Abstract
This study aims to explore whether wine CI (Collective Intelligence) platforms, such as Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast, can provide a wine rating effect on price, as Robert Parker’s does in the Korean wine market. To achieve the purpose of the study, we collected information with wine evaluation ratings and on-premise prices from three wine evaluation sites and seven restaurants in South Korea. The researchers calculated the Pearson’s rho between the wine evaluation ratings and on-premise prices based on country, region, vintage, and type of wine. Based on the results of the study, the CI of wine ratings shows statistically the same association degree to price as wine guru Robert Parker’s score. This study can academically extend the research of CI’s application in the wine industry and provide strong support for a sustainable e-business model and pricing tactics in the wine industry.
1. Introduction
One might say that one of the representative Collective Intelligences is Wikipedia. Collective Intelligence (CI) [1] is defined as a shared or group intelligence that emerges from collective efforts, collaboration, and competition of many individuals and appears in consensus decision-making [2]. The Collective Intelligence requires groups of individuals acting collectively in ways that seem intelligent [3]. According to the definition of CI, we can describe so many CI platforms around us, from offline decision-making methods, such as the traditional Delphi method, to online platforms, such as Procter + Gamble’s Connect and Develop, Salesforce.com’s IdeaStorm, Netflix’s contest, and open-source software. These examples show that CI has been utilized in various industries such as IT, stock market, mass communication, etc. [4,5,6].
Although CI platforms are well-documented in various industries, CI platforms in the wine industry have not been explored from the academic and field practitioners’ perspectives. This paper is focused on CI platforms in the wine industry. The authors insist that the CI concept can be witnessed in wine industries worldwide. According to the CI definition from Wikipedia, Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, Decanter.com and Vivino.com can be regarded as CI platforms in the wine industry.
Many researchers have reported that Collective Intelligence strongly contributes to the power shift from the individual person to the Collective Intelligence [7]. In the wine industry, some researchers report the role of Collective Intelligence concerning wine tourism [8], wine marketing [9,10], and wine trademark rights [11]. However, in the wine industry, traditionally and absolutely, many practitioners and academicians believed and reported that professional wine critics’ wine grades, namely Robert Parker’s wine scores, affect the market’s wine prices and consumers’ wine choices. Robert Parker’s ratings effect on price and customer purchase behaviors are well documented in this industry [12,13,14,15,16,17]. In this regard, in the wine industry, we cannot insist that Collective Intelligence has overpowered wine critics in respect to knowledge and power for wine evaluation and price effect.
Furthermore, academic and empirical research of the comparison between CI and wine critics in respect to wine evaluation performance toward market response has not accumulated. That is, reports of the effects of CI for wine evaluation on price in practice have been relatively rare [14]. Therefore, academicians should fill the gap by investigating CI’s effect and usefulness in wine industry.
In respect to business model, wine evaluation websites have the power as e-business platforms. Many practitioners in the wine industry have believed that wine reviews and evaluation grades, published through websites and wine books or magazines, exercise much power toward wine prices and customers’ purchase behaviors: good grades may cause prices to increase highly, while bad or low grades may leave wines practically unsalable unless their prices are adjusted downwards [12,13]. Therefore, most wine evaluation websites are operated as paid sites, providing wine quality ratings based on their influential power that are being used for selecting and purchasing wine by individual customers. That is, wine evaluation information as contents has been sold as a commodity for a fee. Information gathered in the form of CI becomes a model of e-business and a profit model and gets attention from practitioners and academicians.
The purpose of this study is to identify the general conditions for being accepted as a CI through a literature review, and to confirm that wine evaluation sites exist as CI platforms in the wine industry. Second, the researchers aim to explore whether wine CI platform such as Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast can provide wine rating effects on prices, as Robert Parker’s rating does. The researchers explore the difference in the correlation between price and wine ratings from two sources: other wine CI platforms vs. Robert Parker. Based on the results of the study, the researchers can report whether the CI on wine evaluation has a relationship to on-premise prices in the wine market or not. Furthermore, the researchers can report whether the CI on wine ratings can relate to price more accurate than Robert Parker’s score or not. Consequently, the researchers can not only academically accumulate research on CI’s application to the wine industry, but also practically provide extended information about the evaluation of wine price as a sustainable e-business model.
In terms of marketing tactics, if the correlation between the wine quality evaluation by the CI and price is strong, it is an opportunity to increase profits on the seller’s side. This is because retailers can set a retail price that is corresponding to quality. On the other hand, on the buyer’s side, the association information between two variables can be used as a wine selection criterion. This is because purchasers can check out whether the price is equal to the quality of the wine.
Especially, Simon and Fassnacht [18] suggest a taxonomy of a pricing study from interdisciplinary perspectives. They categorize a pricing study into three approaches: rationality assumptions of classical economics, behavioral economics with a qualitative approach, and marketing science with a quantitative/methodology-based approach. Among these approaches, the behavioral economics approach calls the rationality assumption into question. Perspectives from behavioral economics give opportunities to explore the new research themes with the psychology of price and process-related or organizational aspects of price decision-making within a company. As one of the variables of behavioral science of pricing, the wine critics’ subjective quality rating outside of the wine-seller side is being used in this paper as a determinant of price setting inside wine sellers. As a result, the study of the relationship between wine critics’ subjective quality rating and price will be a comprehensive empirical contribution for wine industry-specific behavioral economic approaches in pricing studies academically.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Online Wine Quality Evaluation Providers
Wines satisfy the criteria of commodities consumed as foods or beverages, but, at the same time, they are also categorized as a product in a highly specialized professional territory. That is why there are professional information providers of wine evaluation results and reviews.
This section provides a comprehensive review of some of the world’s leading wine quality information-providing websites: Robertparker.com, Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, Decanter.com and Vivino.com.
Robert Parker, U.S. wine critic, started his own wine-related business in 1978 by releasing his first offline wine review, Wine Advocate, and started an e-business by introducing an online version of his magazine, Robertparker.com, in 2000 (Figure 1). In 2001, he teamed up with wine experts to make better and more effective collective information and evaluation reports on wines. His wine evaluation system employs a 50–100 point quality scale, well-known as Parker Points; this is influential in worldwide wine buying and is therefore a major factor in setting the prices for newly released Bordeaux wines especially. This made him the most widely known and influential wine critic in the world [19].
