The Relevance of Grated Inlets within Surface Drainage Systems in the Field of Urban Flood Resilience. A Review of Several Experimental and Numerical Simulation Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hydraulic Performance of Urban Drainage Systems
2.1. Surface Drainage Systems in Urban Areas
2.2. Inlet Hydraulic Performance
2.3. Experimental Campaigns to Estimate Hydraulic Efficiency of Grated Inlets and UPC Method
2.4. UPC Experimental Campaigns to Estimate Hydraulic Efficiency of Continuous Transverse Grates
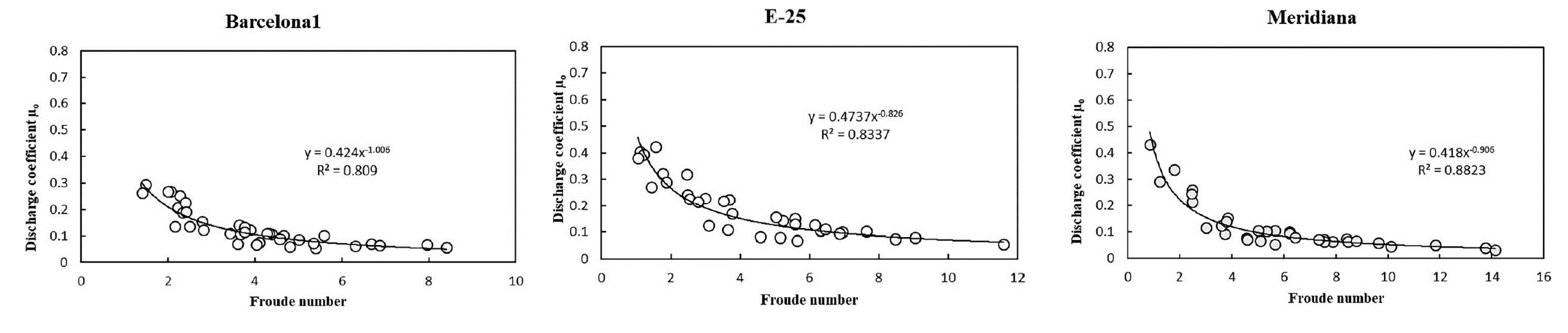
2.5. UPC Experimental Campaigns to Estimate Discharge Coefficients of Grated Inlets
2.6. UPC Experimental Campaigns to Achieve Grated Inlets Clogging Factors
3. Numerical Modeling Applied to the Field of Surface Drainage Hydraulic Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djordjević, S.; Butler, D.; Gourbesville, P.; Mark, O.; Pasche, E. New policies to deal with climate change and other drivers impacting on resilience to flooding in urban areas: The CORFU approach. Environ. Sci. Policy 2011, 14, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Union Directive 2007/60/EC of the European Counil and European Parliment of 23 October 2007 on the assessment and management of flood risks. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2007, 288, 27–34.
- Diogo, A.F.; Antunes do Carmo, J. Peak flows and stormwater networks design—Current and future management of urban. Water 2019, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammond, M.J.; Chen, A.S.; Djordjević, S.; Butler, D.; Mark, O. Urban flood impact assessment: A state-of-the-art review. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, J.H.; Christensen, O.B. A summary of the PRUDENCE model projections of changes in European climate by the end of this century. Clim. Chang. 2007, 81, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Navarro, X.; Casas, M.C.C.; Ribalaygua, J.; Russo, B.; Pouget, L.; Redaño, A. Influence of climate change on IDF curves for the metropolitan area of Barcelona (Spain). Int. J. Clim. 2014, 34, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, B.; Velasco, M.; Locatelli, L.; Sunyer, D.; Yubero, D.; Monjo, R.; Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Forero-Ortiz, E.; Sánchez-Muñoz, D.; Evans, B.; et al. Assessment of urban flood resilience in Barcelona for current and future scenarios. The RESCCUE project. Sustainablity 2020, 12, 5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, B.; Velasco, M.; Monjo, R.; Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Sánchez, D.; Domínguez, J.L.; Gabàs, A.; Gonzalez, A. Evaluación de la resiliencia de los servicios urbanos frente a episodios de inundación en Barcelona. El Proyecto RESCCUE. Ing. Agua 2020, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, B.; Gómez, M.; Macchione, F. Pedestrian hazard criteria for flooded urban areas. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Gómez, M.; Russo, B. Experimental study of the stability of pedestrians exposed to urban pluvial flooding. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 1259–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Gómez, M.; Russo, B.; Sánchez, P.; Montes, J.A. Methodology for the damage assessment of vehicles exposed to flooding in urban areas. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, e12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, A.; Colli, M.; Candela, A.; Aronica, G.T.; Lanza, L.G. Pluvial flooding in urban areas: The role of surface drainage efficiency. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S663–S676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.G.; Thomas, M.; Ettrich, N. Analysis and modeling of flooding in urban drainage systems. J. Hydrol. 2004, 299, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.B. Comment on ‘Analysis and modeling of flooding in urban drainage systems’. J. Hydrol. 2006, 317, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Macchione, F.; Russo, B. Methodologies to study the surface hydraulic behaviour of urban catchments during storm events. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 2666–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Valentín, M.; Macchione, F.; Russo, B. Hydraulic behavior of urban streets during storm events. Ing. Hidraul. Mex. 2009, 24, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardisation (ECS). Gully Tops and Manhole Tops for Vehicular and Pedestrian Area. Design Requirements, Type Testing, Marking, Quality Control; European Committee for Standardisation (ECS): Brussels, Belgium, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardisation (ECS). Drainage Channels for Vehicular and Pedestrian Areas. Classification, Design and Testing Requirements, Marking and Evaluation of Conformity; European Committee for Standardisation (ECS): Brussels, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, M.; Russo, B.; Cabello, À.; Termes, M.; Sunyer, D.; Malgrat, P. Assessment of the effectiveness of structural and nonstructural measures to cope with global change impacts in Barcelona. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, S55–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, L.; Guerrero, M.; Russo, B.; Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Sunyer, D.; Martínez, M. Socio-economic assessment of green infrastructure for climate change adaptation in the context of urban drainage planning. Sustainablity 2020, 12, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, P.; Brito, R.S.; Galvão, A. The contribution of NBS to urban resilience in stormwater management and control: A framework with stakeholder validation. Sustainablity 2020, 12, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrero-Hidalga, M.; Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Evans, B.; Webber, J.; Termes-Rifé, M.; Russo, B.; Locatelli, L. Methodology to Prioritize Climate Adaptation Measures in Urban Areas. Barcelona and Bristol Case Studies. Sustainablity 2020, 12, 4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, J.P.; Simões, N.E.; Pina, R.D.; Ochoa-Rodriguez, S.; Onof, C.; Sá Marques, A. Stochastic evaluation of the impact of sewer inlets’ hydraulic capacity on urban pluvial flooding. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1907–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjević, S.; Prodanović, D.; Maksimović, Č.; Ivetić, M.; Savić, D. SIPSON—Simulation of interaction between pipe flow and surface overland flow in networks. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco, M.; Cabello, À.; Russo, B. Flood damage assessment in urban areas. Application to the Raval district of Barcelona using synthetic depth damage curves. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gomariz, E.; Locatelli, L.; Guerrero, M.; Russo, B.; Martínez, M. Socio-economic potential impacts due to urban pluvial floods in badalona (Spain) in a context of climate change. Water 2019, 11, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leandro, J.; Chen, A.S.; Djordjević, S.; Savić, D.A. Comparison of 1D/1D and 1D/2D coupled (sewer/surface) hydraulic models for urban flood simulation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, A.; Djordjevic, S.; Maksimovic, C.; Blanksby, J. Integrated urban flood modelling. Flood Risk Sci. Manag. 2011, 255–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnbjerg-Nielsen, K. Quantification of climate change effects on extreme precipitation used for high resolution hydrologic design. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Rabasseda, G.H.; Russo, B. Experimental campaign to determine grated inlet clogging factors in an urban catchment of Barcelona. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Parés, J.; Russo, B.; Martínez-Gomariz, E. Methodology to quantify clogging coefficients for grated inlets. Application to SANT MARTI catchment (Barcelona). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2019, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.A.; Schall, J.D.; Morris, J.L.; Doherty, C.L.; Stein, S.M.; Warner, J.C. Hydraulic Engineering Circular No. 22 (HEC-22); FHWA: Lakewood, CO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, M.; Russo, B. Methodology to estimate hydraulic efficiency of drain inlets. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2011, 164, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Russo, B. Hydraulic efficiency of continuous transverse grates for paved areas. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, B.; Gómez, M.; Tellez, J. Methodology to estimate the hydraulic efficiency of nontested continuous transverse grates. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustaffa, Z.; Rajaratnam, N.; Zhu, D.Z. An experimental study of flow into orifices and grating inlets on streets. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2006, 33, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, S.; Schlenkhoff, A. Experimental study on the hydraulic capacity of grate inlets with supercritical surface flow conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinato, M.; Lee, S.; Martins, R.; Shucksmith, J.D. Surface to sewer flow exchange through circular inlets during urban flood conditions. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosco, C.; Gómez, M.; Russo, B.; Tellez-Alvarez, J.; Macchione, F.; Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C. Discharge coefficients for specific grated inlets. Influence of the Froude number. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H. The Design of Storm-Water Inlets; Baltimore, Ed.; Storm Drainage Research Committee, Department of Sanitary Engineering and Water Resources, Johns Hopkins University: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.; Jacop, R.P.; Ellet, B. A review of road-gully spacing methods. Water Environ. J. 1996, 10, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russam, K. Hydraulic Efficiency and Spacing of BS Road Gullies (Report LR277); Transport and Road Research Laboratory: Crowthorne, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Ellett, B.S.G.; Stubbs, F. The Capacity of BS Road Gullies (Report 108); Transport and Road Research Laboratory, Department of Transport: Crowthorne, UK, 1981; ISBN 0266-7045. [Google Scholar]
- Spaliviero, F.; May, R.W.P.; Escarameia, M. Spacing of Road Gullies. Hydraulic Performance of BS EN 124 Gully Gratings and Kerb Inlets; Report SR 533; HR Wallingford: Wallingford, UK, 2000; Volume 44. [Google Scholar]
- Despotovic, J.; Plavsic, J.; Stefanovic, N.; Pavlovic, D. Inefficiency of storm water inlets as a source of urban floods. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argue, J. Storm Drainage Design in Small Urban Catchments: A Handbook for Australian Practice; Australian Government Pub: Adelaide, Australia, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sabtu, N.; Saul, A.J.; Sailor, G. Hydraulic Interaction of a Gully System. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2016, 21, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.P.; Yu, J.T.S.; Wong, A.S.T.; Li, C.W. Hydraulic interception efficiency of gully gratings on steep roads. HKIE Trans. Hong Kong Inst. Eng. 2015, 22, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Eom, K.; Choi, S.; Cho, J. Development of interception capacity equations according to grate inlet types. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 49, 851–861. [Google Scholar]
- Veerappan, R.; Le, J. Hydraulic efficiency of road drainage inlets for storm drainage system under clogging effect. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference th on Flood Risk Management and Response (FRIAR 2016), Venice, Italy, 29 June 2016; Volume 1, pp. 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Md Wakif, S.A.; Sabtu, N. Hydraulic performance of vertically depressed and non-depressed grate. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellez-Alvarez, J.; Gómez, M.; Russo, B. Quantification of Energy Loss in Two Grated Inlets under Pressure. Water 2020, 12, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Russo, B. Comparative study of methodologies determine inlet efficiency from test data. HEC-12 methodology vs. UPC method. In Water Resources Management III; WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment; WIT Press: Algarve, Portugal, 2005; Volume 80, pp. 623–632. ISBN 978-1-84564-007-1. [Google Scholar]
