Effect of Biofertilizer in Organic and Conventional Systems on Growth, Yield and Baking Quality of Hard Red Winter Wheat
Abstract
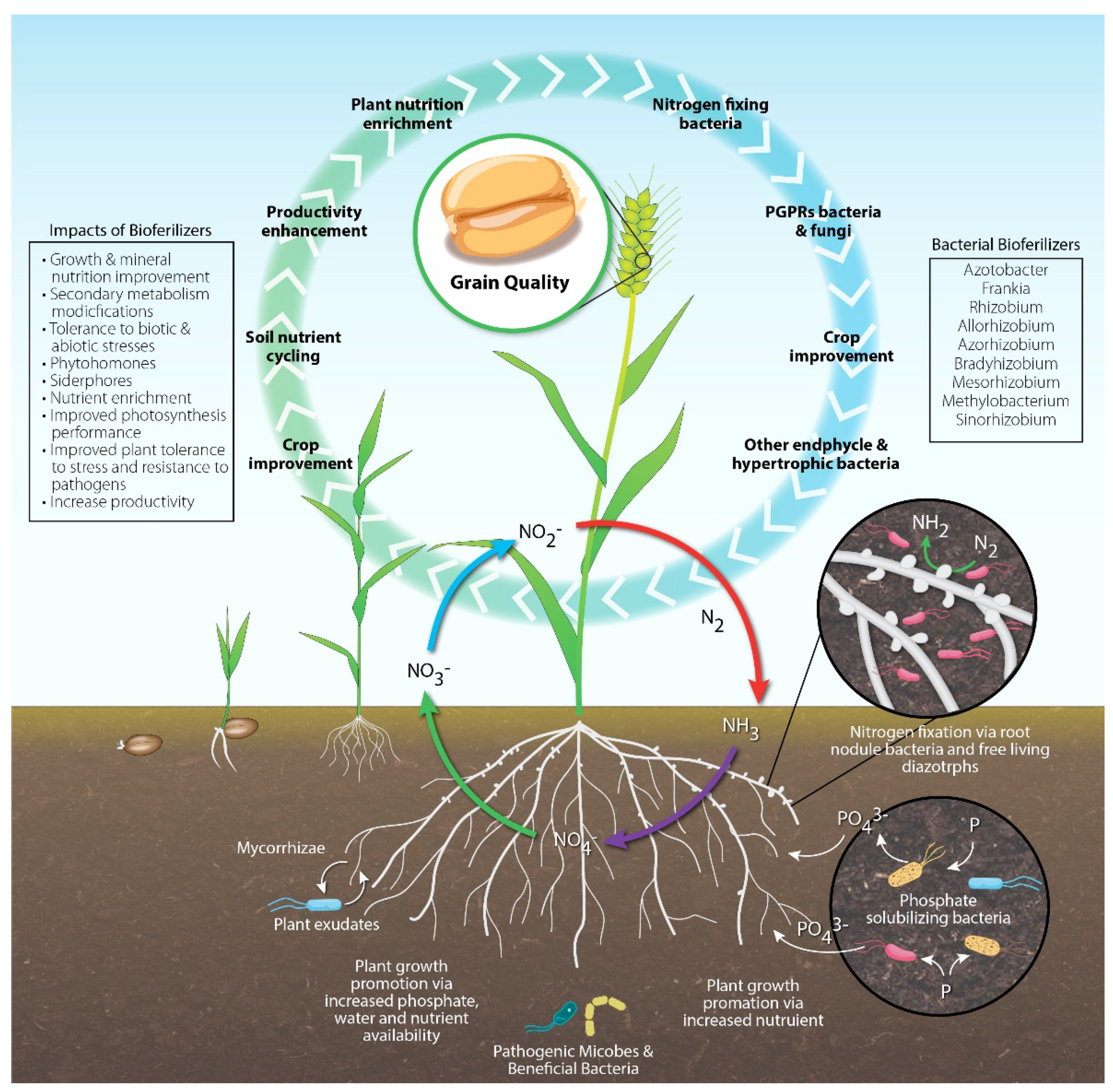
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Experimental Design and Management
3. Results
3.1. Plant Height
3.2. Yield Traits
3.3. Baking Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Farming System Affects Grain Yield and Baking Quality
4.2. Increased Nitrogen Rates Improve Yield and Baking Quality Traits
4.3. Biofertilizers Had Little Effect on Yield and Baking Quality Traits
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Plant Height (cm) | Yield (kg/ha) | TKW † (g) | Protein Content % | SRC ‡ % | SV ¥ (mL) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source of Variance | DF | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | ||||||
| Year | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | |
| N Rate | 2 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.091 ns | ≤0.0001 | 0.5517 ns | 0.2773 ns | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.3884 ns | ≤0.0001 | 0.0011 | 0.0025 |
| System | 1 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.062 ns | 0.0169 | 0.0341 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.0075 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.3601 ns |
| Spray | 2 | 0.0086 | 0.0200 | 0.0005 | 0.1861 ns | 0.1251 ns | 0.0046 | 0.0918 ns | 0.4700 ns | 0.7804 ns | 0.2298 ns | 0.0083 | 0.8719 ns |
| N Rate * System | 2 | 0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.3075 ns | 0.0104 | 0.3553 ns | 0.2773 ns | 0.0020 | 0.6873 ns | 0.4763 ns | 0.1315 ns | 0.3856 ns | 0.6164 ns |
| N Rate * Spray | 4 | 0.1805 ns | 0.2280 ns | 0.1889 ns | 0.5652 ns | 0.2959 ns | 0.0751 ns | 0.9026 ns | 0.6873 ns | 0.6846 ns | 0.6366 ns | 0.1390 ns | 0.5489 ns |
| System * Spray | 2 | 0.0371 | 0.0790 ns | ≤0.0001 | 0.2945 ns | 0.7664 ns | 0.3676 ns | 0.1331 ns | 0.1020 ns | 0.8700 ns | 0.0942 ns | 0.2319 ns | 0.2150 ns |
| N Rate * System * Spray | 4 | 0.5180 ns | 0.5820 ns | 0.4102 ns | 0.4670 ns | 0.7697 ns | 0.3231 ns | 0.4419 ns | 0.4388 ns | 0.7187 ns | 0.5988 ns | 0.8026 ns | 0.2968 ns |
References
- Plains Grains, I. Hard Red Winter Wheat, 2019 Regional Quality Survey. Available online: https://www.plainsgrains.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/Plains-Grains-2019-Winter-Wheat-Report-Web.pdf (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- USDA-NASS. Small Grains 2020 Summary; USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- May, L.; Van Sanford, D.; Finney, P. Soft wheat milling and baking quality in a soft red winter x hard red winter wheat population. Cereal Chem. 1989, 66, 378–381. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Herbek, J. A Comprehensive Guide to Wheat Management in Kentucky; University of Kentucky, College of Agriculture: Lexington, KY, USA, 2009; pp. 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, G.R.; Edwards, N.M. Criteria of wheat and flour quality. In Wheat: Chemistry and Technology, 4th ed.; Khan, K., Peter, R., Shewry, P.R., Eds.; Cereals & Grains Association: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2009; pp. 