Abstract
Based on the Sustainable Development Goals and competitiveness index, an evaluation index system for sustainable development of tourism cities was established. The sustainable development level of 221 outstanding tourism cities in 2018 was evaluated, and their sustainable development paths were designed accordingly. The results show the following: (1) There is a large gap in sustainable development scores. In general, no city has achieved a strong sustainable development model. Natural and cultural resources and protection systems are the shortcomings of the systems. (2) The weights of natural and cultural resources and protection systems are the largest, and the weights of natural and cultural resources endowment, degree of tourism infrastructure construction, and economic support for natural and cultural resources are larger. Nature reserve coverage index, network popularity, and other indicators have greater weight. (3) There is a gap in the sustainable development level of tourism cities in the eight comprehensive economic zones. The economic zones in the eastern and southern coastal areas are better than those in the northwest and the middle reaches of the Yellow River. (4) The driving factors of the eight types of tourism cities distinguished by their characteristics are basically the same, but the obstacles are different.
1. Introduction
The global Agenda 21 points out that sustainable development indicators must be designated in order to provide a solid theoretical basis for decision makers at all levels and to promote an integrated and self-regulating capacity for sustainable development of the environment and development systems [1]. In September 2015, the leaders of all UN member states adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in the form of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The 17 SDGs seek to solve economic, social, and environmental problems in a sustainable way, supported by good governance [2]. Since then, the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators (IAEG-SDGs) has put forward a global monitoring indicator framework applicable at the country level [3]. There is growing recognition of the importance of implementing the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals and achieving the SDGs at the local level [4]. Achieving these global aspirations requires local commitment and action by local governments [5]. The Global Task Force on Local and Regional Government points out that localization is about how the SDGs provide a framework for local development policies as well as how local and regional governments support achieving the SDGs through bottom-up action [6]. In terms of SDG localization, previous research has shown that the main challenges and opportunities are in cities, and they affect all SDGs, not just SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities) [7,8,9].
Over the past decades, travel and tourism, with their beneficial ecosystems, have proved to be important drivers of economic growth, contributing more than 10% of global GDP and accounting for one in ten jobs globally. The sector continues to be a force for good, offering unique opportunities for developing and emerging countries to move up the value chain. In the context of the rapid development of the cultural tourism industry, evaluating the sustainability of tourism destinations is a key direction of sustainable tourism research [10]. By applying and developing sustainable development evaluations and implementing strategies at the city level, sustainability research has become integral to the current high-quality development of the tourism industry and cities. Savage [11] notes that adopting a holistic view is conducive to measuring the sustainability of urban tourism development. Lee et al. [12] pointed out that in order to achieve long-term sustainability, it is necessary to ensure the sustainable use of the ecological environment and improve the reliability of destinations and the quality of tourism services. At present, there are many studies on the sustainable development of tourism, but relatively few on the sustainable development of tourism cities. Based on previous studies, Wang [13] tried to establish an evaluation index system of sustainable development capacity of small and medium-sized tourism cities. Taking Lijiang city as an example, Li [14] discussed the roots and internal mechanism of the vulnerability of the economic systems of tourism-oriented cities, and put forward countermeasures and suggestions to realize their sustainable development. Yin [15] put forward the context of sustainable development of tourism cities in terms of the time, space, and development scales, and presented countermeasures and suggestions for sustainable development of international tourism cities. Perez et al. [16] constructed a set of indicators to measure the sustainability of urban tourism. Different from the traditional static evaluation, Blancas et al. [17] established a dynamic evaluation index suitable for tourism-oriented cities through the objective planning method.
With increased competitiveness among tourism cities, studies evaluating this competitiveness arise at a historic moment. Most studies point out that the competitiveness of tourist destinations is a complex concept with multiple dimensions [18], which should be discussed from multiple perspectives. Many studies in this field have tried to quantify the competitiveness of tourism destinations using surveys conducted directly with tourists and other stakeholders [19,20], or using official statistics. Regardless of the source of information, most studies use a series of statistical techniques to quantify comprehensive competitiveness indicators. These indicators are conceptual-based and constructed by multiple variables in different dimensions [21,22]. However, there is no competitiveness evaluation index system for sustainable development in academic research, and the existing system often lacks social and economic basic data, which cannot truly reflect the development potential of tourism cities.
From the above literature review, it can be seen that under the background of the rapid development of cultural tourism industry and the rise of tourism cities, tourism cities have gradually become an important city type. At present, the evaluation of sustainable development of tourism cities mostly stays at the level of theoretical research, such as establishing an index system and identifying problems. There are few pieces research on the quantitative evaluation and practice of sustainable development of tourism cities based on SDGs.
