The Alerting Effect from Rising Public Awareness of Air Quality on the Outdoor Activities of Megacity Residents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Analytical Method
2.2.1. Index and Comparison Days
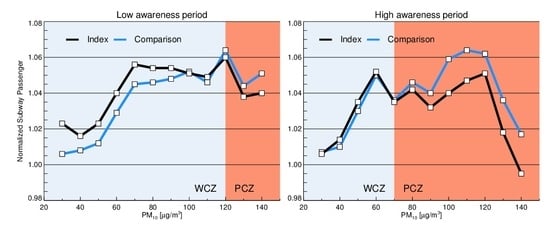
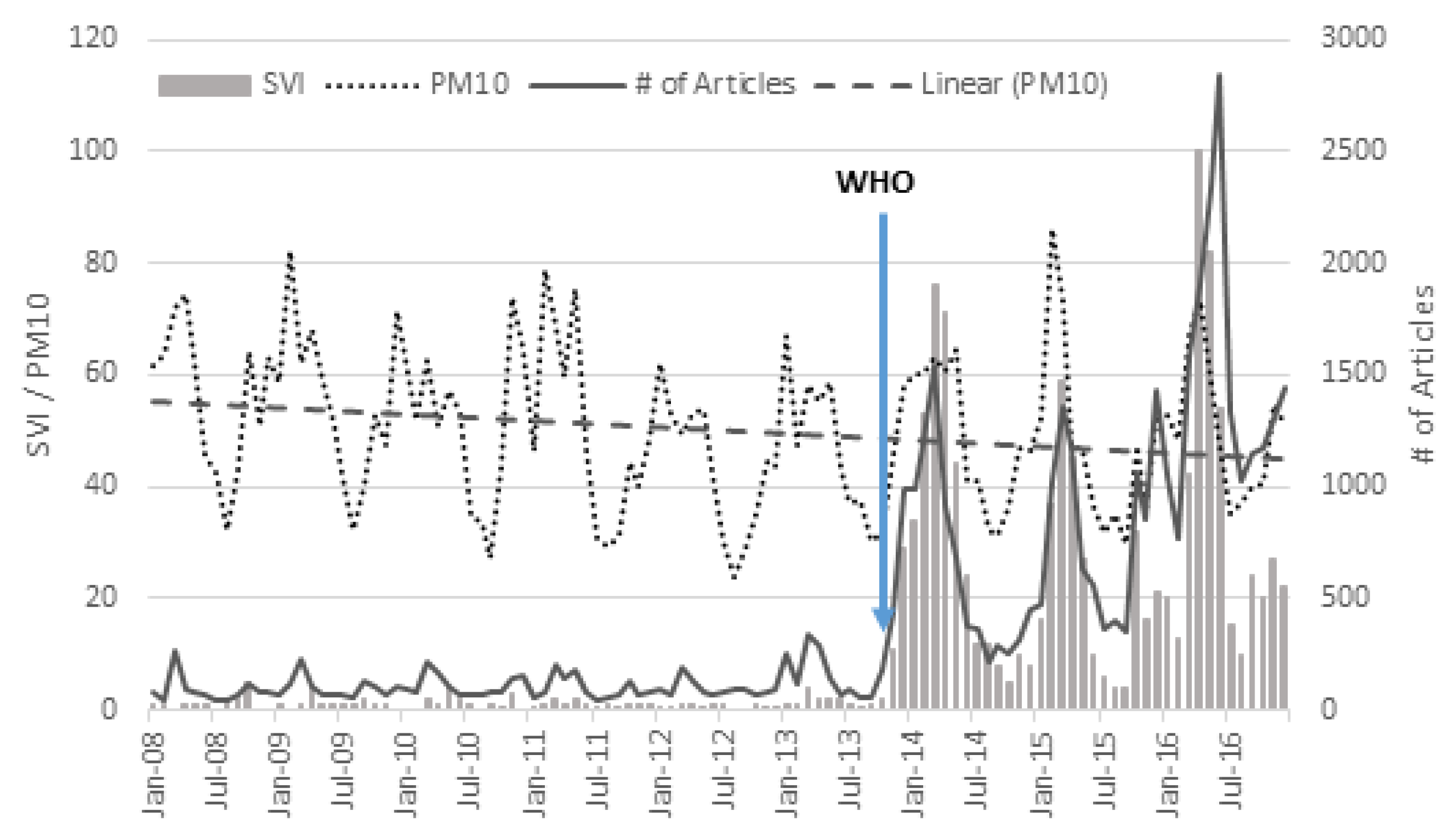
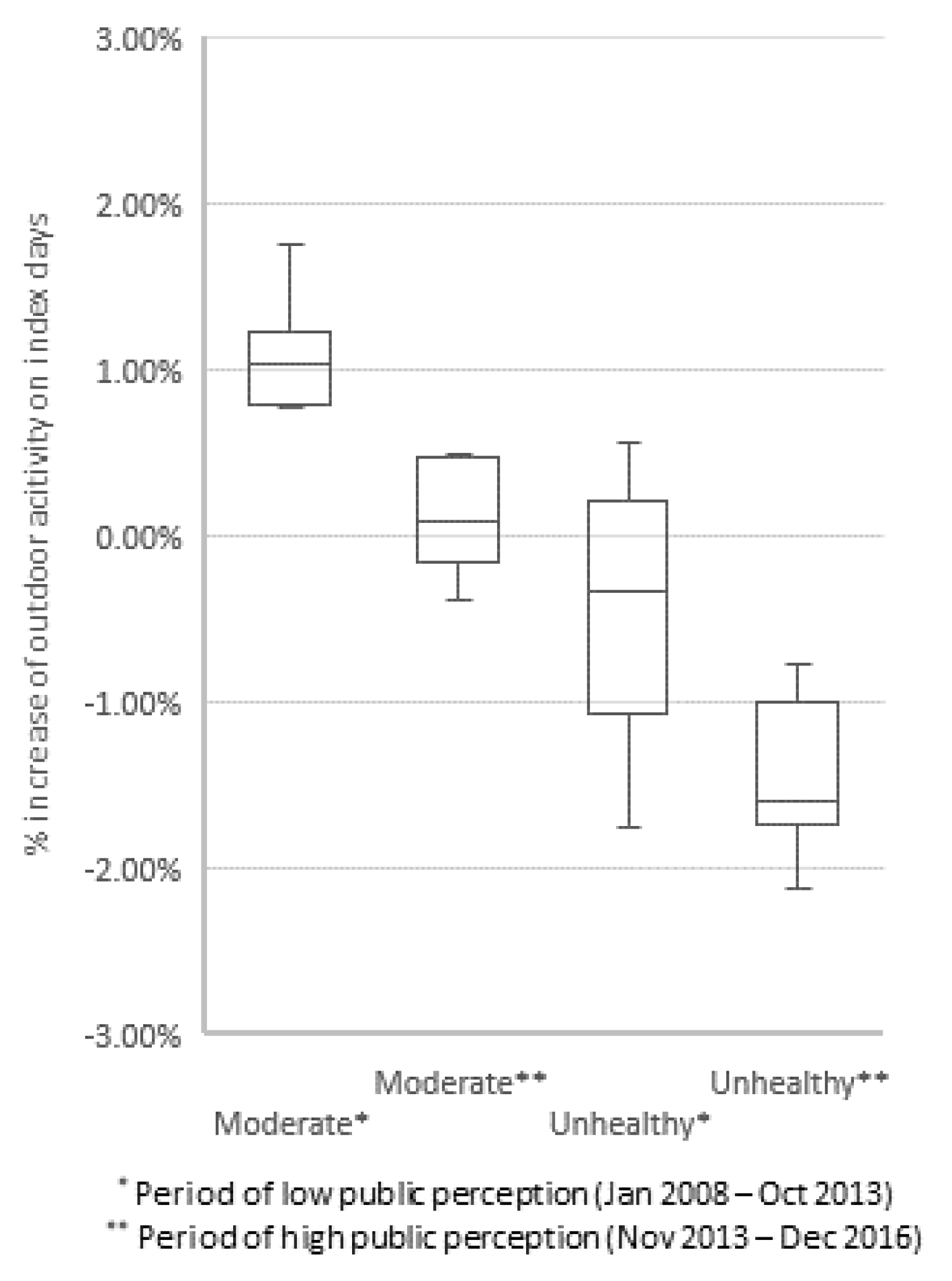
2.2.2. High and Low Public Awareness Periods
3. Results
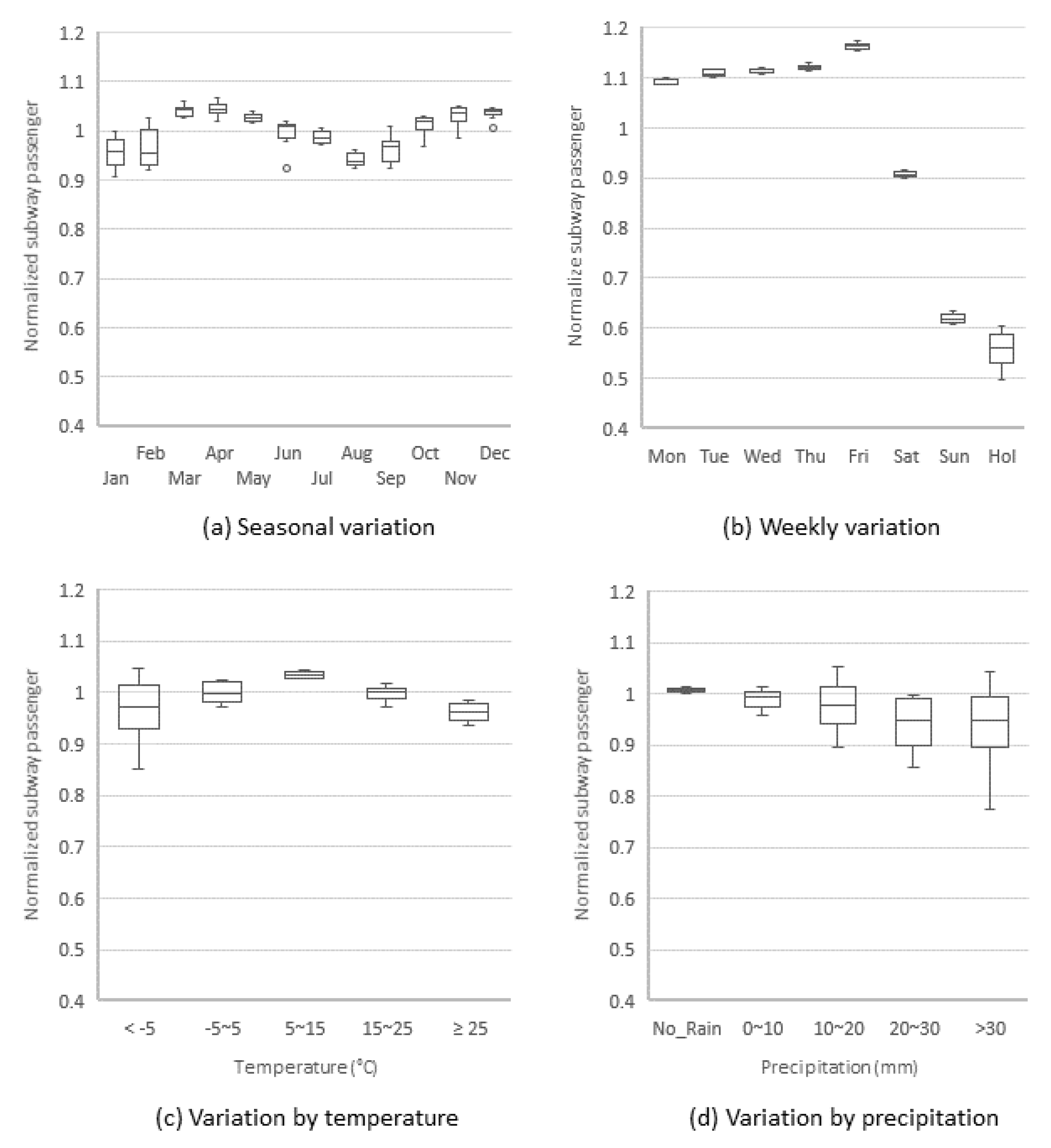
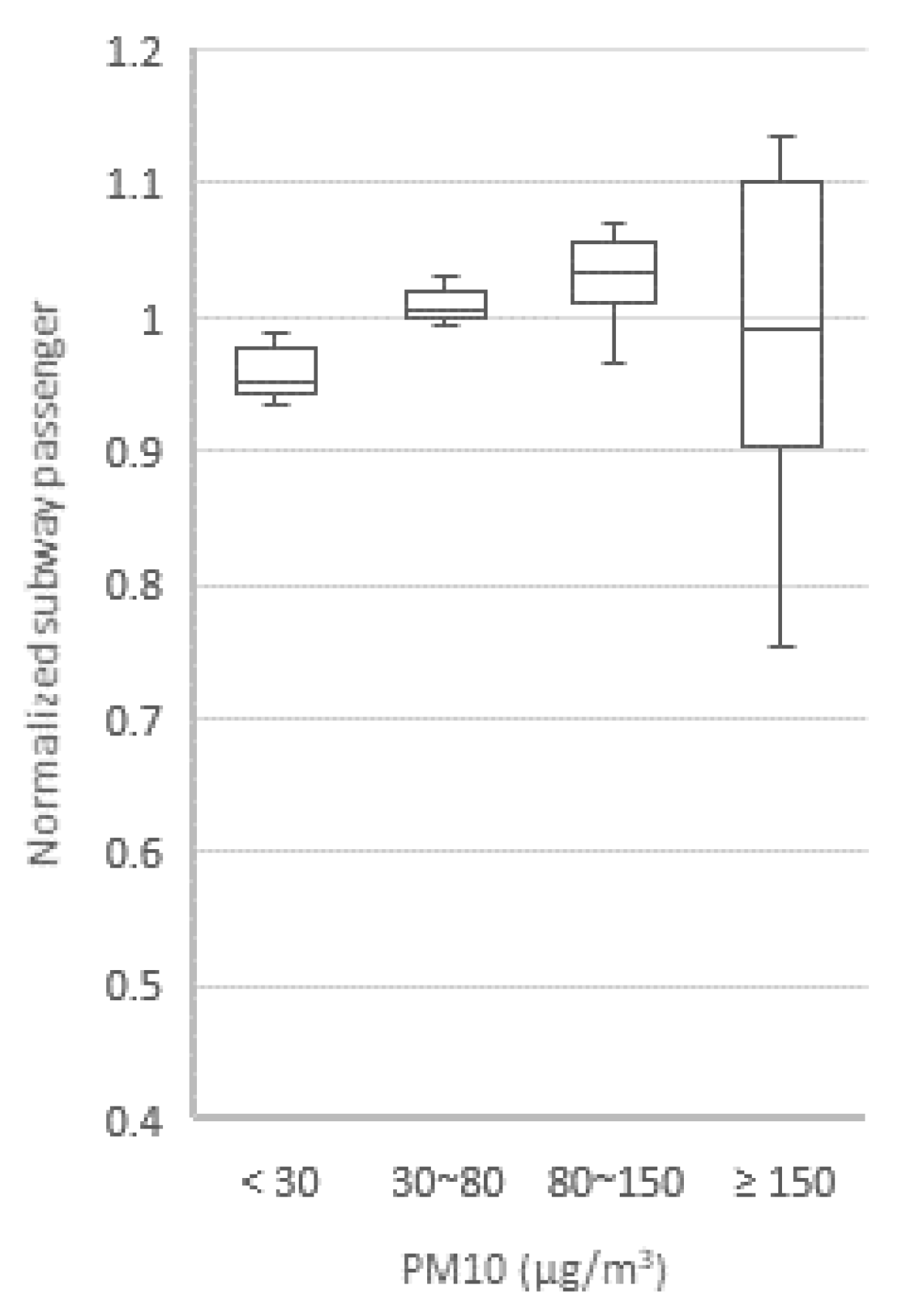
3.1. Environmental Variables and Outdoor Activity
3.2. Weather and Pollution Effects on Activity
3.3. Effect of Public Awareness
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.-U.; Kim, O.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, S. Influence of fossil-fuel power plant emissions on the surface fine particulate matter in the Seoul Capital Area, South Korea. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lighty, J.S.; Veranth, J.M.; Sarofim, A.F. Combustion Aerosols: Factors Governing Their Size and Composition and Implications to Human Health. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 1565–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoneit, B.R. Biomass burning—A review of organic tracers for smoke from incomplete combustion. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 129–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Ezzati, M.; Dockery, D.W. Fine-particulate air pollution and life expectancy in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Kabir, S. A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.-C.; Chan, C.-C.; Wang, P.-Y.; Lee, C.-T.; Cheng, T.