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, A. Managing Cover Crops Profitably; Diane Publishing: Collingdale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hills, K.M.; Goldberger, J.R.; Jones, S.S. Commercial Bakers’ View on the Meaning of “Local” Wheat and Flour in Western Washington State. J. Agric. Food Syst. Community Dev. 2013, 3, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, F. Introduction to Nitrogen Management in Agricultural Systems; Technical report: IAEA-TCS-29/CD; International Atomic Energy Agency: Seibersdorf, Austria, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, R.K.; Bhardwaj, D.; Tuteja, N. Biofertilizers: A sustainable eco-friendly agricultural approach to crop improvement. In Plant Acclimation to Environmental Stress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 403–432. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, K.; Singh, A. Realizing the potential of a low-cost technology to enhance crop yields: Evidence from a meta-analysis of biofertilizers in India. Agric. Econ. Res. Rev. 2019, 32, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, R.; Peukert, M.; Succurro, A.; Koprivova, A.; Kopriva, S. The role of soil microorganisms in plant mineral nutrition—Current knowledge and future directions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, B.; Joe, M.M.; Jaleel, C.A.; Deiveekasundaram, M. Effect of root inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on plant growth, alkaloid content and nutrient control of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Nat. Croat. 2010, 19, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M.; Hassani, D.; Bilal, M.; Asad, F.; Huang, D. Influence of bio-fertilizer containing beneficial fungi and rhizospheric bacteria on health promoting compounds and antioxidant activity of Spinacia oleracea L. Bot. Stud. 2017, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taie, H.A.; El-Mergawi, R.; Radwan, S. Isoflavonoids, flavonoids, phenolic acids profiles and antioxidant activity of soybean seeds as affected by organic and bioorganic fertilization. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2008, 4, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Cortivo, C.; Ferrari, M.; Visioli, G.; Lauro, M.; Fornasier, F.; Barion, G.; Panozzo, A.; Vamerali, T. Effects of seed-applied biofertilizers on rhizosphere biodiversity and growth of common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Ansari, M.W.; Sahoo, R.K.; Tuteja, N. Biofertilizers function as key player in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility, plant tolerance and crop productivity. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Large, E.C. Growth stages in cereals illustration of the Feekes scale. Plant Pathol. 1954, 3, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U. Growth Stages of Mono-And Dicotyledonous Plants; Blackwell Wissenschafts-Verlag: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. National Organic Program. Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/NOP%20Preamble%20Full%20Version.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2021).
- Hrušková, M.; Škodová, V.; Blažek, J. Wheat sedimentation values and falling number. Czech J. Food Sci. 2004, 22, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, J.; Quick, J. A modified screening test for rapid estimation of gluten strength in early-generation durum wheat breeding lines. Cereal Chem. 1983, 60, 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Teferra, T.F. Laboratory Manual for Engineering Properties of Foods; Hawassa University: Awassa, Ethiopia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kobua, C.K.; Jou, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-M. Advantages of Amending Chemical Fertilizer with Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria under Alternate Wetting Drying Rice Cultivation. Agriculture 2021, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, M.J.; Tubeileh, A.; Goorahoo, D. A review of the use of organic amendments and the risk to human health. Adv. Agron. 2013, 120, 275–379. [Google Scholar]
