Abstract
Recently, 6G-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) is gaining attention and addressing various challenges of real time application. The artificial intelligence plays a significant role for big data analytics and presents accurate data analysis in real time. However, designing big data analysis through artificial intelligence faces some issues in terms of security, privacy, training data, and centralized architecture. In this article, blockchain-based IoT framework with artificial intelligence is proposed which presents the integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain for IoT applications. The performance of the proposed architecture is evaluated in terms of qualitative and quantitative measurement. For qualitative measurement, how the integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence addresses various issues are described with the description of AI oriented BC and BC oriented AI. The performance evaluation of proposed AI-BC architecture is evaluated and compared with existing techniques in qualitative measurement. The experimental analysis shows that the proposed framework performs better in comparison with the existing state of art techniques.
1. Introduction
A smart city requires information technology for the integration and management of physical, social, and business infrastructures in order to deliver better facilities to its residents while confirming efficient and optimal use of available resources [1]. Information of things is an approach that helps to provide interconnection among humans and devices with the internet, termed as Internet of Things (IoT). These devices are capable of performing intercommunication including smart homes, intelligent automotives, smart industries, and smart vehicles [2]. There are many solutions for various fields provided by Internet of Things to optimize their production effectively and efficiently. Considering all the advantages, IoT also faces some issues like data security, centralization, data analytics, connectivity and other hardware constraints. In an analysis, more than 800,000 user devices were reported to be compromised through spam emails and distributed phishing in the year of 2015 [3]. Cui et al. [1] suggested that with the increasing number of smart devices, a huge volume of data is being produced. Therefore, big data analytics is a critical issue for any IoT application. To address this issue of data analytics, various research has contributed and proposed different solutions with technologies such as artificial intelligence and deep learning for IoT applications [2]. The deep learning analytical tool is implemented for the analysis of huge data and to provide necessary information for decision making, prediction and classification processes. The deep learning analytics tool supports feature extraction and scaling of a huge volume of data from IoT applications [3]. Osuwa et al. [4] presented the study for the integration of artificial intelligence and IoT. Their study also discusses about the profits, future opportunities, and open research issues in various IoT applications. Misra et al. [5] suggested a user-oriented IoT system that works on two mechanisms; first is a bidirectional method of processing, and the other is an uncertainty-oriented arbitration approach.
Blockchain technology provides a decentralized, distributed, and secure network. Each node in blockchain technology is connected in a distributed peer-to-peer manner where every transaction is recorded quickly along with timestamps and transactions are shared without any outside interference. The blockchain approach provides an efficient solution for areas such as agriculture, healthcare, security, and finance. The data available in blocks are further attached and secured in chains with digital signs through cryptographic hashing. It is impossible for the hackers to hack transactions by adding malicious input to the system since each block relates to the last block. The integration of the blockchain approach with artificial intelligence for Internet of Things frameworks has addressed various issues such as digital signature, validation, smart contract, decentralization, secure sharing, and immutable explainable artificial intelligence. Recently, with the evolution of smart IoT devices and with their interconnections, data at a huge volume is generating in a centralized form. Therefore, issues such as space, security and privacy are regularly generated by the evolution of technology. A decentralized database framework is implemented to address these concerns with the integration of blockchain and AI for IoT [6]. The transaction should be secure, digitally signed, immutable, validated, and explainable while sharing the transaction with any other person in a network. Such a concept of secure transaction can be implemented in the majority of applications such as the healthcare sector, smart-home, agricultural, military, industrial, smart transportation, and many others [7]. The idea of smart contract is implemented by blockchain technology for enhancing network security, and further, it is stored in a digital ledger [8]. Fakhri et al. [9] proposed a security model for IoT applications for delivering highly secure and scalable data in a decentralized manner at fog intelligence. Their architecture resolves the concern of centralization in an IoT framework.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is implemented in various fields of advanced technologies like decentralized AI, blockchain (BC), intelligence of things, machine automation and many others. The integration of artificial intelligence and IoT creates benefits in a way for collecting maximum number of information and its analysis. Mohanta et al. [10] presented a study that highlights intelligent machines that eliminates the effects of humans for the application, such as medical science, automated industries, and others. In recent years, with continuous evolution in smart and digital technologies, artificial intelligence, blockchain and IoT have gained attention from various researchers and become the most popular technologies, providing innovation ideas in many research areas. The fundamental convergence of blockchain and artificial intelligence for the IoT application is depicted in Figure 1. This paper presents the discussion of various issues such as privacy, latency, accuracy, and centralization by the integration of blockchain and AI for IoT applications.
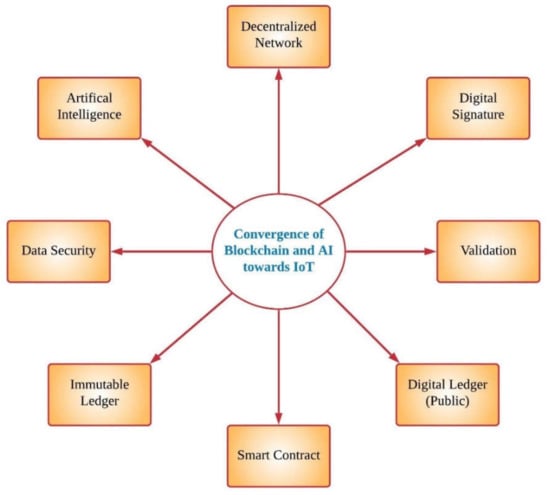
Figure 1.
