Environmental Citizenship Questionnaire (ECQ): The Development and Validation of an Evaluation Instrument for Secondary School Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
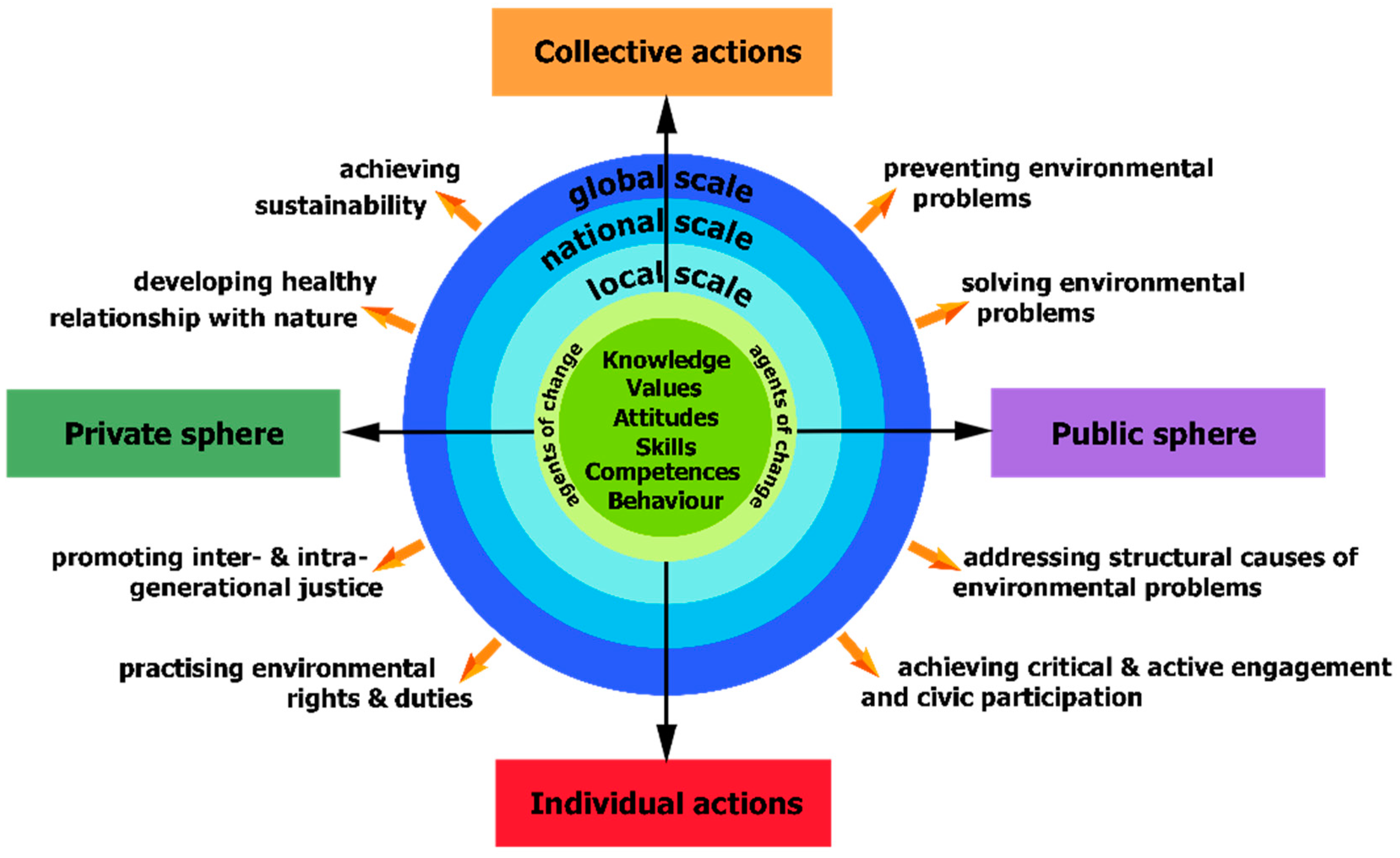
“the responsible pro-environmental behaviour of citizens who act and participate in society as agents of change in the private and public spheres on a local, national and global scale, through individual and collective actions in the direction of solving contemporary environmental problems, preventing the creation of new environmental problems, achieving sustainability and developing a healthy relationship with nature. ‘Environmental Citizenship’ includes the practice of environmental rights and duties, as well as the identification of the underlying structural causes of environmental degradation and environmental problems, the development of the willingness and the competences for critical and active engagement and civic participation to address those structural causes, and to act individually and collectively within democratic means, taking into account inter- and intra-generational justice”[11].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Developing the ECQ
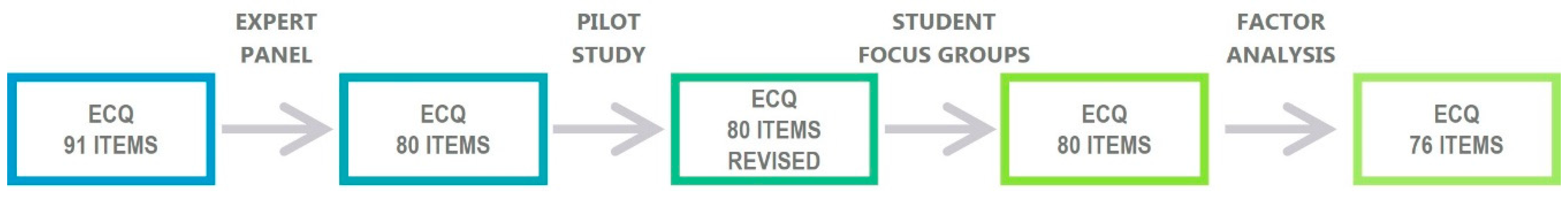
2.1.1. Generation of the Items
2.1.2. Review of Items
2.1.3. Pilot Study
2.1.4. Student Focus Groups
2.1.5. Final Version of ECQ
2.2. ECQ Sample
2.3. Item Analysis and Reliability
3. Results
3.1. Factor Analysis
3.2. Sampling Adequacy and Sphericity Test
3.3. Eigenvalues and Percentage of Variance
3.4. Correlation between Factors
4. Discussion and Educational Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environment Agency. The European Environment—State and Outlook 2015: Synthesis Report; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cheah, S.L.; Huang, L. Environmental Citizenship in a Nordic Civic and Citizenship Education Context. Nord. J. Comp. Int. Educ. 2019, 3, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schild, R. Environmental citizenship: What can political theory contribute to environmental education practice? J. Environ. Educ. 2016, 47, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimick, A.S. Supporting youth to develop environmental citizenship within/against a neoliberal context. Environ. Educ. Res. 2015, 21, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A. Environmental citizenship: Towards sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 2007, 15, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A. Environmental Citizenship and Pro-Environmental Behavior: Rapid Research and Evidence Review; Sustainable Development Research Network: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, J. Resistance is fertile: From environmental to sustainability citizenship. In Environmental Citizenship; MIT Press: London, UK, 2006; pp. 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Jagers, S.C.; Matti, S. Ecological Citizens: Identifying Values and Beliefs that Support Individual Environmental Responsibility among Swedes. Sustainability 2010, 2, 1055–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Evidence Australia. A Review of Best Practice in Environmental Citizenship Models; Environmental Evidence Australia: Victoria, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjichambis, A.C.; Reis, P. Introduction to the conceptualization of Environmental Citizenship for twenty-first century education. In Conceptualizing Environmental Citizenship for 21st Century Education; Hadjichambis, A.C., Reis, P., Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 9–24. ISBN 978-3-030-20249-1. [Google Scholar]
- European Network for Environmental Citizenship—ENEC. Defining Environmental Citizenship. 2018. Available online: http://enec-cost.eu/our-approach/enec-environmental-citizenship/ (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Simonova, P.; Cincera, J.; Kroufek, R.; Krepelkova, S.; Hadjichambis, A. Active Citizens: Evaluation of a Community-Based Education Program. Sustainability 2019, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Network for Environmental Citizenship—ENEC. Defining Education for Environmental Citizenship. 2018. Available online: http://enec-cost.eu/our-approach/education-for-environmental-citizenship/ (accessed on 15 December 2019).
