Abstract
Basil (Ocimum basilicum) was cultivated in northern Germany in three different hydroponic components: grow pipes, a raft, and an ebb-and-flood gravel substrate. The nutrients originated from the intensive production of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) with 140 fish/m3 under decoupled aquaponic conditions. After 41 days, plants were significantly taller in the gravel components (101.8 ± 8.3 cm), followed by the grow pipes (96.7 ± 7.0 cm), and the raft (94.8 ± 8.6 cm) components (gravel > grow pipes = raft). The leaf number was high and not significantly different between the grow pipes (518.0 ± 81.4), gravel (515.1 ± 133.0), and raft components (493.7 ± 124.8; grow pipes = raft = gravel). Basil in the grow-pipe subsystems developed rapid root growth and clogged the pipes with heterogeneous plant growth. Basil production in northern Germany in grow-pipe, raft, and gravel hydro-components is possible by using effluents from intensive C. gariepinus aquaculture without additional fertilizer in the plant grow-out phase. Further research should focus on optimizing grow pipes by maintaining an optimal root–water contact area, as well as on new technologies such as aquaponics (s.l.) gardening.
1. Introduction
Aquaponic systems include single-loop or coupled aquaponics [1], two-loop decoupled systems [2,3], and specific multi-loop aquaponics [4]. Each system is suitable for a variety of applications, ranging from domestic fish and plant production, demonstration units, e.g., for aquaponics in schools and research institutions, to commercial aquaponic production [5]. The common objective of all aquaponic systems is to maximize fish and plant yields by using sustainable production methods with minimal use of fertilizer and water [6]. Aquaponics requires only a fraction of the land surface area used for conventional agriculture and can also be applied in urban regions [6]. In many cases, economic benefits are achieved by the plant production units, especially for fresh herbs such as basil [7]. Optimal cultivation conditions for the plants are crucial for the success of aquaponic systems, for both domestic and commercial use.
In aquaponics, only a few hydroponic subsystems are currently in use. The most commonly used systems are (i) floating raft (raft, also called deep water culture (DWC) or deep flow technique (DFT)), (ii) media beds with different organic/inorganic substrates and frequently built as ebb-and-flood troughs, and (iii) the nutrient film technique (NFT) [8]. Drip irrigation (iv) [9] is relatively new in aquaponics [10,11], and still causes malfunctions due to drip line blockages by larger unconsumed feed or solid particles, requiring further development [12]. All these subsystems originate from hydroponics and have been adopted and modified for aquaponics. Surveys of aquaponic producers in the United States and South Africa showed the following distribution of subsystems: (I) floating raft (77%; 14%), (II) media beds (76%; 96%), and (III) NFT (29%; 16%), with basil being the most commonly cultivated plant (81%; 50%) [13,14]. For other suitable aquaponic plants, there is no evidence for the preferred subsystem.
Comparative studies on plant growth in different hydroponic subsystems are one of the important endeavours in aquaponics [15]. However, only limited studies are available and sometimes demonstrate conflicting evidence. For example, green oak lettuce (Lactuca sativa) grew best in gravel beds, followed by raft and NFT (gravel > raft > NFT) when cultivated together with Murray cod (Maccullochella peelii peelii) [16]. In contrast, lettuce combined with goldfish (Carassius auratus) grew better in an NFT system, compared with floating raft and vertical felt systems [17]. Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum) were tested in combination with Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), and the average cumulative yield of marketable fruits was best in a drip irrigation system (18,323 ± 667 g/m²) compared to NFT (17,176 ± 364 g/m²) and raft (16,857 ± 341 g/m²). The latter was not recommended due to a lower tomato dry matter content, fruit quality, and possible anoxic conditions in the subsystem basins [18]. Basil (Ocimum basilicum) was studied in combination with channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) [19], with fresh leaf mass, total vegetative (non-root) biomass, and aquaponic yield all higher in the raft-DWC system. In contrast, basil height and absolute growth rate (media bed 1.20 ± 0.0349 cm/day vs. DWC 1.16 0.0287 cm/day) showed better results in the media-filled bed (hydroton) subsystem [19]. These results demonstrated that morphological plant parameters are influenced not only by the chosen plant or fish species, but also by the hydroponic subsystem choice. It is therefore necessary to identify the most efficient hydroponic subsystem for each cultivated plant species to optimize aquaponic plant yield.
Basil (O. basilicum) is one of the most popular culinary herbs for food production [20,21] and is also popular among farmers [22]. Basil extracts can have antimicrobial, insecticidal, nematicidal, and fungistatic effects [23,24]. For these reasons, basil is likewise interesting for the pharmaceutical, perfume, and food industries, as well as in traditional medicine [25]. To date, O. basilicum is one of the most popular plants produced in aquaponics [13,14], especially under coupled aquaponic conditions [1]. In an extensive coupled ebb-and-flood gravel substrate system, basil showed good growth performance in combination with African catfish (Clarias gariepinus), Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) [26,27,28]. Compared with classical hydroponics, basil also showed a better growth rate in combination with White River crayfish (Procambarus zonangulus) in a raft system [29]. High NH4 and PO4 removal rates were described for basil as a part of the biological filter in a coupled aquaponic system with gravel beds and the production of Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) [30]. However, comparative studies in other hydroponic subsystems are limited.
African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) is popular in Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, northern Germany, since its aquacultural production increased by 47% from 2018 (497 t [31]) to 2019 (930 t [32]). Because it exhibits high growth rates, high stocking densities, and disease resistance, it was also introduced to aquaponics [1]. A feed conversion ratio (FCR) of 1.23 for 30–40 g African catfish was reported in co-cultivation with water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) [33], and an FCR of 1.0 was described for adult C. gariepinus of 480.23 g (± 75.68) initial weight and an extensive stocking density of 6.72 kg/m3 in a coupled ebb-and-flood gravel substrate aquaponic system [26]. In small raft aquaponics, C. gariepinus of 214.42 g had an FCR of 1.02 in combination with cucumber (Cucumis sativus) [34], and 96.38 g–102.73 g African catfish reached an FCR of 1.03 to 1.14 in co-cultivation with basil (Ocimum basilicum) by using coupled aquaponics [35]. Juvenile African catfish (3.92 g) performed well with a feed conversion of 0.61, at a very low stocking density (1.6 kg/m3), in combination with basil (Ocimum basilicum), parsley (Petroselinum crispum), and marjoram (Origanum majorana) [27]. These studies demonstrated that African catfish of different ages are suitable for aquaponic production, even under very low stocking densities.
