Evaluation of the Potential Role of Bacillus altitudinis MT422188 in Nickel Bioremediation from Contaminated Industrial Effluents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Sampling and Isolation of Bacteria
2.2. Determination of MIC and Cross Heavy-Metal Resistance Pattern
2.3. Molecular Characterization of Selected Bacterial Isolate
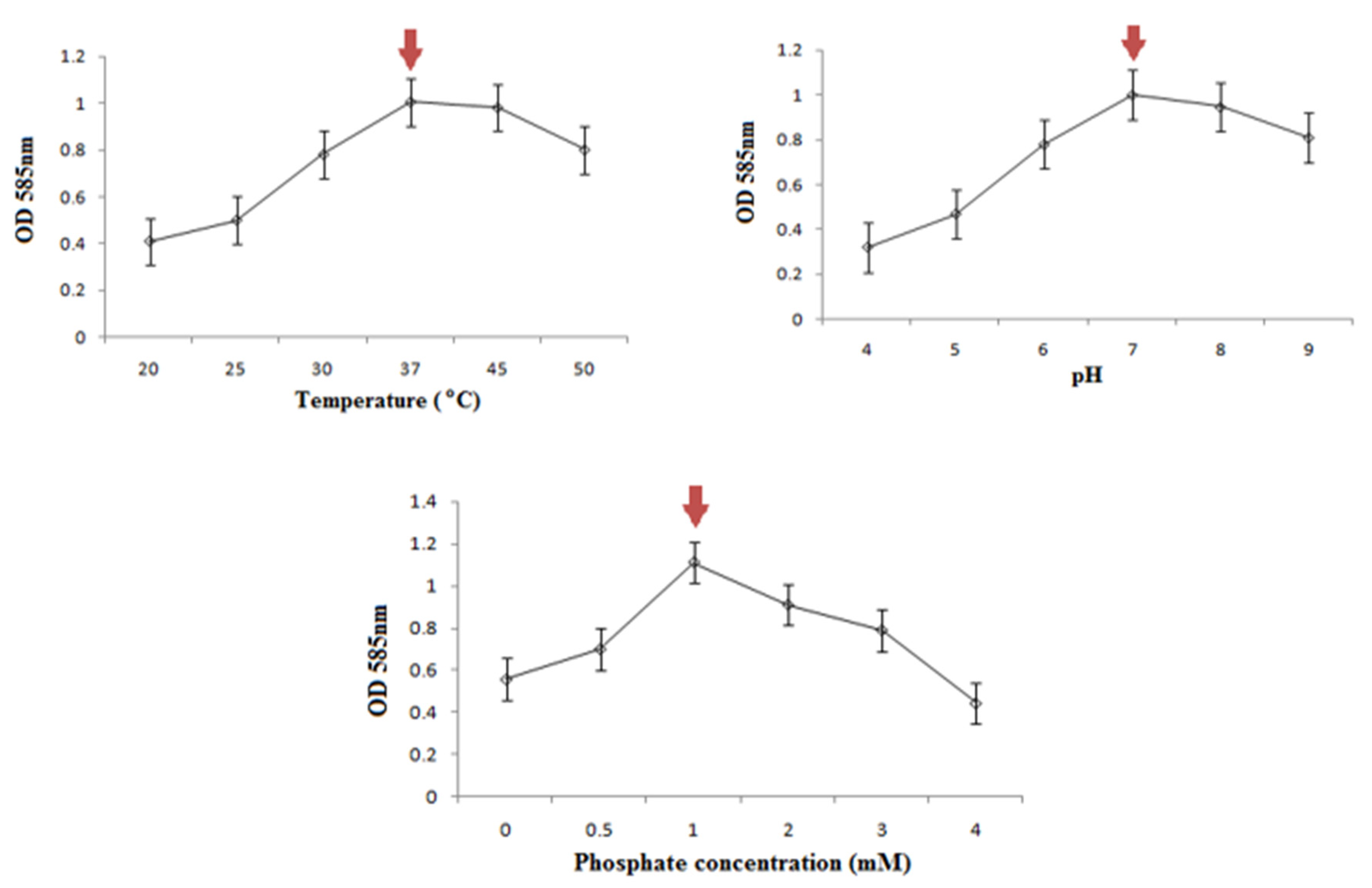
2.4. Determination of Optimum Growth Conditions
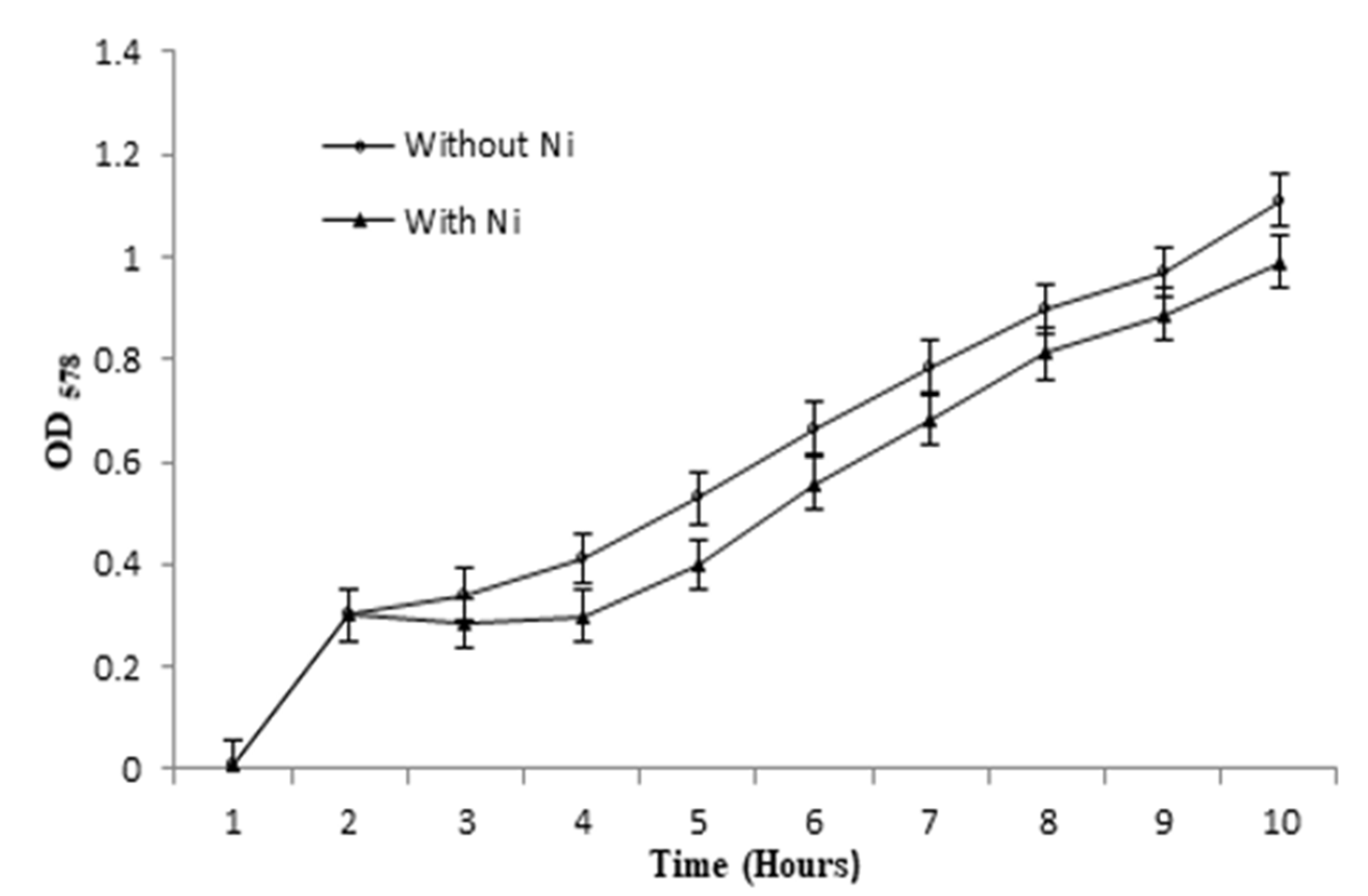
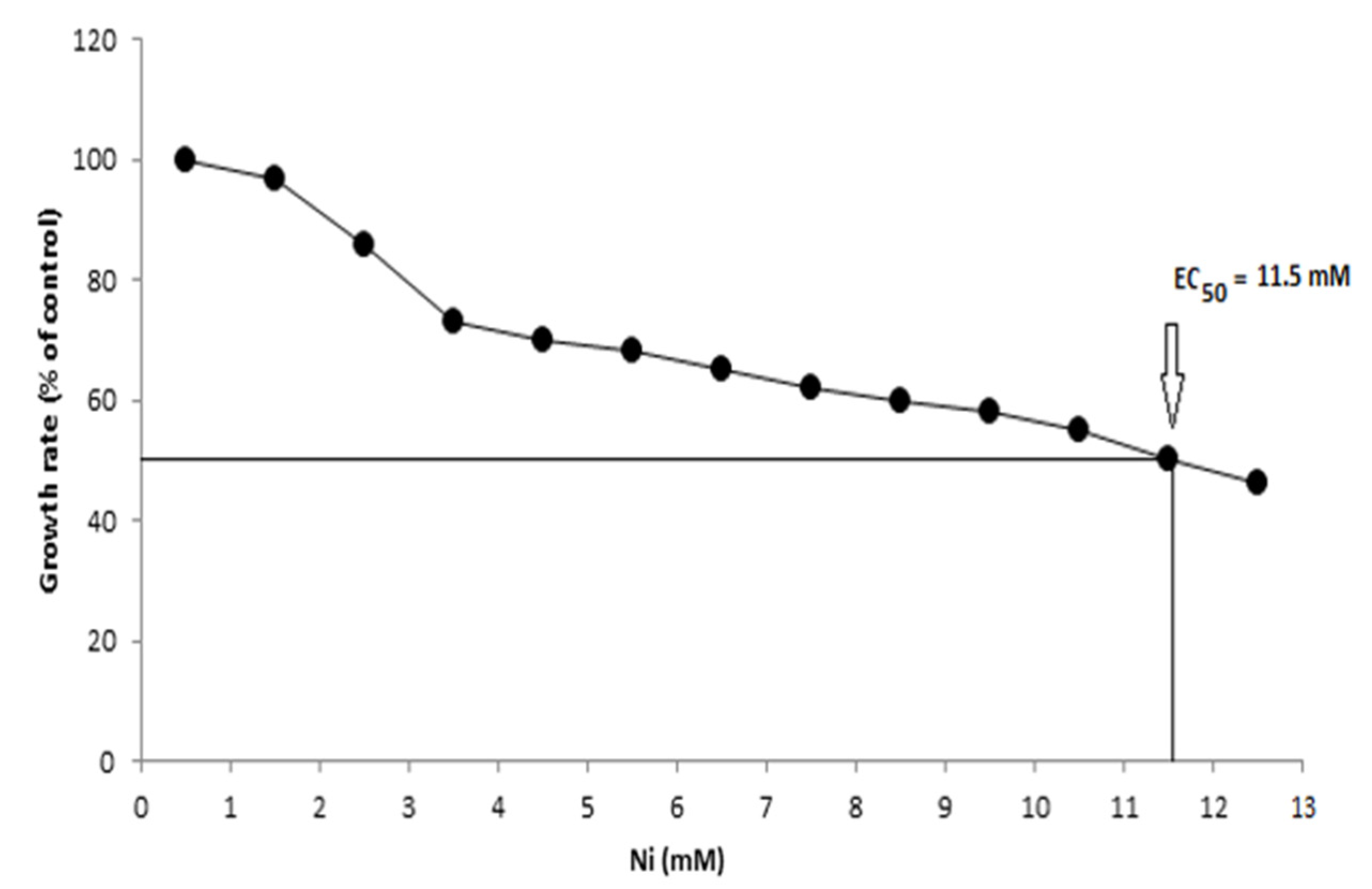
2.5. Evaluation of Bacterial Growth and EC50 in Presence of Ni
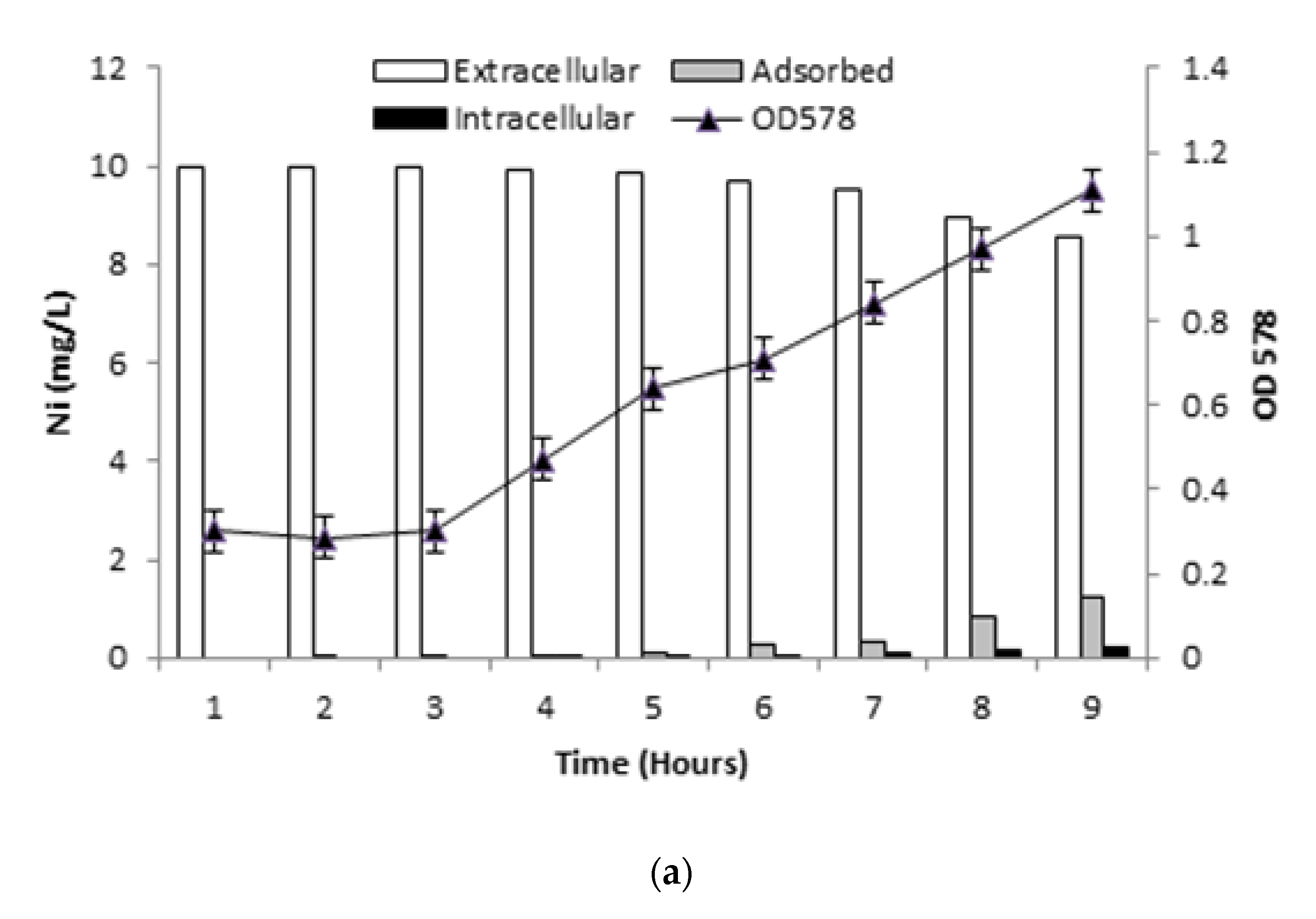
2.6. Ni Biosorption Experiments
2.6.1. Determination of Ni Uptake
2.6.2. Ni Uptake in Presence of Inhibitors
2.6.3. Ni Removal by Killed Bacterial Cells
2.6.4. Pilot-Scale Study for Ni Removal
2.7. Profiling of Antioxidative Enzymes
2.8. Profiling of Proteins and Metallothioneins
2.9. Determination of Motility and Chemotactic Behavior
2.10. Isothermic, Thermodynamics, and Adsorption Kinetic Studies
2.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis of Bacterial Cells
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enumeration of Ni-Resistant Bacterial Isolates
3.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Cross Heavy-Metal Resistance
3.3. Selection and Molecular Identification of Bacterial Isolate
3.4. Optimum Growth Conditions
3.5. Bacterial Growth and EC50
3.6. Ni Biosorption Experiments
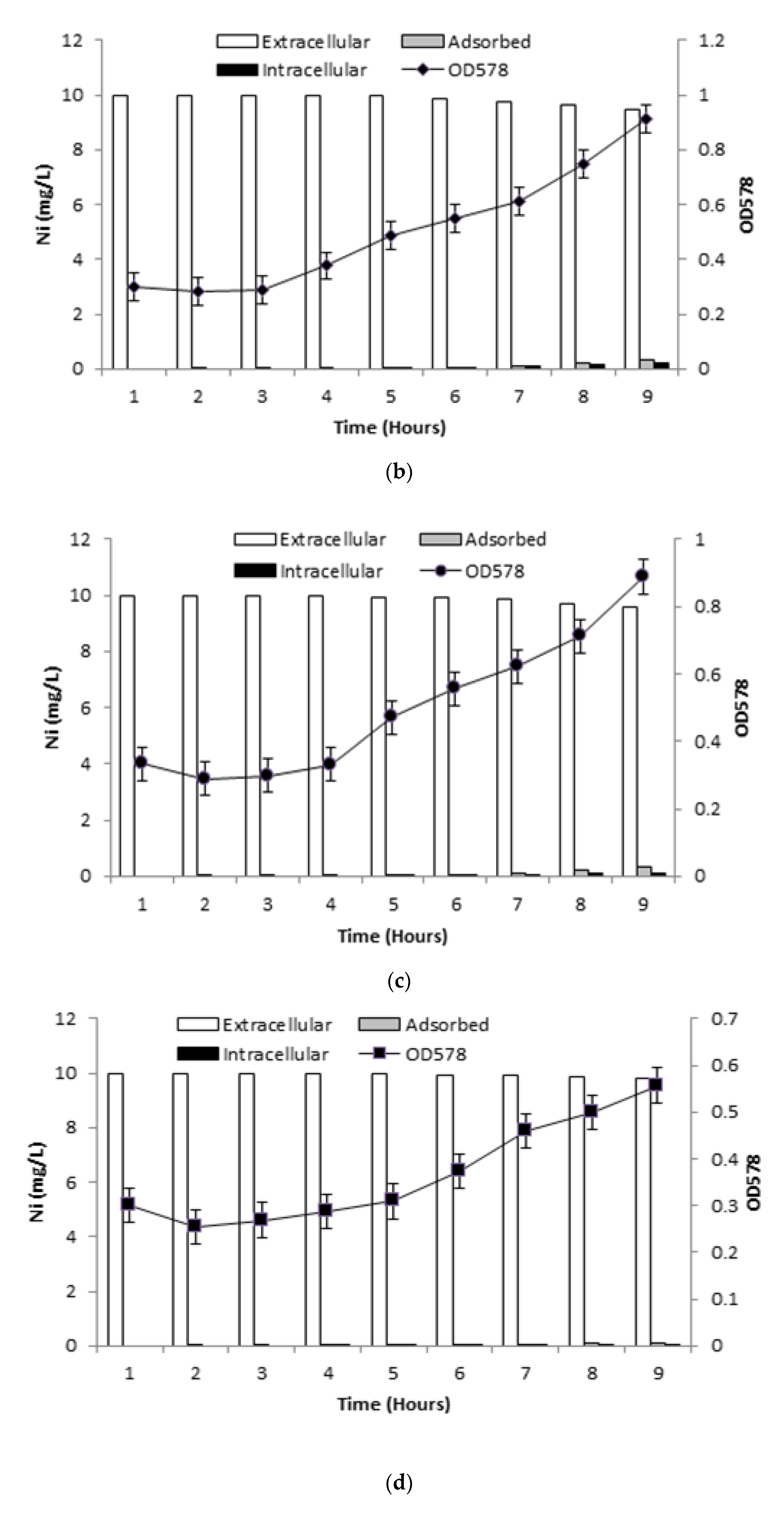
3.6.1. Ni Uptake by Live Bacterial Cells
3.6.2. Ni Uptake in Presence of Inhibitors
3.6.3. Ni Removal by Killed Bacterial Cells
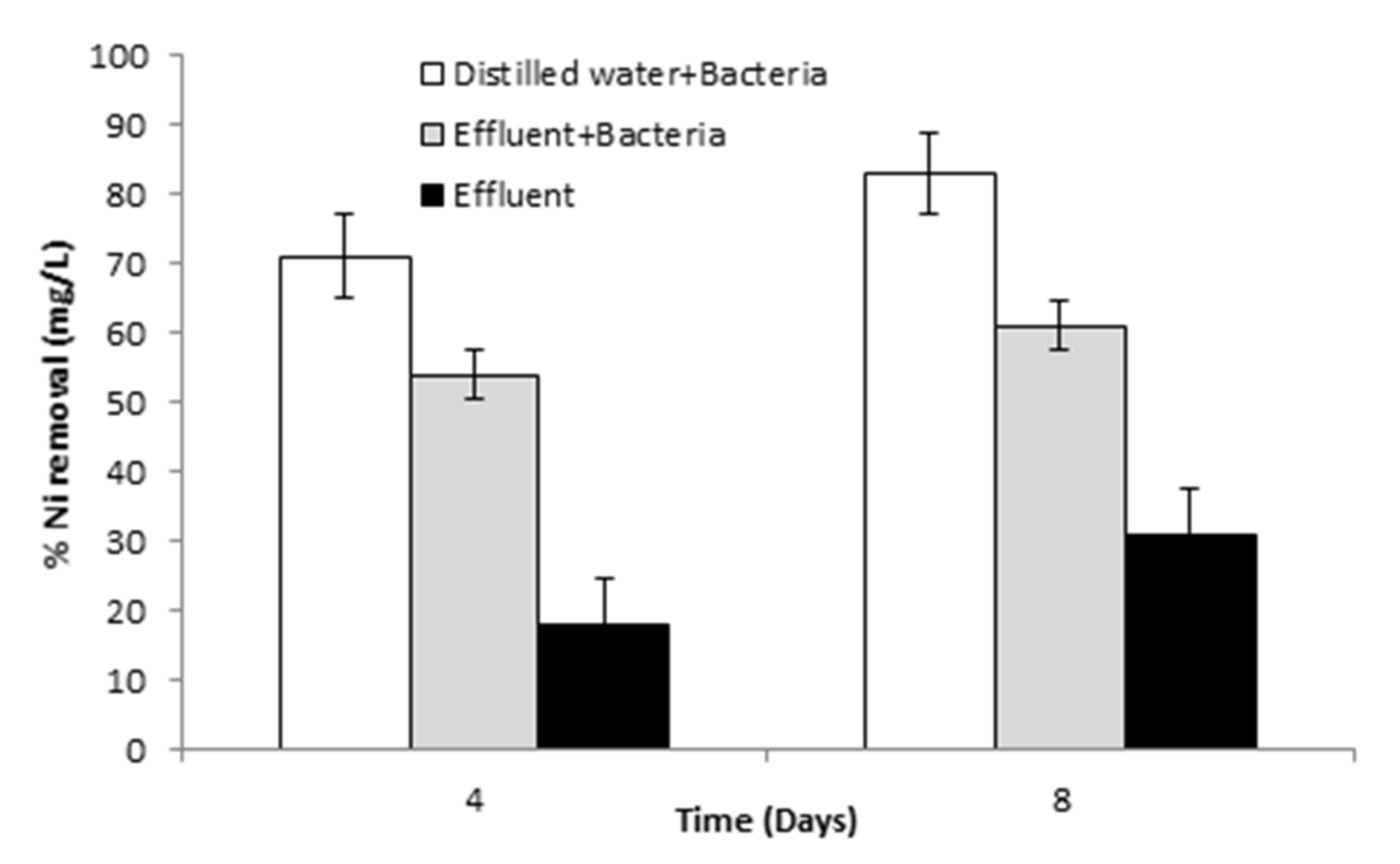
3.6.4. Pilot-Scale Study for Ni Removal
3.7. Profiling of Antioxidative Enzymes
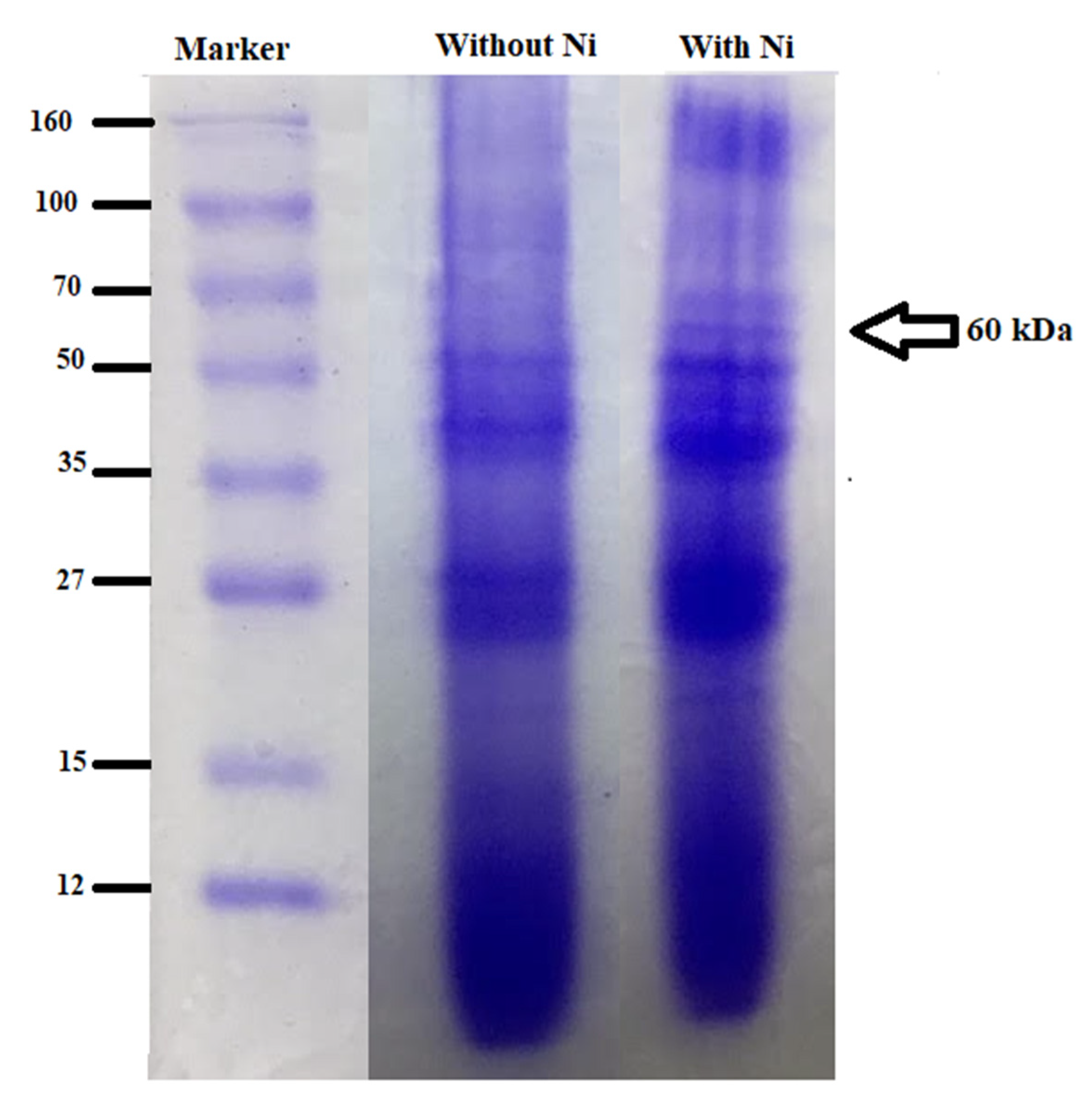
3.8. Profiling of Metallothioneins
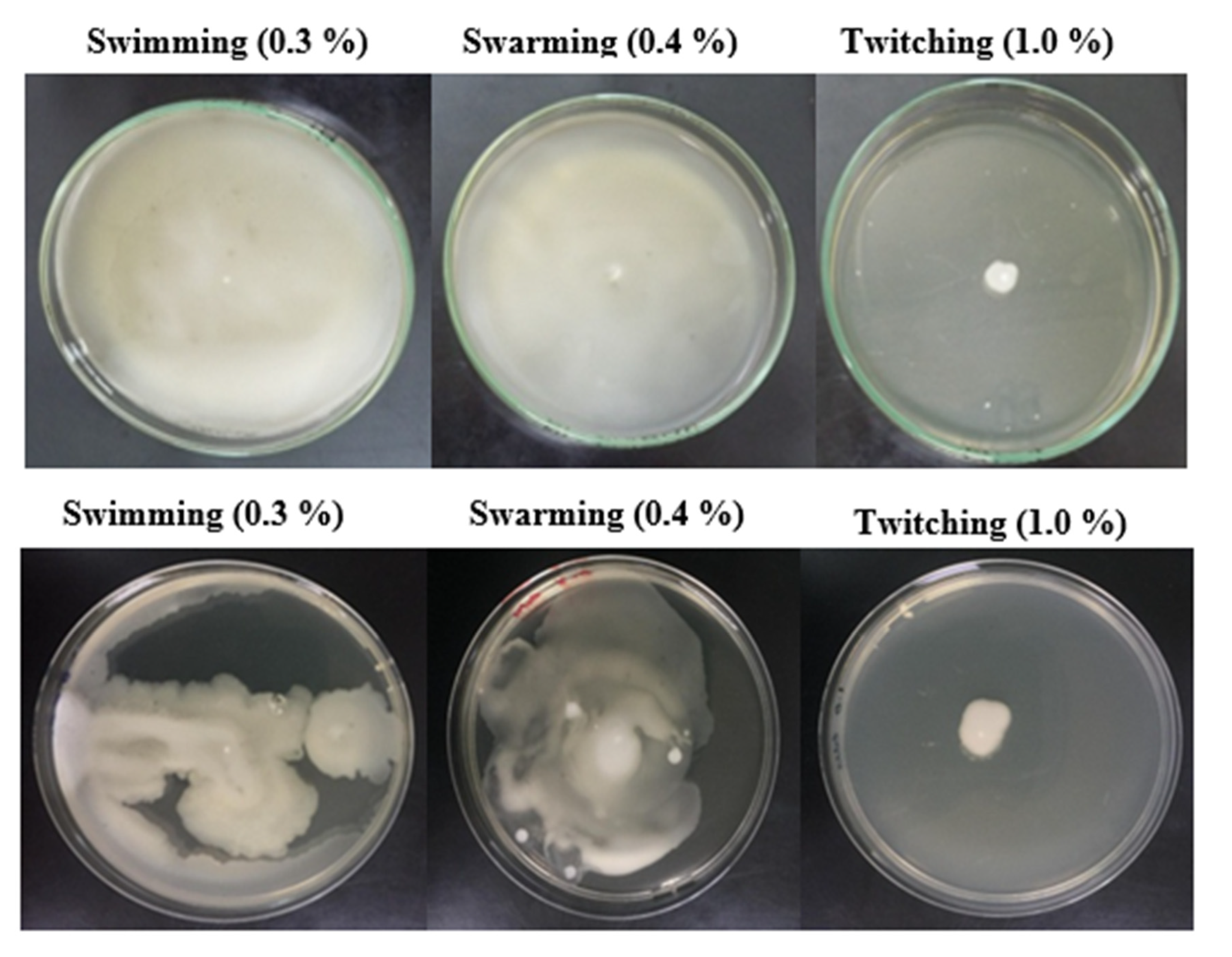
3.9. Pattern of Motility and Chemotactic Behavior
3.10. Isothermic, Thermodynamic, and Adsorption Kinetic Studies
3.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
