Abstract
This paper investigates how two fundamental consumer characteristics, self-esteem (inner-self) and status seeking (outer-self), influence consumers’ purchasing behaviors of CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) products via two mediating effects: brand image and self-enhancement. In particular, we analyze these effects in two different CSR domains: environmental and social. By doing so, we are able to verify the underlying mechanisms of how different types of consumers respond to various CSR promotions. We propose a distinctive CSR consumption model incorporating both inner-self and outer-self components. We collected data from two countries, the US and China, using two commonly used online survey platforms: Amazon M-Turk and Loop Information Technology. Using structural equation modeling, our analysis in the environmental domain revealed that both inner-self and outer-self components play a significant role in consumers’ desire to purchase CSR products. Additionally, this process is mediated by the brand image of the firm and the tendency to enhance self-value. Interestingly, we found that in the social domain, self-enhancement mediated consumer characteristics and purchasing behavior of CSR product, whereas brand image did not. This indicates that environmental CSR activities increase brand value and its impact on purchase intention, while social CSR activities do not. Additionally, we found similar patterns for both US and Chinese consumers.
1. Introduction
Due to the rapid economic growth and technological development of the last century, more people currently enjoy opulent lifestyles than ever before. However, in this time of abundance, economic inequality has been deepening and fairness and morality have moved to the forefront of issues that are important to members of society. This trend also applies to the contemporary commercial context. Consumers and their peer groups are now focusing on “doing the right thing” and paying attention to whether companies they choose to be involved with exemplify ethical behaviors. As a response to this, corporate social responsibility (CSR) is increasingly not just an option but a requirement for firms and managers increasingly need to go beyond questioning whether, or how much, they adopt this new perspective but ask a more specific question: how they can implant CSR activities into their business model in response to consumer demand and consumer characteristics.
This challenging question is exemplified by Starbucks. Starbucks has initiated a series of sustainability activities and has seen rapid expansion, opening more than 17,000 stores throughout the world, by building its brand image as an environmentally friendly and responsible player in society [1]. As a result, Starbucks is generally viewed as an ethical company [2]. To continue to cement its reputation in this area Starbucks issued the first U.S. Corporate Sustainability Bond in May of 2016. As its CFO declared, “sustainability is not just an add-on but an integral part of Starbucks, including our strategy and finances” [3].
Within corporate marketing it is important for managers to understand that CSR relies on both internal and external stakeholders and requires the simultaneous involvement of both [4]. Within the business literature CSR is a key topic, with one of the main foci being on the relationship between CSR activities and the firm’s financial performance [5]. Scholars have looked more specifically at whether, and how, CSR activities influence management issues, ranging from employee productivity to risk management [6], how firm characteristics moderate CSR consumption [7], as well as whether CSR activities lead to favorable brand images and how consumers evaluate CSR products [8,9]. However, the link between CSR activities and financial performance is not as straightforward as expected and still debatable [10,11]. Thus, it is beneficial for managers to focus on the strategic implementation of CSR activities and this requires managers to understand which type of consumers are concerned more with which types of CSR activities.
When looking more specifically at how consumers engage with firms, it is important to understand the motivations of these consumers and how they fit with the given firm’s CSR. Qualitative work has shown that for fair trade consumption, ethical attitudes and values have a relatively small impact on consumption, while habit, health, well-being, self-satisfaction, and social guilt play a larger role [12]. While this provides an intriguing look at potential motivations for ethical consumption, there is still a lot to be done in order to understand fundamental questions about what motivates consumer concern about CSR activities and the nature of the underlying mechanism of the purchase of CSR products. The answers to these two questions are of interest to managers as they aim to build up a successful business model for their firms’ CSR activities.
Thus, in the present work, we contribute both managerially and theoretically by proposing a distinctive CSR consumption model incorporating intrinsic characteristics of human nature that encourages people to buy CSR products. More specifically, the consumers’ self-esteem (inner-self component) impacts their intention to purchase CSR products due to the influence that these products have on how the individual feels about himself or herself [13]. Alternatively, the status seeking of the consumers (outer-self component) can also drive their purchase intention through the perceived impact that CSR products will have on their status with others, as these products may enhance the perception of those around them that they are a good person [14]. The former self-esteem and latter status-seeking lead consumers to purchase CSR products, as they enhance their self-value as well as increase the consumers’ perception of the brand image associated with the products. Thus, we specify a structural equation model (SEM) to verify how these two fundamental consumer characteristics, self-esteem and status-seeking, influence their purchasing behaviors in relation to CSR products mediated through their perceived self-enhancement and the brand image associated with the CSR product.
In order to achieve these objectives, we conduct a survey using a hypothetical environmentally friendly notepad to establish a model. In this survey, participants from the United States are reached through Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk) and are prompted with a notebook that was manufactured from recycled materials. In addition, we test our proposed model in another CSR domain by conducting a survey using a hypothetical donation engaged product. By doing so, we aim to provide a more nuanced view of the CSR product consumption process for consumers based on key inner-self and outer-self characteristics. Furthermore, we expand our study by collecting survey data from Chinese consumers using the Loop Information Technology Company, a professional Chinese online survey company (Loop is operated similarly to MTurk.). By analyzing both studies, we are able to examine whether the effect of intrinsic consumers’ characteristics on CSR product purchasing intention may be heterogeneous across different countries. Our analysis reveals that self-esteem and status-seeking play key roles to induce consumers to purchase environmentally friendly CSR products. These relationships are further established through the brand image of the CSR products and the tendency to enhance the individual’s self-value. Interestingly, when the CSR domain differs and the target CSR products are designed for donation, brand image fails to bridge between the two individual characteristics and consumers’ CSR purchase decisions. This suggests that when CSR activities are centered on the social domain, self-enhancement is the only effective way to induce consumers to get involved in CSR purchase decisions.
Further, we find consistent patterns across both country’s samples. In the social domain, both types of consumers fail to connect the firm’s CSR activity to its brand image. Instead they purchase the CSR product only by enhancing the consumers’ self-value. In the environmental domain, the individual characteristics drive both brand image and self-value, which also drives purchase intention. This finding suggests that these two motivational factors that are based on human beings’ fundamental nature would be applicable in a more general context. From a managerial perspective, our findings provide meaningful implications to construct a successful business model related to CSR activities by helping managers properly target their customers and select effective promotions for this target group. For the remainder of the paper, we discuss the relevant prior literature and introduce our conceptual model. Then, we describe our study design and our data. Further, we fully discuss the empirical results of our studies. Finally, we provide a conclusion by discussing the key contribution of our paper, the limitation, and potential for future study.
