An Integrated Multi Criteria Decision Making Model for Evaluating Park-and-Ride Facility Location Issue: A Case Study for Cuenca City in Ecuador
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data Collection and Methods
3.1. Survey
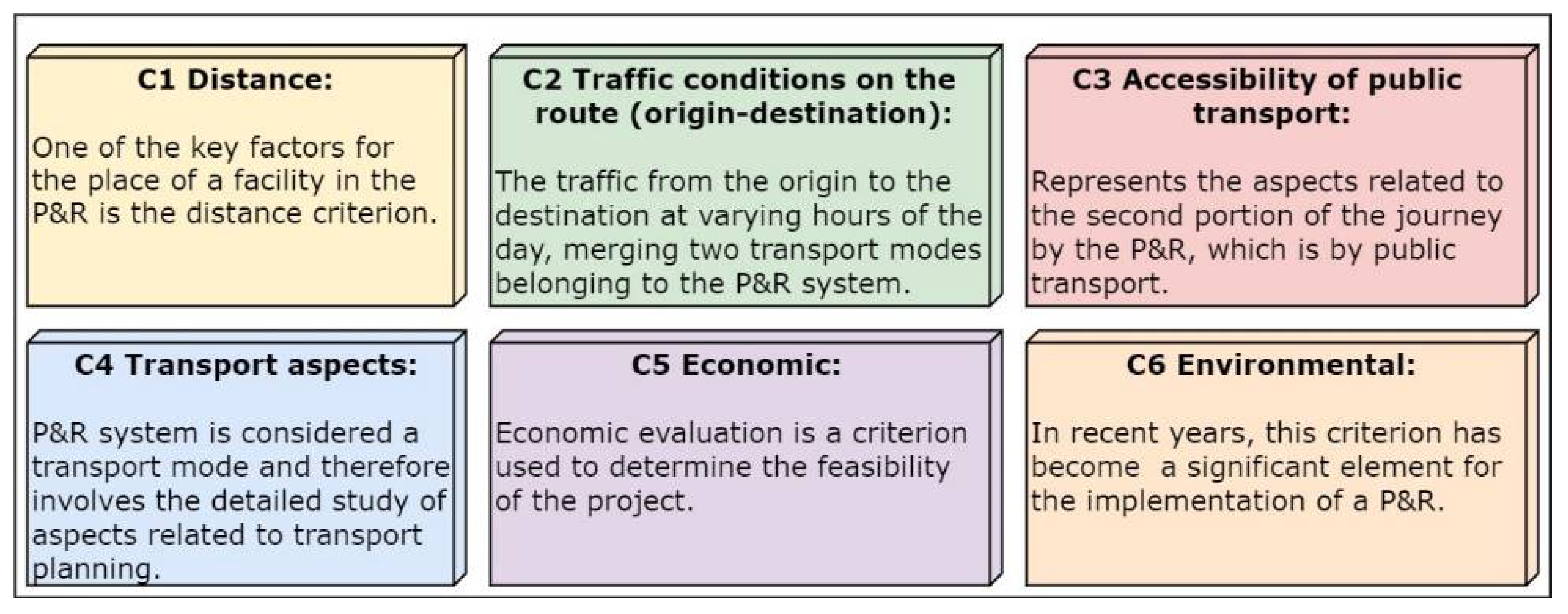
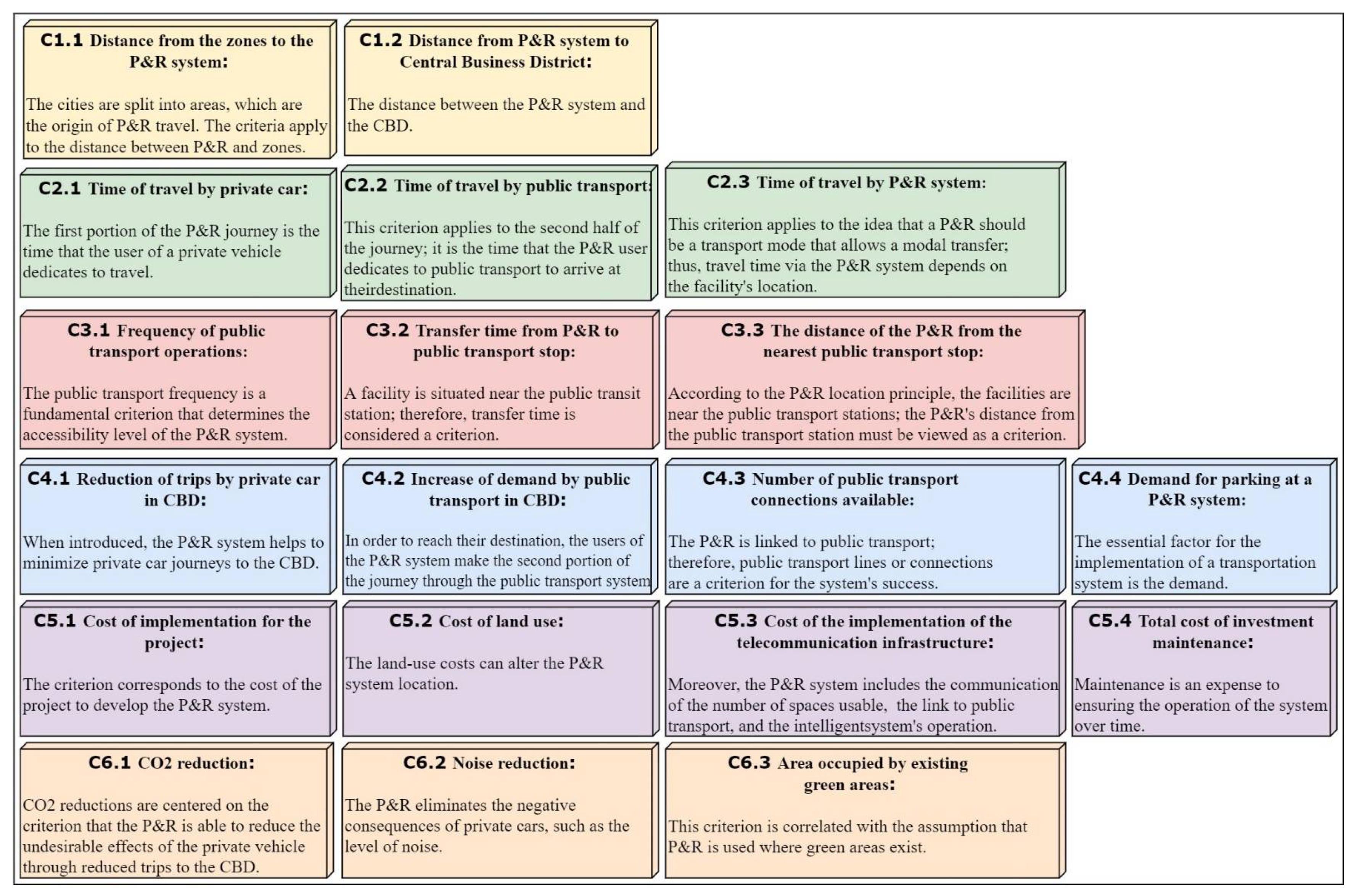
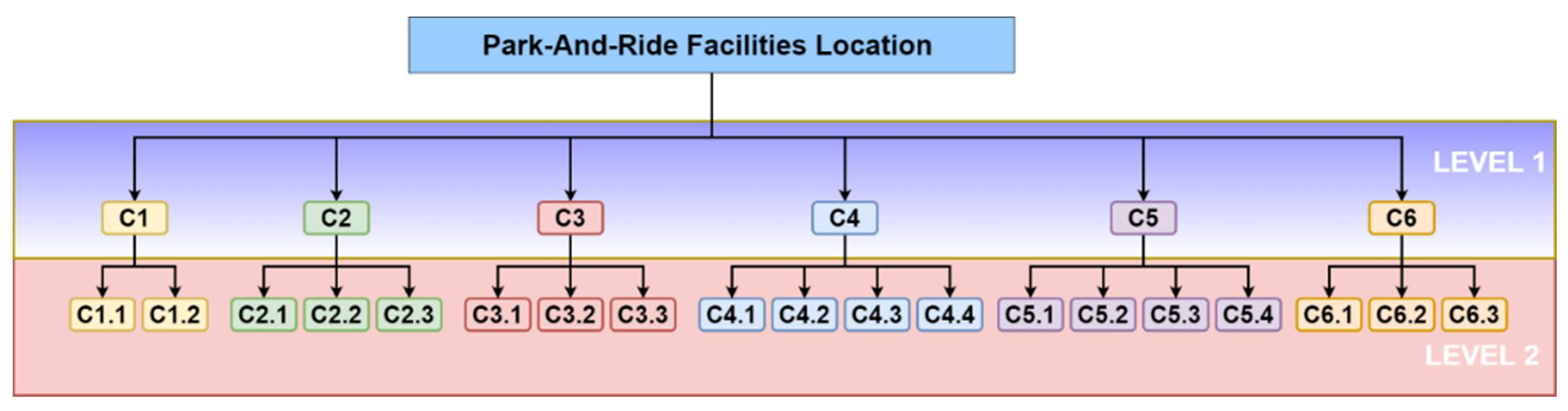
3.2. Design of the Saaty Scale and Description Criteria
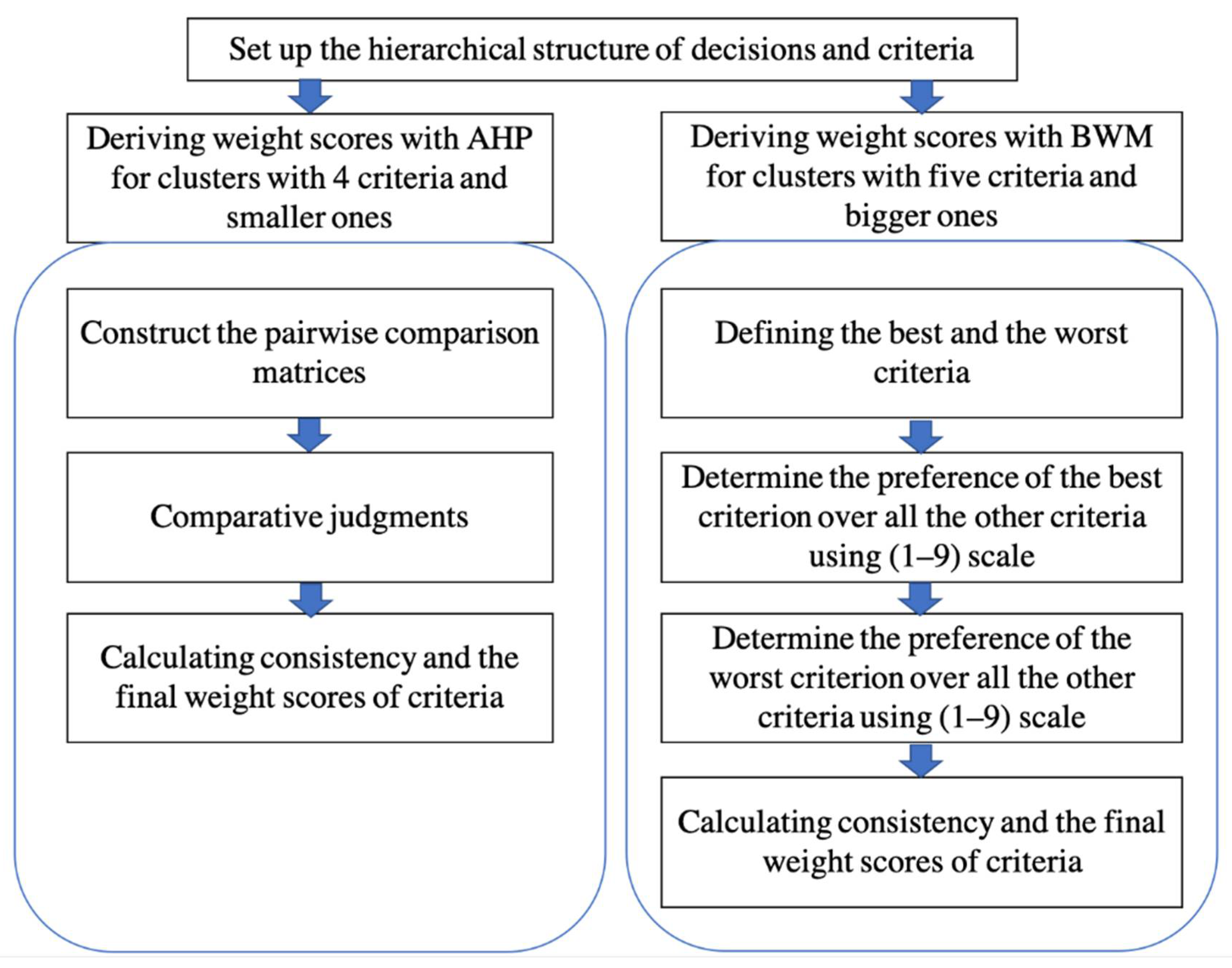
3.3. Description of the Conventional Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
- setting up the hierarchical structure of the decision problem,
- formulating PCMs dependent on the hierarchy,
- planning the questionnaire sample,
- testing the accuracy,
- aggregation by the geometric mean,
- calculating weight vectors,
- estimating the global ratings,
- sensitivity evaluation.
3.4. Best Worst Method
- Determination of decision-making criteria;
- Identifying the least (worst) and most important (best) parameters;
- Identifying the most relevant (best) criterion of priority over all other metrics;
- Identifying the least relevant (worse) criterion of all the less significant priority;
- Testing for coherence;
- Evaluation of values of weight.
3.5. The Proposed AHP-BWM Model
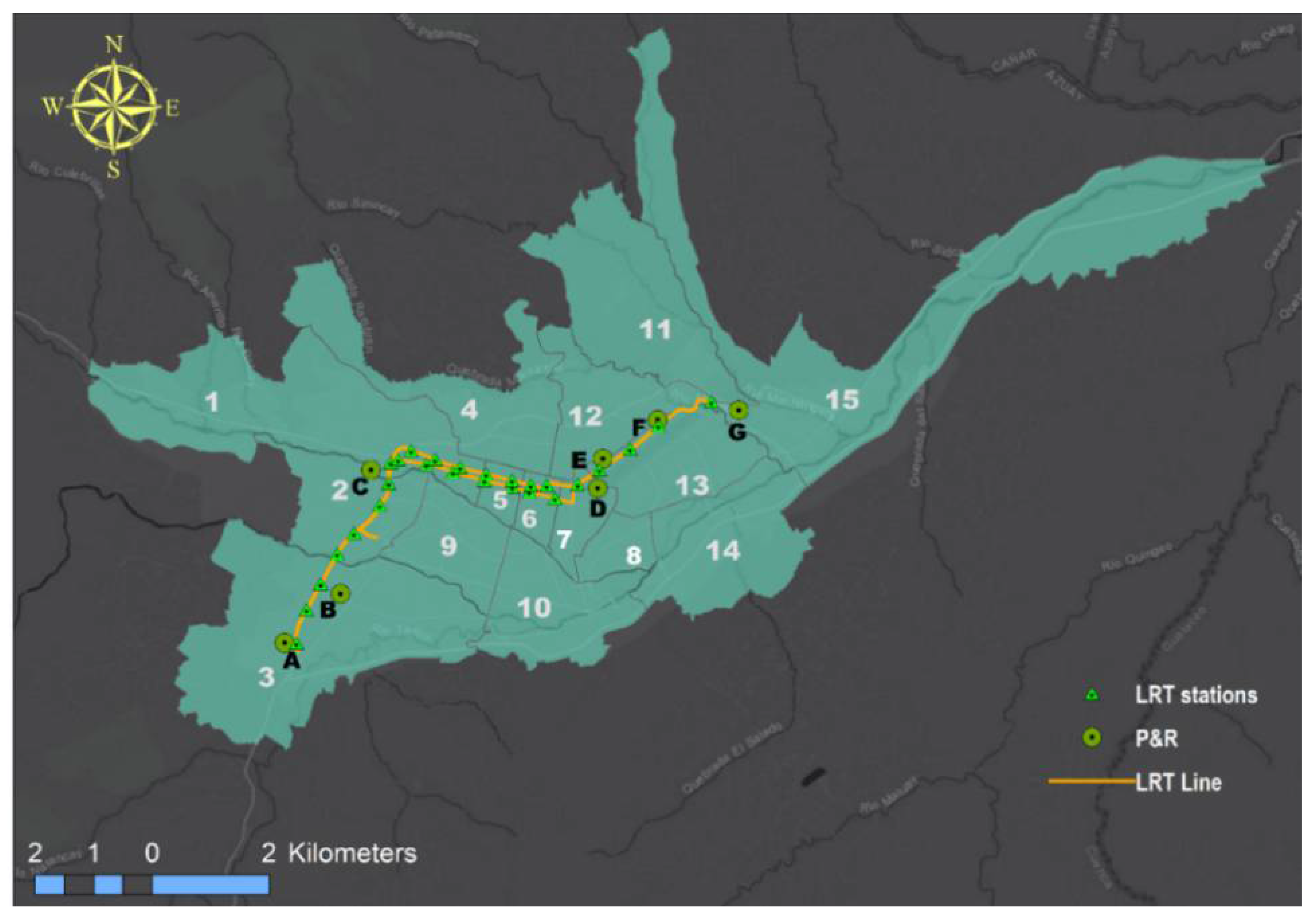
4. Case Study
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozos-Blanco, M.Á.; Pozo-Menéndez, E.; Arce-Ruiz, R.; Baucells-Aletà, N. The way to sustainable mobility. A comparative analysis of sustainable mobility plans in Spain. Transp. Policy 2018, 72, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, J.M.; Lopez-Lambas, M.E.; Gonzalo, H.; Rojo, M.; Garcia-Martinez, A. Methodology for assessing the cost effectiveness of Sustainable Urban Mobility Plans (SUMPs). The case of the city of Burgos. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 68, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenio, E.; Martens, K.; Di Ciommo, F. Sustainable urban mobility plans: Bridging climate change and equity targets? Res. Transp. Econ. 2016, 55, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehne, C.G.; Chester, M.V. Greenhouse gas and air quality effects of auto first-last mile use with transit. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 53, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentouati, B.; Javaid, M.S.; Bouchekara, H.R.E.H.; El-Fergany, A.A. Optimizing performance attributes of electric power systems using chaotic salp swarm optimizer. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2020, 15, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dell’Olio, L.; Cordera, R.; Ibeas, A.; Barreda, R.; Alonso, B.; Moura, J.L. A methodology based on parking policy to promote sustainable mobility in college campuses. Transp. Policy 2019, 80, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizopoulos, D.; Esztergár-Kiss, D. A Method for the Optimization of Daily Activity Chains Including Electric Vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolín, G.; Ibeas, Á.; Alonso, B.; Dell’Olio, L. Modelling parking behaviour considering users heterogeneities. Transp. Policy 2018, 67, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, S.; Pungillo, G.; Bruzzone, F. How to evaluate and plan the freight-passengers first-last mile. Transp. Policy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, F.; Cavallaro, F.; Nocera, S. The integration of passenger and freight transport for first-last mile operations. Transp. Policy 2021, 100, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.A.; Zefreh, M.M.; Torok, A. Public transport accessibility: A literature review. Period. Polytech. Transp. Eng. 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, J.C.; Irawan, B.; Caulfied, C. Development of location-based services for recommending departure stations to park and ride users. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2014, 48, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, J.C.; Irawan, B. Development of fuzzy logic forecast models for location-based parking finding services. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 473471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.T.; Honda, K.; Wang, Y.C. Development of location-based services for recommending departure stations to park and ride users: A note. Int. J. Internet Manuf. Serv. 2015, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslem, S.; Farooq, D.; Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Blaschke, T. Application of the AHP-BWM model for evaluating driver behavior factors related to road safety: A case study for Budapest. Symmetry 2020, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beria, P.; Maltese, I.; Mariotti, I. Multicriteria versus Cost Benefit Analysis: A comparative perspective in the assessment of sustainable mobility. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2012, 4, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIoszek, E.; Kurek, A. The use of a park and ride system a case study based on the City of Cracow (Poland). Energies 2020, 13, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchari, E. Transportation demand management: A park and ride system to reduce congestion in Palembang city Indonesia. Procedia Eng. 2015, 125, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirgaokar, M.; Deakin, E. Study of park-and-ride facilities and their use in the San Francisco Bay Area of California. Proc. Transp. Res. Rec. 2005, 1927, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Tóth, J.; Péter, T. Mapping the Catchment Area of Park and Ride Facilities within Urban Environments. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Hamadneh, J.; Esztergár-Kiss, D.; Tóth, J. Simulation of the Daily Activity Plans of Travelers Using the Park-and-Ride System and Autonomous Vehicles: Work and Shopping Trip Purposes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Tóth, J.; Péter, T.; Moslem, S. An Integrated Model of Park-And-Ride Facilities for Sustainable Urban Mobility. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguı´n-Veras, J.; Yushimito, W.F.; Aros-Vera, F.; Reilly, J.J. User rationality and optimal park-and-ride location under potential demand maximization. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2012, 46, 949–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.M.; Liu, B.; Wei, H.; Qu, Y.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, X. How Many and Where to Locate Parking Lots? A Space–time Accessibility-Maximization Modeling Framework for Special Event Traffic Management. Urban Rail Transit 2016, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balsa-Barreiro, J.; Valero-Mora, P.M.; Menéndez, M.; Mehmood, R. Extraction of Naturalistic Driving Patterns with Geographic Information Systems. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, M.W.; Grubesic, T.H. A GIS-based planning approach to locating urban rail terminals. Transportation 2001, 28, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsa-Barreiro, J.; Valero-Mora, P.M.; Berné-Valero, J.L.; Varela-García, F.A. GIS mapping of driving behavior based on naturalistic driving data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, B.; Murray, A.T. A GIS-Based Approach for Delineating Market Areas for Park and Ride Facilities. Trans. GIS 2005, 9, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; He, W.; He, M. The Attitude and Preference of Traveler to the Park & Ride Facilities: A Case Study in Nanjing, China. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 43, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Olaru, D.; Smith, B.; Xia, J.C.; Lin, T.G. Travellers’ Attitudes Towards Park-and-Ride (PnR) and Choice of PnR Station: Evidence from Perth, Western Australia. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 162, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavadas, J.; Antunes, A.P. An optimization model for integrated transit-parking policy planning. Transportation 2019, 46, 1867–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wang, D.Z.W. Continuum modeling of park-and-ride services considering travel time reliability and heterogeneous commuters—A linear complementarity system approach. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2014, 71, 58–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Bridgelall, R. A fuzzy Delphi analytic hierarchy model to rank factors influencing public transit mode choice: A case study. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2021, 39, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Anbanandam, R. Location selection of multimodal freight terminal under STEEP sustainability. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2019, 33, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.K.K.; Lian, S.J.; Huang, S.H.S. An assessment model based on a hybrid MCDM approach for the port choice of liner carriers. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu Gündoğdu, F.; Duleba, S.; Moslem, S.; Aydın, S. Evaluating public transport service quality using picture fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and linear assignment model. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslem, S.; Çelikbilek, Y. An integrated grey AHP-MOORA model for ameliorating public transport service quality. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2020, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, O.; Moslem, S.; Blaschke, T.; Duleba, S. Sustainable Urban Transport Planning Considering Different Stakeholder Groups by an Interval-AHP Decision Support Model. Sustainability 2018, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duleba, S. An AHP-ISM approach for considering public preferences in a public transport development decision. Transport 2019, 34, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duleba, S. Introduction and comparative analysis of the multi-level parsimonious AHP methodology in a public transport development decision problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.W.; Li, H. Application of the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in multi-criteria analysis of the selection of intelligent building systems. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, M.M.; Evers, M.; Almoradie, A.D.S. Participatory flood vulnerability assessment: A multi-criteria approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duleba, S.; Moslem, S. Examining Pareto optimality in analytic hierarchy process on real Data: An application in public transport service development. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 116, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligmann-Zielinska, A.; Jankowski, P. Spatially-explicit integrated uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of criteria weights in multicriteria land suitability evaluation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 57, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.H.; Pan, F.F.C. Application of Monte Carlo AHP in ranking dental quality attributes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaraghi, N.; Tabesh, P.; Guan, P.; Zhuang, J. Comparison of AHP and Monte Carlo AHP under different levels of uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2015, 62, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervás-Peralta, M.; Poveda-Reyes, S.; Molero, G.; Santarremigia, F.; Pastor-Ferrando, J.-P. Improving the Performance of Dry and Maritime Ports by Increasing Knowledge about the Most Relevant Functionalities of the Terminal Operating System (TOS). Sustainability 2019, 11, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, I.; Daǧdeviren, M. Using the analytic network process (ANP) in a SWOT analysis—A case study for a textile firm. Inf. Sci. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergu, D.; Kou, G.; Shi, Y.; Shi, Y. Analytic network process in risk assessment and decision analysis. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozóki, S.; Fülöp, J. Efficient weight vectors from pairwise comparison matrices. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 264, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, S.; Kahraman, C. Evaluation of firms applying to Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award: A modified fuzzy AHP method. Complex Intell. Syst. 2019, 5, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseli, G.; Sheikh, R.; Sana, S.S. Base-criterion on multi-criteria decision-making method and its applications. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2020, 15, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Kar, S. Multi-criteria analysis of supply chain risk management using interval valued fuzzy TOPSIS. OPSEARCH 2016, 53, 474–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, A.; Kar, S. Assessment of environmental factors causing wetland degradation, using Fuzzy Analytic Network Process: A case study on Keoladeo National Park, India. Ecol. Modell. 2015, 316, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method: Some properties and a linear model. Omega 2016, 64, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozóki, S.; Fülöp, J.; Poesz, A. On reducing inconsistency of pairwise comparison matrices below an acceptance threshold. Cent. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 23, 849–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakusic, S. Ranking conceptual locations for a park-and-ride parking lot using EDAS method. J. Croat. Assoc. Civ. Eng. 2018, 70, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierek, S.; Bieńczak, M.; Zmuda-Trzebiatowski, P. Multiple criteria evaluation of P&R lots location. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 47, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Tóth, J.; Moslem, S.; Péter, T.; Duleba, S. An Integrated Approach of Analytic Hierarchy Process and Triangular Fuzzy Sets for Analyzing the Park-and-Ride Facility Location Problem. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 234–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.A.A.; Gupta, H. Evaluating green performance of the airports using hybrid BWM and VIKOR methodology. Tour. Manag. 