Abstract
The objective of this study is to investigate the conditions of family agriculture and the respective environmental impacts of agribusiness. The research methodology is grounded on a theoretical survey of study descriptions of the area, a characterization of rural communities and local population through interviews, an identification of medium and large agricultural enterprises through documentary research on environmental licensing processes, and determination of the environmental impacts of agribusiness via an interaction matrix. Based on the data generated, it was found that the majority of the population has an incomplete elementary education; is involved in agricultural activity, livestock farming, and honey production, which provide a family income of up to one minimum wage; and is located in rural communities with environmental sanitation restrictions. Moreover, it was found that irrigated agriculture has positive impacts, such as the generation of employment and income. It was also evidenced that this activity causes adverse socioeconomic impacts and adverse impacts on the traditional activities of local rural communities through plant removal, water scarcity, and pesticide use. Thus, to mitigate the problems, it is necessary to apply the principles of Brazilian Environmental Law as correlated with the instruments of the National Environment Policy through environmental management guidelines.
1. Introduction
The history of agriculture in the world begins after hundreds of millions of years of biological, technical, and cultural evolution. It was in the Neolithic (−10,000 thousand years ago) that the human being began to cultivate and create, and in this period, there emerged two main forms of agriculture that spread throughout the world, the system of breeding grazing animals and cultivation through burning and felling. With this, the main function of ancient agriculture was to produce food to supply and ensure the survival of the local population, i.e., subsistence agriculture. That said, population growth was one of the biggest reasons to increase food production through technologies and through the development of food production throughout the year and on a large scale; this development is characterized as an Agricultural Revolution. Thus, for the first time in history, with the first agricultural revolution, there appears an agriculture capable of permanently producing a marketable agricultural surplus representing more than half of the total production [1].
Specifically, the economic development model adopted in Brazil frequently consolidates Brazil’s insertion in the international market through the production of rural and mineral commodities through activities such as the expansion of cattle farming in the Amazon region, growing sugarcane and fruit for exportation in the Northeast, advancing steel parks in the Southeast, and growing transgenic soybean and corn monocultures in the Midwest and South of the country [2].
In the specific case of agriculture, it was possible to observe the restructuring of its production chain, which is based on the capitalist model of production, with the emergence of agribusiness based on agricultural modernization [3]. Thus, agribusiness involves aspects of agriculture, industry, market, and finance, which enables the formation of an economic development model controlled by transnational corporations that work with commodities and operate in several other sectors of the economy [4].
The emergence of the Green Revolution, which makes use of chemical (fertilizers and pesticides), mechanical (mechanical tractors), and biological (improved varieties) inputs, provided for the expansion of the agribusiness model, which quickly promoted an intense standardization of agricultural practices and artificialization of the environment [5].
The expansion of agribusiness resulted in implications for work, environment, and health, enabling the following deleterious effects: land concentration and compulsory displacement of the population; violence; the compromise of food security; changes in social practices and bonds of community life; imposition of new cultural habits; changes in the dynamics of neighboring cities; intensive use of new mechanization technologies and inputs; precarious working conditions with low pay; non-compliance with labor law; intensification of work; exposure to health risk situations; reduction of biodiversity and environmental services; soil degradation; high water consumption; contamination of air and surface groundwater; exposure of communities to pesticides [6].
Thus, the environmental problem of agribusiness is being investigated by researchers with multiple approaches; there is an emphasis on the socio-environmental conflicts generated by agribusiness [7,8,9,10,11], the environmental damage caused by irrigated agriculture [12,13,14,15], the impacts of irrigated perimeters [16,17,18,19,20,21], the territorialization processes of agribusiness [22,23,24], and systems of agricultural activity and environmental externality [25]. These studies are mostly centered on the agricultural boundary of the Midwest, South, and Southeast Brazil.
In Brazil, a determining factor for the emergence of agribusiness is technological advances in the field, which allowed agribusiness to expand in all regions [26]. In northeastern Brazil, one of the manifestations of agribusiness is the use of irrigated perimeters, where working conditions are precarious and mechanization predominates [27].
Specifically in Chapada do Apodi, a territorial-geographical complex located on the left bank of the Apodi-Mossoró River and the right bank of the Jaguaribe River, therefore including the states of Rio Grande do Norte and Ceará, the state began an intervention with the Jaguaribe-Apodi irrigation project for agribusiness in the 1980s [28].
As a result, the process of deterritorialization of the Chapada do Apodi through extensive monoculture, exports, and use of the technological package of the Green Revolution saw the emergence of public health problems; land concentration; environmental, social and political problems [28]; worsened workers’ conditions [28]; and pesticide use [12].
Given this panorama, the territory of Chapada do Apodi became the object of scientific research with several approaches, including the studies of the research group “Núcleo TRAMAS—Trabalho, Meio Ambiente e Saúde”, da Universidade Federal do Ceará. Since these studies are mostly concentrated in Chapada do Apodi-Ceará, there is a need to investigate the Rio Grande do Norte, since agricultural companies are already developing their activities in this area.
Given the lack of studies on the environmental problem of agribusiness in Chapada do Apodi in Rio Grande do Norte (RN), this work aims to investigate the spatial planning of Brazilian semi-arid land from the experience of coexistence and conflicts caused in Chapada do Apodi (RN) between family agriculture and the expansion of agribusiness. Justifying the relevance of this research is the fact that it will allow us to know the origin of the uses and occupations of this environment as well as to identify possible environmental conflicts.
That is to say, the research becomes relevant because it investigates a contemporary theme, which is understood holistically, using multidisciplinary methods and the concept of sustainability. The author presents a comprehensive view that is not restricted to natural resources but comprises five dimensions: social, economic, ecological, spatial, and cultural [29]. In the social dimension, the expansion of agribusiness causes problems of rural exodus. In the economic dimension, the theme is justified because the development of this agricultural model shows how economic incomes concentrate in large corporations. In the ecological dimension, it is observed that there is the potential of soil contamination, aquifer pollution, biota modification, and changes in air quality. When it comes to cultural aspects of the theme, there are problems related to the reduction of family farming and responsibility for an ecologically balanced environment.
