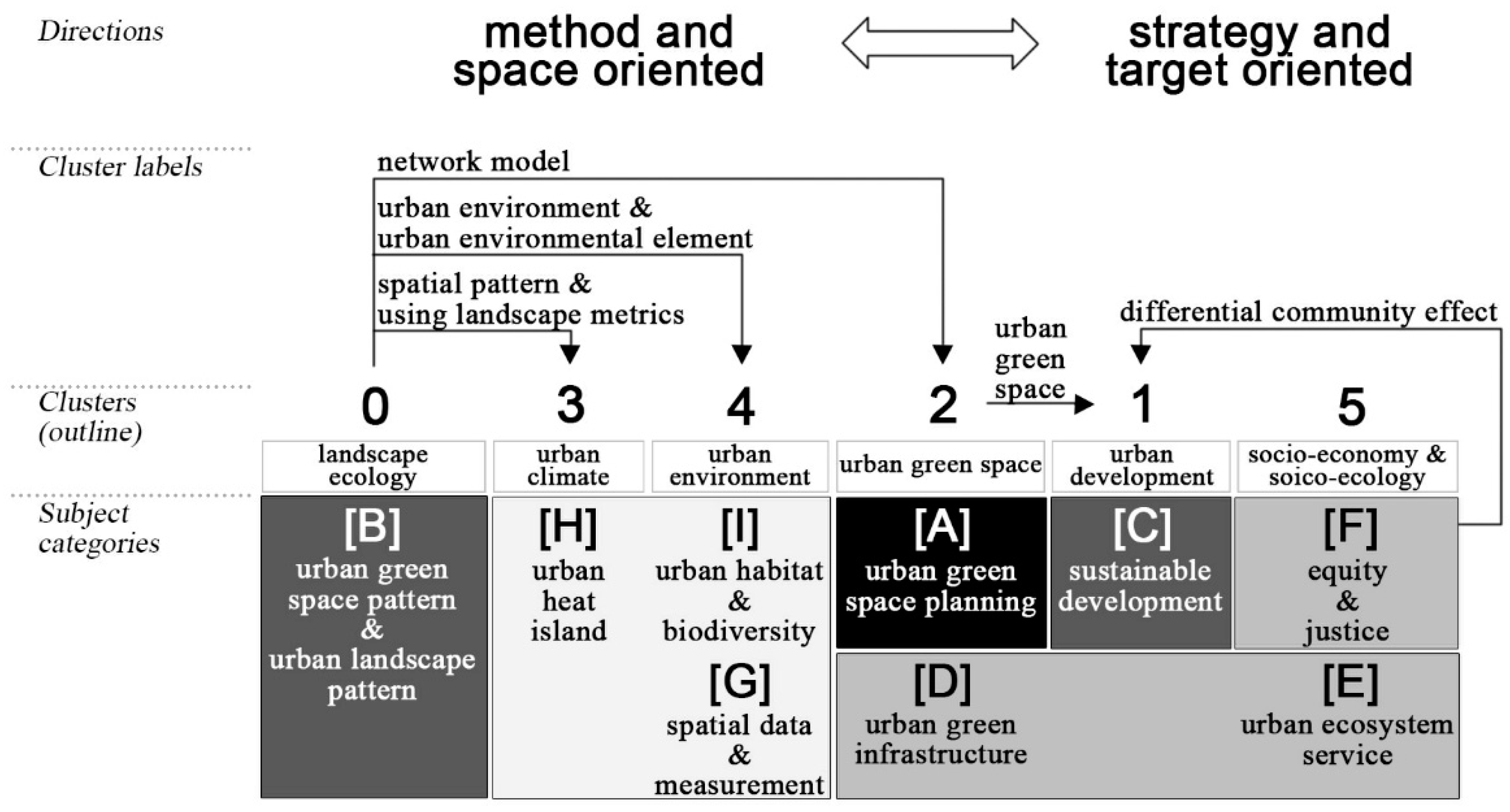
| Clusters | Size | Silhouette | Extracted Cluster Labels from Keywords Based on LLR Algorithm (1.0 × 10−4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20 | 0.889 | spatial-temporal gradient analysis (169.28); Xiamen island (161.75); using landscape metrics (152.92); network model (148.60); urban environmental element (136.46); residential housing price (136.46) |
| 1 | 20 | 0.69 | compact city (201.21); Hong Kong (192.12); differential community effect (134.86); compact cities (118.45); sustainable urban greening strategies (118.45); urban green space (118.37) |
| 2 | 36 | 0.62 | urban green space (409.43); urban greenspace (397.97); urban agriculture (387.92); Chinese cities (276.55); comparative study (276.55) |
| 3 | 34 | 0.923 | spatial pattern (311.98); land surface temperature (301.77); urbanized Beijing metropolitan area (166.1); urban heat island pattern (158.66); anisotropic cooling distance (150.02) |
| 4 | 20 | 0.744 | biodiversity conservation (102.32); urban environment (102.32); street tree (94.36); aerial photograph (68.76); high spatial resolution (68.76); urban residential landscape (68.76); mapping land cover (68.76) |
| 5 | 32 | 0.755 | socio-economic inequalities (140.58); private land (140.58); carbon storage (133.14); urban tree stock (124.50); socio-ecological exploration (108.35) |
| Clusters | Subject Categories | Sum of Studies |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | (A) The Study of Urban Green Space Planning: urban greenway, urban green belt, urban green wedge, urban green space system and urban green/ecological network | 18 |
| 0 | (B) The Study of Urban Green Space Pattern and Urban Landscape Pattern | 32 |
| 1 | (C) The Study of Sustainable Development of Urban Green Space: strategies, planning management and solutions for sustainable development of urban green space | 26 |
| 2 | (D) The Study of Urban Green Infrastructure: urban green infrastructure, urban forest and urban agriculture | 14 |
| 5 | (E) The Study of Urban Ecosystem Service: the theories and strategies of urban ecosystem service, and its supporting service and regulating service (including pollination, air purification, climate regulation, runoff regulation, storm resistance and noise regulation) | 30 |
| 5 | (F) The Study of Equity and Justice of Urban Green Space: environmental equity and justice in urban social economy are reflected by measuring accessibility, availability, visiting fluxes and population exposure | 60 |
| 4 | (G) The Study of Spatial Data and Measurement of Urban Green Space: geoinformatics measurement and spatial data effects | 16 |
| 3 | (H) The Study of Urban Heat Island: urban thermal environment and urban heat island related to urban green space | 40 |
| 4 | (I) The Study of Urban Habitat and Biodiversity: relationships between the anthropogenic activities and urban biodiversity in the urban habitat are investigated, through the analysis of green space connectivity, internal species abundance/richness, species distribution, and plant community | 48 |
| — | (J) Other Related Studies | 20 |
| Types | China a | Asia (Except China) b | Europe c | America d | Oceania e | Africa f | Sum | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 18 | 5.9 |
| B | 23 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 32 | 10.5 |
| C | 5 | 3 | 12 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 26 | 8.5 |
| D | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 4.6 |
| E | 14 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 9.9 |
| F | 15 | 5 | 25 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 60 | 19.7 |
| G | 7 | 0 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 16 | 5.3 |
