Educated Millennials and Credence Attributes of Food Products with Genetically Modified Organisms: Knowledge, Trust and Social Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Empirical Strategy and Hypotheses
3. Results
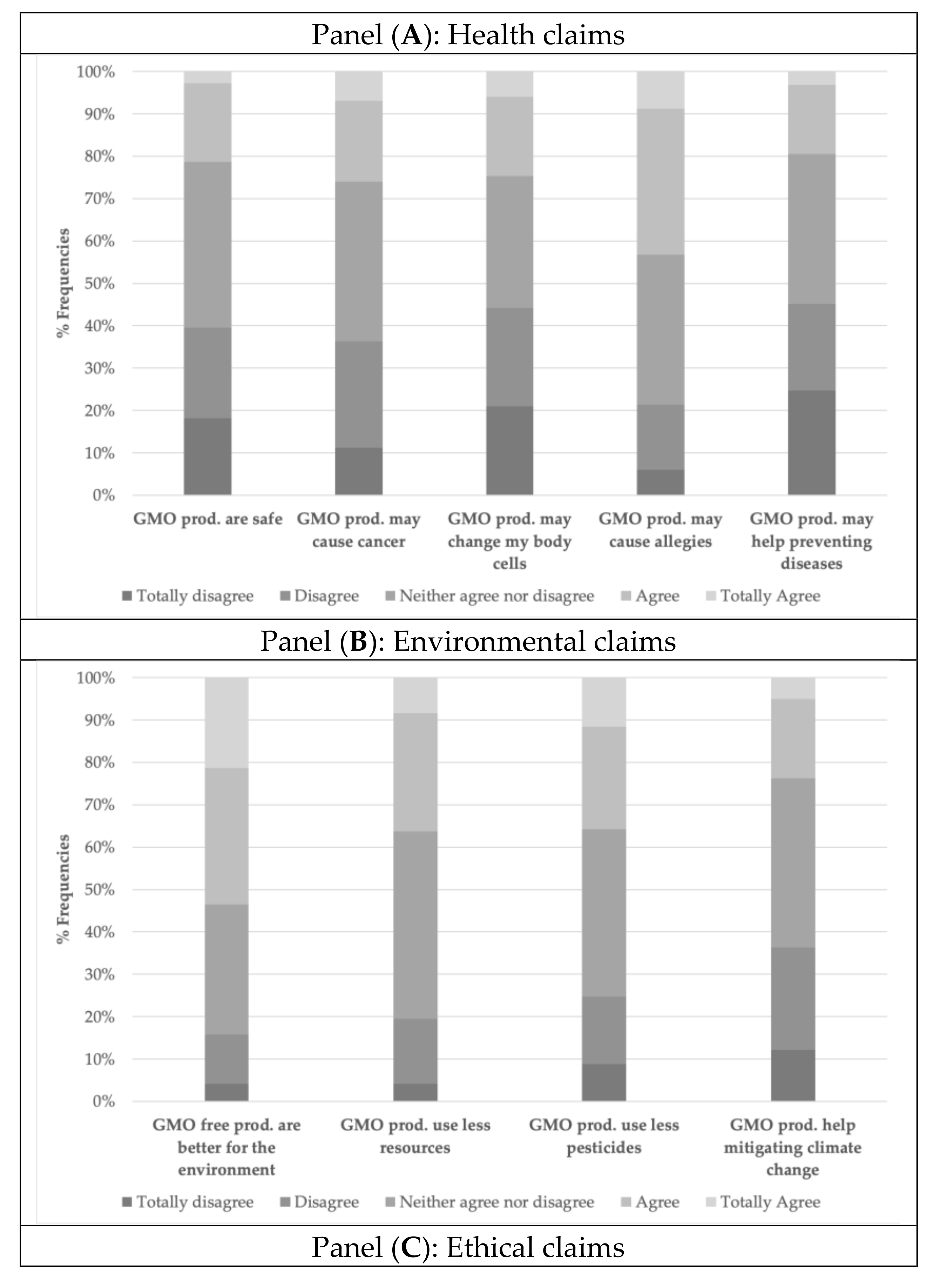
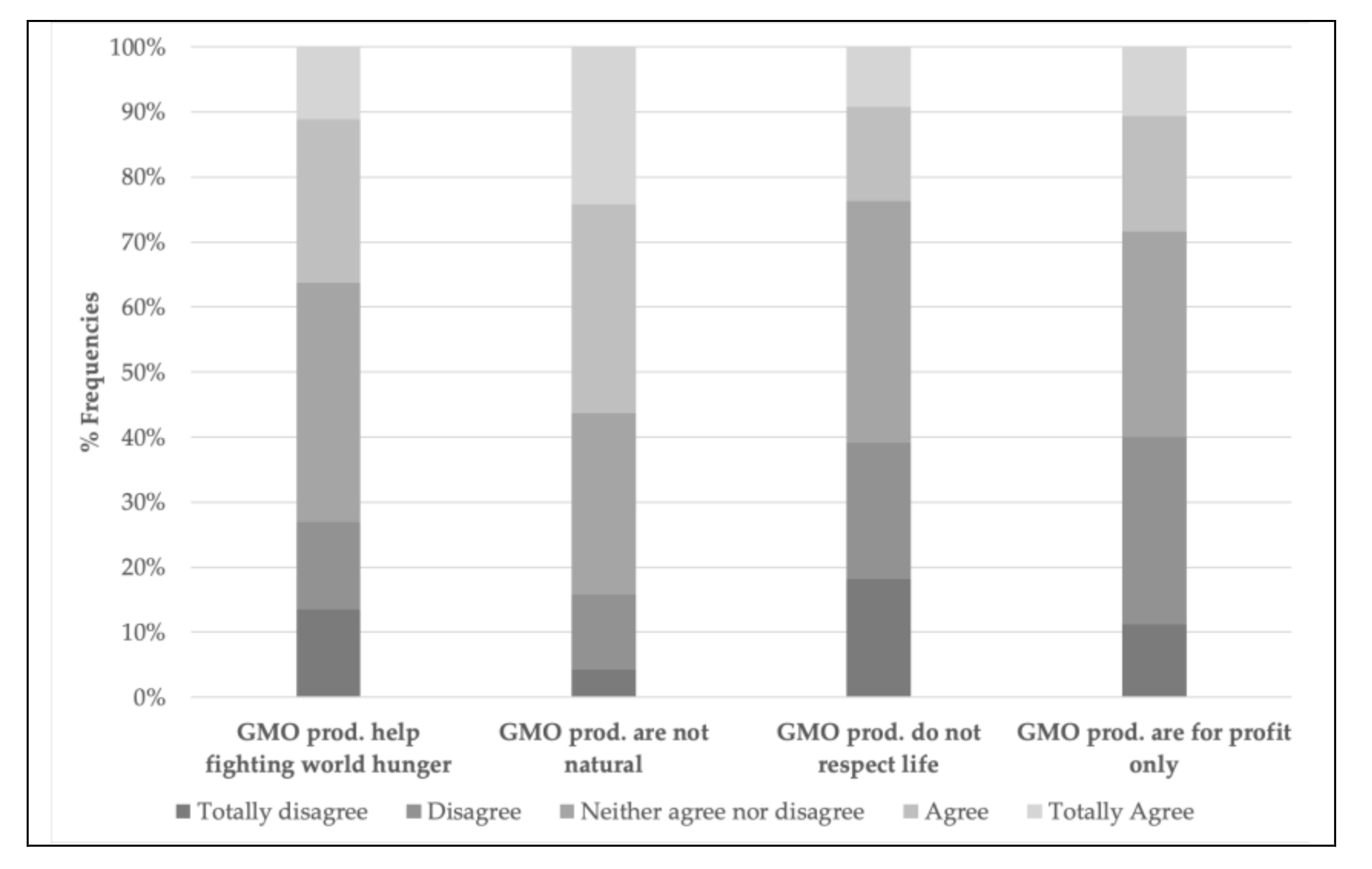
3.1. Measuring Subjective Assessment of Truthfulness
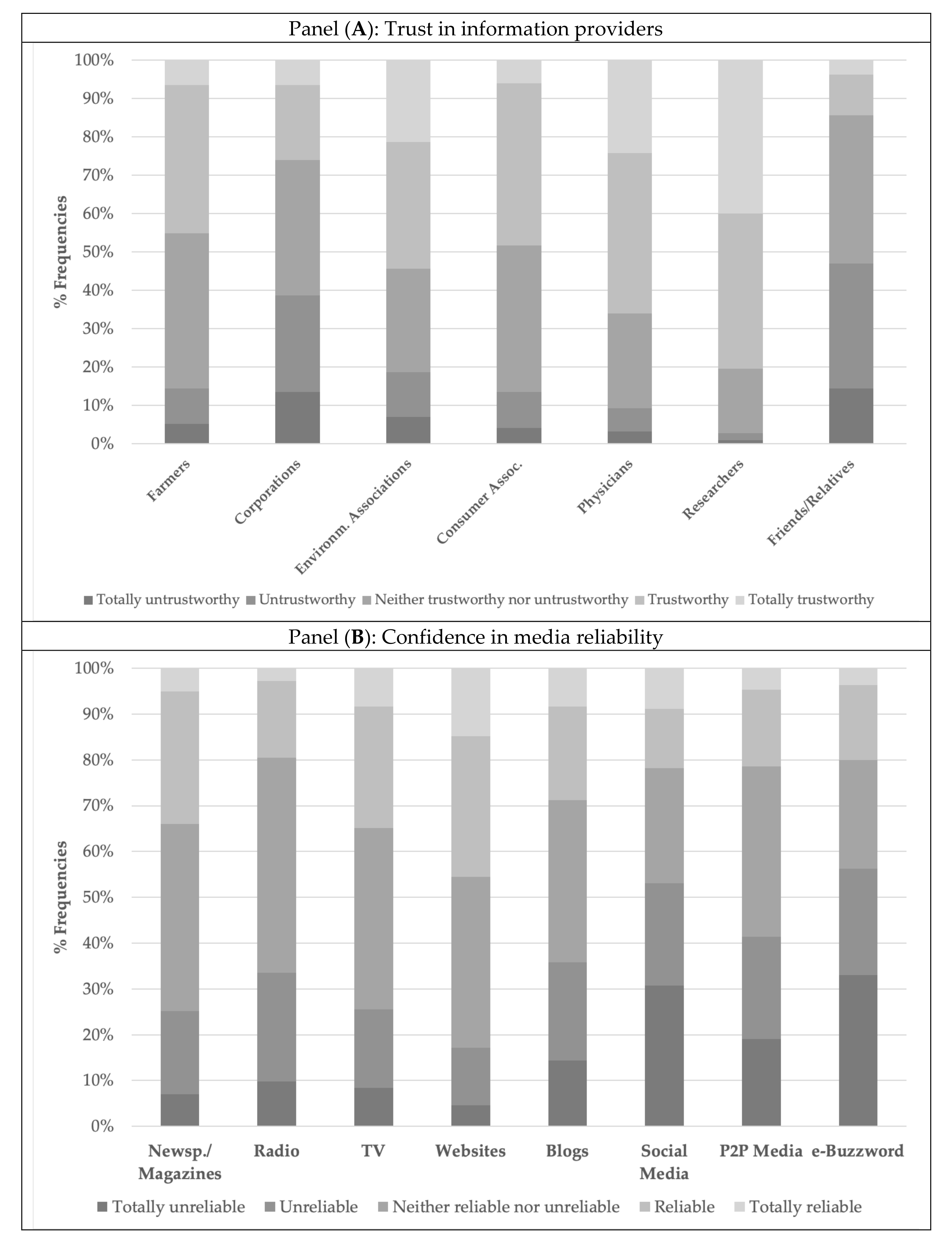
3.2. Measuring Trust in Information Providers and Confidence in Media
- Farmers
- Corporations
- Environmental associations
- Consumer associations
- Physicians
- Researchers
- Friends/Relatives
- Other information providers
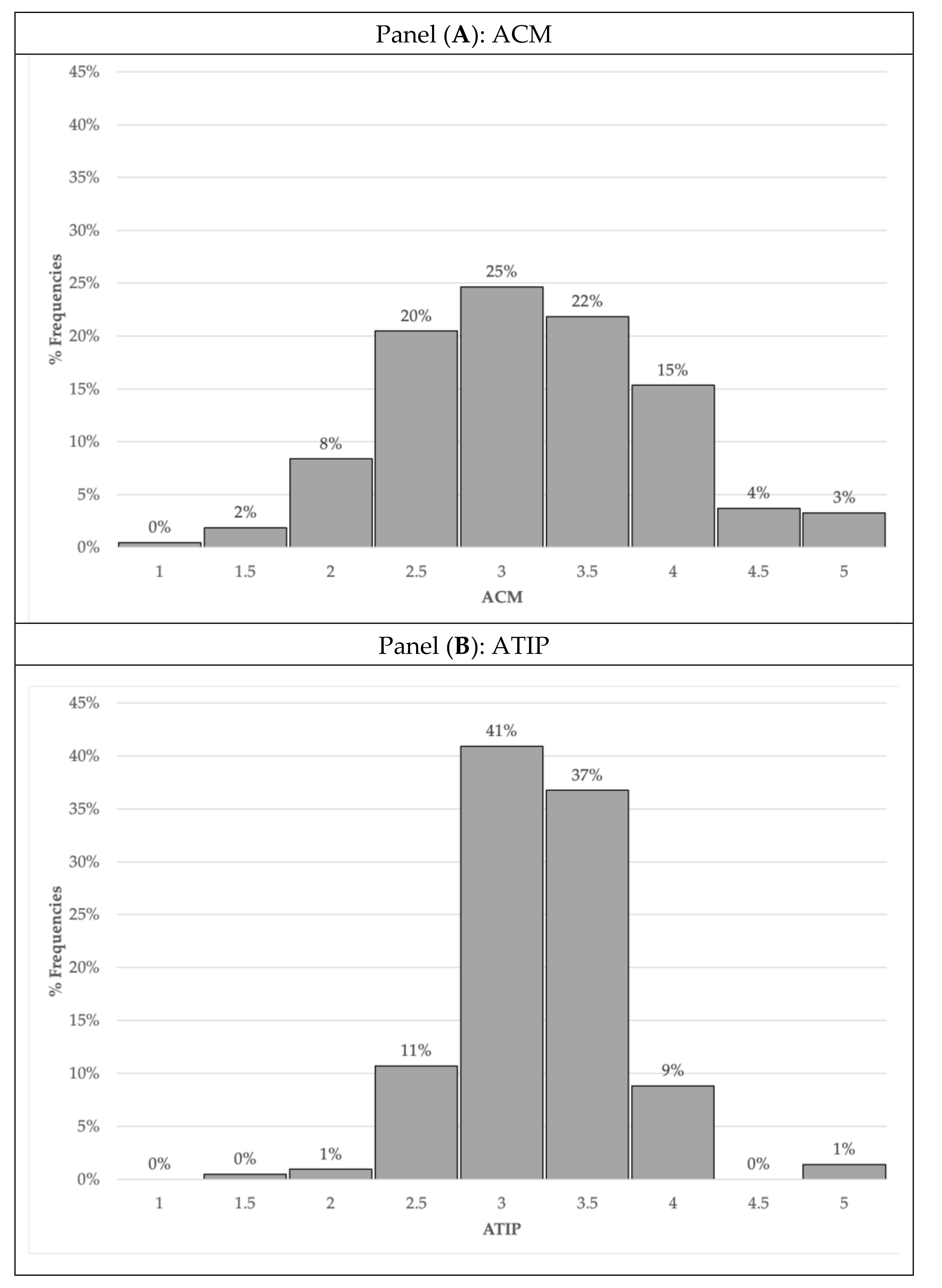
3.3. Measuring Respondents’ Ability to Process Scientific Information
3.4. The Regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. English Translation of the Questionnaire
- No ☐
- Yes, undergraduate ☐
- Yes, master’s ☐
- Yes, other ☐
- STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) field ☐
- Other fields ☐
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| GMO products are safe | |||||
| GMO products may cause cancer | |||||
| GMO products may change my body cells | |||||
| GMO products may cause allergies | |||||
| GMO products may help preventing diseases | |||||