The fundamental integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence for the IoT application.
The major contributions of this paper are:
- Blockchain and artificial intelligence is studied for IoT applications.
- Considering the advantages of integrating blockchain and artificial intelligence a secure intelligent blockchain framework is proposed which includes four intelligences. The proposed model consists of intelligence at cloud, fog, edge, and device level.
- The proposed methodology for the combination of blockchain methods and artificial intelligence is provided.
- The qualitative and quantitative analysis of the proposed architecture is presented. Using parameters accuracy, energy consumption, latency, data privacy and security.
- This work presents the summary of research challenges along with their solutions.
2. Related Work
AI and BC are the primary techniques representing various IoT applications. Blockchain technology is capable for providing distributed and decentralized paradigm for the applications of IoT. Whereas the AI is capable of providing analysis and processing of data for the application of IoT and thereby providing intelligent decision for machine. The contribution of various research works is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Contribution of this study in relation with existing literature.
2.1. Blockchain Technology
The blockchain technology represents a collection of blocks, where each of the blocks consists of four portions, timestamp, transaction detail such as Ethereum and bitcoin, and hashing of previous and present block. The blockchain technique is a public digital ledger, decentralized and distributed network that is used for storing transaction in different nodes. It provides unique cryptographic value to each block previous and present block; therefore, any third party cannot access or record the transaction. Each of the transaction in blockchain technology is signed with cryptographic value by hashing that is particularly verified by each miner.
Figure 2 presents the basic overview of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology, where blockchain holds the duplicate value of complete ledger and details about blocks of each transaction. Blockchain technology provides the capability of sharing the ledger information in distributed, trusted, secure and decentralized form [11]. The decentralized storage in blockchain method is utilized for storing large volume data that connected with current block and earlier block through smart contract. In the current scenario Swarm, IPFS, LitecoinDB and BigchainDB are few of the databases which are utilized considering decentralized database [12]. IPFS is an interplanetary file system, which is decentralized, distributed and point-to-point database connected for transferring common files [13]. IPFS is also represented as a significant storage database, which is utilized by the blockchain method for the majority of IoT frameworks in order to attain high throughput [14].
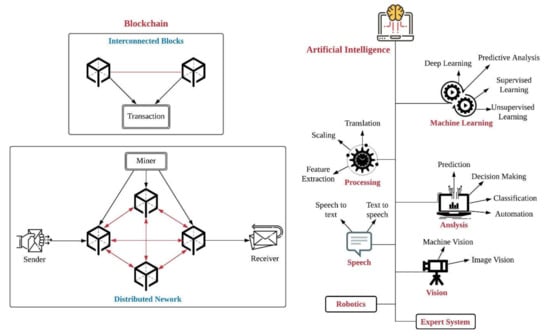
Figure 2.
Overview of artificial intelligence and blockchain.
Yue et al. [15] presented three different categories of Internet of Things such as sensor based, internet based, and knowledge based. The internet based IoT represents the combination of various smart devices, which relate to Internet, and generates a huge volume of data regularly. The sensor based IoT represents the deployment of sensor devices such as temperature/humidity, and RFID for the collection of data. The knowledge based IoT represents the collection of knowledgeable information, which is used for IoT applications [16,17]. IoT is one of the most emerging technologies that uses a variety of applications, providing unique addresses and communicates among each other through internet simultaneously. The huge amount of data generated in IoT applications has various challenges such as fault tolerance, security vulnerabilities and data privacy. To address these challenges, various researchers have suggested blockchain technology as a solution for IoT applications [18,19]. Blockchain technology involves less delay and significant computational overhead and energy consumption. There are many applications where blockchain technology can be implemented for providing security and privacy, such as Industrial automation, smart home, smart healthcare, agriculture, smart city, and many others. The blockchain technology provides a peer-to-peer connection among networks for robustness and authentication against different attacks. The integration of IoT and blockchain provides the extensive management of data and improves complexity.
2.2. Artificial Intelligence Technology
Programmed machines that can execute a variety of operations such as learning, identifying, and solving various problems routinely is termed as artificial intelligence. Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL) and Neural Network (NN) were implemented for solving various complex problems automatically, and the benchmark for AI concerns a human level of reasoning, vision, and speech. Intelligent machines are utilized for making smart decisions and to remove human tasks in various fields like automatic sensing applications, medical applications, automated farming and automated vehicle driving [20]. AI technology takes the input of raw data, processes it for performing decision-making, and at last presents the maximum number of outputs for a specific task [21]. Recently, various researchers have found many challenges in Internet of Things such as big data analytics, privacy and security, energy efficiency and traffic congestion. To overcome these issues, many AI techniques for IoT applications have designs such as such machine learning, deep learning and neural network. The implementation of deep learning approaches particularly solves the issue of energy efficiency in IoT. The data association and its prediction are analyzed for energy management, and it leads designers to select the most significant settings in controlling the energy consumption [22].