| H | 28 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 13.2 |
| I | 7 | 3 | 18 | 12 | 6 | 2 | 48 | 15.8 |
| J | 9 | 1 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 20 | 6.6 |
| Sum | 122 | 27 | 95 | 42 | 14 | 4 | 304 | 100.0 |
| Percentage | 40.1 | 8.9 | 31.3 | 13.8 | 4.6 | 1.3 | 100.0 | -- |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 42 |
| 2018 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 46 |
| 2017 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 11 | 3 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 48 |
| 2016 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 29 |
| 2015 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 32 |
| 2014 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 27 |
| 2013 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 15 |
| 2012 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 12 |
| 2011 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
| 2010 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 11 |
| 2009 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| 2008 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| 2007 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 2006 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 2005 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| 2004 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 2003 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 2002 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 2000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1995 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sum | 18 | 32 | 26 | 14 | 30 | 60 | 16 | 40 | 48 | 20 | 304 |
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landscape and Urban Planning | 2 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 13 | 3 | 47 |
| Urban Forestry & Urban Greening | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 1 | 29 |
| Sustainability | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 14 |
| Urban Ecosystems | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 11 |
| Ecological Indicators | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 8 |
| Journal of Urban Planning and Development | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
| Landscape Ecology | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 6 |
| International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| PLoS One | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| Morphological Levels | Methods Used * | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | FG | GDA | GIS | GTM | LM | LS | MSA | MSPA | O | R | RS | SI | SS | |
| D | 3 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
| FS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| FR | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| P | 1 | 0 | 12 | 17 | 3 | 17 | 0 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 0 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, H.; Wang, X. Progress and Gaps in Research on Urban Green Space Morphology: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031202
Zou H, Wang X. Progress and Gaps in Research on Urban Green Space Morphology: A Review. Sustainability. 2021; 13(3):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031202
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Hao, and Xiaojun Wang. 2021. "Progress and Gaps in Research on Urban Green Space Morphology: A Review" Sustainability 13, no. 3: 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031202
APA StyleZou, H., & Wang, X. (2021). Progress and Gaps in Research on Urban Green Space Morphology: A Review. Sustainability, 13(3), 1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031202