Figure 1.
Homepage of Robertparker.com.
Although he retired in 2019 and the number of Robertparker.com’s wine reviewers is currently 10 [20], Parker’s wine evaluation system is still so famous and well-known that it is based on the individual professional’s wine-related intelligence [19]. With his name on the domain, Robertparker.com introduces the method of his (now his team’s) wine quality evaluation: single-blind conditions (meaning that the same types of wines are tasted against each other and the producers’ names are not known). The ratings reflect an independent and critical look at the wines. Neither price nor the reputation of the producer/grower affects the rating in any manner [20].
Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, and Decanter.com are other wine information providing websites with wine expert panels’ wine ratings. They have also transferred their contents from offline magazines to online websites. Vivino.com is a wine review website where the reviews are reported, collected, and distributed by public individuals.
Wine Spectator, known as a lifestyle magazine that focuses on wine and wine culture, contains from 400 to more than 1000 wine reviews from professional editors with their tasting notes and drink recommendations for each issue, which consist of wine ratings based on a 50–100 scale and tasting notes (Figure 2). It was founded as a San Diego-based tabloid newspaper in 1976 and it was ranked by the Luxury Institute as the #1 business and consumer publication among wealthy readers in 2008 [21].
Figure 2.
Homepage of WineSpectator.com.
The number of Wine Spectator’s senior wine tasters is 11, and with their tasting results, Wine Spectator reports the reviews of more than 15,000 wines each year in blind tastings with strict standards relying on the proven ability and experience of editors as tasters and critics. Its online site reaches more than 3 million readers worldwide. Under its 100-point scale standard, wines, reviewed from the bottle in blind tastings, are given a single score. A score given as a range (e.g., 90–94) indicates a preliminary score, usually based on a barrel tasting of an unfinished wine [22].
Wine Enthusiast Magazine was first published in 1988 as a guide to the latest wine trends, ratings and reviews, food and travel, award-winning commentary, and more. It was conceived and executed by a team of editors based in New York, California, Washington, France, England, and Italy (Figure 3). This website insists that while each editor offers a unique set of expertise, personality, and perspective to the Wine Enthusiast team, the editors are all united by one mission: to taste, enjoy, and communicate their love of the best wines, spirits, and food in the world to readers in a fresh and accessible way [23]. They do not focus on wine only. Wine Enthusiast’s aim is to provide consumers with information on the world of wine and spirits, review hundreds of wines each month, and provide comprehensive coverage of wine and lifestyle topics peripheral to wine, such as entertainment, travel, restaurants, and notable sommeliers. The Wine Enthusiast is published 14 times a year. It is known that there are over 800,000 readers worldwide [24].
Figure 3.
Homepage of WineEnthusiast.com.
Decanter is a wine and wine-lifestyle magazine, published in about 90 countries on a monthly basis. The magazine includes industry news, vintage guides, and wine and spirits recommendations (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Homepage of Decanter.com.
Following the success of wine columns in British newspapers, the magazine was founded in London in 1975 [25]. It is the oldest consumer wine publication in the United Kingdom. As of 2011, it was published in 91 countries, including China as its last addition in 2005. Columnists and regular contributors include several Masters of Wine. The magazine mainly focuses on wines available in the United Kingdom’s market. While it is aimed at consumers, a significant part of its audience also consists of both traders and producers [26]. Additionally, three experts in their field review chosen flights of wines through Decanter.com’s famous panel tastings. Its content includes news, topical dissertations, travel surveys, interviews, analysis, and market reports [27]. Differently to other magazines, which focus on many wines from various regions and countries, Decanter.com issues offer in-depth reviews of wines from two regions at a time [25].
The magazine launched its website, Decanter.com, in 1999. The website is considered as a leading online wine magazine [28]. Among its services, it offers a wine investment guide in conjunction with Berry Bros. & Rudd [29]. Its subscribers are generally younger than those of similar publications, with 41% of readers being under 45 years old [28]. With its professional wine-related assets, Decanter founded a famous wine competition, the World Wine Awards (DWWA), in 2004. It is known as the world’s biggest wine competition with over 15,000 entries per year. The results of the competition are published on Decanter.com and its magazine in the August edition [26].
Vivino.com is an online wine community, database, and mobile application where users can buy, rate, and review wines (Figure 5). Vivino was founded in 2010 by Heini Zachariassen and Theis Sondergaard who knew very little about wine and used that ignorance in the development of an smart phone application for ordinary people. As of 2018, vivino.com had a wine database containing over 9 million different wines, and had 31 million users [30]. In July 2013, the database had 1 million wines [31], and in December 2018, the database has 10 million wines, 37.5 million wine reviews, and 33.9 million users. Vivino.com’s headquarter is in Copenhagen, Denmark, but the company also has offices in the USA, Ireland, Ukraine, and India [30].
Figure 5.
One of the webpages of vivino.com.
2.2. CI as Online Wine Quality Evaluation Providers
One of the elements of CI, the opinion leader’s review, influences the consumer purchasing process [32]. Are the wine quality information-providing websites CI? Researchers have been investigating the characteristics or conditions of CI from various perspectives: mass collaboration, the information quality guarantee, how to improve the decision-making of CI, and how to avoid the biases from the decision-making of individual human beings.
First, some researchers focus on mass collaboration as a condition for CI. Tapscott and Williams required four conditions for a CI platform: openness, peering, sharing, and acting globally [33]. Investigating the above conditions, we believe that all of the wine evaluation sites we have explored satisfied CI conditions in Tapscott and Williams’s perspectives.
Second, Lichtenstein and Parker [34] insisted that researchers generally agree that the core information quality criteria for an information resource comprise as CI [34,35,36,37]. They summarized seven conditions from several studies: purpose, authority, accuracy, objectivity, currency, coverage, and accessibility. These criteria can be used to judge that a wine evaluation site can be a CI platform and an information quality guarantee. With the above conditions, we could not agree that Vivino.com has authority because it provides wine ratings from ordinary people’s reviews.
