Earth Observations and Statistics: Unlocking Sociodemographic Knowledge through the Power of Satellite Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics for Urban Poverty Mapping
2.2. Case Study Selection
3. Cases Studies: Unlocking the Sociodemographic Knowledge with EO-Methods
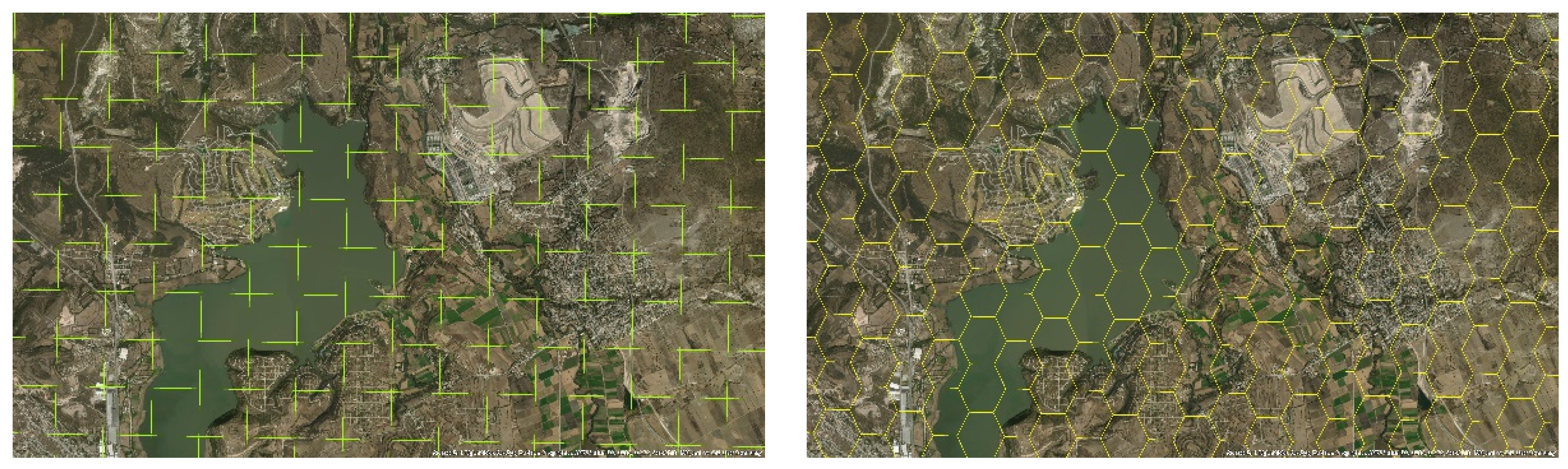
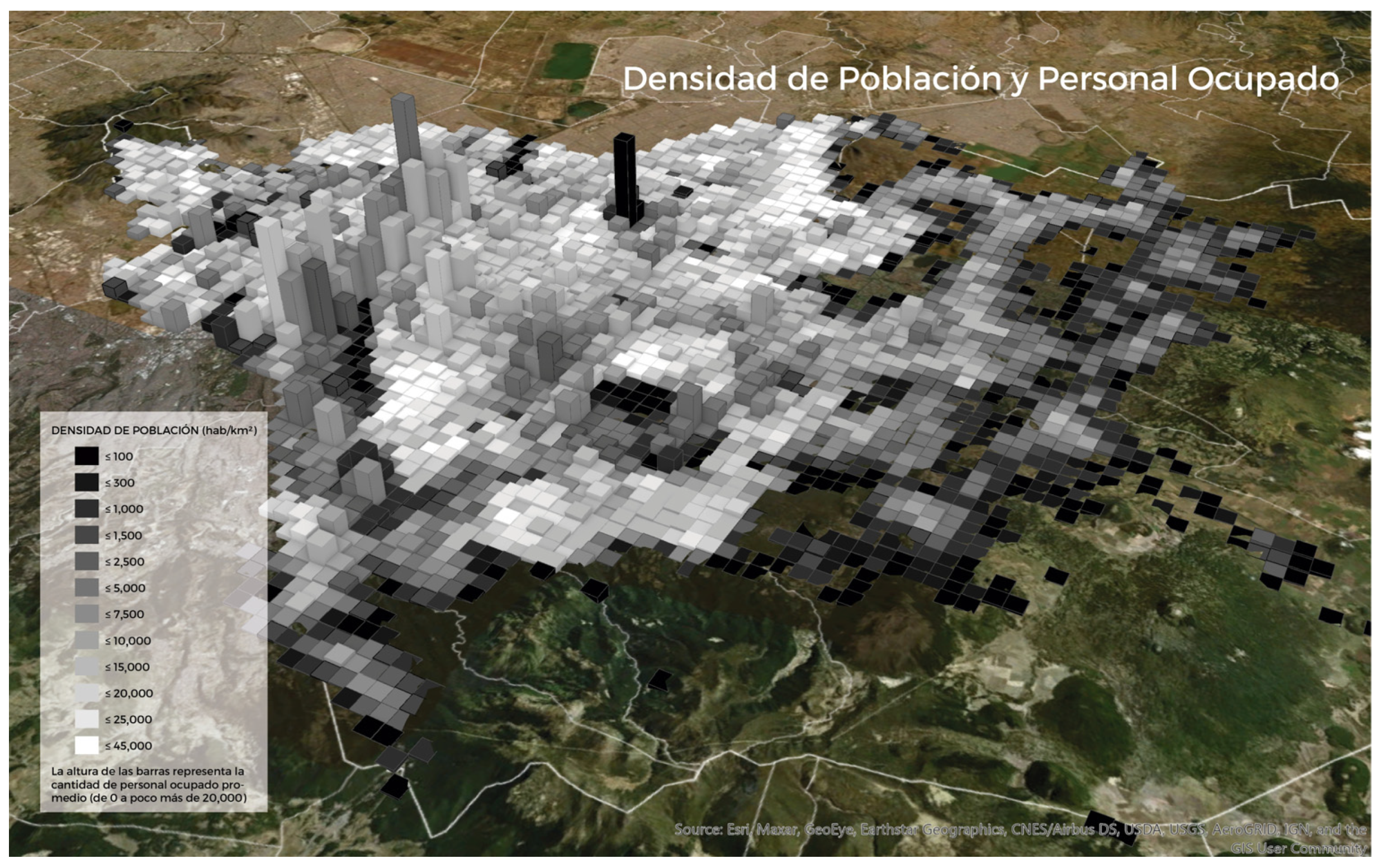
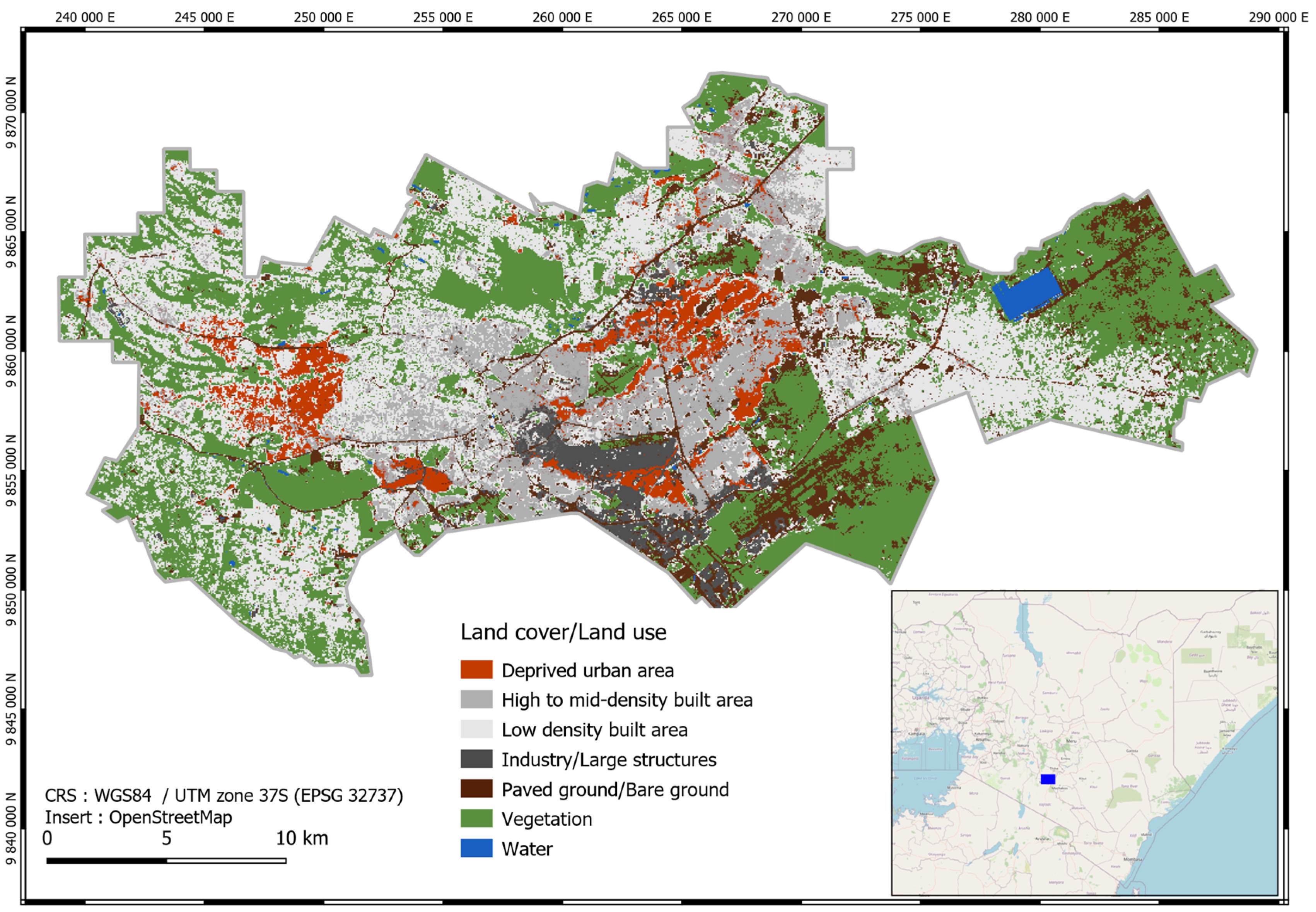
3.1. Gridded Systems for Collecting Sociodemographic Data and the Role of Data Cubes
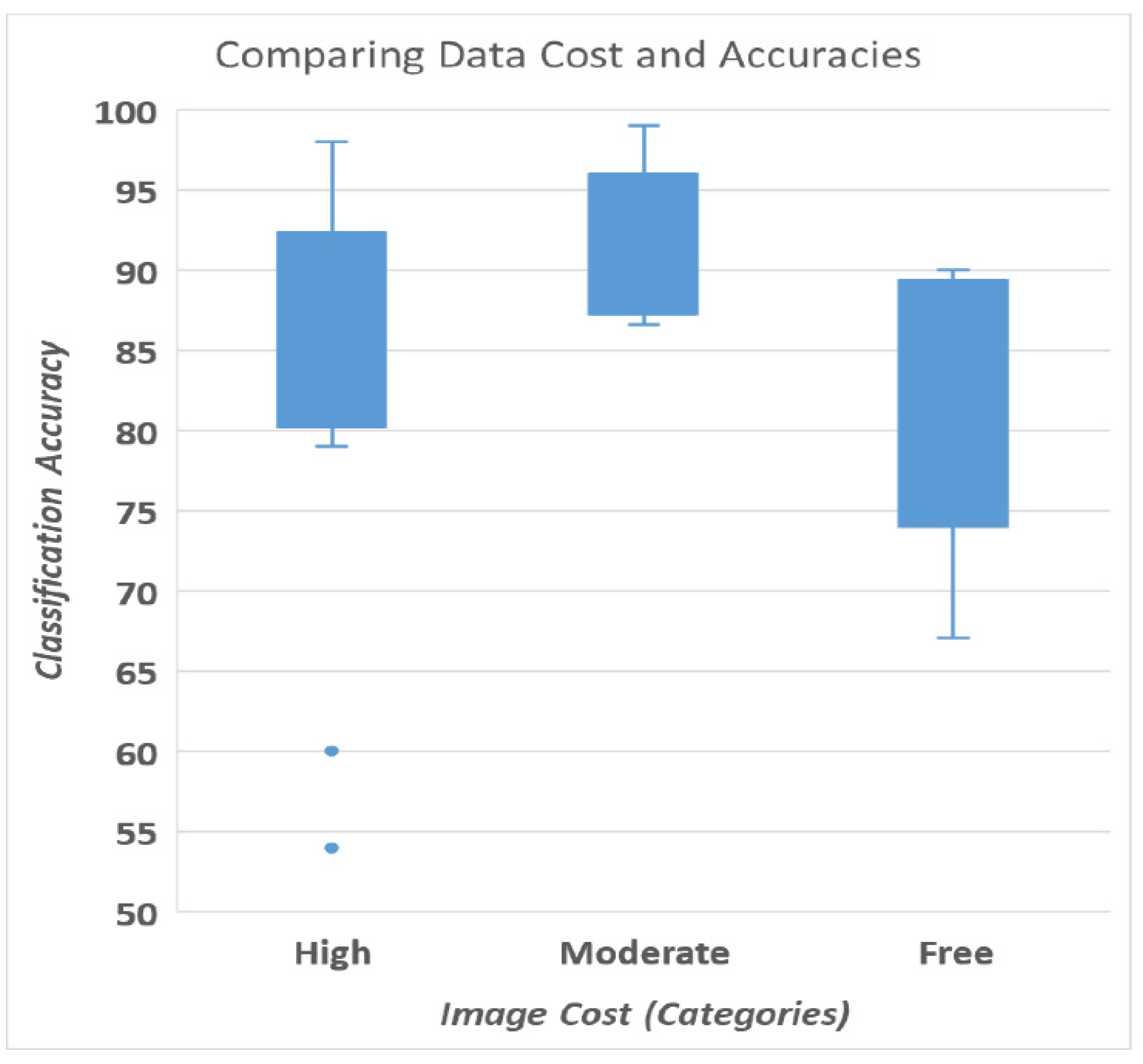
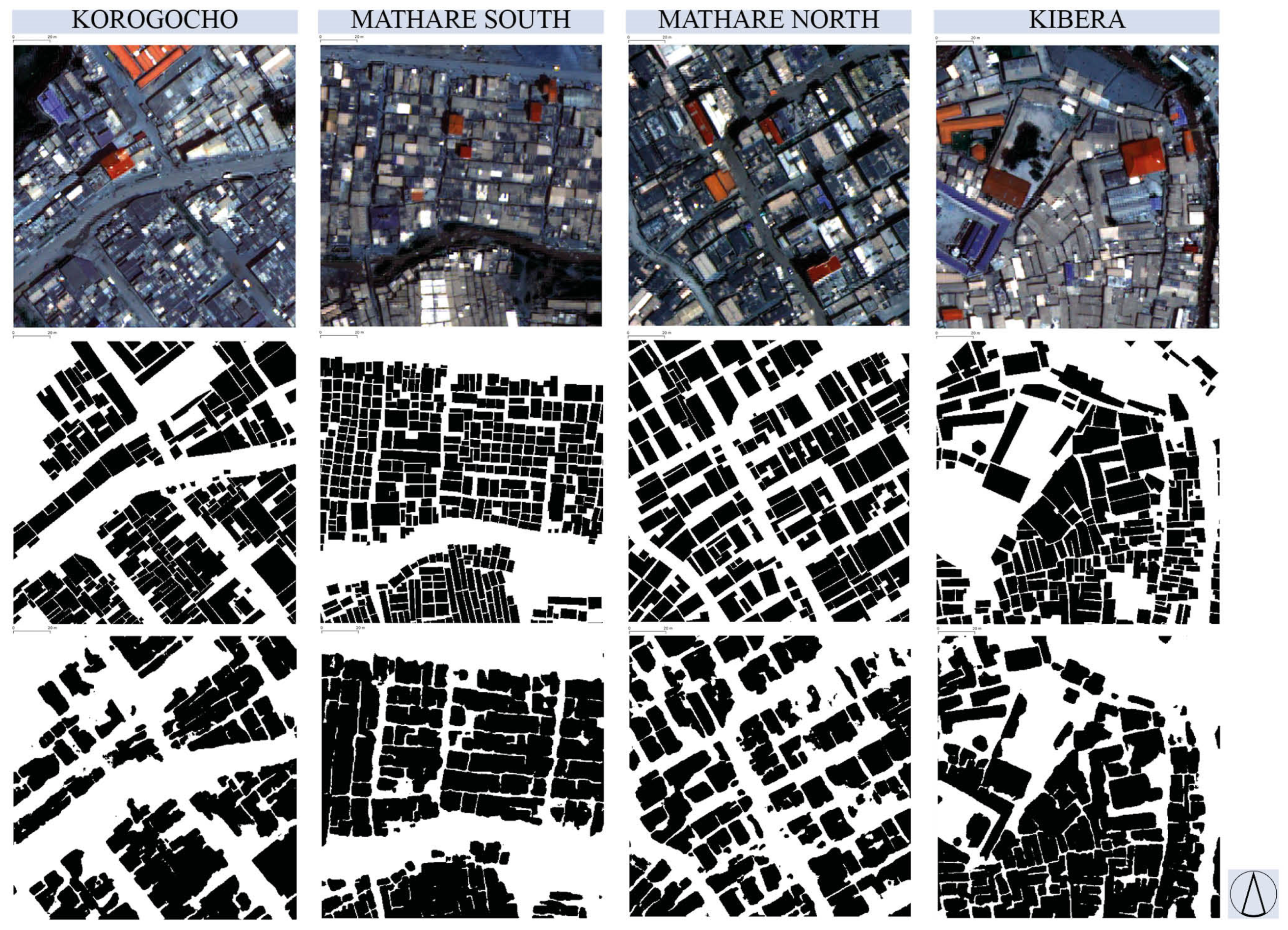
3.2. The Role of Low-Cost Data for Mapping Slums
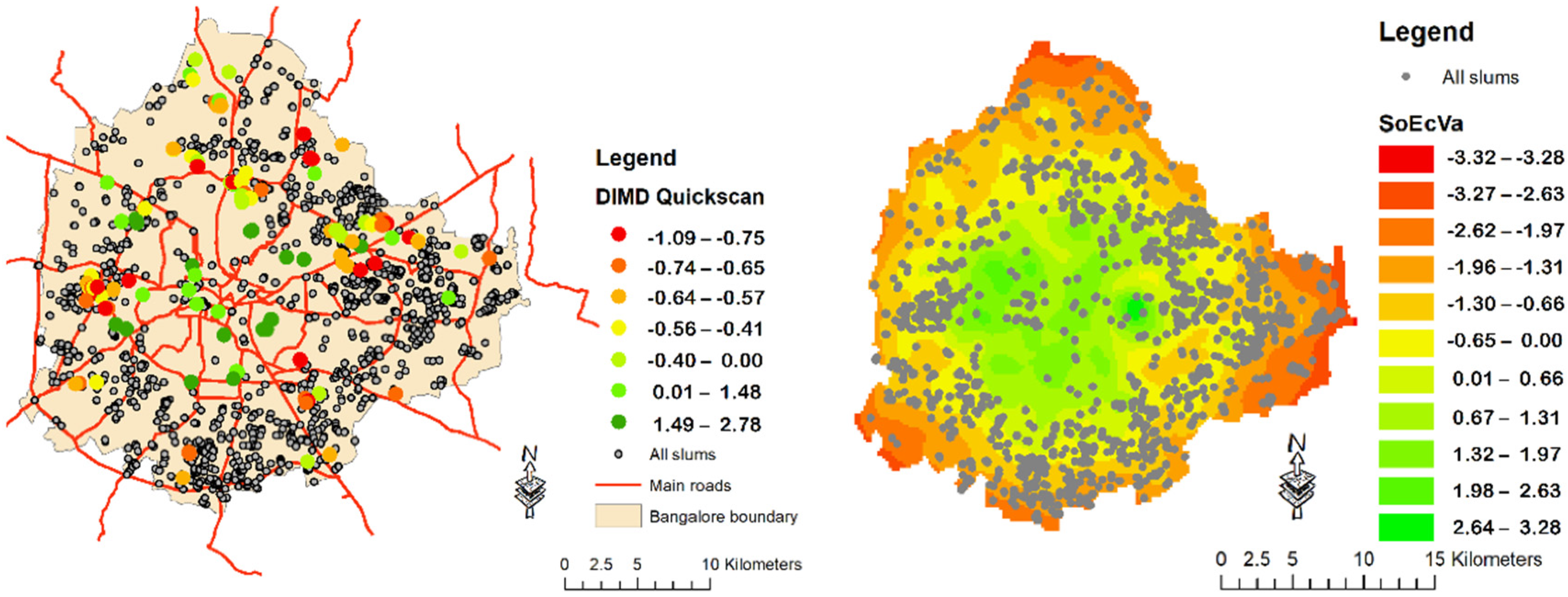
3.3. Socio-Economic Inequalities and Deep Learning
4. Discussion
- Strengthening local capacities to use and sustain these methods through methods that are easily reproducible and the promotion of training. In particular, those relevant in case of crisis and disasters, providing readily available data for fast responses. For example, such data have been mostly absent for COVID-19 responses (further discussed in Section 4.1).