-J. Effects of Asian dust event particles on inflammation markers in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage in pulmonary hypertensive rats. Environ. Res. 2004, 95, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-T.; Son, J.-Y.; Cho, Y.-S. A comparison of mortality related to urban air particles between periods with Asian dust days and without Asian dust days in Seoul, Korea, 2000–2004. Environ. Res. 2007, 105, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Lee, K.-K. Effects of Asian dust events on daily asthma patients in Seoul, Korea. Meteorol. Appl. 2014, 21, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-C.; Pan, X.-C.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, K.; Park, E.-J.; Jin, X.; Yi, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, C.-H.; Song, S.; et al. Asian Dust Storm and pulmonary function of school children in Seoul. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Lu, B. Dust events as a risk factor for daily hospitalization for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Minqin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7048–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.; Yiallouros, P.; Kleanthous, S.; Kolokotroni, O.; Schwartz, J.; Dockery, D.W.; Demokritou, P.; Koutrakis, P. A 10-year time-series analysis of respiratory and cardiovascular morbidity in Nicosia, Cyprus: The effect of short-term changes in air pollution and dust storms. Environ. Health 2008, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chiu, H.; Goggins, W.B. Effects of Asian dust storm events on daily stroke admissions in Taipei, Taiwan. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.M.; Kim, H.S.; Park, H.; Ye, S.; Lee, D.; Ha, E.H. Does exposure to PM 10 decrease age at menarche? Environ. Int. 2018, 117, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, E.; Bae, C.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, B.-U.; Kim, S. Regional contributions to particulate matter concentration in the Seoul metropolitan area, South Korea: Seasonal variation and sensitivity to meteorology and emissions inventory. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10315–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.P.; Lee, G. Trend of Air Quality in Seoul: Policy and Science. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.-U.; Jin, C.-S.; Hong, S.; Park, R.; Son, S.-W.; Bae, C.; Bae, M.; Song, C.-K.; et al. Recent increase of surface particulate matter concentrations in the Seoul Metropolitan Area, Korea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.-S.; Cho, A.; Park, H.; Nam, K.; Kim, D.; Hong, J.-H.; Song, C.-K. Human-model hybrid Korean air quality forecasting system. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.X.; Zhao, B.; Cai, S.Y.; Klimont, Z.; Nielsen, C.P.; Morikawa, T.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Fu, X.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. Emission trends and mitigation options for air pollutants in East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6571–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McLinden, C.A.; Li, C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Celarier, E.A.; Marchenko, S.V.; Swartz, W.H.; Bucsela, E.J.; Joiner, J.; Duncan, B.N.; et