The present study examined the decoupled production of basil (O. basilicum) in combination with the commercial intensive staggered production of African catfish without additional fluid fertilizer. Fish and plant growth parameters and chemo-physical water parameters were analysed in order to identify the best hydroponic component for this fish–plant combination: grow pipes, floating raft (raft), and ebb-and-flood gravel substrate (gravel). The best possible options and conditions for decoupled O. basilicum aquaponics are discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FishGlassHouse (FGH) and Aquaponic System Design
The experiment was conducted in the FishGlassHouse from 9 June 2016 to 17 August 2016 (70 days), at the University of Rostock (UoR, Germany), Faculty of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences (AUF, GPS: latitude: 54.075714, longitude: 12.096591), which includes a 1000 m2 total production area with 300 m² of aquaculture units and a 600 m² VENLO greenhouse (100 m² corridor/water transfer unit; GTW Gewächshaustechnik Werder GmbH, Germany, automatic climate control Hempel und Rülcker, Gesellschaft für elektronische Klimaregelsysteme GmbH, Germany). The present experiment used effluent water from the intensive aquaculture unit (IAU, 100 m², trickling filter: 11.8 m3, sump: 4 m3, sedimenter: 1.7 m3, tank ≈ 1 m3, manufacturer PAL Anlagenbau GmbH, Germany) under staggered production of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) with a maximum stocking density of 200 kg/m3 fish per tank (140 fish/m3). Basil (Ocimum basilicum) production took place in grow-pipe, raft, and ebb-and-flood gravel hydroponic subsystems inside hydroponic cabin 1_05 (100 m²) of the FishGlassHouse. The nutrient-enriched water was used in one direction from the intensive aquaculture unit (IAU) to hydroponics under decoupled aquaponic conditions (Figure 1).
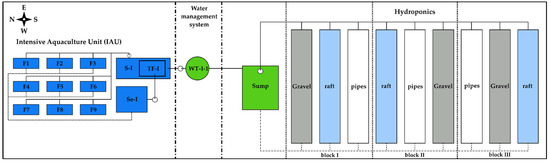
Figure 1.
Schematic view of the FishGlassHouse operational unit. Intensive aquaculture unit (IAU) with fish tanks (≈ 1 m3) 1‒9 (F1‒F9), solids separation unit, sedimenter (Se‒I), and sump (S‒I) with trickling filter (TF‒I). The aquaculture unit was connected to the hydroponics via the water management system tanks, with the inflow from the IAU into the water transfer tank (WT‒I‒1). The nutrient-enriched water was pumped to the hydroponics and stored in a sump, circulating it through the gravel, raft, and grow-pipe components. Continuous lines mark inflows, and dotted lines return flows.
2.2. Experimental Hydroponic Components
The experimental hydroponic components were arranged in a randomized block design in triplicate, with each subsystem in a different relative location within three blocks (Figure 1). The fish process water was first directed to a sump (0.4 m3) and was then pumped continuously at a rate of 4 L/min to the nine hydroponic components, and then returned by gravity back to the sump, in a closed water-recirculating unit configuration. The three gravel beds had a total water volume of 255.53 L, the three raft tanks of 786.24 L, and the three grow pipes of 46.65 L (in total 1088.42 L). The water in the pump sump was drained when it reached 200 L. The sump and the complete recirculation system with the hydro-components were filled with intensive process water from the IAU commercial aquaculture system at the beginning of the experiment and twice a week during the study. Each hydroponic component held seven basil plants with a total number of 63 plants inside the whole system.
The grow pipes were built of orange sewage drainage pipes [36]. The pipes (275 cm × 12 cm, volume: 16 L, slope: 2.12%) had seven holes (diameter: 5 cm) for inserting the grid pots with basil seedlings and a space of 30 cm [37,38]. The process water level inside the pipes was 2.5 cm. At the beginning of the experiment, the basil seedlings were too small to reach the water surface with their roots. Metal wire was used to fix the grid pots at a lower position inside the pipes until the roots reached the process water.
The floating raft (raft)/deep water culture (DWC) and the ebb-and-flood gravel substrate hydroponics were arranged in glass-fibre-reinforced plastic (GRP) tanks (280 cm × 40 cm × 45 cm, volume: 0.50 m3 filled with 262 L water). The rafts were made of polystyrene (URSA XPS DN-III-PZ, surface: 15.75 cm2, height: 20 mm) with seven holes for culturing basil seedlings, which were grown in grid pots (diameter: 5 cm). The raft channels had a stand pipe to keep the water level constant, and the water inside the channels was oxygenated by a membrane air pump (Aqua Medic Mistral 4000, AQUA MEDIC GmbH, Germany) via air stones.
The ebb-and-flood gravel substrate components (GRP tanks, 280 cm × 40 cm × 45 cm, volume: 0.50 m3 used half 0.25 m3 for gravel) were filled with 393.05 kg of washed Baltic Sea gravel (grain size of 16–32 mm, coarse gravel, pebble). A bell siphon [39] at the end of the troughs allowed a discontinuous water passage with an inflow rate of 4 L per minute and a water drain interval of one minute (six times per half an hour), thus following the ebb-and-flood principle. The upper edge of the pebbles inside the gravel beds was adjusted to the water levels inside the raft tanks and the grow-pipe subsystems.
2.3. Plant and Fish Species
Seeds of basil (O. basilicum, Kiepenkerl, Baldur Garten GmbH, Germany) were planted for germination in Grodan rockwool cubes (Grodan ROCKWOOL B.V., The Netherlands) three weeks before the beginning of the experiment. The seedlings were watered with a mixture of tap water and commercial fertilizer solution (Scotts Everris Universol Orange 16–5–25 + 3.4MgO + TE) and covered with a translucent upper shell. After three weeks, 63 seedlings (seven plants per channel, 21 plants per treatment) were transplanted to the hydroponic components with a spacing of 30 cm. The basil seedlings grew inside grid pots, except the seedlings for the ebb-and-flood gravel beds, which were planted in rockwool cubes directly into the gravel. After 41 days, all plants were cut 5 cm above ground level (2 cm above the lowest lateral branch) to determine plant parameters (without roots). The wet weight of the plants was measured and, thereafter, the dry weight after drying in a drying oven UF750 plus (Memmert GmbH & Co. KG, Germany), for three days at 60 °C and two hours at 120 °C, modified after [40]. Root stumps were left in the hydroponic subsystems, and growth was continued for additional 30 days. After 71 days, roots and cut shoots were harvested, and wet and dry weights were measured, following the protocol above.
African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) from Fischgut Nord eG (Abtshagen, Germany, MV) were stocked with a mean initial weight of 761.9 g. Nine fish tanks were stocked with 140 fish each for staggered production by size: small-sized fish (161.0 g ± 0.2) in tanks 1, 4, and 7 on 14 June 2016 (out on 17 August 2016), medium-sized fish (639.7 g ± 45.2) in tanks 2, 5, and 8 on 09 June 2016 (out on 17 August 2016), and large-sized fish (1484.9 g ± 7.2) in tanks 3, 6, and 9 stocked on 09 June 2016 (out on 31 July 2016). The fish feed (Skretting ME-4.5 Meerval 44-14, France) consisted of 44% crude protein, 14% crude fat, 1.4% fibre, 8.5% ash, 2% calcium, 0.5% sodium, 1.2% phosphorus, 42 mg iron, 2.1 mg iodine, 5 mg copper, 16 mg manganese, and 200 mg zinc. Fish were fed according to an experimental feeding protocol (PAL GmbH, Germany) at 75% of the recommended feed input by automatic feeders.