3.12. SEM and EDS Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hao, X.; Zhu, J.; Rensing, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.-R. Recent advances in exploring the heavy metal(loid) resistant microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Borah, S.S.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk assessment for surficial sediments of Deepor Beel, India. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Dinis, P.A. Estimation of Risk to the Eco-Environment and Human Health of Using Heavy Metals in the Uttarakhand Himalaya, India. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.S.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. Heavy metals of Santiago Island (Cape Verde) top soils: Estimated Background Value maps and environmental risk assessment. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 101, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.M.V.G.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Dinis, P. Geochemistry of subtropical arenosols from Kui-to region (Angola). Urbanization effects and environmental implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 183, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malea, P.; Mylona, Z.; Panteris, E.; Kevrekidis, D.P.; Kevrekidis, T. Nickel uptake kinetics and its structural and physiological impacts in the seagrass Halophila stipulacea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Bhagat, M.; Urfan, M.; Ahmed, B.; Langer, A.; Ali, V.; Vyas, D.; Yadav, N.S.; Hakla, H.R.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nickel excess affects phenology and reproductive attributes of Asterella wallichiana and Plagiochasma appendiculatum growing in natural habitats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.-S.; Jiang, L. Refining health risk assessment by incorporating site-specific background concentration and bioaccessibility data of Nickel in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581-582, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human Health and Environmental Toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mardiyono; Sajidan; Masykuri, M.; Setyono, P. Bioremediation of nickel heavy metals in electroplating industrial liquid waste with Bacillus subtilis. In Proceedings of The International Conference on Science and Applied Science (ICSAS) 2019; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2202, p. 020084. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Balouch, A.; Pathan, A.A.; Abdullah; Jagirani, M.S.; Mahar, A.M.; Zubair, M.; Laghari, B. Remediation of Nickel ion from wastewater by applying various techniques: A review. Acta Chem. Malays. 2019, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ent, A.; Callahan, D.L.; Noller, B.N.; Mesjasz-Przybylowicz, J.; Przybyłowicz, W.J.; Barnabas, A.; Harris, H.H. Nickel biopathways in tropical nickel hyperaccumulating trees from Sabah (Malaysia). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, M. A comprehensive study on the bacterial biosorption of heavy metals: Materials, performances, mechanisms, and mathematical modellings. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 20190016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesbrough, M. Biochemical tests to identify bacteria. In District Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries-Part 2; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Pattanapipitpaisal, P.; Brown, N.L.; Macaskie, L.E. Chromate reduction and 16S rRNA identification of bacteria isolated from a Cr(VI)-contaminated site. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamim, S. Comparative Analysis of Metal Resistance, Accumulation and Antioxidant Enzymes in Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 and Pseudomonas putida mt2 during Cadmium Stress. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Punjab, Punjab, Pakistan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shamim, S.; Rehman, A. Cadmium resistance and accumulation potential of Klebsiella pneumoniae strain CBL-1 isolated from industrial wastewater. Pak. J. Zool. 2012, 44, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Shamim, S.; Rehman, A.; Qazi, M.H. Cadmium-Resistance Mechanism in the Bacteria Cupriavidus metallidurans CH34 and Pseudomonas putida mt2. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Heipieper, H.J.; Fischer, J.; Ruta, M.; Volterrani, M.; Focardi, S.E. Membrane fatty acids adaptive profile in the simultaneous presence of arsenic and toluene in Bacillus sp. ORAs2 and Pseudomonas sp. ORAs5 strains. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israr, M.; Sahi, S.V.; Jain, J. Cadmium Accumulation and Antioxidative Responses in the Sesbania drummondii Callus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Asada, K. Purification of Ascorbate Peroxidase in Spinach Chloroplasts; Its Inactivation in Ascorbate-Depleted Medium and Reactivation by Monodehydroascorbate Radical. Plant Cell Physiol. 