Comparative Study of Cationic Dye Adsorption Using Industrial Latex Sludge with Sulfonate and Pyrolysis Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
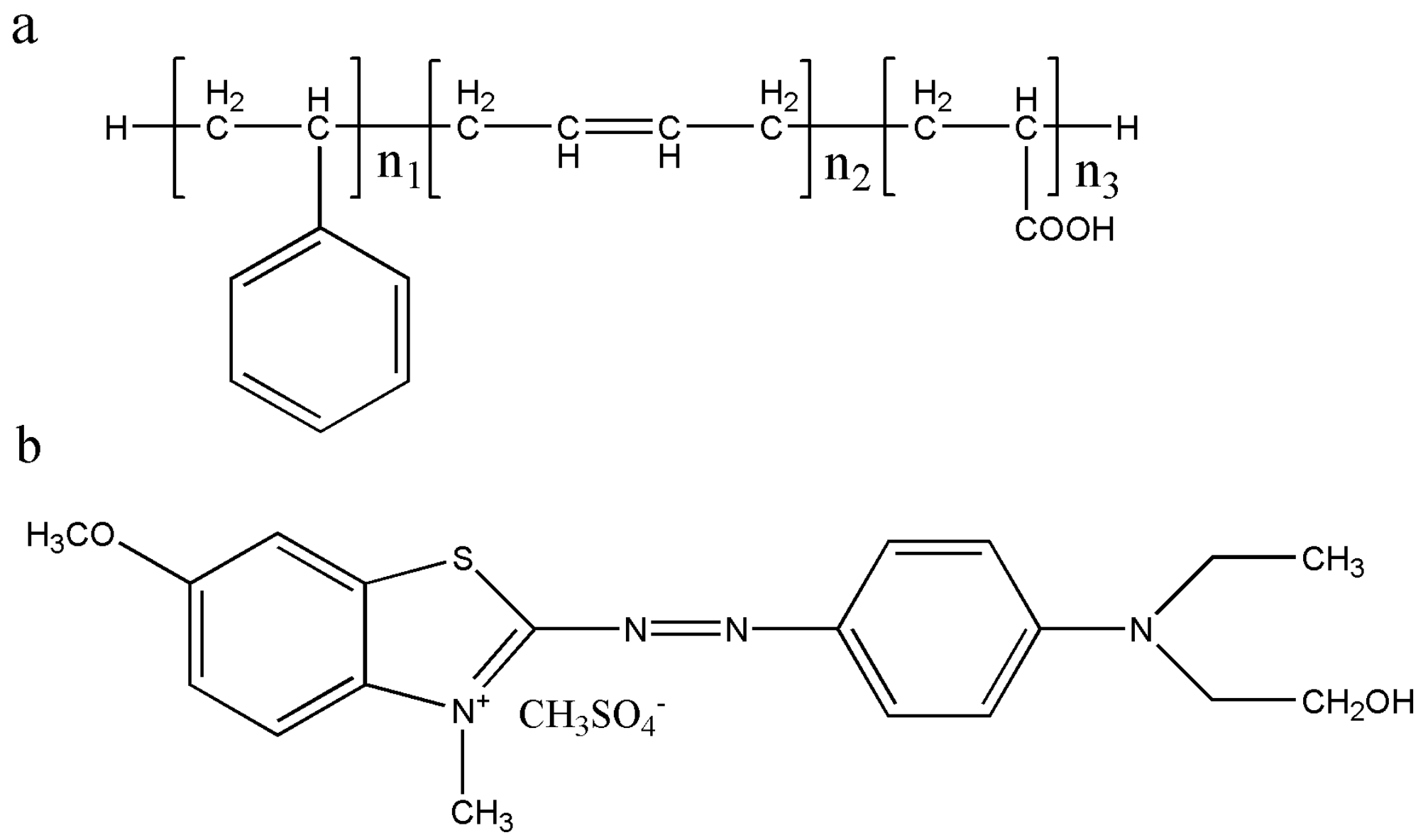
2.2. Preparation of Sulfonated Latex Sludge
2.3. Preparation of Latex Sludge Activated Carbon
2.4. Measurement Techniques
2.5. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
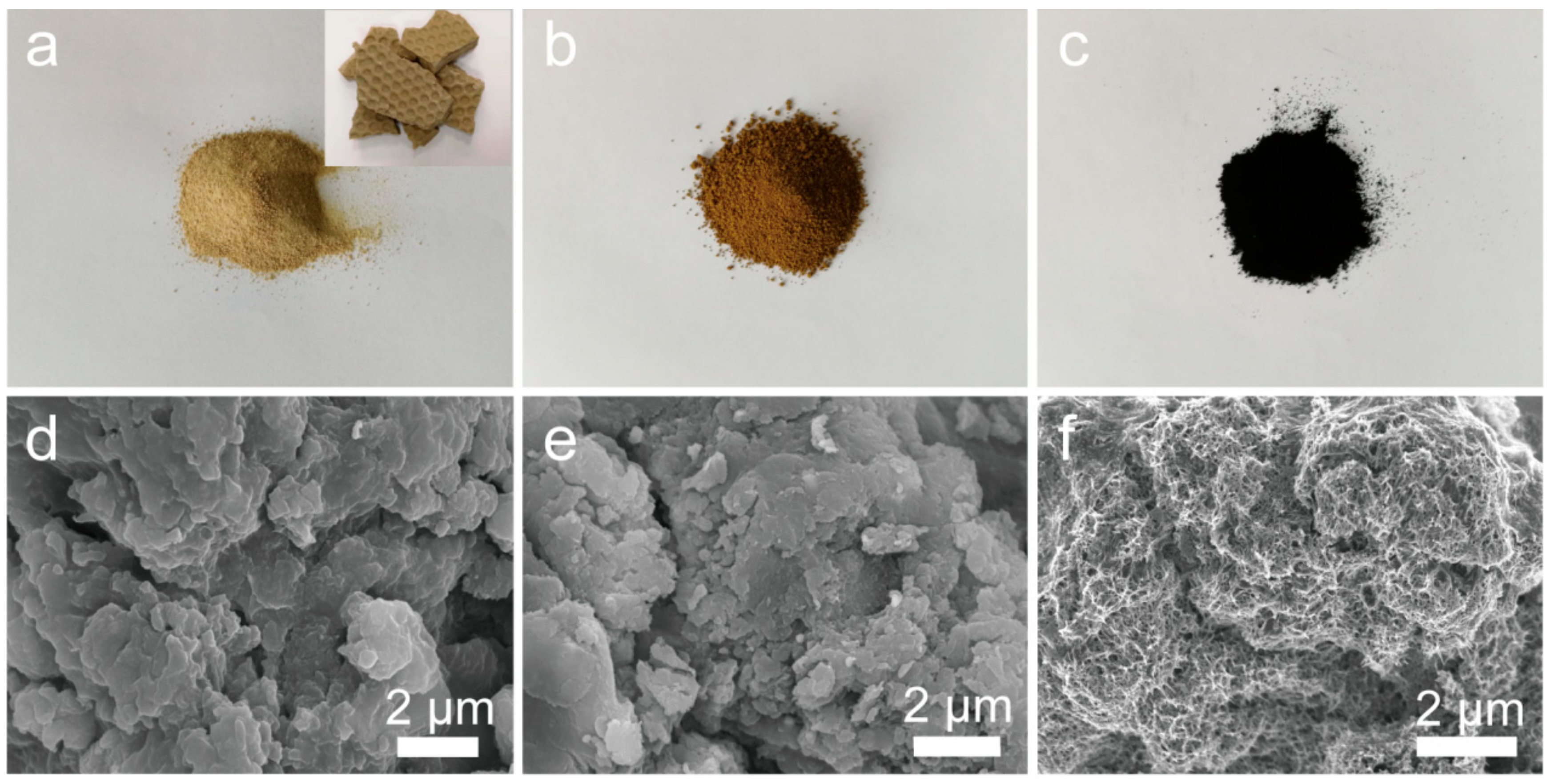
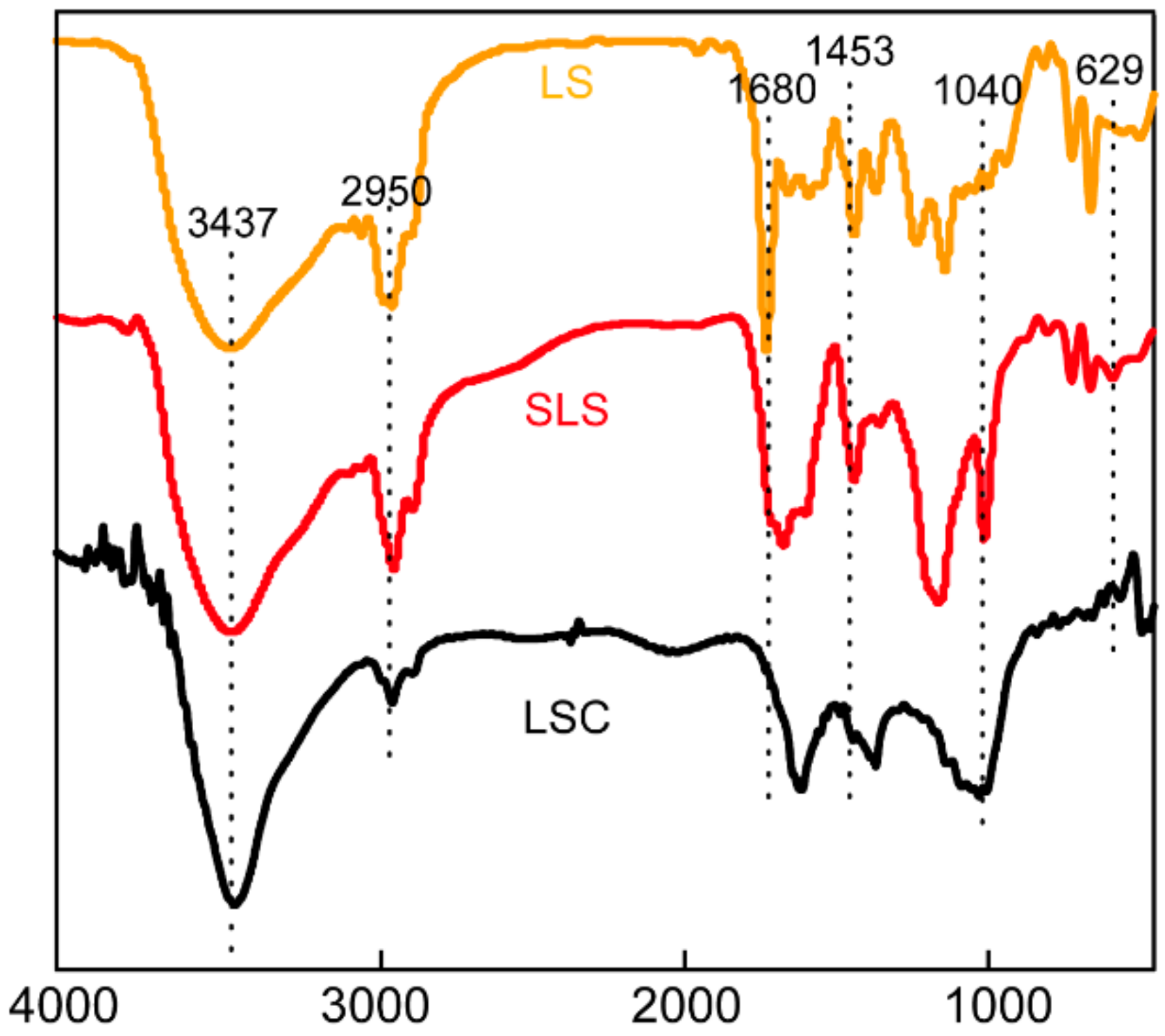
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
3.2. Adsorption Performance in Batch Experiments
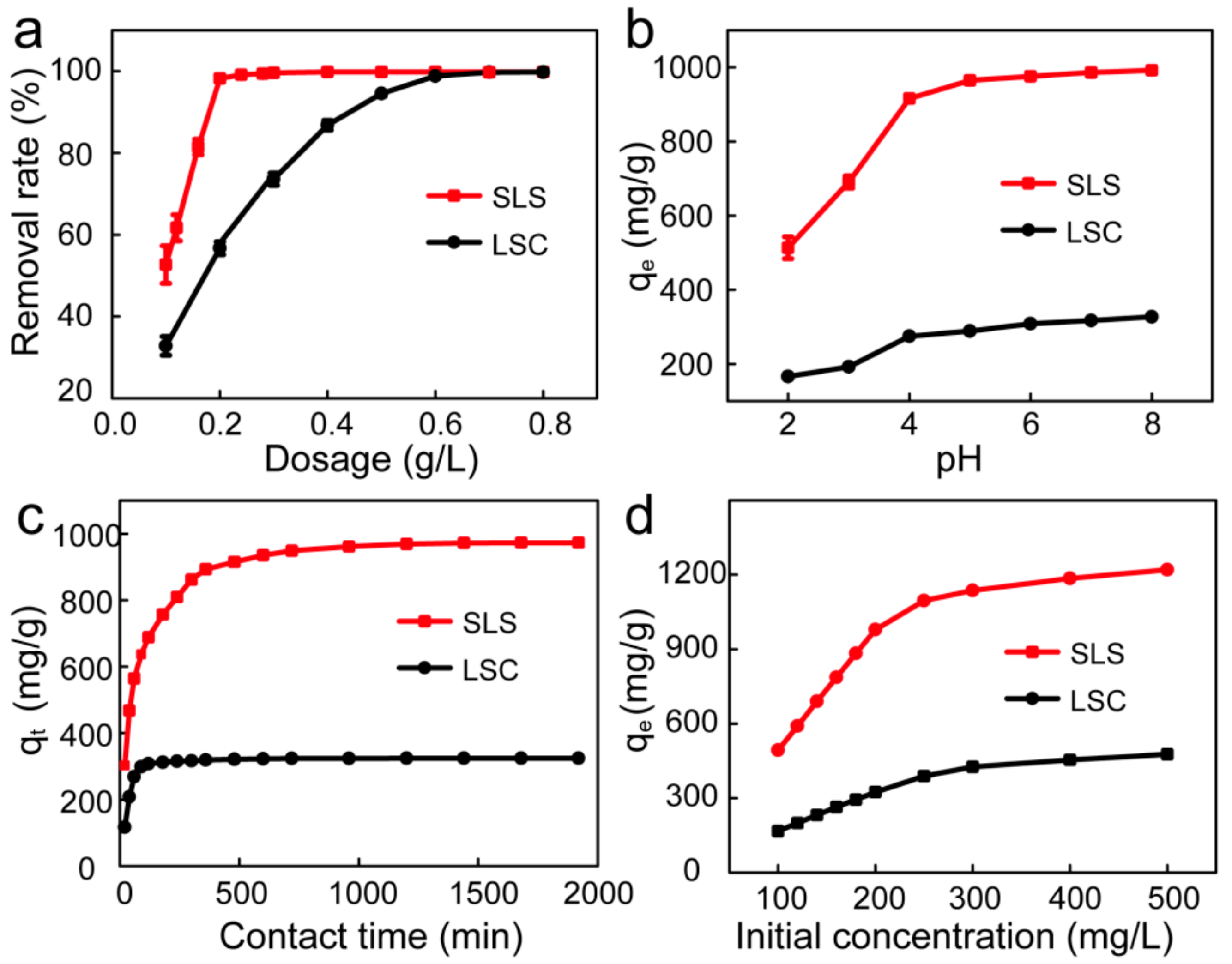
3.2.1. Effects of Adsorbent Dosage on X-GRRL Adsorption
3.2.2. Effects of Solution pH on Adsorption
3.2.3. Effects of Contact Time on X-GRRL Adsorption
3.2.4. Effects of Initial Concentration on X-GRRL Adsorption
3.3. Kinetics Studies
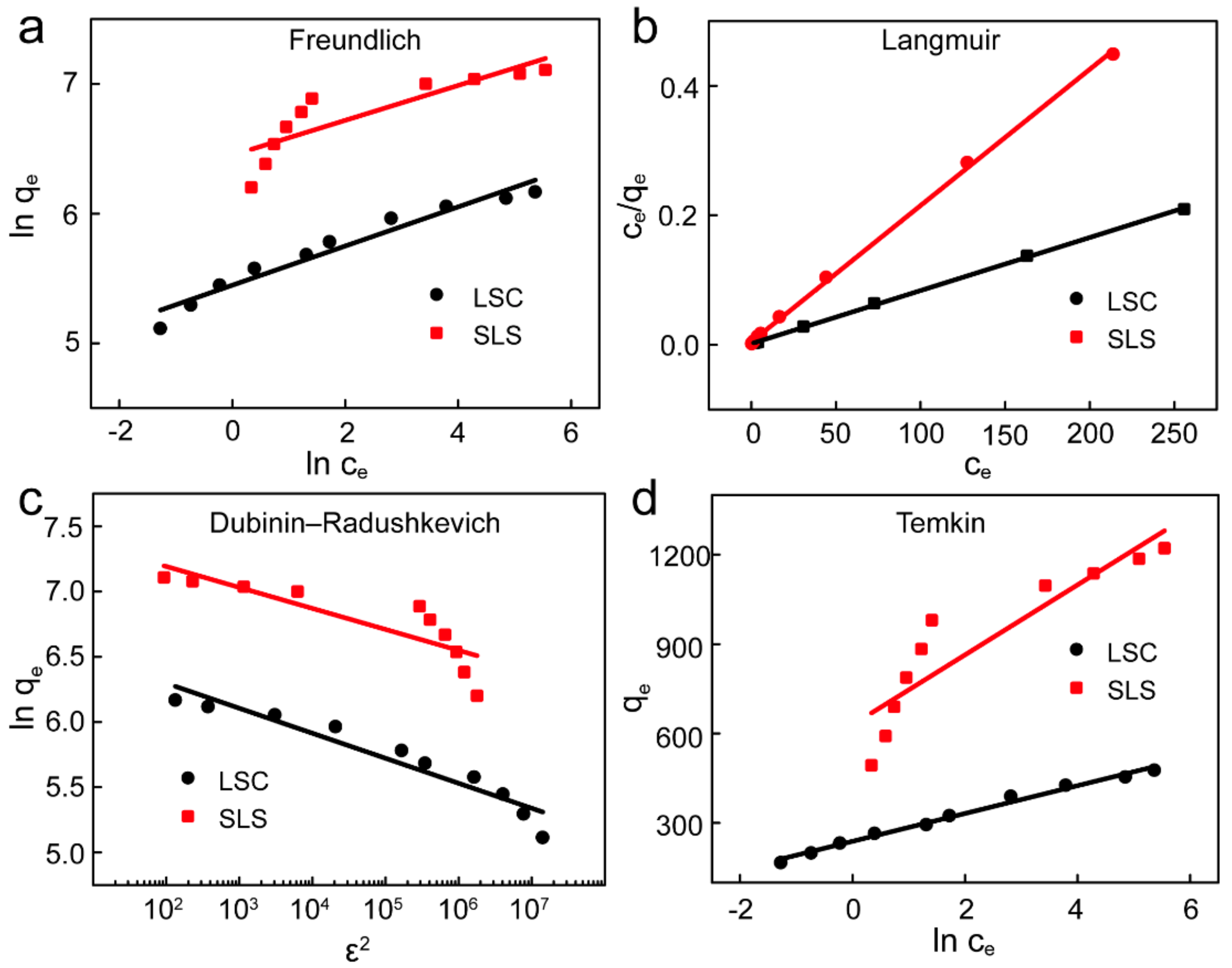
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Thermodynamic Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, W.; Xie, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, P.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. One-step synthesis of nitrogen-doped sludge carbon as a bifunctional material for the adsorption and catalytic oxidation of organic pollutants. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 680, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017: Wastewater, The Untapped Resource; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017; Available online: http://www.unesco.org/new/en/natural-sciences/environment/water/wwap/wwdr/2017-wastewater-the-untapped-resource/ (accessed on 11 March 2017).