- Improving data infrastructure through data standards and formats that promote spatial interoperability, Analysis Ready Data (ARD), and scalable workflows like cloud computing [10]. For example, in support of local and national SDG monitoring (further discussed in Section 4.2).
- Accelerating validation of promising new approaches and assessing their cost/benefit and suitability for purpose, as well as account for uncertainties in data (further discussed in Section 4.3).
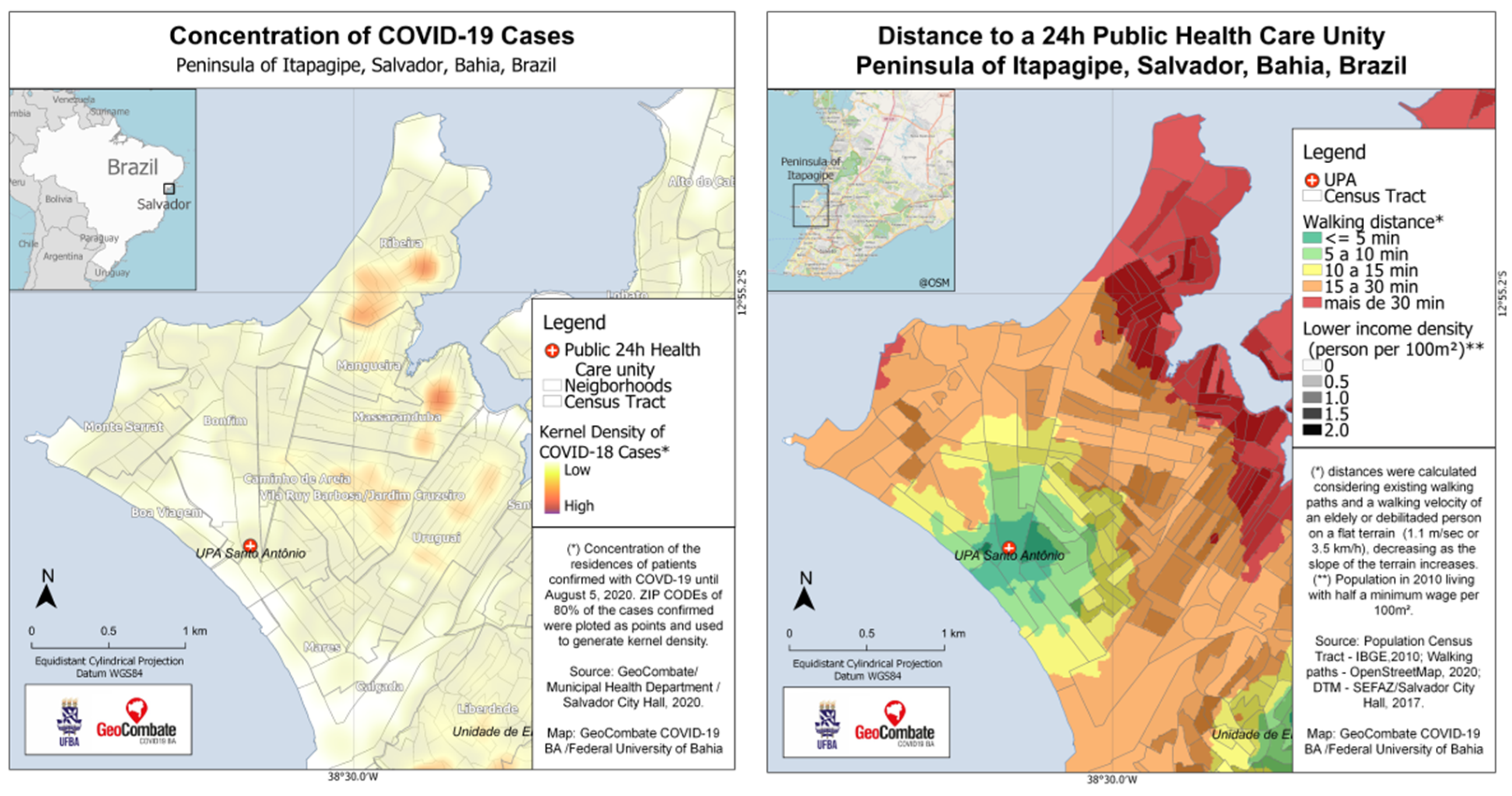
4.1. EO Data for COVID-19 Responses in Slums
4.2. EO Data for Local and National SDG 11 Monitoring
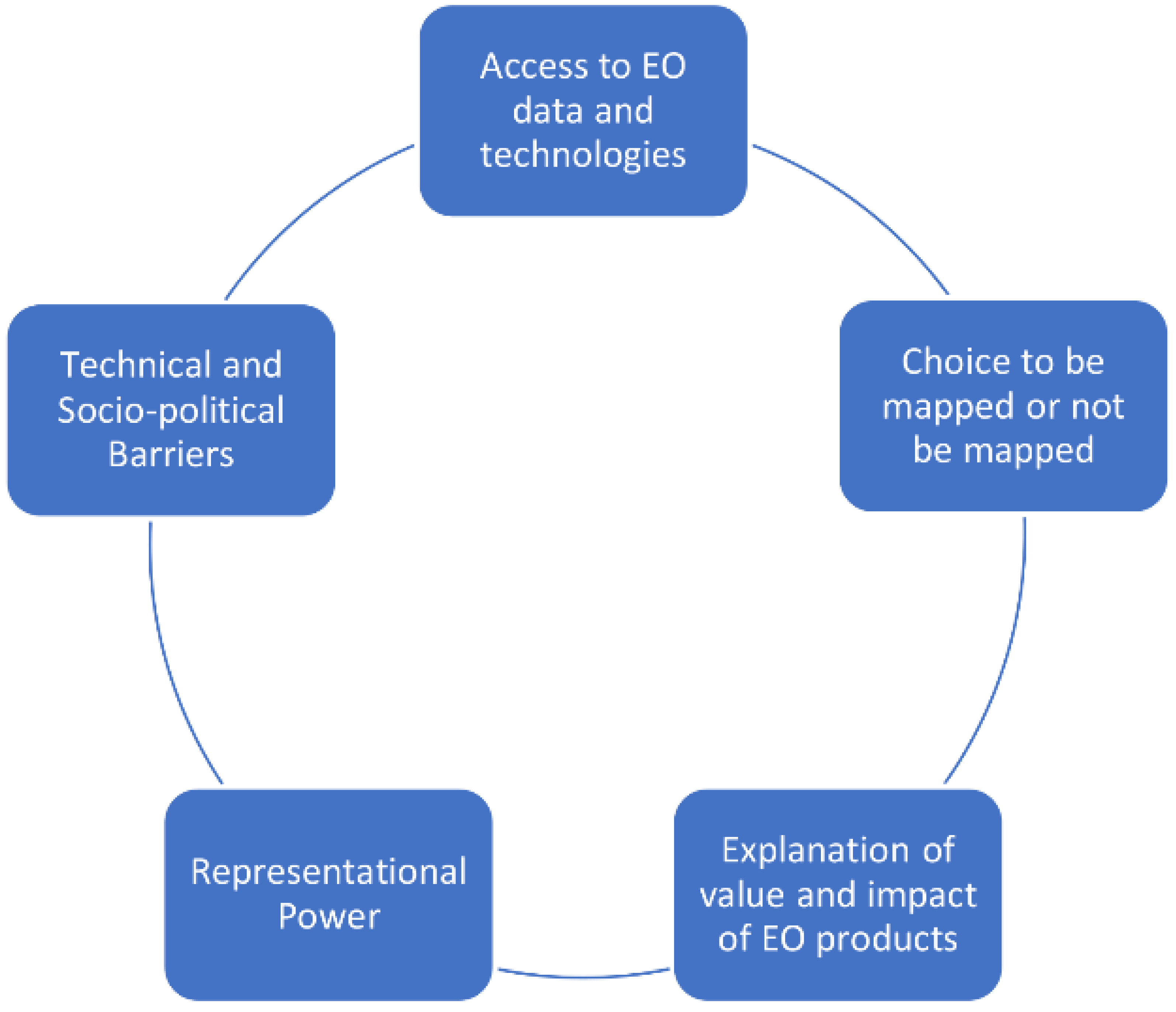
4.3. Data Dissemination, Validation and Accounting for Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Global COVID-19 Survey of National Statistical Offices
| Type of Census Planned for 2020 | Number of Countries That Were Planning One |
Saw an Impact on Preparatory Activities (Percentage of Those Who Answered) | Had to Postpone Field Work to Later in 2020 or to 2021 or Beyond (Percentage of Those Who Answered) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population and Housing Census | 61 | 58% | 53% |