2. Theory and Hypotheses
2.1. Corporate Social Responsibility
Over the past few decades, governments, businesses, and society have shown enormous interest in CSR. According to the European Commission’s definition of CSR, firms voluntarily interact with their stakeholders and integrate social and environmental concerns into corporate management [15]. More broadly, CSR has traditionally been conceptualized as “the managerial obligation to take action to protect and improve both the welfare of society as a whole and the interest of organizations” [16] (p. 6). Another more recent definition comes from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). They define CSR as the firms’ decision-making in accordance with transparent and ethical behavior and the responsibility of the firm to consider the impact of the organization’s decisions and activities on both society and the environment [17]. It is even viewed as the company’s “status and activities with respect to or responsiveness to its perceived societal obligations” [5] (p. 68). From this perspective, business is an essential element of society and should perform its functions in ways that permit it to co-exist with the assorted stakeholders in society [18]. Although some researchers do claim that CSR refers exclusively to social activities, and environmental responsibility goes beyond it, the broad concept of CSR represents achieving success in an ethical manner with respect to people, community, and even environment. For example, many CSR researchers have studied environmental protection activities (e.g., energy consumption, water, and waste generated), social activities (e.g., community investments), and workplace activities (e.g., employee training courses, company policies for the protection of human rights and the fight against corruption) [19]. A comprehensive summarization of CSR actions published in Socrates: The Corporate Social Ratings Monitor, a database that collects over 600 companies about their CSR records, shows that CSR initiatives undertaken by these companies belonged to six domains, including (1) community support, (2) diversity, (3) employee support, (4) environment, (5) non-U.S. operations, and (6) products [20].
As a result of the importance of CSR in business and society, research has increased in relation to CSR issues within a range of business fields. In the initial stage of CSR research, demonstrating the commercial benefit of CSR received considerable attention. Freeman [21] argued in his seminal paper that firms can benefit from their CSR activities by improving their relationships with different groups of stakeholders. His “stakeholder theory” has also been well-accepted in subsequent research [22,23,24]. For instance, firms who are committed to social responsibility issues not only attract employees and motivate them at work but also reduce the expenses involved with recruiting and training [25]. Furthermore, CSR activities have also been shown to improve employee productivity and morale [26,27,28].
However, a growing body of research has revealed mixed results on the relationship between CSR activities and firms’ financial performance [6,28,29,30,31,32]. For instance, Becker-Olsen et al. [33] found that consumers are favorable toward CSR activities only when it matches with the firm’s image. Luo and Bhattacharya [34] also showed that CSR activities can harm the firm when the firm’s innovative capabilities are not strong enough. While ceaseless debates about the profitability of CSR activities remain [6,28,29,32], the question of how effective CSR programs are implemented has become key. Since CSR is neither a pure cost nor a magic wand for a brand, as Bhattacharya and Sen [8] mentioned in their review paper, a prescriptive approach toward CSR activities is needed. As many firms implement various CSR programs to address their beliefs and responsibilities as social leaders, managers need to understand how to effectively manage CSR activities rather than simply understand whether CSR activities are beneficial or not.
2.2. CSR Products
While CSR has broad applications within the firm, the product domain of CSR includes several components such as “product safety, research and development/innovation, marketing/contracting controversies, and antitrust disputes”, which all provide opportunities for the firm to integrate CSR into the products that it offers to consumers [20] (p. 226). Among these components, one of the most challenging issues is the successful development of CSR products, because understanding consumers’ motivation and intention to purchase CSR products is needed. In the previous literature, many researchers focused on why and how a consumer purchases CSR products [5,9,10]. For instance, Brown and Dacin [5] (p. 80) concluded that “negative CSR associations can have a detrimental effect on overall product evaluations, whereas positive CSR associations can enhance product evaluations”. Later, Sen and Bhattacharya [20] examined the company- and consumer-specific differences of CSR effectiveness and suggested that CSR products increase consumers’ purchase intention indirectly through creating favorable company evaluations. Further, Sen and Bhattacharya [20] found that CSR products increase consumers’ purchase intention directly by increasing product attractiveness only in some domains (e.g., employee working condition) and only for some consumers (e.g., who believe that the firm is able to make quality products). Bhattacharya and Sen [8] later argue that consumers are not likely to sacrifice the core attributes of the products (e.g., price) in order to appreciate their CSR aspects.
As such, much recent CSR product literature focuses on identifying the boundary conditions of CSR products. For instance, Luchs et al. [9] suggest that sustainability is not always an asset even though consumers care about environmental issues. They demonstrated that when a product needs strength (e.g., car shampoo), consumers are less likely to choose sustainable options than typical options because consumers tend to associate ethicality with gentleness. Further, Lin and Chang [35] found that consumers consider environmentally friendly products (e.g., detergent) to be ineffective and therefore often consume them too much. Servaes and Tamayo [10] analyzed secondary firm-level financial data and found that consumers’ awareness of the brands, not CSR, plays a key role in influencing the CSR activities on the companies’ financial performance.
CSR has been considered as cause-related marketing that can lead consumers to purchase the focal product by stimulating their feelings about a “good cause” [36,37,38,39,40]. Varadarajan and Menon [36] mentioned that cause-related marketing is neither a typical sales promotional tool nor corporate philanthropic activities. They provide a formal definition of cause-related marketing as “the process of formulating and implementing marketing activities that are characterized by an offer from the firm to contribute a specified amount to a designated cause when customers engage in revenue-providing exchanges that satisfy organizational and individual objectives.”
Researchers have recently studied how to effectively implement cause-related marketing. Koschate-Fischer et al. [39] investigated the relationship between firms’ implementation factor, such as the donation amount, and willingness to pay (WTP) of customers. They argued that the donation amount does not always have a positive relationship with WTP. It can be a negative relationship depending on the degree of company-cause fit. Also, Robinson et al. [38] found that cause-related marketing receives more support from the consumers when the donation becomes a choice option for the consumers. They argued that this choice option would be helpful if it increases the perception of a consumer’s personal role in the contribution. In addition, Kim and Kim [40] examined how people’s moral emotion influences the cause-related marketing from cross-cultural studies. Using several experiments, they found that pride and guilt, among other moral emotions, increase consumers’ purchase intention for CSR products. They also argued that it could be different across countries and cultures (US vs. Korea).
2.3. CSR Consumption Model
While prior studies focused on why and how consumers purchase CSR products, as previously discussed, little literature addresses fundamental strategic questions about how to approach consumers for the CSR product: the match between consumers and specific types of CSR products. To maximize the effectiveness of CSR activities on CSR product development, a more strategic approach is necessary for understanding consumers’ fundamental needs. Thus, in this paper, we propose a distinctive CSR consumption model based on intrinsic characteristics of consumers, as the nature of CSR consumption is derived from a higher hierarchical level of human needs (e.g., self-fulfillment or psychological needs) rather than basic needs (physiological or safety needs). Specifically, to understand the consumption mechanism of CSR products, we begin with two representative intrinsic traits of consumers, self-esteem vs. status-seeking. Along with these two characteristics, we include two channels related to purchase intention of the CSR product, brand image and self-value enhancement, which have seen adoption as key factors for why a consumer wants to purchase a CSR product in the literature.
