Proposing Stewardship Theory as an Alternate to Explain the Relationship between CSR and Employees’ Pro-Environmental Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature and Hypotheses Development
3. Methods
Measures and Addressing the Issue of Social Desirability
4. Results
4.1. Common Method Variance
4.2. Factor Loadings, Validity, and Reliability
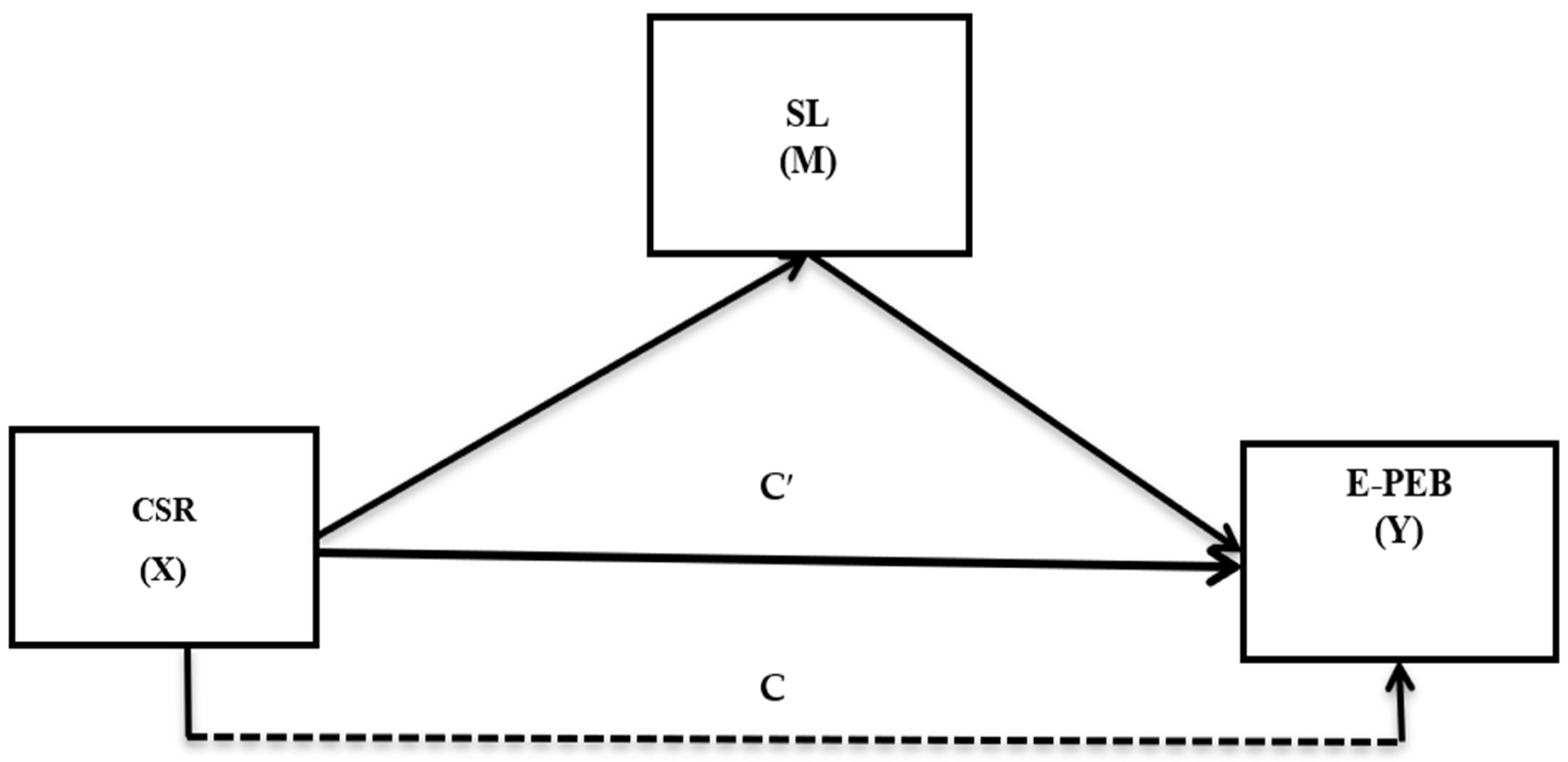
4.3. Hypotheses Testing
5. Discussion
5.1. Implications
5.2. Limitations and Directions for the Future
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aprile, M.C.; Fiorillo, D. Water conservation behavior and environmental concerns: Evidence from a representative sample of Italian individuals. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sabate, R.; Sabaté, J. Consumer attitudes towards environmental concerns of meat consumption: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ince, F. International businesses and environmental issues. In Promoting Global Environmental Sustainability and Cooperation; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 86–111. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Chen, J.; Del Giudice, M.; El-Kassar, A.-N. Environmental ethics, environmental performance, and competitive advantage: Role of environmental training. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, S.; Subramanian, N.; Jabbour, C.J.; Chong, T. Green human resource management and the enablers of green organisational culture: Enhancing a firm’s environmental performance for sustainable development. Bus. Strat. Environ. 2019, 28, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, W.G.; Choi, H.-M.; Phetvaroon, K. The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees’ eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 76, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilal, F.G.; Ashraf, Z.; Gilal, N.G.; Gilal, R.G.; Channa, N.A. Promoting environmental performance through green human resource management practices in higher education institutions: A moderated mediation model. Corp. Soc. Responsab. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, N.; Mahmood, N.H.N.; Yusliza, M.Y.; Ramayah, T.; Faezah, J.N.; Khalid, W. Green Human Resource Management for organisational citizenship behaviour towards the environment and environmental performance on a university campus. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissing-Olson, M.J.; Iyer, A.; Fielding, K.S.; Zacher, H. Relationships between daily affect and pro-environmental behavior at work: The moderating role of pro-environmental attitude. J. Org. Behav. 2013, 34, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.M.; Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. How transformational leadership and employee motivation combine to predict employee proenvironmental behaviors in China. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zou, J.; Chen, H.; Long, R. Promotion or inhibition? Moral norms, anticipated emotion and employee’s pro-environmental behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillé, P.; Boiral, O. Pro-environmental behavior at work: Construct validity and determinants. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 36, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, E.; Tosti-Kharas, J.; King, C.E. Empowering employee sustainability: Perceived organizational support toward the environment. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 128, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raub, S.; Robert, C. Differential effects of empowering leadership on in-role and extra-role employee behaviors: Exploring the role of psychological empowerment and power values. Hum. Relat. 2010, 63, 1743–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedahanov, A.T.; Lee, D.H.; Rhee, J.; Yoon, J. Entrepreneur’s paternalistic leadership style and creativity. Manag. Decis. 2016, 54, 2310–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khokhar, A.M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M. Linking ethical leadership to employees’ performance: Mediating role of organizational citizenship behavior and counterproductive work behavior. Pak. J. Commer. Soc. Sci. 2017, 11, 222–251. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.G.; McGinley, S.; Choi, H.-M.; Agmapisarn, C. Hotels’ environmental leadership and employees’ organizational citizenship behavior. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 87, 102375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Scholz, M.; Arshad, M.Z.; Jafri, S.K.A.; Sabir, R.I.; Khan, W.A.; Han, H. The inter-relation of corporate social responsibility at employee level, servant leadership, and innovative work behavior in the time of crisis from the healthcare sector of pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsar, B.; Cheema, S.; Javed, F. Activating employee’s pro-environmental behaviors: The role of CSR, organizational identification, and environmentally specific servant leadership. Corp. Soc. Responsab. Environ. Manag. 2018, 25, 904–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Chung, C.Y.; Young, J. Study on the Relationship between CSR and Financial Performance. Sustainability 2019, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Rodríguez, M.R.; Martín-Samper, R.C.; Köseoglu, M.A.; Okumus, F. Hotels’ corporate social responsibility practices, organizational culture, firm reputation, and performance. J. Sustain. Tour. 2019, 27, 398–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.-E.; Lu, W.-M.; Hung, S.-W. Does CSR matter? Influence of corporate social responsibility on corporate performance in the creative industry. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 278, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-E.; Li, Y.-W.; Cheng, T.Y.; Lam, K. Corporate social responsibility and investment efficiency: Does business strategy matter? Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 73, 101585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Fernández, M.; Fernández-Torres, Y. Does gender diversity influence business efficiency? An analysis from the social perspective of CSR. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, J.; Stackhouse, M.; Osiyevskyy, O. I love that company: Look how ethical, prominent, and efficacious it is—A triadic organizational reputation (TOR) Scale. J. Bus. Ethics 2018, 153, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Aslam, H.; Rashid, K. Antecedents of pro-environmental behavior of supply chain managers: An empirical study. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2021, 32, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, L.; Davis, J.H. Stewardship theory or agency theory: CEO governance and shareholder returns. Aust. J. Manag. 1991, 16, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.H.; Schoorman, F.D.; Donaldson, L. Toward a stewardship theory of management. In Business Ethics and Strategy; Routledge: Milton Park, UK, 2018; pp. 473–500. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, N. Stewards, agents, and the founder discount: Executive compensation in new ventures. Acad. Manag. J. 2006, 49, 960–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, M. Promoting stewardship behavior in organizations: A leadership model. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 80, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbi, M. Environmental Stewardship and Corporate Social Responsibility: Implication for Consumers’ Resistance to Negative Information. The Case of Apple in China; Beijing Normal University (BNU)—School of Normal Social Development: Beijin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuttner, M.; Feldbauer-Durstmüller, B.; Mitter, C. Corporate social responsibility in Austrian family firms: Socioemotional wealth and stewardship insights from a qualitative approach. J. Fam. Bus. Manag. 2021, 11, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, J.; Malhotra, A.; Falkenberg, L. Multi-level corporate responsibility: A comparison of Gandhi’s trusteeship with stakeholder and stewardship frameworks. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 141, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSuwaidi, M.; Eid, R.; Agag, G. Understanding the link between CSR and employee green behaviour. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2021, 46, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmuss, A.; Agyeman, J. Mind the gap: Why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environ. Edu. Res. 2002, 8, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raza, A.; Farrukh, M.; Iqbal, M.K.; Farhan, M.; Wu, Y. Corporate social responsibility and employees’ voluntary pro-environmental behavior: The role of organizational pride and employee engagement. Corp. Soc. Responsab. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Ali, G.; Asad, H. Environmental CSR and pro-environmental behaviors to reduce environmental dilapidation. Manag. Res. Rev. 2019, 42, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Ullah, Z.; Arshad, M.Z.; waqas Kamran, H.; Scholz, M.; Han, H. Relationship between corporate social responsibility at the micro-level and environmental performance: The mediating role of employee pro-environmental behavior and the moderating role of gender. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmotaleb, M.; Mohamed Metwally, A.B.E.; Saha, S.K. Exploring the impact of being perceived as a socially responsible organization on employee creativity. Manag. Decis. 2018, 56, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Akhouri, A. CSR perceptions and employee creativity: Examining serial mediation effects of meaningfulness and work engagement. Soc. Res. J. 2019, 15, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shabbir, M.S.; Ahmad, N.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Vega-Muñoz, A.; Han, H.; Scholz, M.; Sial, M.S. A contemporary issue of micro-foundation of CSR, employee pro-environmental behavior, and environmental performance toward energy saving, carbon emission reduction, and recycling. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, B.; Umrani, W.A. Corporate social responsibility and pro-environmental behavior at workplace: The role of moral reflectiveness, coworker advocacy, and environmental commitment. Corp. Soc. Responsab. Environ. Manag. 2020, 27, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendjaya, S.; Sarros, J.C. Servant leadership: Its origin, development, and application in organizations. J. Leadersh. Org. Stud. 2002, 9, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, K.C.; Backs, S.; Hoon, C. What makes nonfamily employees act as good stewards? Emotions and the moderating roles of stewardship culture and gender roles in family firms. Fam. Bus. Rev. 2020, 0894486520968826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, F.; Stone, S.; Deno, F. Servant leadership: An ancient style with 21st Century relevance. Rev. Int. Compar. Manag. 2017, 18, 350–361. [Google Scholar]
- Faraz, N.A.; Ahmed, F.; Ying, M.; Mehmood, S.A. The interplay of green servant leadership, self-efficacy, and intrinsic motivation in predicting employees’ pro-environmental behavior. Corp. Soc. Responsab. Environ. Manag. 2021, 28, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, B. Deconstructing CSR: Stewardship Theory. Available online: https://www.reutersevents.com/sustainability/deconstructing-csr-stewardship-theory (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- Bibi, A. Servant leadership and nurse’s pro-environmental behavior: The role of autonomous and external motivations. Dinasti Int. J. Manag. Sci. 2020, 1, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, I.; Ensari, N. The role of transformational leadership and organizational change on perceived organizational success. Psychol. Manag. J. 2009, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, A.R.; Eddy, E.J.; Lorenzet, S. The relationship between enduring leadership and organizational performance. Leadersh. Org. Dev. J. 2014, 35, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.R.; Hung-Baesecke, C.-J.F. Examining the internal aspect of corporate social responsibility (CSR): Leader behavior and employee CSR participation. Commun. Res. Rep. 2014, 31, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthi, L. Examining the relationship between corporate social responsibility, performance, employees’ pro-environmental behavior at work with green practices as mediator. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Ullah, I.; Ullah, Z.; Zeeshan, M.; Hussain, A.; Rahman, H.U. Adoption of green banking practices and environmental performance in Pakistan: A demonstration of structural equation modelling. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Rabbani, M.R.; Ahmad, N.; Sial, M.S.; Cheng, G.; Zia-Ud-Din, M.; Fu, Q. CSR, Co-Creation and green consumer loyalty: Are green banking initiatives important? A moderated mediation approach from an emerging economy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GermanWatch. Global Climate Risk Index 2020. Available online: https://www.germanwatch.org/ (accessed on 2 October 2020).