1987, 28, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, F.H. Catalase. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Bergmeyer, H.U., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 885–894. [Google Scholar]
- Reuveni, R.; Shimoni, M.; Karchi, Z.; Kuch, J. Peroxidase activity as a biochemical marker for resistance of muskmelon Cucumis melo to Pseudopernospora cubensis. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.V.; Paliyath, G.; Ormrod, D.P. Ultraviolet-B- and Ozone-Induced Biochemical Changes in Antioxidant Enzymes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1996, 110, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-Dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, T.S.; Ledizet, M.; Kazmierczak, B.I. Swarming motility, secretion of type 3 effectors and biofilm formation phenotypes exhibited within a large cohort of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. J. Med Microbiol. 2010, 59, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, J. A Method for Measuring Chemotaxis and Use of the Method to Determine Optimum Conditions for Chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1973, 74, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption process simulation tools. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzba, S. Biosorption of lead(II), zinc(II) and nickel(II) from industrial wastewater by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Bacillus subtilis. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 17, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joo, J.-H.; Hassan, S.; Oh, S.-E. Comparative study of biosorption of Zn2+ by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus cereus. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2010, 64, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gel€oster stoffe, Kungliga Svenska Veten-skapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Aksu, Z. Equilibrium and kinetic modelling of cadmium (II) biosorption by C. vulgaris in a batch system: Effect of temperature. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 21, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Batch Sorber Design Using Equilibrium and Contact Time Data for the Removal of Lead. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 124, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar, A.R.; Lin, L.-Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Ling, Y.-C. Single-walled carbon nanotube coated antibacterial paper: Preparation and mechanistic study. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Rehman, A.; Hussain, S.Z.; Nisar, M.A.; Zulfiqar, S.; Shakoori, A.R. Cadmium resistance and uptake by bacterium, Salmonella enterica 43C, isolated from industrial effluent. AMB Express 2016, 6, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonge, B.A.; Larissa, M.T.; Egbe, A.M.; Afanga, Y.A.; Fru, N.G.; Ngole-Jeme, V.M. An assessment of heavy metal exposure risk associated with consumption of cabbage and carrot grown in a tropical Savannah region. Sustain. Environ. 2021, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alboghobeish, H.; Tahmourespour, A.; Doudi, M. The study of Nickel Resistant Bacteria (NiRB) isolated from wastewaters polluted with different industrial sources. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhenggang, X.; Yi, D.; Huimin, H.; Liang, W.; Yunlin, Z.; Guiyan, Y. Biosorption Characteristics of Mn (II) by Bacillus cereus Strain HM-5 Isolated from Soil Contaminated by Manganese Ore. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 28, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashokkumar, P.; Loashini, V.M.; Bhavya, V. Effect of pH, temperature and biomass on biosorption of heavy metals by Sphaerotilus natans. Int. J. Microbiol. Mycol. 2017, 6, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, A.M.; Rasool, M.H.; Waseem, M.; Aslam, B. Assessment of heavy metal tolerance and biosorptive potential of Klebsiella variicola isolated from industrial effluents. AMB Express 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, P.; More, N.; Raj, A.; Bharagava, R.N. Characterization and identification of bacterial pathogens from treated tannery wastewater. Microbiol. Res. Int. 2017, 5, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirbhavane, H.M.; Bagde, U.S. Study of lead and nickel resistance mechanism in Enterobacter species. Indian J. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 5, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speir, T.W.; Van Schaik, A.P.; Hunter, L.C.; Ryburn, J.L.; Percival, H.J. Attempts to derive EC50 values for heavy metals from land-applied Cu-, Ni-, and Zn-spiked sewage sludge. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denic, M.; Turlin, E.; Michel, V.; Fischer, F.; Khorasani-Motlagh, M.; Zamble, D.; Vinella, D.; de Reuse, H. A novel mode of control of nickel uptake by a multifunctional metallochaperone. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Gheethi, A.A.; Mohamed, R.M.; Jais, N.M.; Efaq, A.N.; Halid, A.A.; Wurochekke, A.A.; Amir-Hashim, M.K. Influence of pathogenic bacterial activity on growth of Scenedesmus sp. and removal of nutrients from public market wastewater. J. Water Health 2017, 15, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saad, A.M.; Saad, M.M.; Ibrahim, N.A.; El-Hadedy, D.; Ibrahim, E.I.; El-Din, A.Z.K.; Hassan, H.M. Evaluation of Aspergillus tamarii NRC 3 biomass as a biosorbent for removal and recovery of heavy metals from contaminated aqueous solutions. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas-Castillo, A.M.; Mejía-Escobedo, Y.; Rojas-Avelizapa, N.G. Study of Bacillus megaterium potential application for high metal content residues biotreatment. Open J. Bacteriol. 2018, 2, 004–008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karmakar, R. State of the art of bacterial chemotaxis. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Shamim, K.; Dubey, S.K.; Meena, R.M. Metallothionein assisted periplasmic lead sequestration as lead sulfite by Providencia vermicola strain SJ2A. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; Rehman, A. Metal resistance and uptake by Trichosporon asahii and Pichia kudriavzevii isolated from industrial effluents. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2018, 44, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, A.; Bhola, J.; Bhadekar, R. Protein profiling and antioxidant enzyme activity of cadmium and lead tolerant Kocuria sp. BRI 36. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 8357–8363. [Google Scholar]