The IoT authentication based on machine learning provides a solution in terms of security including approaches such as supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, access control, and secure offloading for the protection of data privacy [23]. The analytics capability of AI for the collection of data in IoT applications provides the identification patterns, and based on those, more informed decisions are generated for new ecosystems. The basic approaches and concepts that are used in artificial intelligence are depicted in Figure 2.
2.3. Current Trending Techniques
Many authors have suggested the open research challenges of blockchain for artificial intelligence and artificial intelligence for blockchain in IoT applications. Vara et al. [24] have presented the overview for the integration of IoT and artificial intelligence, and discussed various challenges for the convergence of IoT with AI. Chen et al. [25] discussed the key characteristics of blockchain technology, applications, consensus algorithm and the technical issues in the existing research. Debauche et al. [26] presented the importance of Ethereum-based edger for smart contract, and it is also found that it is a low-price tool that provides comparatively high accuracy in resource management. Vo et al. [27] have discussed the advantages of blockchain technology considering artificial intelligence and security enhancement. Kim et al. [28] discussed the basic concept of blockchain for artificial intelligence and presented some of the open research challenges in implementing blockchain for AI. Rao et al. [29] discussed operational levels of IoT such as application network and perception layer and discussed security issues in each of these layers. Ferrag et al. [30] conducted research for identifying the potential solution to each challenge in the integration of IoT and blockchain to improve the safety in supply chain systems. Minoli et al. [31] discussed how blockchain technology improves the security in IoT applications. The authors have also conferred the relationship among blockchain and IoT along with the concerns in blockchain based IoT applications. Qian et al. [32] suggested security solutions for IoT applications, which include limitation of available IoT based datasets that are utilized by both study and business communities.
Hassija et al. [33] discussed all the possible security threats to blockchain technology and presented some possible real attacks. The authors have reviewed solutions for the security enhancement implementing blockchain technology. Tsang et al. [34] proposed a system for the food traceability based on integration of IoT and blockchain. Their proposed work is self-organized, trusted and a natural solution for intelligent agriculture systems. Pavithran et al. [35] analyzed the basic structures of blockchain in practical applications. The authors have discussed development parameter of blockchain by analyzing the present application and technologies. Cai et al. [36] proposed a knowledge acquisition design for the analysis of data in cloud layer.
The contribution of proposed study in relation with the existing literature is presented in Table 1. It highlights the existing research considering various technological parameters such as blockchain based artificial intelligence and artificial intelligence based blockchain, various open research challenges and their solutions. The present study significantly differs from other existing research for providing better integrated discussion impressiveness and extensiveness for the convergence of blockchain and artificial intelligence for Internet of Things. Based on the conducted research, an intelligent architecture is presented for IoT applications by the integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence.
As mentioned in the preceding section, this present work addresses significant challenges such as centralization, accuracy, latency, privacy, and security in huge amount of data. This research work is primarily focused on the integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence at different layers for cloud, fog, and edge in order to address above-mentioned challenges. Truong et al. [37] proposed a secure framework for IoT applications to deliver secure IoT data with decentralized network at fog player. Debauche et al. [38] provided the basic overview of integrating artificial intelligence and IoT for increasing the efficiency and removing unwanted interruption in IoT applications. Mohanty et al. [39] proposed a framework for the management of security based on blockchain for IoT applications. A secure blockchain-based deep learning framework for providing reliable data transmission in IoT application is suggested [40]. Their approach achieves high latency and accuracy in IoT data. Pan et al. [41] presented decentralized supply management based on blockchain technology to address the issue of resource management utilizing a dynamic voltage frequency approach. Considering the benefits of integrating blockchain and artificial intelligence for IoT applications, an intelligent architecture is proposed and discussed in the subsequent sections [42].
3. Proposed Methodology
This section describes the proposed intelligent architecture, integrated design of blockchain (BC) and artificial intelligence (AI) technology for IoT applications. The performance of the proposed architecture is measured for four different platforms such as cloud platform analysis, fog platform, edge platform and device intelligence analysis. A proposed architecture demonstrates how big data analysis, centralization issues and security issues are addressed with the integration of BC and AI.
3.1. Overview of Proposed Framework
Figure 3 depicts the layered architecture of proposed integrated artificial intelligence blockchain design AI-BC for IoT application. The proposed model consists of four operational platforms such as intelligence at device platform, edge platform, fog and cloud intelligence platform. The first platform, device deployment, consists of multiple smart devices with AI and BC implementation. In this platform, a huge amount of data is generated, which is transmitted to the edge intelligence platform. The second platform, which is edge intelligence, comprised of an artificial intelligence oriented base station, which is connected with blockchain at the network edge. In the fog platform, every fog node with blockchain technology consists of an artificial intelligence enabled base station.
