Evaluation of Outdoor Particle Infiltration into Classrooms Considering Air Leakage and Other Building Characteristics in Korean Schools
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Description of Classrooms
2.3. Air Leakage Testing Method
2.4. Outdoor Particle Infiltration
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.5.1. Normality Test
2.5.2. Correlation Coefficient
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Building Characteristic of Classrooms
3.2. Air Leakage Characteristics of Classroom
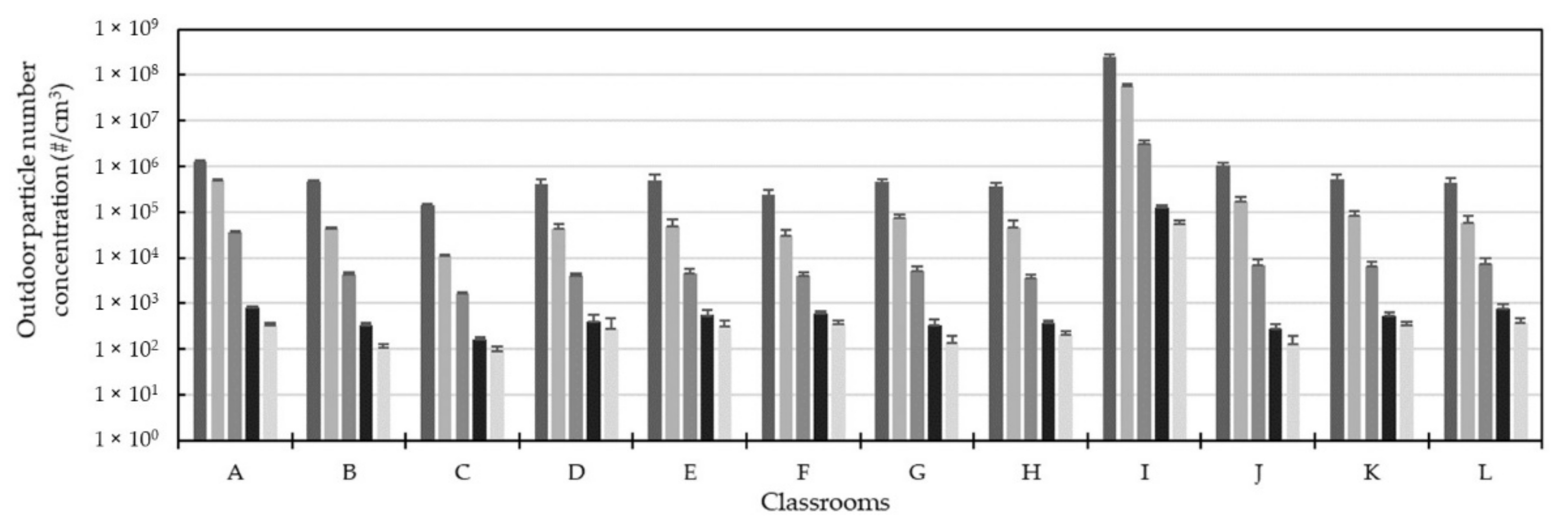
3.3. Outdoor Particle Infiltration
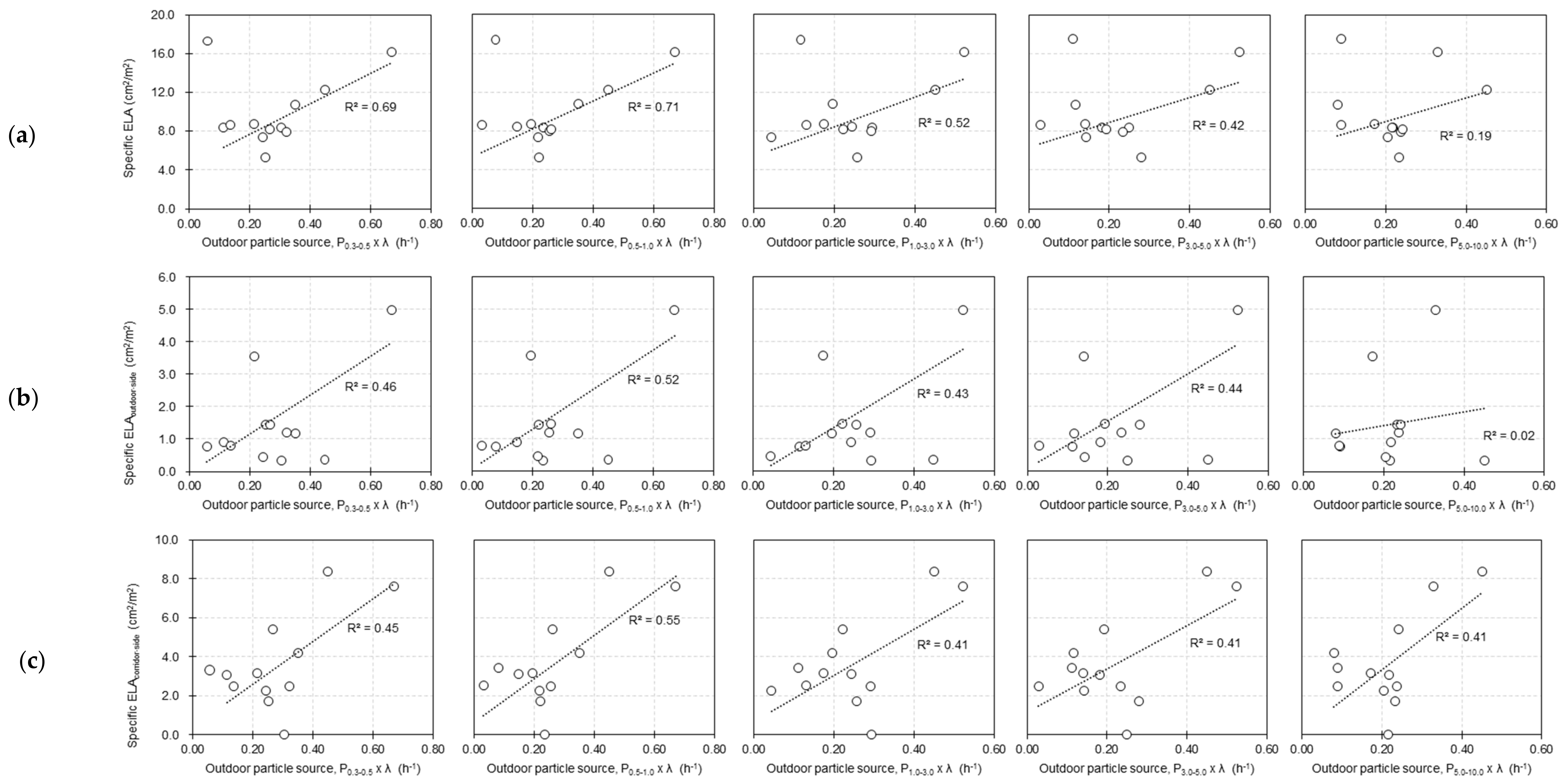
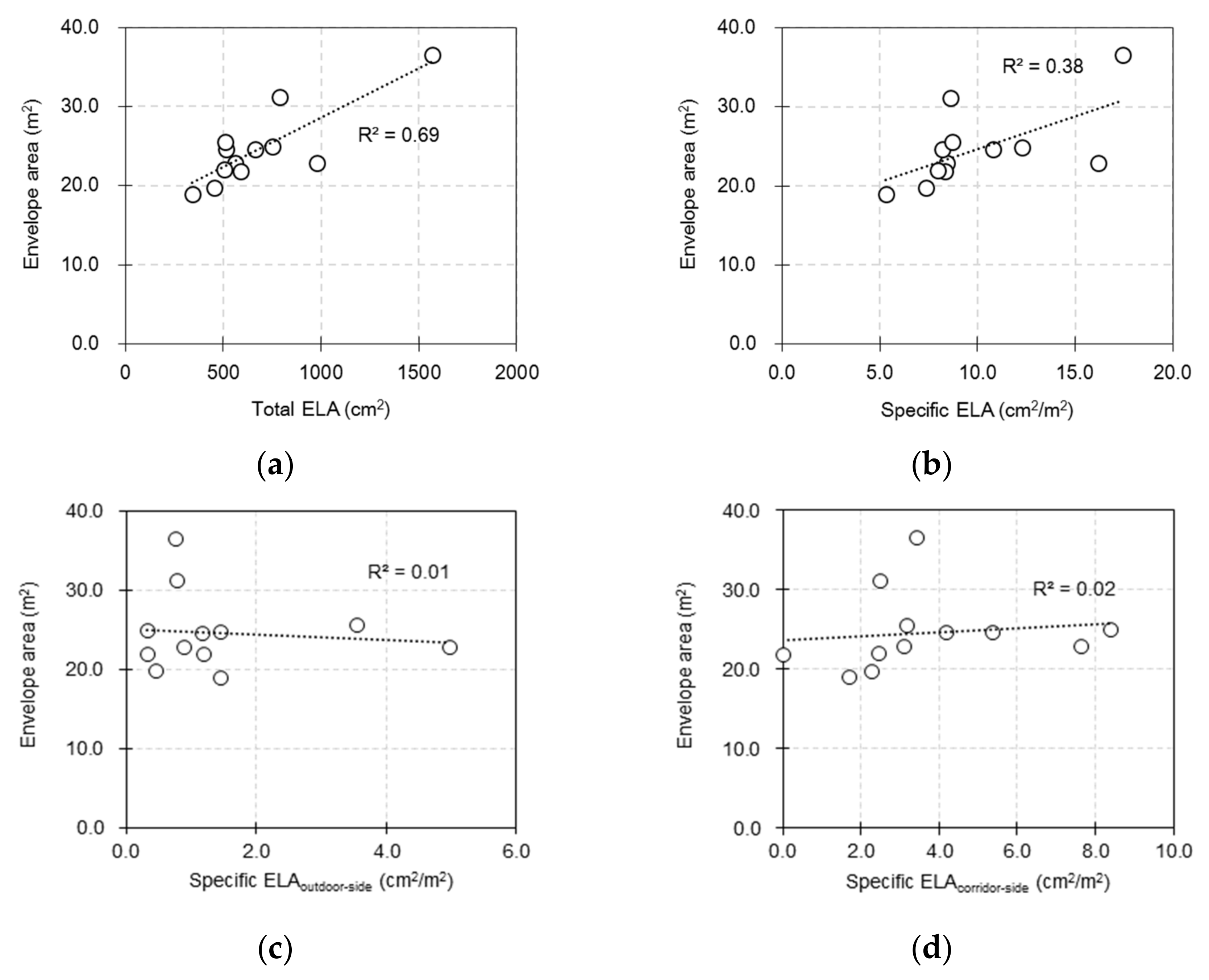
3.4. Relationship between Air Leakage Characteristics, Other Building Characteristics, and Outdoor Particle Infiltration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Particle Size (μm) | Kolmogorov-Smirnov | Shapiro-Wilk | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | Significance Level (α) | T | Significance Level (α) | ||||
| Penetration coefficient (P) | 0.3–0.5 | 0.175 | 0.200 * | 0.855 | 0.042 | 0.977 | 0.058 |
| 0.5–1.0 | 0.170 | 0.200 * | 0.914 | 0.238 | 0.505 | 1.019 | |
| 1.0–3.0 | 0.099 | 0.200 * | 0.981 | 0.986 | 0.132 | 0.474 | |
| 3.0–5.0 | 0.149 | 0.200 * | 0.958 | 0.761 | 0.181 | 0.392 | |
| 5.0–10.0 | 0.141 | 0.200 * | 0.947 | 0.598 | 0.334 | 1.012 | |
| Deposition loss rate (k) | 0.3–0.5 | 0.163 | 0.200 * | 0.933 | 0.418 | 0.727 | 0.357 |
| 0.5–1.0 | 0.171 | 0.200 * | 0.932 | 0.401 | 0.524 | 0.963 | |
| 1.0–3.0 | 0.140 | 0.200 * | 0.963 | 0.827 | 0.578 | 0.111 | |
| 3.0–5.0 | 0.121 | 0.200 * | 0.975 | 0.953 | 0.217 | 0.605 | |
| 5.0–10.0 | 0.144 | 0.200 * | 0.929 | 0.367 | 0.808 | 0.291 | |
References
- Pope, C.A., III; Ezzati, M.; Dockery, D.W. Fine-Particulate Air Pollution and Life Expectancy in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzivian, T. Outdoor Air Pollution and Asthma in Children. J. Asthma 2011, 48, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendell, M.J.; Heath, G.A. Do Indoor Pollutants and Thermal Conditions in Schools Influence Student Performance? A Critical Review of the Literature. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The Effects of Air Pollution on Children’s Health and Development: A Review of the Evidence; WHO: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Diapouli, E.; Chaloulakou, A.; Spyrellis, N. Indoor and Outdoor Particulate Matter Concentrations at Schools in the Athens Area. Indoor Built Environ. 2007, 16, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranger, M.; Potgieter-Vermaak, S.S.; Van Grieken, R. Characterization of indoor air quality in primary schools in Antwerp, Belgium. Indoor Air 2008, 18, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.M.; Canha, N.; Silva, A.; Freitas, M.C.; Pegas, P.; Alves, C.; Evtyugina, M.; Pio, C.A. Children exposure to atmospheric particles in indoor of Lisbon primary schools. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7594–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.T.; Alleman, L.Y.; Coddeville, P.; Galloo, J.C. Indoor particle dynamics in schools: Determination of air exchange rate, size-resolved particle deposition rate and penetration factor in real-life conditions. Indoor Built Environ. 2017, 26, 1335–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, T.J.; Park, M.J.; Oh, H.; Jo, Y.M. Effects of air cleaners and school characteristics on classroom concentrations of particulate matter in 34 elementary schools in Korea. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 106437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Dufresene, A.; Infante-Rivard, C. Indoor ultra-fine particles and childhood asthma: Exploring a potential concern. Indoor Air 2007, 17, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wa, Z.; Ferm, M.; Liang, Y.; Norback, D. Asthmatic Symptoms among Pupils in Relation to Winter Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution in Schools in Taiyuan, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, V.; Timperio, A.; Salmon, J.; Hume, C.; Baur, L.A.; Crawford, D. Predictors of time spent outdoors among children: 5-year longitudinal findings. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2010, 64, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, R.; Islam, T.; Shankardass, K.; Jerrett, M.; Lurmann, F.; Gililand, F.; Gauderman, J.; Avol, E. Childhood Incident Asthma and Traffic-Related Air Pollution at Home and School. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elbayoumi, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Yusof, N.F.F.M.; Madhoun, W.A. Spatial and seasonal variation of particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in Middle Eastern classrooms. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, S. Association of Traffic-Related Air pollution with Children’s Neurobehavioral Functions in Quanzhou, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohai, P.; Kweon, B.S.; Lee, S.; Ard, K. Air Pollution around Schools Is Linked To Poorer Student Health and Academic Performance. Health Aff. 2011, 30, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebelt, S.T.; Wilson, W.E.; Brauer, M. Exposure to Ambient and Nonambient Components of Particulate Matter: A Comparison of Health Effects. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köenig, J.Q.; Mar, T.F.; Allen, R.W.; Jansen, K.; Lumley, T.; Sullivan, J.H.; Trenga, C.A.; Larson, T.V.; Liu, L.-J. Pulmonary Effects of Indoor and Outdoor-Generated Particles in Children with Asthma. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwozdziak, A.; Sówka, I.; Krupinska, B.; Zwozdziak, J.; Nych, A. Infiltration or indoor sources as determinants of the elemental composition of particulate matter inside a school in Wroc1aw, Poland? Build. Environ. 2013, 66, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, E.; Suh, E.H.; Catalano, P.; Koutrakis, P. Relative Contribution of Outdoor and Indoor Particle Sources to Indoor Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3579–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y.H.; Wan, M.P.; Cheng, C.K. Penetration coefficient and deposition rate as a function of particle size in non-smoking naturally ventilated residences. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Air infiltration rate distributions of residences in Beijing. Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Kang, D.H. Infiltration of Ambient PM2.5 through Building Envelope in Apartment Housing Units in Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.H.; Kang, D.H. Indoor/Outdoor Relationships of Airborne Particles under Controlled Pressure Difference across the Building Envelope in Korean Multifamily Apartments. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, B.; Siegel, J.A. Penetration of ambient submicron particles into single-family residences and associations with building characteristics. Indoor Air 2012, 22, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, F.; Du, S. Ventilation effect on different position of classrooms in “line” type teaching building. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 886–902. [Google Scholar]
- Vellingiri, K.; Kim, K.; Ma, C.; Kang, C.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.; Brown, R.J.C. Ambient particulate matter in a central urban area of Seoul, Korea. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E779. Standard Test Method for Determining Air Leakage Rate by Fan Pressurization; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Lee, B.H.; Yee, S.W.; Kang, D.H.; Yeo, M.S.; Kim, K.W. Multi-zone simulation of outdoor particle penetration and transport in a multi-story building. Build Simul. 2017, 10, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E741–2011. Standard Test Method for Determining Air Change in a Single Zone by means of a Tracer Gas Dilution; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- Pietrogrande, M.C.; Casari, L.; Demaria, G.; Russo, M. Indoor Air Quality in Domestic Environments during Periods Close to Italian COVID-19 Lockdown. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, R.B.; Greenwell, D.J.; Sparks, L.E.; Guo, Z.; Tucker, W.G.; Fortmann, R.; Whitfield, C. Penetration of Ambient Fine Particles into the Indoor Environment. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.M.; Suh, H.H.; Catalano, P.J.; Koutrakis, P. Using Time-and Size-Resolved Particle Data to Quantify Indoor Penetration and Deposition Behavior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Quakenboss, J.; Rodes, C. Continuous measurements of particles, PAH, and CO in an occupied townhouse in Reston, VA. In AWMA/EPA Symposium on the Measurement of Toxic and Related Air Pollutants; EPA/600/J-84/312, 860–871; Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, A.C.K.; Nazaroff, W.W. Modeling indoor particle deposition from turbulent flow onto smooth surfaces. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, J. Particle deposition in indoor environments: Analysis of influencing factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, T.L.; Layton, D.W. Deposition, resuspension and penetration of particles within a residence. Atmos Environ. 