Abstract
Roundabouts are considered as one of the most efficient forms of intersection that substantially reduce the types of crashes that result in injury or loss of life. Nevertheless, they do not eliminate collision risks, especially when human error plays such a large role in traffic crashes. In this study, we used a driving simulator and an eye tracker to investigate drivers’ eye movements under cell phone-induced distraction. A total of 45 drivers participated in two experiments conducted under distracted and non-distracted conditions. The results indicated that, under distracting conditions, the drivers’ fixation duration decreased significantly on roundabouts, and pupil size increased significantly.
1. Introduction
Roundabouts are a proven safety countermeasure and are safer than conventional signal-controlled and stop sign intersections. Nevertheless, they do not eliminate the risk of traffic crashes. Navigating through roundabouts can be an intricate task because of driver–car interactions, circulatory geometry, and environment perception. According to the Professional Association of Training Companies in Logistics, Transportation, and Road Safety, the majority of drivers make one or more mistakes when passing through roundabouts. That is, 65% do not occupy an appropriate lane as they exit roundabouts, 15% drive straight into roundabouts by crossing lanes, and 60% do not use proper turn signals [1]. Similar results were presented in the annual crash reports provided by Spain’s National Traffic Department (DGT), which stated that traffic accidents at roundabouts increased by 34% from 2012 to 2016 and that fatal accidents in these road junctions doubled during the same period [2]. Most traffic crashes that occur at roundabouts are entering/exiting circulating crashes, rear-end crashes, collisions with pedestrians and cyclists, and collisions with parts of roundabouts (e.g., central island, curb) [3,4]. Arndt and Troutbeck [3] reported that roughly 80% of traffic crashes at roundabouts take place on entry lanes, mostly because of a driver’s failure to give the right of way to oncoming traffic or vulnerable road users [5].
Distraction is one of the critical threats to the health and the safety of drivers, accounting for 22% of rear-end crashes [6] and 3% of single-vehicle crashes at roundabouts [7]. These statistics are supported by the findings of [8] from a roadside observation intended to capture the prevalence of drivers’ secondary behaviors. The authors found that 21.1% of drivers are engaged in distracting activities at roundabouts and that the most common sources of distraction are holding and/or talking on a phone (8.4%) and having a conversation with passengers (3.4%). Distraction is also prevalent among pedestrians crossing the road [9,10]. According to the survey conducted by [9], talking on a mobile phone while crossing the street increases the risk of conflict with a vehicle.
As distraction is generally underreported in national databases and police reports, previous research attempted to determine its potential sources and prevalence using surveys [11,12,13] and experimental testing [14,15,16,17,18]. Although survey questionnaires can be used to identify potentially distracting activities that lead to traffic crashes, major concerns arise as to the reliability of self-reported data. In contrast, experimental testing approaches such as naturalistic driving studies, field observations, and driving simulations provide researchers with realistic information regarding distracting activities and driver performance.
Past research efforts uncovered that the use of cell phones while driving impairs a driver’s performance [19,20,21]. However, most of these works focused on occurrences on straight road segments [22,23], intersections [24,25,26,27], and railway crossings [28,29]. Few investigated cell phone-induced distraction effects on drivers’ performance parameters at roundabouts [30,31]. Nonetheless, these roundabout-oriented works did not assess drivers’ eye movements on roundabouts under distracted and non-distracted conditions. Table 1 shows some driving simulation studies that revolved around cell phone-induced distraction.

Table 1.
Summary of previous works.
Eye Movement and Distracted Driving
Given the increase in distracted driving-related crashes around the world, various researchers [33,34,35] attempted to investigate the visual characteristics relevant to distracted driving, as eye movement data can uncover important information in the assessment of secondary tasks. For example, Bao and Boyle [33] evaluated drivers’ visual scanning behaviors using in-vehicle cameras to monitor drivers’ head movements as they make right- and left-hand turns and straight-through driving maneuvers at intersections. Romoser and Fisher [34] used an eye tracker to determine participants’ points of gaze during turns at intersections in two different conditions: (1) when drivers are stationary at an intersection and are waiting for a break in traffic to execute a turn and (2) when drivers begin a turn and are aiming to move in the direction from which other vehicles are most likely to come into conflict with their vehicles. Similarly, Romoser, Pollatsek, Fisher, and Williams [35] used an eye tracker to assess the glance patterns of drivers who approach and enter intersections.
In consideration of the above-mentioned issues, the present study was aimed at investigating differences in scanning behaviors under distracting and non-distracting conditions on roundabouts. We chose to focus on these junctions rather than intersections, as some crashes still occur on the former. Moreover, as some dominantly occurring crash types on roundabouts such as rear-end crashes, entering-circulating crashes, and single-vehicle collisions occur at different parts of roundabouts [4], we examined five locations on roundabouts to assess drivers’ behaviors.
