Research on the Relationship between Shared Leadership and Individual Creativity-Qualitative Comparative Analysis on the Basis of Clear Set
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review, Model Building and Research Method
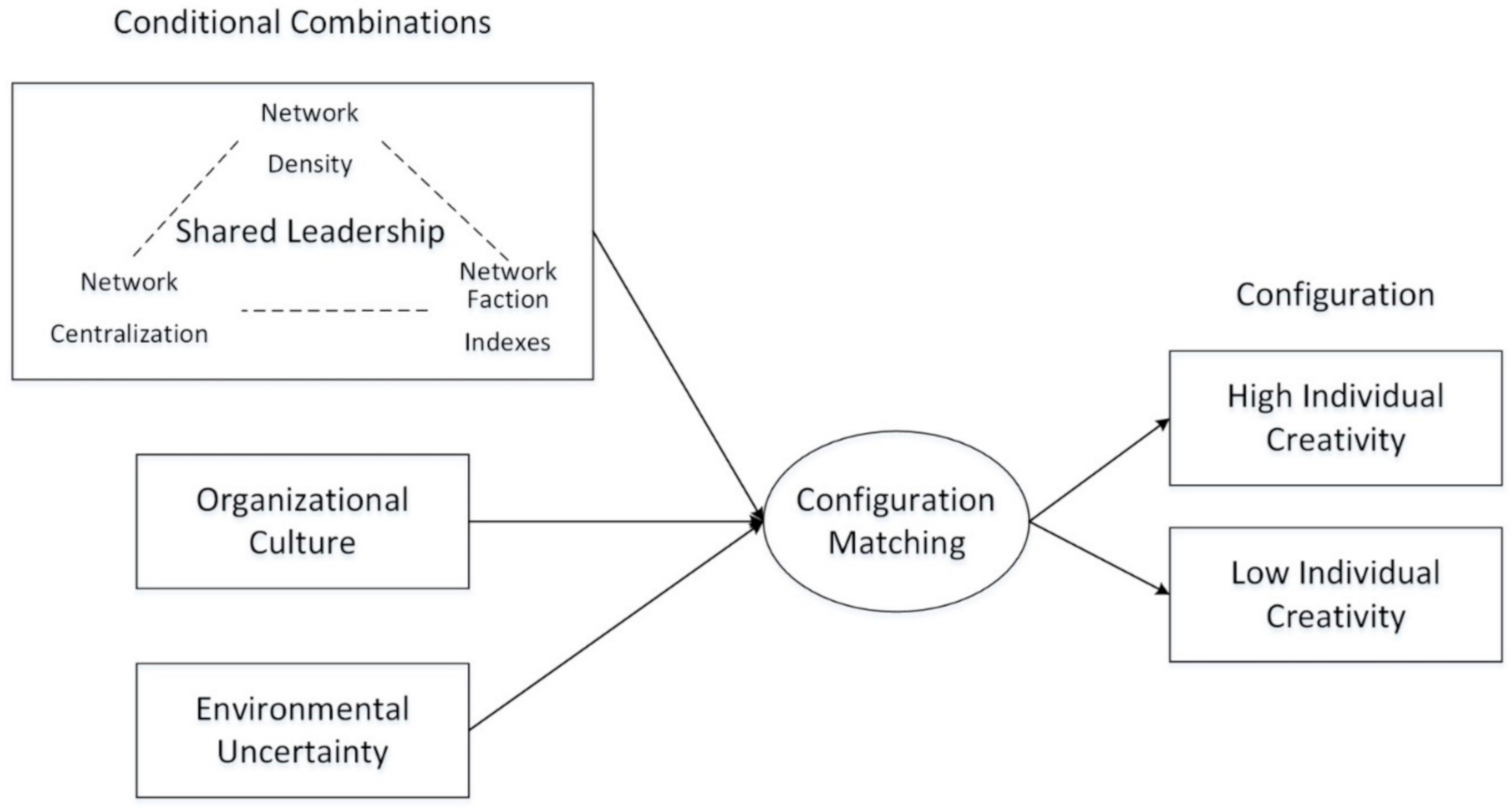
2.1. Literature Review and Model Building
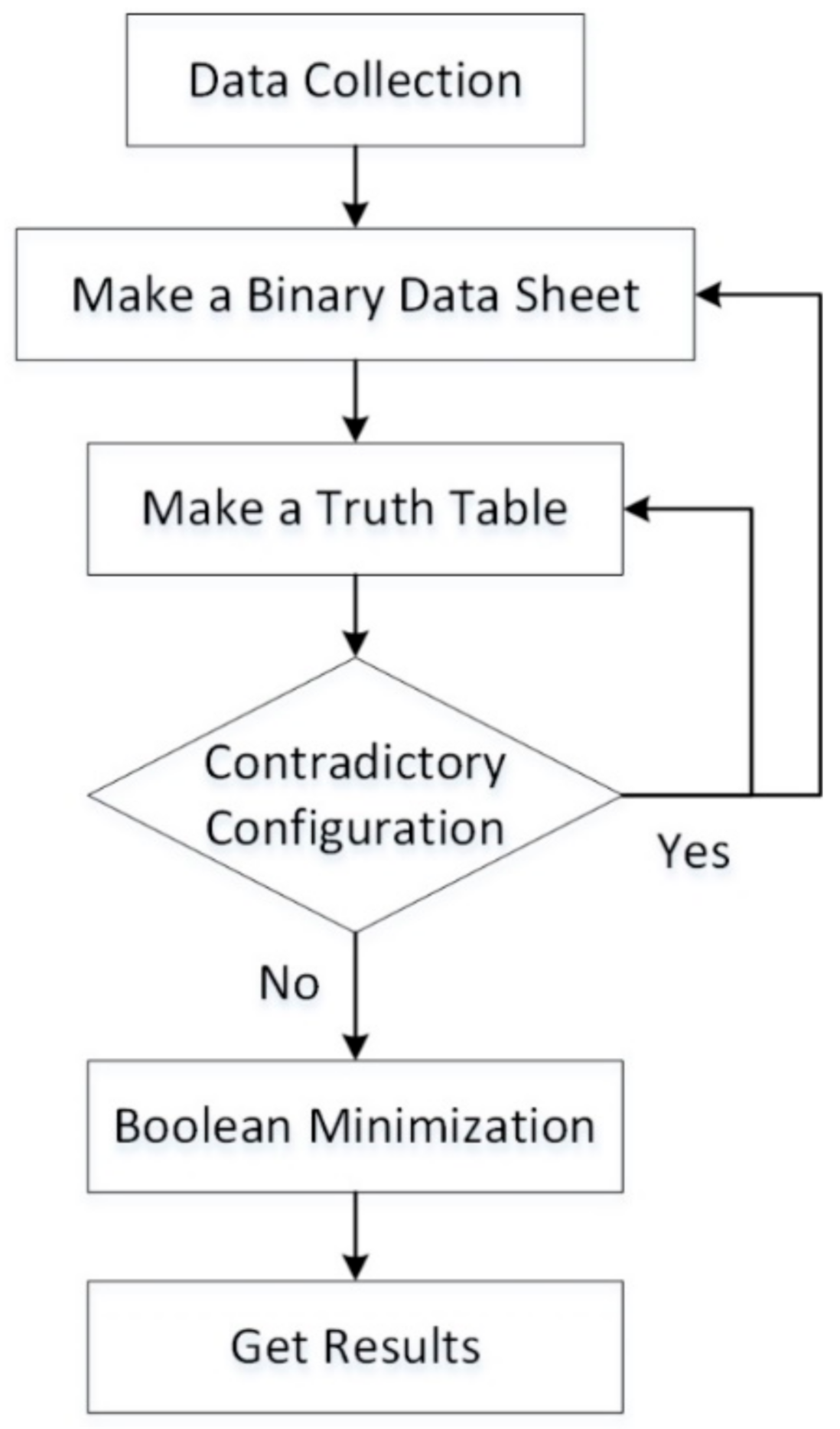
2.2. Qualitative Comparative Analysis Method
3. Data Collection, Measurement and Analysis
3.1. Data Collection and Measurement
3.2. Data Reliability and Validity Test
4. QCA Comparative Analysis
4.1. Data Calibration
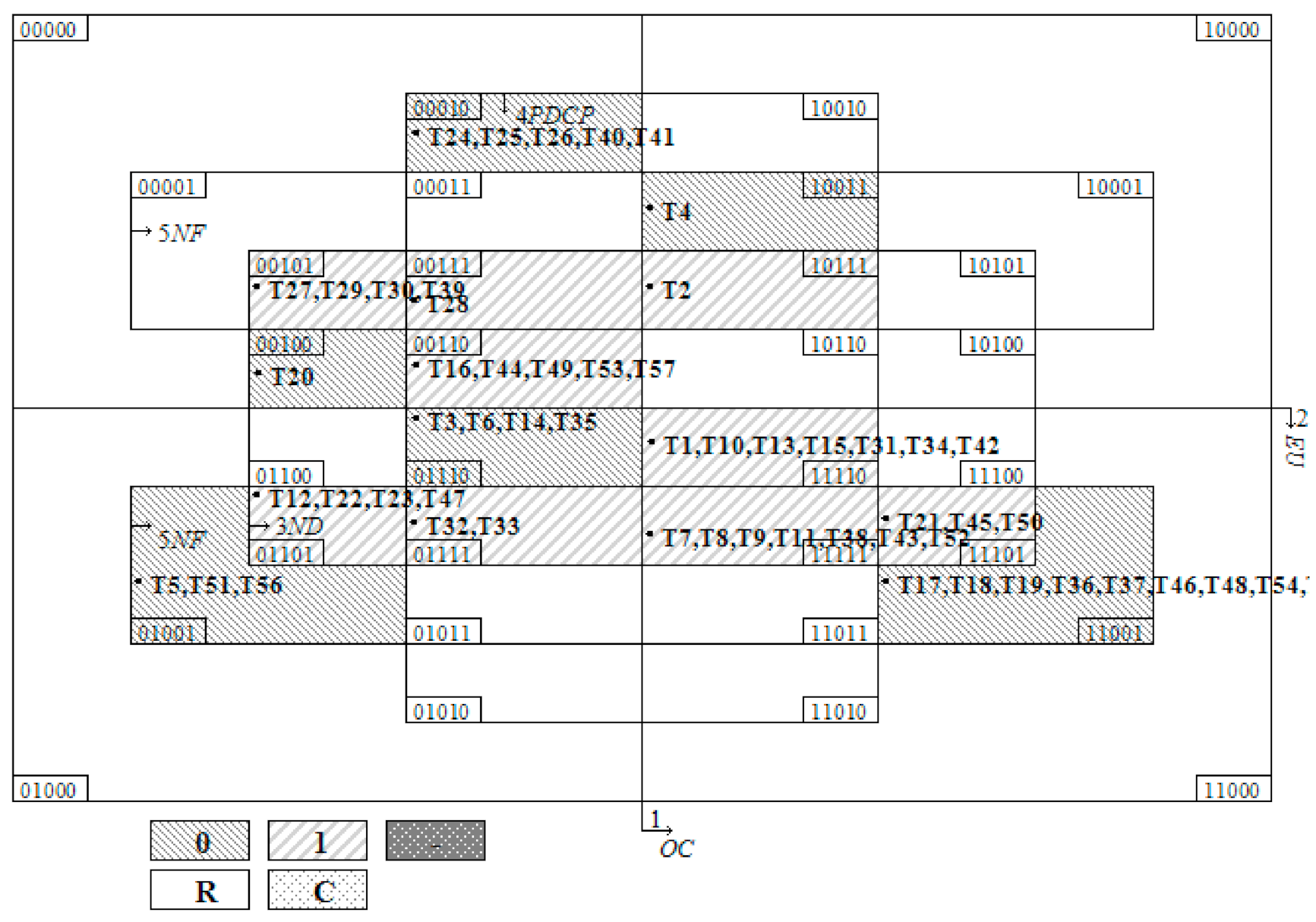
4.2. Constructing a Truth Table
4.3. Configuration Analysis
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Discussion of the Configuration Results That Can Impact the Individual Creativity
5.1.1. Discussion of the Configuration Results That Can Improve the Individual Creativity
5.1.2. Discussion of the Configuration Results That Can Decrease the Individual Creativity
5.2. Research Contribution and Management Implications
5.3. Research Limitation and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, P. Content Structure of Shared Leadership for Knowledge Employees. Psychol. Sci. 2012, 35, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Yi, L. The cross-level effect of entrepreneurial leadership on team creativity. Foreign Econ. Manag. 2020, 42, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J. When the presence of creative coworkers is related to creativity: Role of supervisor close monitoring, developmental feedback, and creative personality. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Luo, J. A Study about the Influence of Shared Leadership on Team Creativity in R&D Team—A Moderated-mediation Model. Technol. Econ. Manag. Res. 2020, 9, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gronn, P.; Rawlings-Sanaei, F. Principal recruitment in a climate of leadership disengagement. Aust. J. Educ. 2003, 47, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, C.C.; Sims, H.P., Jr. Leading workers to lead themselves: The external leadership of self-managing work teams. Adm. Sci. Q. 1987, 14, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandori, A.; Furnari, S. A chemistry of organization: Combinatory analysis and design. Organ. Stud. 2008, 29, 459–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, Y. Theoretical Discussion about the Influence of Dynamic Team Environment on Venture Team Innovation and the Mechanism. Sci. Manag. Res. 2019, 4, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lv, S. Research on Relationship of Intellectual Capital, Innovation Type and Product Innovation Performance. Sci. Sci. Manag. S. & T. 2014, 2, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Rihoux, B.; De Meur, G. Configurational Comparative Methods: Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) and Related Techniques; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 33–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q. Analysis of the empirical mediating effect of innovative SMEs’ organizational situation. Sci. Res. Manag. 