2.4. Physical and Chemical Parameters
Physical water parameters were taken once daily at the same time from the sump in the hydroponics. Temperature (°C), dissolved oxygen (mg/L) and saturation (%), conductivity (EC, µS/cm), pH, and redox potential (mV) were measured by a HQ40D multimeter (Hach Lange GmbH, Germany). The photosynthetically active radiation (photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD), µmol/m2s) was measured by a “Field Scout” Solar Electric Quantum Meter (Spectrum Technologies, Inc., USA), and the illumination level (lx) was measured by a “Dr. Meter” (Digital Illuminance/Light Meter LX1330B) once a week above each individual hydroponic component.
Water samples were taken twice a week from the sump in the hydroponic components for chemical water parameter analyses of ammonium (NH4+), nitrite (NO2−), nitrate (NO3−), phosphate (PO43−), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), and calcium (Ca2+) in duplicates, by using a Gallery™ Automated Photometric Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA USA) and standard protocols: NH4⁺: ISO 7150‒1 (DIN 38406‒5:1983‒10), NO2−: ISO 6777:1984 (DIN EN 26777:1993‒04), PO43−: EN ISO 6878‒1‒1986 (DIN 38405 D11‒4). TON (total oxidized nitrogen), as N and nitrate by calculation (TON-nitrite), was analysed by colorimetric hydrazine method (Template: D08896_01© 2020 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.). Nitrate was reduced to nitrite by hydrazine under alkaline conditions. The total nitrite ions reacted with sulphanilamide and N-1-naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride under acidic conditions to form a pink azo-dye. The absorbance was measured at 540 nm and was related to the TON concentration by means of a calibration curve. Nitrate (as N) value was obtained by calculating TON (as N)-nitrite (as N).
2.5. Mathematical and Statistical Analyses
At the beginning of the experiment, basil seedlings were measured (three weeks after germination) before planting them in the hydroponic components, for plant height (cm), plant weight (g), leaf number (no), leaf length (mm), and leaf width (mm) (n = 33). After 41 days, plant growth parameters were measured, including final weight (g), height (cm), leaf number (no), leaf length (cm), and width (cm) from the biggest leaves of the upper three leaf branches; after 71 days of culture, root wet and dry weights (g) were measured.
Fish growth parameters, including initial weight (kg), final weight (kg), weight gain (kg), initial biomass (kg), final biomass (kg), feed conversion ratio (FCR), and specific growth rate (SGR), were calculated at the beginning and the end of the experiment for three age classes and for three associated tanks.
where Wt = final biomass (kg), W0 = initial biomass (kg), t = time in days.
The experiment was performed in a completely randomized block design (CRD, Figure 1, block I-III) with three replicates by using mean value comparisons at a significance level of p ≤ 0.05. All data were analysed with the SPSS 20.0 statistical software package [41] and Microsoft Excel [42]. Means of fish growth data and plant growth differences between the three hydroponic components, grow pipes, raft, and gravel, and dissolved oxygen (DO mg/L), oxygen saturation (OS %), temperature (°C), PPFD (μmol/m2s), and light intensity (lx) were determined by a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) if the data were normally distributed. A post hoc Tukey HSD test was used for data with homogeneity of variance; otherwise, a Dunnett T3 test showed the differences. If the sample size was different between groups and the data were not normally distributed, the nonparametric Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA was used.
3. Results
3.1. Fish Growth
The initial mean weights of the three size classes were 0.04 kg (small, 5.60 kg in total), 0.35 kg (medium, 49.55 kg), and 1.14 kg (large, 157.17 kg), respectively (Table 1). The final fish weights were 0.33 kg (45.82), 1.02 kg (141.73 kg), and 1.85 kg (252.75 kg), respectively. The C. gariepinus mean weight gain was best for large catfish with 0.71 kg, followed by medium (0.66 kg), and small (0.29 kg) fish. The tank weight gain was not significantly different between large (95.58 kg) and medium fish (92.18 kg). The best feed conversion ratio (FCR) was observed in small fish with 0.74, followed by medium fish with 0.84, and large fish with 0.91. Specific growth rate (SGR) was also best in small fish (3.23 %/d), followed by medium (1.50 %/d) and large fish (0.90 %/d). Mortality was generally low and not significantly different, with a maximum of 1.00% in the large fish class and a minimum of 0.33% in the small fish.

Table 1.
Clarias gariepinus production parameters in the FishGlassHouse, divided into three weight-based size classes: small fish at 40 g (tanks 1, 4, 7; 65 d), medium fish at 350 g (tanks 2, 5, 8; 70 d) and large fish at 1140 g (tanks 3, 6, 9; 53 d) in means (±SD), different letters showing different groups (p < 0.05).
3.2. Plant Growth
O. basilicum (initial weight at germination: 0.8 ± 0.2 g, root weight: 0.1 ± 0.0 g, leaf length: 40.2 ± 4.9 mm, leaf width: 22.8 ± 3.6 mm, n = 33) grew well in all three hydroponic components. Three weeks after germination, plant heights were not significantly different before transplantation into the hydro-components (grow pipes: 4.2 ± 0.6 cm, raft: 3.9 ± 0.7 cm, gravel: 4.1 ± 0.7 cm, Table 2). Basil plants began to develop flowers 36 days after planting. Beginning with day 35 (week six of the experiment), the basil showed significant differences in plant height (p < 0.05, Table 2) with the highest plant height in the gravel components (89.9 ± 9.3 cm), followed by raft (84.9 ± 10.3 cm), and grow pipes (79.7 ± 8.1 cm).

Table 2.
O. basilicum growth parameters in different hydroponic components, grow pipes, raft, and gravel, after 0, 35, 41 and 71 days. Means (±SD), different letters showing different groups (p < 0.05).
The tallest basil plants (Table 2) were found in the gravel components on day 41 (week seven, plant height cut 5 cm above ground) with 101.8 ± 8.3 cm, followed by grow pipes (96.7 ± 7.0 cm), and raft (94.8 ± 8.6 cm). Average leaf area was significantly greater in gravel (96.4 ± 16.8 cm²), followed by grow pipes (86.2 ± 18.8 cm²), and raft (82.5 ± 18.1 cm²). Basil plants cultured in grow pipes were significantly lower at plant positions 5 and 7 than plants grown in the gravel media beds (Figure 2).
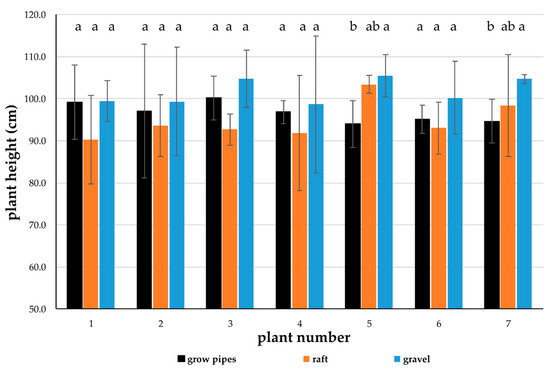
Figure 2.
O. basilicum plant height (cm) in means (±SD) at specific positions of plant number 1 (water inlet) to 7 (water outlet) in grow-pipe, raft, and gravel media bed hydroponic components (day 41), different letters showing different groups (p < 0.05).