- Cheng, R.; Ou, S.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xiang, B. Ethylenediamine modified starch as biosorbent for acid dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.; Mittal, J.; Malviya, A.; Kaur, D.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of hazardous dye crystal violet from wastewater by waste materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 343, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Choi, E.; Jang, E.; Gil Hong, S.; Lee, S.R.; Ravindran, B. Adsorption Characteristics of Ammonium Nitrogen and Plant Responses to Biochar Pellet. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cui, B.; Dai, J.; Li, D. Mechanism of adsorption of anionic dye from aqueous solutions onto organobentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P. A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour from textile wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-Kiakhani, M.; Tehrani-Bagha, A. Cationic ester-containing gemini surfactants as retarders in acrylic dyeing. Colloids Surfaces Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 479, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Deng, S.-Q.; Jin, X.; Cai, S.-L.; Zheng, S.-R.; Zhang, W.-G. The construction of amorphous metal-organic cage-based solid for rapid dye adsorption and time-dependent dye separation from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.K.; Jun, J.W.; Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of p-arsanilic acid from water using mesoporous zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadami, A.A.; Naushad, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Ahamad, T.; Alothman, Z.A.; AlShehri, S.M.; Ghfar, A.A. Efficient removal of toxic metal ions from wastewater using a recyclable nanocomposite: A study of adsorption parameters and interaction mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-D.; Lin, Y.