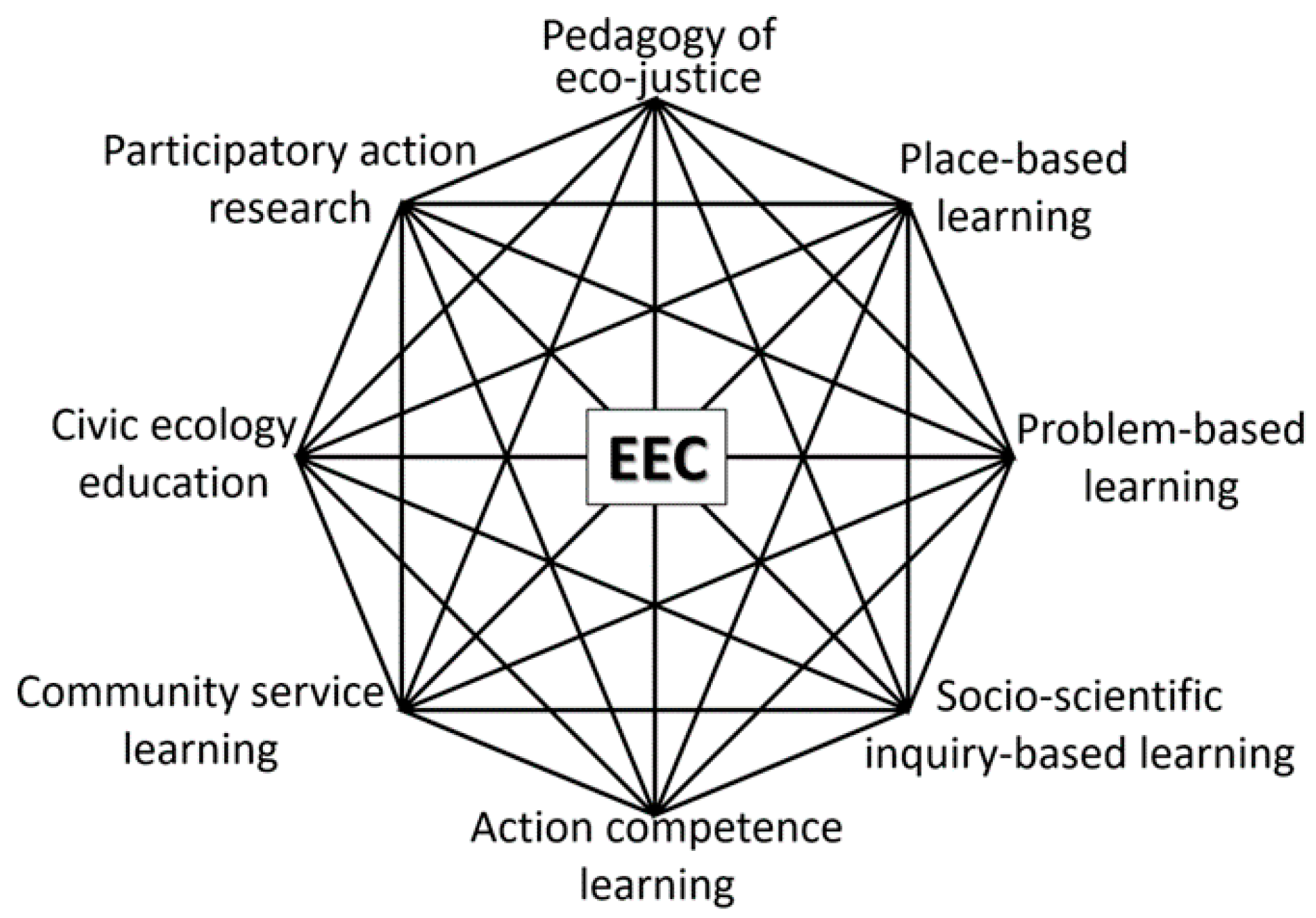
- Hadjichambis, A.C.; Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D. Education for Environmental Citizenship: The Pedagogical Approach. In Conceptualizing Environmental Citizenship for 21st Century Education; Hadjichambis, A.C., Reis, P., Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 262–292. ISBN 978-3-030-20249-1. [Google Scholar]
- Melo-Escrihuela, C. Promoting ecological citizenship: Rights, duties and political agency. Acme Int. E. J. Crit. Geogr. 2008, 7, 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, P. Toward a coherent theory of environmentally significant behavior. J. Soc. Issues 2000, 56, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, D.W. Why Care for Nature? In Search of an Ethical Framework for Environmental Responsibility and Education; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Westheimer, J.; Kahne, J. Educating the “good” citizen. Political Choices and Pedagogical Goals. Polit. Sci. Polit. 2004, 2, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osler, A.; Vincent, K. Citizenship and the Challenge of Global Education; Stoke: Trentham, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Held, D. Models of Democracy, 2nd ed.; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, W.; Carstens, R.; Losito, B.; Fraillon, J. International Civic and Citizenship Education Study (ICCS); International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA) (Student Questionnaire): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, T.; Steg, L.; Kiers, H.A. Measuring values in environmental research: A test of an environmental portrait value questionnaire. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gericke, N.; Boeve-de Pauw, J.; Berglund, T.; Olsson, D. The Sustainability Consciousness Questionnaire: The theoretical development and empirical validation of an evaluation instrument for stakeholders working with sustainable development. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using SPSS, 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Comrey, A.L.; Lee, H.B. A First Course in Factor Analysis, 2nd ed.; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ary, D.; Jacobs, L.C.; Razavieh, A.; Sorensen, C.K. Introduction to Research in Education, 8th ed.; Cengage Learning: Bellmont, CA, USA; Wadsworth, OH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, H.F.; Rice, J. Little jiffy, mark IV. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1974, 34, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corner, A.; Markowitz, E.; Pidgeon, N. Public engagement with climate change: The role of human values. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Molina, M.A.; Fernández-Sáinz, A.; Izagirre-Olaizola, J. Environmental knowledge and other variables affecting pro-environmental behaviour: Comparison of university students from emerging and advanced countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 61, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, M.; Dietlind, S.; Berlin, D. Habits of sustainable citizenship: The example of political consumerism. In The Habits of Consumption: The Example of Political Consumerism; Warde, A., Southerton, D., Eds.; Helsinki Collegium for Advanced Studies: Helsinki, Finland, 2012; pp. 141–163. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, P.; Greenhalhj, T. Selecting, designing and developing your questionnaire. BMJ 2004, 328, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
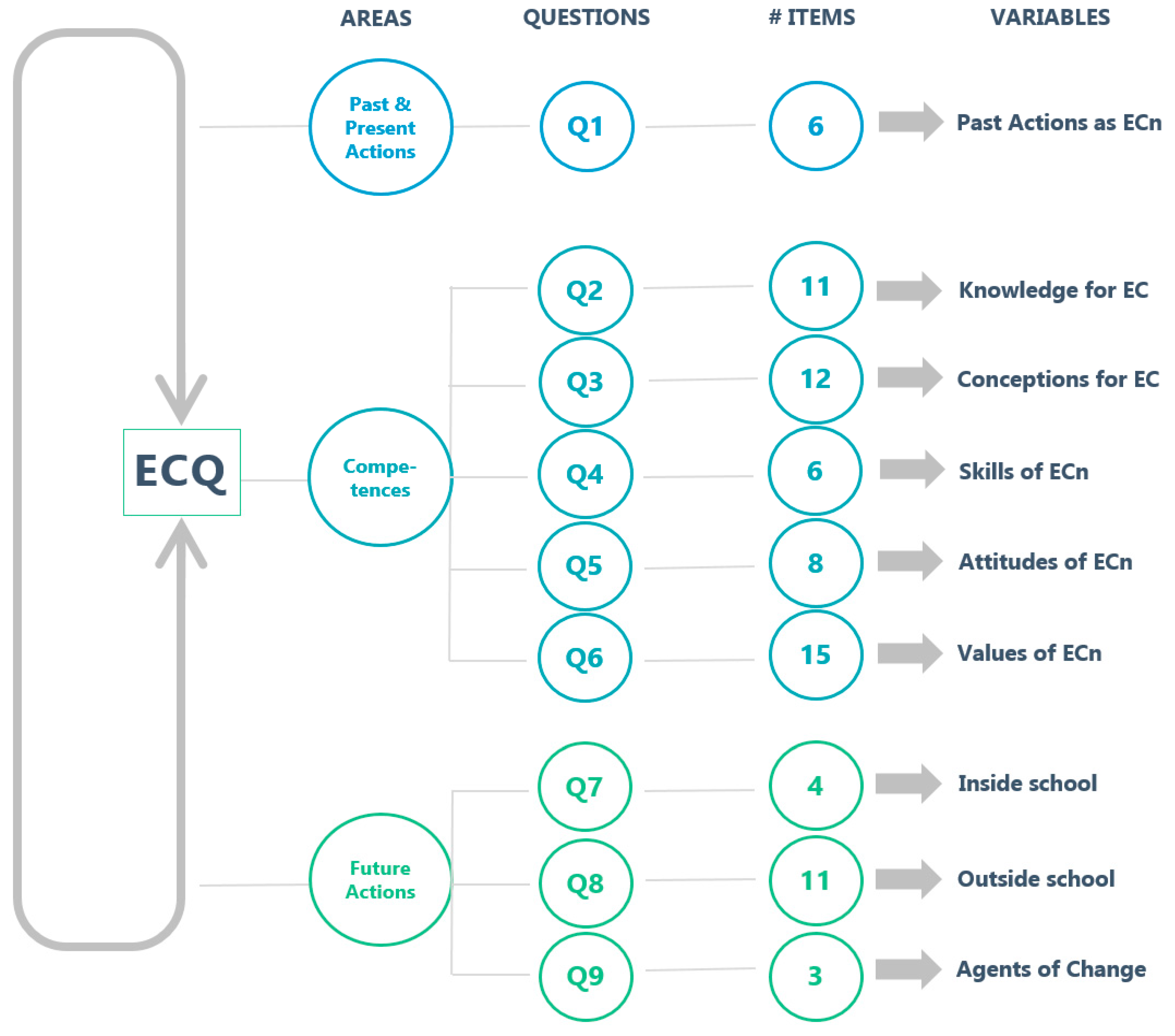
| Question | Focus Area | Source of the Question and Adjustments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Past and present actions as ECn | Modified from ICCS, Student Questionnaire, Schulz et al. [21], Q15 |
| 2 | Knowledge for EC | Developed based on EEC Model, Hadjichambis and Paraskeva-Hadjichambi [14] |
| 3 | Conceptions for EC | Modified from ICCS, Student Questionnaire, Schulz et al. [21], Q23 |
| 4 | Skills of ECn | Modified from ICCS, Student Questionnaire, Schulz et al. [21], Q29 |
| 5 | Attitudes of ECn | Adopted from “The Sustainability Consciousness Questionnaire”, Gericke et al. [23] |
| 6 | Values of ECn | Adopted from “The Environmental Portrait Value Questionnaire”, Bouman et al. [22] |
| 7 | Future actions inside school | Modified from ICCS, Student Questionnaire, Schulz et al. [21], Q30 |
| 8 | Future actions outside school | Modified from ICCS, Student Questionnaire, Schulz et al. [21], Q32 |
| 9 | Future actions as agents of change | Developed based on EEC Model, Hadjichambis and Paraskeva-Hadjichambi [14] |
| Individual Dimension | Collective Dimension | |
|---|---|---|
| Private Sphere | 1a, 1b, 1c, 1g, 8a, 8b, 8h, 8i | / |