2.3.1. Self-Esteem
Self-esteem has been widely studied as a way to understand the way humans behave [41]. While there have been many definitions given for self-esteem, we follow past work which views self-esteem “as a global personality construct that measures the extent to which a person has a positive attitude about him- or herself” [41] (p. 292) [13]. More precisely, we contextualize self-esteem as “the extent to which one prizes, values, approves, or likes oneself” [42] (p. 115). Due to peoples’ intrinsic desire to maintain a positive self-concept, a large amount of psychological research indicates that self-esteem is a fundamental psychological need [43].
In general, those who have higher self-esteem tend to evaluate themselves as positive and in situations where they find a basis for their self-worth they would be motivated to seek contact with others who can reinforce this perspective for them [44]. Following these self-verification processes, Malär, Krohmer, Hoyer, and Nyffenegger [45] propose that consumers high in self-esteem feel closer and have more positive feelings toward a brand that reflects their actual self. From a CSR perspective this would mean that consumers who have higher self-esteem may feel closer to firms that leverage CSR as a means to connect with the consumer.
Banerjee et al. [46] analyzed the contents of a convenience sample of 95 green TV ads and 173 green print ads. They found that many advertisers attempted to link consumers’ environmental behaviors with their self-esteem. In total, 42% of the TV ads and 55% of the print ads presented highlighted their role in protecting the environment and presented a positive view of environmentally responsible consumers. This advertisers’ strategy can be attributed to the self-standard that consumers hold, that is, people should behave in an ethical and sustainable manner. On the whole, consumers highlight that ethical and sustainability criteria should be a component of their consumption [47]. A recent study conducted by Peloza et al. [48] demonstrated that when consumers’ desire to live up to internal self-standards was activated, they were more likely to choose products promoted by ethical appeals. Sen and Bhattacharya [20] mentioned that “identification with an organization engaged in do-good CSR actions can contribute to consumers’ self-esteem.”
Furthermore, research has shown that consumers can build a connection with the corporation or a corporate culture, which play an important role in consumption behavior [49]. Research has shown that the CSR image of the brand can lead to purchase intention [50]. The authors show that this is driven by self-definitional principles as consumers seek to identify themselves with brands that confirm their personal identity or aspirations. Extending the previous findings, we hypothesize that consumers with high self-esteem will evaluate the brand image of a product made by a company announcing CSR activities more favorably, because they not only consider this brand as reflecting their actual life but also aim to abide by this self-standard, thus attributing more to the brand.
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Self-Esteem is Positively Related to Brand Image.
Self-enhancement encompasses an individual’s desire to increase their positive self-concept or, alternatively, to decrease their negative self-concept as a way to make them feel good about who they are [51]. As a result, self-enhancement is commonly related to people having a more positive view of themselves and their own potential than that of others. More specifically, these individuals have a tendency to rate themselves more positively compared to others in terms of basic comparisons as well as potential outcomes and experiences [52,53]. Past research has shown that CSR can have an impact on the personal satisfaction of individuals and that this personal satisfaction plays a mediating role between CSR perception and purchase intention [54].
While self-enhancement is related to positive self-esteem it is also seen in people with low self-esteem. Kunda [55] discusses the mechanisms involved as people process new information. She highlights that people will exhibit bias when evaluating information by searching for information that conforms to their desired status. This leads people to work to enhance their self-concept by focusing on the positive information while also avoiding negative information that may confirm or demonstrate negative self-concepts. This suggests that higher self-esteem consumers will want to purchase CSR products due to the perceived match with their own self-esteem and their ability to reinforce this perception. However, the perception from lower self-esteem consumers and their match with a CSR product will create a dissonance, leading them to avoid the product as it serves as a potential reminder of their relatively lower level of self-esteem. Similarly, Snyder and Omoto [56] argue that volunteers tend to have a higher self-esteem and psychological well-being because when they help others voluntarily, their feeling of social connectedness increases, suggesting that consumers with high self-esteem are more likely to be involved with CSR activities to enhance themselves.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Self-Esteem is Positively Related to Self-Enhancement.
2.3.2. Status-Seeking
As Goldsmith et al. [57] claim, consumers desire status or social prestige by purchasing and consuming products. MacRae [14] described this as “status seekers are continually straining to surround themselves with visible evidences of the superior rank they are claiming.” In this way the consumption choices of status-seeking consumers allow them to represent the status that they see for themselves.
While investigating the behavioral characteristics of status seekers, Clark et al. [58] identified that status-seekers tend to consider status as a reward for purchasing a brand that carries a specific level of perceived status. Naturally, status-seeking is an established driver for luxury consumption. For instance, Han et al. [59] found that consumers with the high need for status are likely to purchase luxury products because they signal affluence, while Goldsmith et al. [60] suggest that consumers’ consumption for status can influence their price sensitivity of the product.
We hypothesize that status-seekers are susceptible to the cues associated with CSR and therefore evaluate CSR brands highly. Intuitively speaking, we argue that CSR products play a role in allowing the individual to show off to others in the current business context which is increasingly paying more attention to issues around shared value. This suggests that consumers who seek status are more likely to evaluate a CSR related brand higher because the CSR focus of the brand has the ability to provide the consumer with the status that they seek. The Toyota Prius or the Tesla Model S (“Status Seekers” Economist, Dec. 2nd 2010 (http://www.economist.com/node/17627313)) provide evidence that status is a key driver in the CSR purchase decision because it plays a role as a signal of their enlightenment, generosity, and wealth. Ireland [61] considered the Nash equilibrium in voluntary contribution and argues that an individual is able to satisfy their perceived status with voluntary contributions because contribution size works as a signal of their income that would not be observed otherwise.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Status Seeking is Positively Related to Brand Image.
Researchers have focused on the motivation and incentives involved with status-seekers’ product consumption and evaluation. For example, some researchers have looked at how status-seekers choose specific brands to obtain status [62], while other researchers have found that consumers will engage in word-of-mouth (WOM) due to the self-enhancement that they may receive from these transfers [63]. Similar to the impact of brands and WOM, recent CSR studies have provided evidence that enhancing status can be a key driver for purchasing CSR products because the consumers’ altruism is seen as a signal associated with status. This signal then provides status-seekers with an incentive to purchase green products. For instance, Griskevicius et al. [64] argue that buying a pro-environmental, green product is a conspicuous consumption behavior. They found, in an experiment, that participants were more likely to choose green options when they were asked to imagine they were purchasing products in a public store (i.e., primed to enhance social status) than when they were asked to imagine they were purchasing them online, privately. Further, greater status can be obtained when the green product is more expensive than its standard counterpart. Steinhart et al. [65] also found that environmental claims made the product favorable when they focus on consumers’ social status.
