Enhancing the Method of Decentralized Multi-Purpose Reuse of Wastewater in Urban Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
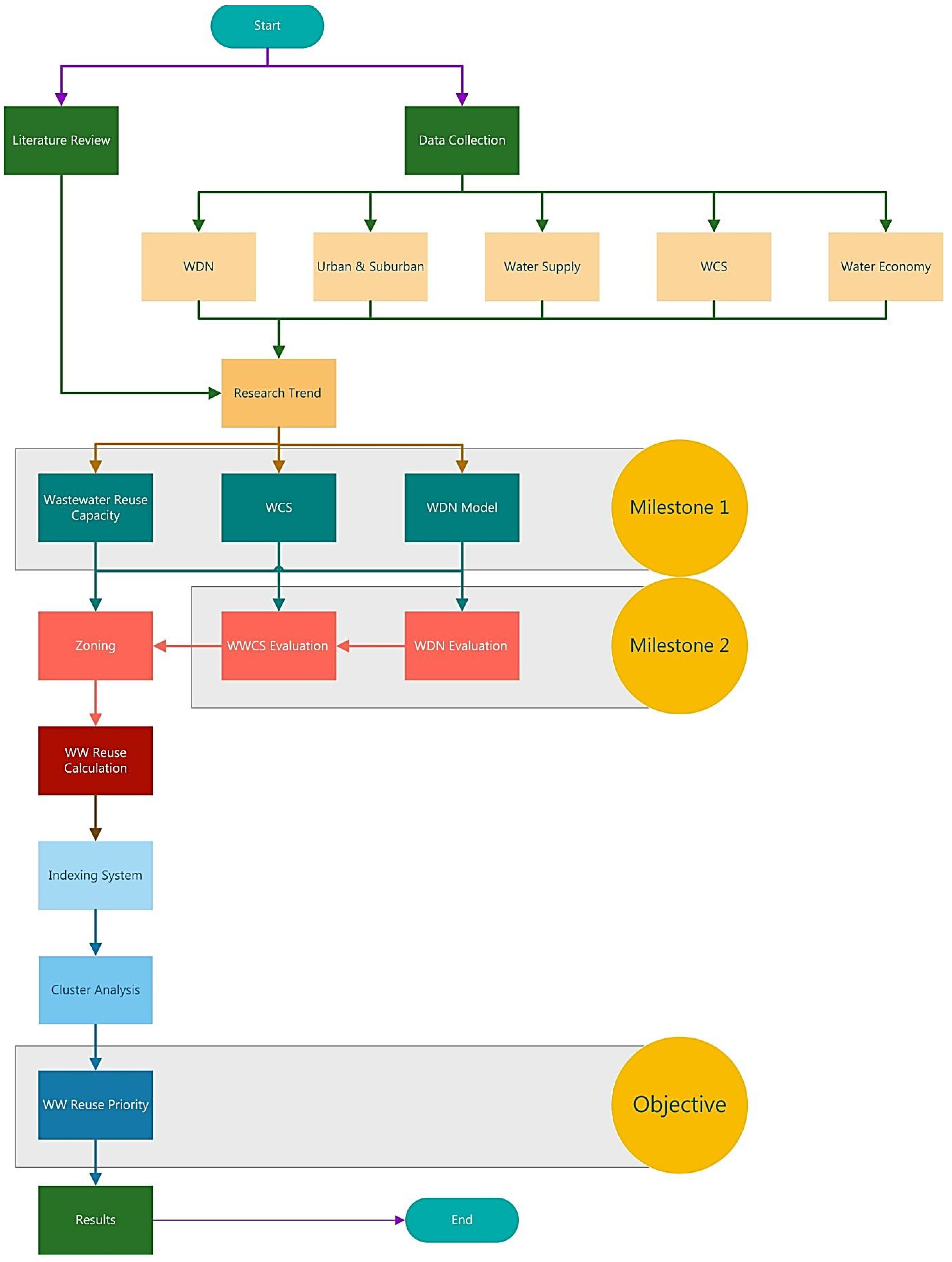
3. Materials and Methods
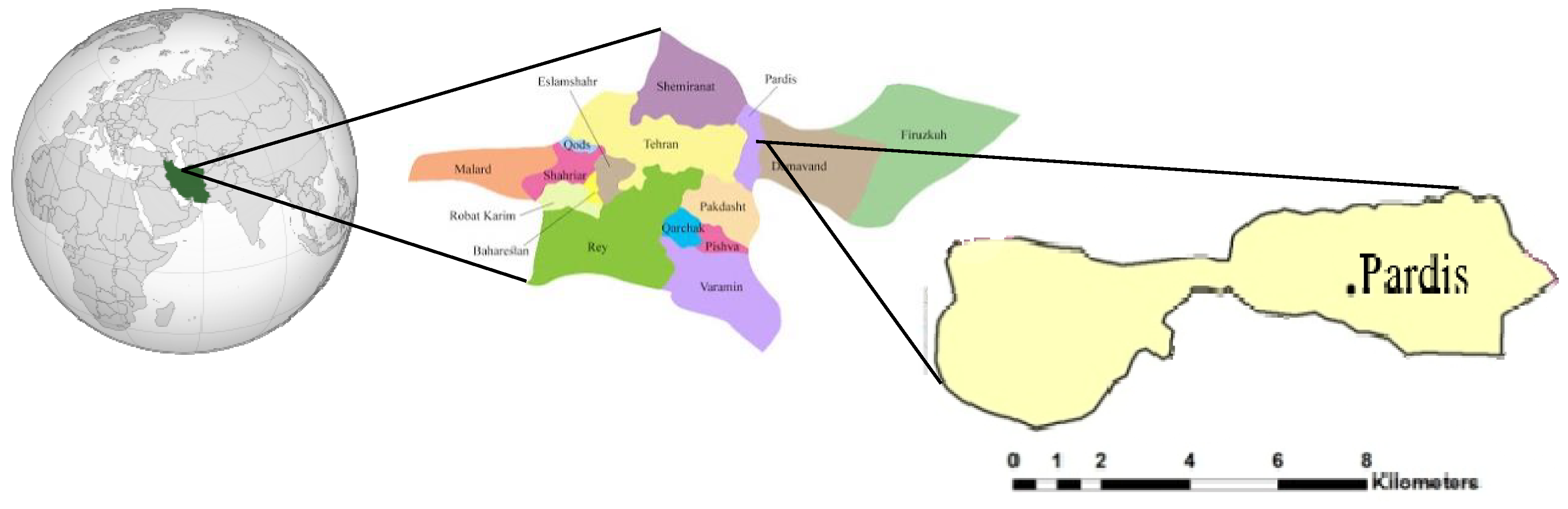
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Dataset Preparation
3.3. Allocating the Potential of Wastewater Reuse According to the Type of Use, Volume and Costs of Wastewater Treatment in a Centralized and Decentralized Manner
3.3.1. Cost Components and Processing per Unit Volume of Wastewater Effluent
3.3.2. Indexing Development
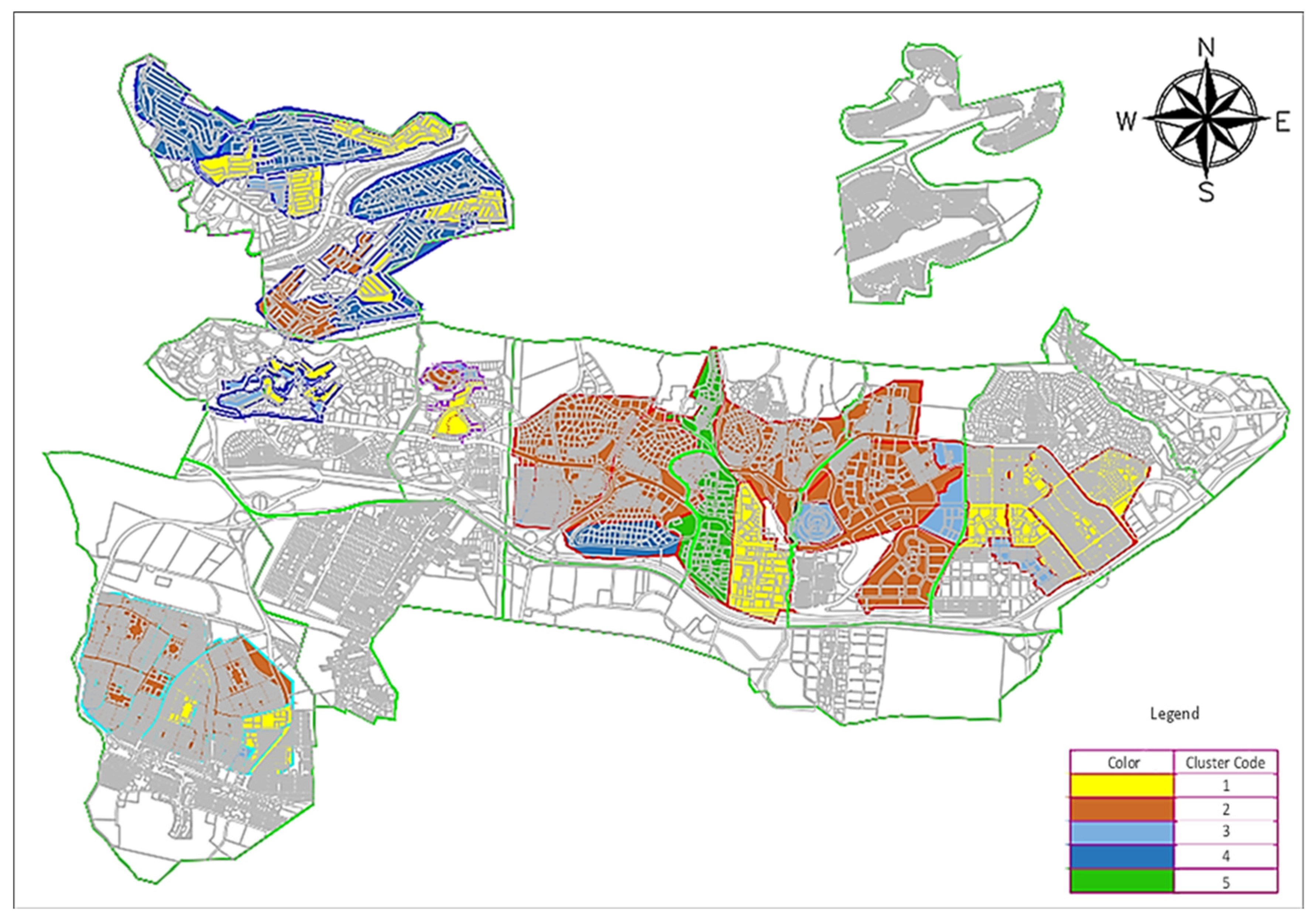
3.3.3. Integration and Cluster Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Data Processing
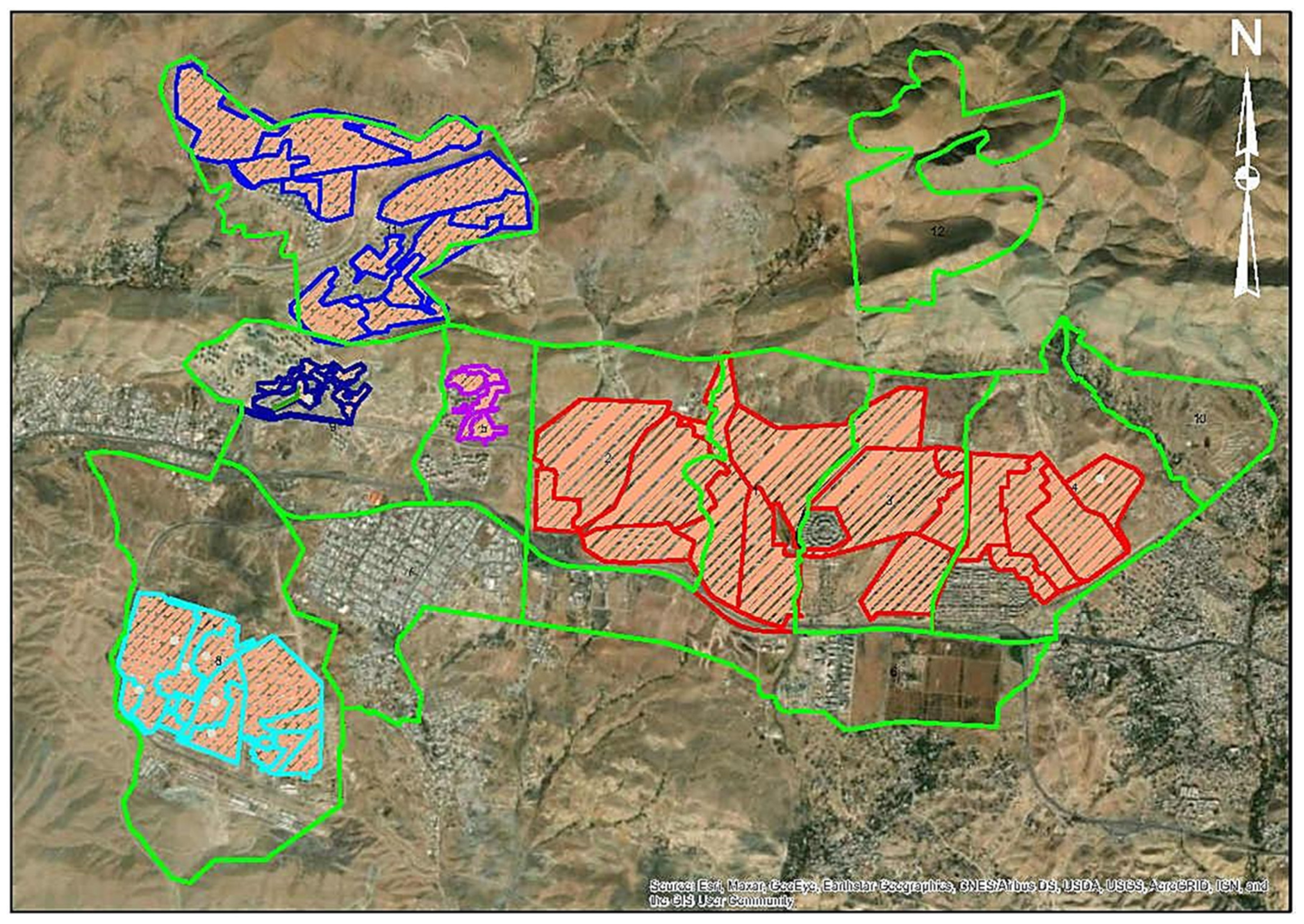
4.1.1. Districting the Study Area
4.1.2. Determining the Amount of Wastewater Consumption
4.1.3. Determining the Value of the Normal Index and Classify the Indices
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aggeli, K.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Bezergianni, S. A proposal of a treated wastewater reuse design system in urban areas. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2009, 18, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jayyousi, O.R. Greywater reuse: Towards sustainable water management. Desalination 2003, 156, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, C.; Memon, M.; Mabuchi, H. Water and Wastewater Reuse: An Environmentally Sound Approach for Sustainable Urban Water Management; United Nations Environmental Program: Osaka, Japan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T. Wastewater Reclamation and Reuse: Water Quality Management Library; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, F.; Farissi, M. Reuse of treated wastewater in agriculture: Solving water deficit problems in arid areas. Ann. West Univ. Timis. Ser. Biol. 2014, 17, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrat, R.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. Development of integrated water reuse strategies. Desalination 2008, 218, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdogan, E.; Sogut, Z. Determination of reuse potential of treated wastewater at urban green area. J. Selcuk. Univ. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2013, 1, 835–845. [Google Scholar]