2. Methodology
2.1. Driving Simulator
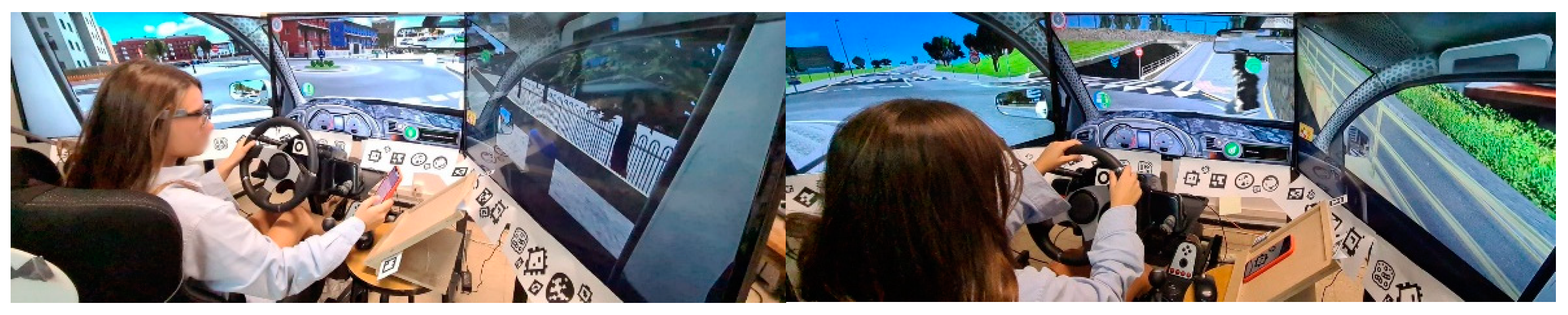
In carrying out our investigation, we used a driving simulator specially designed for training purposes. It enables the simulation of realistic driving scenarios under different traffic and weather conditions in a safe environment. A driving simulation system can calculate speed, acceleration, and other motorist or vehicle characteristics on the basis of the performance of a driver. The system can also configure vehicles through changes to traction, gears, and other components. The apparatus used in this work was equipped with three 43 inch monitors designed to visualize a simulated road environment. Computer graphics were used to produce a front image, a side mirror image, and a rear-view mirror image of road traffic conditions. Figure 1 presents the driving simulator used in our study.

Figure 1.
Driving Simulator.
2.2. Eye Tracker
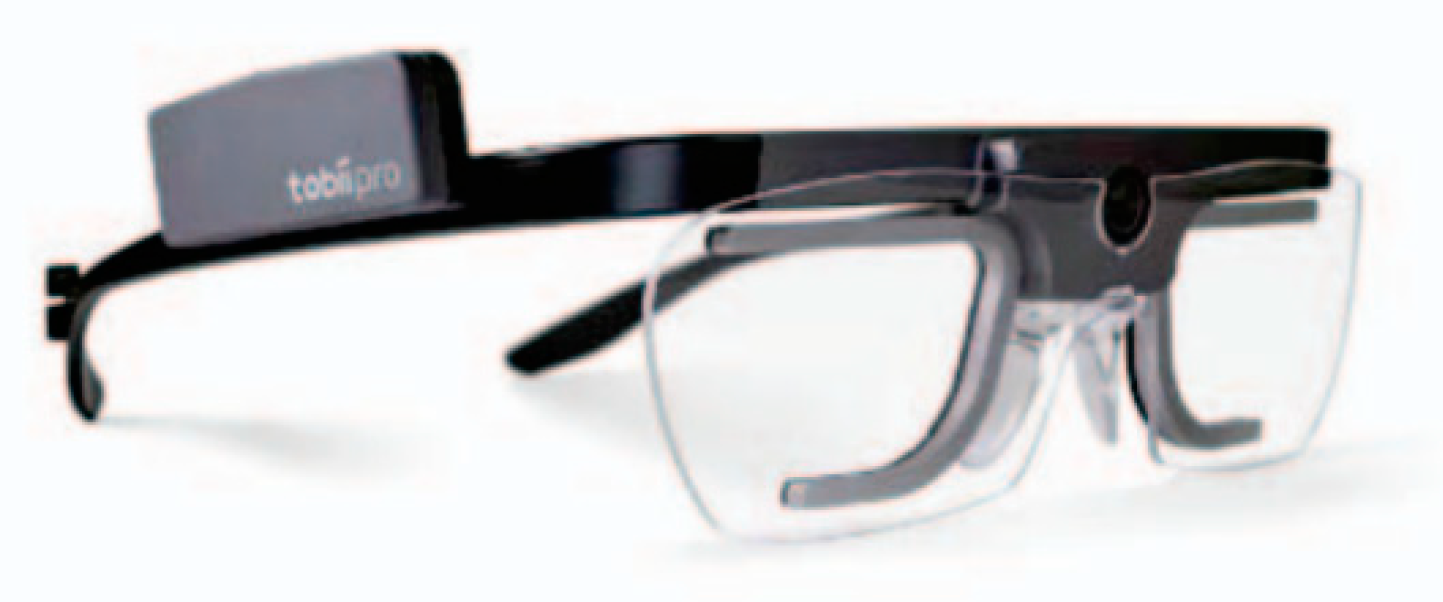
To assess drivers’ eye movements, we used Tobii Pro Glasses 2 (Figure 2), which features a one-point calibration procedure, auto parallax compensation, and slippage compensation, thus allowing for persistent calibration throughout testing. The eye tracker was equipped with two cameras and had a sampling rate of 100 Hz. For the analysis of drivers’ behaviors on roundabouts, we defined various areas of interest (AOIs), namely front mirror, windshield, driver-side mirror and window, and passenger-side mirror and window. The data recorded by the eye tracker were analyzed using the Tobii Pro Lab software, through which participants’ fixation duration and eye pupil size for each AOI were determined. These two metrics are important because they reveal a driver’s visual distraction. As reported by Jiang et al. [36], distraction among pedestrians is associated with increased pupil diameter and reduced fixation duration.