The present work has as a general objective to investigate the conditions of family agriculture and the respective environmental impacts of agribusiness. For this general objective, we also have the following specific objectives: (a) to mention the history of family farming in the study area; (b) identify rural communities and environmental perceptions of the local population; (c) determine the environmental sanitation conditions of the rural communities analyzed; and (d) to characterize the establishment of the irrigated perimeter in the region and to study the environmental impacts of agribusiness in the territory studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
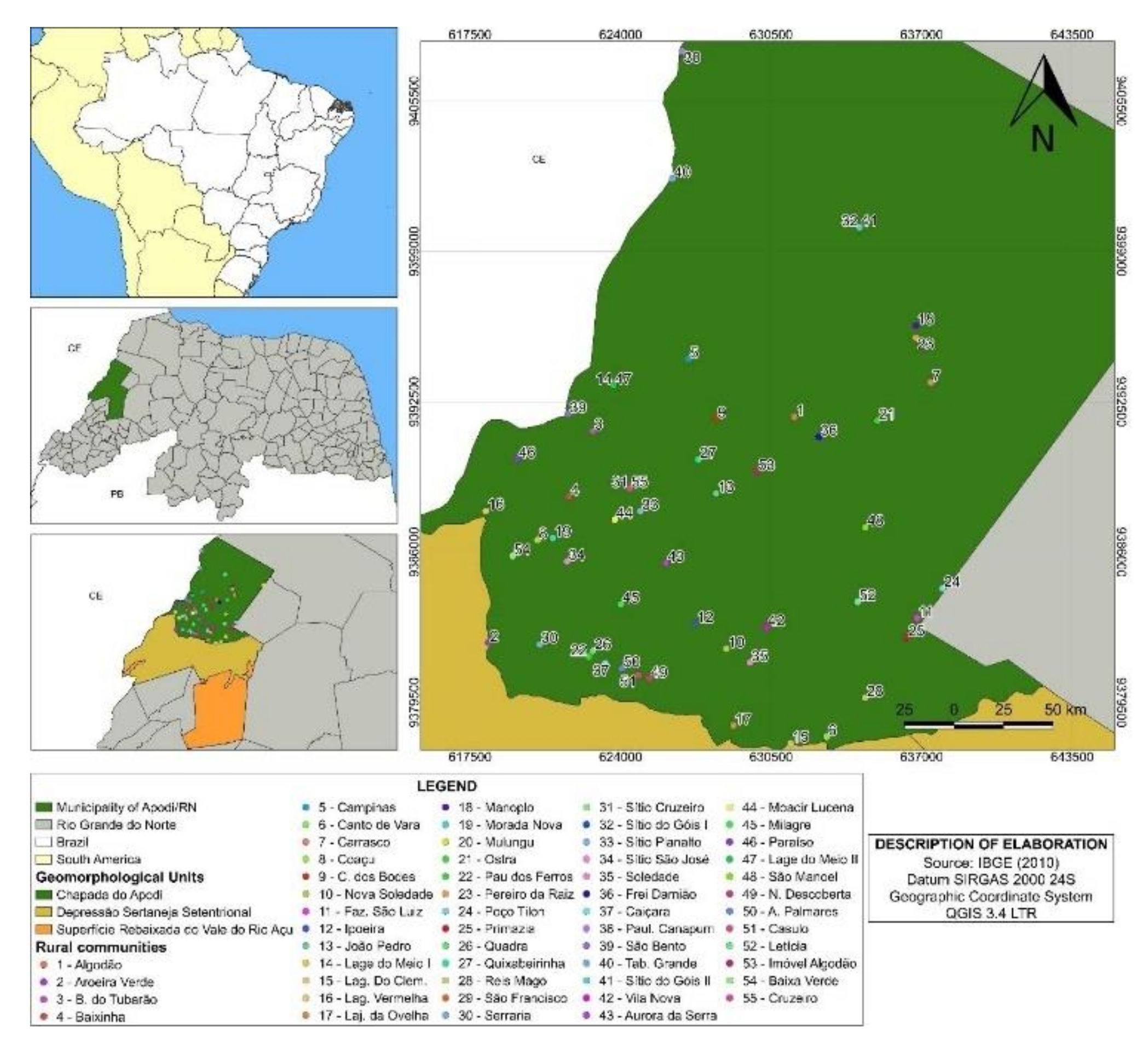
The study was carried out in Chapada do Apodi, located in Rio Grande do Norte, more specifically in the municipality of Apodi, which is located in the microregion of the Apodi plateau. The geomorphological unit called Chapada do Apodi concentrates 55 rural communities (Figure 1). It is approximately 340 km from Natal and 80 km from Mossoró, with a territorial area of 1,602,477 km2 and a population of 34,763 inhabitants, of which 17,531 live in urban areas and 17,232 in rural areas [30].
Figure 1.
Location map of Apodi municipality, Rio Grande do Norte (RN), Brasil, and rural communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN.
2.2. Methodological Procedures
To determine the dynamics of the Chapada do Apodi-RN, we adopted a methodological path composed of the following procedures: Section 2.2.1. A theoretical survey of the historical description process of family farming in Chapada do Apodi/RN; Section 2.2.2. An identification of the socio-economic profile of the population of rural communities in Chapada do Apodi/RN; Section 2.2.3. The definition of environmental sanitation of rural communities in Chapada do Apodi/RN; Section 2.2.4. A characterization of agribusiness in Chapada do Apodi/RN and Section 2.2.5. Determination of the environmental impacts of agribusiness in the region.
2.2.1. Description of the Historical Process of Family Farming in Chapada do Apodi/RN
The theoretical survey of the description of the study area took place with research in official agencies on location, delimitation, physical and biotic conditions, socio-demographic aspects, history, economic activities, and current population data.
From the characterization of the study area, with the contextualization of economic activities, an investigation of documents (scientific articles and books) of the historical process of family farming was carried out in Chapada do Apodi/RN, this was made through bibliographical research, considering an examination of the bibliography for the survey, and analysis of what has been produced on the subject to be investigated [31].