- Tammam, A.; Badr, R.; Abou-Zeid, H.; Hassan, Y.; Bader, A. Nickel and ozone stresses induce differential growth, antioxidant activity and mRNA transcription in Oryza sativa cultivars. J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Tian, Z.; Cheng, H.; Xu, G.; Zhou, H. Adsorption process and mechanism of heavy metal ions by different components of cells, using yeast (Pichia pastoris) and Cu2+ as biosorption models. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 17080–17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, C.; Ai, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; et al. A Novel Pb-Resistant Bacillus subtilis Bacterium Isolate for Co-Biosorption of Hazardous Sb (III) and Pb (II): Thermodynamics and Application Strategy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asare, E.A.; Dartey, E.; Sarpong, K.; Effah-Yeboah, E.; Amissah-Reynolds, P.K.; Tagoe, S.; Balali, G.I. Adsorption Isotherm, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Modelling of Bacillus subtilis ATCC13952 Mediated Adsorption of Arsenic in Groundwaters of Selected Gold Mining Communities in the Wassa West Municipality of the Western Region of Ghana. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 12, 121–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z.; Thomas, L.; Singh, V.P. Biosorption of heavy metals by a lead (Pb) resistant bacterium, Staphylococcus hominis strain AMB-2. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

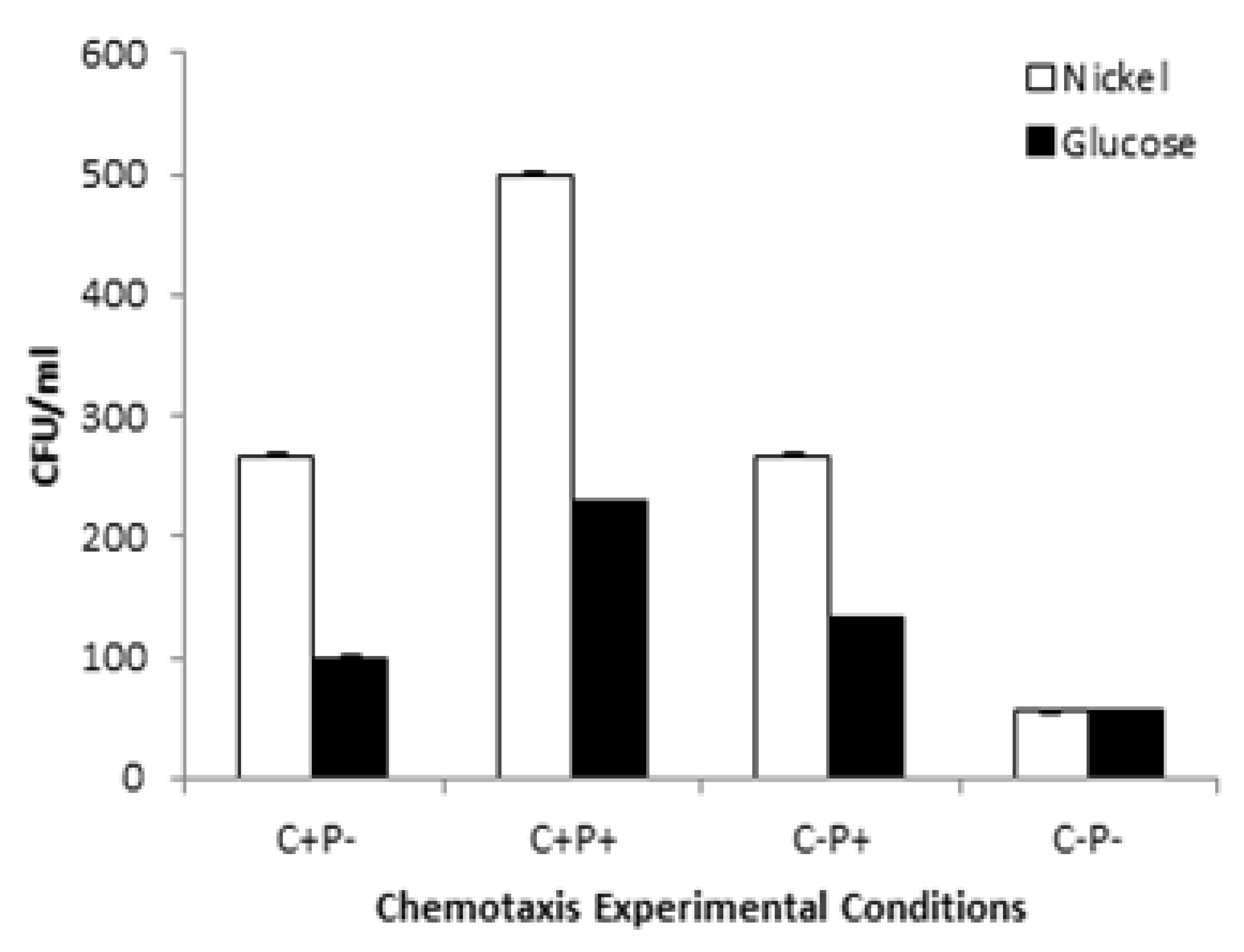

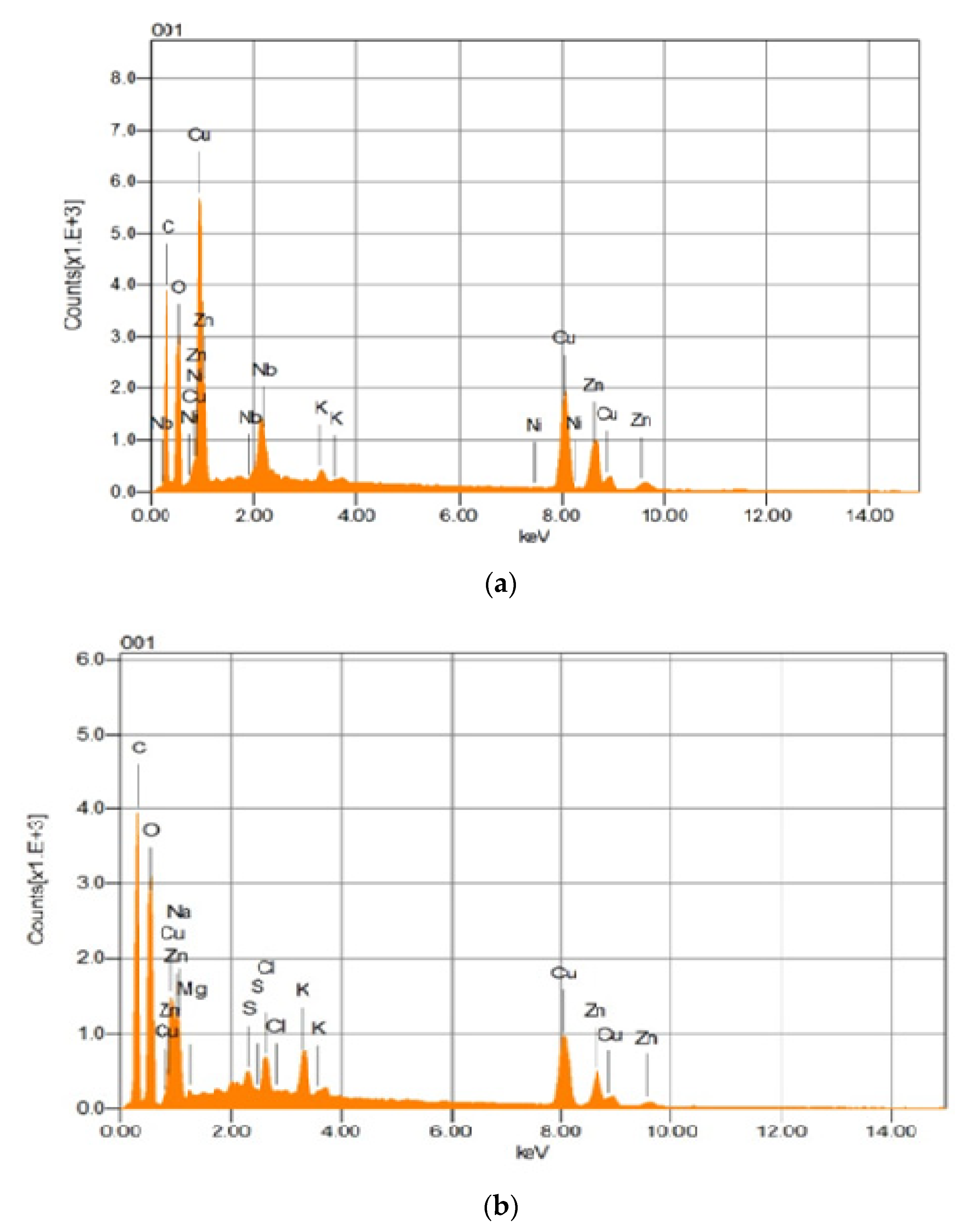
| Experimental Setup | GR (Ug−1FW) | POX (Ug−1FW) | SOD (Ug−1FW) | APOX (Ug−1FW) | CAT (Ug−1FW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | |||||
| B. altitudinis with Ni | 0.001 ± 0.003 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | 0.091 ± 0.003 | - | - |
| B. altitudinis without Ni | 0.004 ± 0.002 | 0.091 ± 0.004 | 0.160 ± 0.005 | - | - |
| Experiments | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax | b | R2 | n | Kf | R2 | |
| Live cells + Ni | 5.955 | 0.00438 | 0.9042 | 1.814 | 1.566 | 0.9999 |
| Live cells + Ni + DNP | 1.6265 | 0.003 | 0.9801 | 1.783 | 1.55 | 0.9999 |
| Live cells + Ni + DCCD | 2.9129 | 0.0015 | 0.911 | 1.7815 | 1.5506 | 0.9999 |
| Live cells + Ni + DNP + DCCD | 1.3594 | 0.0114 | 0.903 | 1.7618 | 1.5409 | 0.9999 |