What is the level of sustainable development of tourism cities? What are the factors that affect the sustainable development of tourism cities? How can a tourism city choose a sustainable development path suitable for its own development? How to evaluate the sustainable development of international tourism cities in the same context? These are becoming greater concerns for the government, scholars, and the general public. It is imperative to establish a sustainable development evaluation technology system for tourism cities, to quantitatively evaluate and scientifically identify bottlenecks that hinder actual needs, and the dual pressures of internal management and competition. The effort made in this article is to answer the above questions. Taking into account that the implementation of SDGs at the city level is an important part of China’s implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the availability of relatively mature and referenceable tourism competitiveness index evaluation practices in the world, this paper constructs an evaluation framework for sustainable development of tourism cities based on the SDGs and tourism competitiveness index, forms a technical evaluation system of sustainable development of tourism cities, and evaluates the sustainable development level of 221 tourism cities in China in 2018.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data and Study Area
Since China started to create outstanding tourism cities in 1998, nine groups of 339 cities have passed inspection. In this study, we eliminated cities with much missing data, and finally determined 221 outstanding tourism cities (prefecture-level and above) as the research objects, and evaluated their sustainable development level in 2018.
The data mainly come from public sources such as statistical yearbooks, statistical bulletins, reports, etc. Some indicators that could not be obtained directly were calculated twice by the raw data collected by the author, and the missing data were interpolated by the Replace Missing Values tool in SPSS.
2.2. Research Methods
The research methods can be summarized into four steps: (1) put forward a comprehensive evaluation system of urban sustainable development, (2) standardize and weigh each index in the evaluation system, (3) use a linear weighting method to calculate the final score of sustainable development of tourism cities, and (4) analyze the results from the point of view of overall results and geographic and characteristic zoning. Step four presents the sustainable development level of Chinese tourism cities, and designs their sustainable development paths with different characteristics according to the results of correlation analysis and comparison with other research results.
2.3. Evaluation Index System of Sustainable Development of Tourism Cities Based on SDGs and Tourism Competitiveness Index
The construction ideas of the evaluation index is shown in Figure 1. In this paper, we construct a sustainable development index system of tourism cities, which includes a protection system (A), a sustainable utilization system (B), and a social support system for natural and cultural resources economic (C); it includes three systems, ten pillars, 22 factor indicators, and 46 specific indicators. The sustainable development index system of tourism cities is closely related to the SDGs. The index system integrates SDG1, SDG3, SDG6, SDG8, SDG9, SDG10, SDG11, SDG12, SDG13, SDG14, SDG15, SDG16, SDG17, and other target indicators, as shown in Table 1. The indicator system includes single indicators (37) and comprehensive indicators (nine). When using this indicator system for evaluation, tourism cities can make adjustments without changing the meaning of the indicators according to their own statistical caliber and capabilities.
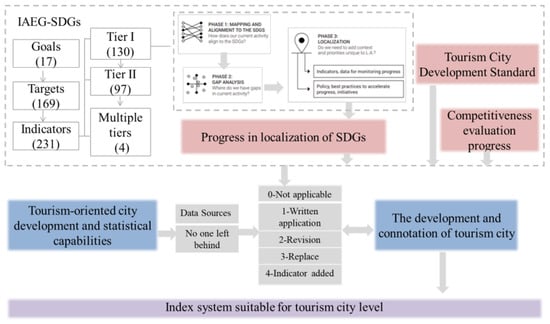
Figure 1.
Construction of sustainable development index system for tourism cities. Note: SDG localization steps refer to Sustainable Development Goals of the City of Los Angeles: A Local Review of Progress in 2019 [23]; SDG localization progress mainly refers to relevant achievements at the global, regional, national, and sub-national level [24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].

Table 1.
Index system of sustainable development of tourism cities.
System A is subdivided into three pillars, which are natural and cultural resource endowment (A1), conservation of natural and cultural resources (A2), and ecological environment protection (A3). System B is subdivided into four pillars, which are degree of exploitation and utilization of natural and cultural resources (B1), degree of tourism infrastructure construction (B2), development of tourism economy (B3), and sustainability of tourism development (B4). System C is subdivided into three pillars, which are economic support for natural and cultural resources (C1), social support for natural and cultural resources (C2), and tourism industry governance (C3).
The evaluation index system adopted in this paper has the following advantages: indicators and definitions in the SDGs are adopted as much as possible, enhancing comparability and extensibility compared with other evaluation index systems, and considering the characteristics and development needs of tourism cities, elements of the index system are added, deleted, and modified in combination with the existing mature competitiveness index and tourism cities development standard. The evaluation index system is constructed according to the basic principle of systematization, and the various aspects of the sustainability of tourism cities are fully described based on hierarchical division.
2.4. Standardization and Weights
2.4.1. Standardization of Indicators
In order to eliminate the influence of dimension and attribute of indicators, this paper adopts the deviation standardization method (i min–max method), which improves the optimal and worst values of indicators to standardize the original data of positive and negative indicators. This paper refers to the five-step decision tree method [36] adopted in the SDG index and dashboard report released by SDSN, and determines the optimal and worst values of the selected indicators after adjustment. Tourism cities that exceed the optimal and worst values are one and zero, respectively, after standardization.
For interval and moderate indicators, the methods in Formulas (3) and (4) are adopted for standardization, in which the optimal interval of interval indicators and the optimum value of moderate indicators are determined by relevant provisions and literature review.
Standardization of positive indicators by the i min-max method is calculated as:
Standardization of negative indicators by the i min-max method is calculated as:
where and represent the optimal and worst value of the ith evaluation index, respectively.
Standardization of moderate indicators is calculated as:
where is the optimum value of the ith evaluation index, and M is the maximum value of the absolute value difference between all index values and the interval optimal value.