2015, 36, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, C.L.; Ensley, M.D. A reciprocal and longitudinal investigation of the innovation process: The central role of shared vision in product and process innovation teams (PPITs). J. Organ. Behav. 2004, 25, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhu, F.; Sun, X. Influencing Factors of Role Identification of Horizontal Leaders in Innovation Projects: A Qualitative Comparative Analysis Based on Fuzzy Set. Nankai Manag. Rev. 2020, 4, 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Mei, J. Research on Influence of Leader Empowerment on Employee Innovation Behavior—A Moderated Mediation Model. Soft Sci. 2018, 32, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Hu, Y. The dynamic impacts of shared leadership and the transactive memory system on team performance: A longitudinal study. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 130, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, B.C.; Paul, E.T.; Jennifer, A.M. Shared leadership in teams: An investigation of antecedent conditions and performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 5, 1217–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Novoselich, B.J.; Knight, D.B. Shared leadership in capstone design teams: Social network analysis. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2018, 144, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, M.J. Too much of a good thing or the more the merrier? Exploring the dispersion and gender composition of informal leadership in manufacturing teams. Small Group Res. 1999, 30, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, E.H. Organizational Culture and Leadership; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, M.A.; Phelps, C.C. Interfirm collaboration networks: The impact of large-scale network structure on firm innovation. Manag. Sci. 2007, 53, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, J.S. The Organizational Culture Perspective; Dorsey Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zain, M.; Kassim, N.M. The influence of internal environment and continuous improvements on firms competitiveness and performance. Proscenia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 65, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Shi, J.; Zhang, T. An Empirical Research on Relationship in LMX, TMX, Organization Climate for Innovation and Innovational Behavior in China. J. Ind. Eng. Eng. Manag. 