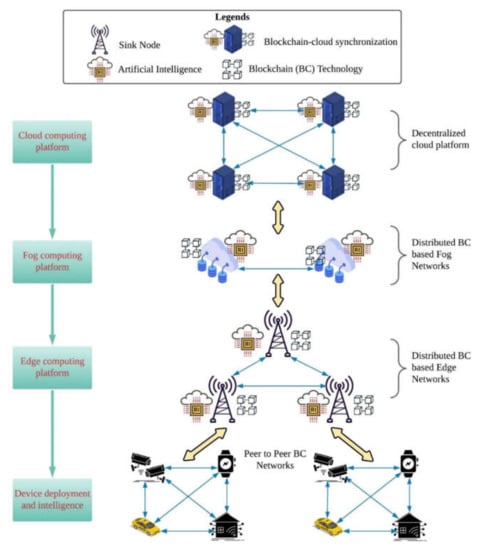
Figure 3.
Layered architecture integrated AI-BC design.
3.2. Transactional Flow of Proposed AI-BC Architecture
The information flow of the proposed AI-BC architecture is depicted in Figure 4. The flow of information consists of six layers of operation. The first layer is a physical layer that corresponds to the device deployment phase for the collection of data in real time. The communication and control layer are responsible for edge computing. The service and managing layer correspond to the fog computing, and the application layer corresponds to the cloud computing. Parameters such as temperature (°C), humidity (%), light intensity (lux), weather and location parameters are identified by the physical layer in cloud computing. In physical layer of different kinds of issues and threats for data privacy exists while transferring data from one node to another. Blockchain technology in artificial intelligence is implemented to overcome such issues, where the transaction from one node to another is carried out in the form of Bitcoin and Ethereum. The collected information in real time is communicated to the communication level that acts as an intermediate for communicating data from one node to another. The integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain for IoT application utilizes a consensus algorithm for achieving security and scalability.
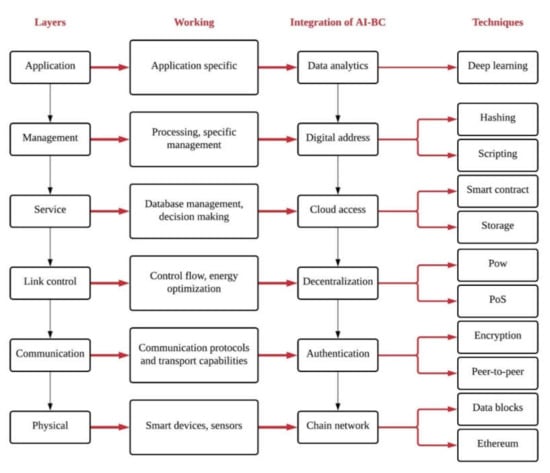
Figure 4.
Information flow of proposed AI-BC IoT architecture.
The integration of AI in blockchain utilizes a distributed platform of cloud, intelligent storing and smart contracts that ensures safe validation in this layer. The data transfer towards the managing layer is responsible for data management and setting the criteria of infrastructure among networks for the application layer. Integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence provides cryptography hashing, digital identity, and encryption codes. At last, the information is transferred to the application layer, which is responsible for global management. The integration of AI and blockchain implements the deep learning data analytics tool for ensuring data privacy and security in the network.
In the recent literature, we can find certain evidence about the importance of this proposed model as a solution to the research gaps. Various applications are enabled with AI and BC models. Various recent studies related to AI and blockchain shows the relevant evidences about the importance of the proposed model. At this point, it is also important to share that, to the best of author’s knowledge, none of literature has been exploited the AI oriented blockchain and blockchain oriented AI for the IoT applications with a detailed study. A decentralized and collaborative AI model for blockchain was proposed to provide the application specific results [43]. Later, authors in [44] proposed a framework where smart cities are enabled with AI and blockchain for the decentralized auditing using blockchain technology. An exhaustive literature review has been performed to study the various challenges, solutions and future scope of the AI and blockchain technology [45]. A detailed study of integration of AI with blockchain [46] and applications of IoT enable smart cities with emergence of AI and blockchain [47,48] has been discussed by various authors. Recently, authors proposed a model using blockchain and IoT based cognitive edge framework for the smart city applications [49].
4. Performance Analysis of AI-BC Framework
In this section, the performance evaluation of the proposed framework design is discussed. During the experimentation, an open source Ethereum blockchain platform is explored. The proposed framework has major differences in terms of its fundamental processes while comparing it other existing techniques. Considering this point, the simulations are favored, and additional platforms are not implemented for the purpose of evaluation. The network performance is evaluated separately because the network operates separately. The performance of the proposed design is studied by using the NS3 simulator for the performance analysis of smart city network. The NS3 simulator is used, as it is beneficial in computing low resource device performance. Another benefit of using this simulator is that it increases the performance of overlay network and provides efficient evaluation of peer-to-peer networks.
The experimental feasibility of proposed AI-BC architecture in Raspberry Pi is measured in terms of four different metrics such as accuracy, latency, and security/privacy analysis. The accuracy analysis for the application of object detection is computed, and it is observed that the percentage accuracy increases with increase in number of edge nodes and 5345 instances are utilized for deep learning operation. The contribution of more nodes increases the training dataset and increases the accuracy in object detection. The variation in object detection time is evaluated for total amount of edge nodes to elaborate the latency improvement. The analysis of security and privacy is computed by estimating the similarity index and calculated object’s Euclidian distance in IoT smart city network. With the increase in Euclidian distance the similarity index value decreases. As a result, the security and privacy in IoT objects is increased with the decrease in value of similarity index.