Standardization of interval indicators is calculated as:
where [a,b] is the optimal interval of the ith evaluation index, and M = max {a − , − b}.
2.4.2. Weight Calculation
The average processing of all SDG index data does not conform to the 28th law of management [37]. Learning from the criticism of scholars on the weight assignment method of the tourism competitiveness index [38], this study adopts the combination weight assignment method. At present, the commonly used objective weight assignment method is the entropy weight method, but it does not consider the influence between indicators, and there is a phenomenon of unreasonable weight allocation to some extent. Therefore, this paper uses the principle of minimum information entropy to obtain the combined weight from the entropy weight and coefficient of variation methods [39].
Here, = 1, wi > 0, and F is the objective function of the minimum information entropy model.
According to the Lagrange multiplier method, the above equation can be optimized as follows:
2.5. Calculation of Sustainable Development Level of Tourism Cities Based on SDGs and Tourism Competitiveness Index
The score of the sustainable development level of tourism cities is calculated by the linear weighted function method and adjusted to the range of 0–100:
where i represents the number of indicators, o represents the number of index layers of each element, h represents the number of pillar layers, and k represents the number of system layers. w is the weight, and the sum of ownership weights of each layer is equal to one; f(x) is the score of the sustainable development level.
Sustainable development is divided into five levels (high, upper medium, medium, low, and extremely low) by referring to the internationally common isometric division method (20 points per interval as a level).
2.6. Three-Axis and Eight-Zone Classification Assessment
In this paper, the scores of systems A, B, and C are discussed in a comprehensive framework. Taking the score of system A as the x-axis, the score of system B as the y-axis, and the score of system C as the z-axis, the coordinate system to evaluate sustainable development of tourism cities was established. Taking the median scores of systems A, B, and C as the reference line, the three axes and eight districts for the evaluation are obtained, and the relevant positions for evaluating tourism cities are described. The region and sustainable development level of tourism cities are the basis for comparing and analyzing the current situation of urban sustainable development and putting forward paths for improvement.
2.7. Multiple Linear Regression Model
A multiple linear regression model is a model with multiple explanatory variables, which is used to explain the linear relationship between the explained variables and other explanatory variables [40]. Because the explained variable is a calculated numerical variable, and the explained variable is also a numerical variable, which accords with the basic conditions of phenomenal regression analysis, a multivariate linear regression model is constructed in this paper. The ordinary least square method is used to fit the regression equation and estimate the parameters [41]. The mathematical model of multiple linear regression is:
The above is a k-ary linear regression model, y is the explained variable, in this paper, it is the sustainable development level of tourism city; x is the explanatory variable, there are k explanatory variables, the explanatory variable in this paper is the sustainable development index of tourism city; β0 is the constant term of the regression model; β1, β2, …., βk is the partial regression coefficient and ε is the random error of the regression model. Among them, the change of the explained variable y consists of two parts, the first part is the linear change part of y caused by the change of k explanatory variables x, and the second part is the change part of y caused by other random factors, namely ε.
3. Results
3.1. Influence Weights of Each Indicator
The weights of systems A, B, and C are 40, 33.35, and 26.52% respectively, indicating that natural and cultural resources and protection systems are the main drivers for evaluating the sustainability of tourism cities. The largest weights of pillars are natural and cultural resource endowment (A1), degree of tourism infrastructure construction (B2), and economic support of natural and cultural resources (C1). The weight distribution of factor indicators, and specific indicators is shown in Figure 2a,b.
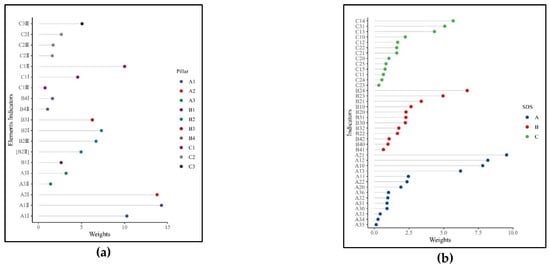
Figure 2.
Weight distribution of (a) factor indicators and (b) specific indicators.
As can be seen from Figure 2a, the factor indicators with the greatest weight in each pillar are resource influence (A1II), ecological environment quality (A3I), tourism service infrastructure (B2I), sustainability of resource utilization (B4I), international openness (C1II), and tourism safety and health care (C2I).
For a given index, the greater the weight, the greater the impact on the sustainable development of tourism cities. Figure 2b shows the five indicators that have the greatest impact on sustainable development: nature reserve coverage index (A21), network fever (A12), heritage index (A10), number of wisdom scenic spots (B24), and well-known city index (A13). The most important indicator is A21, and its influence weight is 9.53%. The influence weights of A12 and A13 are 8.18 and 6.21%, respectively, showing the importance of the popularity and public recognition of tourist cities. The influence weights of A10 and B24 are 7.81 and 6.69%, respectively, which shows the importance of developing intelligent tourism in the new era. The five indicators that have the least impact on the sustainability of tourism cities are income gap between urban and rural residents (C24), ecological index (A33), unemployment rate (C23), proportion of safe treatment of waste water (A34), and rate of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste (A35); the weights of these indicators are 0.54, 0.42, 0.32, 0.26, and 0.13%, respectively.