2009, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, K.; Chou, C. The impact of open innovation on firm performance: The modeling effects of internal R&D and environmental turbulence. Technovation 2013, 33, 368–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yeung, J.H.; Zhang, M. The impact of trust and contract on innovation performance: The moderating role of environmental uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 134, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, S.; Engelen, A.; Brettel, M. Top management’s social capital and learning in new product development and its interaction with external uncertainties. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2012, 41, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Davies, J. “The person with maximum knowledge will win the race”: Conceptualizing knowledge in micro-businesses. J. Small Bus. 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.L.; Sims, H.P. Vertical versus shared leadership as predictors of the effectiveness of change management teams: An examination of aversive, directive, transactional, transformational, and empowering leader behaviors. Group Dyn. Theory Res. Pract. 2002, 6, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boies, K.; Lvina, E.; Martens, M.L. Shared Leadership and Team Performance in a Business Strategy Simulation. J. Pers. Psychol. 2010, 9, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, X. Examining the cross-level relationship between shared leadership and learning in teams: Evidence from China. Leadersh. Q. 2014, 25, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Long, L.R.; He, W. How does shared leadership affect team output? The role of information exchange, passion and environmental uncertainty. Psychol. News 2015, 49, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, J.Z.; Rentsch, J.R.; Small, E.E.; Davenport, S.W.; Berman, S.M. The shared leadership process in Decision-Making teams. J. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 152, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, Y. Theoretical discussion on the influence and mechanism of the dynamics of external environment on the innovation of entrepreneurial teams. Sci. Manag. Res. 2019, 4, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatraman, N. The concept of fit in strategy research: Toward verbal and statistical correspondence. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 3, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmieleski, K.M.; Cole, M.S.; Baron, R.A. Shared authentic leadership and new venture performance. J. Manag. 