- Koutroubas, S.D.; Antoniadis, V.; Damalas, C.A.; Fotiadis, S. Effect of organic manure on wheat grain yield, nutrient accumulation, and translocation. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.; Jeuffroy, M.-H.; Henning, J.; Meynard, J.-M. Yield variation in organic winter wheat: A diagnostic study in the Southeast of France. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2005, 25, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mäder, P.; Hahn, D.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Alföldi, T.; Bergmann, H.; Oehme, M.; Amadò, R.; Schneider, H.; Graf, U. Wheat quality in organic and conventional farming: Results of a 21 year field experiment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammed, A.M.; Ozsisli, B.; Ohm, J.B.; Simsek, S. Relationship between solvent retention capacity and protein molecular weight distribution, quality characteristics, and breadmaking functionality of hard red spring wheat flour. Cereal Chem. 2015, 92, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Park, S.H.; Chung, O.; Caley, M.; Seib, P. Solvent retention capacity values in relation to hard winter wheat and flour properties and straight-dough breadmaking quality. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghagholizadeh, R.; Kadivar, M.; Nazari, M.; Ahmadi, H.; Azizi, M.H. Capability of solvent retention capacity to quality of flat bread in three wheat cultivars. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabourn, B.W.; Xiao, Z.S.; Tilley, M.; Herald, T.J.; Park, S.H. A Rapid, Small-Scale Sedimentation Method to Predict Breadmaking Quality of Hard Winter Wheat. Crop. Sci. 2012, 52, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceseviciene, J.; Slepetiene, A.; Leistrumaite, A.; Ruzgas, V.; Slepetys, J. Effects of organic and conventional production systems and cultivars on the technological properties of winter wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, K.; March, P.; Tipples, K. An assessment of the SDS-sedimentation test for the prediction of Canadian bread wheat quality. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1982, 62, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M.; Smith, D.; Fregeau-Reid, J. Evaluation of the SDS-sedimentation test for the assessment of eastern Canadian bread wheat quality. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1993, 73, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, R.; Jobet, C.; Undurraga, P. Effects of nitrogen on productivity, grain quality, and optimal nitrogen rates in winter wheat cv. Kumpa-INIA in Andisols of Southern Chile. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 70, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.; Lighthiser, E.; Jones, C.; Holmes, J.; Rick, T.; Wraith, J. Pea green manure management affects organic winter wheat yield and quality in semiarid Montana. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2011, 91, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, E.B.; Darby, H. In-season nitrogen effects on organic hard red winter wheat yield and quality. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, X. Effects of Nitrogen Application in the Wheat Booting Stage on Glutenin Polymerization and Structural–Thermal Properties of Gluten with Variations in HMW-GS at the Glu-D1 Locus. Foods 2020, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Rabara, R.; Negi, S. Towards a better greener future-an alternative strategy using biofertilizers. I: Plant growth promoting bacteria. Plant Gene 2017, 12, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igiehon, N.O.; Babalola, O.O. Biofertilizers and sustainable agriculture: Exploring arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 4871–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, B.; Singh, J. A review: Usage of biofertilizer in cereal crops. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, T.; López-Fando, C.; Ellmer, F. Abundance and biodiversity of soil microarthropods as influenced by different types of organic manure in a long-term field experiment in Central Spain. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2006, 33, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, A.; Bajwa, R.; Anjum, T. Effect of heat-sterilization and EM (effective microorganisms) application on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in organic-amended sandy loam soil. Cereal Res. Commun. 2008, 36, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, D.; Razdan, R. Growth, nutrient uptake and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum) as influenced by biofertilizers and nitrogen. Indian J. Agron. 2006, 51, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Chaudhary, F.; Patel, D. Effectiveness of Azotobacter bio-inoculant for wheat grown under dryland condition. J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 34, 927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Treatments | System | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORG | CONV | ||||
| Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | ||
| EM Spray | No spray | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| One Spray | 24 October 2018 | 3 November 2019 | 24 October 2018 | 3 November 2019 | |
| Two Sprays | 24 October 2018 and 23 March 2019 | 3 November 2019 and 8 March 2020 | 24 October 2018 and 23 March 2019 | 3 November 2019 and 8 March 2020 | |
| Nitrogen applications | 5 October 2018, 12 March 2019 and 10 April 2019 | 18 October 2019, 7 March 2020 and 6 April 2020 | 12 March 2019, 10 April 2019 and 2 May 2019 | 7 March 2020, 6 April 2020 and 20 April 2020 | |
| System | Rate | Mean Plant Height (cm) | Mean Yield (kg/ha) | Mean Protein Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | Y2 | Y2 | Y1 | ||
| CONV | High N | 101.18 a | 93.56 a | 4794.05 b | 12.88 a |
| CONV | Med N | 100.54 a | 92.92 a | 4500.72 bcd | 11.96 b |
| CONV | Low N | 99.91 a | 92.29 a | 4083.64 cd | 11.05 c |
| ORG | High N | 100.33 a | 92.49 a | 5512.83 a | 10.54 cd |
| ORG | Med N | 96.73 b | 89.11 b | 4623.69 bc | 10.19 de |
| ORG | Low N | 93.34 c | 85.51 c | 4022.61 d | 9.85 e |
| Main Effect | Plant Height (cm) | TKW (g) | Yield (kg/ha) | Protein Content (%) | SRC (%) | SV (mL) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | ||||||||
| Year | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | Y1 | Y2 | |
| System | CONV | 100.54 a | 92.92 a | 43.13 b | 48.25 b | 5950.24 | 4459.47 b | 11.96 a | 13.47 a | 89.79 a | 107.83 a | 9.39 a | 10.67 |
