Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
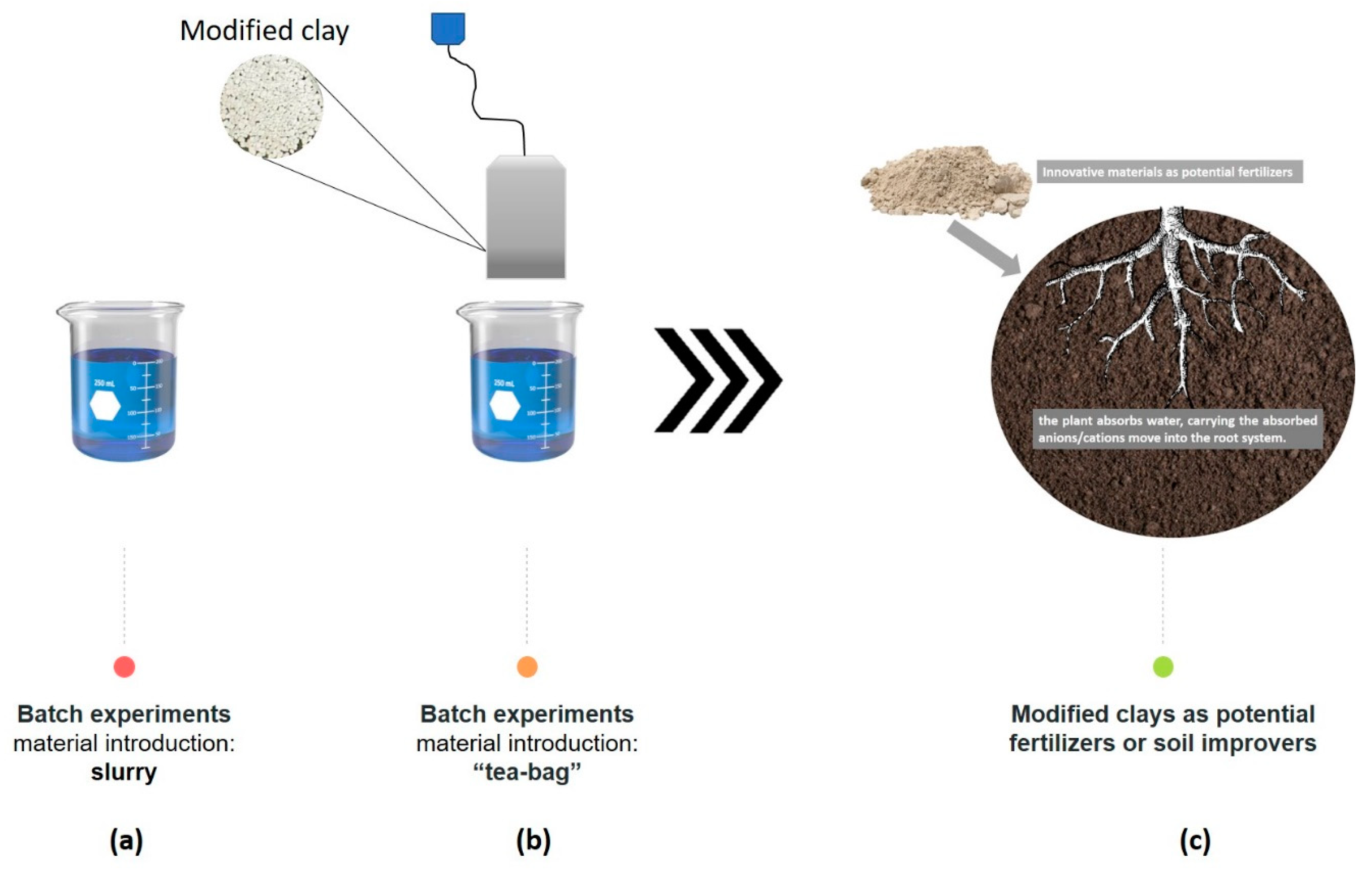
2.2. Batch Experiments
2.2.1. Sorption Capacity
2.2.2. Sorption Kinetics
2.2.3. Effect of LMB and f-MB on Turbidity
2.3. Adsorption Efficiency
2.4. Leaching Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
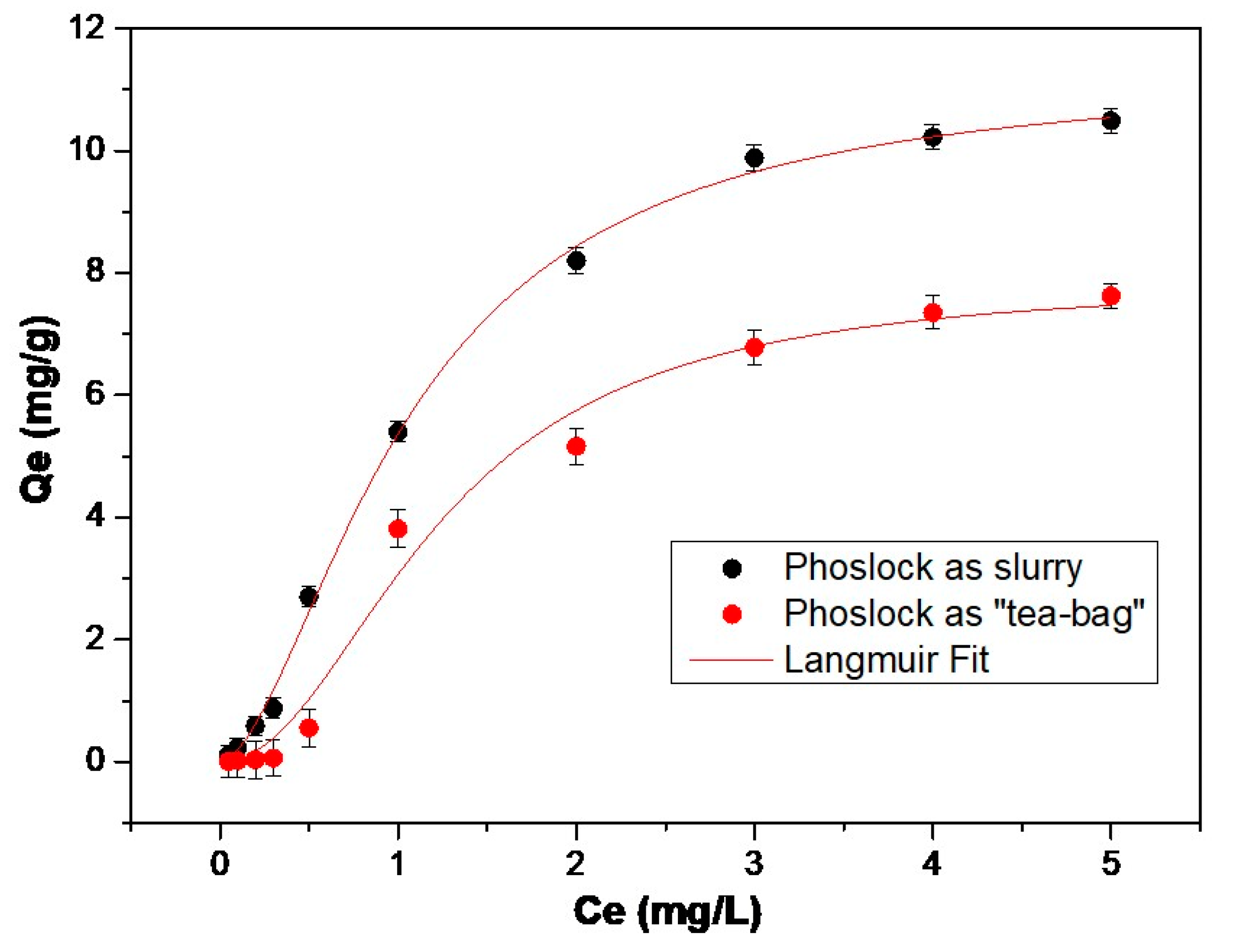
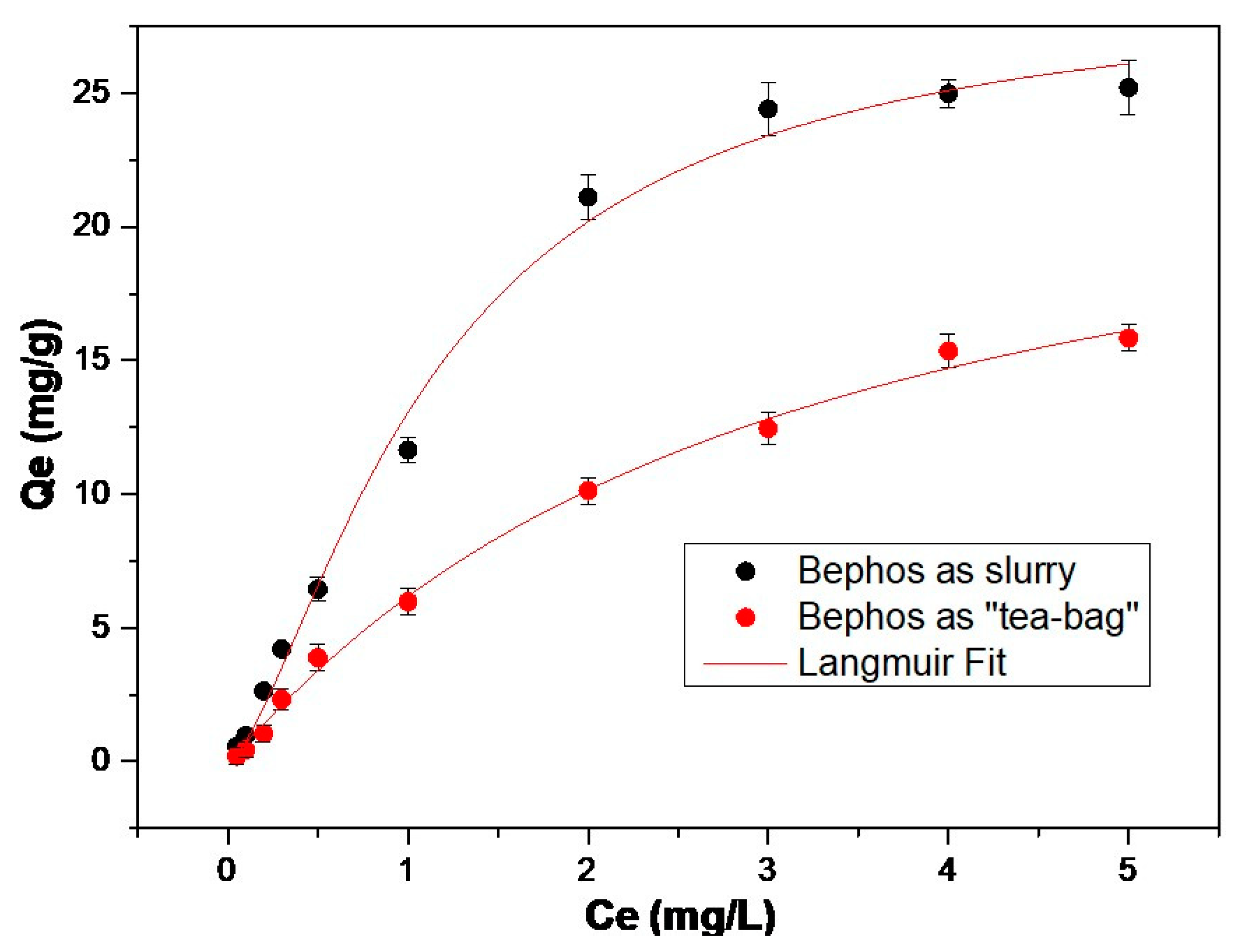
3.1. Adsorption Isotherms
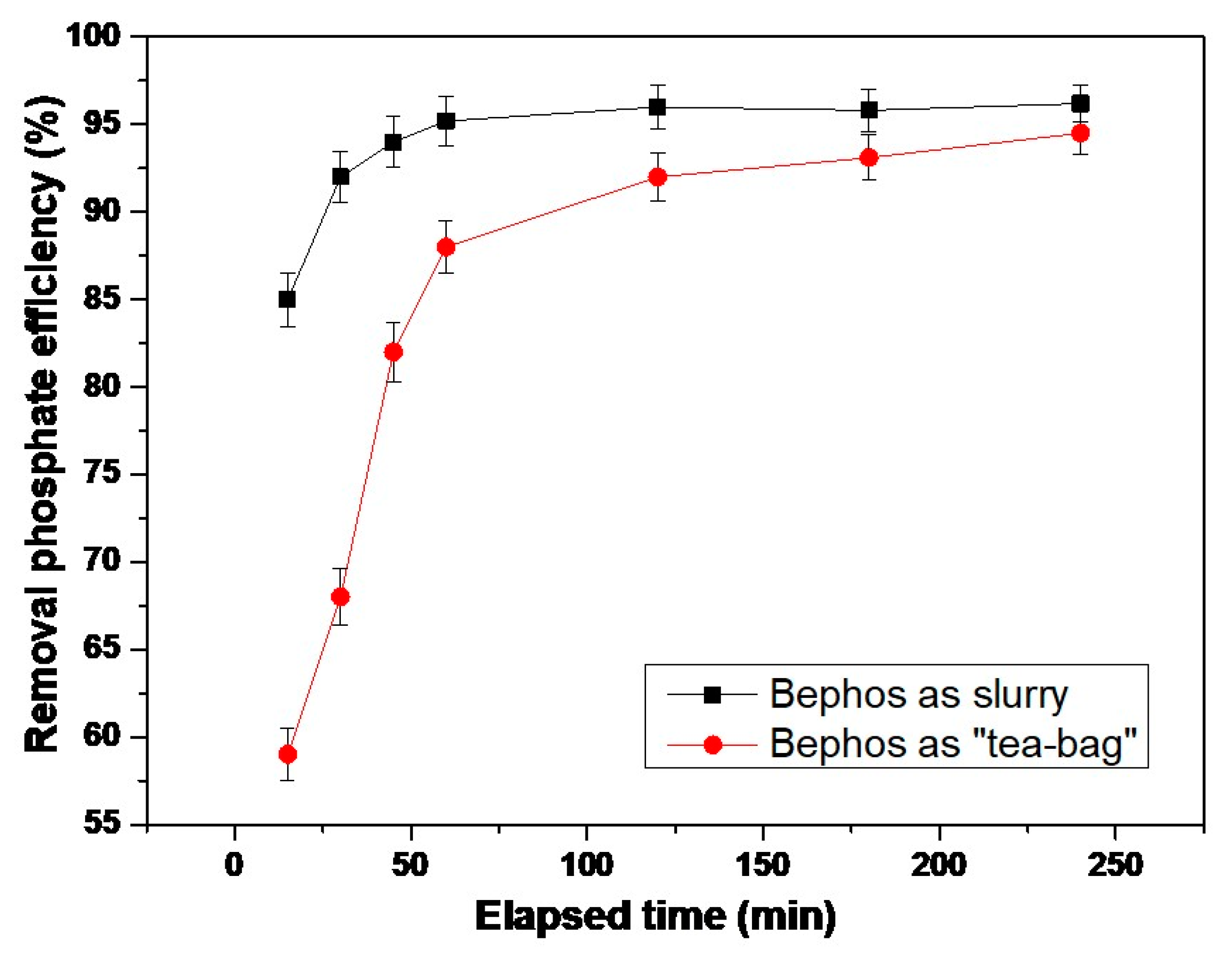
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
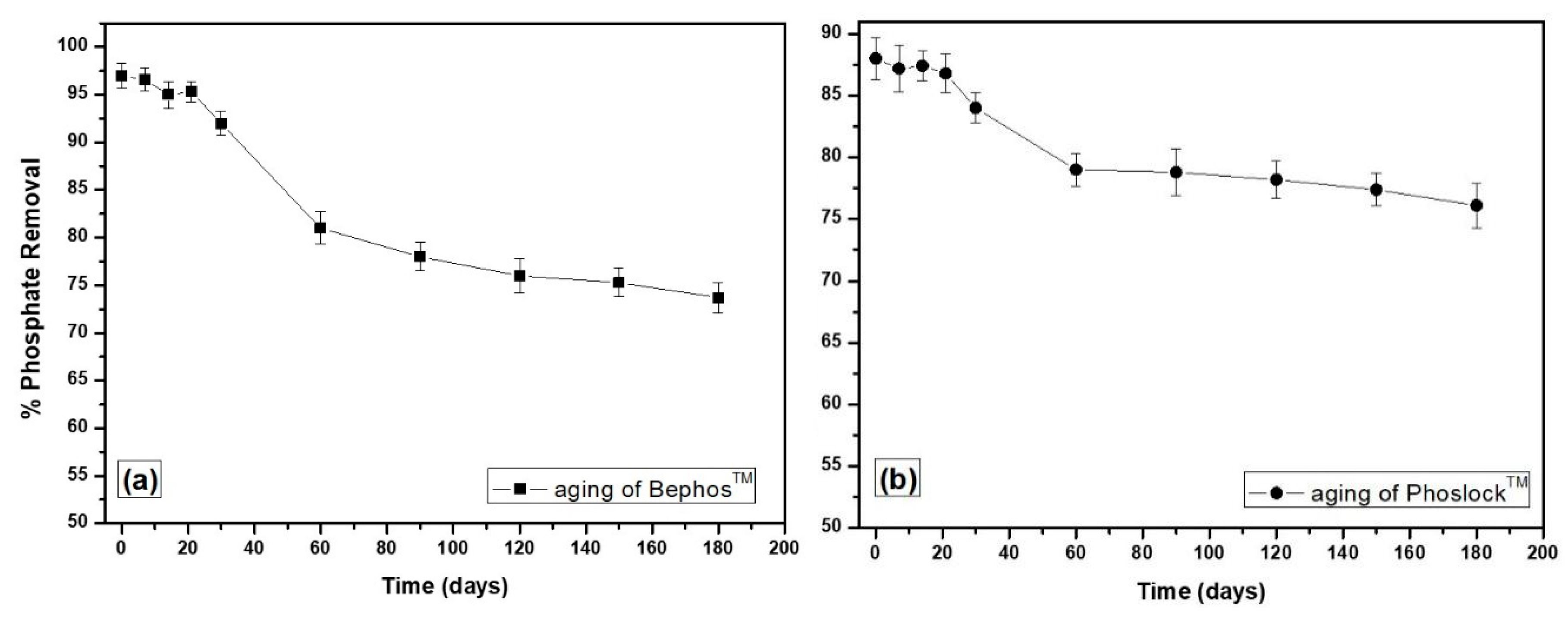
3.3. Aging of LMB and f-MB
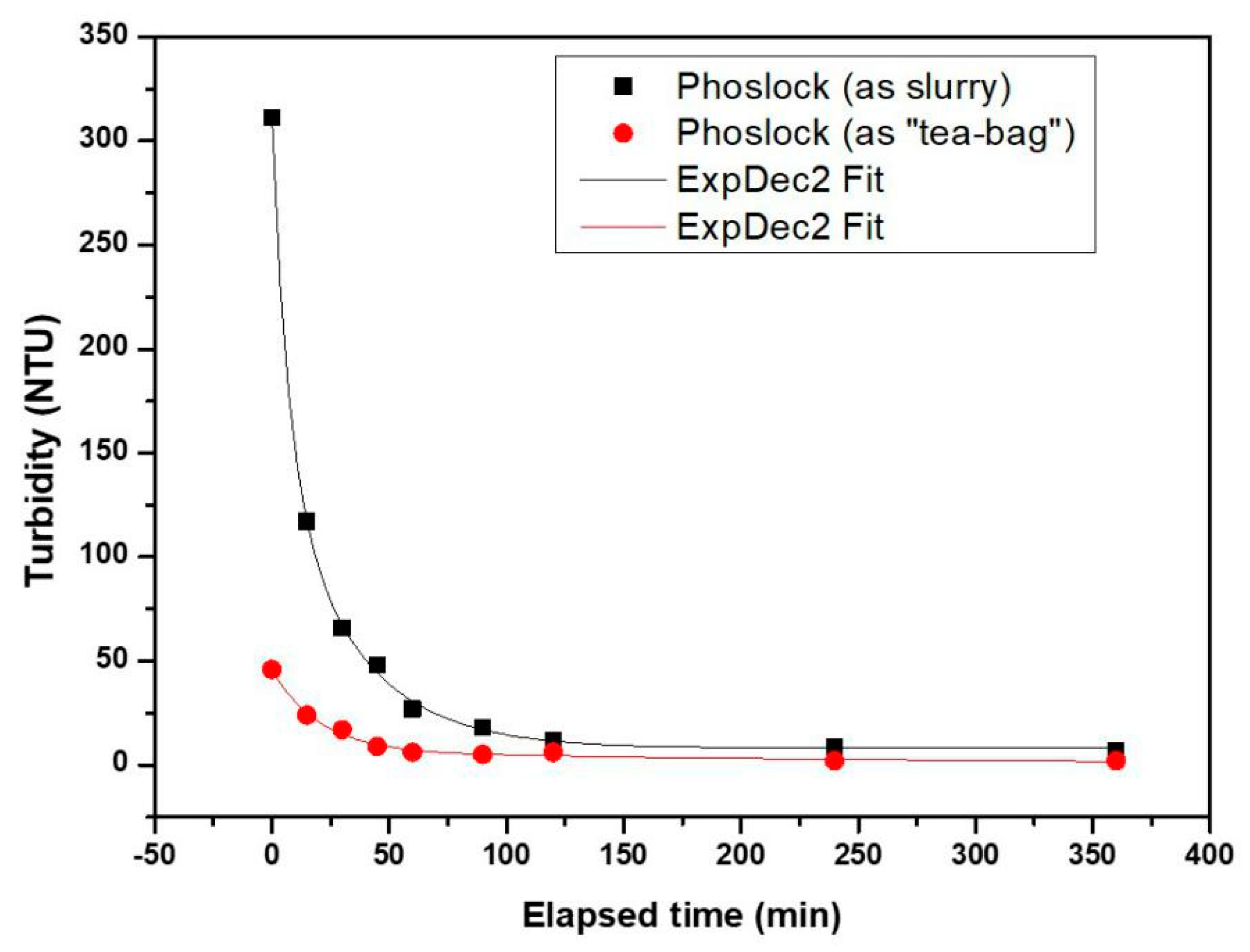
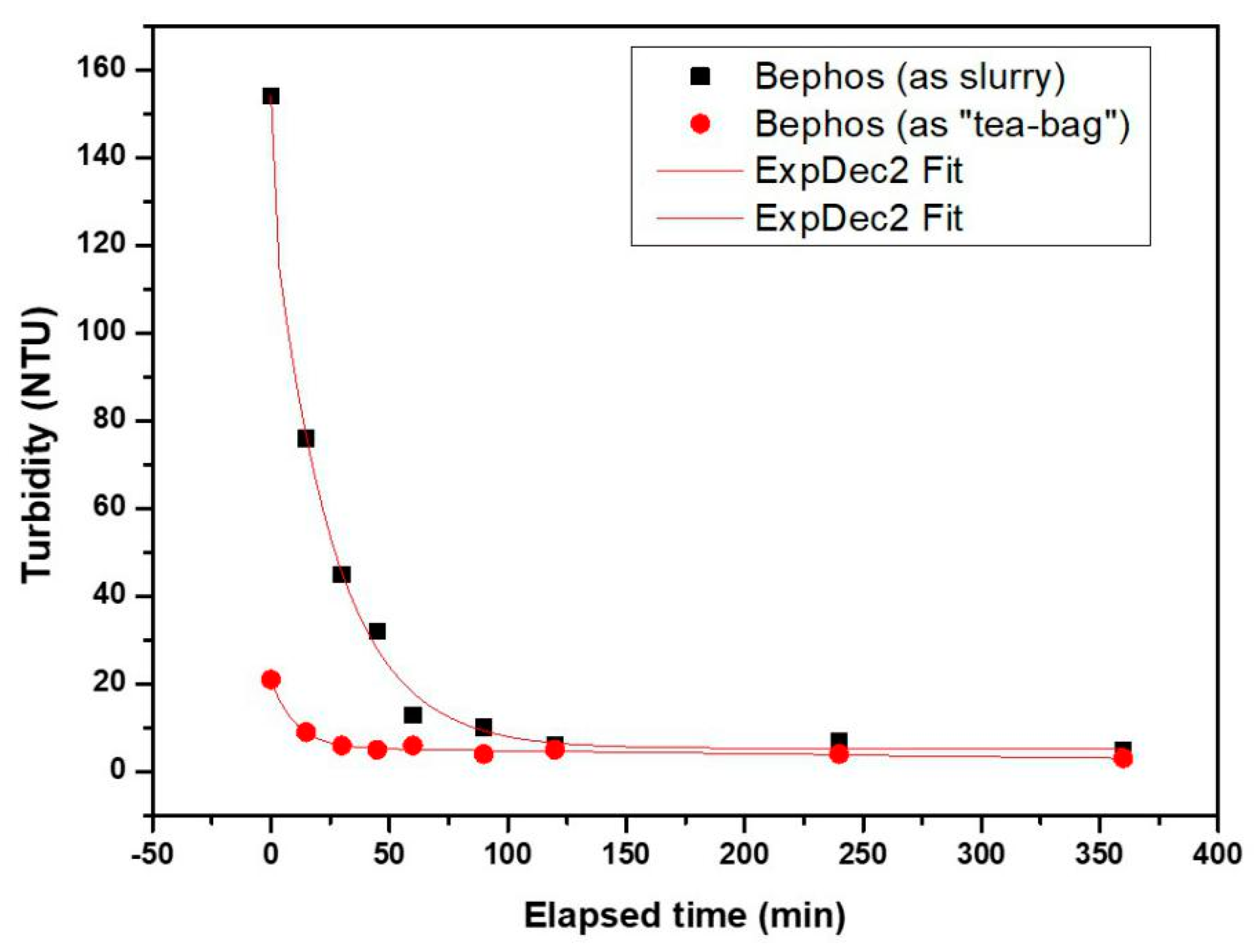
3.4. Turbidity
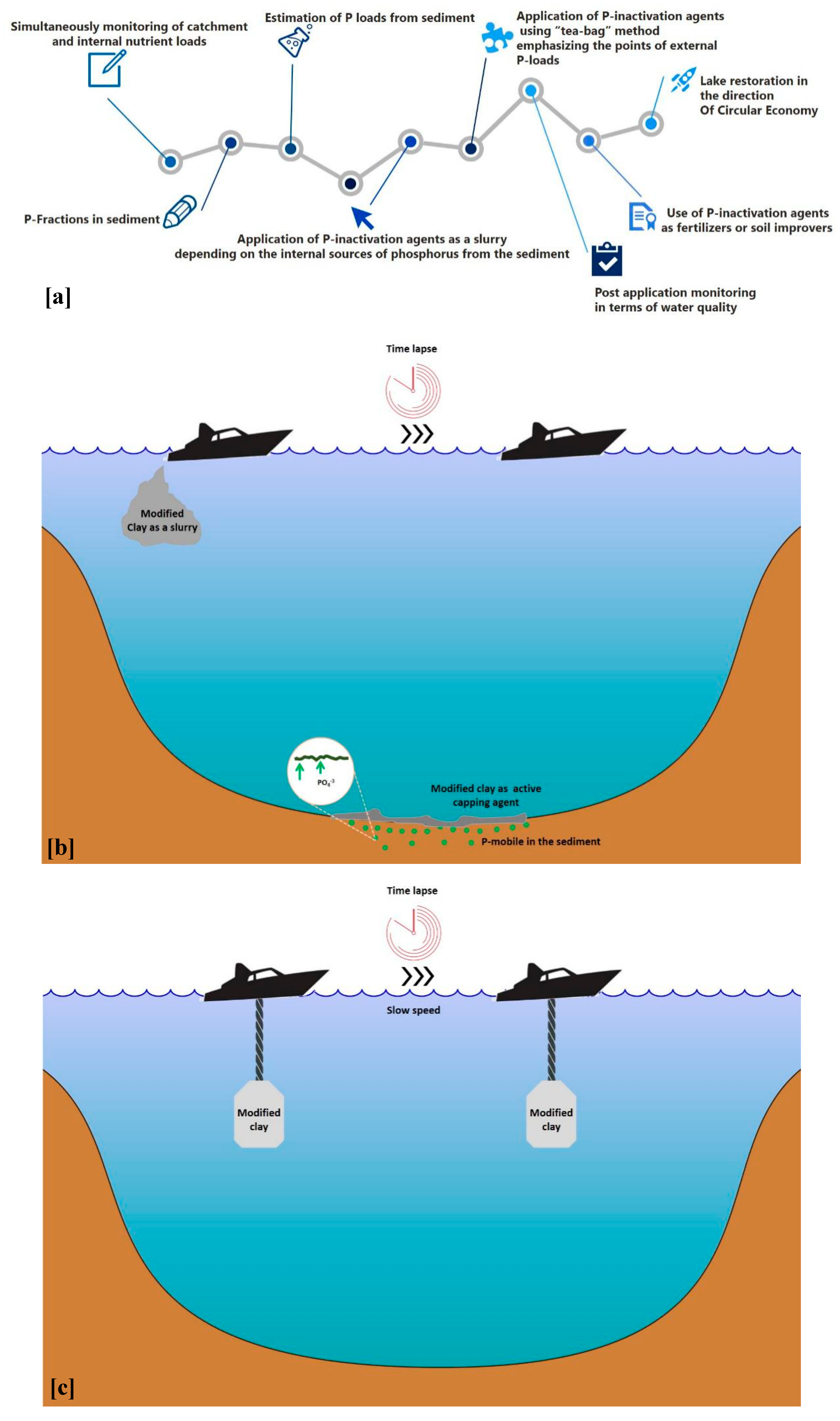
3.5. Challenging Issues of Novel Composite Materials in The Direction of Ecology and Circular Economy (CE)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, Z. Evaluation of sediment capping with active barrier systems (ABS) using calcite/zeolite mixtures to simultaneously manage phosphorus and ammonium release. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, S.W. Coastal marine eutrophication: A definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 1995, 41, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solheim, A.L.; Rekolainen, S.; Moe, S.J.; Carvalho, L.; Phillips, G.; Ptacnik, R.; Penning, W.E.; Toth, L.G.; O’Toole, C.; Schartau, A.-K.L.; et al. Ecological Threshold Responses in European Lakes and Their Fpplicability for the Water Framework Directive (WFD) Implementation: Synthesis of Lakes Results from the REBECCA Project; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kapsalis, V.C.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Aravossis, K.G. Investigation of ecosystem services and circular economy interactions under an inter-organizational framework. Energies 2019, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Kapsalis, V.C.; Aravossis, K.G.; Zamparas, M.; Mitsikas, A. Evaluating circular economy under a multi-parametric approach: A technological review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, C.W.; Gibbs, M.M. Lake sediment phosphorus release management—Decision support and risk assessment framework. New Zeal. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2009, 43, 819–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Gianni, A.; Stathi, P.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Zacharias, I. Removal of phosphate from natural waters using innovative modified bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 62–63, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Zacharias, I. Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads. A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B.; et al. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading—An analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobetičová, K.; Černý, R. Terrestrial eutrophication of building materials and buildings: An emerging topic in environmental studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Drosos, M.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Zacharias, I. Eutrophication control using a novel bentonite humic-acid composite material Bephos™. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3030–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Drosos, M.; Georgiou, Y.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Zacharias, I. A novel bentonite-humic acid composite material Bephos™ for removal of phosphate and ammonium from eutrophic waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, W.M.; McNabb, T.; Cormican, I.; Willis, B.E.; Hyde, S. Operational evaluation of Phoslock phosphorus locking technology in Laguna Niguel Lake, California. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2014, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, M.; Obarska-Pempkowiak, H.; Masi, F.; Gajewska, M. Possibilities of Phoslock® application to remove phosphorus compounds from wastewater treated in hybrid wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 122, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Lürling, M.; Yasseri, S.; Castro-Castellon, A.T.; Gibbs, M.; Meis, S.; McDonald, C.; McIntosh, J.; Sleep, D.; Van Oosterhout, F. Lake responses following lanthanum-modified bentonite clay (Phoslock®) application: An analysis of water column lanthanum data from 16 case study lakes. Water Res. 2013, 15, 5930–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghseresht, F.; Wang, S.; Do, D.D. A novel lanthanum-modified bentonite, Phoslock, for phosphate removal from wastewaters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, K.; Winks, A. Water eutrophication prevention by phoslock flocculation and sediment capping reaction. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Robb, M.; Greenop, B.; Goss, Z.; Douglas, G.; Adeney, J. Application of Phoslock™, an innovative phosphorus binding clay, to two Western Australian waterways: Preliminary findings. In Proceedings of the Hydrobiologia; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Silvenius, F.; Grönroos, J.; Kankainen, M.; Kurppa, S.; Mäkinen, T.; Vielma, J. Impact of feed raw material to climate and eutrophication impacts of Finnish rainbow trout farming and comparisons on climate impact and eutrophication between farmed and wild fish. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Ruan, X.; Fan, Z. Performance of two ornamental plants for purifying eutrophication materials in urban riverway sewages. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical and Control Engineering, Yichang, China, 16–18 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Zhu, J.; Tang, W. Management of nitrogen and phosphorus internal loading from polluted river sediment using Phoslock® and modified zeolite with intensive tubificid oligochaetes bioturbation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, W.M.; Richardson, R.J. Influence of Phoslock® on legacy phosphorus, nutrient ratios, and algal assemblage composition in hypereutrophic water resources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4544–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, K.; Winks, A. Phoslock, a soluble phosphorus binding technology, application in Lake Dianchi eutrophic water purification. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Epe, T.S.; Finsterle, K.; Yasseri, S. Nine years of phosphorus management with lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock) in a eutrophic, shallow swimming lake in Germany. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2017, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nürnberg, G.K. Attempted management of cyanobacteria by Phoslock (lanthanum-modified clay) in Canadian lakes: Water quality results and predictions. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2017, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, B.M.; Mackay, E.B.; Yasseri, S.; Gunn, I.D.M.; Waters, K.E.; Andrews, C.; Cole, S.; De Ville, M.; Kelly, A.; Meis, S.; et al. A meta-analysis of water quality and aquatic macrophyte responses in 18 lakes treated with lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®). Water Res. 2016, 97, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzyk, M.; Gajewska, M. Preliminary results from application Phoslock® to remove phosphorus compounds from wastewater. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, K.; Winks, A. Phoslock®: An effective technology for effective dissolved phosphorus removal in extensive water bodies under a wide range of chemical conditions. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Beijing, China, 11–13 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- van Oosterhout, F.; Lürling, M. The effect of phosphorus binding clay (Phoslock®) in mitigating cyanobacterial nuisance: A laboratory study on the effects on water quality variables and plankton. Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, S.; Spears, B.M.; Maberly, S.C.; Perkins, R.G. Assessing the mode of action of Phoslock® in the control of phosphorus release from the bed sediments in a shallow lake (Loch Flemington, UK). Water Res. 2013, 47, 4460–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; van Oosterhout, F. Case study on the efficacy of a lanthanum-enriched clay (Phoslock®) in controlling eutrophication in Lake Het Groene Eiland (The Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 2013, 710, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada-Ferraz, T.M.; Sueitt, A.P.E.; Oliveira, A.F.; Botta, C.M.R.; Fadini, P.S.; Nascimento, M.R.L.; Faria, B.M.; Mozeto, A.A. Assessment of Phoslock® application in a tropical eutrophic reservoir: An integrated evaluation from laboratory to field experiments. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Lin, J.; Zhang, C.; Tsang, D.C.W. Synergistic adsorption of phosphorus by iron in lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®): New insight into sediment phosphorus immobilization. Water Res. 2018, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzel, K.; Andersen, F.T.; Egemose, S.; Jensen, H.S. Phosphate adsorption by lanthanum modified bentonite clay in fresh and brackish water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, V.; Di Meo, V.; Piccolo, A. Impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi applications on maize production and soil phosphorus availability. J. Geochemical Explor. 