1995, 29, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.L.; Nazaroff, W.W. Modeling pollutant penetration across building envelops. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4451–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.L.; Nazaroff, W.W. Particle Penetration through Building Cracks. Aerosol. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
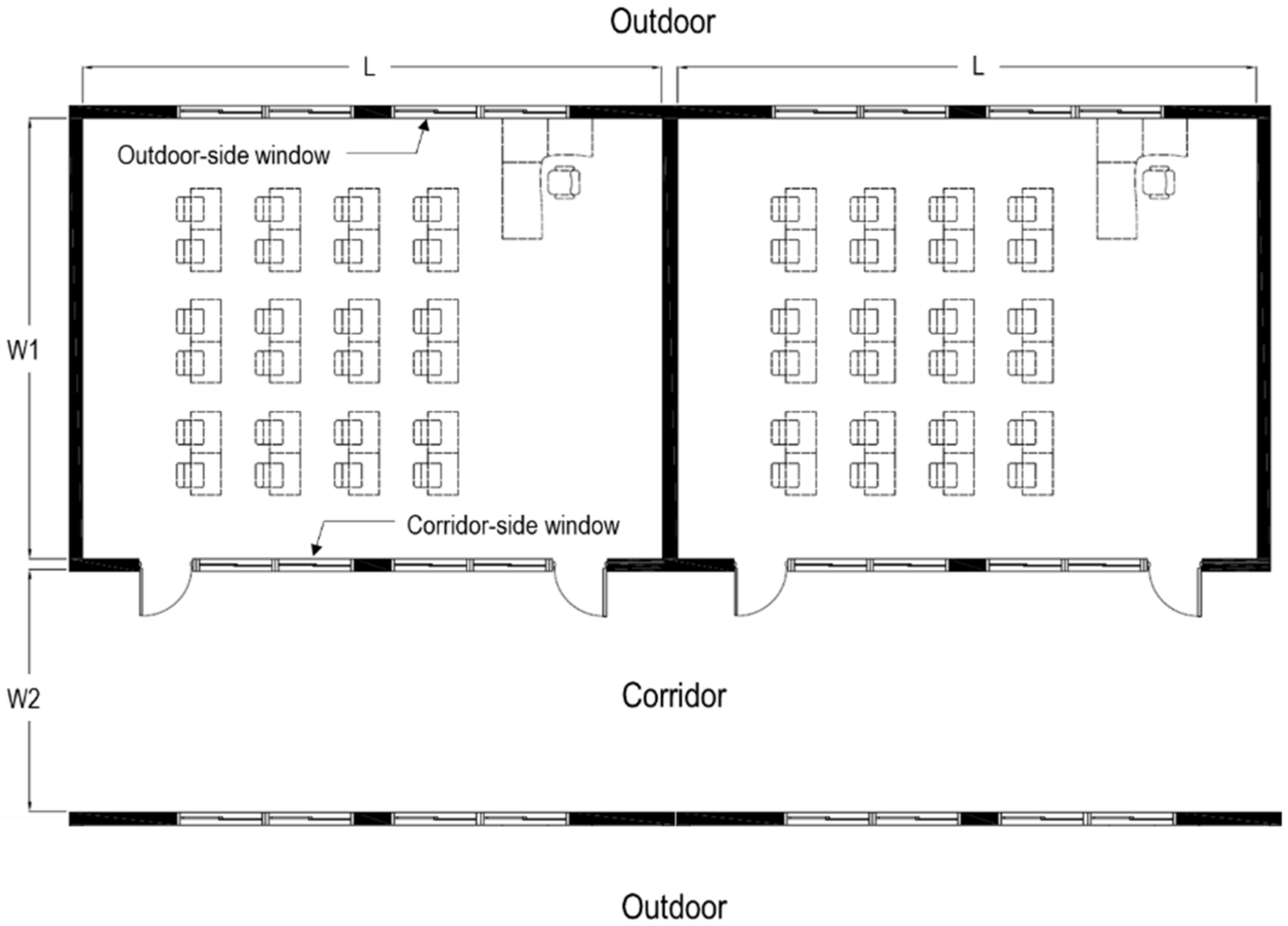
| Class Rooms | Orientation | Built Year (Years) | Renovation Year (Years) | Length, L (m) | Width, W1 (m) | Floor Area (m2) | Height (m) | Floor Level | Mechanical Ventilation | The Number of Students in a Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | SW | 1988 | 2010 | 8.8 | 6.9 | 60.7 | 2.6 | 3 | None | 24 |
| B | S | 1937 | 1993 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 61.6 | 2.8 | 3 | None | 16 |
| C | S | 1989 | 2019 | 8.9 | 6.9 | 61.4 | 2.8 | 3 | None | 22 |
| D | SE | 1961 | 2000 | 8.8 | 7.6 | 66.9 | 2.6 | 2 | None | 20 |
| E | SE | 1944 | 2010 | 8.4 | 8.4 | 70.6 | 2.6 | 1 | Installed (HVAC) | 23 |
| F | SE | 1971 | None | 8.8 | 7.2 | 63.4 | 2.5 | 2 | None | 25 |
| G | S | 1967 | 2014 | 7.9 | 7.8 | 61.6 | 2.5 | 3 | Installed (HVAC) | 26 |
| H | SW | 1937 | 2006 | 8.8 | 7.3 | 64.2 | 2.6 | 4 | None | 26 |
| I | SW | 1983 | 1992 | 8.5 | 7.4 | 62.9 | 2.9 | 1 | None | 28 |
| J | SE | 1944 | 2014 | 8.8 | 7.0 | 58.8 | 2.9 | 2 | Installed (HRV) | 25 |
| K | E | 1998 | None | 13.0 | 6.9 | 89.8 | 2.8 | 1 | Installed (HVAC) | 36 |
| L | S | 1965 | None | 10.8 | 8.5 | 91.8 | 2.9 | 2 | Installed (HRV) | 24 |
| Classrooms | Built Year (Years) | Mechanical Ventilation | Envelope Area (m2) | Window Area (m2) | Material of the Window Frame | Material of the Door | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outdoor Side | Corridor Side | Outdoor Side | Corridor Side | Frame | Panel | ||||
| A | 1988 | None | 22.9 | 8.6 | 6.7 | PVC | Wood | aluminum | Wood |
| B | 1937 | None | 24.6 | 10.4 | 7.4 | PVC | PVC | aluminum | |
| C | 1989 | None | 24.9 | 8.9 | 6.7 | PVC | Wood | aluminum | Wood |
| D | 1961 | None | 22.9 | 13.0 | 6.2 | PVC, Steel | Wood | Wood | |
| E | 1944 | Installed (HVAC) | 21.8 | 9.6 | 0 | Steel | None | Wood | |
| F | 1971 | None | 22.0 | 14.7 | 5.1 | PVC | Steel | Steel | |
| G | 1967 | Installed (HVAC) | 19.8 | 13.4 | 4.8 | PVC, Steel | PVC, Steel | PVC | |
| H | 1937 | None | 19.0 | 15.1 | 4.5 | PVC, Aluminum | Wood | Wood | |
| I | 1983 | None | 24.7 | 13.3 | 6.7 | Steel | Wood | Wood | |
| J | 1944 | Installed (HRV) | 25.5 | 14.2 | 5.5 | PVC | Wood | Wood | |
| K | 1998 | Installed (HVAC) | 36.5 | 15.6 | 2.4 | PVC, Aluminum | PVC | PVC | |
| L | 1965 | Installed (HRV) | 31.2 | 12.0 | 3.7 | PVC, Aluminum | PVC | Wood | |
| Classrooms | C (m3·h−1·Pa-n) | n (-) | ACH50 (h−1) | ELA (cm2) | Specific ELA (cm2/m2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Outdoor Side | Corridor Side | Other | Total | Outdoor Side | Corridor Side | ||||