Individuals who are high in status-seeking will look to a CSR product as a way to reinforce their own perceptions of themselves while focusing on the perceived positive contributions they are making to society through their own CSR consumption. However, those who are not status-seekers will see less of an opportunity to enhance their own value due to them being less concerned with the outward perception that CSR consumption may portray. As a result, we hypothesize that status-seeking consumers are more likely to see an opportunity for self-enhancement in a CSR product situation.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Status-seeking is Positively Related to Self-Enhancement.
2.3.3. Purchase Intention
Past research has shown that a strong positive brand image increases consumers’ willingness to pay (WTP) and purchase intention [66,67,68]. Brown and Dacin [5] found that higher brand equity leads to higher purchase intention because it is highly evaluated by consumers who trust CSR brands. In addition, a firm’s good reputation via CSR activities can increase customers’ loyalty toward the brand, which may increase their purchase intention [8]. The consumer characteristics of self-esteem and status-seeking lead to higher brand image, which in turn leads to higher purchase intention, meaning that brand image is a mediator between self-esteem, status, and purchase intention. As a result, we expect that the brand image attributed to the CSR products will positively relate to the consumers’ purchase intention, as it mediates the relationship between self-esteem, status-seeking, and purchase intention in that a higher brand image will result in an increased intention to purchase the CSR product.
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
Brand Image is Positively Related to Purchase Intention.
Finally, we hypothesize that consumers who find self-enhancement through CSR products are more likely to purchase these CSR products. Sen and Bhattacharya [20] and Bhattacharya and Sen [69] suggest that consumers like to engage CSR products because doing so enhances their feelings of self-value. Status-seeking and self-enhancement drive higher levels of self-enhancement and self-enhancement promotes the likelihood that consumers will purchase the given product. In this way self-enhancement mediates the relationship between status seeking, self-esteem, and purchase intention. As such, we expect that self-enhancement will positively relate to the consumers’ purchase intention.
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
Self-Enhancement is Positively Related to Purchase Intention.
In conclusion, we construct six hypotheses regarding consumers’ purchase intention about CSR products using two personal psychological factors and two mediator motivational factors (Figure 1). In this way we seek to better understand the mechanism for how the consumers’ psychological factors impact their purchase intention through a mediated model.
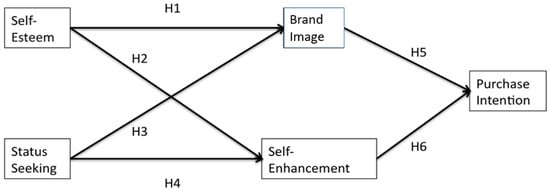
Figure 1.
Purchase intention of corporate social responsibility (CSR) products as a function of self-esteem, status-seeking, brand image, and self-enhancement.
3. Methodology
The objective of this study is to investigate the hypothesized relationships between two individual characteristics (self-esteem and status-seeking), two motivational variables (brand image and self-enhancement), and purchase intention, as well as the overall mediation involved in the model. In order to collect the data on the latent variables in the study a survey was used. Additionally, it is possible that the specific CSR domain changes the consumers’ view of how the product fits with who they are, which would impact the relationships hypothesized in this study. As such, two surveys were developed that measured the relevant variables. The first survey focused on the environmental domain, while the second focused on the social domain.
In order to set up both domains, respondents were asked to evaluate a prompt for a notebook manufactured by a hypothetical company, MACA. A standard notebook was presented and the participants were given a short product description including basic information (“80 narrow ruled sheets”, “College ruled white paper”, and “Spiral-bound”). The first survey represented an environmental CSR component by noting that the notebook was “100% Recycled”, which was also noted in the product description, as seen in Figure 2.
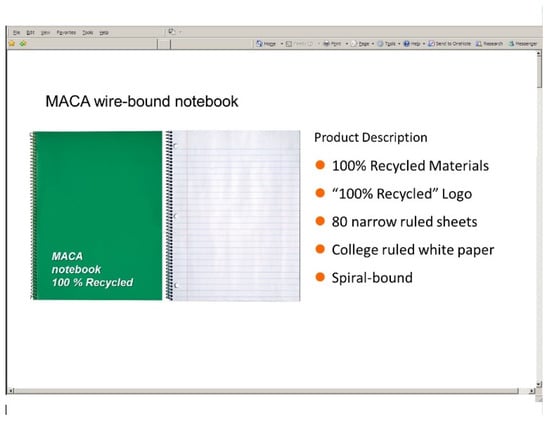
Figure 2.
Environmental domain product description from the survey.
For the social domain, the environmental domain survey was modified to focus on a hypothetical donation campaign. This represents a cause-related marketing approach which has seen growing popularity among marketing managers to promote the socially responsible image of the firm and has also been of focus within the marketing literature [70]. Instead of noting that the product was “100% Recycled”, the key social responsibility aspect was changed to the notebook being advertised as “Buy one, Give one” and provided further information such as “You buy one, we give one to a poor child for educational needs,” as seen in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Social domain product description from the survey.
The five sets of questions used in the survey were modified for context from previous work and their answers were collected on a seven-point Likert-scale (1 = strongly disagree vs. 7 = strongly agree). In our model, presented in Figure 1, our dependent variable, purchase intention, was measured using four questions modified from Podder, Donthu, and Wei [71]. Our mediating variables of brand image and self-enhancement came from a set of four questions by Yoo, Donthu, and Lee [72] and a set of four questions from Grace and Griffen [73], respectively. Finally, our consumer characteristics of self-esteem and status-seeking came from a set of ten questions by Park and John [74] and a set of five questions by Eastman and Liu [75], respectively. The self-esteem scale included five reverse coded items, while the status-seeking scale had one. The specific questions for the measures in the model are in Table 1.

Table 1.
Survey measures for the model.
The main part of the analysis looked at survey data collected in the US, using convenience sampling, through Amazon Mechanical Turk and a reward of 0.75 USD per assignment. After reviewing the data from the surveys on both domains, there were 239 usable responses in the environmental sample and 225 in the social sample, as seen in Table 2. For the environmental sample the average age of respondents was 37, with a range of individuals from 19 to 73. Out of those who responded the average yearly income was 38,140 USD and they represented individuals from a wide range of occupations including, but not limited to, management, education, freelancing, engineering, students, and attorneys. The average age of the donation sample was 36, with a range of individuals from 20 to 80. Out of those who responded the average yearly income was 39,276 USD and individuals came from similar occupations as in the environment sample.

Table 2.
US sample characteristics.
Before testing the model, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy and Cronbach’s Alpha was used to evaluate the suitability of the data. For the environmental sample the overall KMO was 0.91 and the Cronbach’s Alpha for our factors—purchase intention, brand image, self-enhancement, status, and self-esteem—was 0.97, 0.94, 0.94, 0.90, 0.93, respectively. For the donation sample the overall KMO was 0.90 and the Cronbach’s Alpha for our factors—purchase intention, brand image, self-enhancement, status, and self-esteem—was 0.97, 0.94, 0.89, 0.91, 0.95, respectively. In order to evaluate the relationships in the model, and to help investigate the nature of the mediation, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used with Satorra-Bentler robust standard errors to account for any nonnormality present in the data.