Figure 2.
Tobii Pro Glasses 2.
2.3. Participants
Prospective participants were screened for eligibility, and if eligibility criteria were satisfied, they were provided a consent form approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Burgos. A total of 45 individuals, specifically 13 females and 32 males, participated in this study. They were healthy, 19 to 56-year-old adults living in Burgos, Spain, who had no eye diseases and mental illness but had intact physical functioning and limb movement. They were selected based on years of driving experience and frequency of vehicle use in real life.
2.4. Procedure
All the participants were given detailed information about the study in advance, and data were collected from those who provided informed consent. Each participant filled out a survey questionnaire with questions related to demographic factors and particularities of individual driving. They later received an introductory tour of the simulator and were allowed a practice drive for familiarization with the apparatus and simulated road environment. The virtual road environment featured a multi-lane rural and urban roads that encompassed six roundabouts with stable traffic flow and where drivers had a high degree of freedom to select speed and operating conditions; nevertheless, such conditions were somewhat influenced by other vehicles on the road. Additionally, all the participants were tasked to drive in clear weather conditions and during the day. After the training, they were instructed to operate in two counterbalanced experimental drives. Before each experiment, a trained research assistant fitted the eye tracker onto each test participant’s head. During the calibration, the test participant was asked to look at a calibration card (target) held in front of him/her for a few seconds. The assistant then initiated recording using the Tobii Glasses Controller software running on a computer. After the session, the assistant stopped the recording and removed the head unit from the test participant. All interactions with the eye tracker (listing the participants to be tested, initiating calibration, starting/stopping recordings, etc.) were done through the Tobii Glasses Controller software. In the non-distracting experiment, the participants were asked to drive through a simulated route with six roundabouts while refraining from using a cell phone. Depending on each individual driving style and behavior, every subject had to drive for approximately 10 to 15 min without any distraction, keeping attention focused on the road. The other experiment was performed fully under cell phone-induced distraction. That is, the trained research assistant placed a single phone call as well as sent multiple WhatsApp messages to participants during the experiment. During the call, the research assistant maintained a natural conversational flow that required participants to respond to various open-ended questions. Typical questions included inquiries related to future plans, the academic course, and preferred leisure activities. In addition, the participants were asked to open Instagram and go through the feed. These applications were selected because they are downloaded frequently from the app store/play store and are popular among young people, which is this study’s target group. The participants were instructed to drive as they typically would on a real road, adhering to the speed limit as well as other traffic laws outlined by DGT.
