A Fluorescence Method Based on N, S-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Ammonia in Aquaculture Water and Freshness of Fish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Preparation of N, S-CDs
2.4. Detection of Ammonia
3. Results and Discussion
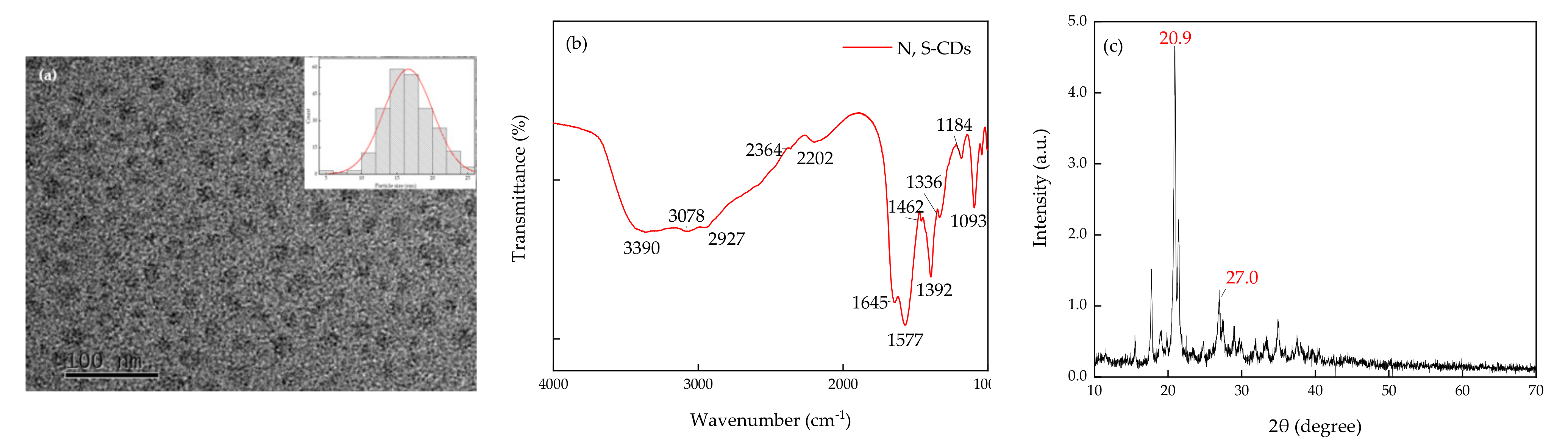
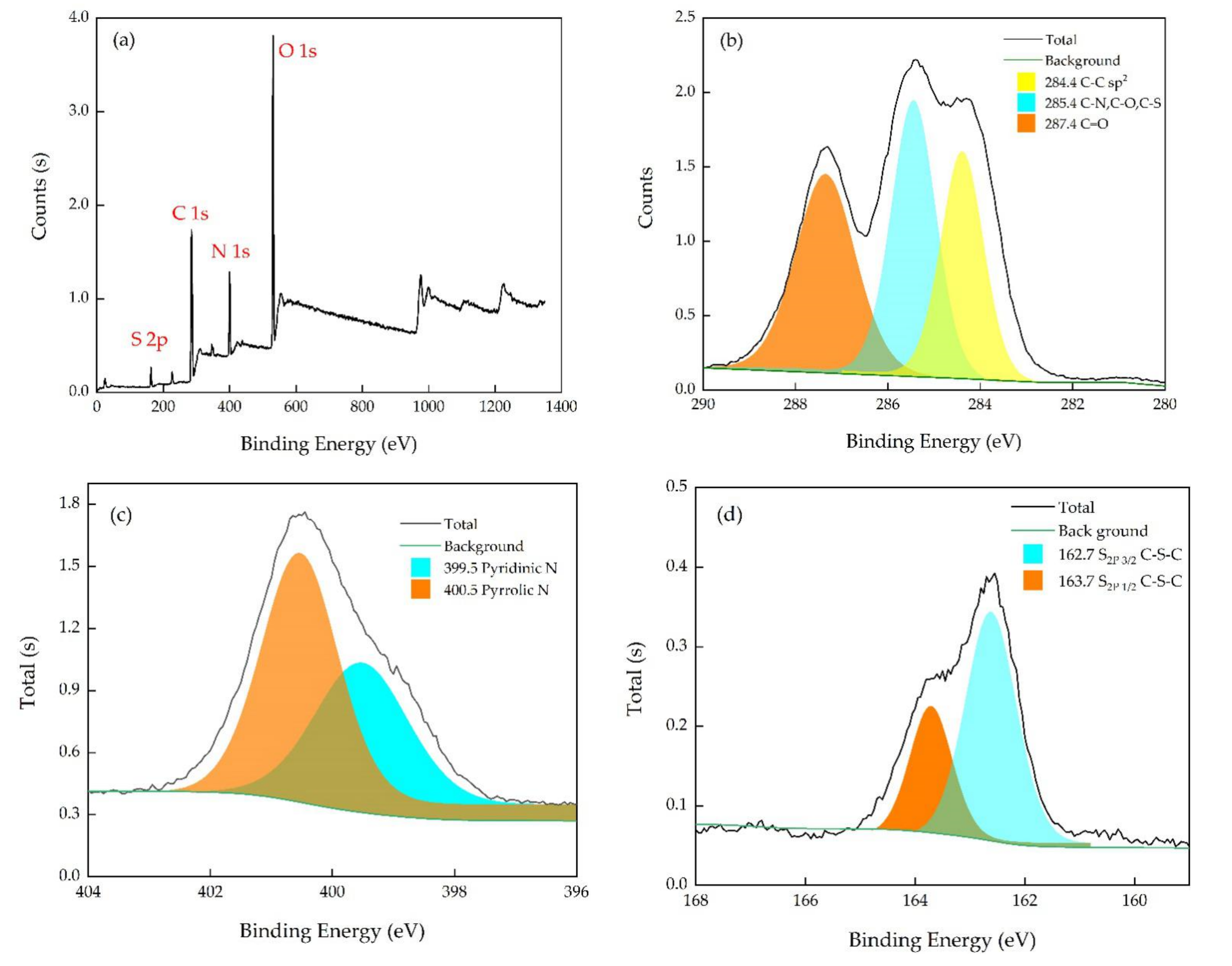
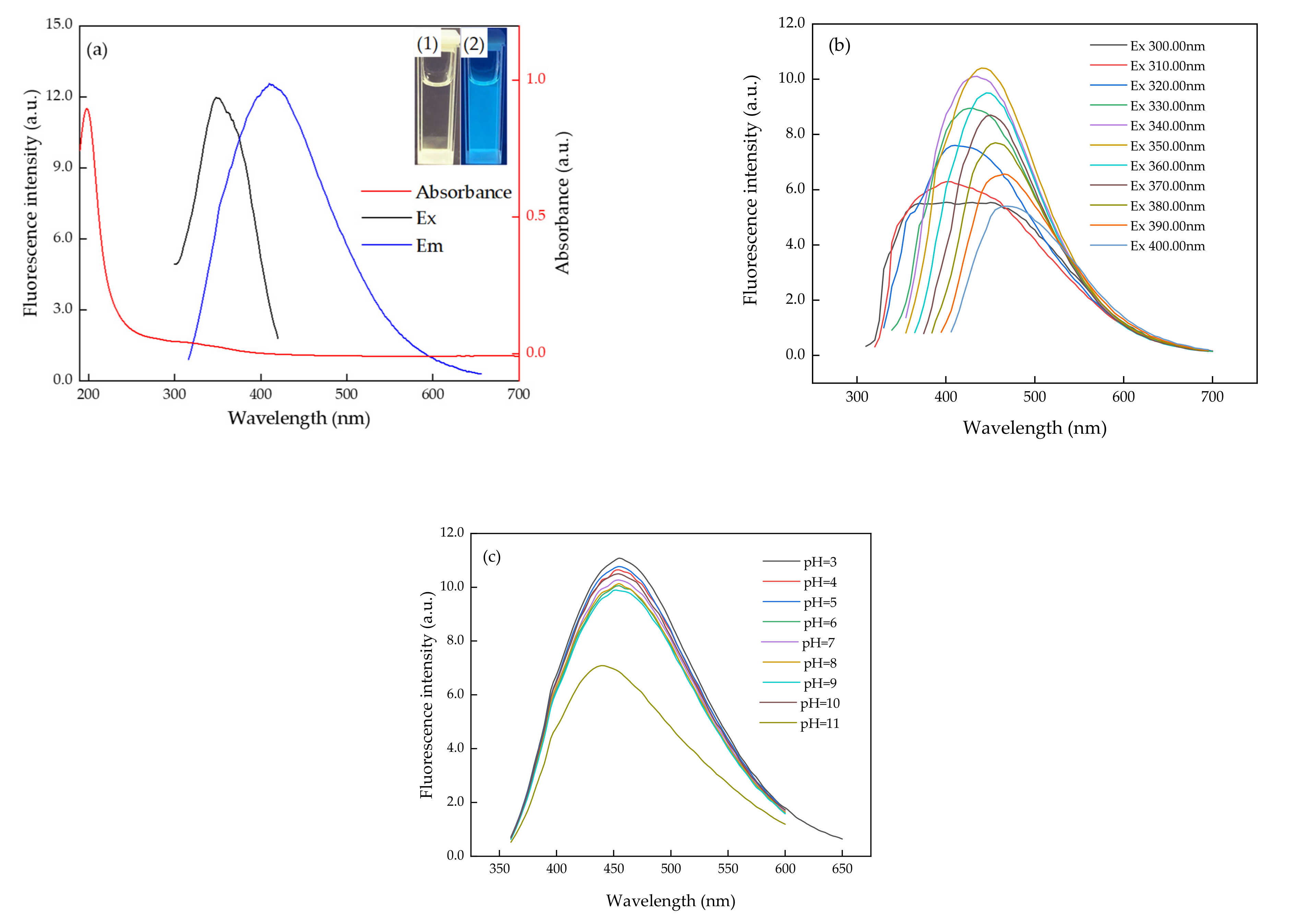
3.1. Characterization of Morphology and Optical Properties of N, S-CDs
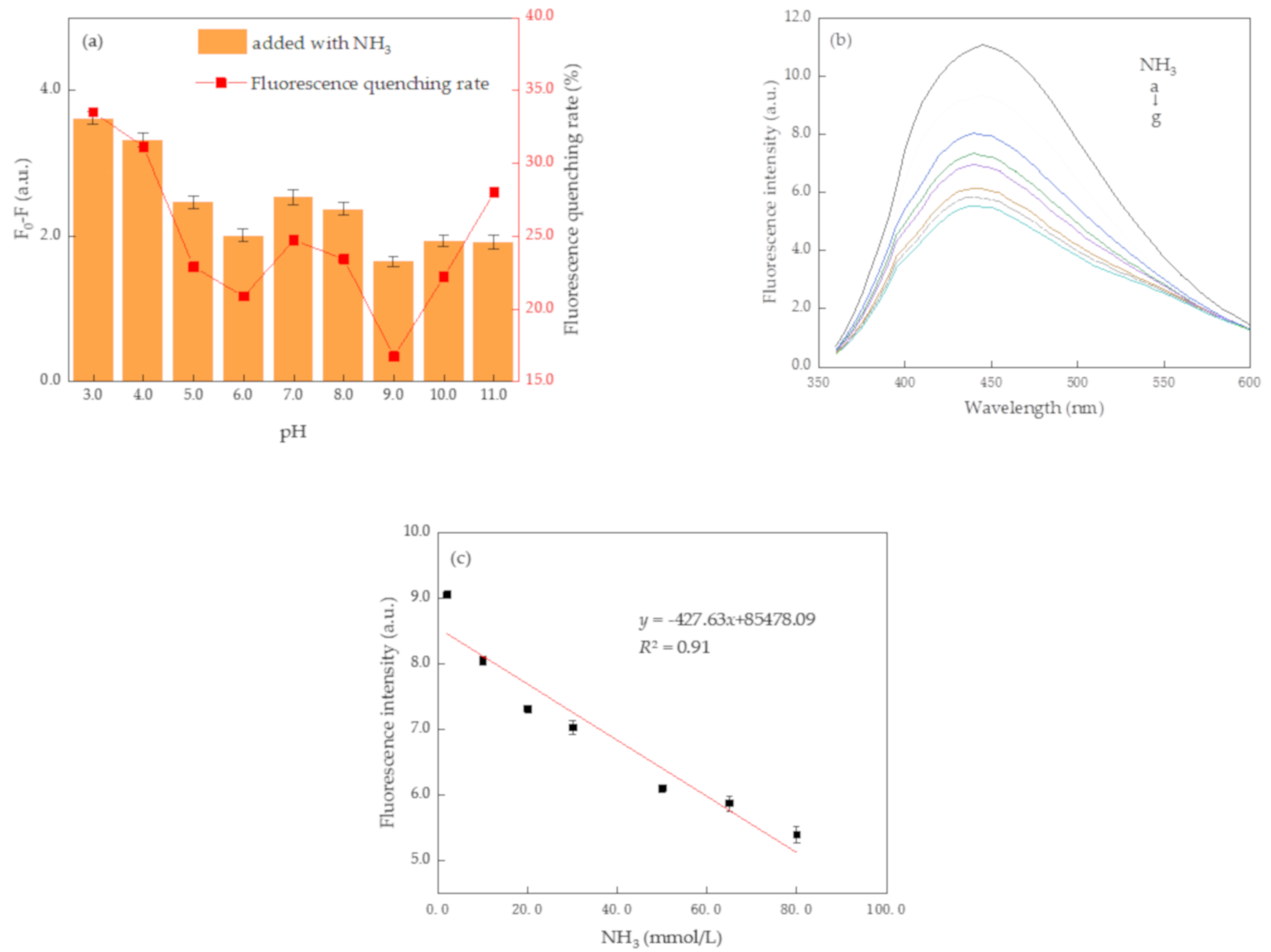
3.2. Detection of NH3 Based on N, S-CDs
3.3. Sensing Mechanism
3.4. Selectivity of N, S-CDs
3.5. Stability of N, S-CDs
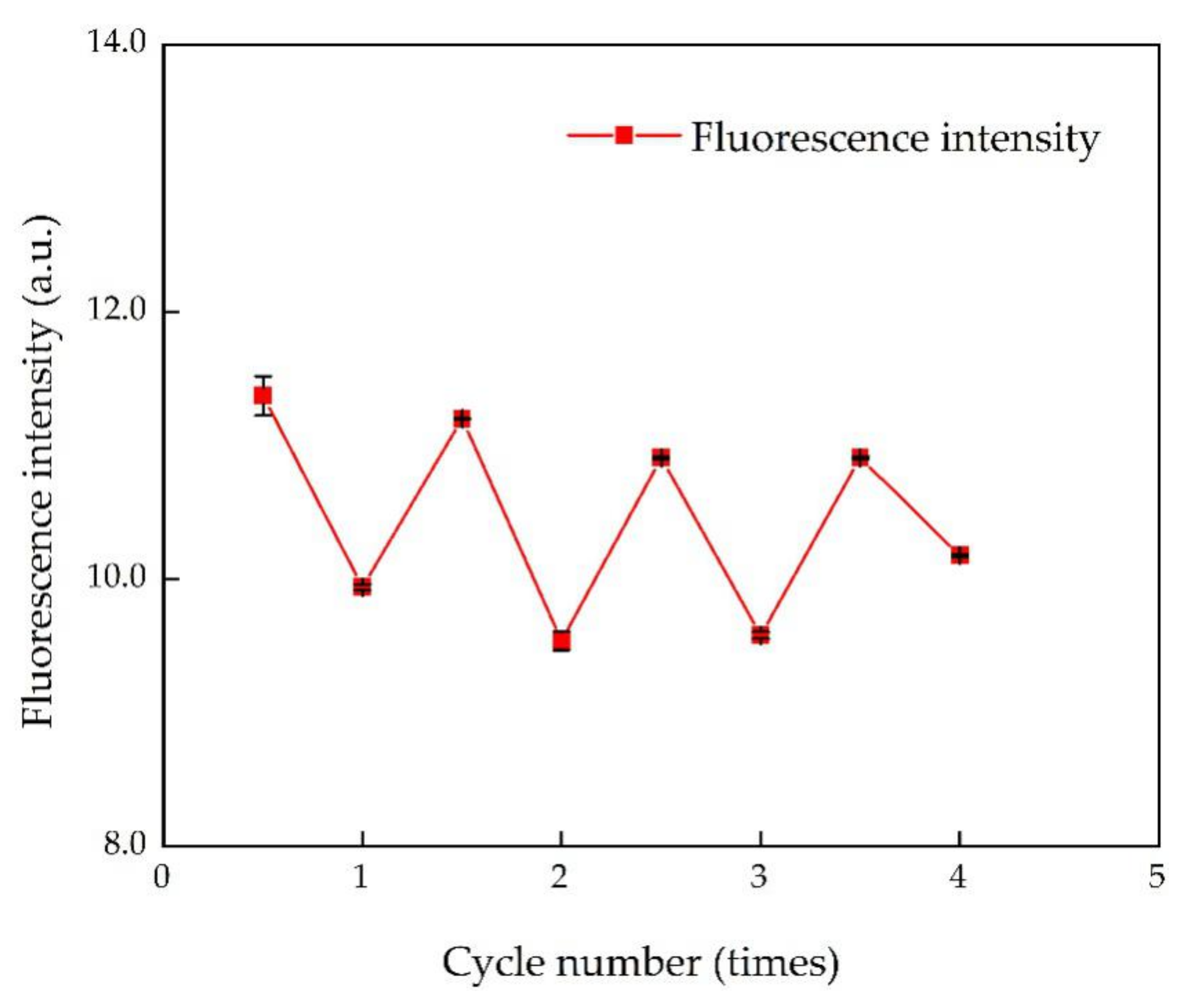
3.6. Reversibility of N, S-CDs
3.7. Applications in Real Water Samples and Fish Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timmer, B.; Olthuis, W.; Berg, A.V.D. Ammonia Sensors and Their Applications—A Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, F.B. Ammonia in Estuaries and Effects on Fish. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 67, 1495–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, Y.K.; Chew, S.F. Ammonia Production, Excretion, Toxicity, and Defense in Fish: A Review. Front. Physiol. 2010, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Lu, H.; Chang, Y.; Hsu, T. Evaluation of the Water Quality and Farming Growth Benefits of an Intelligence Aquaponics System. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.; Ling, B.