| Conventional products (NO GMO) are better for the environment | |||||
| GMO products use fewer natural resources (water, soil, etc.) | |||||
| GMO products use less pesticides | |||||
| GMO products help mitigating climate change | |||||
| GMO products help fighting world hunger | |||||
| GMO products are not natural | |||||
| GMO products do not respect life | |||||
| The only reason for producing GMO products is firms’ profit |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Farmers | |||||
| Corporations | |||||
| Environmental associations | |||||
| Consumer associations | |||||
| Physicians | |||||
| Researchers | |||||
| Friends/relatives | |||||
| Other experts |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Newspapers, magazines | |||||
| Radio | |||||
| TV | |||||
| Websites | |||||
| Blogs | |||||
| Social media (e.g., Facebook, Instagram) | |||||
| P2P media (aggregators of user comments such as TripAdvisor, etc.) | |||||
| e-Buzzword (e.g., WhatsApp, etc.) | |||||
| Other media |
References
- Öz, B.; Unsal, F.; Movassaghi, H. Consumer attitudes toward genetically modified food in the United States: Are Millennials different? J. Transnatl. Manag. 2017, 23, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, C.; Lerro, M.; Stanco, M.; Marotta, G. Do consumers like food product innovation? An analysis of willingness to pay for innovative food attributes. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 1413–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnhoff, S.; Volovich, E.; Smith, M.; Martin, H.M. An Examination of Millennialss Attitudes Toward Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) Foods: Is it Franken-Food or Super-Food? SSRN Electron. J. 2014, 13, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajale, D.B.; Becker, T. Factors Influencing Young Consumers’ Acceptance of Genetically Modified Food in India. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2014, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Méndez, J.I.; Ahmed, S.A.; Claro-Riethmüller, R.; Spiller, A. Acceptance of Genetically Modified Foods with Health Benefits: A Study in Germany. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2012, 18, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Boyd, M. Japanese Consumers’ Acceptance of Genetically Modified (GM) Food. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2006, 12, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, N.; Simeone, M.; Russo, C.; Perito, M.A. Profiling young consumers’ perceptions of GMO products: A case study on Italian undergraduate students. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 21, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, S.; A Gatto, K. Consumer Perception of Genetically Modified Organisms and Sources of Information. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.; Simeone, M. The growing influence of social and digital media. Br. Food J. 2017, 119, 1766–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHughen, A. GM crops and foods. GM Crop. Food 2013, 4, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Russo, C.; Tufi, E. Consumer Behavior Under Conflicting Information Provided by Interested Parties: Implications for Equilibrium in the Market for Credence Goods. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2016, 8, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shew, A.M.; Danforth, D.M.; Nalley, L.L.; Nayga, R.M.; Tsiboe, F.; Dixon, B.L. New innovations in agricultural biotech: Consumer acceptance of topical RNAi in rice production. Food Control. 2017, 81, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Chern, W.S. Willingness to Pay for Non-Genetically Modified Food: Evidence of Hypothetical Bias from An Auction Experiment in Japan 2004. Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/20305/ (accessed on 18 August 2020).