| Public Sphere | 1e, 1f, 7b, 7c, 8d, 8e, 8g, 9a, 9b, 9c | 7a, 7d, 8c, 8f, 8j, 8k |
| Range of Factor Loadings | Number of Items | Percentage of Items | Items |
|---|---|---|---|
| <0.450 | 10 | 13.2% | 6m, 6p, 6o, 3b, 8a, 3d, 3a, 6k, 5e, 6l |
| 0.451–0.550 | 11 | 14.5% | 1e, 8i, 6i, 6f, 6g, 2i, 8b, 5i, 2k, 4f, 8h |
| 0.551–0.650 | 19 | 25.0% | 4d, 1g, 2j, 3f, 5c, 3c, 6c, 3g, 6e, 5b, 1c, 8k, 6h, 6b, 5h, 3j, 2d, 5g, 5f |
| 0.651–0.750 | 20 | 26.3% | 1f, 3e, 5d, 4b, 4c, 8j, 2a, 6q, 8e, 2b, 8d, 3h, 6a, 1b, 3k, 1a, 8g, 8c, 2h, 7d |
| >0.751 | 16 | 21.1% | 6d, 4e, 3i, 7c, 2g, 7a, 9b, 4a, 2f, 3l, 2e, 8f, 2c, 7b, 9c, 9a |
| Areas | Factors | Number of Items | Cronbach’s Alpha | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Past and Present Actions | Past Actions as ECn (F1) | 6 | 0.702 | 0.702 |
| Competences | Knowledge for ECn (F2) | 11 | 0.893 | 0.925 |
| Conceptions for ECn (F3) | 12 | 0.836 | ||
| Skills of ECn (F4) | 6 | 0.755 | ||
| Attitudes of ECn (F5) | 8 | 0.733 | ||
| Values of ECn (F6) | 15 | 0.734 | ||
| Future Actions | Future Actions inside School (F7) | 4 | 0.779 | 0.896 |
| Future Actions outside School (F8) | 11 | 0.839 | ||
| Agents of Change (F9) | 3 | 0.747 | ||
| Cronbach’s Alpha | 76 | 0.944 | ||
| Factor | KMO | Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approx. Chi-Square | df | p-value | ||
| Past Actions as ECn Knowledge for ECn | 0.770 | 490.473 | 15 | <0.001 |
| 0.863 | 3487.770 | 55 | <0.001 | |
| Conceptions for ECn | 0.818 | 2914.836 | 66 | <0.001 |
| Skills of ECn | 0.673 | 939.465 | 15 | <0.001 |
| Attitudes of ECn | 0.752 | 833.139 | 28 | <0.001 |
| Values of ECn | 0.751 | 3277.396 | 105 | <0.001 |
| Future Actions inside School | 0.780 | 541.616 | 6 | <0.001 |
| Future Actions outside School | 0.818 | 2610.993 | 55 | <0.001 |
| Agents of Change | 0.684 | 386.774 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Factor | Eigenvalues | Percentage (%) of Variance |
|---|---|---|
| Past Actions as ECn | 2.441 | 40.683 |
| Knowledge for ECn | 5.370 | 48.820 |
| Conceptions for ECn | 4.519 | 37.661 |
| Skills of ECn | 2.757 | 45.952 |
| Attitudes of ECn | 2.924 | 36.556 |
| Values of ECn | 4.234 | 28.226 |
| Future Actions inside School | 2.411 | 60.274 |
| Future Actions outside School | 4.444 | 40.399 |
| Agents of Change | 2.025 | 67.503 |