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Variations in Water Flow and Quality in the Sanyang Wetland, China: Implications for Environmental Restoration. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkmeister, F.X.; Koide, T.; Nickel, B.A. Ammonia Sensing for Enzymatic Urea Detection Using Organic Field Effect Transistors and a Semipermeable Membrane. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, L.; Lu, B.; Dong, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, B.; Tang, X. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen Content in Duck Meat of Different Varieties Based on Calibration Maintenance and Transfer by Use of a Near-Infrared Spectrometric Model. Spectrosc. Lett. 2020, 53, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongrat, E.; Nuengnit, T.; Panyathip, R.; Chanlek, N.; Hongsith, N.; Choopun, S. Highly Selective Room Temperature Ammonia Sensors Based on ZnO Nanostructures Decorated with Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H. Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen in Natural Waters: Recent Advances and Applications. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Y.; Pan, Y. Toward Sensitive Determination of Ammonium in Field: A Novel Fluorescent Probe, 4,5-Dimethoxyphthalaldehyde Along with a Hand-Held Portable Laser Diode Fluorometer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 276, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, M.; Walcher, A.; Mayr, T.; Klimant, I.; Borisov, S.M. Trace Ammonia Sensors Based on Fluorescent Near-Infrared-Emitting Aza-Bodipy Dyes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.D.; Rhee, J.I. A Ratiometric Fluorescence Sensor for the Detection of Ammonia in Water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 190, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Jalili, R. A Molecularly Imprinted Dual-Emission Carbon Dot-Quantum Dot Mesoporous Hybrid for Ratiometric Determination of Anti-Inflammatory Drug Celecoxib. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Wenjing, L.; Lin, L.; Yuan, J.; Yifang, G.; Shaomin, S. Orange Luminescent Carbon Dots as Fluorescent Probe for Detection of Nitrite. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 47, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, C.; Qi, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. A Strong Blue Fluorescent Nanoprobe Based on Mg/N Co-Doped Carbon Dots Coupled with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Ultrasensitive and Highly Selective Detection of Tetracycline in Animal-Derived Foods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Mwakosya, A.W.; Guo, Z.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zou, X.; et al. Fluorescence and Colorimetric Dual-Mode Sensor for Visual Detection of Malathion in Cabbage Based on Carbon Quantum Dots and Gold Nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2021, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ni, G.