Estimation of Hydrological Components under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in Guder Catchment, Upper Abbay Basin, Ethiopia, Using the SWAT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. SWAT Model Principle and Setup
2.4. Trend Analysis
2.5. Climate Scenarios and Bias Correction
3. Hydrological and Climatic Characteristics in Guder Catchment
3.1. Temporal Characteristics
3.1.1. Annual Characteristics
- (A)
- Rainfall
- (B)
- Surface Runoff
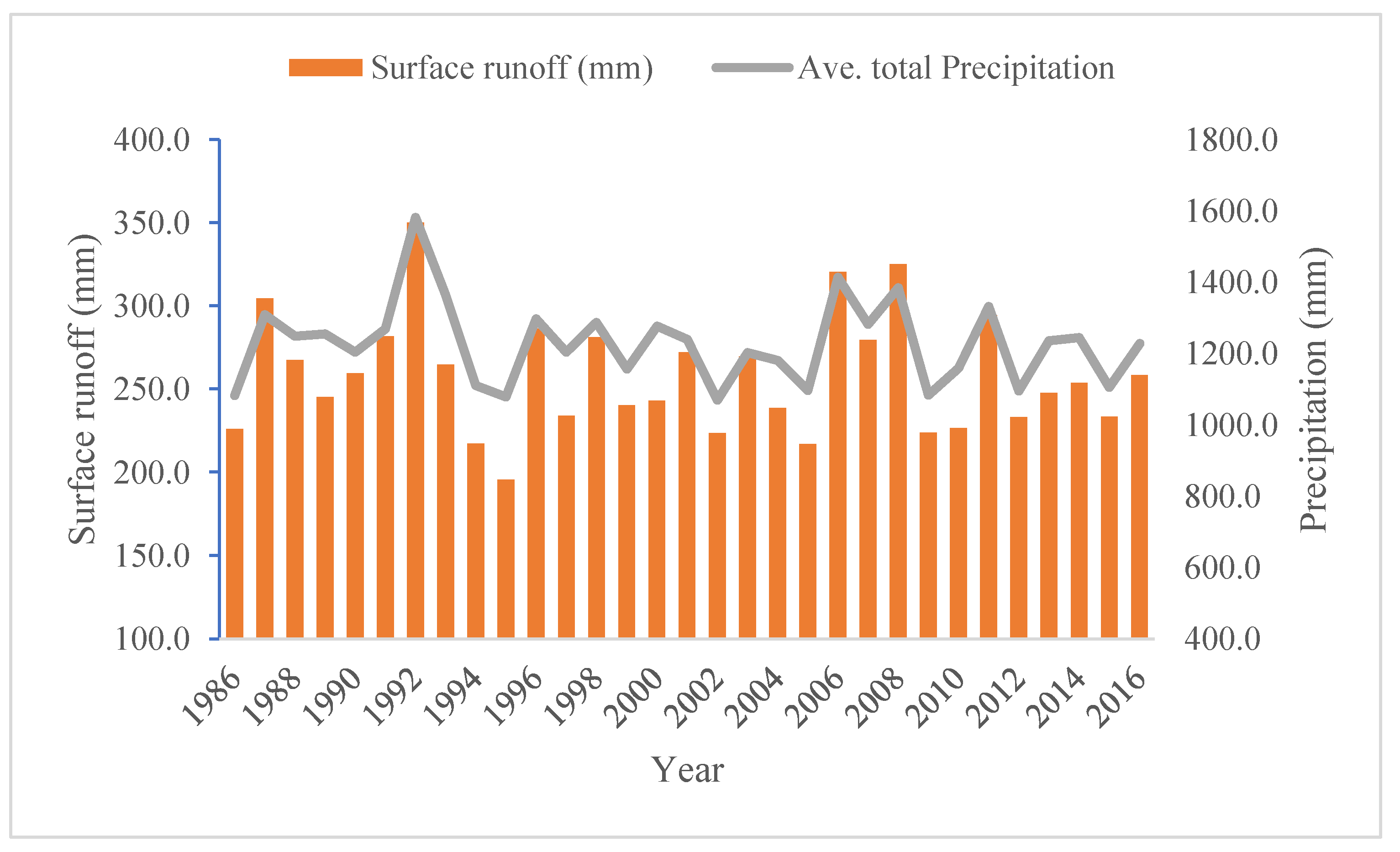
3.1.2. Interannual Characteristics
- (A)
- Rainfall
- (B)
- Surface Runoff