3.2. Overall Result
3.2.1. Overall Score
The score ranges for overall sustainable development and the major systems of China’s tourism cities are [17.05, 62.24], [10.00, 46.61], [18.76, 76.10], and [17.59, 69.68], respectively. The three cities with the highest total scores are Beijing, Chongqing, and Chengdu. The top three cities with the highest scores in the A system are Tianjin, Beijing, and Danzhou. The three cities with the highest scores in the B system are Chengdu, Beijing, and Chengdu. In Chongqing, the three cities with the highest C system scores are Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen. The average scores of the pillars under the A system are 12.59, 18.26, 78.57. The average scores of the pillars under the B system are 21.66, 23.35, 34.16, and 91.06. The average scores of each pillar under the C system are 25.23, 48.2, and 16.18, respectively.
The natural discontinuity classification method (Jenks) in ArcGIS was used to classify all of the scores into five categories. The geographical distribution of the evaluation results is shown in Figure 3.
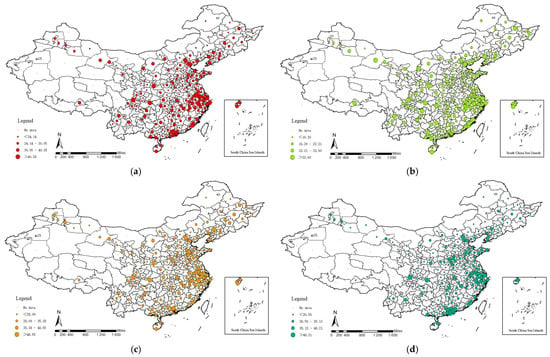
Figure 3.
Geographic distribution of sustainable development scores of tourism cities: (a) overall score; (b–d) B, C, and D system scores.
3.2.2. Sustainability Level
On the whole, none of the tourism cities have reached a high level of sustainable development, and one city has reached upper medium level: Beijing, accounting for 0.41%, nine cities and have reached medium level: Chongqing, Chengdu, Tianjin, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Guangzhou, Xiamen, Shenyang, and Fuzhou, together accounting for 4.07%. In all, 198 cities are at a low level of sustainable development (accounting for 89.59%), while the remaining 12 cities are at a very low level (accounting for 5.43%). The level distribution of the sustainable development systems of tourism cities is similar to the overall results. There is a large gap in the levels of development among the pillars. Pillars with better overall performance are ecological environment protection (A3) and sustainability of tourism development (B4). More than 50% of the cities are at a high level of sustainable development. Pillars with poor performance are natural and cultural resources endowment (A1), conservation of natural and cultural resources (A2), and tourism industry governance (C3), and more than 60% of the cities are at a lower level of sustainable development. Among them, the pillars conservation of natural and cultural resources (A2) in Zhoushan, degree of exploitation and utilization of natural and cultural resources (B1) in Chongqing and Beijing, degree of tourism infrastructure construction (B2) in Chengdu, and tourism industry governance (C3) in Beijing, Chengdu, Chongqing, and Shanghai are all at a high level of sustainable development.
3.3. Results and Analysis of the Eight Economic Zones
According to the report “Strategies and Policies for Coordinated Regional Development” issued by the Development Research Center of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China, the mainland is divided into four plates and eight comprehensive economic zones. In order to facilitate a comparative analysis of cities in their economic zones, we obtained the regional distribution of 221 tourism cities with reference to the eight comprehensive economic zones. The average score of sustainable development of tourism cities in the eight economic zones is shown in Figure 4 As can be seen from Figure 4, the overall average score of sustainable development in the eastern coastal economic zone is the highest, while that of the middle reaches of the Yellow River is the lowest. Economic zones with the highest average scores for sustainable development in pillars A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3, B4, C1, C2, and C3 are the southern coastal areas, the middle reaches of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, the southern and eastern coastal areas, and the eastern coastal economic zone. The lowest economic zones are northwest, northern coastal, northeast, middle reaches of the Yellow River, northeast, northwest, eastern coastal, northwest, southwest, and northern coastal economic zones.
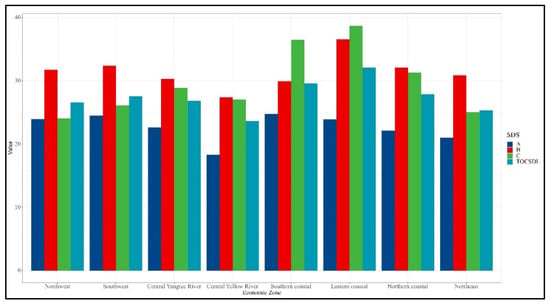
Figure 4.
Average score of sustainable development of tourism cities as a whole and for 3 major systems according to economic zone.
3.4. Three-Axis, Eight-Zone Division Results and Analysis
Taking the median score of sustainable development of the systems for 221 cities, i.e., straight lines x = 19.99, y = 26.83, z = 29.70 as the baseline, sustainable development of the three-axis eight-zones of tourism cities in China was obtained, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Three-axis, eight-zone division of sustainable development of tourism cities.
To explore indicators affecting sustainable development, this paper defines the drivers as the five indicators with the highest sustainable development scores in the eight districts based on three-axis, eight-quadrant zoning, and the obstacles as the five indicators with the lowest scores, as shown in Figure 5. As can be seen from the figure, the main driving factors of and obstacles to sustainable development of tourism cities are different. Specifically, the main driving factors in the eight districts are proportion of safe treatment of wastewater (A34), rate of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste (A35), and greenhouse gas emission intensity (A36) in system A and water resources development and utilization rate (B41) and intensity of tourist space utilization (B42) in system B. Mortality due to road traffic injuries (C20) in system C is also one of the main driving factors. There are great differences among the obstacles to sustainable development: In districts I, II, III, IV, and VIII, system A is the main obstacle to increasing the level of sustainable development. In areas V and VII, systems C and B are the main obstacles, and in area VI, system B is the main hindrance.
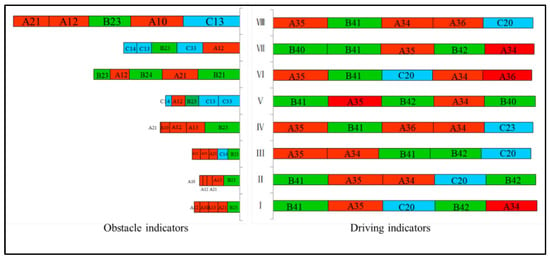
Figure 5.
Obstacles to and drivers of sustainable development of tourism-oriented cities in three quadrants and eight districts. Note: (i) Red represents A, green represents B, blue represents C; (ii) value ranges of horizontal axis of drivers and obstacles are 0–4.80 and 0–0.93, respectively, which are not proportional to the plot.
3.5. Validation and Result Analysis of Multiple Linear Regression Model
It is proved that the values of all the explained variables analyzed in this paper show normal distribution. By setting the significance test level to 0.05 and using the method of stepwise regression analysis, the final model is formed after the following operations. The test indexes in the model are as follows: (1) The DW observation value of the final model is close to two, which reflects that the residual sequence has no autocorrelation, indicating that the regression equation can fully explain the changing law of the explained variables, and the selected regression model is more appropriate. (2) The tolerance of all variables in the final model is greater than 0.50, and the variance expansion factor is less than two, which indicates that the multicollinearity among multiple variables is weak. (3) In the significance test of the regression equation, the final probability p-value of the F test statistics of the final model is 0.000, which is less than the significance test level, indicating that the establishment of the linear regression model is appropriate, and the fitting effect of the model is better.
Using the above model verification method, the overall score and system score of sustainable development of tourism cities are taken as explained variables, and all specific indicators and corresponding specific indicators of each system are taken as explained variables. The stepwise screening strategy is used for multiple linear regression analysis, and the results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of multiple linear regression analysis.
Taking the results of “TOCSD- Specific indicators” regression analysis in Category I as an example, the four indicators that have the greatest influence on the sustainable development level of tourism cities in Category I are C22, A24, C25, C13, and the standardized regression coefficient is in parentheses after the index, which means that if percentage of population covered by mobile network increases by one unit, the score of sustainable development will be increased by 0.489 points. It shows that the improvement of communication readiness can play a significant role in improving the level of sustainable development.
4. Discussion
4.1. Further Discussion
4.1.1. Comparative Analysis with SDG Index and Dashboards
The United Nations Network of Solutions for Sustainable Development (UNSDSN) and the Bertelsmann Foundation have issued five Sustainable Development Goals Index and Dashboard Reports since 2016, examining the extremes, data standardization, and weighted aggregation, and synthesizing countries’ SDG index scores by calculating the average of each subdivision index and the 17 SDG overall goals [42]. The indices related to the SDGs in this paper are processed by equal weight arithmetic weighting to get the average score of each SDG of Chinese tourist cities, and according to the defined color ranking indicated on SDG Dashboards, the color of each SDG indicator of Chinese tourist cities is determined. A comparison between China’s SDG dashboards (SDSN) and tourist city dashboards in 2018 is shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison of Chinese (SDSN) and tourism city SDG dashboards.
As can be seen from Table 4, the SDG scores of tourism cities are in the range of [15.31, 86.62], and the range of the SDG index is [33.50, 99.70]. The color of SDG6 on the Chinese SDG dashboard is the same as that of the dashboards in tourist cities, which is yellow, while the performance of SDG3, SDG10, and SDG13 in tourist cities as indicated by dashboard color is better than that of the Chinese dashboard. The performance of SDG1, SDG8, SDG9, SDG11, SDG12, SDG15, and SDG17 is worse than that of the Chinese dashboard. This is because there is no direct relationship between poverty level and tourism development, so SDG1 in tourism cities does not pay attention to indicators such as the incidence of poverty, but only focuses on the “proportion of expenditure on basic services in total government expenditure”, which reflects social stability. Most of the rest are due to the addition of tourism-related indicators such as per capita tourism consumption expenditure, tourism space utilization intensity, and tourism infrastructure index to the sustainable development index of tourism-oriented cities. These indicators are more general than those in some foreign cities; for example, per capita tourism consumption expenditure reached EUR 2148 (equivalent to RMB 16338.33) in Paris in 2018, compared to RMB 1204 in China’s tourism cities.
4.1.2. Comparative Analysis with the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index
The World Economic Forum (WEF) has released a Tourism Competitiveness Report every two years since 2007, which aims to measure the attractive factors and policies of the tourism industry in different countries, and to evaluate the competitiveness of the industry in major countries around the world by establishing a tourism competitiveness index. The Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019: Travel and Tourism at a Tipping Point covers 140 countries and regions around the world, with ranking by 14 metrics. The equal weight arithmetic average method is to calculate the total score, which ranges from one to seven, with one being the worst and seven the best [43]. The sustainable development index of tourism-oriented cities in this paper is calculated by the same method, and the score of the WEF China tourism competitiveness index is scaled 0–100, so as to facilitate a comparison between the two, as shown for 2019 in Table 5.

Table 5.
Comparison of China’s WEF tourism competitiveness index and level of sustainable development of tourism cities.
As can be seen from Table 5, the score range of sustainable development of the pillars of China’s tourism cities in 2018 is [16.1, 81.54], while that of the tourism competitiveness index in 2019 is [44.29, 100.00]. The main reasons for the gap are as follows: (1) The index system constructed in this paper takes into account the differences in economies of scale and development levels, and adds indicators that reflect the economic and social basis. (2) It is expected that the original indicators of the tourism competitiveness index will have a different impact on competitiveness, and the pillar used by WEF consists of three to 12 indicators; this means that some indicators contribute more to the overall indicators than others. Therefore, this paper uses the entropy method of coefficient of variation to determine the weight of the index, rather than a simple equal weight method. (3) All indicators in this paper are treated on a per capita basis; for example, the tourism competitiveness index takes into account the total number of scenic spots and intangible cultural heritage, but this paper considers per capita number of scenic spots and per capita intangible cultural heritage, which can better reflect the background of natural and cultural resources in tourism cities.
4.2. Policy Implications
Government policies can promote sustainable development, but tourism cities need to explore various sustainable development paths to deal with the inherent differences between them and eliminate the negative impact of institutional mechanisms.
The development of tourism cities in China is uneven, and sustainable development shows obviously uneven spatial distribution. The balanced sustainability of tourism cities should be an important goal to narrow the overall gap between countries. A new mode of governance and participation should be implemented. In order to realize balanced development among tourism cities, regional cooperation must be further strengthened, as well as the substantive mechanism of cooperation.
The geographic locations of the eight comprehensive economic zones are similar, and the natural and cultural bases are also relatively similar, which can strengthen regional cooperation and exchanges on the whole, but the shortcomings and advantages of development in the economic zones are different. Specifically, the eastern and southern coastal economic zones should control the utilization rate of water and land resources within a reasonable range to enhance the sustainability of tourism development. The middle and northern coastal economic zones of the Yellow River should pay attention to the development and protection of natural and cultural resources, improve the development and utilization of natural and cultural resources, and increase the number of tourist associations and their overall planning capacity. The southwest and northwest economic zones should prioritize social and economic development, enhance the development and protection of heritage and scenic spots, improve social stability, and promote stable economic development. The economic zone in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River should further strengthen the construction of tourism infrastructure. The northeast economic zone should strengthen the governance of the tourism industry while excavating natural and cultural resources.
According to the characteristics, the drivers and obstacles in the eight districts are different, so the appropriate planning for a sustainable development path should be carried out. The sustainable development path planning and countermeasures of the eight tourism cities are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Path planning and countermeasures for sustainable development in three quadrants and eight districts.
4.3. Limitations and Future Research Direction
This study explores the evaluation and analysis of the sustainable development level of tourism cities from the point of view of SDGs and tourism competitiveness index for the first time, which has a certain theoretical and practical value. However, the following limitations should be considered when interpreting this study.
First of all, the localization of urban SDGs is relatively weak and lacks a widely accepted theoretical system of SDGs localization methodology, so the construction method and logic of the evaluation index system of sustainable development of tourism cities in the context of SDGs need to be further clarified. Secondly, because the evaluation of sustainable development of tourism cities involves a wide range and the evaluation index system is complex, although a large number of data are used for evaluation and analysis, there are still some indicators that have not been quantified or deleted because of incomplete data and other problems; finally, due to the caliber of urban statistics and the limitation of time and energy, a large number of cities have not been studied for a long time, and time series comparison may be insufficient.
The research on the sustainable development of tourism cities is a complicated subject. How to implement SDGs in tourism cities also needs further research, and more in-depth and comprehensive work needs to be carried out in the future. The sustainable development of tourism cities involves many contexts. In the future, the sustainable development of tourism cities can be analyzed in more detail with SDGs, and the sustainable development indicator dashboard can be used to show the progress of tourism cities in implementing the 2030 sustainable development agenda, and to further explore the contribution of tourism cities in the process of achieving the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. The index system established in this paper is generally applicable to domestic and foreign tourist cities, so in addition to evaluating as many tourism cities in China as possible, we can also select international well-known tourism cities to study together with Chinese tourist cities in the future. On the basis of discovering gaps and advantages, Chinese tourism cities can continue to give full attention to their strengths and learn from the relevant successful experiences of international tourism cities. In addition, the emergence of COVID-19 in December 2019 affected more than 200 countries and regions, and had an impact on industries such as health, biomedicine, environment, and tourism, among which hotels and tourist activities are productive sectors severely affected by the epidemic. The world’s major tourism cities have been hit the hardest. Therefore, based on detailed data in the future, the impacts of COVID-19 on the sustainable development of tourism cities can be quantitatively analyzed, and how tourism cities should improve their crisis management ability and social governance level can be further discussed.