| Agricultural Census | 44 | 50% | 55% |
| Business Census | 26 | 57% | 64% |
References
- UN-Habitat. Cities Alliance. In Analytical Perspective of Pro-Poor Slum Upgrading Frameworks; UN-HABITAT: Nairobi, Kenya, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- UN-DESA. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2018; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, R.; Kuffer, M. Cloud Computation Using High-Resolution Images for Improving the SDG Indicator on Open Spaces. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.V.; Kerle, N.; Stein, A. An ontology of slums for image-based classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat. Metadata Indicator 11.1.1. 2018. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/sites/default/files/2020/06/metadata_on_sdg_indicator_11.1.1.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Openshaw, S. The Modifiable Areal Unit Problem; Geobooks: Norwich, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, D.R.; Linard, C.; Vanhuysse, S.; Steele, J.E.; Shimoni, M.; Siri, J.; Caiaffa, W.T.; Rosenberg, M.; Wolff, E.; Grippa, T.; et al. Extending Data for Urban Health Decision-Making: A Menu of New and Potential Neighborhood-Level Health Determinants Datasets in LMICs. J. Urban Health 2019, 96, 514–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abascal, Á.; Rothwell, N.; Shonowo, A.; Thomson, D.R.; Elias, P.; Elsey, H.; Yeboah, G.; Kuffer, M. “Domains of Deprivation Framework” for Mapping Slums, Informal Settlements, and Other Deprived Areas in LMICs to Improve Urban Planning and Policy: A Scoping Review. Preprints 2021, 2021020242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The Global COVID-19 Survey of National Statistical Offices. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/covid19-response/covid19-nso-survey-report.pdf (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Castelán, C.R.; Weber, I.; Jacques, D.; Monroe, T. Making a better poverty map. In World Bank Blogs; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, D.R.; Kuffer, M.; Boo, G.; Hati, B.; Grippa, T.; Elsey, H.; Linard, C.; Mahabir, R.; Kyobutungi, C.; Maviti, J.; et