Third, Collective Intelligence has been regarded as a tool to avoid the biases from the decision-making of an individual person. Bonabeau [38] described how to mitigate the biases through the use of three Collective Intelligence approaches: outreach, additive aggregation, and self-organization. Outreach is defined as people or groups who traditionally were not included in the company’s decision-making process. Additive aggregation means organizations that can collect information from myriad sources and then perform some kind of averaging. Self-organization is defined as mechanisms among group members which can result in the whole being more than the sum of its parts [4,38].
With the above conditions, it can be said that the wine evaluation sites follow the future direction of CI in terms of efforts to increase the number of evaluation professionals, or to expand the professional and reliable ability to rate the wine. In conclusion, Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast and Decanter.com, of the wine evaluation sites that were mentioned above, seem to have the requirements of a CI platform.
2.3. Profit Model as E-Business in Wine CI
What kind of profit models do wine information sites have? E-commerce, a system of selling wine itself online, rather than selling the contents of wine appraisal information provisions for a fee, is attracting attention in the academic field. Some studies recently explore the key success factors for wine e-commerce, such as time delays and spatial arrangements. [39] Some studies focus on the consumer behavior in wine purchasing situations [40].
However, fundamentally, evaluation information on wine sites is being sold as paid content. This indicates that wine evaluation is a source of revenue for the information providers. In addition, the wine information evaluation site features an e-business through various profit models, such as selling wine and beverage related items, including wine accessories, importer connections and advertising, holding wine events, and so on.
Robertparker.com, Wine Spectator.com, Wine Enthusiast.com, and Decanter.com have used “Freemium” pricing. Simon coined Freemium from free memberships including special paid services [41]. For example, on Robertparker.com, the reader can access more than 300,000 professional tasting notes, Wine Journal, Hedonist’s Gazette’s restaurant reviews, and direct chat with reviewers via the Bulletin Board with a free membership. However, if anyone pays 99 US dollars, he/she can gain access to a matter of tasting events worldwide, global benefits, the Robert Parker mobile app, RP Cellar access, trade directory, and vintage charts. Further, in the case of Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast, subscribers can receive a predetermined amount of magazine issues based on the subscription price paid. Therefore, the researchers can regard Wine Spectator, Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, and Decanter.com as e-business companies with a profit model in CI.
2.4. Correlation between Quality Evaluation and Price
The study of the relationship between Collective Intelligence and price can be roughly classified into two types. Traditionally, there are studies examining the relationship between quality and price, and the relationship between Collective Intelligence and price.
Kwak et al. [14] categorized the research papers regarding the price–quality relationship into six types, as shown in Table 1. Table 1 shows the classification of price–quality relationship, mainly focusing on the wine industry [14]. At the first stage, they categorized studies based on the degree of objectivity of the information quality: subjective quality and objective quality. At the second stage, the researchers used the criterion: the subject of the quality evaluation.

Table 1.
Classification of Price–Quality Ratings and Rating Unit [14,15].
Table 1 shows that the websites of Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, Decanter, and Vivino have different positions. Kwak et al. [14] categorized Robert Parker’s points as subjective with experts/individual quadrant, which is traditionally accepted in the wine industry, especially in the Korean market, because the Parker Point is known as Robert Parker’s individual standard based on his professional and critical intelligence of wine. Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast and Decanter.com, which are considered as CI platforms in this study, are categorized as subjective quality evaluations performed by groups of expert panels. On the other hand, vivino.com is located at the subjective quality with rating performed by public people/individual quadrant [14,15].
There are very few studies or research papers that focus on the relationship between Collective Intelligence and price in e-business. Keber and Schuster [42] suggested a method to find out the power of Collective Intelligence toward price. They applied a method of finding the k-mean of existing statistics for plurality of observations. On the other hand, Kim et al. [43] conducted research on the price of online games set by Collective Intelligence in the Korean MMORPG game market.
The researchers of this study found that the studies on price and Collective Intelligence are conducted in a specific industry, the game industry, only. Therefore, there is room to expand the scope of research on Collective Intelligence in various industries.
2.5. Wine Evaluation and Price
For a long time, it has been studied that wine professional Robert Parker’s ratings affect market prices. The prices used in these studies are En Primeur price and on-premise wine prices. Practically, retail prices in the wine industry can be accessed from three sources: En Primeur wine price, on-premise wine prices, and off-premise wine prices. En Primeur wine price is the prices set by Bordeaux chateaux owners just 6 or 7 months after the grape harvest, i.e., when the wines are still very young and not yet bottled [13]. On-premise wine price is the list price of on-premise outlets, such as restaurants, bars, and cafés where wines are served opened. Offline wine price is the price list on retail stores where wines are sold unopened.
Ali et al. [13] estimated the effect of Parker’s points on En Primeur market prices for 233 Bordeaux wines in 2003. Hay [12] has reported the impact of Parker’s points on the process of price formation through a comparison of the 2005 and 2008 En Primeur campaigns. Nam and Kwak [15] and Nam et al. [16] investigated whether Parker’s points affect the on-premise wine prices in Korea based on the region and vintage of wine production. Thus, the study on any possible relationship between Robert Parker’s points and off-premise wine prices remains undone from academicians’ perspectives.
Studies examining the effect of quality evaluation on price without Robert Parker’s wine evaluation have not been accumulated enough so far. Horowitz and Lockshin [44] investigate the effect of price on quality evaluation in wine. The paper uses the wine-quality ratings devised by James Halliday in Australia and New Zealand Wine Companion 2000 as the dependent variable in a regression-based analysis. This study covers only New Zealand and Australia geometrically. This study looks at the case where price is used as an indicator of quality. Price is the leading variable and quality is the lagging variable. Oczkowski, E., Doucouliagos, H. [45] examines the empirical support for the hypothesized hedonic theoretical relation between the price of wine and its quality. This study points out the inconsistency of expert tasters when evaluating wines.
There are also studies that investigated the relationship between price and quality by objective, rather than subjective, evaluation processes. Zeleny’s wine quality study [46] only examines the wines from the Czech Republic evaluated during the first round of the Prague Wine Trophy 2015 competition. Zeleny [46] reports many different correlation coefficients between the price and quality according to vintage and type.