2.2.2. Identification of Rural Communities in Chapada do Apodi/RN
With the examination of the historical process of occupation in Chapada do Apodi/RN, for obtaining data from primary fields, we conducted technical visits during the periods of October, November, and December 2017 to identify rural communities in the study area. In total there were 12 visits during all weekends that we carry out through 4 visits each month.
Subsequently to that, visits were conducted in the rural communities of Chapada do Apodi-RN so as to draw the socioeconomic profile of the local population, through the application of semi-structured interviews with questions about age group, gender, education, income, occupation, products generated, places of marketing, origin, and how long they were living there.
The sampling procedure occurred by a random method, of the total of 1649 households, using [32] as the data source, with the confidence of 95%, and margin of error of 5%, was calculated according to [33] Equation (1). In this way, we establish a probabilistic sampling carried out at random and distributed proportionally among the rural communities investigated.
Caption: N = Population size; Z-/2 = is the critical value of the normal probability distribution (the Central Limit Theorem is the basis of the Sampling Theory, being in practice the determination of the confidence interval. For 90% confidence, Z = 1.645; for 95%, Z is equal to 1.96); E = Margin of error (for more and for less—in percentage).
The defined sampling was 322 questionnaires, proportionally distributed among the rural communities investigated (Table 1), in which it contains a different quantity for those located around the perimeter or appropriate location (INCRA Sitting Project or Fundy Credit Design).

Table 1.
Distribution of the population by rural communities of Chapada do Apodi, RN.
Based on that, the research was carried out with the local population of the rural communities of Chapada do Apodi-RN between January, February, and March 2018. In the first moment, a pre-test was performed with 10% of the sampling (32 interviews) to adjust the variables, optimize the time, and plan the execution of the survey application. In the second moment, the survey took place, with the application of interviews about the research actors, and the Term of Free Consent and Clarification—TCLE was presented at this time. The choice of the survey method is because it allows descriptive, explanatory and exploratory statements about a population, that is, to discover the distribution of certain characteristics and attributes with a sample of the group [34].
Finally, after the field research, the Excel software was used to obtain graphs for better visualization and interpretation of the data.
2.2.3. Determination of Environmental Sanitation of Rural Communities in Chapada do Apodi/RN
To investigate the environmental problem of the study area, the environmental perception was used, since it is understood as a sustainability tool that better understands the interrelations between man and the environment [35], thus allowing to analyze the environmental conditions of rural communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN, as well as their vulnerabilities in the activities of agribusiness.
To meet this method, we adopted: (a) definition of the interview instrument with questions about the components of environmental sanitation; (b) sampling process, taking into account Equation (1) (322 interviewees); (c) field research, with pre-test (10%) and survey [34]; and (d) data processing, with software SPSS version 26.0.
Regarding the multivariate linear regression model, we tried to identify the associated variables through the coefficient of determination (R2), at a significant level (p < 0.05), also processed through the SOFTWARE SPSS version 26.0.
2.2.4. Characterization of Agribusiness in Chapada do Apodi/RN
The characterization of agribusiness in the area investigated occurred in 2018, with data collection from the information system of the Instituto de Desenvolvimento Econômico e Meio Ambiente—IDEMA (IDEMA is an institute of the state of Rio Grande do Norte, which works with the environmental policy of the sustainable environment, taking advantage of the regional potentials in search of improving the quality of life of the population of the state.) of the State of Rio Grande do Norte, following the steps: consultation of licenses, type of process, division of Activity, Activity group, and period of completion of the process.
Next, 13 projects were identified in the study area related to the purpose of the research, which was analyzed from the establishment of the following categories: the interested party, process identification, generating factor, size of the work, size of the work, the polluter pays, type of license and date of concession.
Therefore, the data were categorized and analyzed through the discussion with research on the environmental impacts of agribusiness in Chapada do Apodi/RN, in Brazil and worldwide.
2.2.5. Determination of the Environmental Impacts of Agribusiness in Chapada do Apodi-RN
The determination of the environmental impacts of agribusiness in the Chapada do Apodi-RN was evidenced from the technical visits in April and May 2018 to identify in the study area through the Check-List method because it is a fast and concise [36]. The variables addressed in this research instrument were based on [37]: location of the study area; location of users of natural resources; types of uses of natural resources; potential or effectively polluting sources of the study area; effects of environmental pollution and environmental pollution control techniques. The primary and secondary data obtained were exposed through an interaction matrix [36], containing the physical, biotic and anthropic means versus the stages of the production process.
3. Results
3.1. Family Farming in Chapada do Apodi/RN
The municipality of Apodi/RN has a population of 35,814 inhabitants, most of them in the rural area (almost 52%) [38]. Thus, this municipality presents a remarkable characteristic in the rural environment, and taking into account the geological formations of the rural area, the city is divided, namely: Açu Formation (Apodi Sand Region); Crystalline Foundation (Apodi Stone Region); Alluvial Deposits (Apodi Valley); and Jandaíra (Chapada do Apodi).
The Region of Chapada do Apodi/RN has its territorial planning process, over the years, correlated with agricultural activities. Considering that a few decades ago it was occupied by large landowners in the late 1970s and early 1980s, a process of popular organization of the rural workers of the municipality of Apodi could emerge, due to actions carried out by the churches through the Basic Ecclesial Communities—CEBs, and with the creation of Community Associations in rural communities [39].
This work of articulation of the farmers of Apodi culminated, in the 1990s, in the creation of the Sindicato dos Trabalhadores e Trabalhadoras Rurais de Apodi—STTR (STTR is a union that covers rural workers in the city of Apodi), today, an important articulator of family agriculture in the region. Thus, from 1990 on, the municipality of Apodi began to present significant changes in the rural context, caused by the cotton crisis, which weakened the large landowners, and by the struggle of rural workers in search of the long-dreamed agrarian reform [39].
From this scenario farmers/es obtained their land, through expropriations carried out by Instituto Nacional de Colonização e Reforma Agrária—INCRA (INCRA is an organ of the federal government responsible for executing land reform and carrying out national land planning) and rural communities from land credit, making that region where the land prevailed today is characterized by various settlements and traditional rural communities, which work with family farming based agroecologically [39].