After 71 days of culture, the leaf number was significantly higher in basil plants in the gravel components (1.3 ± 3.4), followed by raft (0.4 ± 1.3), and grow pipes (0.3 ± 1.1, Table 2). Root wet and dry weights were highest in the grow-pipe plants (wet weight: 73.6 ± 20.9 g, dry weight: 8.3 ± 1.8 g), and lower in the raft (wet weight: 33.2 ± 13.1 g, dry weight: 5.7 ± 1.7 g) and the gravel system (wet weight: 30.3 ± 9.0 g, dry weight: 5.1 ± 1.5 g, Table 2). Root dry weight of grow-pipe plants was significantly higher compared to the gravel hydroponic components at positions 1, 2, and 7 (Figure 3).
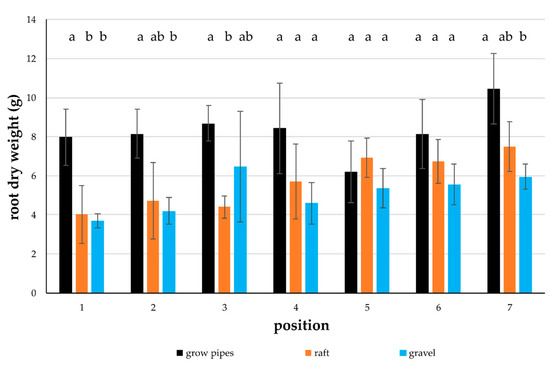
Figure 3.
O. basilicum root dry weight (g) in means (±SD) at specific positions of plant number 1 (water inlet) to 7 (water outlet) in grow-pipe, raft, and gravel media bed hydroponic components (day 71), different letters showing different groups (p < 0.05).
3.3. Physico-Chemical Parameters
The hydroponic components showed no significant differences in physical parameters of dissolved oxygen (DO), oxygen saturation (OS), and temperature (Table 3). PPFD was significantly higher in the raft system (219.4 ± 89.9 µmol/m2s), followed by gravel (172.5 ± 44.5 µmol/m2s), and grow pipes (166.8 ± 36.3 µmol/m2s), which were not significantly different. Light intensity was highest in the grow pipes (952.0 ± 157.4 lx) and raft (929.4 ± 154.4 lx), but significantly different from the gravel system (823.8 ± 119.1 lx).

Table 3.
Comparison of physical parameters inside and above the hydroponic components (grow pipes, raft, gravel; means, ±SD); different letters indicate different groups (p < 0.05).
In the sump of the hydroponic components, dissolved oxygen (DO) averaged (mean ±SD) 7.7 ± 0.3 mg/L, oxygen saturation (OS) 98.7 ± 2.3%, temperature 27.9 ± 1.7 °C, pH 6.6 ± 0.4, redox potential (Red-Ox) 165.8 ± 34.7 mV, and electrical conductivity (EC) 1619.4 ± 205.6 μS/cm (y = 9.39x + 1284.22, R² = 0.87; Figure 4).
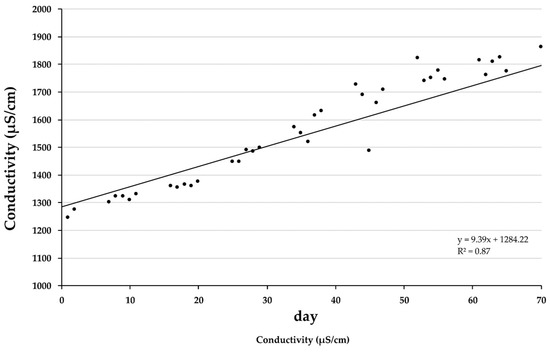
Figure 4.
Development of the electrical conductivity (EC) in the hydroponic sump during the experiment (71 days).
The mean ammonium concentration was 3.8 ± 2.6 mg/L, nitrite averaged 0.04 ± 0.04 mg/L, and the nitrate concentration was at 102.9 ± 20.2 mg/L. Total oxidized nitrogen (TON) showed a mean value at 103.0 ± 20.2 mg/L and total dissolved nitrogen (TDN) at 106.8 ± 21.6 mg/L. The phosphate concentration was 9.4 ± 1.3 mg/L, potassium 60.6 ± 8.9 mg/L, magnesium 26.8 ± 4.2 mg/L, and calcium 176.2 ± 27.4 mg/L.
4. Discussion
4.1. Fish Growth
Fish growth parameters demonstrated very good results for each weight class of C. gariepinus. Feed conversion (0.74–0.91) was better than described for fish (initial weights of 81.3 g and 188.1 g) fed with two different protein diets: (A) low protein (31%) with FCRs from 1.11–1.25 and (B) high protein (40%) with FCRs of 0.97–1.30 in combination with sweet basil (O. basilicum) [43]. Comparable feed conversion rates of 0.8 and 0.9 were reported in African catfish with initial weights between 82.4 g and 192.6 g [44]. Younger C. gariepinus with an initial weight of 3.92 g can achieve an even better FCR of 0.61 under aquaponic conditions combined with basil (O. basilicum), parsley (P. crispum), and marjoram (O. majorana, [27]). Under intensive rearing conditions, an FCR of 0.97, close to the present study in weight class III (large), was reported for 140 fish/tank and a grow-out (staggered) of 40 g to 1560.9 g individual weight [45].
The specific growth rate of African catfish was better than expected. In the present study, the SGR of weight class II (1.5%/d) was twofold higher than described for fish with an initial weight of 365 g (0.6%/d) under aquacultural conditions [46]. An SGR of 1.36%/d, comparable to weight class II, was described for 188.1 g C. gariepinus fed a high protein diet (40%) and combined with O. basilicum [43]. Under production conditions (intensive: 140 fish/tank) and a feeding period of 204 days, C. gariepinus also showed a comparable specific growth rate of 1.80%/d, which corresponded to the growth of weight class II (medium) [45]). However, the total feed input was twofold higher (155 kg), and the feeding period was 2.9-fold longer. Fish performance in the present study was in accordance with earlier studies.
4.2. Physico-Chemical Parameters in the Hydroponic Components
Environmental parameters for the cultivation of O. basilicum were not optimal under summer glasshouse conditions in northern Germany. The temperature at germination and the grow-out stages was higher (28 °C) than recommended (20–25 °C), and the mean pH (6.6) of the aquaponics process water was also slightly higher than suggested (5.5–6.5) [36]. The mean PPFD was substantially lower (186.23 ± 28.86 µmol/m2s), compared with basil production under optimal hydroponic greenhouse conditions (293–308 µmol/m2s), a difference of 36–39% [47]. The light regime was not reflected in the growth performance of basil. In the raft system, the PPFD value was significantly higher and in both the grow-pipe and raft components the light intensity was significantly higher and should have increased basil biomass. However, wet and dry weight, lateral branches, and leaf numbers were not significantly different among all components at day 41, which is in contrast to the light conditions. Rather, the gravel component showed the highest significant values for plant height and leaf area (same with grow pipes) in contrast to the lowest values of light intensity and PPFD (same with grow pipes), demonstrating that light was not the limiting factor.