2013, 129, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, S.; Spears, B.M.; Maberly, S.C.; O’Malley, M.B.; Perkins, R.G. Sediment amendment with Phoslock® in Clatto Reservoir (Dundee, UK): Investigating changes in sediment elemental composition and phosphorus fractionation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burska, D.; Pryputniewicz-Flis, D.; Bankowska-Sobczak, A.; Brenk, G.; Woszczyk, T. The Efficiency of P-Removal from Natural Waters with Sorbents Placed in Water Permeable Nonwovens. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Zacharias, I. Phosphate adsorption from natural waters and evaluation of sediment capping using modified clays. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, A.; Zamparas, M.; Papadas, I.T.; Kehayias, G.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Zacharias, I. Monitoring and Modeling of Metal Concentration Distributions in Anoxic Basins: Aitoliko Lagoon, Greece. Aquat. Geochemistry 2013, 19, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, E.; Özacar, M.; Şengil, I.A. Adsorption of malachite green onto bentonite: Equilibrium and kinetic studies and process design. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Huang, H.-G.; Jin, X.-Y.; Lu, X.-Q.; Chen, Z.-L. Synthesis, characterization and kinetic of a surfactant-modified bentonite used to remove As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosos, M.; Jerzykiewicz, M.; Deligiannakis, Y. H-binding groups in lignite vs. soil humic acids: NICA-Donnan and spectroscopic parameters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosos, M.; Leenheer, J.A.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Deligiannakis, Y. H-binding of size- and polarity-fractionated soil and lignite humic acids after removal of metal and ash components. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 3963–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, W.F. A Rapid Test for Possible Excesses of Copper in Sandy Soils, 544th ed.; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Zamparas, M.; Drosos, M.