The performance of the proposed architecture is measured in terms of qualitative and quantitative analysis. In qualitative measurement, two cases are discussed determining how the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain (BC) is beneficial for IoT applications. First case represents artificial intelligence-oriented block chain for IoT application, and second case represents blockchain-oriented artificial intelligence for IoT frameworks. In this study, the issues of blockchain technology in IoT applications are also addressed along with artificial intelligence and described solution for addressing these issues of artificial intelligence with BC technology by presenting advanced structures. Whereas in quantitative measurement the performance evaluation of proposed AI-BC architecture is evaluated and compared with existing state of art approaches considering performance indices such as latency, data privacy and security, accuracy, energy consumption and computational complexity.
4.1. Qualitative Measurement
In quantitative measurement two cases, AI oriented blockchain and blockchain oriented AI for the IoT applications are presented. AI on the other hand boosts blockchain technology by providing accurate prediction and efficient decision making for IoT applications. Therefore, how AI addresses issues of blockchain is termed as artificial intelligence oriented blockchain, i.e., case 1, and how BC addresses the issues of artificial intelligence is defined as BC oriented AI, i.e., case 2.
Case 1—Artificial intelligence oriented blockchain
AI driven blockchain leverages many fields such as manufacturing, Internet of Things and big data, logistics, healthcare, industrial, and many others. In all these applications, AI plays a significant role in processing of data or performing automating tasks to process the information into blockchain technology. It is observed from many experiments that AI can be as effective as humans at tasks and AI is argued as better as it can function 24*7 without facing failure or inclined to human error. The implementation of artificial intelligence for blockchain technology in IoT applications is discussed. There are many limitations of implementing blockchain technology such as complexity, size of network and high cost of transaction.
To address these limitations the artificial intelligence is integrated with blockchain. These limitations are classified in five categories and depicted in Figure 5. The first category represents the hardware, which delivers the data from IoT applications utilized by AI and blockchain. The second category is security and privacy, which supports the cryptographic hashing and provides digitally signed transactions across nodes in a network. The third category presents scalability, which determines nodes capability to manage and grow demand supply for the productivity. The fourth class represents effectiveness, where the comparison among input and output assessment is observed in terms of timing and energy consumption for the IoT applications. The fifth category represents the energy consumption in which the overall power consumed by the miners in blockchain technology is observed.
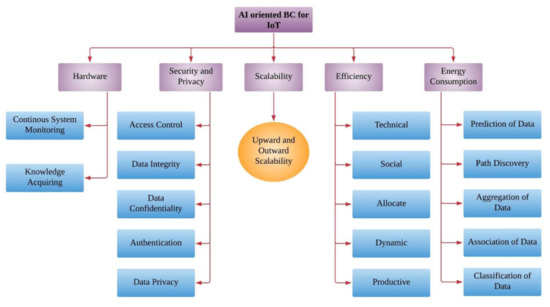
Figure 5.
Classification of artificial intelligence (AI) oriented blockchain (BC) for IoT.
Case 2—Blockchain oriented artificial intelligence
In this case, how blockchain technology addresses the issues of AI is discussed. The taxonomy of the blockchain oriented artificial intelligence for IoT application is depicted in Figure 6. The AI issues for IoT application are addressed by integrating blockchain technology. There are five different categories of AI issues, which are addressed by blockchain. These issues are categorized as data sharing, security and privacy, explainable AI, effectiveness, and AI trust. The first category is data sharing, where the data resources are shared from one device to another and provide various communication facilities. The second category is security and privacy, where collected data is communicated from one device to other in a secure manner and digital signature is provided for each transaction through cryptographic hashing.
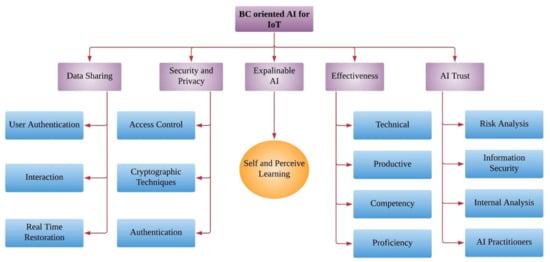
Figure 6.
Classification of blockchain (BC) oriented artificial intelligence (AI) for Internet of Things.
The third category is explainable AI, where the techniques of artificial intelligence can be trusted and made understandable by human. This category deals with the self and perceived learning approaches. The fourth category deals with the effectiveness of artificial intelligence aiming to provide the predictive analysis methods for users. The fifth category is artificial intelligence trust, which aims to provide problem-solving capability through neuron science. In this category, various tasks such as risk analysis, information security analysis, internal analysis and practitioner’s analysis are performed. Blockchain technology allows distributed marketplaces and management platforms that can be implemented in many modules of Artificial Intelligence, which comprises computing data, algorithms, and power. Blockchain driven AI has the potential to process, manage and securely store the data without relying on a third party. Blockchain provides the solution for acute problems of data security and storage, supply chains, government processes, secure voting, crowdfunding, transactions processing and intellectual property. Hence, blockchains are progressively adopted for providing the transparency transactions and information to customers. The potentials are limitless if there’s a technique for blockchain designers to adopt AI into their platforms.