For optimal growth, basil needs a high amount of water but also proper drainage and periods without irrigation [48]. In the ebb-and-flood gravel component, these conditions were established with a flooding interval every four minutes, resulting in the best plant growth. However, the experimental ebb-and-flood system used had a very high flooding interval and did not correspond to conventional hydroponic components. Electrical conductivity (EC) seemed to be optimal as conducted for basil hydroponic greenhouse production with 1600 µS/cm [47], though the EC can be even higher (2800 µS/cm) [49]. In aquaponics generally, lower conductivity values are described, ranging from 300‒600 µS/cm [50], and in commercial outdoor coupled aquaponics, conductivity levels were reported between 0.8 mS/cm [51] and 0.65–0.69 dS/m [52] with the production of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and basil cultivation.
In aquaponics, macronutrient levels have been found to be even lower than in the present study, with P (as PO43−) of 6.6 mg/L, total N of 10.6 mg/L, K+ of 50.8 mg/L, Ca2+ of 129.6 mg/L, and Mg2+ of 20.9 mg/L [53]. Recommended fertilizer solution levels in O. basilicum greenhouse production reach nitrogen levels of up to 210 mg/L, phosphorus 80 mg/L, potassium 275 mg/L, magnesium 80 mg/L, and calcium 180 mg/L [54]. Only calcium was in the range for optimal growth. It has been demonstrated that basil can show a relatively good canopy fresh weight (26.42 g) in contrast to a canopy weight of 35.18 g under high nitrogen application, and a nearly identical leaf surface area (top region) of 11.04 cm² (low nitrogen), compared to 11.54 cm² (high nitrogen) [55]. Also, the root fresh weight and root length of basil were higher (14.74 g; 23.24 cm) under a low nitrogen regime, compared with high nitrogen application (12.32 g; 17.27 cm). Consequently, though the macronutrient levels in the present study were below the recommended concentrations for optimal growth, the hydroponics had adequate macronutrient concentrations to allow regular basil growth.
4.3. Plant Growth Parameters
4.3.1. Leaf Development
Leaf numbers showed no significant differences between the hydro-components and exhibited high variance (Table 2). For herbs and especially for basil, the number of leaves and leaf dimensions are decisive, since their glandular hairs are the main location of biosynthesis and the accumulation of flavour compounds and essential oils [56,57]. In hydroponics, a higher leaf number (585.36 leaf/plant) and leaf area (235.44 cm2/plant) were reported with a longer cultivation time of 70 days and a reduced daytime culture temperature of 24 °C [58]. In contrast and in hydroponics, leaf number can be much lower (114.58 leaves/plant), even with much higher conductivity levels of 2.32–2.42 EC dS/m and an ideal pH = 6.0 at a similar reduced experimental temperature of 24.8 °C [59]. Under hydroponics with the use of “seaweed extracts” as a fertilizer and a higher temperature (maximum 30 °C), the basil leaf number reached only 91.3 leaves/plant [60]. Basil cultivation in the open field also did not reach comparable results. Under the high temperature variance (maximum 30–40 °C) of northern India’s sub-tropical plains, a very small leaf number was reported (67.3 leaves/seedling) [61]. Consequently, during our experiments, the leaf numbers of O. basilicum with C. gariepinus aquaponics were higher than described for most reported hydroponic and field cultures. This indicates a beneficial effect of fish effluent water from C. gariepinus production on basil growth, in combination with the high cultivation temperature and the incidence of light in northern Germany. Basil cultivation was possible without additional commercial fertilizer, and this was evident for all three selected hydroponic components, the grow pipes, raft, and gravel media bed; indeed, all systems are adequately suited for domestic or commercial basil aquaponics.
4.3.2. Plant Biomass Development
The wet and dry weights of O. basilicum were not significantly different between the subsystems (Table 2). Comparable basil yields (393.5 total g/plant) were reported from a conventional greenhouse ebb-and-flood culture with a similar EC and low pH culture regime (0.7–2.2 dS/m, pH 5.8) after 120–124 culture days [62]. Under optimized greenhouse production conditions, O. basilicum can reach 585 g after 141 days of cultivation in rockwool cubes, even with reduced temperature (day: 20 °C, night: 15 °C) [54]. However, results of basil biomass production can vary substantially, even under relatively good nutrient conditions and environmental parameters. A reduced wet weight of basil (55.02 g) was reported after 68 days of greenhouse culture and slightly lower temperatures (day: 26 °C, night: 25 °C) with the use of commercial fertilizer and a high N input (250 kg N/ha) [63]. Under coupled aquaponics conditions outdoors in the Caribbean (UVI-commercial-aquaponics-system), the mean plant weight of basil was lower under batch (286.5 g) and staggered (244.7 g) plant cultivation with Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) [64]. Higher plant yield of Genovese sweet basil was reported in the same system with tilapia in the summer with calculated 923 g per plant (16.15 plants/m² with yield of 14.91 kg/m²), whereas the harvest in fall with approximately 415 g per plant (16.15 plants/m² with yield of 6.70 kg/m²) corresponded to wet weights of plants in our gravel bed and was higher than plant weights in grow-pipe and raft subsystems [52]. Compared to commercial greenhouse O. basilicum production, our plants performed well in terms of yield, especially since no fluid fertilizer was added. This was surprising since the nutrient content of the fish effluent water was much lower than under the use of conventional fertilizers. We suggest that additional factors in the process water were responsible for the good growth performance of the basil in the present study. Our results showed yields similar to autumn harvests in coupled aquaponics in the Caribbean and demonstrated that the cultivation of basil with aquacultural effluents of C. gariepinus is possible.
Comparative studies under aquaponic conditions with basil and different hydroponic subsystems are scarce. Another herb, mint (Mentha arvensis), showed significantly better yield in crushed stone media beds (size: 0.5–1.0 cm, yield: 1.076 kg), compared to floating raft (0.916 kg) in combination with common carp (Cyprinus carpio) [65]. Aquaponic production of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) in combination with Murray cod (Maccullochella peelii peelii) had the best plant growth in the gravel subsystem with constant flood [16]. The resulting plant yield was gravel > floating (raft) > NFT, while in our study, no significant differences were found between the hydroponic components in plant weight. Production of tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum) in co-cultivation with Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) showed no significant differences in average cumulative yield between a raft culture system (16,857 ± 341 g/m²) and an NFT system (17,176 ± 364 g/m²) [18]. NFT also supported a good growth performance of lettuce (Lactuca sativa), compared to a raft system and a vertical felt system in combination with goldfish (Carassius auratus) in aquaponics. It was suggested that a slightly higher water temperature in the NFT system increased nitrification and nutrient uptake by the plants with increasing lettuce yields [17]. During the present study, temperature was not significantly different between the subsystems (Table 3). Our relatively high plant yields during summer 2016 can be attributed to a relatively high temperature and a high conductivity level, though ebb-and-flood gravel systems, in particular, can be suboptimal due to the clogging of substrates with unaerated areas [36].