| Experiments | Pseudo First Order | Pseudo Second Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qexp | k1 | qcal | R2 | k2 | qcal | R2 | |
| Live cells + Ni | 9.34 | 0.0497 | 2.639 | 0.9997 | 1.302 | 10.95 | 0.9903 |
| Live cells + Ni + DNP | 8.64 | 0.0502 | 2.55 | 0.9885 | 0.214 | 10.416 | 0.9844 |
| Live cells + Ni + DCCD | 8.78 | 0.505 | 2.568 | 0.9999 | 0.2476 | 10.416 | 0.9856 |
| Live cells + Ni + DNP + DCCD | 8.34 | 0.2766 | 2.589 | 0.9357 | 0.1841 | 10.3842 | 0.9884 |
| Dead cells + Ni | 2.09 | 0.1121 | 1.376 | 0.9581 | 0.2898 | 10.504 | 0.9896 |
| ∆G° (kJ/mol) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermodynamic Parameters | ∆H° (kJ/mol) | ∆S°(kJ/mol/K) | 10 °C (283.15 K) | 25 °C (298.15 K) | 37 °C (310.15 K) | 45 °C (318.15 K) |
| Values | 3.0436 | 0.0224 | –9.3962 | –9.67012 | –10.0085 | –4.1655 |
| FTIR Spectra | B. altitudinis without Ni | B. altitudinis with Ni | Functional Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Region (cm−1) | 1637.22 | 1636.77 | Hydroxyl (–OH) |
| 3279.39 | 3272.97 | Carboxyl (–C=O) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babar, Z.; Khan, M.; Chotana, G.A.; Murtaza, G.; Shamim, S. Evaluation of the Potential Role of Bacillus altitudinis MT422188 in Nickel Bioremediation from Contaminated Industrial Effluents. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137353
Babar Z, Khan M, Chotana GA, Murtaza G, Shamim S. Evaluation of the Potential Role of Bacillus altitudinis MT422188 in Nickel Bioremediation from Contaminated Industrial Effluents. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137353
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabar, Zarka, Maryam Khan, Ghayoor Abbas Chotana, Ghulam Murtaza, and Saba Shamim. 2021. "Evaluation of the Potential Role of Bacillus altitudinis MT422188 in Nickel Bioremediation from Contaminated Industrial Effluents" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137353
APA StyleBabar, Z., Khan, M., Chotana, G. A., Murtaza, G., & Shamim, S. (2021). Evaluation of the Potential Role of Bacillus altitudinis MT422188 in Nickel Bioremediation from Contaminated Industrial Effluents. Sustainability, 13(13), 7353. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137353