2020, 76, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liang, H.; Chan, F.T.S. Urban sewage sludge, sustainability, and transition for Eco-City: Multi-criteria sustainability assessment of technologies based on best-worst method. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 116, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslem, S.; Campisi, T.; Szmelter-Jarosz, A.; Duleba, S.; Nahiduzzaman, K.M.; Tesoriere, G. Best-worst method for modelling mobility choice after COVID-19: Evidence from Italy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, D.; Guerrero, M.L. Exploring the influence of road network structure on the spatial behaviour of cyclists using crowdsourced data. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 1314–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermida, C.; Cordero, M.; Orellana, D. Analysis of the influence of urban built environment on pedestrian flow in an intermediate-sized city in the Andes of Ecuador. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2019, 13, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairo, O.; János, T.; Tamás, P. A spatial study of the catchment area of P&R facilities. In Proceedings of the X. International Conference on Transport Sciences Győr 2020, Gyor, Hungary, 29–30 October 2020; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, J.; Tóth, J.; Péter, T. Estimation of parking needs at Light Rail Transit System stations. In Proceedings of the Conference on Transport Sciences 2019, Gyor, Hungary, 22–23 March 2019; p. 8. [Google Scholar]

| Numerical Values | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Two elements have the same importance |
| 3 | Expertise and judgment favor an aspect in contrast |
| 5 | One element that is strongly important |
| 7 | One element is very strongly dominant |
| 9 | A factor is benefited by at least one order of scale |
| 2, 4, 6, 8 | It is used to compromise two rulings |
| m | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.9 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 | 1.49 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 0 | 0.44 | 1.0 | 1.63 | 2.3 | 3.0 | 3.73 | 4.47 | 5.23 |
| Factor | Weight | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.0971 | 5 |
| C2 | 0.0622 | 6 |
| C3 | 0.3719 | 1 |
| C4 | 0.1442 | 3 |
| C5 | 0.1082 | 4 |
| C6 | 0.2164 | 2 |
| Criteria | Local Weight | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| C1.1 | 0.8294 | 1 |