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, W. Synthesis of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots and Its Application as Fluorescent Sensor for Hg2+. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2016, 36, 2846–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiga, M.; Cyriac, J. Fret Based Ammonia Sensor Using Carbon Dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Dong, J.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, S.G.; Geng, S.; Ling, Y.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. A Smartphone-Coalesced Nanoprobe for High Selective Ammonia Sensing Based on the pH-Responsive Biomass Carbon Nanodots and Headspace Single Drop Microextraction. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travlou, N.A.; Secor, J.; Bandosz, T.J. Highly Luminescent S-Doped Carbon Dots for the Selective Detection of Ammonia. Carbon 2017, 114, 544–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travlou, N.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Algarra, M.; Labella, A.M.; Rodriguez-Castellon, E.; Bandosz, T.J. S-and N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Surface Chemistry Dependent Antibacterial Activity. Carbon 2018, 135, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Shen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Ge, J. Facile Synthesis of Biomass Waste-Derived Fluorescent N, S, P Co-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Fe3+ Ions in Solutions and Living Cells. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xia, Y. Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-Doped Carbon Dots as Selective and Visual Sensors for Monitoring Cobalt Ions. Opt. Mater. 2021, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, Y. Preparation of N/S Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application in Nitrite Detection. Rsc Adv. 2021, 11, 10922–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, L.; Liang, G. Synthesis and Characterization of N and S Co-Doped Carbon Dots. J. Jiangsu Univ. 2018, 39, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Shen, H.; Luo, Y. Quality Predictive Models of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon Idellus) at Different Temperatures During Storage. Food Control 2011, 22, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Chen, B.B.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z. Carbon Dots: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism, Fluorescence Origin and Sensing Applications. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Pang, H.; Yang, H.B.; Guo, C.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Li, C.M.; Yu, T. Carbon-Based Dots Co-Doped with Nitrogen and Sulfur for High Quantum Yield and Excitation-Independent Emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, H.; Huang, J. Facile Ultrasonic Synthesized NH2-Carbon Quantum Dots for Ultrasensitive Co2+ Ion