-C.; Ho, S.-H.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, N.-Q. Highly efficient adsorption of dyes by biochar derived from pigments-extracted macroalgae pyrolyzed at different temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Fu, C.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Mijowska, E.; Chen, M.-J.; Wang, D.-Y. Large-scale converting waste coffee grounds into functional carbon materials as high-efficient adsorbent for organic dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toumi, K.; Bergaoui, M.; Khalfaoui, M.; Benguerba, Y.; Erto, A.; Dotto, G.L.; Amrane, A.; Nacef, S.; Ernst, B. Computational study of acid blue 80 dye adsorption on low cost agricultural Algerian olive cake waste: Statistical mechanics and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 271, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.C.; Vilar, V.J.; Boaventura, R. Waste metal hydroxide sludge as adsorbent for a reactive dye. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, J.-L. Adsorption removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using ceramic adsorbents prepared from industrial waste coal gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaria, G.; Silva, C.P.; Oliveira, J.A.; Santos, S.M.; Gil, M.V.; Otero, M.; Calisto, V.; Esteves, V.I. Production of highly efficient activated carbons from industrial wastes for the removal of pharmaceuticals from water—A full factorial design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 370, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.S. Waste-cellulose-derived porous carbon adsorbents for methyl orange removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, Y.; Ogata, F.; Saenjum, C.; Nakamura, T.; Kawasaki, N. Removing Sr(II) and Cs(I) from the Aqueous Phase Using Basil Seed and Elucidating the Adsorption Mechanism. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, E.T.; Ortaboy, S.; Atun, G. Adsorptive removal of thiazine dyes from aqueous solutions by oil shale and its oil processing residues: Characterization, equilibrium, kinetics and modeling studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Liu, J.; Kuo, J.; Buyukada, M.; Evrendilek, F. Thermal characteristics, kinetics, gas emissions and thermodynamic simulations of (co-)combustions of textile dyeing sludge and waste tea. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z. Chemical treatment of CNTs in acidic KMnO4 solution and promoting effects on the corresponding Pd–Pt/CNTs catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. Chem. 2012, 356, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larous, S.; Meniai, A.-H. Adsorption of Diclofenac from aqueous solution using activated carbon prepared from olive stones. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 10380–10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-García, A.; Sanz-Calcedo, J.G.; Carrasco-Amador, J.P.; Segura-Cruz, R. Adsorption of Paracetamol in Hospital Wastewater through Activated Carbon Filters. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Guo, L.; Xu, W.; Xu, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Xu, G.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y.; Wan, Y. Sulfonated polystyrene magnetic nanobeads coupled with immunochromatographic strip for clenbuterol determination in pork muscle. Talanta 2014, 129, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Cong, H.; Li, G.; Peng, Q.; Yang, C. Synthesis and application of sulfonated polystyrene/ferrosoferric oxide/diazoresin nanocomposite microspheres for highly selective removal of dyes. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.K.; Tan, M.C.; Chin, N.L. Effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on adsorbent in dye adsorption compared with ultrasound simultaneous adsorption. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Parashar, V.; Mishra, S.; Mishra, A. Fe3O4 MNPs and gum xanthan based hydrogels nanocomposites for the efficient capture of malachite green from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, W.; Liu, S.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium Using Banana Pseudostem Biochar and Its Mechanism. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M. Solar Red and Brittle Blue direct dyes adsorption onto Eucalyptus angophoroides bark: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Mango stone biocomposite preparation and application for crystal violet adsorption: A mechanistic study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 239, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Charmas, B.; Skubiszewska-Zięba, J.; Pasieczna-Patkowska, S. Effect of sewage sludge properties on the biochar characteristic. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 112, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Saroha, A.K. Utilization of sludge based adsorbents for the removal of various pollutants: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 578, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Guo, X.; Park, H.-S. Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of polyvinyl alcohol from aqueous solution on powdered activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, I. Kinetics of the adsorption of reactive dyes by chitosan. Dye. Pigment. 2006, 70, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tan, C.; Sun, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C. Porous activated carbons derived from waste sugarcane bagasse for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Dai, Q.; Yu, X.; Yu, P.; Zhai, S.; Liu, R.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Effects of sludge thermal-alkaline pretreatment on cationic red X-GRL adsorption onto pyrolysis biochar of sewage sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, C.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X. Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of U(VI) on reduced graphene oxide-supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşçı, Y.; Nurbaş, M.; Açıkel, Y.S. A comparative study for the sorption of Cd(II) by soils with different clay contents and mineralogy and the recovery of Cd(II) using rhamnolipid biosurfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Frankl. Inst. 1917, 183, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, I.; Yildiz, I.; Alyammahi, A.; Obaidalla, F.; AlMehairbi, M.; Alkhajeh, S.; Alhammadi, T.A. Adsorptive removal capacity of gravel for metal cations in the absence/presence of competitive adsorption. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 7530–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Eriobotrya japonica seed biocomposite efficiency for copper adsorption: Isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamic and desorption studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Srivastava, V.; Banerjee, S.; Weng, C.-H.; Sharma, Y.C. Adsorption characteristics of modified sand for the removal of hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solutions: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Catena 2013, 100, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by graphene modified with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SL | 3.45 | 0.02 | 15.97 |
| SLS | 6.13 | 0.07 | 44.37 |
| LSC | 313.39 | 1.12 | 15.19 |
| Materials | C % | O % | H % | N % | S % | O/C | H/C | N/C | S/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LS | 58.27 | 19.34 | 6.96 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 0.3319 | 0.1194 | 0.0094 | 0.0134 |
| SLS | 56.41 | 27.11 | 6.12 | 0.41 | 7.34 | 0.4806 | 0.1085 | 0.0073 | 0.1301 |
| LSC | 23.16 | 20.95 | 2.74 | 0.5 | 0.55 | 0.9046 | 0.1183 | 0.0216 | 0.0238 |
| SLS | LSC | |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order model | ||
| K1 (min−1) | 0.00426 | 0.00522 |
| qe (mg/g) | 544.0 | 69.1 |
| R2 | 0.9764 | 0.8690 |
| Pseudo-second-order model | ||
| K2 (g/(mg·min)) | 2.093 × 10−5 | 2.153 × 10−4 |
| qe (mg/g) | 1009.8 | 328.9 |
| R2 | 0.9999 | 0.9997 |
| Intra-particle diffusion model | ||
| Kint (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 17.228 | 3.522 |
| C | 456.2 | 227.6 |
| R2 | 0.7496 | 0.3661 |
| Elovich model | ||
| α (mg/(g·min)) | 91.725 | 469.564 |
| β (g/mg) | 6.4 × 10−3 | 2.7 × 10−2 |
| R2 | 0.9487 | 0.6344 |
| SLS | LSC | |
|---|---|---|
| Langmuir isotherm model | ||
| KL (L/mg) | 0.443 | 0.451 |
| qm (mg/g) | 1219.5 | 476.2 |
| R2 | 0.9996 | 0.9990 |
| RL | 0.004–0.0221 | 0.004–0.0217 |