2012, 38, 1476–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Sun, Z.Z.; Liu, X.M. The influence of social network on employee knowledge concealment and individual creativity. Soft Sci. 2018, 32, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Rihax, L. QCA Design Principles and Applications: A New Approach beyond Qualitative and Quantitative Research; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, K.S.; Quinn, R.E. Diagnosing and Changing Organizational Culture: Based on the Competing Values Framework; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 23–59. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Yang, C. The R&D and marketing cooperation across new product development stages: An empirical study of Taiwan’s IT industry. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2004, 33, 593–605. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Tang, C. Employees’ knowledge searching in professional virtual forums and in teams: A complement or substitute. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 74, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Donthu, N. Developing and Validating a Multidimensional Consumer-Based Brand Equity Scale. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.D. Particularistic trust and general trust—A network analysis in Chinese organizations. Manag. Organ. Rev. 2005, 1, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Johanson, M.; Davies, J.; Dana, L.-P.; Budhathoki, T. Compassionate customer service in ethnic minority microbusinesses. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 5, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, C.L.; Manz, C.C.; Sims, H.P. The roles of vertical and shared leadership in the enactment of executive corruption: Implications for research and practice. Leadersh. Q. 2009, 20, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staw, B.M.; Sandelands, L.E.; Dutton, J.E. Threat rigidity effects in organizational behavior: A multilevel analysis. Adm. Sci. Q. 1981, 26, 501–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, W.; Quan, Y. The Impact of work pressure on employees’ creativity. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2021, 2, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Day, D.V.; Gronn, P.; Salas, E. Leadership capacity in teams. Leadersh. Q. 2006, 15, 857–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vias, C.N.; Kate, A.L.; Tiffani, R.C.; Alan, J.T.; Eric, J.W.; Stephen, J.Z.; Jose, M.C. The shared leadership of teams: A meta-analysis of proximal, distal, and moderating relationships. Leadersh. Q. 2014, 25, 923–942. [Google Scholar]