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Sorption of phosphate from innovative composite material focusing on physicochemical interactions. Desalin. WATER Treat. 2019, 151, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oosterhout, F.; Waajen, G.; Yasseri, S.; Manzi Marinho, M.; Pessoa Noyma, N.; Mucci, M.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Lanthanum in Water, Sediment, Macrophytes and chironomid larvae following application of Lanthanum modified bentonite to lake Rauwbraken (The Netherlands). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.C.; Muir, C.L.; Hauser, O.A. Detrimental effects of sedimentation on marine benthos: What can be learned from natural processes and rates? Ecol. Eng. 2002, 19, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolam, S.G.; Barrio-Frojan, C.R.S.; Eggleton, J.D. Macrofaunal production along the UK continental shelf. J. Sea Res. 2010, 64, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Kapsalis, V.C.; Drosos, M.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Application of novel composite materials as sediment capping agents: Column experiments and modelling. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 170, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Gavriil, G.; Coutelieris, F.A.; Zacharias, I. A theoretical and experimental study on the P-adsorption capacity of Phoslock™. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 335, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Kapsalis, V.C.; Kanteraki, A.E.; Vardoulakis, E.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Drosos, M.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Novel composite materials as P-adsorption agents and their potential application as fertilizers. Glob. Nest J. 2019, 21, 48–57. [Google Scholar]

| SHA | SHA + f-MB | H2O + f-MB | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 3.80 ± 0.01 | 3.02 ± 0.01 | - |
| Cu | - | 6.35 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Fe | 2.13 ± 0.01 | 2.10 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Model | Parameter | As a Slurry | As “Teabag” | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir Equation | LMB | qm [mg/gr] | 11.28 | 7.80 |
| b | 0.9 | 0.6 | ||
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.6 | ||
| Langmuir Equation | f-MB | qm [mg/gr] | 28.9 | 25.1 |
| b | 0.8 | 0.3 | ||
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Key-Aspects of Future Development | Material | Environment | Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technological maturity/Industrial scalability | ++ | + | + |
| Technical adaptability to other techniques of environmental remediation | +++ | +++ | ++ |
| Ecosystems’ protection and sustainability | + | +++ | ++ |
| Economic scalability | + | +++ | ++ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamparas, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.L.; Drosos, M.; Kapsalis, V.C.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K. Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083397
Zamparas M, Kyriakopoulos GL, Drosos M, Kapsalis VC, Kalavrouziotis IK. Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy. Sustainability. 2020; 12(8):3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083397
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamparas, Miltiadis, Grigorios L. Kyriakopoulos, Marios Drosos, Vasilis C. Kapsalis, and Ioannis K. Kalavrouziotis. 2020. "Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy" Sustainability 12, no. 8: 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083397
APA StyleZamparas, M., Kyriakopoulos, G. L., Drosos, M., Kapsalis, V. C., & Kalavrouziotis, I. K. (2020). Novel Composite Materials for Lake Restoration: A New Approach Impacting on Ecology and Circular Economy. Sustainability, 12(8), 3397. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083397