- Eslamian, S.; Okhravi, S.; Reyhani, M.N. Urban water reuse: Future policies and outlooks. In Urban Water Reuse Handbook; Eslamian, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 1107–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Qadir, M.; Sato, T. Water reuse in arid zones. In Urban Water Reuse Handbook; Eslamian, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Wastewater irrigation: Past, present, and future. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2019, 6, e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shreideh, B. Reuse of treated waste water in irrigation and agriculture as a non-conventional resource in Jordan. In Advanced Short Course: Water Saving and Increasing Water Productivity: Challenges and Options, Amman (Jordan); CIHEAM-IAMB: Bari, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.; Gikas, P. Water reuse: Overview of current practices and trends in the world with emphasis on EU states. Water Util. J. 2014, 6, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bahri, A. Water Reuse in Tunisia: Stakes and prospects. In Atelier du PCSI (Programme Commun Systèmes Irrigués) sur une Maîtrise des Impacts Environnementaux de l’Irrigation; Cirad-IRD-Cemagref: Montpellier, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bazza, M. Wastewater recycling and reuse in the Near East Region: Experience and issues. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E. Water reuse—An integral part of water resources management: Israel as a case study. Water Policy 2001, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, D.; Irusta, R. The cost of wastewater reclamation and reuse in agricultural production in the Mediterranean countries. In Proceedings of the IWA Conference on Water Economics, Statistics and Finance, Rethymo, Greece, 8–10 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rawy, M.; Zlotnik, V.A.; Al-Raggad, M.; Al-Maktoumi, A.; Kacimov, A.; Abdalla, O. Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water resources with aquifer recharge by treated wastewater: Evaluation of management scenarios in the Zarqa River Basin, Jordan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajkowicz, S.; Collins, K. A review of multiple criteria analysis for water resource planning and management. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, R.; Gale, S.; Doyle, C.; Lesjean, B.; Gibert, M. Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) Effluent Reused in Agriculture–Is There a Concern? In Proceedings of the First Symposium Water Recycling Australia, Adelaide, Australia, 19–20 October 2000; CSIRO Land and Water, and Australian Water Association: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pintilie, L.; Torres, C.M.; Teodosiu, C.; Castells, F. Urban wastewater reclamation for industrial reuse: An LCA case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 139, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, C.; Asano, T. The potential for industrial wastewater reuse. Wastewater Recycl. Reuse Reclam. 2009, 1, 299–313. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Regional Overview of Wastewater Management and Reuse in the Eastern Mediterranean Region; World Health Organization, Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean Regional, California Environmental Health Association: Cairo, Egypt, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Balawenah, A.; Al-Karadsheh, E.; Qadir, M. Community-based reuse of greywater in home farming in Food security and climate change in dry areas. In Proceedings of the an International Conference, Amman, Jordan, 1–4 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barrio, D.H.; Irusta, R.; Fatta, D.; Papadopoulos, A.; Mentzis, A.; Loizidou, M. Analysis of Best Practices and Success Stories for Sustainable Urban Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in the Agricultural Production in the Mediterranean Countries; REWAS’04—Global Symposium on Recycling, Waste Treatment and Clean Technology: Madrid, Spain, 2005; pp. 1255–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Braadbaart, O. An Assessment of Centralized and Decentralized Wastewater Reclamation Systems in Beijing. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nitivattananon, V.; Sa-nguanduan, N. Urbanization and water reuse. In Urban Water Reuse Handbook; Eslamian, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Schoups, G.; Addams, C.L.; Minjares, J.L.; Gorelick, S.M. Sustainable conjunctive water management in irrigated agriculture: Model formulation and application to the Yaqui Valley, Mexico. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmo, O.; Imseih, N. Overview of wastewater management practices in the Mediterranean region. In Waste Water Treatment and Reuse in the Mediterranean Region; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 155–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, R.; Murray, D. Guidelines for Water Reuse; US EPA Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Reznik, A.; Feinerman, E.; Finkelshtain, I.; Fisher, F.; Huber-Lee, A.; Joyce, B.; Kan, I. Economic implications of agricultural reuse of treated wastewater in Israel: A statewide long-term perspective. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 135, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kümmerer, K. Advanced Treatment Technologies for Urban Wastewater Reuse; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado-Ramos, G.C. Water and the political ecology of urban metabolism: The case of Mexico City. J. Political Ecol. 2015, 22, 98–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyebode, O.J. Effective management of wastewater for environment, health and wealth in Nigeria. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6, 1028–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Bahri, A. Global challenges to wastewater reclamation and reuse. Water Front. 2011, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, M.H.; Kalantari, N.; Sharifidoost, M.; Kazemi, M. Quality assessment of treated wastewater to be reused in agriculture. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 4, 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, J.; Fu, P. Strategic zoning for urban wastewater reuse in China. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, S.; Nurse, L.; Stoddard, A. Monitoring the Effect of below Average Precipitation on Water Resources in Paget Farm, Bequia, Grenadines; MSc Research Report Submitted to Center for Resource Management and Environmental Studies: Cave Hill, Barbados, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sambito, M.; Freni, G. Strategies for improving optimal positioning of quality sensors in urban drainage systems for non-conservative contaminants. Water 2021, 13, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Row | Component | Price (IRR * in m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Costs of transmitting and treatment of raw water from water resource | 6210 |
| 2 | Water price (tariff) | 36,183 |
| 3 | Installation and operation of local wastewater treatment package | 23,425 |
| 4 | Environmental costs of wastewater disposal | 53 |
| 5 | Social and business income | 2404 |
| 6 | Costs of installation and operation of decentralized wastewater treatment packages | 0.055 |
| 7 | Savings of replaced wastewater (million IRRs per year for every 1000 cubic meters) | 66,592 |
| 8 | Household financial savings and replaced landscape effluent (million IIRs per year for every 1000 cubic meter) | 65,871 |
| Practical Advice | First Group (n) | Second Group (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Essential for reusing wastewater | Severe degree of water consumption | Drinking water consumption Annual landscape water consumption |
| Acceptable degree of water consumption | Water consumption of commercial/recreational/workshop units Effluent recycling possible Financial savings of replaced effluent | |
| Economical to reuse wastewater | Economic advice for using wastewater locally | Generate annual local surplus revenue of annual wastewater after recycling |
| Level of Need for Wastewater Reuse | The Level of Economic Feasibility of Reusing Wastewater | Definition and Explanation of Clusters |
|---|---|---|
| High | High | Cluster I: Due to the need to provide the main uses and the conditions of the local economy, the use of wastewater needs to be recommended and implemented as the main priority and alternative source. To this end, emphasis and basic executive actions by the city administration are necessary. |