- Bennett, A.B.; Chi-Ham, C.; Barrows, G.; Sexton, S.; Zilberman, D. Agricultural Biotechnology: Economics, Environment, Ethics, and the Future. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2013, 38, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Font, M.; Gil, J.M.; Traill, W.B. Consumer acceptance, valuation of and attitudes towards genetically modified food: Review and implications for food policy. Food Policy 2008, 33, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frewer, L.J.; Coles, D.; Houdebine, L.-M.; Kleter, G. Attitudes towards genetically modified animals in food production. Br. Food J. 2014, 116, 1291–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolia, A.; Manzo, A.; Veronesi, F.; Rosellini, D. An overview of the last 10 years of genetically engineered crop safety research. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2013, 34, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, G. The necessary “GMO” denialism and scientific consensus. J. Sci. Commun. 2016, 15, Y01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, K. Why are US and EU policies toward GMOs so different? AgBioForum 2003, 6, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bäck, H.; Debus, M.; Tosun, J. Partisanship, Ministers, and Biotechnology Policy. Rev. Policy Res. 2015, 32, 556–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseler, J.; Kalaitzandonakes, N. Present and Future EU GMO Policy. In Palgrave Advances in Bioeconomy: Economics and Policies; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 245–256. [Google Scholar]
- Popek, S.; Halagarda, M. Genetically modified foods: Consumer awareness, opinions and attitudes in selected EU countries. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2017, 27, 277–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, N.; Perito, M.A.; Lupi, C. Consumer acceptance of cultured meat: Some hints from Italy. Br. Food J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Marre, K.N.; Witte, C.L.; Burkink, T.J.; Grünhagen, M.; Wells, G.J. A Second Generation of Genetically Modified Food. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2007, 13, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Bordonaba, J.G. A literature review on the safety assessment of genetically modified plants. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T. Consumer Buying Behavior of Genetically Modified Fries in Germany. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2013, 19, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurău, C.; Ranchhod, A. The futures of genetically-modified foods: Global threat or panacea? Futures 2016, 83, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsakis, A.M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Kouretas, D.; Balias, G.; Savolainen, K.; Tutelyan, V.A.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Lee, J.D.; Yang, S.-H.; Chung, G. Environmental impacts of genetically modified plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.E.; Inbar, Y.; Rozin, P. Evidence for Absolute Moral Opposition to Genetically Modified Food in the United States. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2016, 11, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, A.T.; Andersen, M.M.; Kappel, K. Are current EU policies on GMOs justified? Transgenic Res. 2019, 28, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.G.; Barone, B.; Behrens, J.H. Genetically modified foods and their social representation. Food Res. Int. 2016, 84, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J. The Nobel Laureates’ Campaign Supporting GMOs. J. Innov. Knowl. 2018, 3, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perito, M.A.; Di Fonzo, A.; Sansone, M.; Russo, C. Consumer acceptance of food obtained from olive by-products. Br. Food J. 2019, 122, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Basu, A.K. Pricing Strategy for GM Food: Impact of Consumer Attitude Heterogeneity and GMO Food Labelling. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 291, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wohlhueter, R.; Zhang, H. Genetically modified foods: A critical review of their promise and problems. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsten, I. Focus on Metaphors: The Case of “Frankenfood” on the Web. J. Comput. Commun. 2006, 8, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniazeva, M. Marketing “Frankenfood”. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2006, 11, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, B.; Perrissol, S.; Facca, L.; Smeding, A. From risk perception to information selection… And not the other way round: Selective exposure mechanisms in the field of genetically modified organisms. Food Qual. Prefer. 2017, 58, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComas, K.A.; Besley, J.C.; Steinhardt, J. Factors influencing U.S. consumer support for genetic modification to prevent crop disease. Appetite 2014, 78, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielby, H.; Sandøe, P.; Lassen, J. The role of scientific knowledge in shaping public attitudes to GM technologies. Public Underst. Sci. 2012, 22, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Hwang, J.Y.; Lee, H.G.; Song, M.K.; Kang, Y.S.; Rhee, M.S. Strategic approaches to communicating with food consumers about genetically modified food. Food Control. 2018, 92, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Lee, S.Y. Genetically Engineered Food Labels, Information or Warning to Consumers? J. Food Prod. Mark. 2003, 9, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamotani, S.; Hooker, N.; Smith, S.; Lee, K. Consumer Acceptance of Ozone-Treated Whole Shell Eggs. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, S103–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusk, J.L.; Roosen, J.; Bieberstein, A. Consumer Acceptance of New Food Technologies: Causes and Roots of Controversies. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2014, 6, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marette, S.; Roosen, J. Bans and labels with controversial food technologies. In The Oxford Handbook of the Economics of Food Consumption and Policy; Roosen, J., Lusk, J.L., Shogren, J.F., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 499–519. [Google Scholar]
- Lerro, M.; Raimondo, M.; Stanco, M.; Nazzaro, C.; Marotta, G. Cause Related Marketing among Millennial Consumers: The Role of Trust and Loyalty in the Food Industry. Sustainability 2019, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, T.; Lavelle, F.; Spence, M.; Elliott, C.T.; Dean, M. The development and validation of a toolkit to measure consumer trust in food. Food Control. 2020, 110, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderoni, S.; Perito, M.A. Sustainable consumption in the circular economy. An analysis of consumers’ purchase intentions for waste-to-value food. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Shepherd, R. Effects of information from sources in conflict and in consensus on perceptions of genetically modified food. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.T. Elements of public trust in the American food system: Experts, organizations, and genetically modified food. Food Policy 2013, 41, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, C.; Bird, N.; Nucci, M. The Flow of Scientific Knowledge from Lab to the Lay Public. Sci. Commun. 2004, 26, 44–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Steur, H.; Liqun, G.; Van Der Straeten, D.; Lambert, W.; Gellynck, X. The Potential Market for GM Rice with Health Benefits in a Chinese High-Risk Region. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2014, 21, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, K.T. A New Approach to Consumer Theory. J. Political Econ. 1966, 74, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddala, G.S. Limited-Dependent and Qualitative Variables in Econometrics; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Font, M.; Gil, J.M. Meta-attitudes and the local formation of consumer judgments towards genetically modified food. Br. Food J. 2012, 114, 1463–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpato, D.; Rotondo, G.; Simeone, M.; Gómez, A.; Gutiérrez, P. How can food companies attract the consumer concerned about food safety? A logit model analysis in Spain. Br. Food J. 2017, 119, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perito, M.A.; Coderoni, S.; Russo, C. Consumer Attitudes towards Local and Organic Food with Upcycled Ingredients: An Italian Case Study for Olive Leaves. Foods 2020, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Talia, E.; Simeone, M.; Scarpato, D. Consumer behaviour types in household food waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, M.; Scarpato, D. Sustainable consumption: How does social media affect food choices? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 124036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Count | Age (Average) | Gender (Proportion) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Program | Degree | No. | Years | F | M |