| A | 410.2 | 0.58 | 24.8 | 981.2 | 301.7 | 462.6 | 216.9 | 16.2 | 5.0 | 7.6 |
| B | 264.8 | 0.61 | 16.7 | 663.7 | 72.0 | 257.5 | 334.3 | 10.8 | 1.2 | 4.2 |
| C | 295.4 | 0.62 | 19.6 | 752.7 | 20.4 | 514.9 | 217.4 | 12.3 | 0.3 | 8.4 |
| D | 212.2 | 0.65 | 15.6 | 562.9 | 60.3 | 206.9 | 295.7 | 8.4 | 0.9 | 3.1 |
| E | 203.7 | 0.71 | 18.1 | 589.3 | 23.0 | 175.6 | 390.7 | 8.3 | 0.3 | 2.5 |
| F | 200.4 | 0.61 | 14.0 | 505.3 | 76.4 | 156.7 | 272.2 | 8.0 | 1.2 | 2.5 |
| G | 161.0 | 0.70 | 15.9 | 453.9 | 28.0 | 140.2 | 285.7 | 7.4 | 0.5 | 2.3 |
| H | 133.9 | 0.62 | 9.1 | 340.8 | 93.0 | 110.5 | 137.3 | 5.3 | 1.4 | 1.7 |
| I | 209.4 | 0.60 | 11.8 | 514.8 | 91.7 | 339.0 | 84.0 | 8.2 | 1.5 | 5.4 |
| J | 222.4 | 0.55 | 11.3 | 511.6 | 209.3 | 186.2 | 116.1 | 8.7 | 3.6 | 3.2 |
| K | 671.3 | 0.56 | 22.5 | 1566.9 | 69.1 | 309.3 | 1188.5 | 17.4 | 0.8 | 3.4 |
| L | 322.8 | 0.59 | 12.3 | 787.3 | 72.3 | 228.9 | 486.1 | 8.6 | 0.8 | 2.5 |
| Classrooms | Penetration Coefficient, P a | Air Exchange Rate a, λ (h−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3–0.5 μm | 0.5–1.0 μm | 1.0–3.0 μm | 3.0–5.0 μm | 5.0–10.0 μm | ||
| A b | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.49 | 0.67 |
| B b | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.35 |
| C b | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.45 |
| D | 0.26 ± 0.20 | 0.32 ± 0.18 | 0.51 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.11 | 0.43 ± 0.16 | 0.48 ± 0.10 |
| E | 0.71 ± 0.27 | 0.55 ± 0.28 | 0.71 ± 0.27 | 0.61 ± 0.33 | 0.52 ± 0.23 | 0.42 ± 0.05 |
| F | 0.68 ± 0.31 | 0.50 ± 0.19 | 0.47 ± 0.19 | 0.35 ± 0.24 | 0.37 ± 0.20 | 0.54 ± 0.28 |
| G | 1.00 ± 0.00 | 0.88 ± 0.16 | 0.18 ± 0.26 | 0.58 ± 0.31 | 0.83 ± 0.24 | 0.25 ± 0.01 |
| H | 0.83 ± 0.29 | 0.73 ± 0.39 | 0.89 ± 0.18 | 0.95 ± 0.09 | 0.77 ± 0.40 | 0.30 ± 0.09 |
| I | 0.77 ± 0.39 | 0.76 ± 0.41 | 0.63 ± 0.35 | 0.56 ± 0.33 | 0.70 ± 0.28 | 0.36 ± 0.06 |
| J | 0.88 ± 0.20 | 0.81 ± 0.19 | 0.72 ± 0.27 | 0.59 ± 0.36 | 0.72 ± 0.28 | 0.25 ± 0.03 |
| K | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 0.50 ± 0.15 | 0.29 ± 0.18 | 0.25 ± 0.19 | 0.53 ± 0.39 |
| L | 0.54 ± 0.65 | 0.12 ± 0.13 | 0.43 ± 0.49 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.31 ± 0.41 | 0.39 ± 0.19 |
| AM c | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.51 | 0.41 |
| s.d c | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.25 | 0.13 |
| GM c | 2.05 | 1.87 | 1.79 | 1.65 | 1.71 | 1.50 |
| GSD c | 1.41 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 1.38 | 1.36 | 1.20 |
| Classrooms | Deposition Loss Rate (k) a | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3–0.5 μm | 0.5–1.0 μm | 1.0–3.0 μm | 3.0–5.0 μm | 5.0–10.0 μm | |
| A b | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.89 | 0.89 |
| B b | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.53 | 0.70 | 0.84 |
| C b | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 0.85 | 1.25 |
| D | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.06 | 0.46 ± 0.14 | 1.05 ± 0.19 |
