The Impact of Water and Soil Scarcity and Pollution on Industrial Agglomeration: Evidence from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of the Related Research Literature
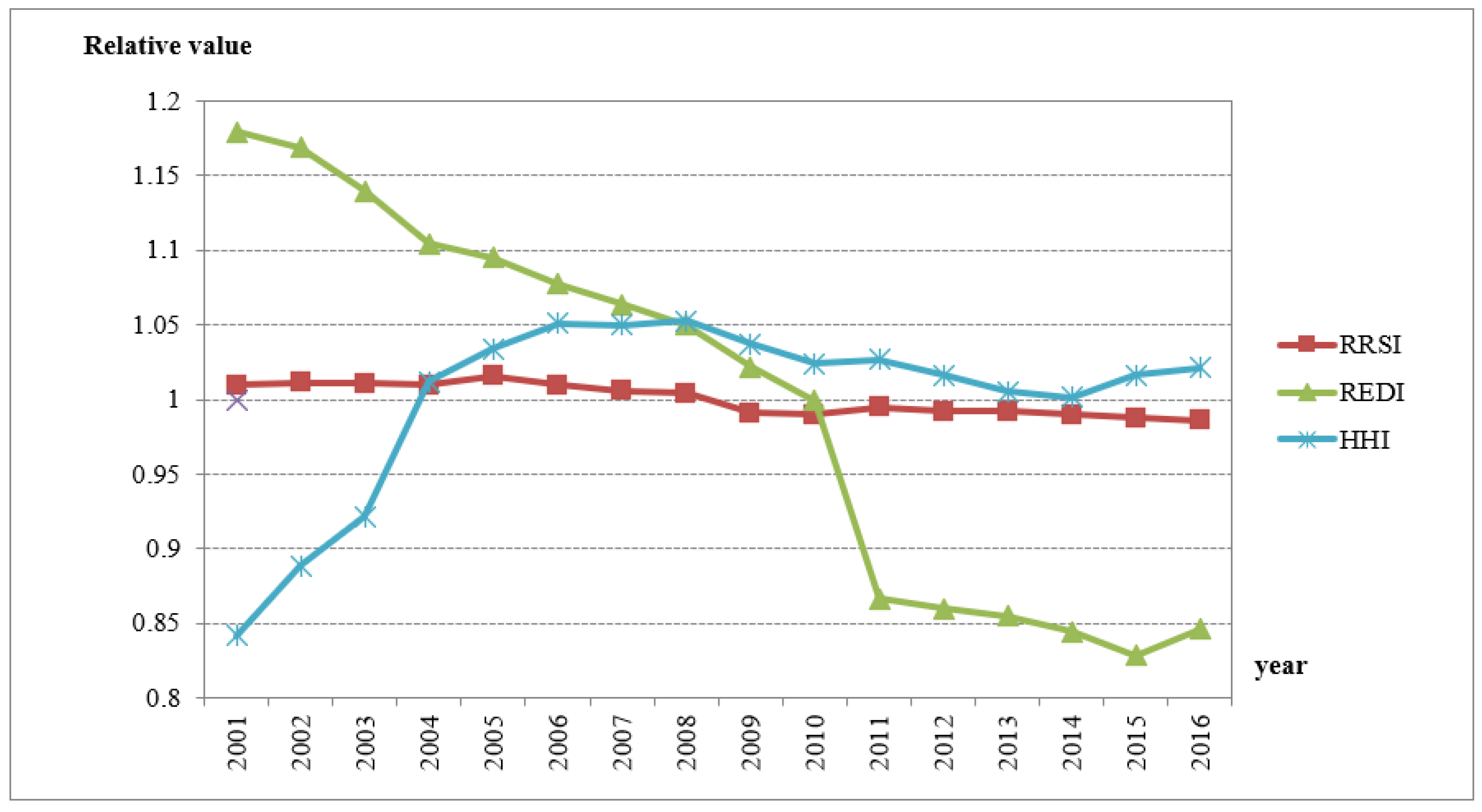
3. Changes in Industrial Agglomeration, Resource Shortages, and Environmental Damage Degrees in China over Time
4. Theoretical Framework and Empirical Model
4.1. Theoretical Model
4.2. Empirical Model
5. Econometric Analysis Results
5.1. Empirical Results
5.2. Robustness Check
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Industries Used in the Construction of HHI
| GB/T 4754-2002 Industrial Classification for National Economic Activities | China Industrial Statistics Yearbook | Industries Used in the Construction of HHI |
| 06 Mining and washing of coal | Mining and washing of coal | Mining and washing of coal |
| 07 Extraction of petroleum and natural gas | Extraction of petroleum and natural gas | Extraction of petroleum and natural gas |
| 08 Mining and processing of ferrous metal ores | Mining and processing of ferrous metal ores | Mining and processing of ferrous metal ores |
| 09 Mining and processing of non-ferrous metal ores | Mining and processing of non-ferrous metal ores | Mining and processing of non-ferrous metal ores |
| 10 Mining and processing of nonmetal ores | Mining and processing of nonmetal ores | |
| 11 Mining of other ores | ||
| 13 Processing of food from agricultural products | Processing of food from agricultural products | Processing of food from agricultural products |
| 14 Manufacture of foods | Manufacture of foods | Manufacture of foods |
| 15 Manufacture of beverages | Manufacture of beverages | Manufacture of beverages |
| 16 Manufacture of tobacco | Manufacture of tobacco | Manufacture of tobacco |
| 17 Manufacture of textiles | Manufacture of textiles | Manufacture of textiles |
| 18 Manufacture of textile, apparel, footwear, and caps | Manufacture of textile, apparel, footwear, and caps | |
| 19 Manufacture of leather, fur, feather, and related products | ||
| 20 Processing of timber, manufacture of wood, bamboo, rattan, palm, and straw products | ||
| 21 Manufacture of furniture | ||
| 22 Manufacture of paper and paper products | Manufacture of paper and paper products | Manufacture of paper and paper products |
| 23 Printing and recorded media | ||
| 24 Manufacture of articles for culture, education, and sport activity | ||
| 25 Processing of petroleum, coking, processing of nuclear fuel | Processing of petroleum, coking, processing of nuclear fuel | Processing of petroleum, coking, processing of nuclear fuel |
| 26 Manufacture of chemical raw materials and chemical products | Manufacture of chemical raw materials and chemical products | Manufacture of chemical raw materials and chemical products |
| 27 Manufacture of medicines | Manufacture of medicines | Manufacture of medicines |
| 28 Manufacture of chemical fibers | Manufacture of chemical fibers | Manufacture of chemical fibers |
| 29 Manufacture of rubber | ||
| 30 Manufacture of plastics | ||
| 31 Manufacture of non-metallic mineral products | Manufacture of non-metallic mineral products | Manufacture of non-metallic mineral products |
| 32 Smelting and processing of ferrous metals | Smelting and pressing of ferrous metals | Smelting and pressing of ferrous metals |
| 33 Smelting and pressing of non-ferrous metals | Smelting and processing of ferrous metals | Smelting and processing of ferrous metals |
| 34 Manufacture of metal products | Manufacture of metal products | Manufacture of metal products |
| 35 Manufacture of general purpose machinery | Manufacture of general purpose machinery | Manufacture of general purpose machinery |
| 36 Manufacture of special purpose machinery | Manufacture of special purpose machinery | Manufacture of special purpose machinery |
| 37 Manufacture of transport equipment | Manufacture of transport equipment | Manufacture of transport equipment |
| 38 Manufacture of railway, ship, aerospace, and other transport equipment | ||
| 39 Manufacture of electrical machinery and equipment | Manufacture of electrical machinery and equipment | Manufacture of electrical machinery and equipment |
| 40 Manufacture of communication equipment, computers, and other electronic equipment | Manufacture of communication equipment, computers, and other electronic equipment | Manufacture of communication equipment, computers, and other electronic equipment |
| 41 Manufacture of measuring instruments and machinery for cultural activity and office work | Manufacture of measuring instruments and machinery for cultural activity and office work | Manufacture of measuring instruments and machinery for cultural activity and office work |
| 42 Manufacture of artwork and othermanufacturing | ||
| 43 Recycling and disposal of waste | ||
| 44 Production and distribution of electric power and heat power | Production and distribution of electric power and heat power | Production and distribution of electric power and heat power |
| 45 Production and distribution of gas | ||
| 46 Production and distribution of tap water |
References
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook; Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y. China’s water scarcity. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3185–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Increasing Returns and Economic Geography. J. Political Econ. 1991, 99, 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Krugman, P. When is the economy monocentric: Von Thiinen and Chamberlin unified? Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1995, 25, 505–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, S.S.; Strange, W.C. The determinants of agglomeration. J. Urban Econ. 2001, 50, 191–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Regions, resources, and economic geography: Sources of U.S. regional comparative advantage, 1880-1987. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1999, 29, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, G.; Glaeser, E.L. The geographic concentration of industry: Does natural advantage explain agglomeration? Am. Econ. Rev. 1999, 89, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, G.; Glaeser, E.L. Geographic Concentration in U.S. Manufacturing Industries: A Dartboard Approach. J. Political Econ. 1997, 105, 889–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, C.; Lu, M.Q.; Lu, Y.Q. Assessing the suitability of regional human settlements environment from a different preferences perspective: A case study of Zhejiang Province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pu, Y.J. Studies of welfare effects and countermeasures of negative externalities of regional excessive agglomeration: The simulation analysis based on the method of Spatial Economics. J. Financ. Econ. 2008, 34, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.Y. The effect of agglomeration of international vertical specializations on China’s environment. Acad. Forum. 2012, 35, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Q.; Li, W.N. Agglomeration externalities, environment technical efficiencies and energy saving. Soft Sci. 2011, 25, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.Z.; Su, L.; Qiao, J. Investigation of the relationship of industrial agglomeration development and environmental pollutions: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2011, 29, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm, M. In Search of a Basis for Location Theory: Microeconomics or Welfare Economics? Prog. Geogr. 1997, 3, 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.M. Human Geography: A Welfare Approach; Edward Arnold: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bale, J. Externality Gradients. Area 1978, 10, 334–336. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, K. The Limits of Regional Agglomeration and Social Cost. In Contemporary Industrialization; Hamilton, F.E.I., Ed.; Longman: London, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, H. Spatial Aspects of Environmental Economics. In Handbook of Natural Resource and Energy Economics; Kneese, A.V., Sweeney, J.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Markusen, J.R.; Morey, E.R.; Olewiler, N. Non-cooperative equilibria in regional environmental policies when plant locations are endogenous. J. Public Econ. 1995, 56, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, M. Environmental regulation and the location of polluting industries. Int. Tax Public Financ. 