Additionally, study on wine quality information-providing websites that are considered as CI platforms is relatively rare. Kwak et al. (2012) studied the effects of Wine Spectator’s ratings and Parker’s points on the on-premise wine market in Korea depending on wine type, vintage, country-of-origin, and region-of-origin [14]. However, Kwak et al. (2012) did not compare the predictability of scores from two rating sources statistically. Therefore, research on the relationship between Collective Intelligence and price remains a blank in terms of En Primeur wine prices and off-premise wine prices. Additionally, it can be said that the relative comparison of the powers of Parker’s points and the online CI providers toward prices remains blank.
According to the results of literature review, it was found that several variables act as moderators in the relationship between wine quality evaluation and price: evaluation subject, such as CI or individual, country-of-origin, region-of-origin, vintage, and wine type (Figure 6).
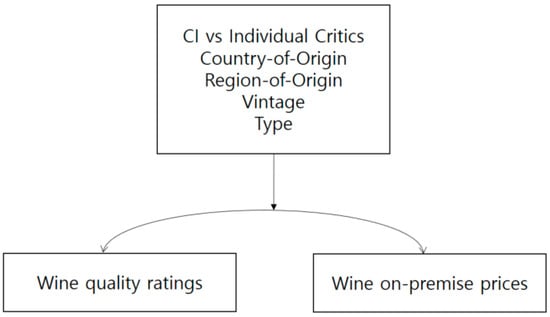
Figure 6.
A model between wine quality ratings and on-premise prices.
2.6. Pricing Study in Economics and Marketing
Let us discuss where the research in this paper belongs in the field of price research and how the papers contribute to pricing research. Absolutely, price is an important topic in economics and marketing. Price is viewed differently depending upon the approach. As mentioned at introduction, Simon and Fassnacht [18] suggest a taxonomy of pricing using economic and marketing classifications. Because the purpose of the proposed study is to explore the relationship between the quality evaluation and price, behavioral economics with a qualitative-based approach will be employed.
Furthermore, Yoo [47] reviews the historical development of pricing research in marketing in Europe and the United States. According to Yoo’s classification, pricing issues can be divided into three areas: normative, descriptive, and behavioral. Researchers utilizing the normative approach have dealt with the setting and measurement issue of price. Descriptive studies have investigated the process of determining price, while behavioral studies have explored the psychological issues associated with price. Based on Yoo’s classification scheme, the current study utilizes a behavioral approach as a price association with a subjective quality evaluation. Additionally, because the process of price determination often incorporates psychological aspects of pricing, such as price as an indicator of quality, the researcher expects to explore various behavioral characteristics of price in this study. Conclusively, by Simon and Fassnacht [18] and Yoo’s [47] classification, this study utilizes both the behavioral approach in pricing and contributes to expanding the understanding of the process of pricing in the wine industry.
2.7. Research Questions
Previous studies have reported that wine prices correlate with their quality. However, it is different in terms of quality assessment. In other words, wine quality mainly used ratings in competitions [46], ratings of consumer surveys [45], and ratings of a specific institute [44]. Then, what is the impact of CI evaluation?
The researchers of this study aimed to explore whether wine CI platforms, such as the websites of Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast, can have any effect of the wine rating on price as Robert Parker’s ratings does. The researchers set the standard of data sampling for a comparison between CI and individual wine quality evaluation websites.
We select CI information for wine evaluation and price based on country-of-origin (COO), region-of-origin (ROO), vintage, and type of wine color. The researchers of this study developed research questions based on these criteria. The Country-of-Origin Effect (COE), also known as the made-in image and the nationality bias, is a psychological effect describing how consumers’ attitudes, perceptions, and purchasing decisions are influenced by products’ country of origin labeling. Region-of-Origin (ROO) is a psychological effect describing how consumers’ attitudes, perceptions and purchasing decisions are influenced by products’ region of origin labeling [48].
For example, one can perceive the difference in preference or quality among wines from Bordeaux in France, Bourgogne in France, and Piemonte in Italy. Therefore, according to Region-of-Origin, the wine qualities will be evaluated differently by a reviewer. Furthermore, the same wine label will be evaluated differently by harvest year, that is, vintage. Finally, at the same country, region, and vintage, the wine ratings differ depending on the type of wine: white wine, red wine, and/or sparkling wine. Therefore, Research Questions 1 and 2 were developed based on COO, ROO, vintage, and type of wine.
[Research Question 1]: Are there differences in correlation among the on-premise prices in the Korean market and the wine quality ratings of Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, and Wine Enthusiast regardless of country, region, vintage and type of wine?
Robert Parker is traditionally known for his excellent reputation for French wine evaluation. If you compare the evaluation conducted by CI with Robert Parker’s evaluation of French wine, what would the result be? This was developed as Research Question 2.
[Research Question 2]: Are there differences in the correlation between the on-premise prices of French wines in the Korean market and the wine quality ratings of Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, and Wine Enthusiast?
On the other hand, the type of wine can be a benchmark for comparing the performance of CI and Robert Parker. To check this, the researchers of this study investigated whether there is a difference in the correlation between price and wine quality ratings of CI platforms and of Robert Parker, specifically on the French red wines that have traditionally been evaluated by Robert Parker.
[Research Question 3]: Are there differences in the correlation between the on-premise prices of French red wines the in Korean market and the wine quality ratings of Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, and Wine Enthusiast?
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Data Source
In the literature review, researchers of this study found four wine quality evaluation sites as potential CI platforms: Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, Decanter.com and Vivino.com. Among them, Vivino.com was eliminated, as its rating scores are made by people including personal wine lovers, rather than identified professionals. Therefore, in this study, the websites of Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, and Decanter are defined as CI platforms of wine-related e-businesses. Among them, the wine quality rating data from the websites of Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast were selected for analysis for this study.
The ratings for wine quality of individual experts are collected from Robert Parker’s online site, www.Robertparker.com. The year the data set was collected is 2017, when Parker represents all the professional wine evaluations and content. Although the number of Robertparker.com’s wine reviewers was 10 at that time [20], its rating score was still regarded as an individual professional’s evaluation in the Korean market because Parker’s wine evaluation system has been well-known for being based on the individual professional’s wine-related intelligence [19]. In the case of Wine Spectator and Wine Enthusiast, because multiple wine ratings on a given item by vintage exist, the researchers used mode instead of an average for the wine ratings for a given wine item by vintage.
The dataset for the on-premise price in the Korean market is collected from two sources of information: on-premise prices of 6 hotel restaurants with a five-star grade, and 1 wine restaurant located in Seoul, South Korea. This study focuses on on-premise prices because the En Primeur price is only centered on Bordeaux wine.
3.2. Sample, Variables, and Methodology
Data samples for this study were collected from 7 restaurants’ wine lists that include 2,430 items of wines in 2017. This is the raw wine data for analysis for the research. We needed the wine ratings and on-premise price data. On 7 restaurants’ wine lists, we found the on-premise price for each wine. For the research, at a given vintage, country, region, and type of wine, if 3 observations were found at each site, the researchers included the wine as a sample. For example, if a particular restaurant had three or more wines on the wine list for 2000 Bordeaux red wines, it was sampled. If less than two wines were listed, they were removed from the sample. Further, we collected the price data on the wine list and searched the quality evaluation score from the three wine evaluation sources. Then, the researchers calculated the Pearson’s rho between the wine quality ratings and prices from the site. Table 2 shows the dataset for research 1.

Table 2.
The Number of rho for Research Question 1 from Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, and Wine Enthusiast.
We explored the relationship between the wine quality evaluation and on-premise price using a correlation coefficient because of the opposite arguments between two variables regarding time lag. Practically, Parker’s evaluation is usually reported worldwide prior to on-premise pricing. However, the price for wine is set before CI evaluation in the case of Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast, Decanter.com, and Vivino.com, or sometimes vice versa. Therefore, the researchers could not distinguish the causal effect between the two variables. Most wine studies with a quality evaluation with price information have used the correlation analysis to investigate the phenomenon. [12,13,14,15,16]
The number of rho from Robert Parker’s point and the on-premise prices of wines with vintage 1975 to 2008 is 93 from 8 countries, 23 regions, and 4 types of wine.
The number of rho observed between Wine Spectator and the on-premise prices of wines with vintage 1975 to 2008 is 113 from 9 countries, 27 regions, and 4 types of wine. Wine Spectator shows a more broad rating coverage on wine standards. However, Wine Enthusiast shows 64 rho observations from 7 countries, 13 regions, and only 2 types of wine (Table 3).

Table 3.
The Collected rho for Type of Wine from Robert Parker.com, Wine Spectator, Wine Enthusiast for Research Question 1.
For research question 2, the researchers of this study identified new dataset from Robert Parker’s point and Wine Spectator’s ratings. Wine Enthusiast’s wine quality ratings were eliminated because of its very few rho observations.
Based on the given vintage and type, when a given region has more than 5 wine items from the wine lists of the seven restaurants, the region and vintage combination were selected as a subject of this study. Of the 2430 wine ratings from the three wine quality evaluation sources, 1380 wine items with the Parker’s point were found. Among these 1380 wine items, 950 wine times with Wine Spectator’s ratings were found. Among these 950 wine items, only 574 wine items were selected by Region-of-Origin (ROO) and vintage criteria. There were 17 vintages from 1995 to 2008 of French wines from Bordeaux, Bourgogne, and Rhone selected. Ten vintages of Italian wines from Piemonte and Tuscany were selected. Nine vintages of American wines from California were collected as samples for this study. Thus, total observations are 36 vintages by regions, respectively, from the wine quality ratings of Robert Parker and Wine Spectator. Table 4 shows the description of the dataset for the research question 2. The Bordeaux wine has 12 observations among a total of 36 data samples.

Table 4.
The Description of the Dataset for Research Question 2.
For research question 3, the researchers of this study narrowed down the dataset of research 1.
The number of rho from Robert Parker’s point and the on-premise price with the vintages from 1975 to 2008 of French wines is 39. In the case of Wine Spectator, the number of rho of French wines is 44. Wine Enthusiast shows 31 rho observations in French wines (Table 5).

Table 5.
The Description of the Dataset for Research Question 3.
For research question 3, only red wine, the researchers of this study narrowed down the dataset of research 3 to the French red wine.
The number of rho from Robert Parker’s point and the on-premise price of the vintages from 1975 to 2008 of French red wines is 31. In the case of Wine Spectator, the number of rho from French red wines is 32. The number of rho from the Wine Enthusiast rating and the on-premise price of the given vintages of French red wines is 24 (Table 6).

Table 6.
The Description of the Dataset for Research Question 3: only red wine.
4. Results
4.1. The Comparison in Rho among Three Online Wine Quality Evaluation Providers
Research Question 1 is to explore the differences in correlation among the Parker’s points, Wine Spectator’s wine ratings, and Wine Enthusiast’s wine ratings and on-premise prices, regardless of country, region, vintage, and type of wine. ANOVA was conducted to investigate the average difference in Pearson’s rho among three wine quality evaluation providers: Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, and Wine Enthusiast. Table 7 shows the descriptive results for the average comparison for the rho. The results show that the average rho has a significant difference among the three sources (F = 9.141, p = 0.001).

Table 7.
The Result of AVOVA in rho from Three Sources for Research Question 1.
The result of the Scheffe test shows that the correlation coefficients between Robert Parker and Wine Spectator has a similar average statistically; however, the rho from Wine Enthusiast shows a low number in comparison to Robert Parker and Wine Spectator, statistically (Table 8).

Table 8.
The Results of the Scheffe Test for Post-Comparison for Research Question 1.
That is, the correlation between Robert Parker’s points and price has no statistically significant difference of rho between Wine Spectator’s wine quality ratings and price. This demonstrates that the effect of the CI’s wine quality evaluation on price is equivalent to the quality evaluation of individual wine professionals. However, one of the CIs, Wine Enthusiast, does not show its effect on the price as much as Robert Parker, which reports that Wine Enthusiast’s wine quality ratings do not have an effect on price as much as the individual wine professional’s rating.