Thus, in this area, successful experiences of food production in an agroecological and family way in the Northeast have been consolidated in recent years, covering 55 rural communities [40], with 1649 families.
3.2. Socio-Economic Profile of the Population of the Communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN
Based on the scenario of family farming existence in the study area, we sought to survey the socio-economic profile of the actors in this agricultural model. Among the population questioned, a numerous percentage had the municipality of Apodi/RN as birthplace (69.88%), and these are divided into 50.31% male and 49.69% female (Table 2).

Table 2.
Socio-economic profile of the population of the communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN.
Aiming at a new form of coexistence with the semi-arid, the economic activities that deserve to be highlighted and that are focused on the food security of peasant families, especially the availability of underground water resources present in the locality, the mention stand out food production with 52.80% through the agriculture sector (66.46%), which are, in their largest totality, used for their subsistence (58.39%).
It is also noticed that already a considerably low situation of family income, in which more than half of the population (61.49%) it survives on up to a minimum wage and although there is a great economic dynamism caused by agribusiness and the growing activity of agro-industries, the distribution of wealth occurs in a concentrated way and, therefore, traditional communities are subject to the removal of this economic rise. In addition, there is also a low level of education among the residents of the region, where the majority (50.62%) have incomplete elementary school and only 14.60% with completed high school, which reflects the large number of lack of employability (43.17%). Thus, the lack of skilled labor influences the acquisition of industrial jobs that are predominant in the region.
Therefore, the lack of opportunity of the local population in the productive chair of large industries due to the lack of specialized labor, as well as the significant presence of low-income families in the region, deduces as one of the factors for a predominance of socioeconomic vulnerability among residents that may make it impossible to improve their prospects for quality of life.
3.3. Environmental Sanitation Communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN
To understand the problems experienced by the communities surveyed, it became crucial to identify the sanitary conditions. With this, it was found a scarcity in the water supply system, since the largest total population interviewed (64.29%) does not perform any treatment for water use, and the remaining percentage make use of unconventional technologies. Also, it was verified that rural communities do not adopt any type of solution for the treatment of effluents, with the predominance of the use of rudimentary pit (48.14%), and most of them perform inadequate disposal of solid waste through burning (54.97%) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Environmental sanitation of the communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN and correlation between prevalence of diseases and sanitation variables.
Given these results, it is perceived that inadequate sanitation conditions favor the manifestation of diseases resulted from the exposure of an unhealthy environment, once, it was possible to explain, through the coefficient of determination (R2) associated with multiple regression between the variables, a significant progression of 99.06% (R2 = 0.9906) between water treatment (independent variable) and the prevalence of diseases, as well as a correlation between the independent variable and housing conditions 99.90% (R2 = 0.9990). This implies that the mismanagement of water resources used by the population associated with unhealthy and inadequate conditions in the infrastructure sanitation governs, provide a possible greater exposure of the inhabitants of this region to the occurrence of diseases.
It is also noticed that the correlations between the form of supply, form of treatment and priority use of water presented significant results through multiple regression. However, the other correlations between the occurrence of diseases and sanitation variables, as shown in Table 3, were not statistically significant. It is emphasized that the results presented between the correlations should be analyzed more thoroughly in a prolonged time period.
For a better understanding, environmental sanitation components in the rural communities of Chapada do Apodi-RN are presented in Figure 2, which reveals scenarios from 2018.
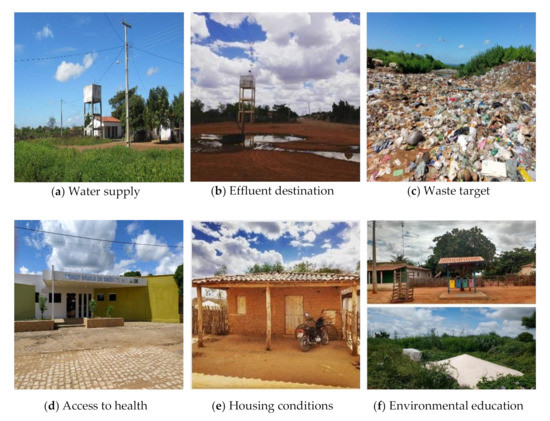

Figure 2.
Components of environmental sanitation in rural communities in Chapada do Apodi-RN.
Therefore, it is evident that despite family farming in Chapada do Apodi-RN has been established for decades, it has a context of socio-economic limitations and structural deficiencies, especially for sanitation, consequently becoming a vulnerable environmental territory. He adds that this scenario corroborates the line of thought of a risk society, which is currently experiencing a moment of reconfiguration of modern society, which takes on new contours in the face of global risks being categorized by the accumulation of risks (ecological, biochemical, financial and informational) that are ubiquitous, today, in the world, in a global way [40].
3.4. Agribusiness in Chapada do Apodi-RN
To understand holistically the spatial planning of Chapada do Apodi-RN makes it necessary to identify the occurrence of agribusiness in this area. Thus, agribusiness is defined as a complex system comprising agriculture, industry, market and finance technology, laws, and symbolic production. The movement of this complex and its policies form a model of development controlled by transnational corporations working with one or more commodities and operate in several other sectors of the economy [4].
From this perspective, in the Chapada do Apodi/RN, most projects have been classified and developed with medium size and with large polluting potential (Table 4). Given the incorporation of these activities of high polluting potential, and the need to comply with the requirements and conditions established through the implementation of public management instruments by the Environmental Licensing Law No. 6,938/1981—which has the Política Nacional do Meio Ambiente —PNMA (Brazilian Policy Law which intends to regulate activities that encompass environmental issues, aiming for preservation, improvements and recovery of environmental quality) [41]. It was found that of the projects investigated in the study area three presented Prior Licenses, two Installation Licenses, three Installation and Operating Licenses, one Forest Products Exploration License, two Operating Regularization Licenses and two Operating Licenses. Approximately 10,508 hectares were licensed (Table 4).

Table 4.
Characterization of agricultural enterprises in Chapada do Apodi/RN.
Taking the previous table into consideration, it can be affirmed that the process of capital territorialization in the agrarian space of Chapada do Apodi/RN configured as one of the determining factors for the alteration of the local production process due to insertion of technological innovations, methods of appropriation, constructions and management of the territory.