al. Need for an Integrated Deprived Area “Slum” Mapping System (IDEAMAPS) in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs). Soc. Sci. 2020, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.R.; Gaughan, A.E.; Stevens, F.R.; Yetman, G.; Elias, P.; Chen, R. Evaluating the Accuracy of Gridded Population Estimates in Slums: A Case Study in Nigeria and Kenya. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilford, R.; Kyobutungi, C.; Ndugwa, R.; Sartori, J.; Watson, S.I.; Sliuzas, R.; Kuffer, M.; Hofer, T.; Porto de Albuquerque, J.; Ezeh, A. Because space matters: Conceptual framework to help distinguish slum from non-slum urban areas. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e001267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr-Hill, R. Missing millions and measuring development progress. World Dev. 2013, 46, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Wang, J.; Nagenborg, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C. The Scope of Earth-Observation to Improve the Consistency of the SDG Slum Indicator. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wardrop, N.A.; Jochem, W.C.; Bird, T.J.; Chamberlain, H.R.; Clarke, D.; Kerr, D.; Bengtsson, L.; Juran, S.; Seaman, V.; Tatem, A.J. Spatially disaggregated population estimates in the absence of national population and housing census data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3529–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, M.; Ramage, S.; Kavvada, A.; Goodman, S. Open Earth Observations for Sustainable Urban Development. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Thomson, D.R.; Boo, G.; Mahabir, R.; Grippa, T.; Vanhuysse, S.; Engstrom, R.; Ndugwa, R.; Makau, J.; Darin, E.; et al. The Role of Earth Observation in an Integrated Deprived Area Mapping “System” for Low-to-Middle Income Countries. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, J. An Introduction to Satellite Imagery and Machine Learning—Azavea Blog. 2019. Available online: https://www.azavea.com/blog/2019/11/05/an-introduction-to-satellite-imagery-and-machine-learning/ (accessed on 27 February 2021).