The correlation coefficients between the prices and wine quality ratings of Robert Parker and Wine Spectator show the similar min, max, means, and standard deviations at a glance (Table 9).

Table 9.
The Descriptive Result of Correlation Coefficients between Ratings of Wine Spectator and Robert Parker and Prices for Research Question 2.
A t-test was conducted to investigate the difference in the Pearson’s rho average between Wine Spectator and Robert Parker’s wine quality ratings. The result shows that the difference in the Pearson’s rho mean between two groups is not found statistically and significantly at a 99% confidence interval (p = 0.348) (Table 10).

Table 10.
The t-test in Pearson’s rho between Wine Spectator and Robert Parker’s Wine Ratings.
This result shows that the correlation between Robert Parker’s wine quality rating and price is not statistically different from the correlation between Wine Spectator’s wine quality rating and price. This demonstrates that the CI platform has a power of evaluation that statistically affects the price in the market as much as an individual wine professional does.
4.2. The Comparison in Rho in French Wine
Research question 2 is to empirically explore the differences in correlation among the on-premise prices and Parker’s points, Wine Spectator’s wine ratings, and Wine Enthusiast’s wine ratings on French wines. The dataset for the research Question 1 has the rho from nine countries. As Figure 7 shows, three sources of wine quality ratings show the variation of rho depending on the country and information source.
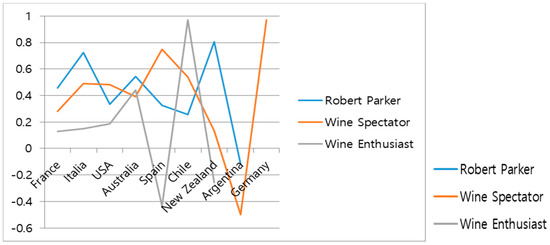
Figure 7.
The variation of rho by three sources at research Question 1.
Among nine countries, ANOVA was conducted to investigate the average difference in Pearson’s rho only in French wines from three wine quality rating sources: Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, and Wine Enthusiast. Table 11 shows the descriptive results for the average comparison of rho. The results report that the average rho has a significant difference among three sources, statistically (F = 4.409, p = 0.0001).

Table 11.
The Result of AVOVA in rho from Three Sources on French Wines for Research Question 2.
As Table 12 shows, the result of the Scheffe test reports that the correlation coefficients between Robert Parker’s points and Wine Spectator’s wine quality ratings show a similar average, statistically.

Table 12.
The Result of the Scheffe Test for Post-Comparison of French Wines for Research Question 2.
However, the rho from Wine Enthusiast’s ratings shows a lower number than that of Robert Parker’s points, statistically. In other words, in the case of French wines, the correlation between Robert Parker’s wine quality evaluation and on-premise price shows no significant difference in rho statistically with the correlation between Wine Spectator’s wine quality evaluation and on-premise price in the Korean market. This demonstrates that the effect of the CI’s ratings on French wines toward on-premise prices is comparable to that of individual wine professionals in the Korean market.
4.3. The Comparison in rho in French Red Wine
Research question 3 is only to explore the differences in correlation among the on-premise price and Parker’s points, Wine Spectator’s wine quality ratings, and Wine Enthusiast’s wine quality ratings on French red wine. ANOVA was conducted to investigate the average difference in Pearson’s rho among three sources: Robert Parker’s points, Wine Spectator’s wine quality ratings, and Wine Enthusiast’s wine quality ratings. Table 13 shows the descriptive result of the average comparison of rho. The result shows that the average rho has a significant difference among the three sources at 99% confidence level (F = 4.059, p = 0.0001).

Table 13.
The Results of AVOVA in rho From Three Sources on French Red Wines for Research Question 3.
As seen in Table 14, the result of the Scheffe test shows that the correlation coefficients between Robert Parker’s points and Wine Spectator’s wine quality ratings show a similar average, statistically. However, the rho for Wine Enthusiast shows a low level of rho in comparison to that of Robert Parker’s points, statistically, at the 99% significant level.

Table 14.
The Result of the Scheffe Test for Post-Comparison for French Red Wines for Research Question 3.
In other words, the correlation between Robert Parker’s points and the on-premise price in the case of French red wine was not statistically different from the correlation between CI’s wine quality ratings, that is, Wine Spectator’s wine quality ratings and on-premise prices in the Korean market. The result also demonstrates that the effect of the CI’s ratings on French red wines toward on-premise prices is comparable to that of individual wine professional in Korea market.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
The researchers of this study aimed to explore the difference in correlation between on-premise price and wine quality ratings from online wine quality evaluation-providing sources: wine Collective Intelligence (CI) platforms vs. an individual wine professional, Robert Parker. In the wine industry, Parker’s wine quality evaluation, Parker’s point, traditionally has had power in setting the price of wine, and it has been studied and proven by various researchers [12,13,14,15,16].
As other wine quality rating providers exist, and most of them have extended their content channels from offline to online, professional wine information has been getting more approachable for people in the world. Thus, the researchers of this study aimed to find out any possible difference between the power of wine quality evaluation of the individual wine professional and other wine quality information providers on market price.
With reviewing studies that were previously carried out, the researchers set a standard for the CI of wine industry, and two online platforms among 4 major wine quality providers, WineSpectator.com and WineEnthusiast.com were selected for the study. With 2430 wine items produced in nine countries of seven on-premise outlets in Korea, the researchers conducted ANOVA and a Scheffe test to find differences in the effect of quality rating toward price between CI and the individual professional in the same or different conditions of wine production country, region, vintage, and type of wine. With the results of the ANOVA and Scheffe test, it was found that WineSpecator.com’s wine quality ratings and Parker’s points’ effects on market price are equivalent. Further, in the case of French red wines, the same result was found.
The result of the study tells us that the CI on wine quality ratings has a similar influence on price to that of an individual wine professional’s ratings in the Korean wine industry. Further, it is reported that the wine quality ratings provided by Wine Spectator, one of the CI platforms in the wine industry, have a significant correlation with on-premise prices in the Korean market as much as Robert Parker’s points do.