3.5. Environmental Impacts of Agribusiness in the Communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN
In this sense, in order to understand the extents and scopes of the environmental aspects of agribusiness in the Chapada do Apodi-RN, these impacts were measured from a correlation between the changes in the dimensions of the physical, biotic and anthropic environment through the production process of the territorial properties of large corporations (Table 5), where “X” represents the occurrence of environmental impacts in rural communities.

Table 5.
Environmental impacts of agribusiness in the communities of Chapada do Apodi/RN.
The economic dynamism in Chapada do Apodi favors, in addition to the diffusion of agribusiness, the emergence of positive impacts of regional projection, as well as adverse impacts in the face of different contexts of risk and socio-environmental vulnerability, as well as interference in the health conditions of the population due to the deficient basic sanitation compartments, high anthropic pressure through agriculture, deforestation, contamination of water resources and the use of pesticides of potentially polluting economic activities of agroindustries. The linear regression examination with association measures was statistically significant for the variables “main activities” and “most frequent diseases” (R2 = 0.9220), as well as “main activities” and “housing conditions” (R2 = 0.9960), thus, it can be inferred that the variability of the increase in agro-industrial activities increase in environmental unhealthiness in the housing components and in the occurrence of associated diseases.
The conflict may derive from the dispute of the same resource base or different bases but connected by ecosystem interactions mediated by the atmosphere, soil, and, waters [42]. From this perspective, it is evident that Chapada do Apodi-RN is configured as a territory that is currently in transformation due to the expansion of agribusiness, which results in conflicts with local rural communities (Figure 3).
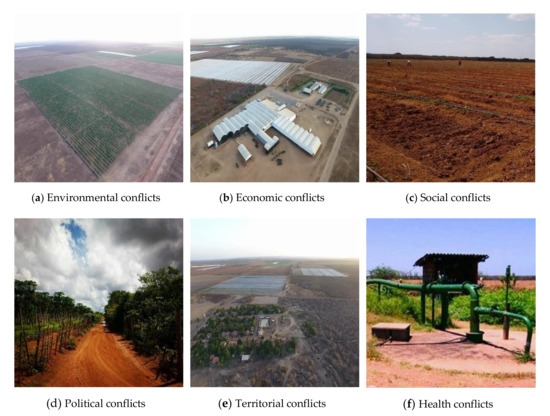

Figure 3.
Systemic conflicts between agribusiness and rural communities in Chapada do Apodi/RN: (a) Environmental conflicts with landscape substitution and ecosystem services of the caatinga by planting irrigated meon. (b) Economic conflicts with the expansion of the agribusiness complex. (c) Social conflicts with seasonal jobs in the preparation of land for planting. (d) Conflicts between political agribusiness actors with monoculture system and family farming with sustainable management of the caatinga. (e) Territorial conflicts due to the expansion of agribusiness to close to the areas of family farming. (f) Health conflicts with access to water being prioritized for agribusiness.
In view of the present discussion, Chapada do Apodi-RN can be viewed as a territory that over the years has been modified undergoing transformations from the models of agricultural production; being formerly related to landowners who had characteristics of idleness in their lands, moving to decentralized models in land use, such as family farming and, even intensive use with agribusiness projects, making the area a scenario of socioeconomic and environmental conflicts, thus requiring a broader discussion on agricultural sustainability, in which take into account the medium and long-term effects for environmental compartments and human health, as well as the research for production alternatives.
4. Discussion
The territory of Chapada do Apodi-RN presented a distinct territorial planning dynamics over the years, which resulted in antagonistic agricultural models, being initially established by large landowners, therefore, affirmed by the family agriculture with agroecological experiences and, finally, is currently evidenced by agribusiness from the irrigated perimeter.
In this line of interpretation, it is observed that the territory analyzed in its beginning of occupation has a characteristic of financial speculation, being categorized by [43] large landowners for cotton monoculture, which with the emergence of pests in that culture and its crisis, began to present significant changes in this rural context. Thus, it is perceived that access to natural resources in the area of study has always been prioritized for certain sectors and society plots.
So, it is evidenced that from social movements to access landing properties, it was established a new model of agricultural production, which is characterized in agriculture by the generation of jobs and food production, primarily, for own consumption, aiming to meet the social criteria before the economic ones, respecting life, health and the environment [44].
This process of establishing family farming in the area of study proves to be challenging, since, despite being more than 30 years old, in some rural communities, it presented restrictions on access to environmental sanitation components, making the area a scenario of environmental unhealthiness. It is understood that this area is a territory that urgently needs to achieve the 17 Sustainable Development Goals—SDGs listed by the United Nations—UN [45].
In this sense, sustainable actions aim to achieve the aforementioned UN SDGs: 01—eradicate poverty (a significant part of the population investigated have economic restrictions); 02—eradicate hunger (the population analyzed do not have access to a healthy diet); 03—quality health (expand access to basic health care); 04—quality education (allow the development of rural education for local population); 05—gender equality (seeking to insert women in the productive processes); 06—drinking water and sanitation (ensuring access to the quality and quantity of drinking water and, effectiveness of domestic effluent treatment system); 07—renewable and affordable energies (develop biome projects as a form of social insertion); 08—decent work and economic growth (allow the establishment of agroecology projects such as emancipatory action); 09—industry, innovation and infrastructure (seek access to environmental technologies aimed at agriculture); 10—reducing social inequalities (ensuring satisfactory economic incomes for the local population continue their agroecological activities); 11—sustainable cities and communities (ensuring the establishment of man in the countryside to reduce the process of rural exodus to the peripheries of urban centers); 12—sustainable production and consumption (stimulating organic production); 13—climate action (recovering the caatinga to reduce the risks of desertification); 14—protect marine life (decreased access to coastal zone); 15—protect terrestrial life (ensuring an agricultural model with respect to the resilience capabilities of ecosystems); 16—peace, justice and effective institutions (reducing the risk of environmental displaced persons and environmental injustices); and 17—partnerships for the implementation of the objectives (articulation of environmental agencies to comply with the principles, objectives and instruments of environmental policies) [45].