| Not STEM | Undergrad. | 58 | 21 | 0.59 | 0.41 |
| Master | 22 | 25 | 0.82 | 0.18 | |
| STEM | Undergrad. | 126 | 21 | 0.71 | 0.29 |
| Master | 9 | 24 | 0.78 | 0.22 | |
| Total | 215 | 21 | 0.69 | 0.31 | |
| GMO Products Are Safe | GMO Products May Cause Cancer | GMO Products May Change My Body Cells | GMO Products May Cause Allergies | GMO Prod. May Help Preventing Diseases | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | |
| GEN | 0.385 | 0.169 | 0.022 | −0.190 | 0.159 | 0.232 | −0.089 | 0.172 | 0.606 | −0.035 | 0.159 | 0.824 | −0.076 | 0.169 | 0.654 | |
| GRAD | −0.251 | 0.285 | 0.379 | 0.645 | 0.366 | 0.078 | −0.258 | 0.281 | 0.358 | −0.390 | 0.259 | 0.132 | −0.270 | 0.297 | 0.363 | |
| STEM | 0.704 | 0.205 | 0.001 | −0.446 | 0.195 | 0.022 | −0.315 | 0.188 | 0.094 | −0.222 | 0.191 | 0.244 | 0.372 | 0.182 | 0.042 | |
| STEM*GRAD | 0.548 | 0.525 | 0.296 | −0.503 | 0.435 | 0.247 | −0.180 | 0.505 | 0.721 | 0.474 | 0.527 | 0.369 | 0.527 | 0.541 | 0.330 | |
| tipj variables | Farmers | 0.019 | 0.109 | 0.862 | −0.072 | 0.103 | 0.487 | 0.209 | 0.111 | 0.060 | −0.085 | 0.103 | 0.409 | −0.224 | 0.106 | 0.034 |
| Corporations | 0.345 | 0.095 | 0.000 | −0.291 | 0.101 | 0.004 | −0.361 | 0.087 | 0.000 | −0.144 | 0.095 | 0.130 | 0.126 | 0.090 | 0.163 | |
| Environ. Assoc. | −0.246 | 0.088 | 0.005 | 0.248 | 0.092 | 0.007 | 0.240 | 0.100 | 0.016 | 0.028 | 0.088 | 0.753 | −0.257 | 0.081 | 0.001 | |
| Cons. Assoc. | −0.058 | 0.116 | 0.617 | 0.066 | 0.115 | 0.563 | −0.179 | 0.119 | 0.132 | 0.168 | 0.114 | 0.139 | −0.115 | 0.109 | 0.291 | |
| Physicians | −0.062 | 0.118 | 0.600 | 0.001 | 0.107 | 0.993 | −0.029 | 0.099 | 0.772 | −0.097 | 0.115 | 0.398 | −0.093 | 0.102 | 0.365 | |
| Researchers | 0.530 | 0.126 | 0.000 | −0.364 | 0.104 | 0.000 | −0.221 | 0.113 | 0.052 | −0.054 | 0.109 | 0.619 | 0.183 | 0.109 | 0.092 | |
| Friends/Relativ. | −0.065 | 0.098 | 0.506 | 0.150 | 0.123 | 0.221 | 0.142 | 0.113 | 0.210 | 0.080 | 0.118 | 0.495 | 0.086 | 0.104 | 0.413 | |
| ATIP | 0.711 | 0.235 | 0.002 | −0.459 | 0.193 | 0.017 | −0.156 | 0.253 | 0.537 | 0.229 | 0.235 | 0.331 | 0.527 | 0.226 | 0.020 | |
| cml variables | Newsp./Mag. | −0.144 | 0.157 | 0.359 | 0.188 | 0.164 | 0.232 | −0.028 | 0.193 | 0.887 | 0.351 | 0.159 | 0.027 | −0.303 | 0.155 | 0.051 |
| Radio | 0.086 | 0.146 | 0.553 | 0.079 | 0.149 | 0.597 | 0.328 | 0.162 | 0.043 | −0.051 | 0.163 | 0.757 | 0.103 | 0.157 | 0.509 | |
| TV | 0.015 | 0.158 | 0.926 | −0.149 | 0.139 | 0.284 | −0.091 | 0.150 | 0.544 | 0.138 | 0.164 | 0.400 | −0.138 | 0.149 | 0.352 | |
| Websites | 0.177 | 0.135 | 0.191 | −0.032 | 0.142 | 0.822 | −0.091 | 0.178 | 0.611 | 0.063 | 0.154 | 0.682 | −0.051 | 0.152 | 0.739 | |
| Blogs | 0.031 | 0.134 | 0.815 | −0.049 | 0.148 | 0.743 | 0.097 | 0.149 | 0.514 | 0.287 | 0.147 | 0.051 | −0.331 | 0.162 | 0.042 | |
| Social Media | 0.063 | 0.124 | 0.610 | 0.087 | 0.109 | 0.423 | 0.048 | 0.119 | 0.685 | 0.109 | 0.139 | 0.432 | 0.044 | 0.130 | 0.734 | |
| P2P Media | −0.137 | 0.137 | 0.319 | −0.104 | 0.148 | 0.482 | 0.133 | 0.142 | 0.350 | 0.157 | 0.170 | 0.358 | −0.176 | 0.160 | 0.272 | |
| e-Buzzword | 0.058 | 0.122 | 0.634 | −0.076 | 0.102 | 0.453 | 0.053 | 0.107 | 0.622 | −0.036 | 0.130 | 0.782 | −0.115 | 0.121 | 0.341 | |
| ACM | −0.073 | 0.158 | 0.641 | 0.349 | 0.143 | 0.015 | 0.125 | 0.154 | 0.415 | 0.004 | 0.148 | 0.981 | −0.060 | 0.142 | 0.674 | |
| constant | −1.651 | 0.788 | 0.036 | 5.469 | 1.490 | 0.000 | 1.759 | 0.743 | 0.018 | 1.251 | 0.739 | 0.090 | −0.698 | 0.667 | 0.295 | |
| Trust effect | 𝜒2(7) | 49.817 | 0.000 | 48.986 | 0.000 | 47.820 | 0.000 | 8.434 | 0.296 | 32.151 | 0.000 | |||||
| Media effect | 𝜒2(8) | 6.305 | 0.505 | 2.801 | 0.903 | 7.075 | 0.421 | 3.976 | 0.783 | 9.882 | 0.273 | |||||
| Education eff. | 𝜒2(3) | 21.392 | 0.000 | 13.389 | 0.004 | 4.344 | 0.227 | 2.891 | 0.409 | 9.065 | 0.028 | |||||
| Conventional Products Are Better for the Environment | GMO Products Use Less Natural Resources | GMO Products Have Less Pesticide Residuals | GMO Products May Help Mitigating Climate Change | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | |
| GEN | −0.119 | 0.166 | 0.475 | 0.011 | 0.173 | 0.951 | 0.255 | 0.166 | 0.125 | −0.624 | 0.190 | 0.001 | |
| GRAD | −0.075 | 0.282 | 0.790 | −0.349 | 0.241 | 0.148 | 0.266 | 0.281 | 0.345 | −0.850 | 0.328 | 0.010 | |
| STEM | −0.021 | 0.186 | 0.911 | −0.208 | 0.181 | 0.249 | 0.247 | 0.177 | 0.162 | −0.429 | 0.174 | 0.014 | |