4. Results
We used two SEM models, one for the environmental sample and one for the social sample. First, we assessed the model fit of the SEM models on the respective samples as we identified the hypothesized relationships between fundamental consumer characteristics and their consumption patterns related to CSR products. Both SEM models included covariances between self-enhancement and brand image as well as within items for self-esteem and within items for self-enhancement being included. The SEM model for the environmental sample demonstrated acceptable fit as follows: Chi-Square = 410.574 (degrees of freedom [df] = 305), Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.980, Tucker Lewis Index (TLI) = 0.977, Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) = 0.038, and Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR) = 0.046. The SEM model for the donation sample also demonstrates acceptable fit: Chi-Square = 440.399 (df = 305), CFI = 0.971, TLI = 0.967, RMSEA = 0.044, and SRMR = 0.060.
We start our discussion of the results with the environmental sample, as shown in Table 3. Consistent with hypotheses 1 and 2, self-esteem was positively related to brand image (BI<--SEs; β = 0.174, p < 0.01) and to self-enhancement (SEn<--SEs; β = 0.207, p < 0.01). This suggests that higher levels of self-esteem were positively correlated with a higher evaluation of brand image for the hypothetical brand in our survey, as well as feelings of self-enhancement. Hypotheses 3 and 4 suggest that status-seeking is positively related to both brand image and self-enhancement and the model supported these hypotheses with a positive estimate for brand image (BI<--SS; β = 0.257, p < 0.001) and for self-enhancement (SEn<--SS; β = 0.392, p < 0.001). These results suggest that individuals who are status-seekers were both more likely to evaluate the hypothetical notebook with CSR attributes as coming from a higher reputation brand and that they were more inclined to seek enhancement of their self. Further, support was found for both hypotheses 5 and 6, with brand image (PI<--BI; β = 0.346, p < 0.001) and self-enhancement (PI<--SEn; β = 0.296, p < 0.01) being positively related to purchase intention. The results from hypothesis 5 imply that individuals who have higher brand perception, related to the hypothetical CSR notebook, were more likely to purchase the CSR product. Additionally, the results from hypothesis 6 suggest that individuals who work to enhance their own self-image were more likely to show intention to purchase the hypothetical CSR product.

Table 3.
Results for the US environmental sample.
While self-esteem and status-seeking were not modeled with direct paths to purchase intention, the total indirect effect for each could also be calculated with the use of SEM. We obtained the indirect effects for each mediation path by using the delta method for the Satorra-Bentler standard errors. The indirect effect of status-seeking to purchase intention was 0.204 (p < 0.001), while the indirect effect from self-esteem to purchase intention was 0.136 (p < 0.01). In this way we can see the impact that status-seeking and self-esteem have on purchase intention through brand image and self-enhancement. Taken together, we find broad support for our hypotheses and the impact of specific individual characteristics on purchase intention when looking at the environmental sample.
We also investigated the model with the social sample, as shown in Table 4. Results show that for the social sample the impact was through self-enhancement. No support was found for hypothesis 1, as self-esteem was not significantly related to brand image (BI<--SEs; β = 0.104). Consistent with hypothesis 2, self-esteem was found to have a significant positive impact on self-enhancement (SEn<--SEs; β = 0.252, p < 0.001). Hypotheses 3 and 4 suggest that status-seeking is positively related to both brand image and self-enhancement. However, no support was found for hypothesis 3 and the link between status-seeking and brand image (BI<--SS; β = −0.013). Support was found for hypothesis 4, showing a positive relationship between status-seeking and self-enhancement (SEn<--SS; β = 0.139, p < 0.05). In contrast to the environmental sample, support for hypothesis 5 was not found for the link between brand image and purchase intention (PI<--BI; β = 0.143), while support is found for hypothesis 6 with the positive link between self-enhancement and purchase intention (PI<--SEn; β = 0.599, p < 0.001).). We again obtained the indirect effect for each mediation path by using the delta method for the Satorra-Bentler standard errors. The indirect effect of status-seeking to purchase intention was 0.083 but was not significant, while the indirect effect from self-esteem to purchase intention was 0.170 (p < 0.01). The results in the social sample stand in contrast to some of the findings from the environmental sample. While the environmental sample showed mediation through both self-enhancement and brand image, the social sample only showed mediation through self-enhancement. This suggests that for the notebook that was linked to environmental CSR there was an impact on brand image as well as the ability for the individual to enhance their self-perception. However, for the social CSR component the effect was only through self-enhancement. This distinction is interesting for two reasons. First, it shows that the CSR domain is important to consider, as the consumption process is distinct depending on whether it is in the environmental or social domain. Second, there are brand implications for the type of campaign that is chosen by the firm. Consumers may associate environmentally conscious campaigns with the broader brand image, suggesting that there are possible spillover effects. However, the social campaigns involving donations may be limited to the desire to enhance their own self-perception.

Table 4.
Results for the US social sample.
Extension Study
As an extension, the same set of surveys was administered to participants in China. China provides a unique environment for these issues as it is both a developing economy and it is continuing to gain an international marketing presence. In terms of CSR, China is also of interest as it ranks 133rd out of 135 in the World Giving Index, a composite score based on individuals’ willingness to help others, donate money, and volunteer time [76], yet research has also shown that Chinese consumers are more supportive of CSR activities [77,78]. This duality presents an interesting context to provide an exploratory investigation into consumers’ CSR consumption process. In order to conduct our survey, the services of Loop Information Technology Company (Loop) were utilized. While Loop was founded in 2004, Loop’s self-service online questionnaire design and related services started in 2007 and provides these services to large companies, universities, and research institutions. Loop sends the questionnaire to a random sample from their sample pool, which is based on users who must sign up and be confirmed by Loop.
The survey included the same questions as the surveys that were sent to participants in the United States. The survey was translated and tested on a pilot group for clarity and understanding before being provided to the final participants. Like the US sample, the China sample involved two sets of surveys, one with an environmental prompt and one with a social prompt.
The Chinese environmental sample consisted of 161 responses with respondents ranging in age from 18 to 51, with an average age of 30. Respondents had an average monthly salary of 6415 RMB and had various occupations including, but not limited to, sales, management, R and D, education, and students. The Chinese social sample also totaled 161 responses, as seen in Table 5. Additionally, the average monthly salary was 7044 RMB and a similar range of occupations.

Table 5.
China sample characteristics.