2.5. Data Analysis
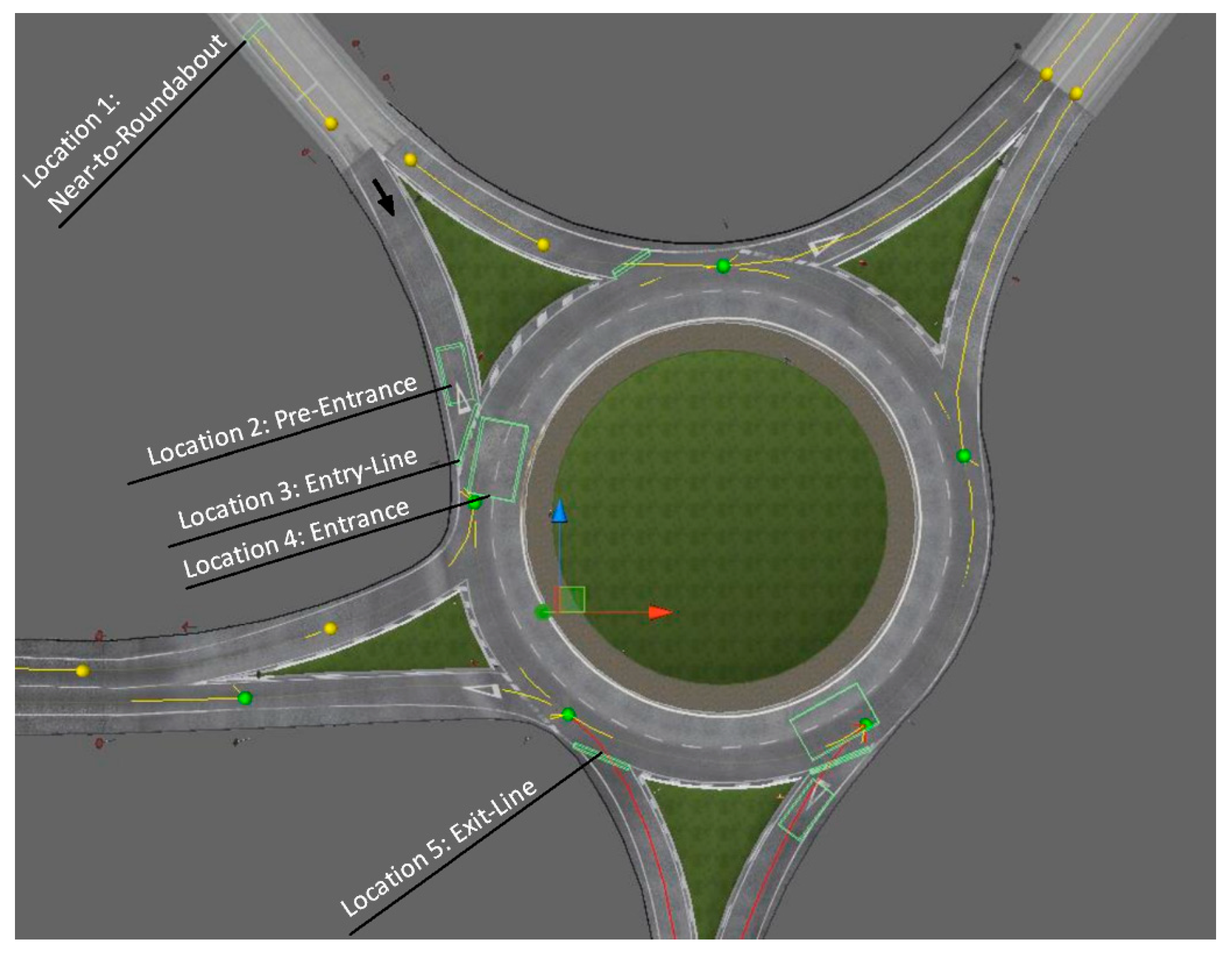
First, the Tobii Pro Lab software was used to output videos and corresponding CSV files. Second, we extracted information related to pupil diameter and fixation duration via the AOIs and for each location inside and outside roundabouts. As shown in Figure 3, all the measurements were made in five roundabout locations, namely, (1) 50 m behind the entry line, (2) pre-entrance, (3) at the entry line, (4) at the entrance, and (5) on the exit line. The total fixation duration for each AOI inside roundabouts was measured. For between-group comparisons (distracting vs. non-distracting conditions), multiple paired t-tests were conducted for matched samples to determine whether the measured parameters under distracting and non-distracting conditions significantly differed. Paired t-tests were chosen, as the observations were not independent of one another (e.g., each subject participated in both experiments.). For each participant, we essentially looked into differences in the values of fixation duration and eye pupil diameter and tested whether the mean of these differences was equal to zero. We also used a one-sided alternative that involved calculating the task load (TL) score in cases wherein such load was higher under distracted driving than under non-distracted driving:
H0: mean (TLdistracting − TLNon-distracting) = 0
Ha: mean (TLdistracting − TLNon-distracting) > 0
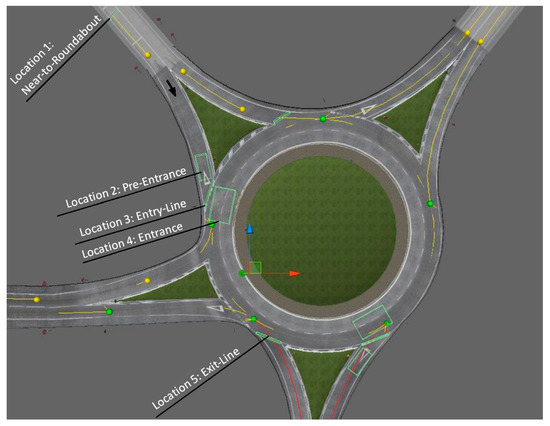
Figure 3.