- The News. Islamic Banks’ Market Share Up. Available online: https://www.thenews.com.pk/print/746679-islamic-banks-market-share-up#:~:text=The%20market%20share%20of%20Islamic%20banks’%20assets%20stood%20at%2015.3,2020%2C%20primarily%20due%20to%20investments (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Jafri, R. A Panoramic View of Pakistan’s Banking System. Available online: https://www.globalvillagespace.com/a-panoramic-view-of-pakistans-banking-system/ (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- NBP. CSR Initiatives. Available online: https://www.nbp.com.pk/csr/index.aspx (accessed on 24 July 2021).
- ABL. Community Services. Available online: https://www.abl.com/the-bank/community-services/ (accessed on 24 July 2021).
- UBL. Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives. Available online: https://www.ubldigital.com/About-UBL/Sustainability/CSR-Initiatives (accessed on 24 July 2021).
- MCB. Corporate Social Responsibility. Available online: https://www.mcb.com.pk/investor-relations/corporate-social-responsibility (accessed on 24 July 2021).
- IQAir. Air Quality in Pakistan. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/us/pakistan (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Hyman, L.; Lamb, J.; Bulmer, M. The use of pre-existing survey questions: Implications for data quality. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Quality in Survey Statistics, Cardiff, UK, 24–26 April 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Turker, D. Measuring corporate social responsibility: A scale development study. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 85, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Robertson, J.L. How and when does perceived CSR affect employees’ engagement in voluntary pro-environmental behavior? J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 155, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liden, R.C.; Wayne, S.J.; Meuser, J.D.; Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Liao, C. Servant leadership: Validation of a short form of the SL-28. Leadersh. Q. 2015, 26, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, M.A.; Choi, S.B.; Kang, S.-W. Servant leadership and innovative behaviour: An empirical analysis of Ghana’s manufacturing sector. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mithani, M.A. Innovation and CSR—Do they go well together? Long Range Plan. 2017, 50, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; Organ, D.W. Self-reports in organizational research: Problems and prospects. J. Manag. 1986, 12, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.; Boudreau, M.-C. Structural equation modeling and regression: Guidelines for research practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hair, J.; Anderson, R.; Babin, B.; Black, W. Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, N.F.; Schubring, S.; Hauff, S.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. When predictors of outcomes are necessary: Guidelines for the combined use of PLS-SEM and NCA. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 120, 2243–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, L. Applying multigroup analysis in PLS-SEM: A step-by-step process. In Partial Least Squares Path Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 219–243. [Google Scholar]
- Thakkar, J.J. Applications of structural equation modelling with AMOS 21, IBM SPSS. In Structural Equation Modelling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 35–89. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, Z.; Khan, I.U.; Islam, T.; Sheikh, Z.; Khan, S.U. Corporate social responsibility and employee pro-environmental behaviors. South Asian J. Bus. Stud. 2019, 8, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, V.J.; Jiménez-Barrionuevo, M.M.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, L. Transformational leadership influence on organizational performance through organizational learning and innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2012, 65, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, S. The influence of innovation and transformational leadership on organizational performance. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 57, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, J.Y.; Liou, K.T. Collaborative leadership and organizational performance: Assessing the structural relation in a public service agency. Rev. Public Pers. Admin. 2018, 38, 83–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, A.I.; Akhtar, S.A.; Zaheer, A. Impact of transformational and servant leadership on organizational performance: A comparative analysis. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 116, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donia, M.B.; Raja, U.; Panaccio, A.; Wang, Z. Servant leadership and employee outcomes: The moderating role of subordinates’ motives. Eur. J. Work Org. Psychol. 2016, 25, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyilmaz, A.; Cicek, S.S. How does servant leadership affect employee attitudes, behaviors, and psychological climates in a for-profit organizational context. J. Manag. Org. 2015, 21, 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barauskaite, G.; Streimikiene, D. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance of companies: The puzzle of concepts, definitions and assessment methods. Corp. Soc. Responsab. Environ. Manag. 2020, 28, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belu, C.; Manescu, C. Strategic corporate social responsibility and economic performance. Appl. Econ. 2013, 45, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowokudejo, F.; Aduloju, S.A.; Oke, S.A. Corporate social responsibility and organizational effectiveness of insurance companies in Nigeria. J. Risk Financ. 2011, 12, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony Wong, I.; Hong Gao, J. Exploring the direct and indirect effects of CSR on organizational commitment. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 26, 500–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographics | Frequency (n = 392) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 223 | 56.89 |
| Female | 169 | 43.11 |
| Age group (Years) | ||
| 22–25 | 49 | 12.50 |
| 26–30 | 103 | 26.02 |
| 31–35 | 96 | 24.49 |
| 36–40 | 87 | 22.19 |
| Above 40 | 57 | 14.54 |
| Experience (Years) | ||
| 1–4 | 79 | 20.15 |
| 5–7 | 128 | 32.65 |
| 8–10 | 98 | 25.01 |
| Above 10 | 87 | 22.19 |
| Category | ||
| Manager | 124 | 31.63 |
| Non-Manager | 268 | 68.37 |
| Total | 392 | 100 |
| Item | Λ | λ2 | E-Variance | ∑λ2 | Items | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR1 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.47 | ||||
| CSR2 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.42 | ||||
| CSR3 | 0.82 | 0.67 | 0.33 | ||||
| CSR4 | 0.71 | 0.50 | 0.50 | ||||
| CSR5 | 0.71 | 0.50 | 0.50 | ||||
| CSR6 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.26 | ||||
| CSR7 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.45 | ||||
| CSR8 | 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.24 | ||||
| CSR9 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.19 | ||||
| CSR10 | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.41 | ||||
| CSR11 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 0.31 | ||||
| CSR12 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 7.55 | 12 | 0.63 | 0.95 |
| SL1 | 0.76 | 0.58 | 0.33 | ||||
| SL2 | 0.78 | 0.61 | 0.42 | ||||
| SL3 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.48 | ||||
| SL4 | 0.92 | 0.85 | 0.31 | ||||
| SL5 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.36 | ||||
| SL6 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.41 | ||||
| SL7 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 4.72 | 7 | 0.67 | 0.93 |
| E-PEB1 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.26 | ||||
| E-PEB2 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 0.31 | ||||
| E-PEB4 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.45 | ||||
| E-PEB5 | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.41 | ||||
| E-PEB7 | 0.77 | 0.59 | 0.41 | ||||
| E-PEB8 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 0.34 | 3.82 | 6 | 0.64 | 0.91 |
| Construct | CSR | SL | PEB-E |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSR | 0.92 | 0.53 ** | 0.47 ** |
| SL | 0.89 | 0.48 ** | |
| PEB-E | 0.87 | ||
| Mean | 4.53 | 4.02 | 3.97 |
| SD | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.58 |
| MSV | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.23 |
| ASV | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.23 |
| Path | Estimates | SE | CR | R2 | p-Value | ULCI | LLCI | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR → E-PEB | (β1) 0.310 ** | 0.0714 | 4.18 | 0.296 | *** | 0.328 | 0.263 | Supported |
| SL → E-PEB | (β2) 0.312 ** | 0.0714 | 4.21 | 0.279 | *** | 0.288 | 0.226 | Supported |
| Path | Estimates | SE | Z-Score | p-Value | ULCI | LLCI | Decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSR → SL → E-PEB | (β3) 0.165 ** | 0.028 | 5.89 | *** | 0.128 | 0.091 | Supported |
| Total effect | 0.475 | ||||||
| Indirect effect | 0.165 | ||||||
| Direct effect | 0.310 | ||||||
| Proportion of mediation | 0.35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murtaza, S.A.; Mahmood, A.; Saleem, S.; Ahmad, N.; Sharif, M.S.; Molnár, E. Proposing Stewardship Theory as an Alternate to Explain the Relationship between CSR and Employees’ Pro-Environmental Behavior. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158558
Murtaza SA, Mahmood A, Saleem S, Ahmad N, Sharif MS, Molnár E. Proposing Stewardship Theory as an Alternate to Explain the Relationship between CSR and Employees’ Pro-Environmental Behavior. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158558
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurtaza, Shah Ali, Asif Mahmood, Saima Saleem, Naveed Ahmad, Muhammad Suhail Sharif, and Edina Molnár. 2021. "Proposing Stewardship Theory as an Alternate to Explain the Relationship between CSR and Employees’ Pro-Environmental Behavior" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158558
APA StyleMurtaza, S. A., Mahmood, A., Saleem, S., Ahmad, N., Sharif, M. S., & Molnár, E. (2021). Proposing Stewardship Theory as an Alternate to Explain the Relationship between CSR and Employees’ Pro-Environmental Behavior. Sustainability, 13(15), 8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158558









