Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Relationship between Urbanization Level and Ecosystem Service from a Dual-Scale Perspective: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
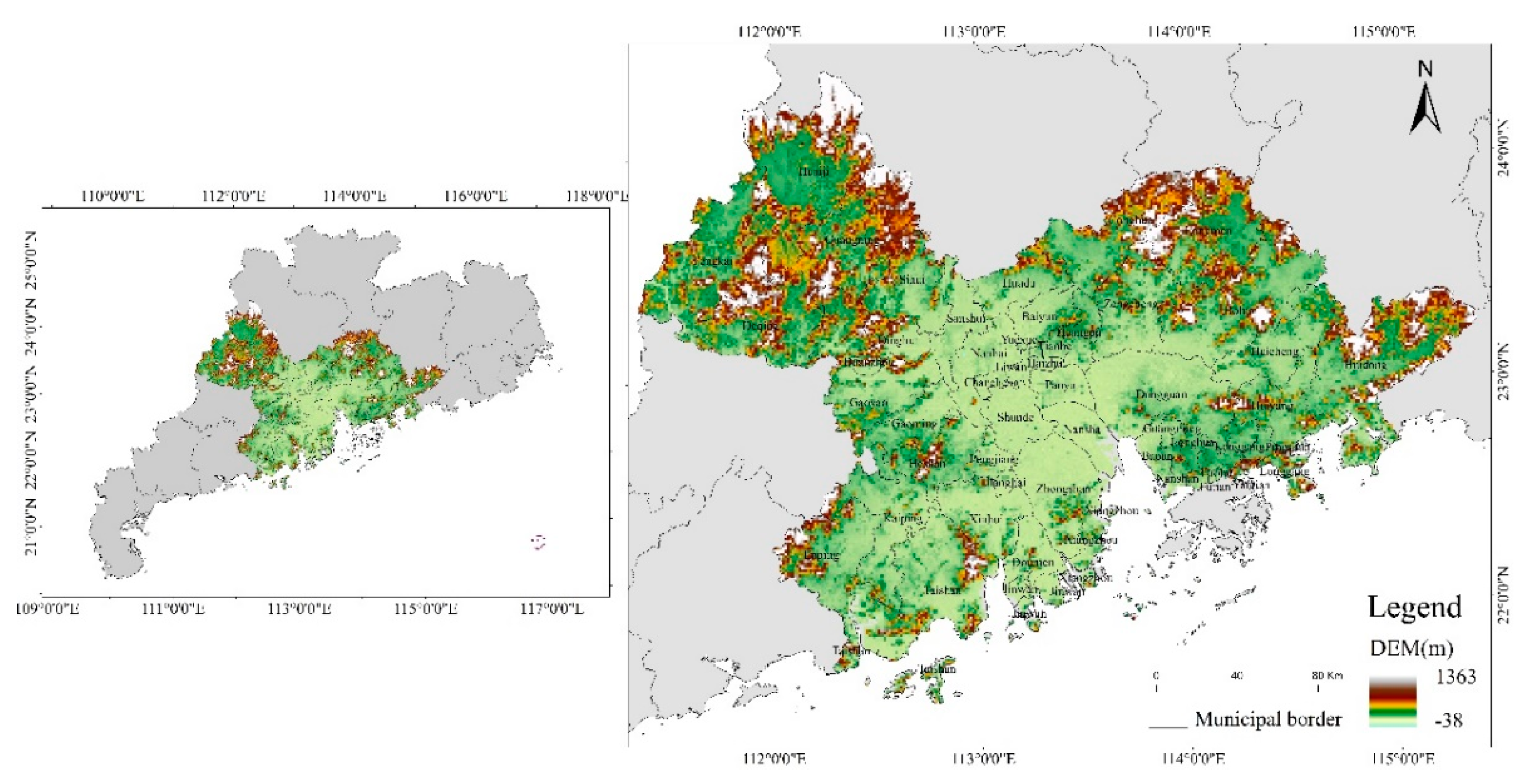
2.1. Overview of the Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Caculation of Value of Ecosystem Service
2.3. Assessment of Urbanization Level
2.3.1. Constructing a Comprehensive Urbanization Level Evaluation System
2.3.2. Weighting Measurement Method
- 1
- Standardization of original data.
- 2
- Given r (k = 1, 2, ..., r) counties, m (I = 1, 2, ..., m) years, and n (j = 1, 2, ..., n) indicators, calculate the weight of the value of the jth indicator in the ith year of kth county:
- 3
- Calculate the information entropy value for the jth indicator:
- 4
- Calculation of indicator weights :
- 5
- Calculate the index score :
2.3.3. Spatialization of Comprehensive Urbanization Level
- 1
- Modified construction of the light index reflecting the level of regional urbanization
- 2.
- Correlation analysis of the light index and the comprehensive urbanization level of cities
- 3.
- Spatialization of comprehensive urbanization level
2.4. Correlation Analysis of Urbanization Level and ESV
2.4.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis
2.4.2. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Evolution of ESV
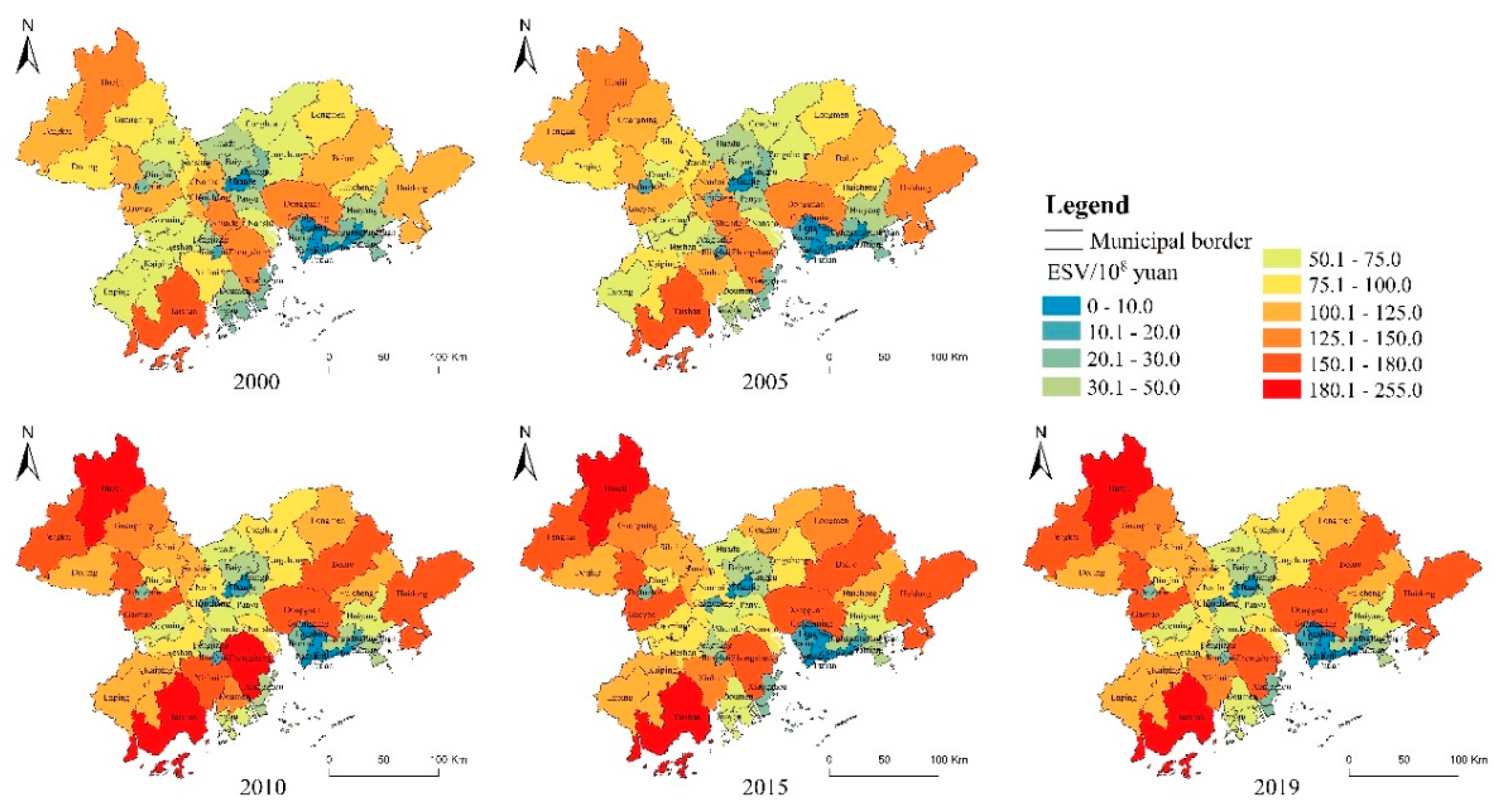
3.1.1. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of ESV at County Scale
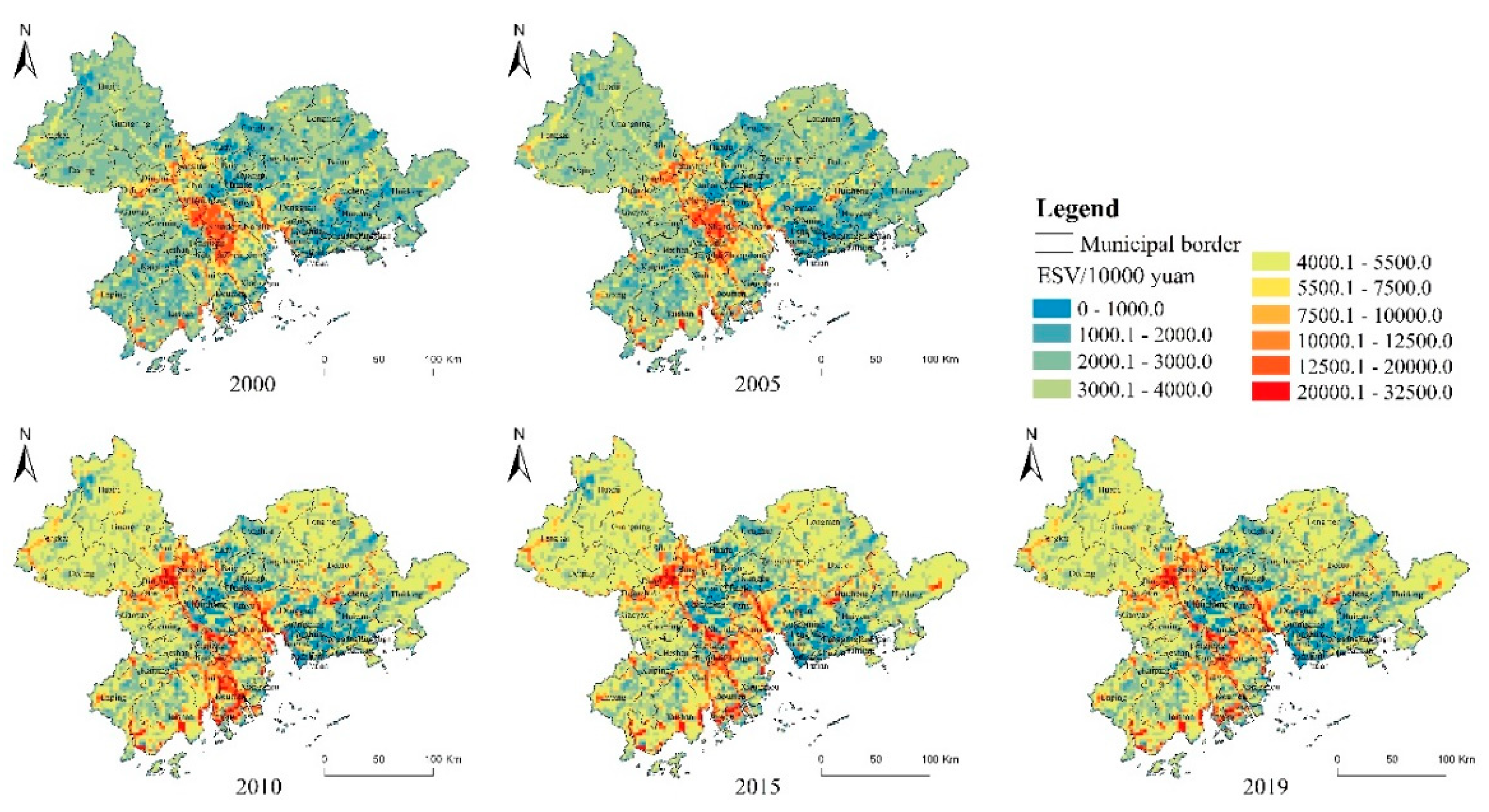
3.1.2. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of the Raster Scale
3.2. Analysis of the Spatial–Temporal Evolution of Urbanization Level
3.2.1. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of Urbanization Level at County Scale
3.2.2. Spatial–Temporal Evolution of the Raster Scale
3.3. Correlation between Comprehensive Urbanization Level and Ecosystem Service Value
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis of Urbanization Level and ESV
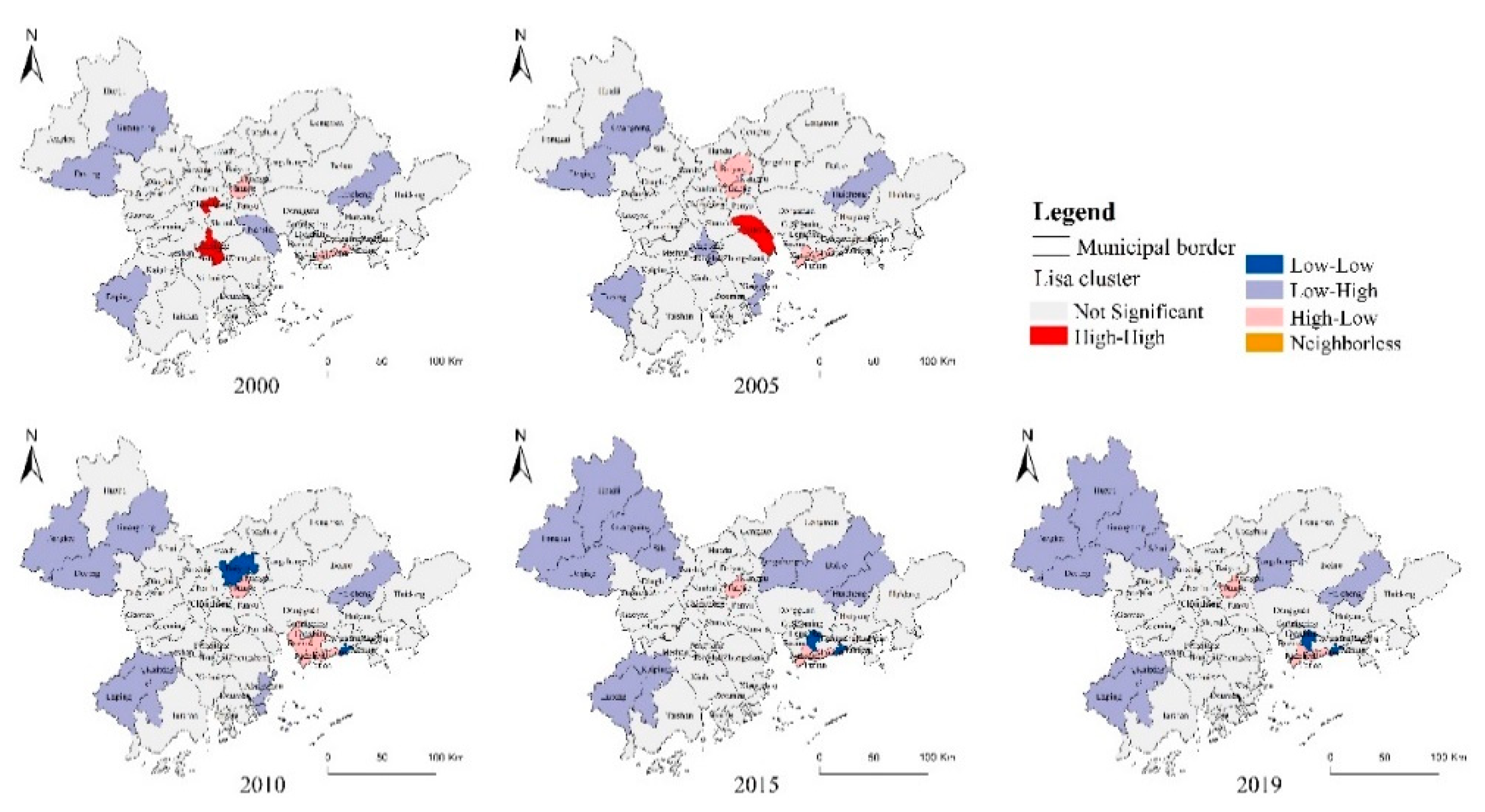
3.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of Comprehensive Urbanization Level and ESV
- Spatial–temporal changes at the county scale
- 2.
- Spatial–temporal variation at the raster scale
4. Discussion
4.1. Calculation of the Ecosystem Service Value in the PRD
4.2. Calculation of Urbanization Level in the Pearl River Delta
4.3. Spatial–Temporal Evolution Patterns of Urbanization Level and ESV
4.4. Spatial Relationship between Urbanization Level and ESV
5. Conclusions
- In the past 20 years, the overall trend of urbanization level and ecosystem service value in the PRD has been on the rise. Among them, the regional differences in urbanization level are significant, and the urbanization spillover effect in the central region drives the development of neighboring regions with centripetal nature; the spatial heterogeneity of ecosystem service value is strong, with the largest change between 2005 and 2010 and a gradual decline after 2010.
- At the numerical level, both single and comprehensive urbanization are significantly correlated with ESV. ESV is negatively correlated with comprehensive, population, and economy urbanization levels, and positively correlated with life urbanization.
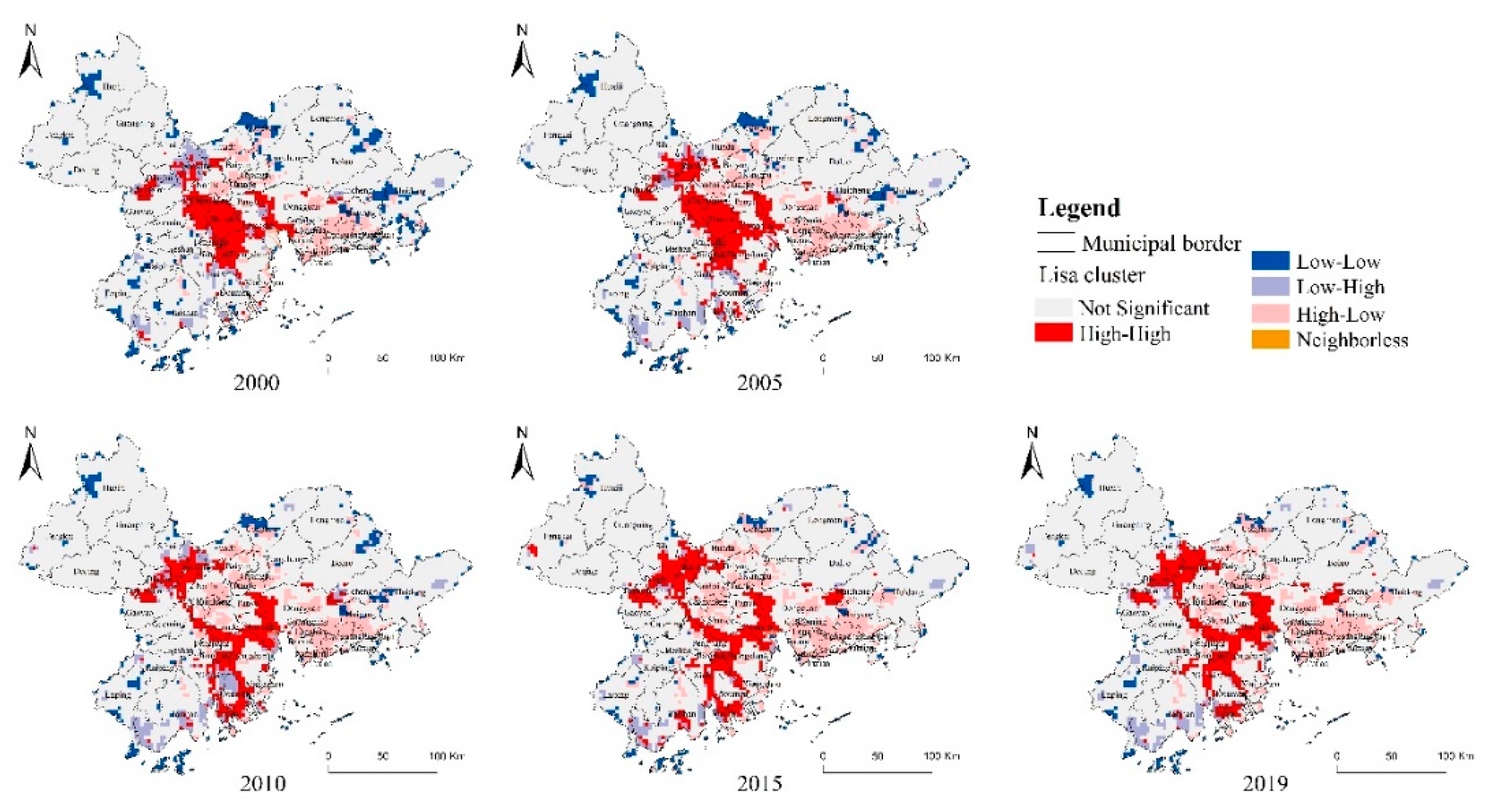
- At the spatial level, comprehensive urbanization and ESV in the PRD from 2000 to 2019 are spatially negatively correlated at the county scale, while the spatial correlation is not significant at the raster scale. From 2000 to 2005, the distribution of “high–high” agglomeration is mainly concentrated in and around Foshan City; from 2010, the “high–low” agglomeration area expands from Tianhe District to Foshan City and occupies Foshan; from 2015 to 2019, the “high–high” and “high–low” agglomeration distribution is dominant.
- Foshan City is the area that has changed most dramatically in the past 20 years, from a “high–high” agglomeration to a “high–low” agglomeration, and the rapid urbanization has damaged to Foshan’s waters and green areas. Tianhe, Yuexiu District in Guangzhou City and Nanshan District in Shenzhen City, have always maintained the “high–low” clustering, indicating that the construction land has encroached on the local natural land cover and the ecological resource environment is poor.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Yang, R. The spatial characteristics and formation mechanism of the county urbanization in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, J. Research progress and prospect on measuring urban ecological land demand. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 333–346. [Google Scholar]
- Van, W.J.; Calow, P.; Dollacker, A.; Maltby, L.; Olander, L.; Tuvendal, M.; Van, H.G. Identifying and assessing the application of ecosystem services approaches in environmental policies and decision making. Integr. Environ. Assess. 2017, 13, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, S. Urbanization impacts on the structure and function of forested wetlands. Urban. Ecosyst. 2004, 7, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, U.P.; Harris, H.G.; Matlock, M.D.; Lacey, R.E. Change in ecosystem service values in the San Antonio area, Texas. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Zhu, X.; He, Q. Incorporating ecosystem services with ecosystem health for ecological risk assessment: A case study in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5478–5489. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, F.; Cao, W. Dynamic analysis of an ecological security pattern relying on the relationship between ecosystem service supply and demand: A case study on the Xiamen-Zhangzhou-Quanzhou city cluster. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4327–4340. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G. Wetland ecosystem services assessment based on emergy: A case of Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2018, 38, 4527–4538. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Kuang, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Mao, Y.; Dong, J. The response of ecosystem services to landscape pattern changes in the Guangdong—Hong Kong—Macao Greater Bay Area from 1996 to 2015. J. South China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 52, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Habitat, U.N.H. Urban Indications Guideliners; United Nations Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, H. A review of literature on urbanization quality evaluation. J. Grad. Sch. Chin Acad. Soc. Sci. 2013, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, J.C. An index of rurality for England and Wales. Reg. Stud. 1997, 11, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Liang, J.; Song, J. Summarization of studies on measuring of urbanization in China. Urban. Stud. 2002, 9, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, D. The Urbanization Process of Loess Plateau and Its Ecological and Environmental Response. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanxi Normal University, Xi’an, Shanxi, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F. Study on the quality measurement and coordinated development of population-land urbanization in Shandong Peninsula Urban Agglomeration. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Fan, D.; Song, Y.; Lin, H. Ecological effects assessment of urbanization in Jilin central urban agglomeration area. Human. Geogr. 2017, 32, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Kong, X. Evaluation and Spatial Correlation Analysis of Urbanization Development Quality in Hubei Province. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin. 2020, 29, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Sun, Z. Comprehensive urbanization level and its dynamic factors of five Central Asian countries. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 367–382. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, R.E. Making a miracle. Econometrica 1993, 61, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, J. International knowledge spillover through trade: A time-varying spatial panel data approach. Econ. Lett. 2018, 162, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambec, S.; Coria, J. Policy spillovers in the regulation of multiple pollutants. J. Environ. Econ Manag. 2018, 87, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, G.; Qi, L.; Ding, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, X. The landscape pattern and ecological service value in Danjiangkou City under land use change from 2003 to 2018. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C. The effects of land use structure and landscape pattern change on ecosystem service values. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Cheng, J.; Fei, L.; Cheng, J. LandUse Transition and changes of ecosystem service function in urban agglomerations of the Yangtze River Delta from 1990 to 2015. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Zeng, J.; Li, W. Spatial correlation characteristics of urbanization and land ecosystem service value in Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Ran, D.; Zeng, J. Mapping the spatial relationship between ecosystem services and urbanization in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomerations. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5137–5150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Sun, Z.; Sun, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Spatial-temporal Dynamic Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. J. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 28, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Yao, S. The coordinated development of environment and economy based on the change of ecosystem service value in Shaanxi province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 3331–3342. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, T.; Zhu, G.; Ma, Z. Services based on landuse: A case study of Bohai Rim. Res. Geogr. 2012, 31, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Xiao, Y.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C. Study on ecosystem services value of food production in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2005, 13, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Z. Coupling and coordination level of the population, land, economy, ecology and society in the process of urbanization: Measurement and spatial differentiation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, D. Study on the coordinated development of urban resilience and urbanization level in the urban agglomeration of Yangtze River Delta. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H. Urbanization-coordinated development level of natural ecology and its impact on urban-rural income gap: Based on the perspective of a comparative study of urban agglomerations in Chengdu-Chongqing, Central Guizhou and Central Yunnan. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 36, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association-LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Geng, Y. Effects of ecological diffusions of cities around Yangtze River Economic Belt basing on spatial relation. J. China Agric. Univ. 2017, 22, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X. Spatial autocorrelation pattern analysis of land use and the value of ecosystem services in northeast Hainan island. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 2366–2377. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Su, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Ji, D. Assessment methods of regional ecosystem service value and a case study of Dongjiang River basin. J. Environ. Engin. Tech. 2018, 8, 212–220. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Han, Y. Changes of landuse and ecosystem service balue in Guangdong-Hongkong-Macau Greater Bay Area: A case study of Guangzhou-Foshan-Zhaoqing. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; Kuang, H.; He, D. Study on the prediction of ecological system service values based on the changes of land use in Guangdong-Hongkong-Macau Greater Bay Area. Ecol. Sci. 2020, 39, 207–212. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, X.; Zhu, X.; He, Q. Spatial interaction between urbanisation and ecosystem services: A case study in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7502–7513. [Google Scholar]
- Maiorano, L.; Falcucci, A.; Boitani, L. Size-dependent resistance of protected areas to land-use change. P. Roy. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Year | Cropland | Woodland | Grassland | Water Body | Wetland | Construction Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 7472.83 | 35,213.10 | 29,437.27 | 237,635.95 | 98,414.31 | 0.00 | 1229.71 |
| 2005 | 8007.84 | 37,734.15 | 31,544.80 | 254,649.24 | 105,460.18 | 0.00 | 1317.75 |
| 2010 | 10,951.28 | 51,604.09 | 43,139.72 | 348,250.66 | 144,224.18 | 0.00 | 1802.11 |
| 2015 | 11,271.51 | 53,113.04 | 44,401.17 | 358,433.86 | 148,441.44 | 0.00 | 1854.80 |
| 2019 | 10,952.34 | 51,609.08 | 43,143.90 | 348,284.36 | 144,238.14 | 0.00 | 1802.28 |
| Target | Guideline | Indicator | Indicator Properties | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanization Level | Life Urbanization | Number of beds per 1000 people [32] | + 1 | 0.06 |
| Energy consumption per unit of GDP [17] | − 2 | 0.08 | ||
| Number of students enrolled in general secondary schools per 1000 population [15] | + | 0.06 | ||
| Economy Urbanization | GDP per capita [18] | + | 0.11 | |
| Percentage of value of secondary and tertiary industries [16] | + | 0.01 | ||
| Total retail sales of social consumer goods [33] | + | 0.32 | ||
| Population Urbanization | Percentage of urban population [34] | + | 0.11 | |
| Population density [26] | + | 0.24 |
| Weighted Combinations (u,v) | R2 | Weighted Combinations (u,v) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0.1,0.9) | 0.55 | (0.6,0.4) | 0.67 |
| (0.2,0.8) | 0.57 | (0.7,0.3) | 0.70 |
| (0.3,0.7) | 0.60 | (0.8,0.2) | 0.74 |
| (0.4,0.6) | 0.62 | (0.9,0.1) | 0.81 |
| (0.5,0.5) | 0.64 | (1,0) | 0.79 |
| County | ESV (108 Yuan) and Its Change Rate (%) in 2000–2019 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 00–05 | 2005 | 05–10 | 2010 | 10–15 | 2015 | 15–19 | 2019 | 00–19 | |
| Baiyun | 30.55 | 0.79 | 30.79 | 41.44 | 43.54 | 4.02 | 45.30 | −4.71 | 43.16 | 41.31 |
| Baoan | 27.34 | −30.89 | 18.90 | 24.33 | 23.49 | −14.90 | 19.99 | −7.18 | 18.56 | −32.12 |
| Boluo | 112.99 | 8.20 | 122.25 | 38.76 | 169.64 | 1.85 | 172.78 | −3.13 | 167.37 | 48.13 |
| Chancheng | 24.34 | −11.03 | 21.66 | −50.49 | 10.72 | −2.36 | 10.47 | −2.52 | 10.21 | −58.07 |
| Conghua | 66.35 | 7.51 | 71.33 | 39.13 | 99.23 | 1.44 | 100.66 | −2.64 | 98.00 | 47.71 |
| Deqing | 83.82 | 6.09 | 88.93 | 36.67 | 121.54 | 2.70 | 124.82 | −2.96 | 121.13 | 44.51 |
| Dinghu | 43.89 | 25.44 | 55.06 | 64.10 | 90.35 | 0.75 | 91.03 | −4.46 | 86.97 | 98.14 |
| Dongguan | 132.45 | −5.37 | 125.34 | 42.25 | 178.30 | −1.04 | 176.46 | −4.50 | 168.51 | 27.22 |
| Doumen | 36.10 | 48.54 | 53.62 | 140.60 | 129.02 | −42.90 | 73.67 | −3.91 | 70.79 | 96.10 |
| Duanzhou | 21.68 | −26.30 | 15.98 | 33.73 | 21.37 | 3.16 | 22.05 | −8.21 | 20.24 | −6.67 |
| Enping | 67.26 | 8.35 | 72.88 | 38.06 | 100.61 | 1.19 | 101.81 | −1.49 | 100.30 | 49.12 |
| Panyu | 47.60 | 3.92 | 49.47 | 32.04 | 65.31 | −2.06 | 63.97 | −3.19 | 61.93 | 30.11 |
| Fengkai | 108.67 | 7.27 | 116.57 | 35.59 | 158.05 | 2.78 | 162.45 | −3.04 | 157.50 | 44.93 |
| Futian | 2.04 | −0.72 | 2.03 | 89.57 | 3.84 | 0.22 | 3.85 | −4.43 | 3.68 | 80.26 |
| Gaoming | 54.66 | 5.67 | 57.76 | 29.17 | 74.61 | 2.11 | 76.18 | −3.07 | 73.84 | 35.09 |
| Gaoyao | 109.50 | 7.99 | 118.25 | 42.22 | 168.18 | 3.01 | 173.24 | −3.52 | 167.15 | 52.65 |
| Guangming | 7.85 | −13.57 | 6.79 | 23.53 | 8.38 | −2.25 | 8.19 | 7.43 | 8.80 | 12.11 |
| Guangning | 95.34 | 7.76 | 102.74 | 36.68 | 140.42 | 2.39 | 143.77 | −2.85 | 139.68 | 46.50 |
| Haizhu | 8.17 | −0.95 | 8.10 | 39.85 | 11.32 | 2.97 | 11.66 | −3.11 | 11.30 | 38.20 |
| Heshan | 58.53 | 3.84 | 60.77 | 27.78 | 77.66 | 1.00 | 78.44 | −3.30 | 75.84 | 29.59 |
| Huadu | 46.17 | 0.37 | 46.34 | 37.93 | 63.91 | 2.23 | 65.34 | −2.63 | 63.62 | 37.80 |
| Huaiji | 128.71 | 6.96 | 137.67 | 37.22 | 188.91 | 2.23 | 193.13 | −2.90 | 187.54 | 45.70 |
| Huangpu | 26.67 | 0.19 | 26.72 | 33.80 | 35.75 | 0.44 | 35.91 | −5.03 | 34.10 | 27.87 |
| Huicheng | 76.79 | 6.02 | 81.41 | 39.19 | 113.31 | 2.30 | 115.91 | −5.36 | 109.70 | 42.86 |
| Huidong | 115.64 | 10.99 | 128.35 | 36.46 | 175.16 | 1.64 | 178.03 | −3.07 | 172.56 | 49.22 |
| Huiyang | 39.32 | 3.48 | 40.69 | 31.71 | 53.60 | 2.17 | 54.76 | −5.94 | 51.51 | 30.98 |
| Jianghai | 19.13 | −1.29 | 18.88 | 4.97 | 19.82 | 5.47 | 20.90 | −4.25 | 20.01 | 4.64 |
| Jinwan | 26.11 | 55.11 | 40.50 | 56.33 | 63.31 | −4.76 | 60.29 | −10.48 | 53.97 | 106.73 |
| Kaiping | 72.78 | 7.15 | 77.98 | 39.04 | 108.43 | 1.15 | 109.67 | −2.69 | 106.72 | 46.64 |
| Liwan | 3.44 | 7.43 | 3.70 | 35.90 | 5.03 | 16.05 | 5.84 | −3.05 | 5.66 | 64.26 |
| Longgang | 24.54 | 2.21 | 25.08 | 36.33 | 34.19 | 0.81 | 34.47 | −2.59 | 33.58 | 36.83 |
| Longhua | 6.26 | −6.52 | 5.86 | 28.77 | 7.54 | −4.41 | 7.21 | −11.24 | 6.40 | 2.14 |
| Longmen | 85.79 | 5.98 | 90.92 | 36.58 | 124.17 | 2.67 | 127.48 | −2.96 | 123.71 | 44.20 |
| Luohu | 3.73 | 7.48 | 4.01 | 43.06 | 5.73 | 2.26 | 5.86 | −2.74 | 5.70 | 52.92 |
| Nanhai | 109.16 | −1.07 | 108.00 | −16.08 | 90.63 | −5.34 | 85.79 | −3.14 | 83.09 | −23.88 |
| Nansha | 59.62 | 15.35 | 68.77 | 42.08 | 97.71 | −7.84 | 90.05 | −1.89 | 88.35 | 48.18 |
| Nanshan | 5.59 | −3.70 | 5.38 | 23.75 | 6.66 | 5.59 | 7.03 | −1.57 | 6.92 | 23.85 |
| Pengjiang | 34.63 | 2.09 | 35.35 | 3.71 | 36.66 | 1.26 | 37.12 | −3.29 | 35.90 | 3.68 |
| Pingshan | 8.96 | −2.56 | 8.73 | 23.27 | 10.76 | −3.11 | 10.42 | −2.76 | 10.14 | 13.18 |
| Sanshui | 82.90 | 5.90 | 87.79 | 36.48 | 119.82 | 1.14 | 121.19 | −3.54 | 116.90 | 41.01 |
| Shunde | 149.99 | −8.99 | 136.51 | −50.39 | 67.73 | −0.61 | 67.32 | −3.61 | 64.89 | −56.74 |
| Sihui | 70.83 | 14.22 | 80.91 | 46.85 | 118.81 | 2.29 | 121.54 | −4.80 | 115.70 | 63.34 |
| Taishan | 154.79 | 14.20 | 176.76 | 40.05 | 247.55 | 2.58 | 253.93 | −2.71 | 247.05 | 59.61 |
| Tianhe | 6.71 | 0.76 | 6.76 | 33.12 | 9.00 | 2.35 | 9.22 | −3.02 | 8.94 | 33.14 |
| Xiangzhou | 20.46 | 19.96 | 24.54 | 36.01 | 33.38 | −25.51 | 24.87 | −5.31 | 23.54 | 15.07 |
| Xinhui | 94.15 | 8.09 | 101.77 | 48.59 | 151.22 | −7.85 | 139.35 | −4.28 | 133.38 | 41.66 |
| Yantian | 4.45 | 0.84 | 4.49 | 34.77 | 6.05 | 0.52 | 6.08 | −2.72 | 5.91 | 32.90 |
| Yuexiu | 1.21 | 36.91 | 1.65 | 45.33 | 2.40 | 3.02 | 2.47 | −2.90 | 2.40 | 99.04 |
| Zengcheng | 62.85 | 4.78 | 65.86 | 37.68 | 90.67 | 2.95 | 93.35 | −3.47 | 90.11 | 43.37 |
| Zhongshan | 149.99 | −3.35 | 144.96 | 26.14 | 182.84 | −7.99 | 168.24 | −3.25 | 162.78 | 8.53 |
| All | 2830.50 | 5.48 | 2985.51 | 32.85 | 3966.35 | −1.33 | 3913.55 | −3.52 | 3775.73 | 33.39 |
| Compr_ur | Pop_ur | Eco_ur | Life_ur | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESV | −0.439 *** | −0.539 *** | −0.281 *** | 0.326 *** |
| Year | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Moran’s I | −0.459 | −0.447 | −0.479 | −0.435 | −0.467 |
| Year | Percentage of Each Cluster/% | Global Moran’s I | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Significant | High–High | Low–Low | Low–High | High–Low | Neighborless | ||
| 2000 | 75.62 | 6.75 | 7.96 | 3.81 | 5.68 | 0.17 | 0.195 |
| 2005 | 74.57 | 7.89 | 6.45 | 3.57 | 7.29 | 0.23 | 0.123 |
| 2010 | 74.07 | 7.63 | 5.56 | 4.35 | 8.15 | 0.24 | 0.051 |
| 2015 | 74.63 | 9.04 | 3.96 | 2.63 | 9.51 | 0.23 | 0.037 |
| 2019 | 74.62 | 8.46 | 3.89 | 3.19 | 9.58 | 0.26 | −0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Z. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Relationship between Urbanization Level and Ecosystem Service from a Dual-Scale Perspective: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158537
Mao Y, Hou L, Zhang Z. Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Relationship between Urbanization Level and Ecosystem Service from a Dual-Scale Perspective: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158537
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Yuanyuan, Lingli Hou, and Zhengdong Zhang. 2021. "Spatial-Temporal Evolution and Relationship between Urbanization Level and Ecosystem Service from a Dual-Scale Perspective: A Case Study of the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8537. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158537