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Rainfall
4. Results
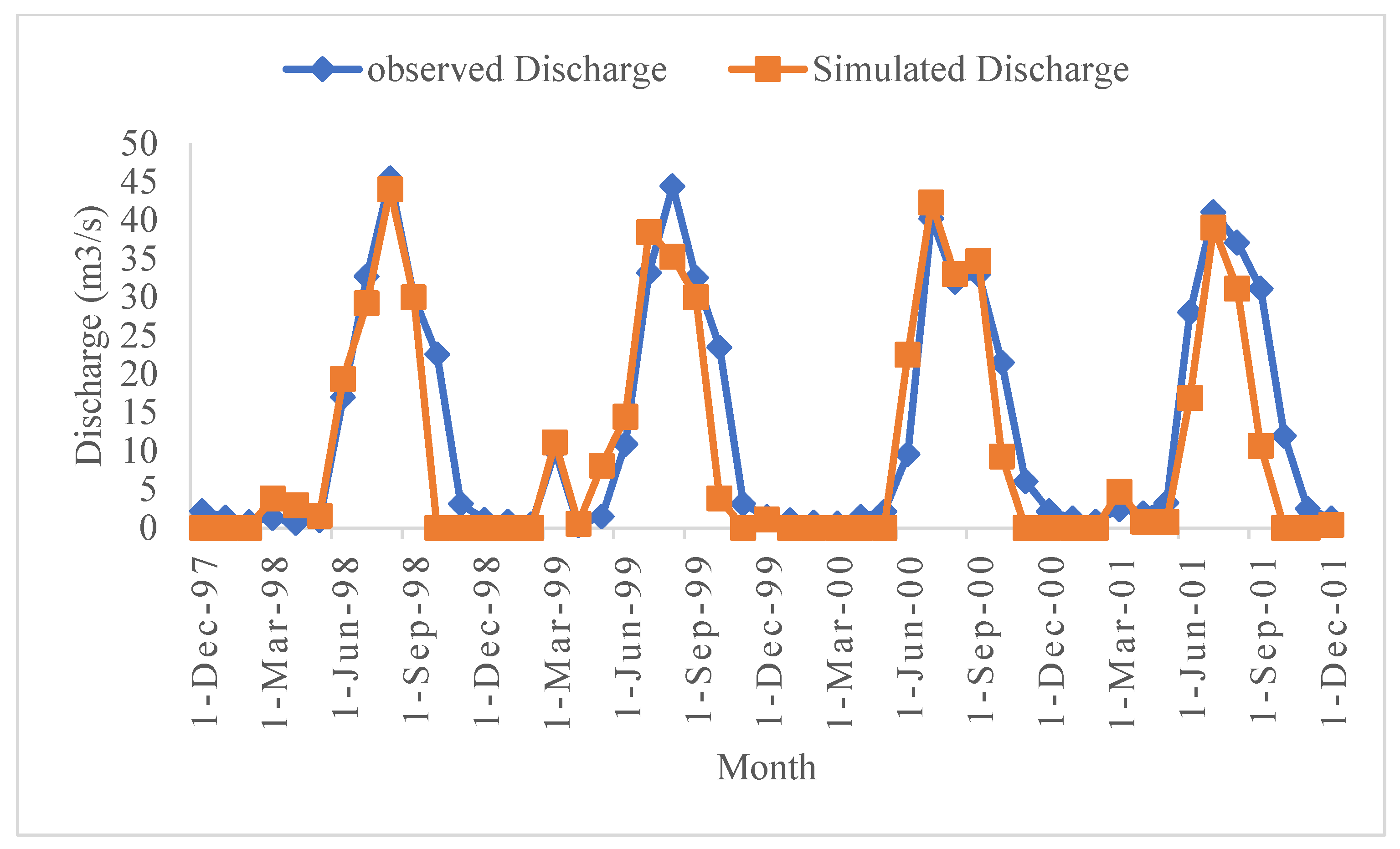
4.1. Model Calibration and Validation
4.2. Water Balances
4.3. Climatic Projections under RCP Scenarios
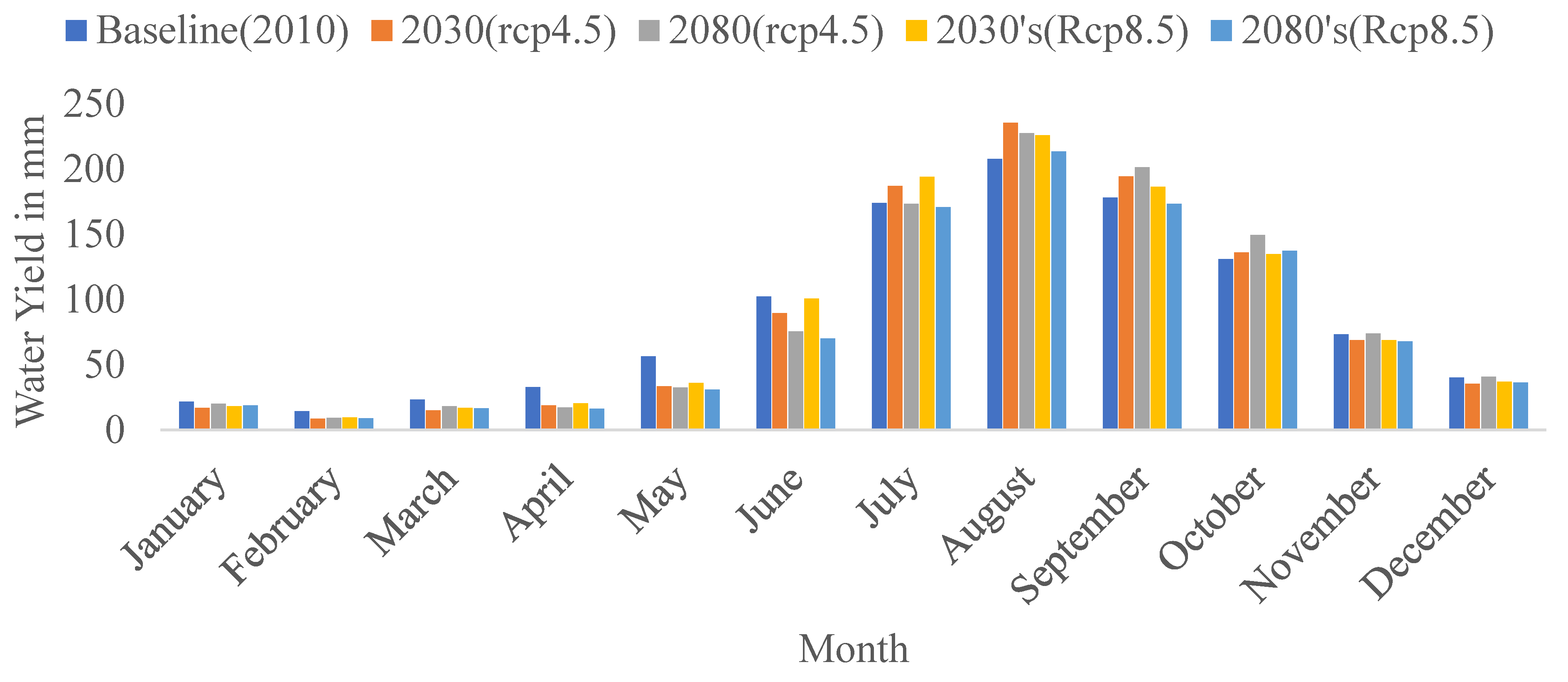
4.4. Trends of Simulated Future Water Yield
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Xue, B.; Yan, Y. The Assessment of Climate Change and Land-Use Influences on the Runoff of a Typical Coastal Basin in Northern China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, G.; Xue, W.; Yao, Z.; Xue, B. Assessing the Adaptability of Water Resources System in Shandong Province, China, Using a Novel Comprehensive Co-evolution Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 33, 657–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.; Murphy, E.J.; Meredith, M.P.; King, J.C.; Peck, L.S.; Barnes, D.K.; Smith, R.C. Climate change and the marine ecosystem of the western Antarctic Peninsula. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC-TGICA. General Guidelines on the Use of Scenario Data for climate impact and adaptation assessment. Finn. Environ. Inst. 2007, 312, 66. Available online: http://www.citeulike.org/group/14742/article/8861417 (accessed on 30 June 2007).
- Arnell, N.W. Climate change and global water resources: SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2004, 14, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, G.E. Climate and Water; Water and Climate Change: London, UK, 1990; Volume 71. [Google Scholar]
- Rientjes, T.H.; Perera, J.B.; Haile, A.T.; Gieske, A.S.; Booij, M.J.; Reggiani, P. Hydrological Balance of Lake Tana, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. In Nile River Basin; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Mengistu, D.; Bewket, W.; Dosio, A.; Panitz, H.J. Climate change impacts on water resources in the Upper Blue Nile (Abay) River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birhane, G. Present and Future Water Resources Development in Ethiopia Related to Research and Capacity Building; Ministry of Water Resources: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2002; pp. 11–21.
- Roth, V.; Lemann, T.; Zeleke, G.; Subhatu, A.T.; Nigussie, T.K.; Hurni, H. Effects of climate change on water resources in the upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conway, D. The climate and hydrology of the Upper Blue Nile river. Geogr. J. 2000, 166, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gemechu, M.G.; Huluka, T.A.; van Steenbergen, F.; Wakjira, Y.C.; Chevalking, S.; Bastiaanssen, S.W. Analysis of spatio-temporal variability of water productivity in Ethiopian sugar estates: Using open access remote sensing source. Ann. GIS 2020, 26, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fentaw, F. Impacts of Climate Change on the Water Resources of Guder Catchment, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Waters 2018, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Lin, H.; Cai, X.; Fang, M.; Ge, Y.; Yingchun, G.; Chen, M.; Li, W. Watershed System Model: The Essentials to Model Complex Human-Nature System at the River Basin Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 3019–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Moriasi, D.; Moriasi, D.; Mikayilov, F.; White, M.J.; Srinivasan, R.; Santhi, C.; Harmel, R.D.; van Griensven, A.; van Liew, M.W.; et al. SWAT: Model use, calibration, and validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1491–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, A.J.; Rowe, R.; McNamara, N.P.; Donnison, I.S.; McCalmont, J.P. Soil & Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) simulated hydrological impacts of land use change from temperate grassland to energy crops: A case study in western UK. GCB Bioenergy 2019, 11, 1298–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sadek, A.; Irvem, A. Evaluating the impact of land use uncertainty on the simulated streamflow and sediment yield of the Seyhan River basin using the SWAT model. Turkish J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayivi, F.; Jha, M.K. Estimation of water balance and water yield in the Reedy Fork-Buffalo Creek Watershed in North Carolina using SWAT. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulakhmadov, A.; Chen, X.; Gulahmadov, N.; Liu, T.; Anjum, M.N.; Rizwan, M. Simulation of the potential impacts of projected climate change on streamflow in the vakhsh river basin in central Asia under CMIP5 RCP Scenarios. Water 2020, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scenarios, I.; Study, C.; Basin, B.N. Runoff Sediment Yield Modeling and Development of Management Hydrology: Current Research Runoff Sediment Yield Modeling and Development of Management Intervention Scenarios, Case Study of Guder Watershed. Hydrol. Curr. Res. 2019, 9, 1000306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, Z.M.; Fuka, D.R.; White, E.; Collick, A.S.; Ashagre, B.; McCartney, M.; Awulachew, S.B.; Ahmed, A.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. A multi basin SWAT model analysis of runoff and sedimentation in the Blue Nile, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7, 3837–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swat Based Estimation of Sediment Yield from Guder Watershed, Abbay Basin, Ethiopia; Addis Abbab University: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2014.
- Abera, F.F. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on the Hydrology of Upper Guder Catchment, Upper Blue Nile. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 8, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Aouissi, J.; Benabdallah, S.; Chabaâne, Z.L.; Cudennec, C. Evaluation of potential evapotranspiration assessment methods for hydrological modelling with SWAT—Application in data-scarce rural Tunisia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegegne, G.; Park, D.K.; Kim, Y.O. Comparison of hydrological models for the assessment of water resources in a data-scarce region, the Upper Blue Nile River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 14, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C.; Vaghefi, S.A.; Srinivasan, R. A guideline for successful calibration and uncertainty analysis for soil and water assessment: A review of papers from the 2016 international SWAT conference. Water 2017, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adla, S.; Tripathi, S.; Disse, M. 2019. Can We Calibrate a Daily Time-Step Hydrological Model Using Monthly Time-Step Discharge Data? Water 2018, 11, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathjens, H.; Bieger, K.; Srinivasan, R.; Arnold, J.G. CMhyd User Manual Documentation for Preparing Simulated Climate Change Data for Hydrologic Impact Studies; Perdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Melesse, A.M.; Abtew, W.; Setegn, S.G. Nile River Basin; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeyer, J.K.W.; Ridgway, R.B.; Edwards, S.B. Assistance To Land Use Planning Ethiopia Land Evaluation. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 1983. Available online: http://197.156.72.153:8080/xmlui/h-andle/123456789/1445 (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Cheng, Q.; Reinhardt-imjela, C.; Chen, X.; Schulte, A.; Ji, X. Improvement and comparison of the rainfall–runoff methods in SWAT at the monsoonal watershed of Baocun, Eastern China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1460–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andualem, T.G.; Guadie, A.; Belay, G.; Ahmad, I.; Dar, M.A. Hydrological modeling of Upper Ribb watershed. Abbay Basin. Ethiopia 2020, 22, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Larbi, I.; Larbi, I.; Obuobie, E.; Verhoef, A.; Julich, S.; Feger, K.; Bossa, A.Y.; Macdonald, D. Water balance components estimation under scenarios of land cover change in the Vea catchment, West Africa. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2020, 65, 2196–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Rainfall Distribution in Ethiopia Mengying Li Columbia University; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Awotwi, A.; Yeboah, F.; Kumi, M. Assessing the impact of land cover changes on water balance components of White Volta Basin in West Africa. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


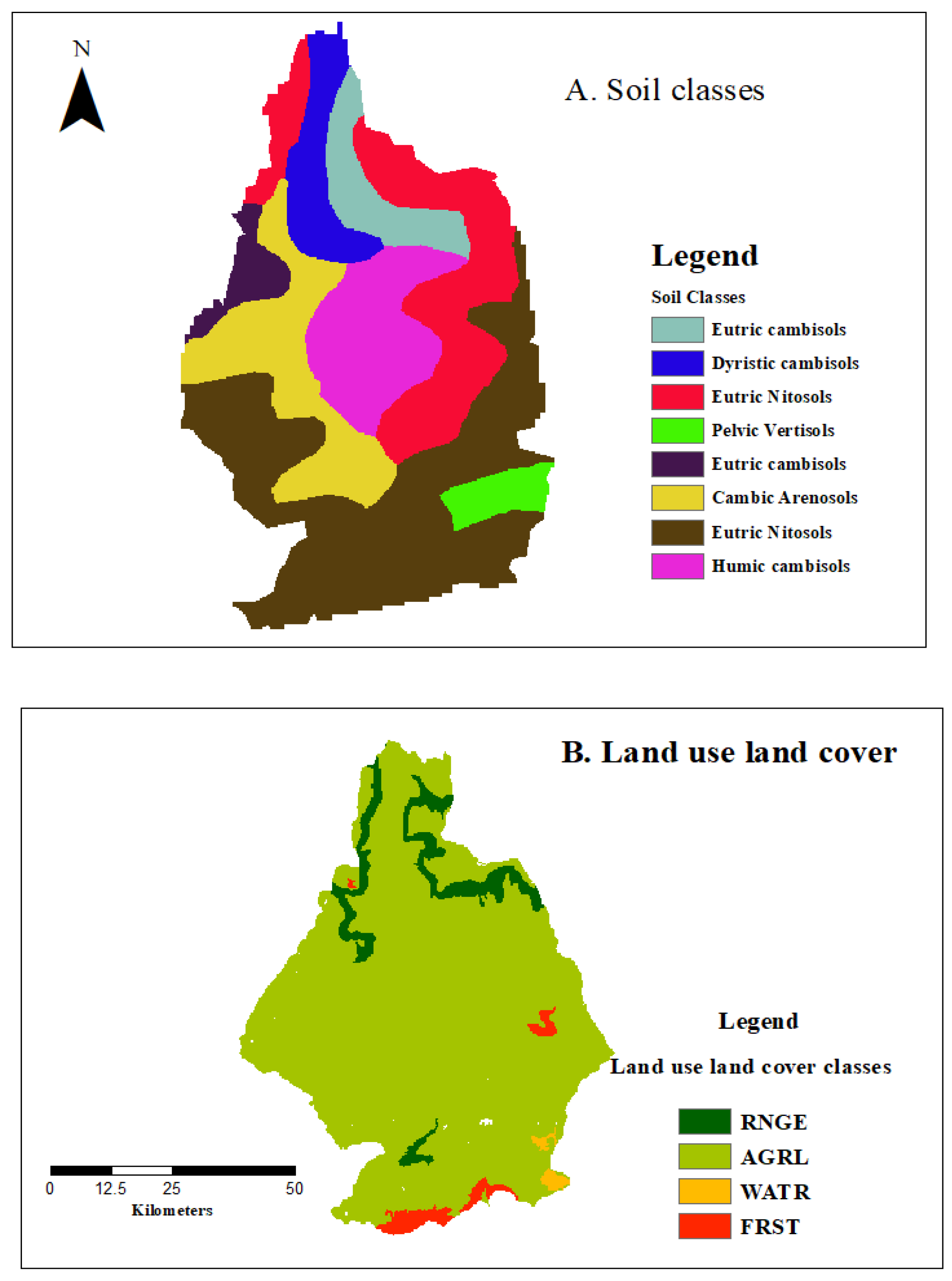








| Landuse | Area (km2) | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Range-Grasses (RNGE) | 411 | 7 |
| Agricultural Land-Generic (AGRL) | 5289.5 | 91.8 |
| Water (WATR) | 14 | 0.24 |
| Forest-Mixed (FRST) | 45.47 | 0.78 |
| Total | 5759 | 100 |
| Value | Surface Runoff | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|
| Cu | 0.29 | 0.27 |
| Surface Runoff | Rainfall | |
|---|---|---|
| Max/Min | 1.79 | 1.46 |
| Max/Mean | 1.36 | 1.26 |
| Min/Mean | 0.76 | 0.86 |
| Cu | 0.21 | 0.18 |
| NS | R2 | Average Simulated (M3/S) | Average Observed (M3/S) | PBIAS (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 0.70 | 0.71 | 10.09 | 12.14 | 16.89 |
| Validation | 0.86 | 0.85 | 9.73 | 10.81 | 9.99 |
| Sensitivity Rank | Name of Parameters | Fitted Value | t-Stat | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | V__GWQMN.gw | 36.18 | 2.02 | 0.05 |
| 2 | V-CH_K2.rte | 31.5 | 1.98 | 0.05 |
| 3 | R__CN2.mgt | 38.79 | 1.92 | 0.06 |
| 4 | R__SOL_AWC (.).sol | 0.42 | −1.67 | 0.10 |
| 5 | V__ALPHA_BNK.rte | −13 | −1.5 | 0.14 |
| 6 | V__ESCO.hru | 0.59 | −1.40 | 0.16 |
| 7 | V__GW_DELAY.gw | 0.5 | −1.05 | 0.29 |
| 8 | R_SOL_K.sol | 12.25 | −0.98 | 0.33 |
| 9 | V__ALPHA_BF.gw | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.40 |
| 10 | V__SFTMP.bsn | −10.2 | 0.70 | 0.48 |
| 11 | V_GW_REVAP | 0.07 | 0.63 | 0.52 |
| 12 | V__CH_N2.rte | 0.29 | −0.36 | 0.71 |
| 13 | R__SOL_BD (...).sol | 0.6 | 0.027 | 0.97 |
| Month | Precipitation | Surface Runoff | Lateral Flow | ET | Percolation to the Shallow Aquifer | Water Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 11.03 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 3.3 | 6.1 | 21.6 |
| February | 15.17 | 2.96 | 0.4 | 4.2 | 8.1 | 14.2 |
| March | 47.68 | 9.7 | 1.3 | 7.7 | 27.1 | 22.8 |
| April | 58.00 | 11.13 | 1.8 | 9.8 | 34.5 | 32.5 |
| May | 104.41 | 21.76 | 3.6 | 11.8 | 65.5 | 57.4 |
| June | 192.42 | 42.14 | 6.8 | 11.7 | 129.3 | 102.3 |
| July | 264.90 | 66.27 | 9.9 | 15.6 | 172.0 | 174 |
| August | 253.89 | 60.78 | 10.2 | 14.2 | 168.4 | 207.5 |
| September | 147.38 | 28.27 | 6.9 | 11.6 | 101.6 | 177.7 |
| October | 45.27 | 9.63 | 2.9 | 5.6 | 29.8 | 131 |
| November | 12.48 | 2.09 | 1.0 | 3.7 | 7.2 | 73.3 |
| December | 7.89 | 1.33 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 4.2 | 40.1 |
| ANNUAL | 1228 | 257.56 | 45.6 | 102.1 | 753.8 | 1054.4 |
| Component | Base Flow/Total Flow | Runoff/Total Flow | Streamflow/Precipitation | Percolation/Precipitation | Deep Recharge/Precipitation | Evapotranspiration/Precipitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio | 0.75 | 0.25 | 0.88 | 0.65 | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| Scenario | Period | P (mm) | ET (mm) | WYLD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1986–2016 | 1228 | 104.2 | 1054.7 |
| RCP 4.5 | 2024–2053 | 1113 (−9.4%) | 87.0 (−16.5%) | 1040.7 (−1.3%) |
| 2057–2086 | 1117 (−9.1%) | 86.4 (−17.1%) | 1040.4 (−1.4%) | |
| RCP 8.5 | 2024–2053 | 1139 (−7.3%) | 88.7 (−14.9%) | 1048.7 (−0.6%) |
| 2057–2086 | 1051.7 (−14.4%) | 87.9 (−15.7%) | 960.6 (−8.9%) |
| Series\Test | Mean | LCL | UCL | Z Statistic | Slope Estimate | Trend Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCP 4.5 | 1040.5 | −3 | 3.3 | 0.2 | 0.37 | Not Significant |
| RCP 8.5 | 1004.6 | −7 | 0.4 | −2.2 | −3.2 | Downward trend |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gemechu, T.M.; Zhao, H.; Bao, S.; Yangzong, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Li, H. Estimation of Hydrological Components under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in Guder Catchment, Upper Abbay Basin, Ethiopia, Using the SWAT. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179689
Gemechu TM, Zhao H, Bao S, Yangzong C, Liu Y, Li F, Li H. Estimation of Hydrological Components under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in Guder Catchment, Upper Abbay Basin, Ethiopia, Using the SWAT. Sustainability. 2021; 13(17):9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179689
Chicago/Turabian StyleGemechu, Tewekel Melese, Hongling Zhao, Shanshan Bao, Cidan Yangzong, Yingying Liu, Fengping Li, and Hongyan Li. 2021. "Estimation of Hydrological Components under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in Guder Catchment, Upper Abbay Basin, Ethiopia, Using the SWAT" Sustainability 13, no. 17: 9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179689
APA StyleGemechu, T. M., Zhao, H., Bao, S., Yangzong, C., Liu, Y., Li, F., & Li, H. (2021). Estimation of Hydrological Components under Current and Future Climate Scenarios in Guder Catchment, Upper Abbay Basin, Ethiopia, Using the SWAT. Sustainability, 13(17), 9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13179689