4.3.3. Plant Root Development
The wet and dry weights of basil roots were highest in the grow-pipe hydroponics and 2.4-fold higher in fresh biomass than in the ebb-and-flood gravel components, with no significant differences between plants in the raft and gravel subsystems (grow pipes > raft = gravel, Table 2). Plants in our setting developed large roots (19% of total plant wet weight), with rapid growth clogging the grow-pipe components [36]. This effect is known from conventional hydroponic tomato production, where roots can reach 15% of the total fresh weight of plants with larger layers of primary and secondary roots [66]. This biomass increase, as a consequence of nutrient stress effects, has been described as “compensatory responses” to the non-uniform distribution of nutrients, causing the stimulation of root growth [67]. A massive stimulation of root growth can occur if nutrients are readily available, whereas in nutrient-poor areas, root growth is reduced. A 2.3-fold length increase of second order lateral roots was reported due to locally supplied NO3−, and an over threefold length increase due to P supply of first order laterals in barley (Hordeum vulgare) [67]. Basil in the pipe systems showed massive root development, which blocked the water flow, and the appearance of numerous small root hairs. This effect has been described in plants with an extensive root system, such as tomatoes and mint, which, with their massive root systems, can clog even larger grow pipes [36] as well as conventional NFT systems with rectangular hydroponic channels [9,68]. Obviously, nutrients were plentiful in the first four positions of the growth pipes, but the blockage due to rapid root development significantly inhibited the growth of the plants in positions 5 and 7 (Figure 2). The plants in the pipe component, located at the most distant position from the inlet (position 7), had the largest roots (Figure 3) but also the lowest plant height (Figure 2) as a result of clogging. The grow-pipe systems themselves, with their relatively small pipe diameters and water volumes, seemed to be responsible. The root–water contact area was consequently limited and resulted in a rapid root biomass increase in the first four positions, and in a heterogeneous and suboptimal nutrient supply in the back positions due to backwater effects. Such heterogeneity of the single plant development in the applied grow-pipe components limits their use for commercial aquaponics basil production even under good adequate growth performance (see Section 4.3.1, Section 4.3.2, Section 4.3.4).
4.3.4. Plant Height Development
O. basilicum was tallest in the ebb-and-flood gravel components, with no significant differences between the grow-pipe and raft systems (gravel > grow pipes = raft). Comparable plant height was reported in raft aquaponics (89.9 cm) with crayfish (Procambarus spp.) and a longer experimental duration of 98 days at a lower temperature of 23.4 °C [29]. In conventional hydroponics, slightly lower basil heights (74.44 cm/plant) were found at a reduced conductivity of about 0.64 dS/m and 70 days of culture [58]. Also 2.1-fold lower plant heights (46.4–48.3 cm) were reported in hydroponics with the supply of seaweed extract (Ascophyllum nodosum) as an alternate fertilizer and foliar mineral application [60]. In general, O. basilicum can reach a height of 75 to 95 cm as observed in the present study [22].
Best plant height was observed in the media-substrate system and could be the result of supporting nitrification by increased air contact during the dewatering phase and by beneficial bacteria (e.g., Nitrosomonas spp., Nitrobacter spp.) inside the substrate [50]. The gravel substrate may have functioned as a bio-filter with additional nitrification and nitrate production directly at the plant root–water interface [50,69,70]. In raft systems, it has been observed that the plant height of basil rises when NO3− is added and decreases with NH4+ [59]; thus, basil was classified as a moderately NH4+ sensitive plant species [71]. The best basil biomass production was found at 100 mg N/L at a ratio of 50:50 to 75:25 of nitrate-N: ammonium-N [72]. In our experiment, the amount of nitrate was optimal in the hydroponic recirculation system, which could explain the relatively good plant heights. However, the ratio of NO3− to NH4+ was suboptimal with very low values of NH4+, which should reach 30.5%-fold higher to achieve the optimal ratio of 75:25 [72]. The gravel substrate component showed the significantly best plant heights and average leaf area (compared to raft). This may indicate that one potential factor was an improved N ratio in the gravel bed directly at the roots. Though supporting aquaponics basil growth, the applied coarse gravel beds with a grain size of 16–32 mm are very heavy, may clog over time, and are difficult to handle and clean, making commercial application difficult. For aquaponics, basil might need an alternative media substrate, such as new designed pot-able systems which would belong to the nomenclature aquaponics (s.l.) horticulture [5], for adequate handling, optimal growth, and for the “self” mobilisation of nutrients by microorganisms combined with well-oxygenated conditions. The direct comparison of the nutrient situation at the root surfaces in comparison to alternative substrates may be a subject for future investigations.
5. Conclusions
Decoupled aquaponic cultivation of O. basilicum showed good performance with the use of C. gariepinus intensive aquaculture effluents without addition of fertilizer at the grow-out stage. Growth differences between three tested hydro-components were generally small, with the best results obtained in the ebb-and-flood gravel substrate subsystem. Plant height was best in the gravel media beds and not significantly different between grow-pipe and raft subsystems (gravel > grow pipes = raft). Leaf number was comparable between the hydroponic components after 41 days (grow pipes = gravel = raft), was affected by a very high variance, and was higher in the gravel substrate components than in grow pipes (gravel > grow pipes) after cutting of the stems at day 71. The plants of the grow pipes showed decreasing heights towards the outflow with larger root weights, compared to the raft and gravel components (grow pipes > raft = gravel), indicating imbalanced nutrient and water availability.