| E | 0.34 ± 0.27 | 0.21 ± 0.20 | 0.35 ± 0.30 | 1.03 ± 0.57 | 1.29 ± 0.36 |
| F | 0.18 ± 0.15 | 0.14 ± 0.12 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.70 ± 0.25 | 1.22 ± 0.32 |
| G | 0.26 ± 0.16 | 0.33 ± 0.11 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.04 |
| H | 0.04 ± 0.07 | 0.06 ± 0.10 | 0.13 ± 0.10 | 0.45 ± 0.14 | 0.47 ± 0.42 |
| I | 0.38 ± 0.47 | 0.46 ± 0.50 | 0.69 ± 0.24 | 0.95 ± 0.78 | 1.26 ± 0.61 |
| J | 0.61 ± 0.12 | 0.68 ± 0.13 | 0.34 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.05 | 1.07 ± 0.32 |
| K | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.29 ± 0.00 | 0.60 ± 0.28 | 0.96 ± 0.43 |
| L | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.64 ± 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.12 | 0.16 ± 0.16 | 1.01 ± 0.34 |
| AM c | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 1.03 |
| s.d c | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.25 |
| GM c | 1.30 | 1.34 | 1.31 | 1.88 | 2.75 |
| GSD c | 1.31 | 1.34 | 1.24 | 1.47 | 1.48 |
| Penetration Coefficient (P) | Deposition Loss Rate (k) | Outdoor Particle Source (P × λ) | AER | C | n | ACH50 | Total ELA | Specific Total ELA | Specific ELAc | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 –0.5 | 0.5 –1.0 | 1.0 –3.0 | 3.0 –5.0 | 5.0 –10.0 | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.5 –1.0 | 1.0 –3.0 | 3.0 –5.0 | 5.0 –10.0 | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.5 –1.0 | 1.0 –3.0 | 3.0 –5.0 | 5.0 –10.0 | |||||||||
| k | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.613 * | 0.615 * | 0.245 | 0.100 | 0.164 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.5 –1.0 | 0.451 | 0.284 | −0.015 | −0.289 | −0.120 | 0.748 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1.0 –3.0 | 0.377 | 0.468 | 0.323 | 0.127 | 0.027 | 0.653 * | 0.526 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 3.0 –5.0 | 0.292 | 0.465 | 0.471 | 0.433 | 0.141 | 0.361 | −0.092 | 0.692 * | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 5.0 –10.0 | −0.186 | −0.180 | 0.134 | −0.162 | −0.039 | 0.246 | 0.046 | 0.408 | 0.543 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| P × λ | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.733 ** | 0.733 ** | 0.561 | 0.574 | 0.256 | 0.264 | 0.112 | 0.398 | 0.590 * | 0.050 | 1 | |||||||||||
| 0.5 –1.0 | 0.676 * | 0.784 ** | 0.557 | 0.614 * | 0.269 | 0.268 | 0.048 | 0.415 | 0.621 * | 0.024 | 0.970 ** | 1 | |||||||||||
| 1.0 –3.0 | 0.342 | 0.422 | 0.765 ** | 0.596 * | 0.212 | −0.006 | −0.225 | 0.267 | 0.623* | 0.265 | 0.820 ** | 0.827 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| 3.0 –5.0 | 0.456 | 0.570 | 0.699 * | 0.788 ** | 0.440 | −0.060 | −0.340 | 0.177 | 0.593 * | 0.081 | 0.844 ** | 0.871 ** | 0.928 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| 5.0 –10.0 | 0.419 | 0.496 | 0.665 * | 0.790 ** | 0.693 * | −0.037 | −0.375 | 0.103 | 0.501 | 0.272 | 0.656 * | 0.677 * | 0.791 ** | 0.882 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| AER | −0.296 | −0.166 | 0.054 | −0.061 | −0.421 | −0.424 | −0.407 | 0.036 | 0.379 | 0.302 | 0.656 * | 0.443 | 0.630 * | 0.524 | 0.311 | 1 | |||||||
| C | −0.441 | −0.270 | −0.284 | −0.280 | −0.464 | −0.209 | −0.058 | 0.148 | 0.047 | 0.064 | −0.080 | −0.008 | 0.016 | 0.000 | −0.214 | 0.564 | 1 | ||||||
| n | 0.123 | 0.049 | −0.108 | 0.161 | 0.250 | −0.090 | −0.334 | −0.307 | 0.098 | −0.010 | 0.012 | −0.040 | −0.085 | 0.032 | 0.170 | −0.220 | −0.533 | 1 | |||||
| ACH50 | −0.033 | 0.168 | −0.066 | 0.085 | −0.219 | −0.074 | −0.197 | 0.155 | 0.428 | 0.150 | 0.453 | 0.525 | 0.434 | 0.483 | 0.253 | 0.724 ** | 0.690 * | −0.014 | 1 | ||||
| Total ELA | −0.447 | −0.278 | −0.293 | −0.278 | −0.465 | −0.218 | −0.088 | 0.135 | 0.072 | 0.087 | −0.070 | −0.002 | 0.027 | 0.014 | −0.196 | 0.582 * | 0.996 ** | −0.457 | 0.732 ** | 1 | |||
| Specific Total ELA | −0.146 | 0.079 | −0.070 | −0.036 | −0.315 | −0.030 | −0.018 | 0.297 | 0.301 | 0.119 | 0.293 | 0.388 | 0.322 | 0.325 | 0.074 | 0.680 * | 0.908 ** | −0.468 | 0.877 ** | 0.911 ** | 1 | ||
| Specific ELAc | 0.394 | 0.559 | 0.510 | 0.460 | 0.298 | 0.271 | 0.122 | 0.580 * | 0.564 | 0.326 | 0.705 * | 0.777 ** | 0.727 ** | 0.721 ** | 0.680 * | 0.461 | 0.293 | −0.277 | 0.570 | 0.296 | 0.594 * | 1 | |
| Specific ELAo | 0.322 | 0.379 | 0.296 | 0.222 | −0.015 | 0.111 | 0.265 | 0.229 | 0.171 | −0.141 | 0.525 | 0.558 | 0.418 | 0.410 | 0.145 | 0.283 | 0.134 | −0.553 | 0.185 | 0.082 | 0.327 | 0.350 | |
| Penetration Coefficient (P) | Deposition Loss Rate (k) | Outdoor Particle Source (P × λ) | AER | Built Year | Renovation Year | Floor Area | Volume | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3 –0.5 | 0.5 –1.0 | 1.0 –3.0 | 3.0 –5.0 | 5.0 –10.0 | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.5 –1.0 | 1.0 –3.0 | 3.0 –5.0 | 5.0 –10.0 | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.5 –1.0 | 1.0 –3.0 | 3.0 –5.0 | 5.0 –10.0 | |||||||
| k | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.613 * | 0.615 * | 0.245 | 0.100 | 0.164 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 0.5 –1.0 | 0.451 | 0.284 | −0.015 | −0.289 | −0.120 | 0.748 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 1.0 –3.0 | 0.377 | 0.468 | 0.323 | 0.127 | 0.027 | 0.653 * | 0.526 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 3.0 –5.0 | 0.292 | 0.465 | 0.471 | 0.433 | 0.141 | 0.361 | −0.092 | 0.692 * | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 5.0 –10.0 | −0.186 | −0.180 | 0.134 | −0.162 | −0.039 | 0.246 | 0.046 | 0.408 | 0.543 | 1 | |||||||||||
| P × λ | 0.3 –0.5 | 0.733 ** | 0.733 ** | 0.561 | 0.574 | 0.256 | 0.264 | 0.112 | 0.398 | 0.590 * | 0.050 | 1 | |||||||||
| 0.5 –1.0 | 0.676 * | 0.784 ** | 0.557 | 0.614 * | 0.269 | 0.268 | 0.048 | 0.415 | 0.621 * | 0.024 | 0.970 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| 1.0 –3.0 | 0.342 | 0.422 | 0.765 ** | 0.596 * | 0.212 | −0.006 | −0.225 | 0.267 | 0.623 * | 0.265 | 0.820 ** | 0.827 ** | 1 | ||||||||
| 3.0 –5.0 | 0.456 | 0.570 | 0.699 * | 0.788 ** | 0.440 | −0.060 | −0.340 | 0.177 | 0.593 * | 0.081 | 0.844 ** | 0.871 ** | 0.928 ** | 1 | |||||||