al. Aura OMI observations of regional SO 2 and NO 2 pollution changes from 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4605–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pivarnik, J.M.; Reeves, M.J.; Rafferty, A.P. Seasonal Variation in Adult Leisure-Time Physical Activity. Med. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2003, 35, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasqui, G.; Westerterp, K.R. Seasonal Variation in Total Energy Expenditure and Physical Activity in Dutch Young Adults. Obes. Res. 2004, 12, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, P.; Gilliland, J. The effect of season and weather on physical activity: A systematic review. Public Health 2007, 121, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, M.; Gray-Donald, K.; O’loughlin, J.; Paradis, G.; Hanley, J. Influence of Weather Conditions and Season on Physical Activity in Adolescents. Ann. Epidemiol. 2009, 19, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiser, D.; Lade, G.; Rudik, I. Air pollution and visitation at U.S. national parks. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, X.-J.; Balluz, L.; Mokdad, A. Association Between Media Alerts of Air Quality Index and Change of Outdoor Activity Among Adult Asthma in Six States, BRFSS, 2005. J. Community Health 2009, 34, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.E.; Jung, C.H.; Kim, Y.P. Analysis of the measurement difference for the PM 10 concentrations between beta-ray absorption and gravimetric methods at gosan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carneiro, H.A.; Mylonakis, E. Google Trends: A Web-Based Tool for Real-Time Surveillance of Disease Outbreaks. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, T.F.; Schwartz, J. Control for Seasonal Variation and Time Trend in Case-Crossover Studies of Acute Effects of Environmental Exposures. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.G.; Li, J.; Qu, Y.; Han, T.; Hou, L.; Gu, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; et al. Formation and evolution mechanism of regional haze: A case study in the megacity Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4501–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallos, G.; Kassomenos, P.; Pielke, R.A. Synoptic and mesoscale weather conditions during air pollution episodes in Athens, Greece. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1993, 62, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, T.; McMeeking, G.; Minikin, A.; Birmili, W.; Dall’Osto, M.; O’Dowd, C.; Flentje, H.; Henzing, B.; Junninen, H.; Kristensson, A.; et al. Overview of the synoptic and pollution situation over Europe during the EUCAARI-LONGREX field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Z.; Gao, M.; Sun, J.; Fan, S. The impact of synoptic circulation on air quality and pollution-related human health in the Yangtze River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-T.T.; McElroy, M.B. Impacts of boundary layer mixing on pollutant vertical profiles in the lower troposphere: Implications to satellite remote sensing. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1726–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
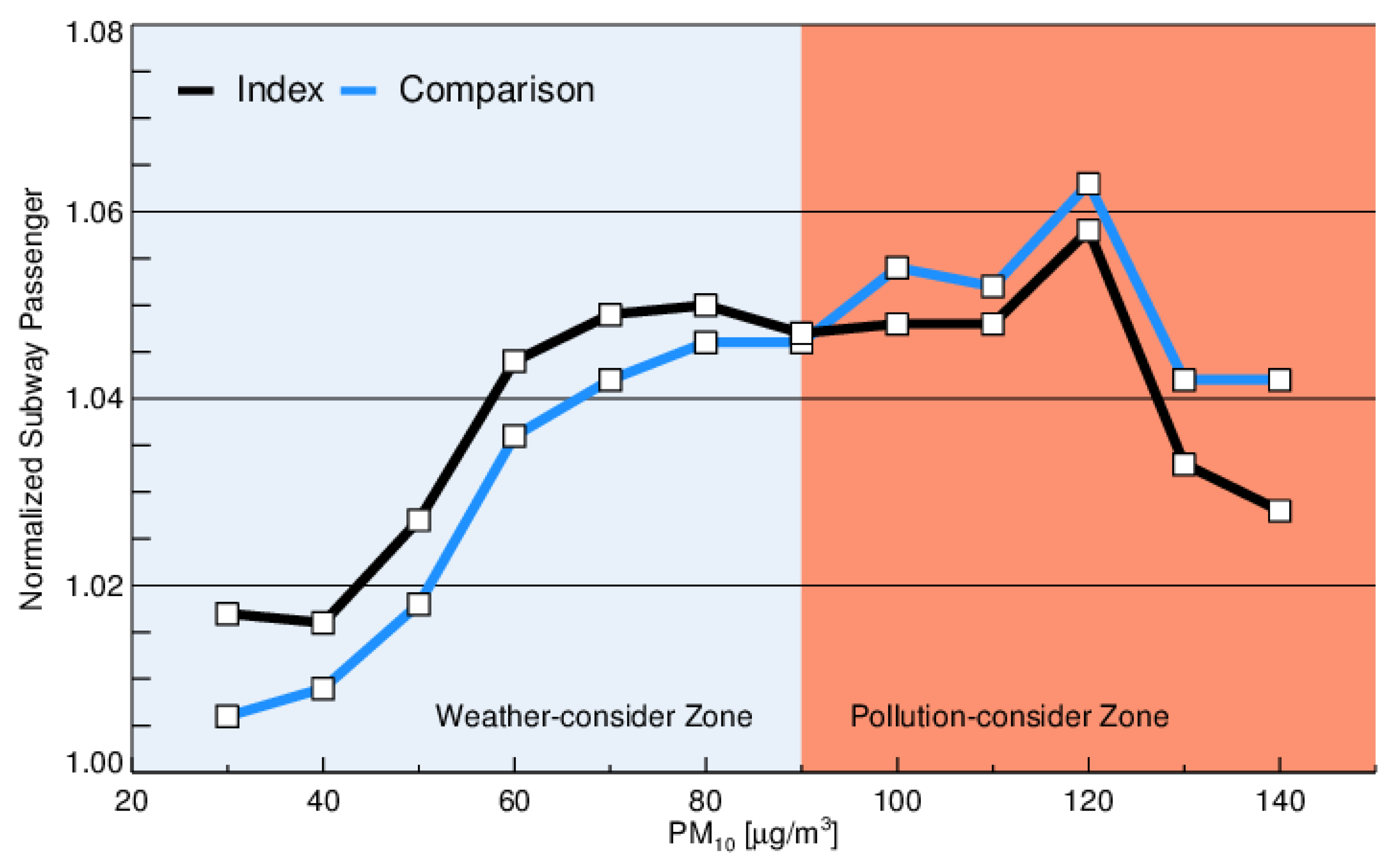

| PM10 (µg/m3) | Index Days | Comparison Days | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (1000) | 95% CI | Mean (1000) | 95% CI | ||
| 30 | 6145 | (6038, 6252) | 6078 | (5970, 6186) | 0.000 ** |
| 40 | 6124 | (6036, 6212) | 6084 | (5997, 6171) | 0.003 ** |
| 50 | 6185 | (6104, 6266) | 6133 | (6054, 6212) | 0.000 ** |
| 60 | 6281 | (6198, 6364) | 6233 | (6151, 6315) | 0.000 ** |
| 70 | 6309 | (6212, 6406) | 6267 | (6172, 6362) | 0.006 ** |
| 80 | 6317 | (6204, 6430) | 6291 | (6180, 6402) | 0.046 ** |
| 90 | 6298 | (6163, 6433) | 6289 | (6179, 6418) | 0.336 |
| 100 | 6301 | (6145, 6457) | 6339 | (6206, 6472) | 0.198 |
| 110 | 6307 | (6130, 6484) | 6329 | (6169, 6489) | 0.241 |
| 120 | 6351 | (6151, 6551) | 6383 | (6201, 6565) | 0.159 |
| 130 | 6192 | (5927, 6457) | 6247 | (6006, 6488) | 0.091 * |
| 140 | 6178 | (5869, 6487) | 6262 | (5989, 6535) | 0.053 * |
| PM10 (µg/m3) | Low Awareness Period | High Awareness Period | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95% CI on Index Days (1000) | 95% CI on Comparison Days (1000) | p-Value | 95% CI on Index Days (1000) | 95% CI on Comparison Days (1000) | p-Value | |
| 30 | 6155 ± 134 | 6050 ± 136 | 0.000 ** | 6126 ± 180 | 6129 ± 177 | 0.451 |
| 40 | 6103 ± 112 | 6057 ± 109 | 0.009 ** | 6158 ± 143 | 6130 ± 143 | 0.082 * |
| 50 | 6135 ± 102 | 6071 ± 101 | 0.000 ** | 6277 ± 130 | 6246 ± 125 | 0.080 * |
| 60 | 6227 ± 102 | 6164 ± 102 | 0.000 ** | 6389 ± 141 | 6375 ± 135 | 0.244 |
| 70 | 6321 ± 113 | 6256 ± 113 | 0.001 ** | 6282 ± 183 | 6287 ± 175 | 0.420 |
| 80 | 6312 ± 134 | 6262 ± 134 | 0.009 ** | 6328 ± 206 | 6352 ± 201 | 0.070 * |
| 90 | 6305 ± 157 | 6269 ± 155 | 0.074 * | 6284 ± 261 | 6333 ± 234 | 0.092 * |
| 100 | 6280 ± 185 | 6283 ± 161 | 0.481 | 6344 ± 291 | 6456 ± 235 | 0.063 * |
| 110 | 6264 ± 209 | 6251 ± 201 | 0.352 | 6405 ± 332 | 6509 ± 255 | 0.058 * |
| 120 | 6328 ± 231 | 6349 ± 212 | 0.299 | 6422 ± 412 | 6487 ± 357 | 0.073 * |
| 130 | 6187 ± 307 | 6225 ± 282 | 0.228 | 6208 ± 543 | 6315 ± 475 | 0.032 ** |
| 140 | 6216 ± 362 | 6284 ± 321 | 0.161 | 6072 ± 621 | 6203 ± 546 | 0.025 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-K.; Park, Y.; Han, S.-P.; Kim, H.C. The Alerting Effect from Rising Public Awareness of Air Quality on the Outdoor Activities of Megacity Residents. Sustainability 2020, 12, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030820
Lee K-K, Park Y, Han S-P, Kim HC. The Alerting Effect from Rising Public Awareness of Air Quality on the Outdoor Activities of Megacity Residents. Sustainability. 2020; 12(3):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030820
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ki-Kwang, YoungKi Park, Sang-Pil Han, and Hyun Cheol Kim. 2020. "The Alerting Effect from Rising Public Awareness of Air Quality on the Outdoor Activities of Megacity Residents" Sustainability 12, no. 3: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030820
APA StyleLee, K.-K., Park, Y., Han, S.-P., & Kim, H. C. (2020). The Alerting Effect from Rising Public Awareness of Air Quality on the Outdoor Activities of Megacity Residents. Sustainability, 12(3), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030820