Compared to conventional basil greenhouse cultivation, nutrient amounts were in general lower of, e.g., total dissolved nitrogen (TDN: 106.8 mg/L), phosphorus (9.4 mg/L), potassium (60.6 mg/L), and conductivity (1619.4 μS/cm; hydroponics: N: 210 mg/L, P: 80 mg/L, K: 275 mg/L, and EC: 2800 μS/cm); however, comparable plant heights and numbers of leaves were obtained in all components as described for hydroponics. In conclusion, aquaponics under intensive catfish production in combination with basil and in the tested hydro-components is possible based on general plant performance. The grow pipes resulted in heterogenous growth, the gravel substrate was difficult to handle, and the raft components had the least performance under the highest water use, questioning its use for commercial aquaponics. Therefore, future studies should consider alternative substrates inside the hydro-components and specified nutrient requirements, such as aquaponics gardening (s.l.), for commercial basil production.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to several aspects of the study, specifically, conceptualization: U.K., S.A. and H.W.P.; methodology: M.P.; software: M.P. and U.K.; validation: U.K., M.P., S.A., L.X. and H.W.P.; formal analysis: U.K., M.P., S.A. and H.W.P.; investigation: U.K.; resources: M.P.; data curation: M.P., U.K., L.X., S.A. and H.W.P.; writing—original draft preparation: U.K., S.A. and H.W.P.; writing—review and editing: U.K., M.P., S.A. and H.W.P.; visualization: U.K.; supervision: U.K., H.W.P. and S.A.; project administration: H.W.P. and U.K.; funding acquisition: H.W.P. and U.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We thank the Ministry of Agriculture, Environment and Consumer Protection of Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania (Germany), the European Union and EIP-AGRI operational groups for supporting research in aquaponics fish and plant production (‘Aquaponik in MV’, BNRZD: 13 903 000 0103; WM-EIP-0007-15). This project was funded through the pilot project “FishGlassHouse: Innovationsinitiative zur ressourceneffizienten Nahrungsmittelproduktion in MV” (European Fisheries Fund–EFF, grant number: VI-560/730-32616-2013/025). We acknowledge financial support from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and Universität Rostock within the funding programme Open Access Publishing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Palm, H.W.; Knaus, U.; Appelbaum, S.; Strauch, S.M.; Kotzen, B. Coupled Aquaponics Systems. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 163–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennert, B.; Drews, M. Eine Möglichkeit der kombinierten Fisch- und Gemüseproduktion in Gewächshäusern. Fortschr. Fisch. Wiss. 1989, 8, 19–27. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Kloas, W.; Groß, R.; Baganz, D.; Graupner, J.; Monsees, H.; Schmidt, U.; Staaks, G.; Suhl, J.; Tschirner, M.; Wittstock, B.; et al. A new concept for aquaponic systems to improve sustainability, increase productivity, and reduce environmental impacts. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2015, 7, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddek, S.; Joyce, A.; Wuertz, S.; Körner, O.; Bläser, I.; Reuter, M.; Keesman, K.J. Decoupled Aquaponics Systems. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 201–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, H.W.; Knaus, U.; Appelbaum, S.; Goddek, S.; Strauch, S.M.; Vermeulen, T.; Jijakli, M.H.; Kotzen, B. Towards commercial aquaponics: A review of systems, designs, scales and nomenclature. Aquac. Int. 2018, 26, 813–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, A.; Goddek, S.; Kotzen, B.; Wuertz, S. Aquaponics: Closing the Cycle on Limited Water, Land and Nutrient Resources. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, C.R. Economics of Aquaponics; Oklahoma State University: Stillwater, OK, USA, 2016; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Maucieri, C.; Nicoletto, C.; van Os, E.; Anseeuw, D.; Van Havermaet, R.; Junge, R. Hydroponic Technologies. In Aquaponics Food Production Systems; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 77–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geilfus, C.M. Hydroponic Systems in Horticulture. In Controlled Environment Horticulture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Aquaponic trends and challenges–A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junge, R.; König, B.; Villarroel, M.; Komives, T.; Jijakli, M.H. Strategic Points in Aquaponics. Water 2017, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, K.A. Productivity of Kale (Brassica oleracea var. acephala) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Culture in Aquaponic Systems. Master’s Thesis, The Center for Applied Research on the Environment and Sustainability (CARES), The American University in Cairo, Cairo, Egypt, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Love, D.C.; Fry, J.P.; Li, X.; Hill, E.S.; Genello, L.; Semmens, K.; Thompson, R.E. Commercial aquaponics production and profitability: Findings from an international survey. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mchunu, N.; Lagerwall, G.; Senzanje, A. Aquaponics in South Africa: Results of a national survey. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Nicoletto, C.; Junge, R.; Schmautz, Z.; Sambo, P.; Borin, M. Hydroponic systems and water management in aquaponics: A review. Ital. J. Agron. 2018, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard, W.A.; Leonard, B.V. A comparison of three different hydroponic sub-systems (gravel bed, floating and nutrient film technique) in an aquaponic test system. Aquac. Int. 2006, 14, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Urrestarazu, L.; Lobillo-Eguíbar, J.; Fernández-Cañero, R.; Victor, M.; Fernández-Cabanás, V.M. Suitability and optimization of FAO’s small-scale aquaponics systems for joint production of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and fish (Carassius auratus). Aquac. Eng. 2019, 85, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmautz, Z.; Loeu, F.; Liebisch, F.; Graber, A.; Mathis, A.; Griessler Bulc, T.; Junge, R. Tomato productivity and quality in aquaponics: Comparison of three hydroponic methods. Water 2016, 8, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunwoody, R.K. Aquaponics and Hydroponics: The Effects of Nutrient Source and Hydroponic Subsystem Design on Sweet Basil Production. Master’s Thesis, University of Central Missouri, Warrensburg, MO, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S. Culinary herb use in southern California restaurants. Calif. Agric. 1991, 45, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.E.; Morales, M.R.; Phippen, W.B.; Vieira, R.F.; Hao, Z. Basil: A Source of Aroma Compounds and a Popular Culinary and Ornamental Herb. In Perspectives on New Crops and New Uses; Janick, J., Ed.; ASHS Press: Alexandria, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, R.S. Ocimum as a promising commercial crop. In The Ocimum Genome, Compendium of Plant Genome; Shasany, A.K., Kole, C., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zheljazkov, V.D.; Cantrell, C.L.; Tekwani, B.; Khan, S.I. Content, composition, and bioactivity of the essential oils of three basil genotypes as a function of harvesting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.E.; Quinn, J.; Murray, R.G. Basil: A source of essential oils. In Advances in New Crops; Janick, J., Simon, J.E., Eds.; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1990; pp. 484–489. [Google Scholar]
- Pushpangadan, P.; George, V. Basil. In Handbook of Herbs and Spices; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, H.W.; Bissa, K.; Knaus, U. Significant factors affecting the economic sustainability of closed aquaponic systems; Part II: Fish and plant growth. AACL Bioflux 2014, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Knaus, U.; Palm, H.W. Effects of fish biology on ebb and flow aquaponical cultured herbs in northern Germany (Mecklenburg Western Pomerania). Aquaculture 2017, 466, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.; Appelbaum, S.; Palm, H.W. Significant factors affecting the economic sustainability of closed backyard aquaponics systems. Part IV: Autumn herbs and polyponics. AACL Bioflux 2018, 11, 1760–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Monroe, A.; Day, M.R. Growth, yield, plant quality and nutrition of basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) under soilless agricultural systems. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa Moya, E.A.; Angel Sahagún, C.A.; Mendoza Carrillo, J.M.; Albertos Alpuche, P.J.; Álvarez-González, C.A.; Martínez-Yáñez, R. Herbaceous plants as part of biological filter for aquaponics system. Aquac. Res. 2016, 47, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destatis E2 Betriebe mit Erzeugung in Aquakultur sowie erzeugter Menge im Jahr 2018 nach Art der Bewirtschaftung. Afrikanischer Raubwels. In Land und Forstwirtschaft, Fischerei; Statistisches Bundesamt: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2018; p. 54. (In German)
- Destatis E2 Betriebe mit Erzeugung in Aquakultur sowie erzeugter Menge im Jahr 2019 nach Art der Bewirtschaftung. Afrikanischer Raubwels. In Land und Forstwirtschaft, Fischerei; Statistisches Bundesamt: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2019; p. 56. (In German)