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergado, J.R.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. Recurrent Multiresolution Convolutional Networks for VHR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6361–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y. Complex-Valued Convolutional Neural Network and Its Application in Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 7177–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullissa, A.G.; Persello, C.; Stein, A. PolSARNet: A Deep Fully Convolutional Network for Polarimetric SAR Image Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 5300–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Jana, A.; Ramamritham, K. Transfer learning approach to map urban slums using high and medium resolution satellite imagery. Habitat Int. 2019, 88, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, A.; Kuffer, M.; Persello, C.; Pfeffer, K. Identifying a Slums’ Degree of Deprivation from VHR Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, D.; Bernal, D.; Lees, M. An exploratory factor analysis model for slum severity index in Mexico City. Urban Stud. 2020, 57, 789–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Baud, I. Extraction of slum areas from VHR imagery using GLCM variance. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, J.C.; Patino, J.E.; Betancourt, A. Exploring the Potential of Machine Learning for Automatic Slum Identification from VHR Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurm, M.; Stark, T.; Zhu, X.X.; Weigand, M.; Taubenböck, H. Semantic segmentation of slums in satellite images using transfer learning on fully convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Kuffer, M.; Persello, C. The Temporal Dynamics of Slums Employing a CNN-Based Change Detection Approach. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, L. Safety in numbers? Group privacy and big data analytics in the developing world. In Group Privacy: New Challenges of Data Technologies; Taylor, L., Floridi, L., van der Sloot, B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, P. General Data Protection Regulation—A Global Standard? Privacy Futures, Digital Activism, and Surveillance Cultures in the Global South. Surveill. Soc. 2019, 17, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beukes, A. Making the Invisible Visible: Generating Data on ‘Slums’ at Local, City and Global Scales; International Institute for Environment and Development: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C.; Vosselman, G. Evaluating the Societal Impact of Using Drones to Support Urban Upgrading Projects. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahabir, R.; Croitoru, A.; Crooks, A.; Agouris, P.; Stefanidis, A. A critical review of high and very high-resolution remote sensing approaches for detecting and mapping slums: Trends, challenges and emerging opportunities. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahabir, R.; Agouris, P.; Stefanidis, A.; Croitoru, A.; Crooks, A.T. Detecting and mapping slums using open data: A case study in Kenya. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2018, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabir, R.; Crooks, A.; Croitoru, A.; Agouris, P. The study of slums as social and physical constructs: Challenges and emerging research opportunities. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2016, 3, 399–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranguelova, E.; Weel, B.; Roy, D.; Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Lees, M. Image based classification of slums, built-up and non-built-up areas in Kalyan and Bangalore, India. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 52, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SDI. Strategic Plan 2018–2022; SDI: Cape Town, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- SDI. Know Your City: Slum Dwellers Count; SDI: Cape Town, South Africa, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leonita, G.; Kuffer, M.; Sliuzas, R.; Persello, C. Machine Learning-Based Slum Mapping in Support of Slum Upgrading Programs: The Case of Bandung City, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brito, P.L.; Kuffer, M.; Koeva, M.; Pedrassoli, J.C.; Wang, J.; Costa, F.; Freitas, A.D.d. The Spatial Dimension of COVID-19: The Potential of Earth Observation Data in Support of Slum Communities with Evidence from Brazil. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Forum for Geography and Statistics (EFGS). New Dataset on Statistical Grids. Available online: https://www.efgs.info/2020/02/27/new-dataset-on-statistical-grids/ (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Ansari, R.A.; Buddhiraju, K.M. Textural segmentation of remotely sensed images using multiresolution analysis for slum area identification. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadiraju, K.K.; Vatsavai, R.R.; Kaza, N.; Wibbels, E.; Krishna, A. Machine Learning Approaches for Slum Detection Using Very High Resolution Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Singapore, 17–20 November 2018; pp. 1397–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, R.; Alagu Raja, R.A. Urban Slum Detection Approaches from High-Resolution Satellite Data Using Statistical and Spectral Based Approaches. J. Ind. Soc. Remote Sens. 2018, 46, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Sieg, T.; Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H. Investigation on the separability of slums by multi-aspect TerraSAR-X dual-co-polarized high resolution spotlight images based on the multi-scale evaluation of local distributions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Baud, I.; van Maarseveen, M. Capturing the Diversity of Deprived Areas with Image-Based Features: The Case of Mumbai. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Persello, C.; Elberink, S.O.; Vosselman, G.; Sliuzas, R. Context-Based Filtering of Noisy Labels for Automatic Basemap Updating from UAV Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2731–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, H. Unsupervised Deep Feature Learning for Urban Village Detection from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2017, 83, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabat, A.; Tapamo, J.-R. A comparative study of the use of local directional pattern for texture-based informal settlement classification. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2019, 15, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevaert, C.M.; Persello, C.; Sliuzas, R.; Vosselman, G. Informal settlement classification using point-cloud and image-based features from UAV data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mboga, N.O.; Persello, C.; Bergado, J.; Stein, A. Detection of informal settlements from VHR images using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badmos, O.S.; Rienow, A.; Callo-Concha, D.; Greve, K.; Jürgens, C. Urban development in West Africa—Monitoring and intensity analysis of slum growth in Lagos: Linking pattern and process. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Kuffer, M.; Roy, D.; Pfeffer, K. Deprivation pockets through the lens of convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 234, 111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, M.; Kuffer, M.; Belgiu, M.; Grippa, T.; Lennert, M.; Georganos, S.; Vanhuysse, S. Towards user-driven earth observation-based slum mapping. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 89, 101681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhuysse, S.; Georganos, S.; Kuffer, M.; Grippa, T.; Lennert, M.; Wolff, E. Gridded urban deprivation probability from open optical imagery and dual-pol sar data. In Proceedings of the IEEE IGARSS 2021, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Persello, C.; Kuffer, M. Towards uncovering socio-economic inequalities using VHR satellite images and deep learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 3747–3750. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, T.K.A.; Wei, T.; Zhu, X. Mapping Urban Slum Settlements Using Very High-Resolution Imagery and Land Boundary Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, R.; Parvathavarthini, B.; Alaguraja, A. Integration of deep convolutional neural networks and mathematical morphology-based postclassification framework for urban slum mapping. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 014515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, V.; Saini, O.; Pandey, K.; Bhardwaj, A. Identification of slum settlements using logistic regression. In Proceedings of the ACRS 2020—41st Asian Conference on Remote Sensing, Deqing, China, 9–11 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Debray, H.; Kuffer, M.; Persello, C.; Klaufus, C.; Pfeffer, K. Detection of Informal Graveyards in Lima using Fully Convolutional Network with VHR Images. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K. The role of spatial heterogeneity in detecting urban slums. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 73, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, R.; Harrison, R.; Mann, M.; Fletcher, A. Evaluating the Relationship between Contextual Features Derived from Very High Spatial Resolution Imagery and Urban Attributes: A Case Study in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom, R.; Pavelesku, D.; Tanaka, T.; Wambile, A. Mapping Poverty and Slums Using Multiple Methodologies in Accra, Ghana. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Vannes, France, 22–24 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Badmos, O.S.; Rienow, A.; Callo-Concha, D.; Greve, K.; Jürgens, C. Simulating slum growth in Lagos: An integration of rule based and empirical based model. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 77, 101369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persello, C.; Stein, A. Deep Fully Convolutional Networks for the Detection of Informal Settlements in VHR Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2325–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, M.; Taubenböck, H. Detecting social groups from space—Assessment of remote sensing-based mapped morphological slums using income data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ella, L.P.A.; Van Den Bergh, F.; Van Wyk, B.J.; Van Wyk, M.A. A comparison of texture feature algorithms for urban settlement classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Boston, MA, USA, 26 September–2 October 2008; Volume 3, pp. III1308–III1311. [Google Scholar]
- Pratomo, J.; Kuffer, M.; Martinez, J.; Kohli, D. Coupling uncertainties with accuracy assessment in object-based slum detections, case study: Jakarta, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moser, C.O.N. The asset vulnerability framework: Reassessing urban poverty reduction strategies. World Dev. 1998, 26, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, I.; Taubenböck, H.; Kuffer, M.; Wurm, M. Misperceptions of Predominant Slum Locations? Spatial Analysis of Slum Locations in Terms of Topography Based on Earth Observation Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Seto, K.C.; Stokes, E.C.; Deng, C.; Pickett, S.T.A.; Taubenböck, H. Understanding an urbanizing planet: Strategic directions for remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebreyesus, T.A. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 10 September 2020).