Locations of interest inside and outside a roundabout.
With regard to the eye pupil size, we proposed a one-sided alternative wherein the median pupil dimeter (PD) under distracting conditions was higher than that under non-distracting conditions:
H0: mean (PDdistracting − PDNon-distracting) = 0
Ha: mean (PDdistracting − PDNon-distracting) > 0
A similar one-sided alternative was put forward for fixation duration, that is, a case wherein fixation duration (FD) under non-distracting conditions was higher than that under distracting conditions:
H0: mean (FDNon-distracting − FDdistracting) = 0
Ha: mean (FDNon-distracting − FDdistracting) > 0
Lastly, in order to realize whether there exist gender differences in fixation durations under distracting condition, the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test was used because of its robust properties in calculating unequal sample size between conditions [37].
H0: Median (FDMale) = Median (FDFemale)
Ha: Median (FDMale) ≠ Median (FDFemale)
To reject the null hypothesis, we considered a level of significance of 0.1 (one-sided) and used STATA (version 16) for this purpose.
3. Results
Between-Group Comparison of Eye Parameters in Roundabouts
A total of 13 participants were excluded from the analysis because their eye movements were not detected by the eye tracker. In location 1, there was a significant between-group difference in fixation durations when the drivers were looking at all the AOIs: front mirror (p = 0.0005), windshield (p = 0.020), driver-side mirror (p = 0.005), driver-side window (p = 0.030), passenger-side mirror (p = 0.034), and passenger-side window (0.003). In location 2, a significant between-group difference in fixation durations was found when the participants were looking at front mirror (p = 0.030), windshield (p = 0.040), driver-side mirror (p = 0.009), driver-side window (p = 0.014), and passenger-side window (p = 0.049). However, no such difference was found with respect to gazes on the passenger-side mirror. With reference to location 3, the between-group difference in fixation durations was significant only when the participants looked at front mirror (p = 0.080), windshield (p = 0.050), driver-side mirror (p = 0.085), and driver-side window (p = 0.077). As regards location 4, a significant between-group difference in fixation duration occurred only when the drivers looked at the driver-side mirror (p = 0.087). Finally, in the matter of location 5, the fixation durations differed significantly between the groups when the driver looked at mirror (p = 0.037), windshield (p = 0.006), and driver-side mirror (p = 0.088). Table 2 summarizes the results.

Table 2.
Paired t-test for the comparison of fixation durations under distracting and non-distracting situations.
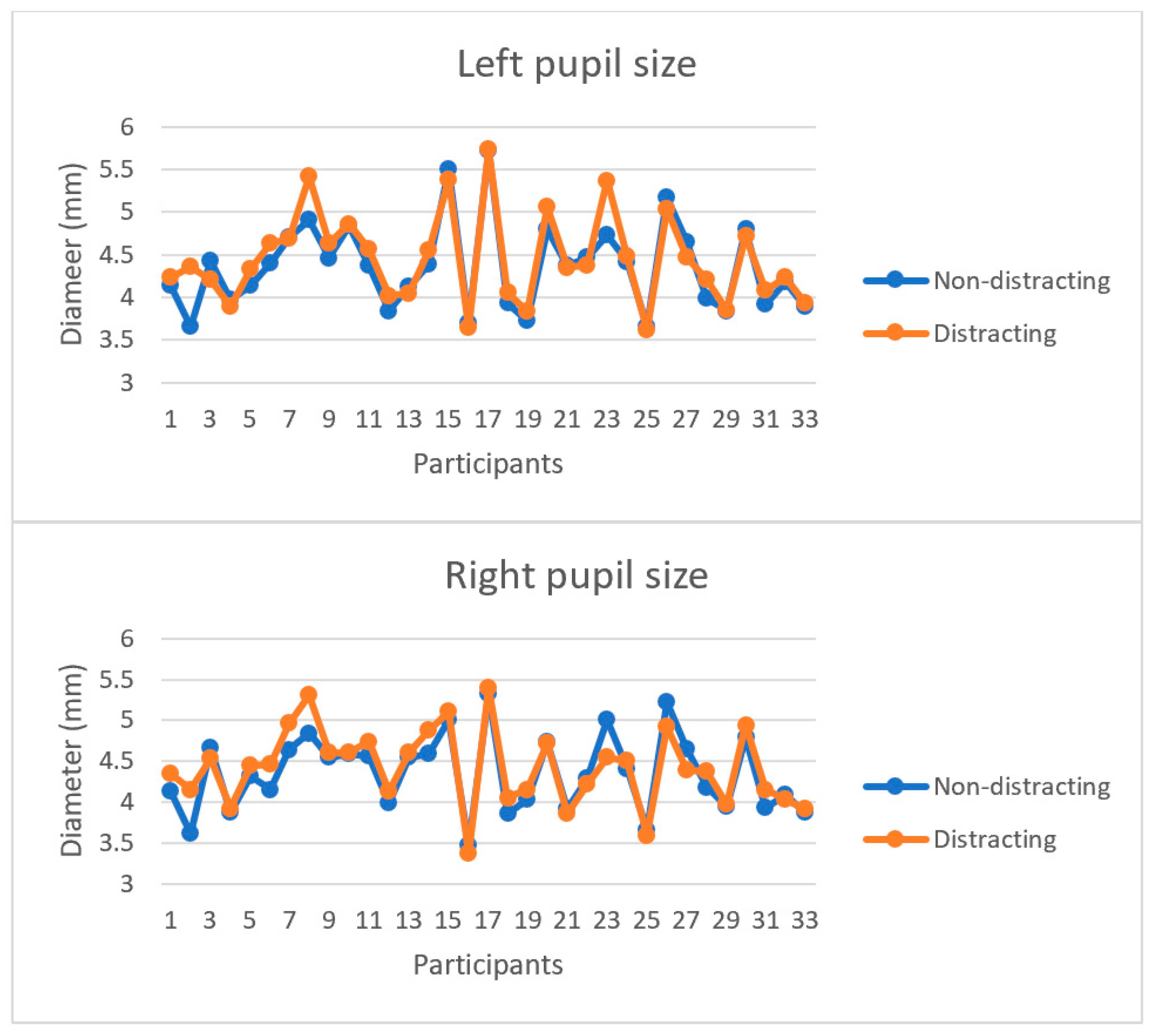