4.2. Quantitative Measurement
In this section, the performance of proposed AI-BC architecture is evaluated and compared with the existing state of art approaches considering various parameters such as accuracy, latency, data privacy and security, energy consumption and computational complexity. The round robin approach and mini approach are the algorithms implemented for arranging the elements in a group in rational order. The process includes initialization from top towards bottom, and then again starting from top element of list and so on. This process takes turns by using computer resources to limit the process for a short time span, then further suspending the process for giving a turn to the next process. The performance analysis of proposed architecture is compared with existing research [7,15,24,26]. Each of the existing studies provides analysis of big data at cloud, fog, edge, and device intelligence. The compatibility of integrated artificial intelligence and blockchain based AI-BC architecture is analyzed by big data analysis. The performance analysis of various existing researches is presented in Table 2 in relation with the proposed AI-BC architecture. The quantitative analysis from the proposed architecture is presented in Table 3. The performance of present study is compared in terms of accuracy, latency privacy and security, energy consumption and computational complexity with the existing techniques. The percentage accuracy calculation for device deployment intelligence is observed as 75%, whereas for edge, fog and cloud computing, the percentage accuracy is observed as 78%, 92% and 70%.

Table 2.
Performance analysis of various existing research.

Table 3.
Quantitative analysis of the proposed model.
The latency is measured as lowest and highest values in milliseconds. At device deployment, intelligence the observed lower and higher value of latency is 57.6 ms and 58.7 ms. At edge computing, the observed lower and higher value of latency is 56.2 ms and 59.3 ms. At fog computing, the observed lower and higher value of latency is 0.0 ms and 12 ms. The similarity index with highest and lowest value are computed for measuring security and privacy. The highest and lowest value of similarity index for device deployment intelligence is in range between 1.2 to 0.02. The highest and lowest value of similarity index for edge computing is in range between 0.59 to 0.3 and for fog computing it is in range between 0.8 to 0.1.
The computational complexity is measured in terms of CPU and memory utilization. At device deployment intelligence, the observed CPU utilization is in a range between 3.2% to 4.5% for IoT, and for edge devices it is 34.2%. The memory usage at device platform for IoT is in range between 12.1% to 15.6%, whereas for edge devices it is observed at 25%. At edge computing, the observed CPU utilization is in range between 3.5% to 4.8% for IoT, and for edge devices it is 37.2%. The memory usage at edge for IoT is in range between 12.5% to 15.8%, whereas for edge devices it is observed at 26%. The CPU usage at fog computing is observed as 92%, whereas the memory usage at fog computing is observed as 94%. The reduction of 55% in energy consumption is observed when compared with round Robin approach, whereas 25% reduction in energy consumption is observed in comparison with Mini Brown approach.
The comparative analysis of the proposed AI-BC architecture with existing state of art techniques for intelligent device deployment, edge computing, fog computing and cloud computing is depicted in Figure 7 and Figure 8. Figure 7 presents the comparative accuracy analysis of proposed integrated AI-BC architecture, and Figure 8 presents the comparative latency analysis. The maximum percentage accuracy for intelligent device deployment with blockchain technology is observed as 75%. The maximum percentage accuracy for edge computing and fog computing with blockchain technology is observed as 78% and 90%. On the other hand, the maximum percentage accuracy without blockchain technology at intelligent device deployment, edge computing and fog computing is observed as 55%, 60% and 81%. Therefore, there are many applications that can be used by various researchers, but for each application, the accuracy percentage is always observed as high by using blockchain for IoT applications. The observed latency with blockchain technology for intelligent device deployment is 58 ms. Similarly for edge computing and for computing, the latency is observed as 60 ms and 22 ms. The observed latency without blockchain technology for intelligent device deployment is 38 ms, whereas at edge and fog intelligence, the latency is observed as 45 ms and 12 ms. The latency is observed to be higher with blockchain technology in comparison to without blockchain technology.
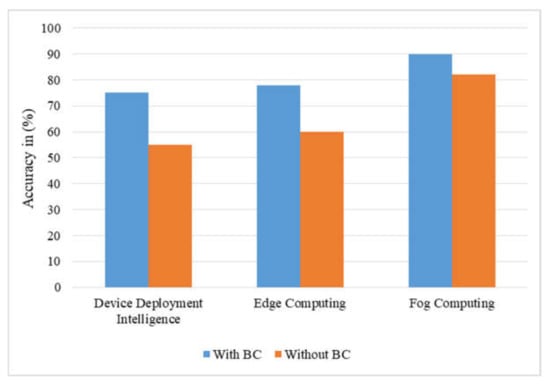
Figure 7.
Comparative accuracy analysis of proposed integrated AI-BC.