5. Conclusions
The research in this paper has theoretical and practical significance, which is mainly reflected in the establishment of a sustainable development evaluation framework for tourism cities that integrates SDGs and competitiveness indexes. This framework is generally applicable to the sustainable development evaluation of international tourism cities, complementing SDGs and the competitiveness evaluation model for the predicament of insufficient guidance for sustainable development evaluation of tourism cities, explores the SDGs-based sustainable development level evaluation technical methods for tourism cities, and takes 221 excellent tourism cities in China as an example. It is proved that the technical methods proposed in this paper are scientific and operable, and provide experience for the evaluation of sustainable development of other similar tourism cities in the world. The main conclusions are as follows.
On the whole, the sustainable development of tourism cities in China has not reached a high level, and there is a large gap in performance among the pillars, among which ecological environment protection (A3) and sustainability of tourism development (B4) perform better as a whole, while conservation of natural and cultural resources (A2) and tourism industry governance (C3) perform poorly. The results show that there is a gap between Chinese and international tourism cities. China also needs to strengthen the cultivation of high-quality tourism cities while expanding the scale of tourism.
From the weight results, the weight of system A is the largest among the three systems; the weights of heritage index (A1), degree of tourism infrastructure construction (B2), and economic support of natural and cultural resources (C1) are larger; and the weights of nature reserve coverage index (A21), network fever (A12), and heritage index (A10) are larger, indicating that tourism cities should pay attention to the exploration and protection of natural and cultural resources in order to improve the level of sustainable development. This is also consistent with the country’s insistence that “history and culture are the soul of the city, and we should protect the city’s historical and cultural heritage as well as our own life”.
From the point of view of geographic divisions, there are obvious differences in the sustainable development level of tourism cities in China’s eight major economic zones. Specifically, the eastern and southern coastal economic zones perform better, while the economic zones in the northwest and the middle reaches of the Yellow River perform poorly. The economic zones should strengthen cooperation and exchanges and pay more attention to their poor performance.
From the point of view of feature division, the main driving factors of tourism cities in the eight districts are proportion of safe treatment of waste water (A34), rate of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste (A35), greenhouse gas emission intensity (A36), and water resource development and utilization rate (B41), but the obstacle factors are different. According to the results of correlation analysis, the systems, pillars, and specific indicators most related to the level of sustainable development level are also different. From the point of view of the path of sustainable development, tourism cities in category I should first consolidate the foundation of economic and social development and gradually improve the speed and quality of tourism development; cities in category VIII should take the road of capacity expansion, quality improvement, and optimization, so as to further improve the level of sustainable development. Tourism cities in the transitional stage (categories II–VII) should expand the supportive and driving role of good system development to the development of other systems in order to ensure a better system. From the point of view of the comparative analysis of existing achievements, based on the unified calculation method, there is consistency between the sustainable development levels of Chinese tourism cities and the SDSN sustainable development index and tourism competitiveness index scores, which shows that the conclusion of this paper is scientific. There are also differences, and the main reason is that this paper focuses on the sustainable development of tourism cities and makes improvements in the design of an index system, specific index attributes, index standardization, and weight assignment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S. and J.G.; Data curation, Z.W.; Methodology, C.S. and Z.W.; Software, J.G.; Supervision, C.S. and Z.W.; Validation, C.S.; Visualization, J.G. and S.C.; Writing—original draft, J.G. and S.C.; Writing—review & editing, C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No.2019YFC0507505) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42071292).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study will be available from the corresponding authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their constructive comments and suggestions for this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- China Environment News. Towards the 21st World-A Literature Compilation of the United Nations Conference on Environment and Developmen; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. SDG Indicators: Global indicator framework for the Sustainable Development Goals and targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- The Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators. Global Indicator Framework for the Sustainable Development Goals and Targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/indicators/indicators-list/ (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- UN General Assembly. Political Declaration of the High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development Convened under the Auspices of the General Assembly. Available online: https://undocs.org/en/A/RES/74/4 (accessed on 21 September 2019).
- Satterthwaite, D. Successful, safe and sustainable cities: Towards a new urban agenda. Commonw. J. Local Gov. 2016, 19, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Global Taskforce of Local and Regional Governments. UN-Habitat, UNDP. Roadmap for Localizing the SDGs: Implementation and Monitoring at Subnational Level. Available online: https://www.uclg.org/sites/default/files/roadmap_for_localizing_the_sdgs_0.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2016).