For each AOI inside roundabouts, a significant between-group difference in total fixation durations arose when the participants looked at front mirror (p = 0.0003), windshield (p = 0.005), driver-side mirror (p = 0.001), driver-side window (p = 0.010), and passenger-side window (0.012). As for pupil size (Figure 4), the results of the paired t-test showed that the median left (p = 0.02) and right (p = 0.04) pupil diameters increased significantly. In contrast, for each AOI inside roundabouts, there was no significant difference between male and female participants in fixation duration under distracting condition.
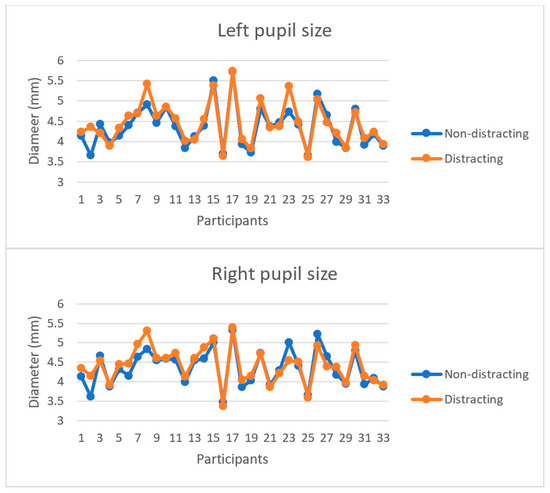
Figure 4.
Comparisons of pupil size under distracting and non-distracting conditions.
4. Discussion
This study investigated the effects of cell phone-induced distraction on drivers’ eye movements inside and outside roundabouts. For this purpose, two driving simulator scenarios featuring distracting and non-distracting conditions were featured in experiments.
The analysis of the drivers’ eye movements suggested that the participants drove less cautiously when they were approaching roundabouts (location 1), considering the reduced fixation durations in all AOIs as a result of cell phone-induced distraction. Similar trends for all the AOIs except the passenger-side mirror were observed in location 2, where the drivers were near entry lines. This similarity can be explained by the attempts of most of the drivers to exit the left lane and keep right when approaching an entry line and before entering a roundabout. Moreover, the majority of the drivers involved in the experimented reduced fixation duration on an entry lane approaching a roundabout (location 3), especially for the driver-side window. This finding is critical, as it indicates that the drivers paid reduced attention to oncoming traffic in roundabouts, which can result in entering-circulating crashes. In contrast, in location 4, no significant change in fixation duration was observed with respect to the driver-side window, meaning that the drivers started paying attention to oncoming traffic only when their vehicles were fully inside the roundabout. This behavior can elevate the risk of side-swipe crashes. As for location 5, a significant drop in fixation duration in connection to front mirror, windshield, and driver-side window was found, thereby likely increasing the risk of rear-end and exiting-circulating crashes when drivers exit a roundabout. Finally, comparing distracting and non-distracting scenarios highlighted that the total fixation duration inside roundabouts decreased by 36% on average, thus posing a significant crash risk. The participants who drove in roundabouts under distracting conditions exhibited wider eye pupil diameters than those shown by those who drove in roundabouts under non-distracting conditions, which is consistent with the findings of [36].