1995, 2, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoel, M. Environmental policy with endogenous plant locations. Scand. J. Econ. 1997, 99, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflüger, M. Ecological dumping under monopolistic competition. Scand. J. Econ. 2001, 103, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, M. Hot Spots, High Smokestacks, and the Geography of Pollution. Paper Presented at the World Congress of Environmental and Resource Economists in Venice, 1998. Available online: http://www.feem-web.it/worldcongress/abs2/rausch2.html (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Rauscher, M. Concentration, separation, and dispersion: Economic geography and the environment. Thünen-Series of Applied Economic Theory. Working Paper No. 109, 2009. Available online: https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/39752/1/610730487.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Elbers, C.; Withagen, C. Environmental policy, population dynamics and agglomeration. Contrib. Econ. Anal. Policy 2004, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Marrewijk, C. Geographical economics and the role of pollution on location. ICFAI J. Environ. Econ. 2005, 3, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lange, A.; Quaas, M.F. Economic geography and the effect of environmental pollution on agglomeration. B.E. J. Econ. Anal. Policy 2007, 7, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.M.; Yang, L.S.; Lü, H.J.; Shen, X. Study of resource shortage, environmental damage and effect on industrial agglomeration: Based on empirical analysis of provincial level industries of China in 21st century. Manag. World 2012, 11, 28–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.C.; Scott, A.J. Industrial agglomeration and development: A survey of spatial economic issues in East Asia and a statistical analysis of Chinese regions. Econ. Geogr. 2003, 79, 295–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.M. Scale economy, technical changes and total factor productivity in regional manufacturing industry: Effect analysis of industrial clusters. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2009, 29, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Lu, D.; He, Y.; Chiu, Y. The efficiencies of resource-saving and environment: A case study based on Chinese cities. Energy 2018, 150, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Niu, S. Evolutional analysis of coupling between population and resource-environment in China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 12, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, J. Marketization and water resource utilization efficiency in China. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2019, 22, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Eshima, N. A population explosion in an evolutionary game in spatial economics: Blow up radial solutions to the initial value problem for the replicator equation whose growth rate is determined by the continuous Dixit–Stiglitz–Krugman model in an urban setting. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2015, 23, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspremont, D.C.; Dos Santos Ferreira, R. The Dixit–Stiglitz economy with a ‘small group’ of firms: A simple and robust equilibrium markup formula. Res. Econ. 2017, 71, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.A.; Feng, X.Y.; Zhao, J.Y. Local government competitions and the reconstruction of market orders. Soc. Sci. China 2004, 1, 56–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Chen, Z. The economic growth of segmentation markets: Why economic opening may aggravate local protection? Econ. Res. J. 2009, 3, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Qiao, Y. How government competitions promote China’s rapid economic growth: Further discussion of market segmentation and economic growth. J. World Econ. 2011, 7, 43–63. [Google Scholar]
- Krugman, P.; Venables, A.J. Globalization and the Inequality of Nations. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 857–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. Geography and Trade; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M. Regional repositioning and agglomeration of China’s industries. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 3, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone, A.; Hall, R. Productivity and the density of economic activity. Am. Econ. Rev. 1996, 86, 54–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. Regression Analysis; Social Sciences Academic Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Variable Definition | Data Source | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level of industrial agglomeration(Hit) | Hirschman-Herfindahl index(HHI) | China Industry Economy Statistical Yearbook, 2002 to 2017 | 0.7231 | 0.6368 |
| Demand scale(Dsit) | The proportion of regional domestic consumption in China | China Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2017 | 1.0177 | 0.7580 |
| Environmental damage costs(Enit) | The sum of environmental damage costs of land, water and atmosphere | China Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2017 | 0.9677 | 0.0584 |
| Resource input costs(Reit) | The sum of input costs of land and water resources | China Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2009, 2011–2017; China Land and Resources Statistical Yearbook, 2017 | 2.9377 | 2.2130 |
| Trade costs(Tcit) | The sum of transaction costs and transport costs | China City Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2017 | 0.0968 | 0.0487 |
| Local government competition(Coit) | FDI/GDP | China Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2017 | 0.0576 | 0.0714 |
| Regional market segmentation(Frit) | Relative price variance | China Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2017 and other data | 0.0001 | 0.0012 |
| Economies of scale(Seit) | The ratio of the total industrial output value to the national share and the number of industrial enterprises to the national share | China Industry Economy Statistical Yearbook, 2002–2017 | 1.0911 | 0.3371 |
| Explanatory Variables | Explained Variables H | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
| C | 0.1351 *** (0.0226) | 0.0641 *** (0.0114) | 0.0778 *** (0.0052) | 0.0604 *** (0.0141) | 0.1405 *** (0.0237) | 0.0543 (0.0364) |
| En | −0.1746 ** (0.0864) | −0.0993 ** (0.0450) | −0.0087 * (0.0174) | −0.0843 ** (0.0475) | −0.2031 ** (0.0909) | 0.0886 (0.0856) |
| Re | −0.0017 * (0.0016) | −0.0003 * (0.0004) | −0.0004 * (0.0003) | −0.0003 * (0.0004) | −0.0038 * (−0.0038) | −0.0028 * (0.0046) |
| Tc | −0.4206 ** (0.1928) | −0.1064 (0.1078) | −0.0133 (0.0449) | −0.0804 (0.1259) | −0.2936 (0.1958) | −0.1953 (0.1217) |
| Se | −0.0026 (0.0057) | −0.0026 ** (0.0013) | −0.0030 *** (0.0009) | −0.0021 (0.0021) | 0.1957 (0.0058) | 0.0003 (0.0054) |
| Ds | 0.0028 * (0.0026) | 0.0323 *** (0.0084) | 0.0012 * (0.0009) | 0.0304 *** (0.0080) | 0.0039 ** (0.0038) | 0.0303 ** (0.0223) |
| Co | 0.0016 (0.0033) | −0.0026 (0.0128) | −0.2061 *** (0.0660) | 0.1735 (0.1413) | ||
| Fr | 0.0573 (0.1332) | 9.6795 (29.0268) | −0.7812 (16.9062) | 0.1413 (50.0465) | ||
| En*Co | −3.1225 *** (0.9755) | −2.3268 (0.01658) | ||||
| Re*Co | −0.0256 *** (0.0228) | −0.0166 (0.01658) | ||||
| En*Fr | 320.3710 (372.5401) | 134.2451 (940.3537) | ||||
| Re*Fr | 372.5401 (12.0955) | 23.7200 (38.9044) | ||||
| The number of samples | 496 | 465 | 496 | 465 | 496 | 465 |
| Regression method | LS | TSLS | LS | TSLS | LS | TSLS |
| Adjusted R-squared | 0.9582 | 0.9640 | 0.9597 | 0.9596 | 0.9593 | 0.9643 |
| Hausman statistics (H0: Random effects) | 23.1209 *** | 28.2763 *** | 49.1567 *** | |||
| Hausman P-value (H0: Exogenous resource environment variables) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||
| LLC statistics Fisher-PP statistic (H0: Unit root) | −9.7085 *** 155.290 *** | −3.5582 *** 225.405 *** | −9.0254 *** 166.873 *** | −4.6606 *** 228.492 *** | −7.1665 *** 193.825 *** | −5.4219 *** 223.825 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. The Impact of Water and Soil Scarcity and Pollution on Industrial Agglomeration: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5428. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105428
Zhu Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Li L. The Impact of Water and Soil Scarcity and Pollution on Industrial Agglomeration: Evidence from China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(10):5428. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105428
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yingming, Yuan Li, Yi Wang, and Lingfeng Li. 2021. "The Impact of Water and Soil Scarcity and Pollution on Industrial Agglomeration: Evidence from China" Sustainability 13, no. 10: 5428. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105428
APA StyleZhu, Y., Li, Y., Wang, Y., & Li, L. (2021). The Impact of Water and Soil Scarcity and Pollution on Industrial Agglomeration: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 13(10), 5428. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105428