In a similar process to the US sample the KMO and the Cronbach’s Alpha were calculated for both samples. Additionally, we again used Satorra-Bentler for robust standard errors in order to account for nonnormality in the data for both China samples and covariances between self-enhancement and brand image as well as within items for self-esteem, within items for status-seeking, and within items for self-enhancement were included. The KMO for the environmental sample was 0.91 and the Cronbach’s Alpha for our factors—purchase intention, brand image, self-enhancement, status, and self-esteem—was 0.91, 0.88, 0.89, 0.85, 0.87, respectively. Overall, the environmental SEM model had acceptable fit-indices: Chi-Square = 417.505 (df = 305), CFI = 0.956, TLI = 0.950, RMSEA = 0.048, and SRMR = 0.083. The KMO for the social sample was 0.91 and the Cronbach’s Alpha for our factors—purchase intention, brand image, self-enhancement, status, and self-esteem—was 0.92, 0.90, 0.87, 0.84, 0.84, respectively. The social domain sample showed acceptable fit-indices: Chi-Square = 430.284 (df = 305), CFI = 0.951, TLI = 0.944, RMSEA = 0.051, and SRMR = 0.069.
In line with the US environmental sample, support was found in the Chinese environmental sample for hypotheses 1 through 4, as shown in Table 6. Consistent with hypotheses 1 and 2, self-esteem was positively related to brand image (BI<--SEs; β = 0.254, p < 0.01) and to self-enhancement (SEn<--SEs; β = 0.324, p < 0.001). Hypotheses 3 and 4 suggest that status-seeking is positively related to both brand image and self-enhancement and consistency in support for these hypotheses was shown, with a positive estimate for brand image (BI<--SS; β = 0.311, p < 0.001) and for self-enhancement (SEn<--SS; β = 0.463, p < 0.001). Further, support was found for both hypotheses 5 and 6, with brand image (PI<--BI; β = 0.387, p < 0.01) and self-enhancement (PI<--SEn; β = 0.503, p < 0.001) being positively related to purchase intention. We again obtained the indirect effects for each mediation path while using the delta method for the Satorra-Bentler standard errors. The indirect effect of status-seeking to purchase intention was 0.350 (p < 0.001), while the indirect effect from self-esteem to purchase intention was 0.356 (p < 0.01). These results confirm the US-based findings on the environmental sample while providing an exploratory look at a unique context.

Table 6.
Results for China environmental sample.
Results show that for the Chinese social sample the impact was again through self-enhancement as shown in Table 7. Consistent with hypotheses 1 and 2, self-esteem was positively related to brand image (BI<--SEs; β = 0.589, p < 0.001) and to self-enhancement (SEn<--SEs; β = 0.677, p < 0.001). Hypotheses 3 and 4 suggest that status-seeking is positively related to both brand image and self-enhancement. No support was found for hypothesis 3 and the link between status-seeking and brand image (BI<--SS; β = 0.093). Support was found for hypothesis 4, showing a positive relationship between status-seeking and self-enhancement (SEn<--SS; β = 0.211, p < 0.01). In contrast to the environmental Chinese sample, support was not found for hypothesis 5, with a lack of significance for the link between brand image and purchase intention (PI<--BI; β = −0.003), while support was found for hypothesis 6, with the positive link between self-enhancement and purchase intention (PI<--BI; β = 0.766, p < 0.01). We again obtained the indirect effect for each mediation path while using the delta method for the Satorra-Bentler standard errors. The indirect effect of status-seeking to purchase intention was 0.147 (p < 0.01), while the indirect effect from self-esteem to purchase intention was 0.882 (p < 0.001).

Table 7.
Results for China social sample.
Our findings support our six hypotheses and provide a basis for potential follow-up studies. First, self-esteem was positively associated with brand image and self-enhancement (H1 and H2), both of which were positively associated with purchase intention (H5 and H6). These findings reflect the dominant message advertised for environmentally friendly products, that is, consumers’ environmental behaviors represent their self-esteem [46]. These findings are also consistent with the recent experimental findings that consumers increase their favorability about ethically promoted products with their desire to live up to internal self-standards [48].
Second, status-seeking was positively associated with brand image and self-enhancement (H3 and H4), both of which were also positively associated with purchase intention. This suggests that status-seekers are more likely to buy a CSR product because it gives them the status they seek which, in turn, provides a higher evaluation of the brand and enhances their own self-view. A similar effect was reported in another study based in a design context. Han et al. [59] suggest that consumers are highly likely to purchase aesthetically pleasing products in public conditions because consumers can show off their taste of aesthetic appeal. Overall, we were able to demonstrate a process through our mediated model, which shows how factors related to the consumers’ characteristics drive purchasing intent.
It is also of interest to note that using SEM, we were able to differentiate between the indirect paths to better understand the effects that the psychological characteristics have on purchase intention. Based on our main US sample in the environmental domain we can see that for self-esteem the mediation through self-enhancement (0.207 × 0.296 = 0.061) was slightly larger than through brand image (0.174 × 0.347 = 0.060). This is consistent with the Chinese sample in the environmental domain; the mediation through self-enhancement (0.324 × 0.503 = 0.163) was larger than through brand image (0.254 × 0.387 = 0.098). This suggests that the possible enhancement of how they see themselves is the stronger reason than brand image for the individuals with higher self-esteem being likely to buy CSR products. For status-seeking individuals, we also found an identical pattern; the effect is larger through self-enhancement as opposed to through brand image (0.116 vs. 0.089, respectively, for the US sample; 0.233 vs. 0.120, respectively, for the Chinese sample). Again, this suggests that for the individuals who care about the status they will gain through the purchase of the product, the self-enhancement that they expect to gain from that purchase is the dominant driver of their purchase intention. For the total effects we see that status-seeking had a slightly stronger effect than self-esteem in the US environmental sample compared to the Chinese environmental sample (0.204 vs. 0.136, respectively, for the US sample; 0.350 vs. 0.356, respectively, for the Chinese sample). To our knowledge, this represents the first time these factors have been investigated simultaneously to demonstrate the way consumers consume CSR products and some of the mechanisms involved.
Also of interest, we found that the domain may indeed play a role in the path from individual characteristics to purchase intention. While our findings are similar, we did find key differences in the results. For the social domain it is apparent that the effect is through the individual’s self-enhancement. This is consistent with our findings discussed previously for the environment domain but seems to be stronger with the donation prompt. We also found that in the donation case the indirect effect of self-esteem on purchase intention is stronger than the status-seeking effect. In the social domain, we found that brand image does not mediate the relationship between our psychological characteristics and purchase intention. This may be because consumers have a different belief about the utilization of the purchase in relation to the actual donation. Unlike the environmental domain, where the company’s CSR activities are observed ex post (e.g., made of 100% recycled material), consumers may not believe the company’s message related to their donation campaign because it is not disclosed to them after the purchase, e.g., whether the donations were made as promised. In 2014, Consumer Reports announced that consumers do not trust charity donations with a purchase campaign because there is a lack of disclosure following the purchase (Consumer Reports December 2014. “A donation-with-purchase might not be the best way to support a charity: http://www.consumerreports.org/cro/magazine/2014/12/a-donation-with-purchase-might-not-be-the-best-way-to-support-a-charity/index.htm). Dean (2004) also argues that a firm’s CSR activities could increase the firm’s image, but only when their campaign is conducted as unconditional regarding the revenue of the firm. Thus, it is possible that in our study the mediation did not appear for brand image because the stated conditional donation is not something that promotes the image of the brand. This suggests that future research should carefully consider the domain of CSR being used.
5. General Discussion
This paper investigated how two intrinsic consumer characteristics, self-esteem (inner-self) and status seeking (outer-self), influence consumers’ purchasing behaviors of CSR products via two mediating effects, brand image and self-enhancement, in two different CSR domains: social and environmental. Along with our proposed model, we verified the underlying mechanism of how a consumer’s fundamental traits influence CSR product purchase intention. Our findings deepen the academic understanding of CSR consumption and provide the potential for interesting future research. First, we identified two individual characteristics and worked to explain the path from these characteristics to purchase intention. We showed that both inner-self and outer-self factors play a role in the CSR consumptions process in that both status-seeking and self-esteem are positively related to purchase intention, although it is an indirect process. By extending on these findings future research can further investigate how these individual characteristics are related to other key CSR outcomes. Second, we discovered two underlying mechanisms, brand image and self-enhancement, which mediated the relationship between status-seeking and purchase intention as well as self-esteem and purchase intention in the environmental sample, while only self-enhancement mediated the relationships in the social sample. Note that the former is a firm side variable and the latter is a consumer side variable. Our research provides a conceptual foundation that future research can use to investigate the relative importance of these two variables in different types of CSR products and activities, as suggested by our secondary analysis with a second domain.
Our findings also provide critical implications for managers looking to maximize the commercial impact of CSR products and activities. First, it enables them to identify who are the optimal target consumers, those individuals who have higher self-esteem and who are seeking status. Second, marketers can learn why some consumers buy CSR products. In both of our analyses it is apparent that our respondents were interested in the products for the possibility of enhancing the view of themselves. These findings provide insight as to both which individuals to target and what to emphasize in this process.
The present work had a few limitations. First, we did not directly manipulate the subjects. In the future, self-esteem and status-seeking could be primed or directly activated to better understand the mechanisms involved in how CSR may be improving the individual’s self-esteem or providing them with the status that they seek. Furthermore, we studied one product. With the potential integration from the literature related to luxury goods, future work could seek to better understand how the individual mechanisms change when the type of product is manipulated. The potential interplay between our consumption findings and the luxury goods research considers the role of pleasure and guilt through conspicuous consumption and style consumption suggest potential interesting effects. Additionally, while we explored the model with two domains and two countries, we focused specifically on the hypothesized model and not the direct comparisons. Future work could investigate the specific role of domain and country-level differences by using invariance testing in order to better understand the distinctions that may exist between consumers in these countries as well as CSR campaigns in different domains.
Author Contributions
All authors have equally contributed to the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hartley, F.R. Marketing Mistakes and Successes, 11th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Top Ten Sustainability Initiatives of Starbucks Corporation, CleanTechies. 2012. Available online: https://cleantechies.com/top-ten-sustainability-initiatives-of-starbucks-corporation/ (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Clancy, H. Why Starbucks Issued Its First ‘Sustainability’ Bond, GreenBiz. 2016. Available online: https://www.greenbiz.com/article/why-starbucks-issued-its-first-sustainability-bond#:~:text=In%20disclosing%20the%20offering%2C%20Starbucks,including%20our%20strategy%20and%20finances.%22 (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Hildebrand, D.; Sen, S.; Bhattacharya, C.B. Corporate social responsibility: A corporate marketing perspective. Eur. J. Mark. 2011, 45, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; Dacin, P.A. The company and the product: Corporate associations and consumer product responses. J. Mark. 1997, 61, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudel, R.; Cotte, J. Does it pay to be good? MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2009, 50, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Foscht, T.; Lin, Y.T.; Eisingerich, A.B. Blinds up or down? The influence of transparency, future orientation, and CSR on sustainable and responsible behavior. Eur. J. Mark. 2018, 52, 476–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, C.B.; Sen, S. Doing better at doing good: When, why, and how consumers respond to corporate social initiatives. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2004, 47, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchs, M.G.; Naylor, R.W.; Irwin, J.R.; Raghunathan, R. The sustainability liability: Potential negative effects of ethicality on product preference. J. Mark. 2010, 74, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servaes, H.; Tamayo, A. The impact of corporate social responsibility on firm value: The role of customer awareness. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, B.A.; Bell, S.J.; Mengüç, B. Corporate reputation, stakeholders and the social performance-financial performance relationship. Eur. J. Mark. 2005, 39, 1184–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, I.A.; Gutsche, S. Consumer motivations for mainstream “ethical” consumption. Eur. J. Mark. 2016, 50, 1326–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M. Society and the Adolescent Self-Image; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- MacRae, J.B. Striving, straining, and status. Phylon Q. 1959, 20, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. The social responsibility of business is to increase its profits. The New York Times Magazine, 13 September 1970; 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.; Blomstrom, R.L. Business and Society: Environment and Responsibility; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.J. Effects of external activities of corporate social responsibility on benefits of employees and shareholders: Mainly from stakeholders’ perspective. Korean Acad. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2009, 16, 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.E.; Wicks, A.C.; Parmar, B. Stakeholder theory and “the corporate objective revisited”. Organ. Sci. 2004, 15, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder-Webb, L.; Cohen, J.R.; Nath, L.; Wood, D. The supply of corporate social responsibility disclosures among U.S. firms. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 84, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Bhattacharya, C.B. Does doing good always lead to doing better? Consumer reactions to corporate social responsibility. J. Mark. Res. 2001, 38, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Perspective; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, M.B.E. The Corporation and Its Stakeholders: Classic and Contemporary Readings; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, T.; Preston, L. The stakeholder theory of the corporation: Concepts, evidence, and implications. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1995, 20, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.; Wicks, A. Convergent stakeholder theory. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1999, 24, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turban, D.B.; Greening, D.W. Corporate social performance and organizational attractiveness to prospective employees. Acad. Manag. J. 1997, 40, 658–672. [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz, M. Choosing socially responsible stocks. Bus. Soc. Rev. 1972, 1, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Parket, I.; Eibert, H. Social responsibility; The underlying factors. Bus. Horiz. 1975, 18, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloman, R.; Hansen, K. It’s Good Business; Atheneum: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Fombrun, C.; Shanley, M. What’s in a name? Reputation building and corporate strategy. Acad. Manag. J. 1990, 33, 233–258. [Google Scholar]
- Aupperle, K.; Carroll, A.; Hatfield, J. An empirical examination of the relationship between corporate social responsibility and profitability. Acad. Manag. J. 1985, 28, 446–463. [Google Scholar]
- McGuire, J.; Sundgren, A.; Schneeweis, T. Corporate social responsibility and firm financial performance. Acad. Manag. J. 1988, 31, 854–872. [Google Scholar]