Detection and Cell Imaging. Talanta 2019, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, M.N. Site Selection for Aquaculture: Chemical Features of Water. In Proceedings of the ARAC, African Regional Aquaculture Centre, Port Harcourt, Nigeria, March 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Svobodová, Z.; Lloyd, R.; Máchová, J.; Vykusová, B. Water Quality and Fish Health; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Senapati, M.; Sahu, P.P. Onsite Fish Quality Monitoring Using Ultra-Sensitive Patch Electrode Capacitive Sensor at Room Temperature. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcicek, Z. The Effects of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) Oil Concentration on Liquid-Smoked Vacuum-Packed Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss Walbaum, 1792) Fillets During Chilled Storage. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Pandey, A.; Chakrabarti, P. Fabrication, Characterization, and Application of CuO Nano Wires as Electrode for Ammonia Sensing in Aqueous Environment Using Extended Gate-FET. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 5779–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Cui, Q.; He, D.; Zhao, C.; Suo, H. Fabricating a Self-Supported Electrode for Detecting Ammonia in Water Based on Electrodepositing Platinum-Polypyrrole on Ni Foam. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 027537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Holmes, M.; Zhang, W.; Zou, X. Titanium Dioxide-Polyaniline/Silk Fibroin Microfiber Sensor for Pork Freshness Evaluation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, S.; Lan, M.; Huang, J.; Song, X. Carbon Dots and a Cdte Quantum Dot Hybrid-Based Fluorometric Probe for Spermine Detection. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

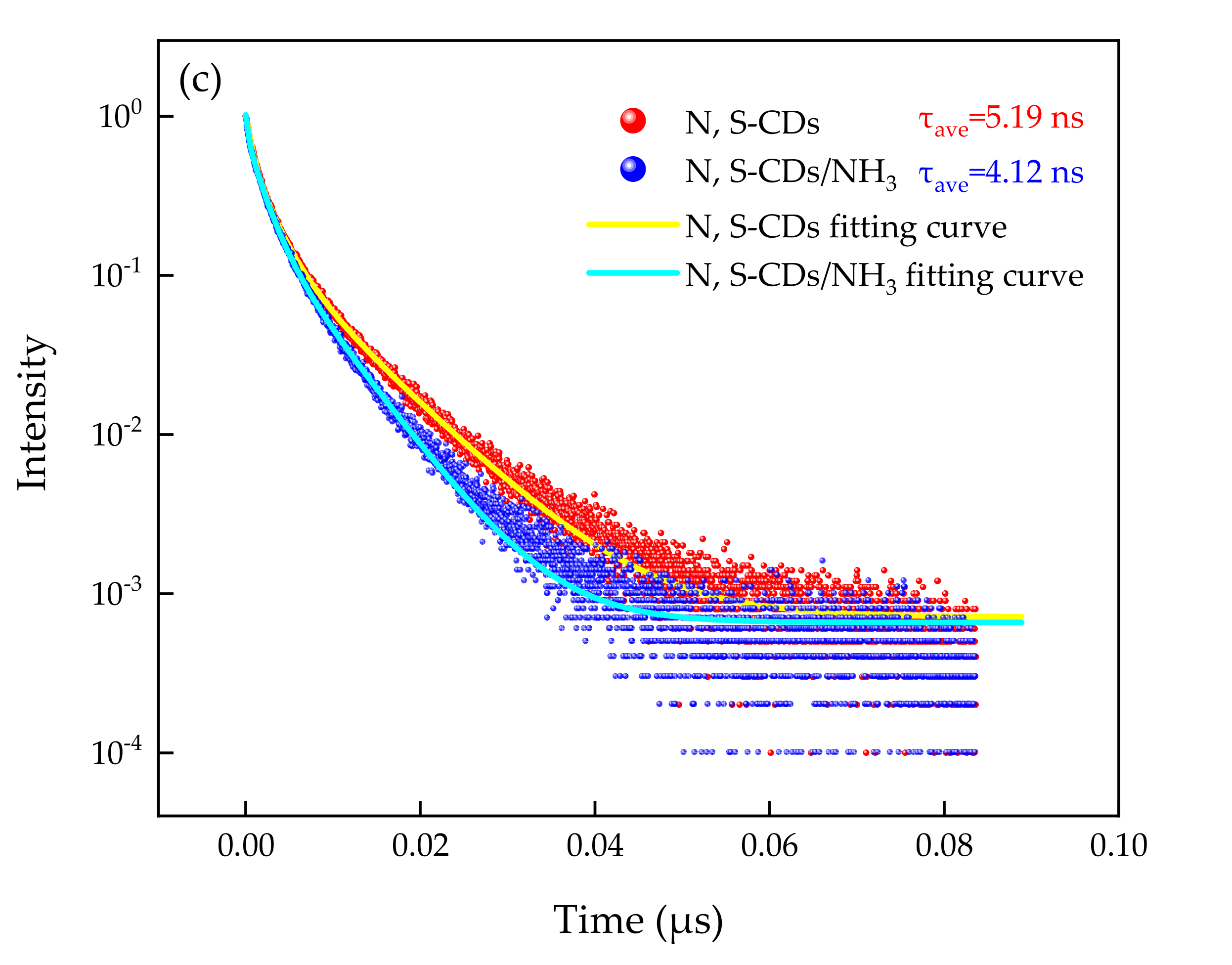



| System | τ1 (ns) | a1 | τ2 (ns) | a2 | τ3 (ns) | a3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N, S-CDs | 0.75 | 406.44 | 2.45 | 434.74 | 8.22 | 171.87 | 5.19 |
| N, S-CDs/NH3 | 0.32 | 257.20 | 1.84 | 534.97 | 5.98 | 229.06 | 4.12 |
| Added (mM) | Real Water Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aquaculture Water | RSD (%) | Recovery | River Water | RSD (%) | Recovery | |
| 0 | Not found | - | - | Not found | - | - |
| 20.00 | 25.20 | 17.13% | 1.18 | 26.94 | 13.23% | 1.27 |
| 30.00 | 37.62 | 8.12% | 1.20 | 40.16 | 3.98% | 1.29 |
| 50.00 | 50.74 | 7.29% | 0.98 | 49.39 | 1.64% | 0.96 |
| 65.00 | 63.00 | 10.20% | 0.95 | 61.92 | 5.00% | 0.93 |
| 80.00 | 78.87 | 4.46% | 0.97 | 77.84 | 0.54% | 0.95 |
| Methods | Materials | Linear Range | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode | CuO nanowire | NH3: 1.5–7.5 ppm | Aqueous Environment | [34] |
| Pt nanoparticles-polypyrrole/Ni foam | NH3: 0.5 μM to 400 μM | Water | [35] | |
| TiO2-PANI | NH3: 0–600 μg/L | Pork | [36] | |
| Ag–SnO2 sol-gel | Mixed gas of DMA, TMA, H2S, NH3: 0–2000 ppb | Tilapia/Ruohu | [32] | |
| Fluorescence | CDs | NH3: 0.5–50 mM | Tap water and river water | [19] |
| S-CDs | NH3: 0–800 ppm | -- | [20] | |
| CDs- Rhodizonate | NH3: 0–200 ppm | Industries gaseous phase | [18] | |
| CDs + CdTe QDs | Spermine: 0–1.0 μM | Pork | [37] | |
| N, S-CDs | NH3: 2–80 mmol/L | Aquaculture water, river water and bighead carps | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Shi, C.; Yang, X. A Fluorescence Method Based on N, S-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Ammonia in Aquaculture Water and Freshness of Fish. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158255
Zhang J, Xu Z, Shi C, Yang X. A Fluorescence Method Based on N, S-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Ammonia in Aquaculture Water and Freshness of Fish. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158255
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiaran, Zeyu Xu, Ce Shi, and Xinting Yang. 2021. "A Fluorescence Method Based on N, S-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Ammonia in Aquaculture Water and Freshness of Fish" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158255
APA StyleZhang, J., Xu, Z., Shi, C., & Yang, X. (2021). A Fluorescence Method Based on N, S-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Ammonia in Aquaculture Water and Freshness of Fish. Sustainability, 13(15), 8255. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158255