As the wine market in Korea is still in its early stage of development, and wine is still recognized as a premium product among the general public [32], experts’ evaluation is one of the most important standards for making a decision to buy. Furthermore, sellers at on-premise outlets where the wine prices are higher than retail shops need professional and persuasive reasons to sell wines with marginal prices to their customers. For them, experts’ quality rating results can be a good backbone to sell wines and to explain the wine’s price.
Although the Korean wine market is in the early stage of development, it has been growing significantly since 2016 (Figure 8). Consumer lifestyles and tastes continue to evolve as Koreans are further exposed to international themes, and demand for wine and knowledge of wine has been increased. With this market environment, consumers become interested in more information on wine, not only from local information sources, but also from international sources throughout global wine expert platforms. Besides Parker, there are worldwide renowned individual wine experts who have their own wine quality rating system, and market players and consumers in Korea market consider the scores in choosing wines to buy. Additionally, Korean consumers have noticed and informed that there are many other influential CI platforms, which makes consumers open their eyes to obtain qualified information on wines. The results of this study show CI has a similar influence on the prices of the on-premise market as Parker’s points, traditionally regarded as the most influential guideline on wine price.
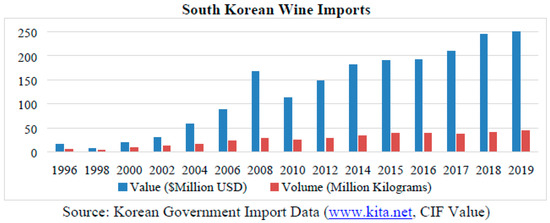
Figure 8.
South Korean Wine Imports.
Furthermore, the correlation between the ratings and price shows a moderate association of around 0.4. This result reflects the quality evaluation of external expert associates to setting the price of wine in a restaurant in practice. The point is that there is a unique organizational decision-making process that considers external evaluations, not customers, in the pricing criteria in the wine industry. In terms of the behavioral economics approach, it represents that the wine industry has an industry-specific pricing process for on-premise pricing from the price study prospective.
Applying the concept of Collective Intelligence to wine industry research, this study not only expands the CI research scope academically, but also proves the wine quality rating’s effect on wine price in the industry field practically. This study has several implications. First, the study introduced the concept of Collective Intelligence to the wine industry. This means that it extended the research of CI’s application to the wine industry and provided strong support for a sustainable e-business model in the wine industry. Agro-food is necessary for the consumer’s choice to deliver experiential values [49,50]. Online Collective Intelligence serves as a platform to deliver these experiential values to consumers in the wine industry. Collective Intelligence extended to the wine industry will contribute to the sustainable competitiveness of the platform-based wine business. Second, the paper found the importance of CI evaluation as one of the factors determining the price of wine. This suggests the possibility that wine evaluations, which have been dependent on a small number of people, could be replaced by CI evaluations. We live in an era when someone’s experience is passed on as meaningful knowledge to someone else. A high level of evaluation formed through Collective Intelligence by participants becomes a basis for creating sustainable consumption [51] conditions for consumers. Third, the study will contribute to the fair price of wine by activating the Collective Intelligence platform in the wine industry. A reasonable price is directly related to customer satisfaction. It will contribute to the development of sustainable tools that enable high consumer acceptance. Collective Intelligence platforms will help the sustainable activation and growth of the wine industry. Fourth, the study results fill the gap of the behavioral approach pricing study in the wine industry. The study of the relationship between CI ratings and price contributes to generalizing wine consumers’ choice behaviors. In terms of behavioral science, companies can implement sustainable marketing strategies by identifying general rules of consumer behavior and satisfying them.
Although the study has academic and practical contributions, there are various needs for future studies, as follows. First, there is more room for studies regarding the effect of country of origin and region of origin, specifically. The unit of correlation analysis in this study is the regional level. For example, the region refers to Bordeaux, Burgundy, and so on, in France. However, even in Bordeaux wine, different quality evaluation results are derived for each sub-region, such as Margaux, Medoc, Saint-Julien, etc. The correlation used in this study ignores these sub-regions, so there is a disadvantage in that the quality evaluation results are mixed in rho value. Second, for this research, at a given vintage, country, region, and type of wine, the researchers include the wine as a sample if three observations are found at each site. To generalize the study results, conducting the study by collecting more samples is needed. In addition to wine information and price information, it is also required to collect consumer information. With broader sample data, studying by type and by vintage of wines can be conducted, and then can provide broader insight. Third, we did not consider wine price in this study. Wine prices vary widely, and consumers and their choice factors are different for each price range, so it is necessary to reflect this in future research. It would be interesting to conduct a similar analysis on the market by price classification, as then it could be measured whether there is any difference in the effect of wine quality rating on price class. Fourth, future research requires consideration of the factors affecting wine prices such as vintage, size of the winery, wine bottle [39], and reputation [52]. In addition, a variety of methodologies need to include a regression model, chi-square analysis, price function [53], etc., according to their research topic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: Y.-S.K., Y.-J.N. and J.-W.H.; methodology: Y.-S.K., Y.-J.N. and J.-W.H.; writing—original draft preparation: Y.-S.K., Y.-J.N. and J.-W.H.; writing—review and editing: Y.-S.K., Y.-J.N. and J.-W.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data can be obtained through the website. Please see the text for details.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the four reviewers and editor.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Malone, T.W.; Bernstein, M.S. (Eds.) Handbook of Collective Intelligence; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Collective_intelligence (accessed on 11 April 2021).