| C1.2 | 0.1706 | 2 |
| C2.1 | 0.1106 | 3 |
| C2.2 | 0.3738 | 2 |
| C2.3 | 0.5334 | 1 |
| C3.1 | 0.6957 | 1 |
| C3.2 | 0.1063 | 3 |
| C3.3 | 0.2232 | 2 |
| C4.1 | 0.3267 | 2 |
| C4.2 | 0.3794 | 1 |
| C4.3 | 0.2197 | 3 |
| C4.4 | 0.0906 | 4 |
| C5.1 | 0.2228 | 2 |
| C5.2 | 0.3569 | 1 |
| C5.3 | 0.2180 | 3 |
| C5.4 | 0.2076 | 4 |
| C6.1 | 0.6445 | 1 |
| C6.2 | 0.2225 | 2 |
| C6.3 | 0.1385 | 3 |
| Criteria | Weight | Rank | Criteria | Weight | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.0971 | 5 | C1.1 | 0.0806 | 4 |
| C1.2 | 0.0166 | 17 | |||
| C2 | 0.0622 | 6 | C2.1 | 0.0069 | 19 |
| C2.2 | 0.0232 | 15 | |||
| C2.3 | 0.0332 | 10 | |||
| C3 | 0.3719 | 1 | C3.1 | 0.2587 | 1 |
| C3.2 | 0.0395 | 8 | |||
| C3.3 | 0.0830 | 3 | |||
| C4 | 0.1442 | 3 | C4.1 | 0.0471 | 7 |
| C4.2 | 0.0547 | 5 | |||
| C4.3 | 0.0317 | 11 | |||
| C4.4 | 0.0131 | 18 | |||
| C5 | 0.1082 | 4 | C5.1 | 0.0241 | 13 |
| C5.2 | 0.0386 | 9 | |||
| C5.3 | 0.0236 | 14 | |||
| C5.4 | 0.0225 | 16 | |||
| C6 | 0.2164 | 2 | C6.1 | 0.1394 | 2 |
| C6.2 | 0.0481 | 6 | |||
| C6.3 | 0.0300 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega, J.; Moslem, S.; Palaguachi, J.; Ortega, M.; Campisi, T.; Torrisi, V. An Integrated Multi Criteria Decision Making Model for Evaluating Park-and-Ride Facility Location Issue: A Case Study for Cuenca City in Ecuador. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137461
Ortega J, Moslem S, Palaguachi J, Ortega M, Campisi T, Torrisi V. An Integrated Multi Criteria Decision Making Model for Evaluating Park-and-Ride Facility Location Issue: A Case Study for Cuenca City in Ecuador. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137461
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega, Jairo, Sarbast Moslem, Juan Palaguachi, Martin Ortega, Tiziana Campisi, and Vincenza Torrisi. 2021. "An Integrated Multi Criteria Decision Making Model for Evaluating Park-and-Ride Facility Location Issue: A Case Study for Cuenca City in Ecuador" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137461
APA StyleOrtega, J., Moslem, S., Palaguachi, J., Ortega, M., Campisi, T., & Torrisi, V. (2021). An Integrated Multi Criteria Decision Making Model for Evaluating Park-and-Ride Facility Location Issue: A Case Study for Cuenca City in Ecuador. Sustainability, 13(13), 7461. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137461