- Auger, P.; Burke, P.; Devinney, T.M.; Louviere, J.J. What will consumers pay for social product features? J. Bus. Ethics 2003, 42, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Olsen, K.L.; Cudmore, B.A.; Hill, R.P. The impact of perceived corporate social responsibility on consumer behavior. J. Bus. Res. 2006, 59, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Bhattacharya, C.B. Corporate social responsibility, customer satisfaction, and market value. J. Mark. 2006, 70, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chang, C.C.A. Double standard: The role of environmental consciousness in green product usage. J. Mark. 2012, 76, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, P.R.; Menon, A. Cause-related marketing: A coalignment of marketing strategy and corporate philanthropy. J. Mark. 1988, 52, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, S. Cause Related Marketing: Who Cares Wins; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.R.; Irmak, C.; Jayachandran, S. Choice of cause in cause-related marketing. J. Mark. 2012, 76, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschate-Fischer, N.I.V.S.; Hoyer, W.D. Willingness to pay for cause-related marketing: The impact of donation amount and moderating effects. J. Mark. Res. 2012, 49, 910–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Johnson, K.K.P. The impact of moral emotions on cause-related marketing campaigns: A cross-cultural examination. J. Bus. Ethics 2013, 112, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Goldsmith, R.E. Market mavens: Psychological influences. Psychol. Mark. 2005, 22, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blascovich, J.; Tomaka, J. Measures of self-esteem. In Measures of Personality and Social Psychological Attitudes; Robinson, J.P., Shaver, P.R., Wrightsman, L.S., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991; pp. 115–160. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.D.; Collins, R.L.; Schmidt, G.W. Self-esteem and direct versus indirect forms of self-enhancement. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1988, 55, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, L.E.; Maner, J.K. Does self-threat promote social connection? The role of self-esteem and contingencies of self-worth. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2009, 96, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malär, L.; Krohmer, H.; Hoyer, W.D.; Nyffenegger, B. Emotional brand attachment and brand personality: The relative importance of the actual and the ideal self. J. Mark. 2011, 75, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Gulas, C.S.; Iyer, E. Shades of green: A multidimensional analysis of environmental advertising. J. Advert. 1995, 24, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotte, J.; Trudel, R. Socially Conscious Consumerism: A Systematic Review of the Body of Knowledge; Network for Business Sustainability: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Peloza, J.; White, K.; Shang, J. Good and guilt free: The role of self-accountability in influencing preferences for products with ethical attributes. J. Mark. 2012, 77, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, J.M.T. Identity based views of the corporation: Insights from corporate identity, organisational identity, social identity, visual identity, corporate brand identity and corporate image. Eur. J. Mark. 2008, 42, 879–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currás-Peréz, R.; Bigné-Alcañiz, E.; Alvarado-Herrera, A. The role of self-definitional principals in consumer identification with a socially responsible company. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 89, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedikides, C.; Strube, M.J. The multiply motivated self. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 1995, 21, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicke, M.D.; Vredenburg, D.S.; Hiatt, M.; Govorun, O. The “better than myself effect”. Motiv. Emot. 2001, 25, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, N.D. Unrealistic optimism about future events. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 806–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.W.; Sen, S.; de Oliveira Mota, M.; de Lim, R.C. Consumer reactions to CSR: A Brazilian perspective. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 91, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunda, Z. The case for motivated reasoning. Psychol. Bull. 1990, 108, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, M.; Omoto, A.M. Who gets involved and why? The psychology of Volunteerism. In Youth Empowerment and Volunteerism: Principles, Policies and Practices; City of University Hong Kong Press: Kowloon, Hong Kong, 2008; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith, R.; Flynn, L.; Eastman, J. Status consumption and fashion behavior: An exploratory study. Assoc. Mark. Theory Pract. Proc. 1996, 15, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.A.; Zboja, J.J.; Goldsmith, R.E. Status consumption and role-relaxed consumption: A tale of two retail consumers. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2007, 14, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Nunes, J.C.; Drèze, X. Signaling status with luxury goods: The role of brand prominence. J. Mark. 2010, 74, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, R.E.; Flynn, L.R.; Kim, D. Status consumption and price sensitivity. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 2010, 18, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, N.J. Status-seeking by voluntary contributions of money or work. Ann. d’Économie Stat. 2001, 63/64, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.K.; Goldsmith, R.E.; Flynn, L.R. Status consumption in consumer behavior: Scale development and validation. J. Mark. Theory Pract. 1999, 7, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wein, A.H.; Olsen, S.O. Understanding the relationship between individualism and word of mouth: A self-enhancement explanation. Psychol. Mark. 2014, 31, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griskevicius, V.; Tybur, J.M.; Van den Bergh, B. Going green to be seen: Status, reputation and conspicuous conservation. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2010, 98, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhart, Y.; Ayalon, O.; Puterman, H. The effect of an environmental claim on consumers’ perceptions about luxury and utilitarian products. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 53, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belch, G.E.; Belch, M.A. The application of an expectancy value operationalization of function theory to examine attitudes of boycotters and nonboycotters of a consumer product. Adv. Consum. Res. 1987, 14, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, K.L.; Aaker, D.A. The effects of sequential introduction of brand extensions. J. Mark. Res. 1992, 29, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.L. Strategic Brand Management: Building, Measuring, and Managing Brand Equity, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, C.B.; Sen, S. Consumer–company identification: A framework for understanding consumers’ relationships with companies. J. Mark. 2003, 67, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.W.; Zhu, W.C.; Gouran, D.; Kolo, O. Moral identity centrality and cause-related marketing: The moderating effects of brand social responsibility image and emotional brand attachment. Eur. J. Mark. 2016, 50, 236–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, A.; Donthu, N.; Wei, Y.J. Website customer orientations, website quality and purchase intentions: The role of web personality. J. Bus. Res. 2009, 62, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Donthu, N.; Lee, S. An examination of selected marketing mix elements and brand equity. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2000, 28, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, D.; Griffen, D. Conspicuous donation behavior: Scale development and validation. J. Consum. Behav. 2009, 8, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; John, D.R. More than meets the eye: The influence of implicit and explicit self-esteem on materialism. J. Consum. Psychol. 2011, 21, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.K.; Liu, J. The impact of generational cohorts on status consumption: An exploratory look at generational cohort and demographics on status consumption. J. Consum. Mark. 2012, 29, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charities Aid Foundation. World Giving Index. 2013. Available online: https://www.cafonline.org/docs/default-source/about-us-publications/worldgivingindex2013_1374aweb.pdf?sfvrsn=e215f440_4 (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Ramasamy, B.; Yeung, M. Chinese consumers’ perception of corporate social responsibility (CSR). J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 88, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.L.; Wong, R.; Yang, W. Consumer responses to corporate social responsibility (CSR) in China. J. Bus. Ethics 2011, 101, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).