- van Deursen, J.A.M. Digital Inequality During a Pandemic: Quantitative Study of Differences in COVID-19–Related Internet Uses and Outcomes Among the General Population. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e20073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadmi, E.; Chen, Y.; Dourado, I.; Faran-Perach, I.; Furler, J.; Hangoma, P.; Hanvoravongchai, P.; Obando, C.; Petrosyan, V.; Rao, K.D.; et al. Health equity and COVID-19: Global perspectives. Int. J. Equity Health 2020, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, M. COVID-19 death rate in deprived areas in England double that of better off places: ONS. Reuters, 2020. Available online: https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-britain-deprived-idUSKBN22D51O (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Iacobucci, G. Covid-19: Deprived areas have the highest death rates in England and Wales. BMJ 2020, 369, m1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secretaria Municipal de Saúde/Prefeitura de Salvador. TABNET. Available online: http://www.tabnet.saude.salvador.ba.gov.br (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Social Distancing. Keep a Safe Distance to Slow the Spread. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/social-distancing.html (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- World Health Organization Country Office for Thailand. The 6 Steps. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/searo/thailand/who-tha-six-steps.pdf?sfvrsn=b81cac2b_0 (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Barber, S.; Diez Roux, A.V.; Cardoso, L.; Santos, S.; Toste, V.; James, S.; Barreto, S.; Schmidt, M.; Giatti, L.; Chor, D. At the intersection of place, race, and health in Brazil: Residential segregation and cardio-metabolic risk factors in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 199, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, A.; Riley, L.W. Slum Health: From Understanding to Action. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagan, J.E.; Moraga, P.; Costa, F.; Capian, N.; Ribeiro, G.S.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Felzemburgh, R.D.M.; Reis, R.B.; Nery, N.; Santana, F.S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Determinants of Urban Leptospirosis Transmission: Four-Year Prospective Cohort Study of Slum Residents in Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johns Hopkins Ressource Centre. Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Brito, P.L.; Viana, M.S.; Delgado, J.P.M.; Brandão, A.C.; Pedrassoli, J.C.; Pedreira Júnior, J.U.; Souza, F.A. Nota Técnica 04—Alertas e Propostas de Ações para Península de Itapagipe Baseadas em Análises Geoespaciais de Suporte ao Combate à COVID-19; GeoCombate: Salvador, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Taubenböck, H.; Baud, I.; Maarseveen, M.v. Capturing the Urban Divide in Nighttime Light Images From the International Space Station. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2578–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat. The Earth Observations Toolkit for Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements. Available online: https://eo-toolkit-guo-un-habitat.opendata.arcgis.com (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Samek, W.; Montavon, G.; Lapuschkin, S.; Anders, C.J.; Müller, K.-R. Explaining Deep Neural Networks and Beyond: A Review of Methods and Applications. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Martínez, B.; Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E.; Atzberger, C.; Camps-Valls, G.; Gilabert, M.A. Understanding deep learning in land use classification based on Sentinel-2 time series. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntoutsi, E.; Fafalios, P.; Gadiraju, U.; Iosifidis, V.; Nejdl, W.; Vidal, M.-E.; Ruggieri, S.; Turini, F.; Papadopoulos, S.; Krasanakis, E.; et al. Bias in data-driven artificial intelligence systems—An introductory survey. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 10, e1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merodio Gómez, P.; Juarez Carrillo, O.J.; Kuffer, M.; Thomson, D.R.; Olarte Quiroz, J.L.; Villaseñor García, E.; Vanhuysse, S.; Abascal, Á.; Oluoch, I.; Nagenborg, M.; et al. Earth Observations and Statistics: Unlocking Sociodemographic Knowledge through the Power of Satellite Images. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212640
Merodio Gómez P, Juarez Carrillo OJ, Kuffer M, Thomson DR, Olarte Quiroz JL, Villaseñor García E, Vanhuysse S, Abascal Á, Oluoch I, Nagenborg M, et al. Earth Observations and Statistics: Unlocking Sociodemographic Knowledge through the Power of Satellite Images. Sustainability. 2021; 13(22):12640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212640
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerodio Gómez, Paloma, Olivia Jimena Juarez Carrillo, Monika Kuffer, Dana R. Thomson, Jose Luis Olarte Quiroz, Elio Villaseñor García, Sabine Vanhuysse, Ángela Abascal, Isaac Oluoch, Michael Nagenborg, and et al. 2021. "Earth Observations and Statistics: Unlocking Sociodemographic Knowledge through the Power of Satellite Images" Sustainability 13, no. 22: 12640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212640
APA StyleMerodio Gómez, P., Juarez Carrillo, O. J., Kuffer, M., Thomson, D. R., Olarte Quiroz, J. L., Villaseñor García, E., Vanhuysse, S., Abascal, Á., Oluoch, I., Nagenborg, M., Persello, C., & Brito, P. L. (2021). Earth Observations and Statistics: Unlocking Sociodemographic Knowledge through the Power of Satellite Images. Sustainability, 13(22), 12640. https://doi.org/10.3390/su132212640