| STEM*GRAD | 0.021 | 0.422 | 0.960 | 0.840 | 0.452 | 0.063 | 0.061 | 0.509 | 0.905 | 0.768 | 0.392 | 0.050 | |
| tipj | Farmers | 0.133 | 0.098 | 0.173 | 0.033 | 0.098 | 0.734 | −0.170 | 0.095 | 0.074 | 0.106 | 0.093 | 0.255 |
| variables | Corporations | −0.255 | 0.099 | 0.010 | −0.105 | 0.092 | 0.255 | 0.154 | 0.098 | 0.115 | −0.287 | 0.092 | 0.002 |
| Environ. Assoc. | 0.171 | 0.091 | 0.062 | −0.246 | 0.089 | 0.006 | −0.293 | 0.092 | 0.001 | −0.013 | 0.084 | 0.879 | |
| Consumer Assoc. | 0.140 | 0.111 | 0.210 | 0.197 | 0.125 | 0.116 | 0.040 | 0.121 | 0.744 | −0.018 | 0.122 | 0.886 | |
| Physicians | −0.114 | 0.105 | 0.278 | −0.116 | 0.109 | 0.289 | 0.199 | 0.104 | 0.055 | −0.112 | 0.113 | 0.321 | |
| Researchers | −0.141 | 0.126 | 0.263 | 0.178 | 0.111 | 0.108 | 0.200 | 0.106 | 0.060 | −0.112 | 0.118 | 0.341 | |
| Friends/Relatives | 0.024 | 0.112 | 0.833 | −0.184 | 0.106 | 0.082 | −0.184 | 0.104 | 0.078 | −0.045 | 0.108 | 0.678 | |
| ATIP | −0.170 | 0.204 | 0.405 | 0.239 | 0.239 | 0.316 | 0.550 | 0.222 | 0.013 | −0.520 | 0.182 | 0.004 | |
| cml | Newspaper | −0.102 | 0.180 | 0.573 | 0.344 | 0.198 | 0.082 | 0.035 | 0.174 | 0.842 | −0.264 | 0.170 | 0.120 |
| variables | Radio | 0.004 | 0.176 | 0.983 | 0.100 | 0.150 | 0.504 | 0.004 | 0.157 | 0.979 | 0.114 | 0.148 | 0.441 |
| TV | −0.112 | 0.153 | 0.465 | 0.146 | 0.147 | 0.321 | 0.077 | 0.156 | 0.623 | −0.156 | 0.158 | 0.324 | |
| Websites | −0.248 | 0.154 | 0.106 | 0.103 | 0.171 | 0.546 | 0.075 | 0.168 | 0.653 | 0.193 | 0.161 | 0.232 | |
| Blogs | −0.156 | 0.164 | 0.339 | 0.238 | 0.176 | 0.176 | −0.117 | 0.155 | 0.449 | 0.047 | 0.170 | 0.781 | |
| Social Media | −0.260 | 0.125 | 0.038 | 0.078 | 0.120 | 0.515 | 0.147 | 0.123 | 0.231 | 0.000 | 0.136 | 0.998 | |
| P2P Media | −0.264 | 0.170 | 0.119 | 0.261 | 0.157 | 0.097 | 0.051 | 0.170 | 0.764 | −0.088 | 0.165 | 0.594 | |
| e-Buzzword | −0.079 | 0.132 | 0.548 | −0.016 | 0.129 | 0.903 | 0.057 | 0.128 | 0.656 | −0.062 | 0.124 | 0.618 | |
| ACM | 0.246 | 0.145 | 0.089 | −0.102 | 0.149 | 0.493 | −0.187 | 0.149 | 0.208 | 0.547 | 0.155 | 0.000 | |
| constant | 1.637 | 0.667 | 0.014 | 1.453 | 0.811 | 0.073 | 0.005 | 0.693 | 0.994 | 1.938 | 0.675 | 0.004 | |
| Trust effect | chi2(7) | 26.109 | 0.000 | 19.896 | 0.006 | 37.070 | 0.000 | 17.233 | 0.016 | ||||
| Media effect | chi2(7) | 9.628 | 0.292 | 8.879 | 0.353 | 3.357 | 0.910 | 8.758 | 0.363 | ||||
| Education eff. | chi2(3) | 0.088 | 0.993 | 3.789 | 0.285 | 3.124 | 0.373 | 9.257 | 0.026 | ||||
| GMO Products may Help Fighting World Hunger | GMO Products Are Not Natural | GMO Products Do Not Respect Life | GMO Products Are for Profits Only | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | Coef. | S. Err. | p-Val. | |
| GEN | 0.294 | 0.169 | 0.082 | −0.236 | 0.171 | 0.169 | −0.432 | 0.186 | 0.021 | −0.220 | 0.189 | 0.245 | |
| GRAD | −0.648 | 0.271 | 0.017 | 0.103 | 0.311 | 0.741 | 0.058 | 0.301 | 0.846 | −0.466 | 0.272 | 0.086 | |
| STEM | 0.201 | 0.177 | 0.256 | −0.239 | 0.202 | 0.238 | −0.446 | 0.184 | 0.015 | −0.162 | 0.180 | 0.370 | |
| STEM*GRAD | 0.359 | 0.378 | 0.342 | −0.313 | 0.438 | 0.475 | 0.300 | 0.398 | 0.451 | 0.800 | 0.394 | 0.042 | |
| tipj | Farmers | −0.083 | 0.109 | 0.446 | 0.055 | 0.111 | 0.623 | 0.064 | 0.098 | 0.518 | 0.216 | 0.097 | 0.026 |
| variables | Corporations | 0.235 | 0.111 | 0.035 | −0.374 | 0.099 | 0.000 | −0.290 | 0.083 | 0.000 | −0.159 | 0.087 | 0.069 |
| Environ. Assoc. | −0.135 | 0.101 | 0.182 | 0.078 | 0.097 | 0.423 | 0.099 | 0.099 | 0.316 | 0.222 | 0.092 | 0.016 | |
| Consumer Assoc. | 0.028 | 0.132 | 0.830 | 0.148 | 0.121 | 0.220 | 0.283 | 0.123 | 0.021 | 0.227 | 0.121 | 0.059 | |
| Physicians | 0.104 | 0.095 | 0.270 | −0.025 | 0.105 | 0.815 | −0.056 | 0.101 | 0.583 | −0.078 | 0.100 | 0.434 | |
| Researchers | 0.162 | 0.117 | 0.169 | 0.013 | 0.118 | 0.912 | −0.218 | 0.118 | 0.064 | −0.269 | 0.116 | 0.020 | |
| Friends/Relatives | −0.129 | 0.112 | 0.248 | −0.006 | 0.103 | 0.951 | 0.099 | 0.103 | 0.337 | 0.189 | 0.110 | 0.087 | |
| ATIP | 0.047 | 0.226 | 0.836 | 0.116 | 0.211 | 0.583 | −0.167 | 0.224 | 0.457 | −0.763 | 0.236 | 0.001 | |
| cml | Newspaper | −0.137 | 0.178 | 0.440 | 0.255 | 0.165 | 0.123 | 0.026 | 0.187 | 0.887 | 0.005 | 0.177 | 0.976 |
| variables | Radio | −0.183 | 0.157 | 0.245 | 0.145 | 0.151 | 0.334 | 0.196 | 0.169 | 0.246 | −0.103 | 0.158 | 0.515 |
| TV | 0.176 | 0.148 | 0.234 | −0.040 | 0.164 | 0.806 | 0.085 | 0.177 | 0.633 | −0.066 | 0.148 | 0.654 | |
| Websites | −0.112 | 0.160 | 0.482 | 0.158 | 0.170 | 0.354 | 0.032 | 0.176 | 0.857 | −0.163 | 0.166 | 0.325 | |
| