Abstract
This article provides a picture of the latest developments in providing BIM-based tools for construction and demolition waste (CDW) management. The coverage and breadth of the literature on offering BIM-based tools and technologies for dealing with CDW throughout the whole life cycle of construction are investigated, and gaps are identified. Findings reveal that, although various BIM-based technologies are closely associated with CDW, much of the existing research on this area has focused on the design and construction phase; indeed, the problem of CDW in post-construction stages has received scant attention. Besides, the now available tools and technologies are lacking in cross-phase insights into project waste aspects and are weak in theoretical rigor. This article contributes to the field by identifying the intellectual deficiencies in offering BIM-based tools and technologies when dealing with CDW. So, too, it points to major priorities for future research on the topic. For practitioners, the study provides a point of reference and raises awareness in the field about the most advanced available BIM-based technologies for dealing with CDW problems.
1. Introduction
Construction and demolition waste (CDW) is generated during construction, renovation and retrofitting, and eventually in demolition [1]. A large volume of CDW is generated because of various reasons like improper methods of handling materials [2,3], poor design quality [4,5], conventional methods of operation [6], change of work and reworks [7], among other things. As a result, every year a huge mass of CDW is generated. The portion of CDW among the whole solid waste varies in different countries: England, 32%; Australia, 20–30%; United States, 20–29%; Canada, 27%; and Brazil, 50% [8]. Regardless of its quantity, CDW causes devastating environmental effects, including soil and water pollution, along with the overconsumption of natural resources [9,10]. In addition, the landfill levies and the costs of waste handling and transportation directly increase the total price of construction projects, hitting the bottom line of construction companies [11,12,13]. In order to tackle these problems, waste minimization regulations are promoted [14,15], and all key stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and construction managers, are expected to play an active role in managing CDW [6]. These remedial solutions—based on a change of regulations and the enforcement of policies—have been only partially influential in some jurisdictions, with little sustained impact [16,17]. The construction industry, therefore, needs to take additional measures; there is a need for a major transition across the industry, where construction procedures and techniques are enhanced and improved through technological innovations, to be more efficient and generate less waste [18].
In recent years, Building Information Modelling (BIM) has emerged as an effective construction methodology, which improves many aspects of delivering projects and offers remedial solutions to the polemic problems associated with construction activities [19]. Anecdotal evidence touts BIM as the future of the construction industry, which offers a major means toward making construction projects sustainable [20]. Technologies associated with BIM can be used to: manage and optimize CDW at the end-of-life of projects in deconstructing buildings [21]; act as a design optimization tool to reduce the generated waste during construction; and assist in optimizing the size of building elements [22]. Additionally, BIM can be used in: estimating the amount of waste generation; developing CDW management plans; choosing the most efficient disposal sites [23]; synthesizing information about the whole construction life cycle [24]; and even assessing environmental dimensions in disassembling and reusing building components at the end-of-life point [21,25]. Data-rich models of BIM are used for organizing just-in-time arrival of equipment, materials and labor by integrating information about material resources and geometry with cost and schedule data [26]. Furthermore, BIM minimizes the impacts of wasteful processes across the life cycle of projects [27,28]. Evidence shows that integrating BIM only at the design phase can result in reducing CDW by up to 2% [22]. According to some sources, CDW prevention can be as high as 4.3–15.2% CDW [5].
Given the various benefits of BIM, as discussed, there is a growing body of research on the role of BIM in managing CDW [29]. The now available body of knowledge on the topic, however, represents a scattered and isolated domain, which lacks cohesiveness; it targets various stages of projects in isolation [19]. That is, some researchers have focused on the use of BIM as a decision-making tool for CDW management in the design phase [30]. Others have targeted the construction phase, to avoid waste through enhancing construction crews’ performance, improving process flow efficiency, and reducing rework. Researchers have also focused on: clash detection; site utilization planning; digital prefabrication; 3D controlling and planning; and quantity take-off [31,32]. By treating the operation and end-of-life phases as disconnected from the rest, another group of studies has explored alternative effective designs for deconstruction. Another group of research studies have analyzed and simulated various end-of-life scenarios, have proposed solutions for operating buildings efficiently, and have offered procedures for recognizing recoverable materials and enhancing collaboration among stakeholders [21,28,33]. This lack of a cohesive and inclusive picture of research efforts leads to confusion in identifying priorities and exacerbates the risk of pivotal areas being overlooked [34,35]. Rigorous critical review studies are warranted when the body of existing research on a topic is scattered [36].
There are few review studies that cover BIM for waste management: Salihi [37], and Won and Cheng [27], synthesized the available literature on the benefits of using BIM. Gupta et al. [38] reviewed BIM-based strategies and tools for minimizing CDW. The potential of BIM for improving existing practices was described as functionalist/technology-centered, which is enabled predominantly by technology [19,39]. Managing CDW by BIM is therefore enabled by the technology dimension of BIM. Nevertheless, there is no review on BIM-related technology, software, techniques, algorithms and add-ins that can be used for managing CDW. Many studies exist on the benefits of various technologies. These studies, however, focus on one specific technology through a narrow lens to provide targeted solutions for isolated problems. This presents researchers with a major problem, as discussed below.
Although individual point solutions to address specific problems are currently provided, defining future inquiries relies on the availability of a satellite view of the landscape of research on the topic; gaps need to be identified from a broad perspective so as to plan future inquiries that address them. To date, the field can be described as one in which individual trees are being explored, while a broad picture of the forest is much needed. This article is an attempt to address this problem and bridge this gap; it aims at answering the following research question:
“What are the major BIM-based technological innovations for managing waste across the life cycle of a project?”
Concomitant objectives are formulated to provide a picture of the potential of BIM for CDW reduction throughout the whole life cycle of construction projects with a bias toward the technological aspects of BIM. This article contributes to the field by offering novel insights into the latest BIM-based developments in using technology for waste management. As the first attempt toward surveying the technology dimension of BIM in managing CDW, this article reveals the gaps and points to future areas where further research is needed. For practitioners, this article provides a point of reference to identify the latest developments in the field; discussions will raise awareness about the available BIM-based technologies for managing CDW in construction projects.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. First, an overall background to the issue of CDW is presented, to set the scene and showcase the significance of using BIM to address the problem. The methods section offers a summary of various research tools and techniques for retrieving related studies and analyzing the data. The section that follows provides a descriptive analysis of the landscape of available research on the topic, where analysis of the content offers insight into the existing gaps and identifies fertile ground for further research. Discussions provide recommendations for future researchers. The paper concludes by offering broad perspectives and acknowledging the limitations of the study.
2. Contextual Background
The construction industry is one of the largest in the world economy [40,41]. On a global scale, construction-related spending accounts for 13% of the world’s gross domestic product (GDP). The total annual revenue of the sector is estimated to be around USD 10 trillion and is predicted to rise to USD 14 trillion by 2025 [40]. The construction industry is also notorious for generating large amounts of waste [22]. During 2017–2018, 569 million metric tons of CDW were collected in the US, 45 million metric tons in Brazil, and 20.4 million metric tons in Australia, of which approximately 66% was recycled. In China, however, approximately 1.8 billion Mt of CDW is generated annually, and yet, the recycling rate is a mere 5% [42]. Wasting building materials is synonymous with wasting large amounts of embedded energy—also termed embodied energy. That is, the entire energy expenditure associated with the extraction, shipment, process, and on-site assembly of materials during their expected life cycle will be wasted [43]. So, too, CDW generation imposes extra costs on projects, alongside environmental problems [44]. To tackle the various problems caused by the sizable amount of CDW, the construction industry has taken a wide range of approaches, including enforcing policies, intensifying quality control and adopting technological innovations [45].
Among available policies, the European Commission has released several guidelines to increase the amount of reusable and recyclable materials extracted from the demolition of buildings or infrastructure projects [46]. The document, titled “The site waste management plans regulations 2008”, enforced in the UK is another example, which informs attempts to reduce, reuse and recycle construction waste [47]. There are similar incentives to reduce the amount of waste streams to landfills and deal with illegal dumping in Australia [48,49].
Construction companies use a wide range of strategies and techniques to fulfill the requirements of these policies and legislations [42]. These can be categorized under the well-known 3-Rs approach. To reduce generation or prevention is the most effective strategy to manage waste, with the least resources needed and the lowest adverse impacts [27,50]. Reuse of the used materials and components for the same function, directly and without any change, is the second most desirable approach [51,52]. Reuse is superior to recycling in terms of saving resources and lowering costs with fewer negative impacts [27]. To recycle is the least desired alternative, where waste reduction and reuse are not viable options. This strategy typically entails sorting, cleaning, treating and remounting CDW [27,50].
Various strategies and methods are being implemented in the construction industry to achieve the objectives of the 3 Rs in managing CDW [38]. These include: waste measurement and prediction [53]; designing for deconstruction (DfD) [54]; site waste management planning [55]; prefabrication and off-site construction [56]; incentives and tax relief [57]; just-in-time delivery (JIT) [58]; alternative packaging [59]; and improving supply chain collaboration [60]. Reaping the full potential of these approaches in real-life projects, however, heavily relies on the use of effective technological innovations that facilitate these approaches through the digitalization of processes [18,38,45]. This is discussed next.
2.1. The Use of BIM for Construction and Waste Management
Many technological innovations, including mechanical sorting equipment, artificial intelligence, radio-frequency identification (RFID), bar code systems, geographical information system (GIS), and image processing techniques have been used to address various dimensions of waste management [61,62]. Of these, BIM is touted as the pivotal element of the system, which facilitates the integration of a coalescence of various technologies [18]. The different applications of BIM associated with waste management are well documented in the literature, of which the major ones are illustrated in Figure 1.
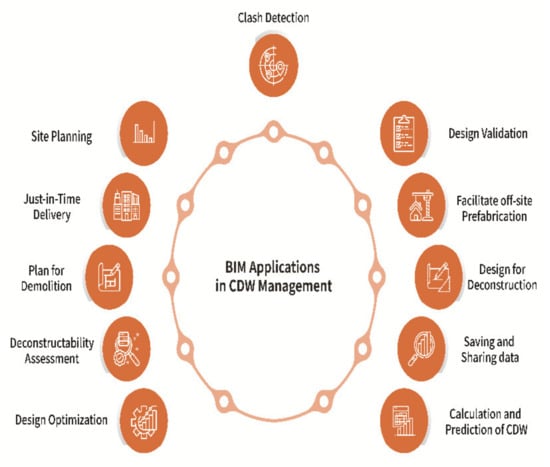
Figure 1.
Major applications of BIM for CDW management.
Research shows that using BIM can reduce the cost of CDW management by up to 57%, compared with conventional CDW management methods [13]. There is also evidence indicating that BIM increases accuracy in quantifying waste, and determines the causes of waste. The use of BIM assists practitioners in making decisions about waste management, considering taxes, cost of transportation, landfill levies and timing of CDW generation, in integration with the project schedule and cost data [12,63,64]. Besides, BIM reduces rework and waste generation through clash detection, design validation and design review procedures, which can reduce the amount of waste by 15%, as stated by Won, Cheng and Lee [5]. Within the design stage, BIM facilitates the visual review of reusable or recyclable materials and products, to increase the rate of reuse and recovery [27]. BIM tools can also help to determine the potential deconstructability of a building during its design [25,65]. In addition, the data extracted from BIM can facilitate the process of fabrication, and catalyze the use of prefabricated components in lieu of cast-in-place ones [44,66], where just the concrete waste can be reduced by up to 70% [67]. Moreover, BIM improves and optimizes design to minimize the waste generated by the trim-cutting of components, rebar, or boarding sheets [22,68,69], and assists in the planning of concrete tasks with minimal waste of concrete [70]. Design for deconstruction (DfD) is another benefit of BIM by changing the design and offering the possibility of deconstruction instead of demolition—such as using joints instead of welding elements in steel structures [21,33]. BIM also acts as the single source of data to be shared among all project stakeholders, offering benefits such as the prevention of waste, which can be generated due to a lack of information and poor coordination [71]. BIM-based site planning can facilitate the handling of materials/components and reduce waste by avoiding layout errors and wasteful shipment [27], classifying all reused and recycled materials, and making plans for moving the usable materials [44]. BIM benefits the demolition/deconstruction of a building by the determination of the type and place of waste, and quantifying the recyclable or reusable waste [72]. So, too, BIM can be linked to a bank of reusable and recyclable materials/components to design a building according to available elements or components in the stock [52]. It assists stakeholders with access to a building that acts as a material and component bank [73]. BIM-based scheduling helps CDW management by the just-in-time delivery of materials/components, to avoid the long-term storage of materials and the ensuing waste [27].
2.2. Previous Review Studies
These are several review studies in the field. Of these, Ahankoob, et al. [74] conducted a review on the potential of BIM in addressing a list of the causes of waste. Likewise, Rajendran and Gomez [66] conducted a literature review on the advantages of using BIM for “designing out waste”, representing opportunities for waste reduction at the initial stages of projects, with scant attention paid to the technical aspects of BIM and tools that play a key role in achieving the benefits. Similarly, the benefits of using structural BIM models for reducing waste were studied by Salihi [37], citing several capabilities of BIM in minimizing waste, and presenting a list of BIM-driven features for CDW reduction, with no attention to BIM tools. Won and Cheng [27], too, conducted a literature review on the potential capabilities of BIM in minimizing CDW, with limited attention to BIM-based tools and the technological innovations pertinent to CDW management. As for Akinade, et al. [75], the authors presented a BIM-based framework through a literature review, based on which they argued that available CDW tools are not effective enough to manage CDW.
In a review study by Gupta, Jha and Vyas [38], CDW management strategies and tools for the planning and designing phase were surveyed and classified into two groups of BIM-based ones and non-BIM-based ones. Besides this, the drawbacks of three BIM-based tools were discussed, with reference to the three concepts of the “Design-out Waste Tool for Buildings (DoWT-B), Demolition and Renovation Waste Estimation (DRWE), and BIM-based Deconstructability Assessment Score (BIM-DAS)”. The study by Gupta, Jha and Vyas [38] represents the closest available one in presenting a picture of the BIM-related tools landscape for CDW management. Despite its value, overlooking BIM-related tools beyond the design stage is one drawback of the analyses provided by Gupta, Jha and Vyas [38] that warrants further research.
In summary, although the now available review studies focus on the applications of BIM for CDW management from various perspectives, none provides a picture of the landscape of the field in terms of the available BIM-related tools. This stands in contrast to the fact that the propensity of BIM for improving CDW in projects almost entirely lies in the power of its various technological elements [19,22].
3. Research Methods
3.1. Scoping Review
A scoping review was chosen as the approach that would inform the research design of this article. A scoping review is an ideal method for focusing on the breadth of coverage of the literature available on a topic, rather than assessing the quality or depth of the existing literature [76]. This was in line with the objectives of the study, namely, to offer a preliminary investigation into the range and nature of existing evidence, to facilitate the formulation of future research studies on the topic [76,77]. Though scoping reviews initially emerged in medical science, it is currently an acceptable technique in construction research [78,79].
3.2. Data Extraction
For identifying any existing studies on the integration between BIM tools and CDW, several databases can be used: Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar. The Scopus database and Web of Science were selected, since these databases collectively provide access to the most comprehensive data available [80]. The keywords of “waste”, “building information modeling” and “Building information modeling” are used, covering various styles of spelling, following the search strings in previous studies to retrieve BIM-related publications [19]. These keywords were applied within the titles, abstracts, and keywords of papers. The last update of running the search was on 30 August 2020, with no time limitation applied. From this search for relevant papers, 232 (from Scopus) and 73 (Web of Science) were obtained by using the keywords (see Figure 2).
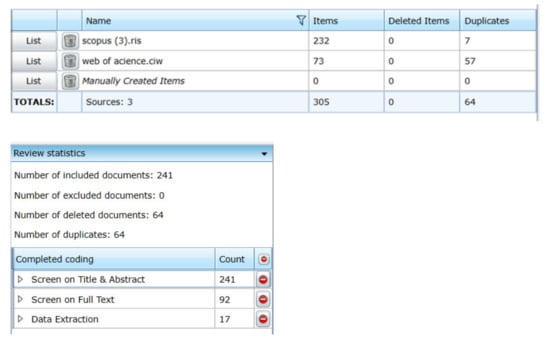
Figure 2.
Details of papers found and selected.
To facilitate the selection of related papers, “EPPI-Reviewer” was used, which is a tool for managing and analyzing data for research synthesis purposes. Besides this capability, this web-based application manages references, stores PDF files, removes any duplications and provides digital forms for extracting review data [81]. As illustrated in Figure 2, references from Scopus and Web of Science were imported to the program. The EPPI-Reviewer helped to identify and remove 64 duplicated papers. Afterward, 241 articles were filtered after screening their titles and abstracts. For tightening the scope, several criteria were used to reduce the number of papers. Studies had to be related to solid construction waste, hence those related to other types of waste—like oil and gas waste, water waste, or information waste—were excluded. Studies devoted to waste without using BIM were excluded. Papers that provided a theoretical framework of how BIM can help CDW management without introducing a tool were also excluded. These conditions were set in EPPI-Reviewer as the “exclude” and “include” child codes in the code set of “Screen on Full Text”. The criteria were used for setting up the screening coding tool in EPPI-Reviewer, as a result of which 92 papers were selected, providing the source of data for the next round of reviewing. To make sure that all related studies were included, references and citations of selected papers were explored too, yet no paper was added to the list.
As illustrated in Figure 3, 92 studies related to BIM and CDW were identified. These were screened to select only those that introduced a workable BIM-based API or algorithm for CDW management. Out of 92, 75 did not meet these conditions and were excluded, while 17 were found to be closely aligned with the criteria and were retained for further detailed analyses (see Figure 2 and Figure 3), as discussed next.
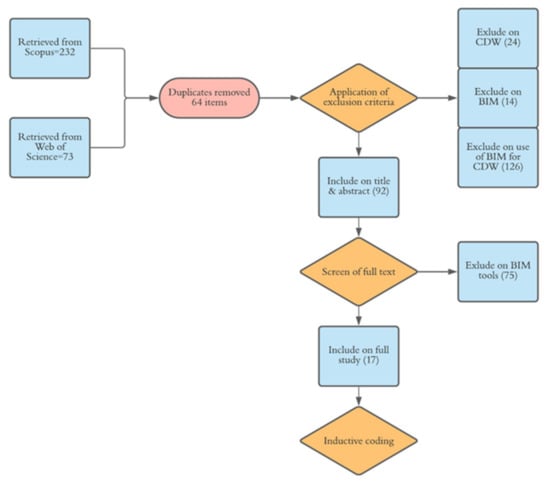
Figure 3.
Data screening process and typology of papers.
4. Findings and Discussions
4.1. Classification of Studies
This review approach is recognized as inductive, hence, “open coding” was utilized. Any relevant information was coded line-by-line to consider every possible piece of information, along with metadata, like geographical source and publication type [82]. Other data that were coded included the phases of the life cycle, outcome, and various tools. Geographical sources were determined according to the institutional origin of the first author, following the approach taken by Gradeci and Labonnote [83]. The type of software for BIM modeling—Revit, Archicad, etc.—was included too. The nature of the output of studies was categorized into concept, proof of concept (PoC), idea, and prototype, as tabulated in Table 1.

Table 1.
General overview of the details of available studies on BIM-based tools for CDW management.
All applied strategies of studies were classified according to the analysis or related strategies of the 3 Rs—reduce, reuse and recycle. Analysis strategies were considered as the initial measures for CDW management during the design stage, such as designing for deconstruction (DfD); calculation and prediction of the amount of waste; prediction of the impacts of waste on the environment; deconstructability assessment of a building; and methods for improving the process of demolition or deconstruction of a building. The phases of the life cycle were grouped into design, construction, operation and end-of-life [89,90], summarized in the form of a T-matrix diagram [91], as tabulated in Table 2. Studies were divided according to two classifications: (1) the life cycle of a construction project (2) analysis or the 3-Rs strategies (Table 2).

Table 2.
CDW BIM-based tools (the analysis or the 3-Rs strategies; and implementation stages in the life cycle of projects).
4.2. Descriptive Analysis
As illustrated in Figure 4, only 7% of the publications related to BIM and CDW (17 out of 241 papers) have focused on developing BIM-based tools for managing CDW. The annual trend of publications on BIM-based tools for managing CDW—Figure 4—illustrates an increase in recent years, while the largest number of publications on the topic was in 2019 [19]. This represents a gap in the BIM body of knowledge, warranting further research into introducing new BIM-based methods and techniques for managing CDW, or developing technological innovations and tools to support and revolutionize the existing methods.
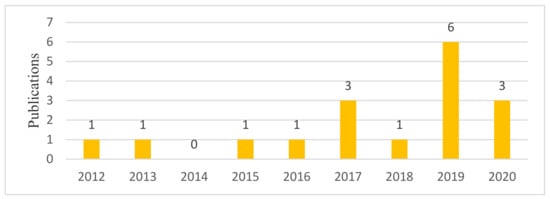
Figure 4.
The trend of published articles on CDW BIM-based tools.
Papers were sorted according to the affiliation of their first authors, as illustrated in Figure 5. The USA and Canada (17% each) contribute the largest number of publications, followed by China, the UK, Hong Kong, and Korea (with 12% each). Australia, Egypt and France have each added 6% to the total number of publications, where other countries have played no role in this area of research. Countries like Brazil that produce sizeable amounts of CDW need to redefine research directions, to reap the benefits of BIM in managing CDW.
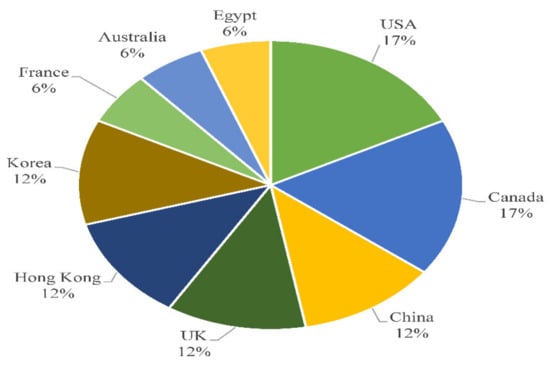
Figure 5.
The distribution of published papers.
As Table 3 illustrates, the majority of journal articles on the topic are in journals related to the generic aspects of waste management and sustainability, rather than traditional outlets of construction management. Except for “Automation in Construction”, none of the typical outlets of construction management have published papers related to the use of BIM technology for managing waste. This reveals a perceived misalignment between the aims and objectives of outlets of the field, and the priorities of common research studies on the topic.

Table 3.
Journals publishing regarding CDW BIM-based tools.
Table 4 illustrates a conspicuous lack of research at the intersection of operation and end-of-life stages of projects, where the field has not considered adopting strategies in these stages (0 to 6%). In fact, the 3 Rs have not been the basis of developing BIM-based technologies to address the problem of CDW at the operation and end-of-life stages, representing a disregard for the waste generated in the renovation and refurbishment of projects, or during the operation or maintenance of projects.

Table 4.
Weights (N/%) of studies in each category.
Moreover, as illustrated in Figure 6, most BIM technologies have been developed with the purpose of analyzing CDW, rather than applying the 3 Rs. Recycling among the 3 Rs has received scant attention in developing BIM-based technologies for managing CDW.
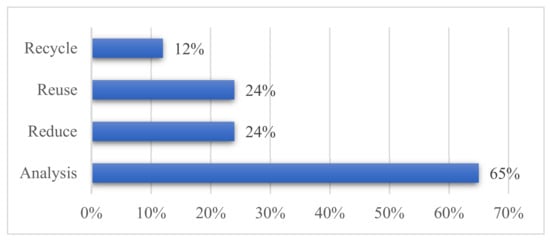
Figure 6.
Percentages of papers devoted to analysis or the 3 R’s strategies.
As for various stages of projects, the focus has been on the design stage, whereas the operation stage has received scant attention, as illustrated in Figure 7.
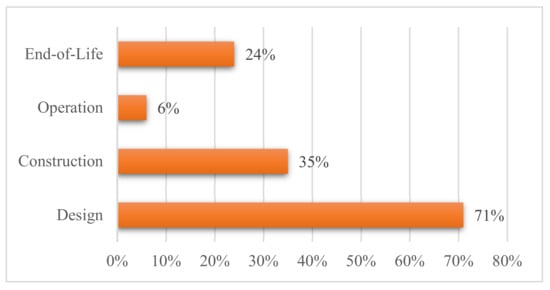
Figure 7.
Percentages of papers devoted to various stages of the life cycle of construction projects.
That is, existing BIM-based technologies developed for managing CDW at various stages of projects have overlooked the significance of operation and maintenance. This stands in stark contrast to the fact that operation and maintenance are the longest phases of the project life cycle, representing the phases in which the largest share of costs are spent. This is understandable, as, despite the intrinsic synergy that exists between BIM and facility management (FM), outright coalescence between BIM and FM remains a problem to be addressed through future research [92].
4.3. Analysis of Contents
What follows provides an analysis of the content of studies that fall within each category, according to the classification proposed in the present study.
4.3.1. “Analysis” of BIM-Based Technologies
Of the 17 papers concerning BIM-based technological innovations, 11 (or 65%) focused on the analysis approach (see Figure 6). Studies in this group have proposed BIM-driven techniques for: design for deconstruction (DFD) [44]; calculation and prediction of CDW [12,30,63,70,84,86]; prediction of the impacts of CDW on the environment [85]; deconstructability assessment of a building [25,65]; and improving the demolition or deconstruction process [72].
4.3.2. Technologies Developed for ‘3 Rs’
As illustrated in Figure 6, 24% of papers have targeted the “reduce” strategy. These published papers have focused on BIM-based design validation [5,30], and methods of minimization of the trim loss of materials [68,69]. Four papers discussed the reuse strategy for BIM-based CDW management. These papers developed BIM tools to create a bank of reusable material/components [52], support design from reusable components [87], and reuse one type of material such as waste concrete [70,88]. The “recycle” strategy was commonly associated with a bank of recyclable materials to be updated across the entire life cycle of a facility [52], or focused on the estimation of one recycled material, like gypsum or concrete [88].
4.4. Stages of Life Cycle
As for “life cycle”, twelve papers (71%) focused on “design”, followed by “construction” at 35%. Fewer papers considered “end-of-life” (24%), followed by “operation”, with just one paper.
Papers that focused on developing tools for the design stage were about design for deconstruction (DfD) [44]; the estimation of CDW [12,30,63,86]; the deconstructability assessment of a building [25,65]; design validation [5,30]; design optimization [68,69]; a bank of reusable and recyclable materials and components [52]; and design from reusable components [87].
The specific attention to design can be justified, given that the significant impacts of design on waste generation are well documented in the literature [4,93]. That is, 33% of on-site construction waste is due to a lack of attention to waste reduction in the design phase [4,66,94].
Most of the papers allocated to construction provide methods of construction waste estimation, including calculation techniques for just one type of material waste, such as concrete [70,84], gypsum [84], or a combination of various types of material within the construction process [30,44]. The other techniques in this category include: BIM-based material and components bank for reusing or recycling [52]; planning for reusing—one type of material such as waste concrete—according to project scheduling with BIM [70]; calculation algorithms for on-site reused concrete and recycled gypsum or concrete [88]; and determining the main sources of construction waste, making decisions for the reconsideration of methods or redesign of components to reduce the amount of waste generation in construction [30].
Lack of attention to BIM for the minimization of CDW in operation and maintenance can be justified in view of the lack of integration between BIM and operation activities [92]. As argued by Won and Cheng [27], the use of BIM in the operation phase cannot significantly affect the amount of CDW, compared to other phases like design or construction.
Papers that discussed end-of-life provided technologies to assess the impacts of waste on the environment [44,85], and improve the demolition or deconstruction processes by making a plan according to the type of the material, place and quantity involved [72]. BIM can also be used in this stage for developing a bank of reusable and recyclable materials/components. Besides, a plan for extracting more reusable or recyclable material is another application of BIM in this phase [52].
4.5. Technologies for “Analysis” or the “3 Rs” across Each Stage of the Life Cycle
As illustrated in Table 4, existing technologies and methods focus on strategies (“analysis” or the “3 Rs”) and stages of the life cycle, a description of the content of each category follows.
4.5.1. Design—Analysis
Most studies developed tools and techniques to predict the amount of waste. Akinade and Oyedele [86], for example, developed a BIM model to predict the amount of construction waste in design by using two predictors of “gross floor area” and “type of construction”. This model came as a BIM API, which was provided by integrating the “Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System” (ANFIS) and BIM. Lu, Webster, Chen, Zhang and Chen [30] developed a BIM API to compute the waste generated in design and construction, to facilitate making decisions with the aim of minimizing waste. This method used the predefined rate of waste for any type of material. Kim, Hong, Park and Cha [63] calculated the waste volume, according to the type of material and components, in the design stage by using a BIM-based framework. This method calculates waste by using the Korean waste factor. Another demolition waste calculation method was introduced by Cheng and Ma [12]. They developed a BIM API in Revit to predict and calculate the demolition and renovation waste, landfill levies, and the number of trucks for the transportation of waste, according to the type of materials and components, by using a table of material waste factors and user input.
Only one study focused on DfD approaches: Jalaei, Zoghi and Khoshand [44] represented DfD according to the types of materials, types of elements and the life span of elements. They worked on a steel structure, and converted welded joints to bolts, to facilitate the extraction of components at the end-of-life. Besides this, they recommended replacing in-cast elements with prefabricated components to reduce waste. Other researchers in this group considered the deconstructability assessment of a facility. Akinade, Oyedele, Bilal, Ajayi, Owolabi, Alaka and Bello [25] calculated a BIM-based deconstructability assessment score (BIM-DAS) as an indicator to determine the potential deconstructability of a building in the design stage. This was offered in the form of a sum of deconstructability score (DSCORE) and recovery score (RSCORE), where DSCORE determines the potential of elements to be disassembled, and RSCORE demonstrates the potential of materials to be reused or recycled. Their model merely considered design to predict the reusability or recyclability of concrete, timber and steel structures. Likewise, Basta, Serror and Marzouk [65] developed a method for assessing the deconstructability of steel structures, which automatically worked for scoring several steel parameters in terms of being deconstructed.
4.5.2. Design—3 Rs
Of the four articles associated with reducing the amount of waste at the design stage, two considered BIM-based design validation [5,30], and others proposed various methods of minimization for the trim loss of materials [68,69].
Won, Cheng and Lee [5] estimated the amount of waste that can be prevented in two construction projects in South Korea, where the amount of prevented waste was up to 4.3–15.2% of the construction waste, compared against conventional design methods. Lu, Webster, Chen, Zhang and Chen [30] considered the amount of waste generation for each component in the design stage to find out which design options generated the largest share of waste, to facilitate making decisions about the redesign of that component to reduce waste. As for trim loss minimization, Porwal and Hewage [68] introduced an algorithm and used BIM as a communication tool for transferring information. They also offered a simulation tool to compare outcomes, make cost-effective decisions and change the design to reduce rebar waste. Another research focusing on the optimization of material waste was conducted by Liu, Singh, Lu, Bouferguene and Al-Hussein [69] in which a BIM-based approach for the automatic design boarding of a layout was developed to plan various alternatives of material sheet cutting, with the purpose of minimizing waste. This system is based on trades’ know-how and rule-based design algorithms, using Autodesk Revit API as a BIM platform.
The reuse of materials and components in the design stage was addressed through developing tools and methods for providing a bank of reusable material and components [52], and design from reusable components [87]. Bertin, Mesnil, Jaeger, Feraille and Le Roy [87] proposed a methodology to design a building from reusable load-bearing elements in the stock. Finite element software was used to find a reusable load-bearing element. Their method included choosing elements from the stock of pre-demolition building and using finite element software to assess elements in terms of loading. Cai and Waldmann [52] proposed a bank of materials and components to manage reusing components and the recycling of materials, even constructing a whole project from an old building by using the BIM platform. Only one paper focused on recycling in the design phase; that is, Cai and Waldmann [52] presented a BIM-based bank of recyclable materials for design purposes, considering the waste that might be generated throughout the whole life cycle of a project.
4.5.3. Construction—Analysis
Published papers in this group mostly target the estimation of waste generated during construction. This includes focusing on the calculation techniques for just one type of material waste, such as concrete waste [70,84] or gypsum [84], or papers that focused on all types of materials [30,44].
As for techniques for calculating one type of waste material, Bakchan, Faust and Leite [70] provided a method for the automatic estimation of concrete waste and the disposal costs, and allocated waste bins in construction sites, similar to the techniques provided by Guerra, Bakchan, Leite and Faust [84]. The amount of waste (concrete or gypsum) was defined as the difference between the total amount of used materials and purchased ones, retrieved from a BIM model.
Regarding the estimation of construction waste, Lu, Webster, Chen, Zhang and Chen [30] quantified construction waste by the multiplication of the number of components and the waste generation factor retrieved from a BIM-based database. Jalaei, Zoghi and Khoshand [44] also calculated the construction waste by using the waste coefficients provided by the Athena software. These coefficients were related to the types of materials and their function.
4.5.4. Construction—The 3 Rs
The possibility of reducing waste within construction processes was represented in just one published paper, where, after the calculation of waste in construction, data were archived in a BIM model. Designers could review the results and recognize the large amount of generated waste in various activities, in order to make decisions, for reconsidering their methods, or optimizing the design of components. This leads to a reduction of the generated waste within construction [30].
There are three published papers concerning the reuse strategy in construction. Techniques provided in this category include BIM-based material and component banks for reusing [52], and making plans for reusing just one type of material, such as waste concrete [70,88].
Cai and Waldmann [52] introduced a material and component bank that can be linked to BIM and manage the reuse of materials and components. At the construction phase, the proposed bank asks BIM models when and where the material and components will be required. BIM models also provide information about available materials and components for reuse. Reusable materials and components can be reused within the construction process at the required place and time. As for reusing concrete waste, Bakchan, Faust and Leite [70] provided the opportunity of reusing the concrete waste as backfill by using a project schedule retrieved from a BIM model. Likewise, Guerra, Leite and Faust [88] proposed an algorithm for calculating the amount of on-site reused concrete. This algorithm was integrated with 4D-BIM to seek the possible opportunity of reusing waste.
There exist two papers that used the “recycle” strategy in the construction stage, including a bank of recyclable materials [52] and making plans for using just one type of recycled materials, such as gypsum or concrete [88].
The bank of materials and components introduced by Cai and Waldmann [52] provides the opportunity of using recyclable material. In addition, the algorithm introduced by Guerra, Leite and Faust [88] estimated the drywall waste for analyzing the possibility of off-site recycling, using 4D-BIM models.
4.5.5. Operation—Analysis
The only paper that belongs to this category is by Jalaei, Zoghi and Khoshand [44], wherein the waste of maintenance was calculated according to a life span of 7 to 20 years for several elements of a building, such as “facility waste, windows, doors, etc.”.
4.5.6. End-of-Life—Analysis
Papers in this category mostly considered the method of the estimation of waste, to provide proper data to assess the impact of the waste on the environment [44,85], or improve the demolition or deconstruction processes [72].
Ge et al. [72] proposed a framework for calculating reusable or recyclable materials and a plan for deconstruction by using as-built BIM models and existing documents. According to this framework, the type of materials, as well as the place and quantity of them, were determined. This framework can also provide the required time and labor hours for demolition. The information provided by this BIM model included the stages of the demolition process, places of waste in the building model, and the possible amount of waste.
Xu, Shi, Xie and Zhao [85] studied BIM-based systems for the calculation of waste and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions at the end-of-life of a facility. They proposed suggestions for recycling or landfilling the material, according to GHG emissions, in order to minimize the total amount of GHG. Jalaei, Zoghi and Khoshand [44] offered a method to calculate the waste generated during a facility’s life span. An add-in BIM tool estimated the amount of waste to be used in life-cycle assessment (LCA), with the aim of reducing the waste and environmental impacts. The authors highlighted the crucial role of BIM in reducing waste throughout the entire life cycle of construction, including at the end-of-life stage.
4.5.7. End-of-Life—The 3 Rs
There is one research study in both groups of “end-of-life” and “reuse and recycle”. As discussed, Cai and Waldmann [52] developed a bank for reusable and recyclable building materials and components by using BIM, to provide a plan for the deconstruction of structures. This was to maximize the extraction of reusable or recyclable materials and components.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
It stands to reason, then, that BIM is seen as the panacea to address many cited challenges in construction projects [18]. So, too, BIM is touted as a major solution to deal with the sizeable amount of CDW generated in the construction industry [21]. The remedial solutions offered by BIM are precipitated by the multifaceted capabilities of BIM in handling data and information. This for the most part relies on various computing features of the BIM technology [95]. Although previous review studies have provided a broad overview of the associations between BIM and CDW, this study stands out in providing a clear picture of the landscape of research allocated to offering the tools and technological capabilities of BIM in addressing waste-related issues. This study contributes to the field by identifying the intellectual deficiencies in offering BIM-based tools and technologies in dealing with CDW. Our findings also reveal the priorities for defining future research on the topic. That is, although various BIM-based technologies are closely associated with CDW, few studies in the relatively sizeable BIM-related literature have offered workable technologies that can benefit from BIM capabilities in addressing the devastating impacts of CDW. Besides this, the majority of the proposed technologies have targeted the design and construction phase. Our findings reveal that addressing the problems of CDW in post-construction has remained an unexplored area. Besides, proposed tools and technologies are mostly lacking in cross-phase insights into the project waste aspects, and are weak in theoretical rigor.
Future studies should consider providing BIM-based technologies, which are supported by the theoretical foundations of managing waste, while moving beyond the design and construction stages. These technologies need to be adaptable across various stages of a project’s life cycle and focus on the smooth transition of data and information throughout all the phases of delivering a project, from its initiation to its operation, maintenance, end-of-life, and afterward. There should be a transition from using the technology offered by BIM as a central source of data for design and construction; indeed, a transition to the concept of digital engineering (DE) is needed [18]. That is, proposed technologies should be enabled by the coalescence of various technological innovations centered around BIM, to facilitate sharing data and information about all the products and components included inbuilt assets beyond project teams; they should act as brokerage systems that link data from models to the market, suppliers, manufacturers, and facility managers of buildings, as argued by Wijewickrama et al. [96].
With the above in mind, the study upends the prevailing perception of previous studies, indicating that the body of knowledge on BIM has been heavily technology-oriented, disregarding the socio-economic aspects of BIM in the construction industry. Previous studies have recommended further research on the socio-economic aspects of BIM [19,97]. This study reveals that, although the available BIM literature has been oriented toward technological aspects from a broad perspective, in further exploration, much more research is needed to develop tools and technological point solutions for dealing with some major challenges in the field, like CDW.
Despite the contributions of the paper, some limitations should be acknowledged. First, the number of reviewed studies is relatively small, mostly due to a lack of related studies in the field. Moreover, given the nature of the study as a scoping review, scant attention has been paid to the depth of knowledge on the topic, in the interest of assessing the coverage and breadth of knowledge. Future studies are therefore needed to assess the quality and practicality of the tools and solutions offered in the literature. Moreover, the field needs studies that provide an integrated solution for the problem of CDW, in lieu of offering point solutions for addressing particular aspects.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.N. and M.R.H.; methodology, B.N. and M.R.H.; software, B.N.; validation, B.N. and M.R.H.; analysis of the literature, B.N.; writing—original draft preparation, B.N.; writing—review and editing, M.R.H., J.W., N.C. and R.R.; visualization, J.W.; supervision and quality control, N.C. and R.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shen, L.; Tam, V.W.; Tam, C.; Drew, D. Mapping approach for examining waste management on construction sites. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2004, 130, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, F.Y.Y.; Nguyen, D.S.A. Strategies for construction waste management in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2013, 3, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmehr, B.; Hosseini, M.R.; Oraee, M.; Chileshe, N. Major factors affecting waste generation on construction sites in Iran. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Engineering, Project, and Production Management (EPPM2015), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 2–4 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Osmani, M.; Glass, J.; Price, A.D. Architects’ perspectives on construction waste reduction by design. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.; Cheng, J.C.; Lee, G. Quantification of construction waste prevented by BIM-based design validation: Case studies in South Korea. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikmehr, B.; Hosseini, M.R.; Rameezdeen, R.; Chileshe, N.; Ghoddousi, P.; Arashpour, M. An integrated model for factors affecting construction and demolition waste management in Iran. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2017, 24, 1246–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esin, T.; Cosgun, N. A study conducted to reduce construction waste generation in Turkey. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangcharoenrat, C.; Intrachooto, S.; Peansupap, V.; Sutthinarakorn, W. Factors influencing construction waste generation in building construction: Thailand’s perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, A.; De Brito, J. Influence of construction and demolition waste management on the environmental impact of buildings. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagapan, S.; Rahman, I.A.; Asmi, A.; Memon, A.H.; Latif, I. Issues on construction waste: The need for sustainable waste management. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Colloquium on Humanities, Science and Engineering (CHUSER), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 3–4 December 2012; pp. 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alwi, S.; Mohamed, S.; Hampson, K. Waste in the Indonesian construction projects. In Proceedings of the 1st CIB-W107 International Conference-Creating a Sustainable Construction Industry in Developing Countries, Pretoria, South Africa, 11–13 November 2002; pp. 305–315. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.C.; Ma, L.Y. A BIM-based system for demolition and renovation waste estimation and planning. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghi, M.; Kim, S. Dynamic modelling for life cycle cost analysis of BIM-based construction waste management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oyedele, L.O.; Regan, M.; von Meding, J.; Ahmed, A.; Ebohon, O.J.; Elnokaly, A. Reducing waste to landfill in the UK: Identifying impediments and critical solutions. World J. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 10, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.S.; Tudor, T.; Bird, H.; Bates, M. A critical review of a key waste strategy initiative in England: Zero waste places projects 2008–2009. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.T.W.; Poon, C.S.; Wong, A.; Yip, R.; Jaillon, L. Impact of Construction Waste Disposal Charging Scheme on work practices at construction sites in Hong Kong. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabirifar, K.; Mojtahedi, M.; Wang, C.C. A Systematic Review of Construction and Demolition Waste Management in Australia: Current Practices and Challenges. Recycling 2021, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Jupp, J.; Papadonikolaki, E.; Mumford, T.; Joske, W.; Nikmehr, B. Position paper: Digital engineering and building information modelling in Australia. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Maghrebi, M.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Martek, I.; Arashpour, M. Analysis of Citation Networks in Building Information Modeling Research. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2018, 144, 04018064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Jiang, S.; Skibniewski, M.J.; Man, Q.; Shen, L. A literature review of the factors limiting the application of BIM in the construction industry. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2017, 23, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akbarnezhad, A.; Ong, K.C.G.; Chandra, L.R. Economic and environmental assessment of deconstruction strategies using building information modeling. Autom. Constr. 2014, 37, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihashemi, S.; Tabadkani, A.; Hosseini, M.R. Integration of parametric design into modular coordination: A construction waste reduction workflow. Autom. Constr. 2018, 88, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.; Al Mamun, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Basri, H.; Begum, R.A. A review on technologies and their usage in solid waste monitoring and management systems: Issues and challenges. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, R.; Browne, M.; Odeyinka, H.; McKeown, C.; McNiff, S. BIM implementation throughout the UK construction project lifecycle: An analysis. Autom. Constr. 2013, 36, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Bilal, M.; Ajayi, S.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Bello, S.A. Waste minimisation through deconstruction: A BIM based Deconstructability Assessment Score (BIM-DAS). Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, C.; Teicholz, P.; Sacks, R.; Liston, K. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Managers, Designers, Engineers and Contractors, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Won, J.; Cheng, J.C. Identifying potential opportunities of building information modeling for construction and demolition waste management and minimization. Autom. Constr. 2017, 79, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärn, E.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Sing, M.C. The building information modelling trajectory in facilities management: A review. Autom. Constr. 2017, 75, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Hu, X.; Tivendale, L.; Hosseini, M.R.; Liu, C. Building information modelling in sustainable design and construction. Int. J. Sustain. Real Estate Constr. Econ. 2018, 1, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Webster, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Computational Building Information Modelling for construction waste management: Moving from rhetoric to reality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.C.; Won, J.; Das, M. Construction and demolition waste management using BIM technology. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Conference of the International Group for Lean Construction, Perth, Australia, 19–23 July 2015; pp. 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksanin, A. Potential for the use of information systems in the management of construction waste. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 196, 04081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Omoteso, K.; Ajayi, S.O.; Bilal, M.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Ayris, L.; Looney, J.H. BIM-based deconstruction tool: Towards essential functionalities. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2017, 6, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, R.; Stengel, J.; Schultmann, F. Building Information Modeling (BIM) for existing buildings—Literature review and future needs. Autom. Constr. 2014, 38, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalcinkaya, M.; Singh, V. Patterns and trends in Building Information Modeling (BIM) research: A Latent Semantic Analysis. Autom. Constr. 2015, 59, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Skibniewski, M.; Wu, Z.; Wang, R.; Le, Y. Information and Communication Technology Applications in Architecture, Engineering, and Construction Organizations: A 15-Year Review. J. Manag. Eng. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihi, I.U. Application of structural building information modeling (S-BIM) for sustainable buildings design and waste reduction: A review. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Jha, K.N.; Vyas, G. Proposing building information modeling-based theoretical framework for construction and demolition waste management: Strategies and tools. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çıdık, M.S.; Boyd, D.; Thurairajah, N. Innovative Capability of Building Information Modeling in Construction Design. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.; Woetzel, J.; Mischke, J.; Ribeirinho, M.J.; Sridhar, M.; Parsons, M.; Bertram, N.; Brown, S. Reinventing Construction through a Productivity Revolution. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/capital-projects-and-infrastructure/our-insights/reinventing-construction-through-a-productivity-revolution (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Opoku, D.-G.J.; Ayarkwa, J.; Agyekum, K. Barriers to environmental sustainability of construction projects. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2019, 8, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, R.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Silva Melo, A.C.; Macêdo, A.N. Reverse supply chain conceptual model for construction and demolition waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 0734242X21998730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, P.L.; Santos, A.L. Embodied energy on refurbishment vs. demolition: A southern Europe case study. Energy Build. 2015, 87, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaei, F.; Zoghi, M.; Khoshand, A. Life cycle environmental impact assessment to manage and optimize construction waste using Building Information Modeling (BIM). Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmehr, B.; Hosseini, M.R.; Martek, I.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Antucheviciene, J. Digitalization as a strategic means of achieving sustainable efficiencies in construction management: A critical review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for the Waste Audits before Demolition and Renovation Works of Buildings. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/31521 (accessed on 20 September 2020).
- Government of the United Kingdom Site Waste Management Plans Regulations 2008. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2008/314/contents/made (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Shooshtarian, S.; Maqsood, T.; Wong, S.; Khalfan, M. Review of Waste Strategy Documents in Australia: Analysis of Strategies for Construction and Demolition Waste. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag 2020, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Construction and Demolition Waste Legislation. Available online: https://www.epa.vic.gov.au/for-business/find-a-topic/manage-industrial-waste/construction-and-demolition-waste/legislation (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Patty, R.; Bera, D.K.; Rath, A.K. Strategies for Construction and Destruction (C&D) Waste Management. In Recent Developments in Sustainable Infrastructure; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 879–889. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Y.Y.; Leo, K.C. Reusing timber formwork: Importance of workmen’s efficiency and attitude. Build. Environ. 2000, 35, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Waldmann, D. A material and component bank to facilitate material recycling and component reuse for a sustainable construction: Concept and preliminary study. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 2015–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader Moyano, P.; Ramirez de Arellano Agudo, A.; Olivares Santiago, M. Calculation methodology to quantify and classify construction waste. Open Constr. Build. Technol. J. 2011, 5, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, B.; Shell, S.; Esherick, H. Design for Deconstruction and Materials Reuse. Proc. CIB Task Group 2006, 39, 189–209. [Google Scholar]
- Price, T. In Site waste management plans, the designer and the CDM principal contractor. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference of the Association of Researchers in Construction Management, Leeds, UK, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 1381–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Tam, V.W.Y. Identifying best design strategies for construction waste minimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 92, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, S.O.; Oyedele, L.O. Policy imperatives for diverting construction waste from landfill: Experts’ recommendations for UK policy expansion. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, L.; Li, H.; Luo, H.; Ding, L.; Zhang, X. Sustainable performance of just-in-time (JIT) management in time-dependent batch delivery scheduling of precast construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.; Baum, H. A novel methodology to estimate the evolution of construction waste in construction sites. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dainty, A.R.; Brooke, R.J. Towards improved construction waste minimisation: A need for improved supply chain integration? Struct. Surv. 2004, 22, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, K.W.; Ismail, R.; Khoo, T.J.; Riazi, S.R.M.; Mohd Nawi, M.N. Innovation technology towards Construction & Demolition (C&D) waste management. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 1971–1985. Available online: http://sersc.org/journals/index.php/IJAST/article/view/9367 (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Li, C.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Yu, B.; Tam, V.W.; Chen, Z.; Ya, Y. Research trend of the application of information technologies in construction and demolition waste management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 121458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Hong, W.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Cha, G.-W. An estimation framework for building information modeling (BIM)-based demolition waste by type. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Won, J.; Cheng, J.C.P. A financial decision making framework for construction projects based on 5D Building Information Modeling (BIM). Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2016, 34, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, A.; Serror, M.H.; Marzouk, M. A BIM-based framework for quantitative assessment of steel structure deconstructability. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Gomez, C.P. Implementing BIM for waste minimisation in the construction industry: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on Management, Langkawi Kedah, Malaysia, 11–12 June 2012; pp. 557–570. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, T.; Moor, P.; Cox, K.; Clark, J. The Gammon Skanska Construction System. In Advances in Building Technology; Anson, M., Ko, J.M., Lam, E.S.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 1073–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Porwal, A.; Hewage, K.N. Building information modeling–based analysis to minimize waste rate of structural reinforcement. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2012, 138, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Singh, G.; Lu, M.; Bouferguene, A.; Al-Hussein, M. BIM-based automated design and planning for boarding of light-frame residential buildings. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakchan, A.; Faust, K.M.; Leite, F. Seven-dimensional automated construction waste quantification and management framework: Integration with project and site planning. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, A. Reducing Material Waste with the Application of Building Information Modelling (BIM). Ph.D. Thesis, Durban University of Technology, Durban, South Africa, March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.J.; Livesey, P.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; He, X.; Zhang, C. Deconstruction waste management through 3d reconstruction and bim: A case study. Vis. Eng. 2017, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- BAMB the Project BAMB—Buildings as Material Banks. Available online: https://www.bamb2020.eu/about-bamb/ (accessed on 16 May 2021).
- Ahankoob, A.; Khoshnava, S.M.; Rostami, R.; Preece, C. BIM perspectives on construction waste reduction. In Proceedings of the Management in Construction Research Association (MiCRA) Postgraduate Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 5–6 December 2012; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Munir, K.; Bilal, M.; Ajayi, S.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Bello, S.A. Evaluation criteria for construction waste management tools: Towards a holistic BIM framework. Int. J. Sustain. Build. Technol. Urban Dev. 2016, 7, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumrill, P.D.; Fitzgerald, S.M.; Merchant, W.R. Using scoping literature reviews as a means of understanding and interpreting existing literature. Work. Read. Mass. 2010, 35, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engebø, A.; Lædre, O.; Young, B.; Larssen, P.F.; Lohne, J.; Klakegg, O.J. Collaborative project delivery methods: A scoping review. J. Civil. Eng. Manag. 2020, 26, 278–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanc, M.; McAndrew, C.; Ucci, M. Conceptual approaches to wellbeing in buildings: A scoping review. Build. Res. Inf. 2019, 47, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskuriy, R.; Selamat, A.; Maresova, P.; Krejcar, O.; David, O.O. Industry 4.0 for the construction industry: Review of management perspective. Economies 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.; Brunton, J.; Graziosi, S. EPPI-Reviewer 4.0: Software for Research Synthesis; EPPI-Center Software, Social Science Research Unit, UCL Institute of Education: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saldaña, J. The coding manual for qualitative researchers. Qual. Res. Organ. Manag. 2015, 12, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradeci, K.; Labonnote, N. On the potential of integrating building information modelling (BIM) for the additive manufacturing (AM) of concrete structures. Constr. Innov. 2019, 20, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.C.; Bakchan, A.; Leite, F.; Faust, K.M. BIM-based automated construction waste estimation algorithms: The case of concrete and drywall waste streams. Waste Manag. 2012, 87, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shi, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, S. A BIM-Based construction and demolition waste information management system for greenhouse gas quantification and reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinade, O.O.; Oyedele, L.O. Integrating construction supply chains within a circular economy: An ANFIS-based waste analytics system (A-WAS). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, I.; Mesnil, R.; Jaeger, J.M.; Feraille, A.; Le Roy, R. A BIM-based framework and databank for reusing load-bearing structural elements. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerra, B.C.; Leite, F.; Faust, K.M. 4D-BIM to enhance construction waste reuse and recycle planning: Case studies on concrete and drywall waste streams. Waste Manag. 2020, 116, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.A.L.; Ramón, X.R.; Domingo, S.G. The circular economy in the construction and demolition waste sector–A review and an integrative model approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.F.; Esmanioto, F.; Huber, N.; Loures, E.R.; Canciglieri, O., Jr. A systematic literature review of interoperability in the green Building Information Modeling lifecycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Systems Thinking Toolbox. Available online: https://www.burgehugheswalsh.co.uk/Systems-Thinking/Tools.aspx (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Hosseini, M.R.; Roelvink, R.; Papadonikolaki, E.; Edwards, D.J.; Pärn, E. Integrating BIM into facility management. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2018, 36, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, B.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Li, J.; Xu, X. Critical factors affecting willingness of design units towards construction waste minimization: An empirical study in Shenzhen, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, S. Developing tools for designing out waste pre-site and on-site. In Proceedings of the Minimising Construction Waste Conference: Developing Resource Efficiency and Waste Minimisation in Design and Construction, London, UK, 21 October 2004. New Civil Engineer. [Google Scholar]
- Gharouni Jafari, K.; Noorzai, E.; Hosseini, M.R. Assessing the capabilities of computing features in addressing the most common issues in the AEC industry. Constr. Innov. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewickrama, M.; Rameezdeen, R.; Chileshe, N. Information brokerage for circular economy in the construction industry: A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 127938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; van Nederveen, S.; Hertogh, M. Understanding effects of BIM on collaborative design and construction: An empirical study in China. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