| 5.0 –10.0 | 0.419 | 0.496 | 0.665 * | 0.790 ** | 0.693 * | −0.037 | −0.375 | 0.103 | 0.501 | 0.272 | 0.656* | 0.677 * | 0.791 ** | 0.882 ** | 1 | ||||||
| AER | −0.296 | −0.166 | 0.054 | −0.061 | −0.421 | −0.424 | −0.407 | 0.036 | 0.379 | 0.302 | 0.414 | 0.443 | 0.630 * | 0.524 | 0.311 | 1 | |||||
| Built year | −0.225 | −0.083 | −0.185 | 0.003 | 0.035 | −0.424 | −0.267 | 0.176 | 0.211 | 0.325 | 0.161 | 0.218 | 0.241 | 0.315 | 0.361 | 0.610 * | 1 | ||||
| Floor area | −0.712 ** | −0.818 ** | −0.474 | −0.627 * | −0.550 | −0.464 | −0.059 | −0.215 | −0.411 | 0.041 | −0.573 | −0.632 * | −0.405 | −0.501 | −0.542 | 0.189 | 0.265 | −0.511 | 1 | ||
| Volume | −0.634 * | −0.736 ** | −0.379 | −0.615 * | −0.494 | −0.286 | 0.137 | −0.032 | −0.382 | 0.110 | −0.562 | −0.613 * | −0.403 | −0.528 | −0.546 | 0.097 | 0.262 | −0.499 | 0.964 ** | 1 | |
| Envelop area | −0.572 | −0.518 | −0.370 | −0.555 | −0.494 | −0.079 | 0.193 | 0.165 | −0.187 | 0.220 | −0.435 | −0.405 | −0.297 | −0.404 | −0.457 | 0.239 | 0.470 | −0.336 | 0.797 ** | 0.876 ** | |
| C | n | ACH50 | Total ELA | Specific Total ELA | Specific ELAc | Specific ELAo | Built Year | Floor Area | Volume | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | −0.533 | 1 | ||||||||
| ACH50 | 0.690 * | −0.014 | 1 | |||||||
| Total ELA | 0.996 ** | −0.457 | 0.732 ** | 1 | ||||||
| Specific Total ELA | 0.908 ** | −0.468 | 0.877 ** | 0.911 ** | 1 | |||||
| Specific ELAc | 0.293 | −0.277 | 0.570 | 0.296 | 0.594 * | 1 | ||||
| Specific ELAo | 0.134 | −0.553 | 0.185 | 0.082 | 0.327 | 0.350 | 1 | |||
| Built year | 0.641 | −0.293 | 0.585 | 0.644 | 0.671 | 0.578 | 0.059 | 1 | ||
| Floor area | 0.62 | −0.196 | 0.121 | 0.631 | 0.283 | −0.309 | −0.353 | 0.265 | 1 | |
| Volume | 0.627 * | −0.349 | 0.054 | 0.625 * | 0.300 | −0.196 | −0.285 | 0.262 | 0.964 ** | 1 |
| Envelope area | 0.847 ** | −0.592 * | 0.294 | 0.831 ** | 0.615 * | 0.072 | −0.091 | 0.470 | 0.797 ** | 0.876 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eom, Y.S.; Park, B.R.; Shin, H.W.; Kang, D.H. Evaluation of Outdoor Particle Infiltration into Classrooms Considering Air Leakage and Other Building Characteristics in Korean Schools. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137382
Eom YS, Park BR, Shin HW, Kang DH. Evaluation of Outdoor Particle Infiltration into Classrooms Considering Air Leakage and Other Building Characteristics in Korean Schools. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137382
Chicago/Turabian StyleEom, Ye Seul, Bo Ram Park, Hee Won Shin, and Dong Hwa Kang. 2021. "Evaluation of Outdoor Particle Infiltration into Classrooms Considering Air Leakage and Other Building Characteristics in Korean Schools" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137382
APA StyleEom, Y. S., Park, B. R., Shin, H. W., & Kang, D. H. (2021). Evaluation of Outdoor Particle Infiltration into Classrooms Considering Air Leakage and Other Building Characteristics in Korean Schools. Sustainability, 13(13), 7382. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137382