- Croese, S.; Green, C.; Morgan, G. Localizing the sustainable development goals through the lens of urban resilience: Lessons and learnings from 100 resilient cities and cape town. Sustainability 2020, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Council for Science. A Guide to “SDG” Interactions: From Science to Implementation; International Council for Science: Paris, France, 2017; pp. 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hull, V.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Tilman, D.; Gleick, P.; Hoff, H.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Xu, Z.; Chung, M.G.; Sun, J.; et al. Nexus approaches to global sustainable development. Sustainability 2018, 1, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-L.; Wu, K.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lim, M.K.; Bui, T.-D.; Chen, C.-C. Assessing sustainable tourism in Vietnam: A hierarchical structure approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, V.R.; Huang, S.; Chang, T.C. The Singapore river thematic zone: Sustainable tourism in an urban context. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 170, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-F.; Huang, H.-I.; Yeh, H.-R. Developing an evaluation model for destination attractiveness: Sustainable forest recreation tourism in Taiwan. J. Sustain. Tour. 2010, 18, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Study on the Sustainable Development of Small and Medium-Sized Tourism Cities. Ph.D. Thesis, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China, 1 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X. Sustainable Development and Image Perception Analysis of Lijiang Urban Tourism under the Goal of Ring Model. Ph.D. Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 1 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.X. The construction of international tourist cities under the guidance of the concept of sustainable development. Managers 2009, 17, 358. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, V.; Hernández, A.; Guerrero, F.; León, M.A.; Da Silva, C.L.; Caballero, R. Sustainability ranking for Cuban tourist destinations based on composite indexes. Soc. Indic. Res. 2015, 129, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancas, F.; Lozano, M.G.; González, M.; Caballero, R. Sustainable tourism composite indicators: A dynamic evaluation to manage changes in sustainability. J. Sustain. Tour. 2016, 24, 1403–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, G.I. Destination competitiveness: An analysis of determinant attributes. J. Travel Res. 2010, 50, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornhorst, T.; Ritchie, J.B.; Sheehan, L. Determinants of tourism success for DMOs & destinations: An empirical examination of stakeholders’ perspectives. Tour. Manag. 2010, 31, 572–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, L.; Cvelbar, L.K.; Edwards, D.; Mihalic, T. Fashioning a destination tourism future: The case of Slovenia. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainaghi, R.; Phillips, P.; Zavarrone, E. Performance measurement in tourism firms: A content analytical meta-approach. Tour. Manag. 2017, 59, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendola, D.; Volo, S. Building composite indicators in tourism studies: Measurements and applications in tourism destination competitiveness. Tour. Manag. 2017, 59, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- City Department of Los Angeles. Sustainable Development Goals: A Local Review of Progress in 2019; City Department of Los Angeles: Los Angeles, LA, USA, 2020; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Measuring Distance from Sustainable Development Goals: Assessment of the Process of Achieving SDGs in OECD Countries in 2019; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2019; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific. Asia and the Pacific SDG Progress Report 2019; The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific: New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Statistical Office of the European Communities. EU SDG Indicator set 2019: Result of the Review in Preparation of the 2019 Edition of the EU SDG Monitoring Report; Statistical Office of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- The Japanese Government. Japan’s Voluntary National Review Report on the Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals; The Japanese Government: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; p. 27.
- Federal Government of Germany. German Sustainable Development Strategy 2016; Federal Government of Germany: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 12–13.
- Monash Sustainable Development Institute. Transforming Australia SDG Progress Report: 2020 Update; Monash Sustainable Development Institute: Monash, Australia, 2020; pp. 67–89. [Google Scholar]
- SDSN; BERTELSMANNS. The 2019 SDG Index and Dashboards Report for European Cities; SDSN: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- SDSN; BERTELSMANNS. The 2019 Italian Cities Sustainable Development Report; SDSN: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Global Environmental Strategies, City of Turku. The Implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in the City of Turku; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Kanagawa, Japan, 2020; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- City Department of Mannheim. The Implementation of the UN SDGs in Mannheim; City Department of Mannheim: Mannheim, Germany, 2019; pp. 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sydney Government. City of Sydney Community Wellbeing Indicators; Sydney Government: Sydney, Australia, 2019; pp. 36–58.
- Institute for Global Environmental Strategies. Shimokawa the Sustainable Development goals Report 2018; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Kanagawa, Japan, 2018; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- SDSN; BERTELSMANNS. 2018 SDG Index and Dashboards Report; SDSN: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.J. Pursue the goal of sustainable development within the "planetary boundary. Econ. Guide Sustain. Dev. 2019, 7, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Fernández, J.I.; Rodríguez-Díaz, B. Reinterpreting the World Economic Forum’s global tourism competitiveness index. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2016, 20, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.G.; Li, X.N.; Li, C.Y. Evaluation of resilience of water resources system based on entropy method of coefficient of variation-A case study of water resources in Heilongjiang Province from 2007 to 2016. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Zheng, C.D.; Xiao, Y.R. A study on the income growth of farmers and herdsmen in Tibet from the perspective of green de-velopment-- based on multiple linear regression analysis. Tibet. Stud. 2018, 6, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.J. Research on low-carbon consumption behaviors and influencing factors of urban residents: A case study of Fuzhou, Fujian Province. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 308–317. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.H.; Dong, Z.F.; Li, H.X.; Ge, C.Z. Analysis and revelation of the 2017 global sustainable development goals index and dashboard report. Environ. Prot. 2018, 46, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- World Economic Forum. The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2019-Travel and Tourism at Tipping Point; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 25–31. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).

