- Ilgen, D.R.; Hollenbeck, J.R.; Johnson, M.; Jundt, D. Teams in organizations: Frominput-process-output models to IMOI models. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2005, 56, 517–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Items | CITC | Rotation Matrix | Cronbach’s Alpha | Cumulative (%) | KMO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor | |||||||
| Organizational Culture (OC) | OC1 | 0.660 | 0.703 | 0.909 | 77.280 | 0.783 | |
| OC2 | 0.831 | 0.937 | |||||
| OC3 | 0.894 | 0.946 | |||||
| OC4 | 0.726 | 0.782 | |||||
| OC5 | 0.634 | 0.679 | |||||
| OC6 | 0.865 | 0.904 | |||||
| Environmental Uncertainties (EU) | MU1 | 0.707 | 0.733 | 0.859 | 87.955 | 0.755 | |
| MU2 | 0.579 | 0.906 | |||||
| MU3 | 0.698 | 0.813 | |||||
| MU4 | 0.655 | 0.857 | |||||
| TU1 | 0.645 | 0.631 | |||||
| TU2 | 0.686 | 0.632 | |||||
| TU3 | 0.732 | 0.804 | |||||
| TU4 | 0.716 | 0.751 | |||||
| Team Individual Creativity (TIC) | TIC1 | 0.722 | 0.804 | 0.833 | 81.005 | 0.869 | |
| TIC2 | 0.835 | 0.761 | |||||
| TIC3 | 0.771 | 0.902 | |||||
| TIC4 | 0.828 | 0.761 | |||||
| TIC5 | 0.782 | 0.866 | |||||
| TIC6 | 0.849 | 0.846 | |||||
| Instrument Total Cronbach’s Alpha→0.783 | |||||||
| CR | AVE | MSV | Max r | OC | MU | TIC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational Culture (OC) | 0.917 | 0.652 | 0.454 | 0.674 | 0.807 | ||
| Environmental Uncertainties (MU) | 0.879 | 0.556 | 0.446 | 0.668 | 0.668 | 0.745 | |
| Team Individual Creativity (TIC) | 0.931 | 0.694 | 0.454 | 0.674 | 0.674 | 0.534 | 0.833 |
| Variables | Type of Variables | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Conditional variables | Network density of shared leadership (ND) | Mean value is 0.482, if the single sample datum is equal or greater than the mean value, the coding is “1”, or it is “0” |
| Point degree central potential of shared network (PDCP) | Mean value is 0.401, if the single sample datum is equal or greater than the mean value, the coding is “1”, or it is “0” | |
| Network faction of shared network (NF) | Mean value is 2.9, if the single sample datum is equal or greater than the mean value, the coding is “1”, or it is “0” | |
| Organizational culture (OC) | Mean value is 6.000, if the single sample datum is equal or greater than the mean value, the coding is “1”, or it is “0” | |
| Environmental uncertainty (EU) | Mean value is 4.867, if the single sample datum is equal or greater than the mean value, the coding is “1”, or it is “0” | |
| Result variable | Individual creativity (TIC) | Mean value is 5.379, if the single sample datum is equal or greater than the mean value, the coding is “1”, or it is “0” |