| High | Low | Cluster II: Due to the specific water shortage, the use of effluent is recommended. However, local economic conditions are not conducive to supporting the required infrastructure. |
| Medium | High | Cluster III: Water shortage is not severe. Since the local economy is good, the use of wastewater can be recommended as one of the options to move towards sustainable urban water management. |
| Medium | Low | Cluster IV: Since urban water shortage is not a limiting factor and local economic conditions are not suitable, the use of wastewater in these conditions is not considered. |
| Low | Low/High | Cluster V: The required water resources are fully available. As a result, even weak economic problems do not occur, and the use of wastewater is not required. |
| Description | Number of Areas | Total Discharge | Very Low and Low Residential Density | Medium to Very High Residential Density | Park and Landscape | Other Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | - | Lit/Sec | Ha | Ha | Ha | Ha |
| Amount | 61 | 3657 | 505.76 | 475.24 | 250.35 | 844.22 |
| Statistic | m1 | m2 | m3 | m4 | m5 | m6 | m7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of observations | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 | 61 |
| Minimum | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Maximum | 8,109,845.971 | 395,950.757 | 684,284.000 | 1.00 | 85,004,346.000 | 82,815,229.000 | 5,640,868.000 |
| 1st Quartile | 94,272.818 | 1393.752 | 17,376.000 | 0.176 | 2,628,459.000 | 1,814,851.000 | 32,847.000 |
| Median | 226,740.041 | 11,342.333 | 45,018.000 | 0.229 | 5,474,447.000 | 3,947,471.000 | 175,104.000 |
| Mean | 461,884.360 | 33,705.526 | 94,526.016 | 0.745 | 8,550,638.230 | 6,330,421.525 | 329,364.377 |
| Category/Index | Grade | m1 | m2 | m3 | m4 | m5 | m6 | m7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | 5 | 0–3 | >45 | >30 | >7 | >30 | >9 | <=1 |
| Medium to high | 4 | 3–5 | 30–45 | 20–30 | 5–7 | 20–30 | 7–9 | 1–2 |
| Medium | 3 | 5–7 | 15–30 | 10–20 | 3–5 | 10–20 | 5–7 | 2–3 |
| Low to medium | 2 | 7–9 | 1–15 | 1–10 | 1–3 | 1–10 | 3–5 | 3–4 |
| Low | 1 | >9 | 1< | 1< | 1< | 1< | 3< | >4 |
| Cluster | I | II | III | IV | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of districts located on this floor | 21 | 14 | 16 | 6 | 4 |
| Variance | 1.848 | 4.676 | 1.992 | 3.700 | 7.917 |
| Minimum distance from the center of the floor | 0.725 | 1.141 | 0.713 | 1.323 | 1.521 |
| Average distance from the center of the floor | 1.245 | 2.009 | 1.289 | 1.715 | 2.311 |
| Maximum distance from the center of the floor | 2.371 | 2.780 | 2.033 | 2.255 | 3.437 |
| Priority | Number of Districts | % | Area | Financial Savings | Extra Income | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2 | % | 106 IRR/year | 106 IRR/year | % | |||
| I | 21 | 15.59 | 2,822,667 | 36.17 | 904,160 | 221,148 | 31.25 |
| II | 14 | 69.72 | 12,626,404 | 23.93 | 598,225 | 221,086 | 31.24 |
| III | 16 | 3.93 | 712,021 | 24.24 | 605,871 | 176,896 | 25.00 |
| IV | 6 | 9.62 | 1,742,015 | 8.71 | 217,843 | 44,246 | 6.25 |
| V | 4 | 1.15 | 207,686 | 6.94 | 173,535 | 44,229 | 6.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghafoori, S.; Hassanpour Darvishi, H.; Mohamadvali Samani, H.; Taherei Ghazvinei, P. Enhancing the Method of Decentralized Multi-Purpose Reuse of Wastewater in Urban Area. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13553. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413553
Ghafoori S, Hassanpour Darvishi H, Mohamadvali Samani H, Taherei Ghazvinei P. Enhancing the Method of Decentralized Multi-Purpose Reuse of Wastewater in Urban Area. Sustainability. 2021; 13(24):13553. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413553
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhafoori, Saeid, Hossein Hassanpour Darvishi, Hossein Mohamadvali Samani, and Pezhman Taherei Ghazvinei. 2021. "Enhancing the Method of Decentralized Multi-Purpose Reuse of Wastewater in Urban Area" Sustainability 13, no. 24: 13553. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413553
APA StyleGhafoori, S., Hassanpour Darvishi, H., Mohamadvali Samani, H., & Taherei Ghazvinei, P. (2021). Enhancing the Method of Decentralized Multi-Purpose Reuse of Wastewater in Urban Area. Sustainability, 13(24), 13553. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132413553