- Malone, T.W.; Laubacher, R.; Dellarocas, C. Harnessing Crowds: Mapping the Genome of Collective Intelligence. 2009. Available online: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1381502 (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Bonabeau, E. Decisions 2.0: The power of Collective Intelligence. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2009, 50, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, C.A. Collective intelligence: A new approach to stock price forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. e-Systems and e-Man for Cybernetics in Cyberspace (Cat. No. 01CH37236), Tucson, AZ, USA, 7–10 October 2001; Volume 5, pp. 2893–2898. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Dong, Y.; Qin, Z. Minority game data mining for stock market predictions in computer architecture: A quantitative approach, agents and data mining interaction. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Agents and Data Mining Interaction, Toronto, ON, Canada, 11 May 2010; pp. 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, A.W.; Aggarwal, I.; Malone, T.W. Collective intelligence and group performance. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 24, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorrano, P. The 2.0 marketing strategies for wine tourism destinations of excellence. Chin. Bus. Rev. 2011, 10, 948–960. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi, B.; Gabbai, M. Territorial identity as a competitive advantage in wine marketing: A case study. J. Wine Res. 2013, 24, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrana, V.; Zafiropoulos, K.; Vagianos, D. An exploration of wine blog. In Social Media in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality: Theory, Practice and Cases; Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.: Farnham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Trappey, C.V.; Trappey, A.J. Collective intelligence applied to legal e-discovery: A ten-year case study of Australia franchise and trademark litigation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, C. Globalisation and the institutional re-embedding of markets: The political economy of price formation in the Bordeaux enprimeur market. New Political Econ. 2007, 12, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.H.; Lecocq, S.; Visser, M. The impact of gurus: Parker grades and enprimeur wine prices. Econ. J. 2008, 118, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, Y.; Nam, Y.; Kwak, Y. A study of quality appraisal’s explanatory power on retail price in Korean wine market. Int. J. e-Serv. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, Y.; Kwak, Y. The influence of wine expert’s on-line ratings on retail price of on-premise market in Korea. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2011, 264, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, Y.; Kwak, Y.; Kwak, Y. A study of the effects of a wine critic’s evaluation on the retail prices in Korea; with on-line evaluation basis. Inf. Int. Interdiscip. J. 2013, 16, 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Oleksy, P.; Czupryna, M.; Jakubczyk, M. On fine wine pricing across different trading venues. J. Wine Econ. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.; Fassnacht, M. Price Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_M._Parker_Jr (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- The Wine Advocate. Available online: https://www.robertparker.com/ (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wine_Spectator (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Wine Spectator Online. Available online: www.winespectator.com (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Wine Enthusiast Companies. Available online: www.wineenthusiast.com (accessed on 8 May 2021).
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wine_Enthusiast_Magazine (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- TI Media Limited. Available online: www.decanter.com (accessed on 13 April 2021).
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decanter_(magazine) (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Veseth, M. Wine Wars: The Curse of the Blue Nun, the Miracle of Two Buck Chuck, and the Revenge of the Terroirists; Rowman and Littlefield Publishers: Lanham, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Resnick, E. Wine Brands: Success Strategies for New Markets, New Consumers and New Trends; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.M.; Mitchell, R. Wine Marketing: A Practical Guide; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vivino. Available online: https://www.vivino.com/ (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- App Advice LLC. Available online: http://appadvice.com/appnn/2013/07/just-like-good-wine-vivino-wine-scanner-gets-better-with-time (accessed on 22 May 2021).
- Carter, S.; Yeo, A.C.M. Internet-enabled Collective Intelligence as a precursor and predictor of consumer behavior. Econ. Manag. Financ. Mark. 2018, 13, 11–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott, D.; Williams, A.D. Wikinomics: How Mass Collaboration Changes Everything; Penguin Group: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein, S.; Parker, C.M. Wikipedia model for Collective Intelligence: A review of information quality. Int. J. Knowl. Learn. 2009, 5, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, R.E.; Smith, L.C. Reference and Information Services: An Introduction; Libraries Unlimited: Englewood, CO, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.P. Evaluation of electronic reference sources. DESIDOC Bull. Inf. Technol. 2003, 23, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stvilia, B.; Twidale, M.B.; Gasser, L.; Smith, L.C. Information quality in a community-based encyclopedia. In Knowledge Management: Nurturing Culture, Innovation, and Technology; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2005; pp. 101–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bonabeau, E.; Mayer, C. Swarm intelligence: A whole new what to think about business. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2001, 79, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Höllea, D.; Aufschnaiter, S.; Bogon, J.; Pfeuffer, C.; Kiesel, A.; Thomaschke, R. Quality ratings of wine bottles in e-commerce: The influence of time delays and spatial arrangement. J. Wine Res. 2020, 31, 152–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parboteeah, D.V.; Taylor, D.C.; Barber, N.A. Exploring impulse purchasing of wine in the online environment. J. Wine Res. 2016, 27, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H. Confessions of the Pricing Man How Price Affects Everything; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Keber, C.; Schuster, M.G. Collective intelligence in option pricing: Determining black-scholes implied volatilities with generalized ant programming. Proc. World Autom. Congr. 2004, 17, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Kwun, O.; Kim, Y. Design of the MMORPG item’s pricing decision system based on Collective Intelligence model. J. Korean Soc. Comput. Game 2013, 26, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz, I.; Lockshin, L. What price quality? An investigation into the prediction of wine-quality ratings. J. Wine Res. 2002, 13, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oczkowski, E.; Doucouliagos, H. Wine prices and quality ratings: A meta-regression analysis. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2015, 97, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleny, J. A relationship between price and quality rating of wines from the Czech Republic. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2017, 29, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, P.H. Pricing research in marketing: The integration of European and American literature. Korean Mark. Rev. 1989, 4, 168–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, C.; Costa Pinto, L.M.; Lourenço-Gomes, L. Effect of region of origin on willingness to pay for wine: An experimental auction. Appl. Econ. 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaia, L.; Maizza, A.; Fait, M.; Scorrano, P. Origin based agro-food products: How to communicate their experiential value online? Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batat, W.; Peter, P.C.; Moscato, E.M.; Castro, I.A.; Chan, S.; Chugani, S.; Muldrow, A. The experiential pleasure of food: A savoring journey to food well-being. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 100, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piligrimienė, Ž.; Žukauskaitė, A.; Korzilius, H.; Banytė, J.; Dovalienė, A. Internal and external determinants of consumer engagement in sustainable consumption. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trestini, S.; Stiletto, A.; Stranieri, S. Price determinants of sparkling wine in Poland: Does reputation really matter. Wine Econ. Policy 2020, 9, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outreville, J.F.; Le Fur, E. Hedonic price functions and wine price determinants: A review of empirical research. J. Agric. Food Ind. Organ. 2020, 18, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).