| Factor | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attitudes of ECn (F5) | 1 | 0.667 ** | 0.314 ** | 0.349 ** | 0.216 ** |
| Values of ECn (F6) | 1 | 0.436 ** | 0.478 ** | 0.479 ** | |
| Future Actions inside School (F7) | 1 | 0.645 ** | 0.615 ** | ||
| Future Actions outside School (F8) | 1 | 0.621 ** | |||
| Agents of Change (F9) | 1 |
| Factors | Min | Max | Mean Value | SD | Theoretical Min–Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Past Actions as ECn | 1.17 | 3.50 | 2.74 | 0.33 | 1–4 |
| Knowledge for ECn | 1.09 | 4.00 | 2.89 | 0.66 | 1–4 |
| Conceptions for ECn | 1.00 | 3.67 | 2.08 | 0.51 | 1–4 |
| Skills of ECn | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.58 | 0.59 | 1–4 |
| Attitudes of ECn | 1.00 | 3.00 | 1.54 | 0.40 | 1–4 |
| Values of ECn | 1.07 | 2.93 | 1.72 | 0.34 | 1–4 |
| Future Actions inside School | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.28 | 0.61 | 1–4 |
| Future Actions outside School | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.55 | 0.51 | 1–4 |
| Agents of Change | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.02 | 0.62 | 1–4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadjichambis, A.C.; Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D. Environmental Citizenship Questionnaire (ECQ): The Development and Validation of an Evaluation Instrument for Secondary School Students. Sustainability 2020, 12, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030821
Hadjichambis AC, Paraskeva-Hadjichambi D. Environmental Citizenship Questionnaire (ECQ): The Development and Validation of an Evaluation Instrument for Secondary School Students. Sustainability. 2020; 12(3):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030821
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadjichambis, Andreas Ch., and Demetra Paraskeva-Hadjichambi. 2020. "Environmental Citizenship Questionnaire (ECQ): The Development and Validation of an Evaluation Instrument for Secondary School Students" Sustainability 12, no. 3: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030821
APA StyleHadjichambis, A. C., & Paraskeva-Hadjichambi, D. (2020). Environmental Citizenship Questionnaire (ECQ): The Development and Validation of an Evaluation Instrument for Secondary School Students. Sustainability, 12(3), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12030821