| ORG | 96.80 b | 89.04 b | 44.11 a | 49.44 a | 5642.74 | 4719.71 a | 10.19 b | 12.35 b | 87.89 b | 104.83 b | 7.76 b | 10.43 | |
| p-Value | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.0341 | ≤0.0001 | 0.062 | 0.0169 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.0075 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.36 | |
| Rate | Low N | 96.63 c | 88.90 c | 43.64 | 48.62 | 5586.99 | 4053.13 c | 10.45 c | 12.14 c | 89.58 | 103.25 c | 7.88 b | 10.01 b |
| Med N | 98.64 b | 91.07 b | 43.87 | 48.91 | 5954.18 | 4562.20 b | 11.07 b | 12.99 b | 88.27 | 106.17 b | 8.63 ab | 10.79 a | |
| High N | 100.75 a | 93.03 a | 43.35 | 49.00 | 5848.28 | 5153.44 a | 11.71 a | 13.59 a | 88.65 | 109.58 a | 9.22 a | 10.86 a | |
| p-Value | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.55 | 0.27 | 0.091 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | 0.38 | ≤0.0001 | 0.0011 | 0.0025 | |
| Spray | No spray | 97.37 b | 89.75 b | 44.13 | 48.79 ab | 6183.05 a | 4505.70 | 11.03 | 12.99 | 88.52 | 106.71 | 8.21 b | 10.48 |
| 1 spray | 98.53 ab | 90.91 ab | 43.71 | 49.29 a | 5910.55 a | 4727.57 | 10.96 | 12.84 | 88.95 | 105.98 | 8.17 b | 10.53 | |
| 2 sprays | 100.12 a | 92.29 a | 43.01 | 48.46 b | 5295.85 b | 4535.50 | 11.23 | 12.88 | 89.04 | 106.31 | 9.35 a | 10.64 | |
| p-Value | 0.0086 | 0.0200 | 0.12 | 0.0046 | 0.0005 | 0.18 | 0.091 | 0.47 | 0.78 | 0.22 | 0.0083 | 0.87 | |
| System | Spray | Mean Plant Height (cm) | Mean Yield (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CONV | No spray | 100.12 a | 7021.08 a |
| CONV | 1 spray | 100.75 a | 5848.21 b |
| CONV | 2 sprays | 100.75 a | 4981.42 c |
| ORG | No spray | 94.61 c | 5345.03 bc |
| ORG | 1 spray | 96.31 bc | 5972.90 b |
| ORG | 2 sprays | 99.48 ab | 5610.29 bc |
| System | Rate | Spray | Loaf wt (g) | Loaf ht (cm) | Loaf Vol (cc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORG | Low N | No spray | 257 | 76.88 | 600 |
| ORG | Low N | 2 sprays | 254 | 75.8 | 610 |
| ORG | High N | No spray | 263 | 76.97 | 610 |
| ORG | High N | 2 sprays | 261 | 75.78 | 595 |
| CONV | Low N | No spray | 259 | 73.5 | 600 |
| CONV | Low N | 2 sprays | 255 | 75.18 | 630 |
| CONV | High N | No spray | 259 | 79.94 | 620 |
| CONV | High N | 2 sprays | 254 | 77.91 | 625 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Zubade, A.; Phillips, T.; Williams, M.A.; Jacobsen, K.; Van Sanford, D. Effect of Biofertilizer in Organic and Conventional Systems on Growth, Yield and Baking Quality of Hard Red Winter Wheat. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413861
Al-Zubade A, Phillips T, Williams MA, Jacobsen K, Van Sanford D. Effect of Biofertilizer in Organic and Conventional Systems on Growth, Yield and Baking Quality of Hard Red Winter Wheat. Sustainability. 2021; 13(24):13861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413861
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Zubade, Ammar, Timothy Phillips, Mark A. Williams, Krista Jacobsen, and David Van Sanford. 2021. "Effect of Biofertilizer in Organic and Conventional Systems on Growth, Yield and Baking Quality of Hard Red Winter Wheat" Sustainability 13, no. 24: 13861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413861
APA StyleAl-Zubade, A., Phillips, T., Williams, M. A., Jacobsen, K., & Van Sanford, D. (2021). Effect of Biofertilizer in Organic and Conventional Systems on Growth, Yield and Baking Quality of Hard Red Winter Wheat. Sustainability, 13(24), 13861. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413861