| Sample | OC | EU | ND | PDCP | NF | TIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T24, T25, T26, T40, T41, T60, T67, T89, T104, T111 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| T20,T59 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| T27, T29, T30, T39, T69,T71,T80,T113 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| T16, T44, T49, T53, T57, T75,T84,T93,T98,T105 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| T28,T66 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| T5, T51, T56, T61, T92, T112 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| T12, T22, T23, T47, T82, T97, T103, T107 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| T3, T6, T14, T35, T72, T108, T109, T114 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| T32, T33,T77, T116 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| T4, T62 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| T2,T101 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| T17, T18, T19, T36, T37, T46, T48, T54, T55, T58, T63, T65, T78, T81, T85, T86, T87, T88, T91, T96 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| T21, T45, T50, T73, T74, T194 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| T1, T10, T13, T15, T31, T34, T42, T64, T76, T79, T90, T95, T106, T110 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| T7, T8, T9, T11, T38, T43, T52, T68, T70, T83, T99, T100, T102, T115 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Conditional Combination | Number of Cases | Proportion % |
|---|---|---|
| ND*NF | 44 | 37.93% |
| OC*ND | 36 | 31.03% |
| eu*ND*PDCP | 14 | 12.07% |
| Conditional Combination | Number of Cases | Proportion % |
|---|---|---|
| nd | 38 | 32.76% |
| oc*EU*pdcp | 8 | 6.90% |
| pdcp*NF | 2 | 1.72% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Wen, T. Research on the Relationship between Shared Leadership and Individual Creativity-Qualitative Comparative Analysis on the Basis of Clear Set. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105445
Sun M, Wang J, Wen T. Research on the Relationship between Shared Leadership and Individual Creativity-Qualitative Comparative Analysis on the Basis of Clear Set. Sustainability. 2021; 13(10):5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105445
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Muyun, Jigan Wang, and Ting Wen. 2021. "Research on the Relationship between Shared Leadership and Individual Creativity-Qualitative Comparative Analysis on the Basis of Clear Set" Sustainability 13, no. 10: 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105445
APA StyleSun, M., Wang, J., & Wen, T. (2021). Research on the Relationship between Shared Leadership and Individual Creativity-Qualitative Comparative Analysis on the Basis of Clear Set. Sustainability, 13(10), 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105445