To tackle distracted driving challenges on roadways, especially on roundabouts, various effective countermeasures are recommended. Awareness campaigns are proven strategies to educate about distracted driving. According to reference [38], a one week distracted driving awareness campaign at a large university, which consisted of mass emails and group discussions with students, substantially improved distracted driving behaviors among students. In addition, legislative countermeasures such as cell phone use bans were associated with reductions in observed handheld phone use among young drivers [39]. As for technology countermeasures, the most current technology is phone-based blocking applications, which often use the phone’s GPS to track whether the user is in a moving vehicle. There are many other technology-based approaches that monitor driver’s performance [40], eye behavior [41], and phone usage [42] and provide real-time alerts to drivers aimed at reducing distracted driving.
5. Conclusions
The results on driver performance and eye movements indicated that between-group differences in fixation durations and eye pupil diameters were significant. That is, the participants drove less cautiously near and inside roundabouts when they were exposed to cell phone-induced distraction. Our exploration into the drivers’ behavior during travel on a roundabout under distracting and non-distracting scenarios showed that the drivers were compelled to exert more effort to keep their eyes on the road as they used their cell phones.
The findings can be used by decision makers as reference in developing distraction-specific technologies so that cell phones cannot be used by drivers on roadways, especially when they pass through roundabouts. The results can also serve as a guide in the establishment of test methods designed specifically to compare eye glance metrics for each AOI with accepted criteria for evaluating whether a task excessively interferes with driver attention and becomes unsuitable for a driver to perform while driving.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A., C.A.C.O. and S.G.-H.; methodology, A.A., S.G.-H. and C.A.C.O.; software, J.M.E. and C.A.C.O.; validation, S.G.-H. and C.A.C.O.; formal analysis, A.A.; investigation, A.A., C.A.C.O. and J.M.E.; resources, J.M.E. and S.G.-H.; data curation, A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, A.A., C.A.C.O., J.M.E., M.Á.M. and S.G.-H.; project administration, S.G.-H.; funding acquisition, S.G.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by FEDER European Regional Development Fund (Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional—Junta de Castilla y León), grant number BU300P18.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Burgos University (protocol code IR 17/2020 on 28 May 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Modino, M. El 80% de los Conductores Comete un Error al Circular por una Rotonda. Available online: https://www.veomotor.com/seguridad-vial/2019/el-80-de-los-conductores-comete-un-error-al-circular-por-una-rotonda/ (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- DGT. Las Principales Cifras de la Siniestralidad Vial; Dirección General de Tráfico: Madrid, Spain, 2019.
- Arndt, O.; Troutbeck, R.J. Relationship between roundabout geometry and accident rates. Transp. Res. Circ. 1998, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Polders, E.; Daniels, S.; Casters, W.; Brijs, T. Identifying crash patterns on roundabouts. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2015, 16, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.W.; Rodegerdts, L.; Scarborough, W.; Kittelson, W.; Troutbeck, R.; Brilon, W.; Bondizio, L.; Courage, K.; Kyte, M.; Mason, J. Roundabouts: An Informational Guide; Federal Highway Administration: McLean, VA, USA, 2000.
- Burdett, B.; Alsghan, I.; Chiu, L.-H.; Bill, A.R.; Noyce, D.A. Analysis of rear-end collisions at roundabout approaches. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2585, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdett, B.; Bill, A.R.; Noyce, D.A. Evaluation of roundabout-related single-vehicle crashes. Transp. Res. Rec. 2017, 2637, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, D.G.; Tison, J.; Chaudhary, N.K.; McCartt, A.T.; Casanova-Powell, T.D. The influence of roadway situation, other contextual factors, and driver characteristics on the prevalence of driver secondary behaviors. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2016, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.; Murphy, S. The effects of mobile phone use on pedestrian crossing behaviour at signalised and unsignalised intersections. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2007, 39, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, H.; Feliciani, C.; Nishiyama, Y.; Nishinari, K. Mutual anticipation can contribute to self-organization in human crowds. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.; Guvensan, M.A.; Yavuz, A.G.; Karalurt, Y. Driver behavior analysis for safe driving: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 16, 3017–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, S.P.; Stevenson, M.R.; Woodward, M. The impact of driver distraction on road safety: Results from a representative survey in two Australian states. Inj. Prev. 2006, 12, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westlake, E.J.; Boyle, L.N. Perceptions of driver distraction among teenage drivers. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2012, 15, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, C.; Harland, K.K.; McGehee, D.V. Examining teen driver crashes and the prevalence of distraction: Recent trends, 2007–2015. J. Saf. Res. 2018, 64, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Calvi, A.; Ferrante, C.; Ciampoli, L.B. Assessment of Driver Distraction Caused by Social Networking Activities Using the Smartphone: A Driving Simulator Study. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–20 July 2020; pp. 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar, J.G.; Brown, T.L. Matters of State: Examining the effectiveness of lane departure warnings as a function of driver distraction. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2020, 71, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.S.; Suzuki, T.; Aoki, H. Evaluating driver cognitive distraction by eye tracking: From simulator to driving. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2020, 4, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Salehi, M.; Mackellar, G. Detecting Driver’s Distraction using Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Network. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11839. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, P.; Velaga, N.R. Effects of phone use on driving performance: A comparative analysis of young and professional drivers. Saf. Sci. 2019, 111, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L.; Drew, F.A. Profiles in driver distraction: Effects of cell phone conversations on younger and older drivers. Hum. Fact. 2004, 46, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Xiang, W.; Wong, S.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Hao, W. Effects of hands-free cellular phone conversational cognitive tasks on driving stability based on driving simulation experiment. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 58, 264–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Ou, Y.-K. Effects of age and the use of hands-free cellular phones on driving behavior and task performance. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2011, 12, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papantoniou, P. Structural equation model analysis for the evaluation of overall driving performance: A driving simulator study focusing on driver distraction. Traffic Inj. Prev. 2018, 19, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caird, J.K.; Chisholm, S.; Lockhart, J. Do in-vehicle advanced signs enhance older and younger drivers’ intersection performance? Driving simulation and eye movement results. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2008, 66, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Sui, X.; Wang, N.; Qu, X.; Green, P. Drivers’ visual scanning behavior at signalized and unsignalized intersections: A naturalistic driving study in China. J. Saf. Res. 2019, 71, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Oviedo-Trespalacios, O.; Rakotonirainy, A. Drivers’ gap acceptance behaviours at intersections: A driving simulator study to understand the impact of mobile phone visual-manual interactions. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 138, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, D.S.; Patil, G.R. Response of major road drivers to aggressive maneuvering of the minor road drivers at unsignalized intersections: A driving simulator study. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 52, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tey, L.-S.; Ferreira, L.; Wallace, A. Measuring driver responses at railway level crossings. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2011, 43, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tung, L.-W.; Khattak, A. Distracted motor vehicle driving at highway–rail grade crossings. Transp. Res. Rec. 2015, 2476, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Oviedo-Trespalacios, O.; Debnath, A.K.; Washington, S. Gap acceptance behavior of mobile phone–distracted drivers at roundabouts. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2602, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, N.; Hayashi, M. Analysis of Driving Behaviors at Roundabout Intersections by Using Driving Simulator. In Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and Services; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Niu, Q.; Hou, H.; Xian, H.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D. Driver cognitive distraction detection using driving performance measures. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Boyle, L.N. Age-related differences in visual scanning at median-divided highway intersections in rural areas. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2009, 41, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoser, M.R.; Fisher, D.L. The effect of active versus passive training strategies on improving older drivers’ scanning in intersections. Hum. Fact. 2009, 51, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoser, M.R.; Pollatsek, A.; Fisher, D.L.; Williams, C.C. Comparing the glance patterns of older versus younger experienced drivers: Scanning for hazards while approaching and entering the intersection. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2013, 16, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, K.; Ling, F.; Feng, Z.; Ma, C.; Kumfer, W.; Shao, C.; Wang, K. Effects of mobile phone distraction on pedestrians’ crossing behavior and visual attention allocation at a signalized intersection: An outdoor experimental study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 115, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahardjo, A.; Nasia, A.A.; Adiatman, M.; Maharani, D. Efficacy of a toothpaste containing 5% potassium nitrate in desensitizing dentin hypersensitivity. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 345–347. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, B.; Zangbar, B.; Bains, S.; Kulvatunyou, N.; Khalil, M.; Mahmoud, D.; Friese, R.S.; O’Keeffe, T.; Pandit, V.; Rhee, P. Injury prevention programs against distracted driving: Are they effective? Traffic Inj. Prev. 2016, 17, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudisill, T.M.; Smith, G.; Chu, H.; Zhu, M. Cellphone legislation and self-reported behaviors among subgroups of adolescent US drivers. J. Adolesc. Health 2018, 62, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, L.; Fang, Y.; Fang, X.; Huang, X. A machine learning-based defensive alerting system against reckless driving in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 12227–12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walavakar, A.; Singh, S.; Salian, R.; Shrivastava, V. Driver Distraction Monitoring and Alerting System. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Advances in Information Technology (ICAIT), Chikmagalur, India, 24–27 July 2019; pp. 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Berri, R.A.; Silva, A.G.; Parpinelli, R.S.; Girardi, E.; Arthur, R. A pattern recognition system for detecting use of mobile phones while driving. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–8 January 2014; pp. 411–418. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).