| Freundlich isotherm model | ||
| KF [(mg/g)/(1/mg)n]1/n·L1/n/g) | 632.7 | 232.2 |
| 1/n | 0.135 | 0.151 |
| R2 | 0.7139 | 0.9464 |
| Temkin isotherm model | ||
| bT | 0.0473 | 0.0188 |
| KT (L/mg) | 212.3 | 165.2 |
| R2 | 0.8121 | 0.9889 |
| D-R isotherm model | ||
| qm (mg/g) | 1832.9 | 796.3 |
| β (mol2/kJ2) | 0.161 | 0.192 |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | 1.763 | 1.616 |
| R2 | 0.6943 | 0.9085 |
| ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔS (J/mol) | ΔG (kJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 K | 303 K | 318 K | |||
| SLS | 32.81 | 151.74 | −10.86 | −13.79 | −15.41 |
| LSC | 13.41 | 85.10 | −11.09 | −12.40 | −13.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, R. Comparative Study of Cationic Dye Adsorption Using Industrial Latex Sludge with Sulfonate and Pyrolysis Treatment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310048
Wei H, Sun J, Zhang B, Liu R. Comparative Study of Cationic Dye Adsorption Using Industrial Latex Sludge with Sulfonate and Pyrolysis Treatment. Sustainability. 2020; 12(23):10048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310048
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Heng, Jiankun Sun, Bin Zhang, and Rongzhan Liu. 2020. "Comparative Study of Cationic Dye Adsorption Using Industrial Latex Sludge with Sulfonate and Pyrolysis Treatment" Sustainability 12, no. 23: 10048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310048
APA StyleWei, H., Sun, J., Zhang, B., & Liu, R. (2020). Comparative Study of Cationic Dye Adsorption Using Industrial Latex Sludge with Sulfonate and Pyrolysis Treatment. Sustainability, 12(23), 10048. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310048