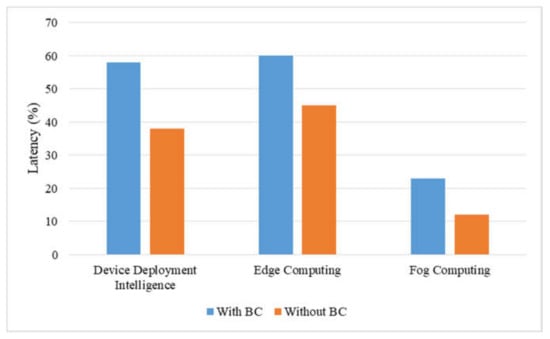
Figure 8.
Comparative latency analysis of proposed integrated AI-BC.
The biggest advantage of the proposed system is that it presents the integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence. The proposed system is a secure intelligent blockchain framework that successfully addresses challenges of accuracy, latency, and security. The key benefit of the proposed approach is real time monitoring of energy consumption and secured transactions. The other key advantages of the proposed scheme considering smart cities application are as follows:
For the access control, initially the blockchain technology delivers database access to each participant. Considering the multiple interconnected devices of the smart cities scenario, the proposed scheme has the capability of providing complete, partial and no access to the data stored in a single database without causing security and privacy issues. The proposed scheme represents an incentive mechanism that can be utilized for motivating citizens to adopt various applications of smart cities.
5. Conclusions
In this article, an integrated blockchain and artificial intelligence based architecture was proposed for IoT application. The objective behind this research was to achieve scalable and secure transaction in IoT at device, cloud, fog and edge intelligence. The performance of the proposed architecture was analyzed considering qualitative and quantitative measurements. In qualitative measurement, BC oriented AI and AI oriented BC were presented with standard taxonomy. The experimental analysis was presented for evaluating the performance of proposed architecture with decentralized and secure big data analytics for 6G-enabled IoT applications. The experimental analysis presents the efficiency of proposed architecture in terms of accuracy, latency, security, and privacy. It is observed from the experimentation that integration blockchain and artificial intelligence successfully addresses the challenges for obtaining high accuracy and security and less latency through decentralized network. The integration of blockchain and artificial intelligence successfully addresses challenges of accuracy, latency, and security, but the computational power issue was not completely addressed with the proposed framework.
In future work, the proposed architecture can be enhanced by adding machine learning intelligence such as scaling process and feature extraction to address the issue of classification.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., E.P., G.S., A.T. (Alexey Tselykh) and A.T. (Alexander Tselykh); methodology, A.S. and E.P.; software, A.S., G.S. and E.P.; validation A.S. and E.P.; formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation A.S. and A.T. (Alexey Tselykh); writing—review and editing; A.S., A.T. (Alexey Tselykh) and A.T. (Alexander Tselykh); visualization, A.S., A.T. (Alexey Tselykh) and A.T. (Alexander Tselykh); supervision, A.T. (Alexander Tselykh); project administration, A.T. (Alexey Tselykh) and A.T. (Alexander Tselykh); funding acquisition, A.S., A.T. (Alexey Tselykh) and A.T. (Alexander Tselykh). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research is supported by postdoc fellowship granted by the Institute of Computer Technologies and Information Security, Southern Federal University, project N° PD/20-03-KT.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cui, F. Deployment and integration of smart sensors with IoT devices detecting fire disasters in huge forest environment. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, K.; Benke, G. Artificial intelligence and big data in public health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Sorour, S.; Guizani, M. Deep learning for IoT big data and streaming analytics: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2923–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veselov, G.; Tselykh, A.; Sharma, A.; Huang, R. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Evolution of Smart Cities and Societies. Informatica 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N.; Dixit, Y.; Al-Mallahi, A.; Bhullar, M.S.; Upadhyay, R.; Martynenko, A. IoT, big data and artificial intelligence in agriculture and food industry. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R. Towards an optimized blockchain for IoT. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM Second International Conference on Internet-of-Things Design and Implementation (IoTDI), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 18–21 April 2017; pp. 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Panarello, A.; Tapas, N.; Merlino, G.; Longo, F.; Puliafito, A. Blockchain and iot integration: A systematic survey. Sensors 2018, 18, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Hilton, B.; Burks, Z.; Reyes, J. Integrating blockchain, smart contract-tokens, and IoT to design a food traceability solution. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhri, D.; Mutijarsa, K. Secure IoT communication using blockchain technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium on Electronics and Smart Devices (ISESD), Bandung, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanta, B.K.; Jena, D.; Satapathy, U.; Patnaik, S. Survey on IoT security: Challenges and solution using machine learning, artificial intelligence and blockchain technology. Internet Things 2020, 11, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.; Alexandre, L.A. An overview of blockchain integration with robotics and artificial intelligence. arXiv Prepr. 2018, arXiv:1810.00329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AlShamsi, M.; Salloum, S.A.; Alshurideh, M.; Abdallah, S. Artificial intelligence and blockchain for transparency in governance. In Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Development: Theory, Practice and Future Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Osuwa, A.A.; Ekhoragbon, E.B.; Fat, L.T. Application of artificial intelligence in Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Cyprus, Turkey, 16–17 September 2017; pp. 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, C.; Yao, H.; Jiang, C.; Guo, S.; Xu, F. Cloud computing assisted blockchain-enabled Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2019, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Junqin, H.; Shengzhi, Q.; Ruijin, W. Big data model of security sharing based on blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications (BIGCOM), Chengdu, China, 10–11 August 2017; pp. 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, P.K. UAV-based framework for effective data analysis of forest fire detection using 5G networks: An effective approach towards smart cities solutions. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, e4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, R. IoT-Based Framework for Smart Agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Inf. Syst. (IJAEIS) 2021, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, A.; Dhiman, G. Line monitoring and identification based on roadmap towards edge computing. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, Y. An integrated fire detection system using IoT and image processing technique for smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H. Securing data with blockchain and AI. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77981–77989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, X. Application of a blockchain platform to manage and secure personal genomic data: A case study of LifeCODE. ai in China. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21, e13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, N.; Asim, M.; Al-Obeidat, F.; Zubair Farooqi, M.; Baker, T.; Hammoudeh, M.; Ghafir, I. The security of big data in fog-enabled IoT applications including blockchain: A survey. Sensors 2019, 19, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Yu, X.L.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Blockchain based data integrity service framework for IoT data. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 468–475. [Google Scholar]
- Casado-Vara, R.; de la Prieta, F.; Prieto, J.; Corchado, J.M. Blockchain framework for IoT data quality via edge computing. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Blockchain-Enabled Networked Sensor Systems, Shenzhen, China, 4 November 2018; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lv, Z.; Song, H. Design of personnel big data management system based on blockchain. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 101, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Cholda, P.; Kumar, R.; Dhiman, G. Risk-aware optimized quickest path computing technique for critical routing services. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 95, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.T.; Mohania, M.; Verma, D.; Mehedy, L. Blockchain-powered big data analytics platform. In International Conference on Big Data Analytics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Deka, G.C. (Eds.) Advanced Applications of Blockchain Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, T.A.; Haq, E.U. Security challenges facing IoT layers and its protective measures. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 179, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Shu, L.; Yang, X.; Derhab, A.; Maglaras, L. Security and privacy for green IoT-based agriculture: Review, blockchain solutions, and challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32031–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoli, D.; Occhiogrosso, B. Blockchain mechanisms for IoT security. Internet Things 2018, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Zhou, M.; Pustišek, M. Towards decentralized IoT security enhancement: A blockchain approach. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 72, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Saxena, V.; Jain, D.; Goyal, P.; Sikdar, B. A survey on IoT security: Application areas, security threats, and solution architectures. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82721–82743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, Y.P.; Choy, K.L.; Wu, C.H.; Ho, G.T.S.; Lam, H.Y. Blockchain-driven IoT for food traceability with an integrated consensus mechanism. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129000–129017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithran, D.; Shaalan, K.; Al-Karaki, J.N.; Gawanmeh, A. Towards building a blockchain framework for IoT. Clust. Comput. 2020, 23, 2089–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xu, B.; Jiang, L.; Vasilakos, A.V. IoT-based big data storage systems in cloud computing: Perspectives and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 4, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.T.T.; Almeida, M.; Karame, G.; Soriente, C. Towards secure and decentralized sharing of IoT data. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–17 July 2019; pp. 176–183. [Google Scholar]
- Debauche, O.; Mahmoudi, S.; Mahmoudi, S.A.; Manneback, P.; Lebeau, F. A new edge architecture for ai-iot services deployment. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 175, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.N.; Ramya, K.C.; Rani, S.S.; Gupta, D.; Shankar, K.; Lakshmanaprabu, S.K.; Khanna, A. An efficient Lightweight integrated Blockchain (ELIB) model for IoT security and privacy. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 102, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.; Park, J.H. A blockchain-based deep learning approach for cyber security in next generation industrial cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 5522–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, J.; Hester, A.; Alqerm, I.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Edge Chain: An edge-IoT framework and prototype based on blockchain and smart contracts. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 4719–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhen, T.; Sharma, A. Smart Farming: An Approach for Disease Detection Implementing IoT and Image Processing. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Inf. Syst. (IJAEIS) 2021, 12(1), 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.D.; Waggoner, B. Decentralized and collaborative AI on blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–17 July 2019; pp. 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yang, Z.; Sinnott, R.O. Decentralized big data auditing for smart city environments leveraging blockchain technology. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 6288–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Gupta, R.; Tanwar, S.; Kumar, N. Blockchain and AI amalgamation for energy cloud management: Challenges, solutions, and future directions. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 143, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Yoon, B.; Shojafar, M.; Cho, G.H.; Ra, I.H. Convergence of blockchain and artificial intelligence in IoT network for the sustainable smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 63, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.N.; Thai, M.T. Ai and blockchain: A disruptive integration. Computer 2018, 51, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Rathore, S.; Park, J.H. Blockiotintelligence: A blockchain-enabled intelligent IoT architecture with artificial intelligence. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 110, 721–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rashid, M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Hassanain, E.; Alhamid, M.F.; Guizani, M. Blockchain and IoT-based cognitive edge framework for sharing economy services in a smart city. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 18611–18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