However, the scenario does not move in this sense of sustainability of rural communities of family agriculture, since an antagonistic model has been established and, quickly, with agribusiness, from irrigated agriculture. In this understanding, [9] it is affirmed that the development of conventional agriculture is closely related to transformations in the base of the production chain, in the mode of production, manual labor, and land structuring, which consequently cause negative impacts on the environment.
Also, in this line of understanding, the debate on the pressure of agricultural activities in the population of rural communities was carried out in a multidisciplinary manner by: [46] it was characterized the auditory and vestibular symptoms of rural workers exposed to organophosphate pesticides; [28] it was found that the mortality rate from neoplasms was 38% higher in the municipalities where agribusiness is located, and the rate of hospitalizations for abortions was 40% higher in them; [13] it was pointed out that the group has the perception that the land is being used improperly by large agricultural enterprises, and may cause, within a few years, the loss of productivity; [14] the existence of land conflict that derives in different contexts of risk and socio-environmental vulnerability was observed; and [21] the inhabitants pointed out that significant amount of the water resources in Jandaíra aquifer are exploited by agribusiness to the detriment of human supply.
Thus, it is evident that in Chapada do Apodi-RN there is an imminent risk of socioeconomic and environmental conflicts in rural communities between agribusiness and family agriculture since in the conception of [28] the transition from the agroecological model to large transnational conglomerates results in the interest in exploring soil, water, and people, being a real governmental ration for agrarian reform to birds. In addition to these factors, it is still possible to highlight the possibility of land conflict, due to the reduction of the territorial extent available for integrated practices of production and reproduction of communal life; as well as the potential for agribusiness pollution that enables the reduction of biodiversity by compromising environmental services essential to the subsistence of families [46].
Moreover agribusiness causes adverse socio-environmental impacts, with emphasis on pesticide exposure [25,28,47]; changes in the pattern of cover and land use [48]; high concentration of salts and soil impoverishment due to inadequate management in irrigated perimeters [16,20]; occupational and food exposure associated with the agricultural production process [25]; a positive mean correlation between health indicators and pesticide consumption [15,25,28]; imbalance in the quality of environmental compartments that have serious risks to human health [10,20,28]; elimination of biodiversity for the implementation of large extensions of intensive monoculture [10,15]; disaggregation of family farming in the face of this development model [49]; and the emergence of new and more complex territorial conflicts between traditional communities [10,50].
In an innovative perspective, in recent years there is also a growing debate regarding sustainability in the national agribusiness, such as the adoption of practical strategies and effective actions for the preservation of natural resources, environmental and social policies [11]. Therefore, as the productive processes impact the natural environment and consequently the health of the populations, it is evident the need for a reflection on the characteristics of the current development model [51,52], as well as to seek alternatives such as Agroecology to build a sustainable rural development strategy and ensure environmental preservation [53]. Since, according to [54], farmers’ awareness of more conservation farming practices can reduce the risk of degradation in the environment.
Therefore, the process of territorialization of capital in the agrarian space that the Chapada do Apodi/RN has been going through causes changes in the forms of appropriation, construction and use of the territory, which need to be discussed holistically from the thought of [29] that contemplates the dimensions social, economic, ecological, spatial and cultural. Besides, it enables economic development by reconciling the maintenance of environmental services and ensuring fundamental human rights.
Thus, it is perceived that the need for democratic, participatory and shared environmental management is necessary; aligned with the thinking of the principles of Brazilian Environmental Law, which address the Principle of the ecologically balanced environment as a fundamental right, Principle of Sustainable Development, Principle of Intergenerational Solidarity, Principle of the socio-environmental function of property, Prevention Principle, Precautionary Principle, Polluter Pays Principle—PPP, User-Pays Principle—PUP, Democratic Principle and Principle of Cooperation [55].
5. Conclusions
Chapada do Apodi is a territory that has been consolidating as one of the new frontiers of Brazilian agribusiness, from the installation of irrigated perimeters in the states of Ceará and Rio Grande do Norte, with emphasis on the perimeters of Jaguaribe-Apodi and Chapada do Apodi, respectively. However, since this expansion, conflicts with traditional local communities have been increased.
Specifically, the Region of Chapada do Apodi/RN has the manifest of experiences of agrarian reform, agroecological practices, and popular organization of workers. Thus, the socioeconomic characteristics of the population of this territory are pointed out by a majority of men (50.31%) in relation to women (49.69%), whereupon both genders are in groups from 30 to 59 years old, whose majority education was incomplete elementary school.
The local population develops agropastoral activities related to agriculture, livestock and beekeeping; producing mainly sorghum and corn fodder, foods such as beans, cajarana, watermelon and papaya, cattle, sheep and goat meat, milk and honey; being produced for own consumption and marketing in the local market; providing for majority family income of up to one minimum wage.
Despite this economic dynamism, this population is inserted in rural communities with health restrictions, since it has deficiencies in the components of environmental sanitation, thus becoming environmentally vulnerable.
Allied to this risk scenario, the investigated territory has been undergoing changes in its production process, which may lead to a scenario of socioeconomic and environmental conflicts. Since 2011, 13,855 ha of land was expropriated to serve as the installation of irrigated agriculture enterprises of various sizes.
With the transition in the production model from family farming to agribusiness, numerous socioeconomic and environmental impacts were enhanced and effected, being considered the most relevant for the population those of positive order: generation of employment, generation of income and valorization of land; while those negative: deforestation, pesticides and burned.
This scenario becomes more complex, mainly due to the low frequency of environmental debates in the study area, enabling the local population to present divergent backgrounds of social, economic, environmental, health, territorial and political conflicts in the region.
Thus, it can be understood that the development of agriculture in the Chapada do Apodi-RN occurs in a heterogeneous way, similar in other experiences of Brazil, where the model of large agriculture is verified with the aid of advances in science, with machinery, producing more food in a shorter amount of time, selecting species of plants and animals with better genetic characteristics and making crosses to obtain genetically modified organisms. However, family farming is without access to technological contributions, with limited production, making a good part of the population vulnerable, living in poverty, with poor living conditions and poor health.