- Holley, E.; Woodward, C.; Brigneti, A.; Ott, C. Hydraulic Characteristics of Recessed Curb Inlets and Bridge Drains; University of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds, M.; Holley, E. Hydraulic Characteristics of Flush Depressed Curb Inlets and Bridge Deck Drains; University of Texas: Austin, TX, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Siphai, S.O. Calibration of a Grate on a Sloping Channel. Master’s Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ozbey, C. Laboratory Investigation of Hydraulic Efficiency of Transverse Grates in Roads. Master’s Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas-Quintero, M.; Carvajal-Serna, F. Review of the hydraulic capacity of urban grate inlet: A global and Latin American perspective. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2575–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.C.Y. Design of street curb opening inlets using a decay-based clogging factor. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begum, S.; Rasul, M.G.; Brown, R.J.; Subaschandar, N.; Thomas, P. An experimental and computational investigation of performance of the green gully for reusing stormwater. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2011, 1, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, P.; Leandro, J.; Carvalho, R.F.; Russo, B.; Gómez, M. Assessment of the Ability of a Volume of Fluid Model to Reproduce the Efficiency of a Continuous Transverse Gully with Grate. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kemper, S.; Schlenkhoff, A. Capacity of street inlets with partially severed grate openings. In Proceedings of the International Junior Researcher and Engineer Workshop on Hydraulic Structures, Lübeck, Germany, 30 May–1 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, M.; Recasens, J.; Russo, B.; Martínez-Gomariz, E. Assessment of inlet efficiency through a 3D simulation: Numerical and experimental comparison. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tellez-Alvarez, J.; Gómez, M.; Russo, B. Hydraulic efficiency and spatial distribution of intercepted flow rate along grated inlet. In Proceedings of the 40th Edition of Italian Conference on Integrated River Basin Management, Cosenza, Italy, 19–22 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, B.; Sunyer, D.; Velasco, M.; Djordjevic, S. Analysis of extreme flooding events through a calibrated 1D/2D coupled model: The case of Barcelona (Spain). J. Hydroinform. 2015, 17, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Russo, B.; Tellez-Alvarez, J. Experimental investigation to estimate the discharge coefficient of a grate inlet under surcharge conditions. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


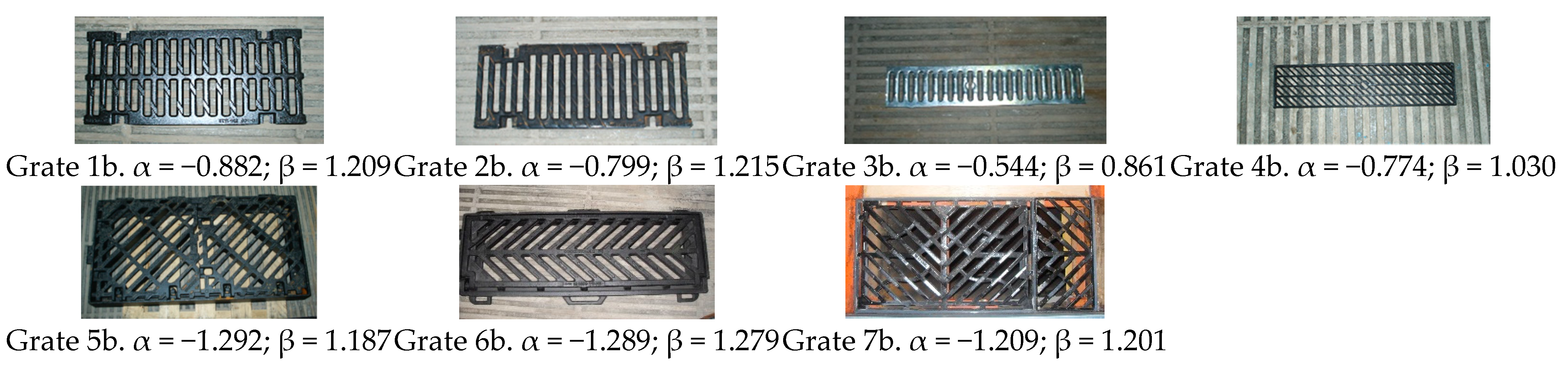


| C0 = ΔE/E | Pattern C1 | Pattern C2 | Pattern C3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grate 1c | 0.451 | 0.502 | 0.674 |
| Grate 2c | 0.265 | 0.400 | 0.677 |
| Grate 3c | 0.234 | 0.360 | - |
| Grate 4c | - | - | 0.545 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, B.; Valentín, M.G.; Tellez-Álvarez, J. The Relevance of Grated Inlets within Surface Drainage Systems in the Field of Urban Flood Resilience. A Review of Several Experimental and Numerical Simulation Approaches. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137189
Russo B, Valentín MG, Tellez-Álvarez J. The Relevance of Grated Inlets within Surface Drainage Systems in the Field of Urban Flood Resilience. A Review of Several Experimental and Numerical Simulation Approaches. Sustainability. 2021; 13(13):7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137189
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Beniamino, Manuel Gómez Valentín, and Jackson Tellez-Álvarez. 2021. "The Relevance of Grated Inlets within Surface Drainage Systems in the Field of Urban Flood Resilience. A Review of Several Experimental and Numerical Simulation Approaches" Sustainability 13, no. 13: 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137189
APA StyleRusso, B., Valentín, M. G., & Tellez-Álvarez, J. (2021). The Relevance of Grated Inlets within Surface Drainage Systems in the Field of Urban Flood Resilience. A Review of Several Experimental and Numerical Simulation Approaches. Sustainability, 13(13), 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137189