- Endut, A.; Jusoh, A.; Ali, N.; Nik, W.W.; Hassan, A. A study on the optimal hydraulic loading rate and plant ratios in recirculation aquaponic system. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baßmann, B.; Brenner, M.; Palm, H.W. Stress and welfare of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822) in a coupled aquaponic system. Water 2017, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baßmann, B.; Harbach, H.; Weißbach, S.; Palm, H.W. Effect of plant density in coupled aquaponics on the welfare status of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2018, 51, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, C.; Cohen, M.; Pantanella, E.; Stankus, A.; Lovatelli, A. Small-Scale Aquaponic Food Production. Integrated Fish and Plant Farming; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper No. 589; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; p. 262. [Google Scholar]
- Bione, M.A.A.; Paz, V.P.S.; da Silva, F.; Sartoratto, A.; Soares, T.M. Production of hydroponic basil essential oil with conventional nutrient solution in brackish waters and organic nutrient solution. In Proceedings of the II Inovagri International Meeting, Fortaleza, Brazil, 13–16 April 2014; pp. 438–448. [Google Scholar]
- Putievsky, E.; Galambosi, B. 2. Production systems of sweet basil. In Basil: The Genus Ocimum; Hiltunen, R., Holm, Y., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, D.H. Aquaponic Design Plans and Everything You Need to Know, 2nd ed.; Howard Publishing: Brentwood, TN, USA, 2018; p. 630. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad-Qasem, M.H.; Cánovas, J.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Micol, V.; Cárcel, J.A.; García-Pérez, J.V. Kinetic and compositional study of phenolic extraction from olive leaves (var. Serrana) by using power ultrasound. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Deutschland GmbH. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0; IBM Deutschland GmbH: Ehningen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Microsoft® Corporation. Microsoft Excel®; Microsoft® Corporation: Redmond, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pantanella, E. Aquaponics and sustainability: Production, quality and nutrient efficiency in Sweet basil and African catfish. In Nutrition and Quality of Aquaponic Systems; Ph.D. Thesis; Universita degli Studi della Tuscia: Viterbo, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, C.I.; Aanyu, M.; Schrama, J.W.; Verreth, J.A. Size distribution in African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) affects feeding behaviour but not growth. Aquaculture 2005, 250, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, H.W.; Knaus, U.; Wasenitz, B.; Bischoff, A.A.; Strauch, S.M. Proportional up scaling of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus Burchell, 1822) commercial recirculating aquaculture systems disproportionally affects nutrient dynamics. Aquaculture 2018, 491, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degani, G.; Ben-Zvi, Y.; Levanon, D. The relationship between body size and growth of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) (Burchell, 1922) fed practical diet. Indian J. Fish. 1988, 35, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, K.J.; Currey, C.J. Hydroponic greenhouse basil production: Comparing systems and cultivars. HortTechnology 2015, 25, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M. Basil: An Herb Society of America Guide; The Herb Society of America: Kirtland, OH, USA, 2003; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Morano, G.; Amalfitano, C.; Sellitto, M.; Cuciniello, A.; Maiello, R.; Caruso, G. Effects of nutritive solution electrical conductivity and plant density on growth, yield and quality of sweet basil grown in gullies by subirrigation. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2017, 31, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rakocy, J.E.; Masser, M.P.; Losordo, T.M. Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems: Aquaponics—Integrating Fish and Plant Culture; SRAC Publ. No. 454; Southern Regional Aquaculture Center: Stoneville, MS, USA, 2006; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Rakocy, J.; Shultz, R.C.; Bailey, D.S.; Thoman, E.S. Aquaponic production of tilapia and basil: Comparing a batch and staggered cropping system. South Pacific Soil. Cult. Conf. 2003, 648, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarezi, R.S.; Bailey, D.S. Basil performance evaluation in aquaponics. HortTechnology 2019, 29, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittsanszky, A.; Uzinger, N.; Gyulai, G.; Mathis, A.; Junge, R.; Villarroel, M.; Kotzen, B.; Komives, T. Nutrient supply of plants in aquaponic systems. Ecocycles 2016, 2, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succop, C.E.; Newman, S.E. Organic fertilization of fresh market sweet basil in a greenhouse. HortTechnoloy 2004, 14, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, S.A.; Chong, J.H. Less is more? Basil growth and flowering under below-recommended nitrogen fertilization rates. J. Environ. Hortic. 2016, 34, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werker, E. Function of essential oil-secreting glandular hairs in aromatic plans of Lamiacea—A review. Flavour Fragr. J. 1993, 8, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, N.; Das, A.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Rahman, S.M.M. Chemical compositions of different extracts of Ocimum basilicum leaves. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhindi, K.M.; El-Din, A.S.; Elgorban, A.M. The impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mitigating salt-induced adverse effects in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiferle, C.; Maggini, R.; Pardossi, A. Influence of nitrogen nutrition on growth and accumulation of rosmarinic acid in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) grown in hydroponic culture. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Elansary, H.O.; Yessoufou, K.; Shokralla, S.; Mahmoud, E.A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K. Enhancing mint and basil oil composition and antibacterial activity using seaweed extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 92, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Absar, N.; Kaur, P.; Singh, A.K.; Khan, N.; Singh, S. Optimization of seed rate and seedling establishment technique for raising the nursery of French basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 85, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortman, S.E. Crop physiological response to nutrient solution electrical conductivity and pH in an ebb-and-flow hydroponic system. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 194, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufalo, J.; Cantrell, C.L.; Astatkie, T.; Zheljazkov, V.D.; Gawde, A.; Boaro, C.S.F. Organic versus conventional fertilization effects on sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) growth in a greenhouse system. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rakocy, J.E.; Bailey, D.S.; Shultz, R.C.; Thoman, E.S. Update on tilapia and vegetable production in the UVI aquaponic system; New dimensions on farmed Tilapia. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Tilapia in Aquaculture, Manila, Philippines, 12–16 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shete, A.P.; Verma, A.K.; Chadha, N.K.; Prakash, C.; Chandrakant, M.H.; Nuwansi, K.K.T. Evaluation of different hydroponic media for mint (Mentha arvensis) with common carp (Cyprinus carpio) juveniles in an aquaponic system. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, C.J. The nutrient film technique. Hortic. Rev. 1983, 5, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D. The responses of plants to non-uniform supplies of nutrients. New Phytol. 1994, 127, 635–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S. Tomorrow’s Agriculture: “NFT Hydroponics”—Grow within Your Budget; Springer International Publishing: Manila, Philippines, 2018; p. 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, A.K.; Biswas, P.; Saha, H. Aquaponics—A step towards urban agriculture. Innov. Farming 2016, 1, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Pantanella, E. Aquaponics Production, Practices and Opportunities. In Sustainable Aquaculture, Applied Environmental Science and Engineering for a Sustainable Future; Hai, F.I., Visvanathan, C., Boopathy, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Manila, Philippines, 2018; pp. 191–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerichs, C.; Daum, D.; Koch, R. Ammoniumtoxizität—Eine Ursache für Wachstums- und Qualitätsbeeinträchtigungen von organisch gedüngtem Basilikum. Ammonium toxicity—One cause for growth and quality impairments on organic fertilized basil? J. Kulturpflanzen 2017, 69, 101–112. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaman, A.R. Irradiance, Total Nitrogen, and Nitrate-N: Ammonium-N Ratio Requirements for Optimal Edible Biomass Production of Basil. Master’s Thesis, Iowa State University, Ames, IA, USA, 2008; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).