Overall, in order to mitigate the problem between family farming and agribusiness in the Chapada do Apodi-RN, it is necessary to develop environmental management guidelines, promoting better conditions of sustainable development in a productive way, improving the quality of life and impacting the environment in a less aggressive way possible. It is also recommended to conduct studies aimed at quantifying the quality of compartments, measuring human health conditions of the local population and proposing guidelines for management of agricultural areas in order to understand the evolution of the environmental issue in this territory.
Author Contributions
J.L.d.O.P.F.: Study proposal, Primary data collection, Bibliographic survey, Secondary data collection, Preparation of manuscript, review, and approval of the final version of the manuscript. A.T.A.d.R.: Primary data collection, Bibliographic survey, Secondary data collection and, Preparation of the manuscript. A.R.d.S.L.: Organization of primary data, Bibliographic survey, Secondary data collection and, Preparation of the manuscript. L.C.: Conceptual review, Preparation of the manuscript, and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universidade Federal Rural do Semi-Árido—UFERSA, and Centro de Estudos de Geografia e Ordenamento do Território—CEGOT.
Acknowledgments
Universidade Federal Rural do Semi-Árido—UFERSA, and Centro de Estudos de Geografia e Ordenamento do Território—CEGOT.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mazoyerm, M.; Roudart, L. História das Agriculturas no Mundo do Neolítico à crise Contemporânea; Unesp: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010; 569p. [Google Scholar]
- Porto, M.F. Desenvolvimento, Conflitos Socioambientais, Justiça e Sustentabilidade: Desafios para a transição. In Ia Conferência Nacional de Saúde Ambiental, 1st ed.; Tambellini, A.T., Ed.; Abrasco: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, D. Agronegócio e desigualdades socioespaciais. In Difusão do Agronegócio e Novas Dinâmicas Socioespaciais, 1st ed.; Elias, D., Pequeno, R., Eds.; BND: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 25–82. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, B.M.; Welch, C.A. Campesinato e Agronegócio da Laranja nos EUA e Brasil. In Campesinato e Agronegócio na América Latina: A Questão Agrária Atual, 1st ed.; Fernandes, B.M., Ed.; Expressão Popular: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 45–69. [Google Scholar]
- Santilli, J. Agrobiodiversidade e Direitos dos Agricultores, 1rd ed.; Editora Petrópolis: São Paulo, Brazil, 2009; pp. 1–520. [Google Scholar]
- Rigotto, R.M.; Teixeira, A.C.A. Desenvolvimento e sustentabilidade socioambiental no campo, na cidade e na floresta. In Ia Conferência Nacional de Saúde Ambiental, 1st ed.; Tambellini, A.T., Ed.; Abrasco: Brasília, Brazil, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Porto, M.F.; Milanez, B. Eixos de desenvolvimento econômico e geração de conflitos socioambientais no Brasil: Desafios para a sustentabilidade e a justiça ambiental. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2009, 14, 1983–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigotto, R.M.; Porto, M.F.F.C.; Faria, N.M.; Augusto, L.G.; Bedor, C.; Burigo, A.; Carneiro, F.F.; Castro, F.P.; Fernandes, G.B.; Ferreira, M.J.M.; et al. Agrotóxicos, Conhecimento científico e Popular: Construindo a Ecologia de Saberes, 1st ed.; Abrasco: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2012; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Fauro, J.C.S.; Toniol, F.P.F.; Serra, E. Técnicas agrícolas, preservação e impactos ambientais na região oeste do paraná. Raega 2016, 36, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.J.M.; Viana Junior, M.M. A expansão do agronegócio no semiárido cearense e suas implicações para a saúde, o trabalho e o ambiente. Interface 2016, 20, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zanella, T.P.; Leismann, E.L. Abordagem da sustentabilidade nas cadeias de commodities do agronegócio brasileiro a partir de sites governamentais. Rev. Metrop. Sustentabilidade 2017, 7, 6–19. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, F.F.; Rigotto, R.M.; Pignati, W. Frutas, cereais e carne do Sul: Agrotóxicos e conflitos ambientais no agronegócio no brasil. Raega 2012, 17, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, V.M.; Rigotto, R.M. Agronegócio: Geração de desigualdades sociais, impactos no modo de vida e novas necessidades de saúde nos trabalhadores rurais. Rev. Bras. Saúde Ocup. 2012, 37, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotto, R.M.; Braga, L.Q.V. Indígenas Tremembé e “trabalho escravo” na monocultura do coco: Relatório de um estudo sobre o conflito e as suas repercussões na saúde. E Cad. CES 2012, 17, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotto, R.M.; Silva, A.M.C.; Ferreira, M.J.M.; Rosa, I.F.; Aguiar, A.C.P. Tendências de agravos crônicos à saúde associados a agrotóxicos em região de fruticultura no Ceará, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2013, 16, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J.F.B.; Andrade, E.M.; Chaves, L.C.G. Impacto da irrigação sobre os solos de perímetros irrigados na Bacia do Acaraú, Ceará, Brasil. Eng. Agríc. 2008, 28, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dantas, J.A.N.; Oliveira, T.S.; Mendonca, E.S.; Assis, C.P. Qualidade de solo sob diferentes usos e manejos no Perimetro Irrigado Jaguaribe/Apodi, CE. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2012, 16, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondim, R.S.; Castro, M.H.; Teixeira, A.S.; Evangelista, S.R.M. Impactos das mudanças climáticas na demanda de irrigação da bananeira na Bacia do Jaguaribe. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. Ambient. 2011, 15, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreira, R.A.; Alcântara, C.R.; Dantas Neto, J.; Barbosa, E.M. Análise Espaço-Temporal da Cobertura Vegetal e do Avanço de Prosopis juliflora (SW) DC Numa Área de Caatinga. Raega 2013, 28, 154–180. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.G.; Cândido, G.A. Sustentabilidade e participação social cooperativa de agricultores familiares no agreste da Paraíba. Rev. Metrop. Sustentabilidade 2014, 4, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.J.M.; Viana Júnior, M.M.; Pontes, A.G.V.; Rigotto, R.M.; Gadelha, D. Gestão e uso dos recursos hídricos e a expansão do agronegócio: “água para que e para quem”? Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2016, 21, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, A.A. Entre a Entre a Ordem e a Des (Ordem): A Construção doTerritório Matogrossense para/pelo Agronegócio. Baru 2016, 2, 45–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bezerra, J.E. Redes de supermercados e a governança do setor agroalimentar: A produção de frutas no Nordeste brasileiro. Raega 2017, 42, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, A.G.V.; Rigotto, R.M.; Silva, J.V. Necessidades de saúde de camponeses em conflito ambiental frente à instalação de Perímetros Irrigados. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2018, 23, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignati, W.A.; Lima, F.A.N.S.; Lara, S.S.; Correa, M.L.M.; Barbosa, J.R.; Leão, L.H.C.; Pignatti, M.G. Spatial distribution of pesticide use in Brazil: A strategy for Health Surveillance. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2017, 22, 3281–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.J. Fundamentos de Agronegócios, 1st ed.; Atlas: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dolinska, A.; D’aquino, P. Farmers as agents in innovation systems. Empowering farmers for innovation through communities of practice. Agric. Syst. 2016, 142, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigotto, R.M. Agrotóxicos, trabalho e saúde: Vulnerabilidade e Resistência no Contexto da Modernização Agrícola no Baixo Jaguaribe/CE, 1st ed.; UFC: Fortaleza, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatistica. Censo Demográfico 2010: Características Gerais da População, Religião e Pessoas com Deficiência, 1st ed.; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, I. Caminhos para o Desenvolvimento Sustentável, 3rd ed.; Garamond: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, J.A. Metodologia Científica: Guia Para Eficiência nos Estudos, 1st ed.; Atlas: São Paulo, Brazil, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Perímetro Irrigado Santa Cruz de Apodi: Projeto de irrigação Santa Cruz Do Apodi: Rio Grande do Norte—2014. Available online: https://dossieperimetrosirrigados.wordpress.com/estudos-de-caso/perimetro-irrigado-santa-cruz-de-apodi/ (accessed on 10 December 2018).
- Bolfarine, H.; Bussab, W.O. Elementos de Amostragem, 1st ed.; Editora Blücher: São Paulo, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Babbie, E. Métodos de Pesquisas de Survey, 1st ed.; UFMG: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Melazo, C.G. Percepção ambiental e educação ambiental: Uma reflexão sobre as relações interpessoais e ambientais no espaço urbano. Olhares e Trilhas 2005, 4, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, L.E. Avaliação de Impactos Ambientais: Conceitos e Métodos, 2nd ed.; Oficina de Textos: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Derísio, J.C. Introdução ao Controle de Poluição Ambiental, 4th ed.; Signus: São Paulo, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Panorama de Apodi-RN. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/rn/apodi/panorama (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Pontes, A.G.V. Saúde do Trabalhador e Saúde Ambiental: Articulando Universidade, SUS e Movimentos Sociais em território Rural. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pontes, A.G.V.; Gadelha, D.; Freitas, B.M.C.; Rigotto, R.M.; Ferreira, M.J.M. Os perímetros irrigados como estratégia geopolítica para o desenvolvimento do semiárido e suas implicações à saúde, ao trabalho e ao ambiente. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2013, 18, 3213–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil. Lei nº 6.938, de 31 de Agosto de 1981. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, Distrito Federal. 1981. Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/L6938.htm (accessed on 30 September 2020).
- Beck, U. Sociedade de Risco: Rumo a Uma Outra Modernidade, 2nd ed.; Editora 34: São Paulo, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Acselrad, H. As práticas espaciais e o campo dos conflitos ambientais. In Conflitos Ambientais no Brasil, 1st ed.; Acselrad, H., Ed.; Relume-Dumará: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2004; Volume 1, pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Guilhoto, J.J.M.; Ichihara, S.M.; Silveira, F.G.; Diniz, B.P.C.; Azzoni, C.R.; Moreira, G.R.C. A Importância da Agricultura Familiar no Brasil e em seus Estados, 1st ed.; NEAD: Brasília, Brazil, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Objetivos do Desenvolvimento Sustentável: 17 Objetivos para Transformar o Nosso Mundo. Available online: https://unric.org/pt/Objetivos-de-Desenvolvimento-Sustentavel/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Hoshino, A.C.H.; Pacheco-Ferreira, H.; Taguchi, C.K.; Tomita, S.; Miranda, M.F. Auto-perception of auditory and vestibular health in workers exposed to organophosphate. Rev. CEFAC 2009, 11, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Siqueira, D.F.; Moura, R.M.; Laurentino, C.G.E.; de Araújo, A.J.; Cruz, S.L. Análise da exposição de trabalhadores rurais a agrotóxicos. Revista Brasileira em Promoção da Saúde 2013, 26, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso, A.G.; Ferreira, M.E.; Rosa, R.; Silva, B.B. Determinação do albedo de superfície em áreas irrigadas do projeto Jaíba (Minas Gerais) mediante imagens Landsat 5 -TM. Raega 2015, 35, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduardo, M.F.; Saquet, M.A. Elementos do ritmo lento da territorialização do agroartesanato familiar em Francisco Beltrão/PR. Raega 2010, 20, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.R.; Cuellar, M.D.Z. Conflitos pela água em tempos de seca no Baixo Jaguaribe, Estado do Ceará. Estudos Avançados. 2015, 29, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.; Araújo Neto, M. Licenciamento ambiental de grandes empreendimentos: Conexão possível entre saúde e meio ambiente. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2014, 19, 3829–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, M.F.S.; Schütz, G.E. Gestão ambiental e democracia: Análise crítica, cenários e desafios. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2012, 17, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Soares, W.L.; Porto, M.F. Atividade agrícola e externalidade ambiental: Uma análise a partir do uso de agrotóxicos no cerrado brasileiro. Ciênc. Saúde Coletiva 2007, 12, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellamatrice, P.; Monteiro, R. Main Aspects of pollution in the Brazilian rivers by pesticides. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agríc. Ambient. 2014, 18, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, C.A.P. Curso de Direito Ambiental Brasileiro, 1st ed.; Saraiva: São Paulo, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).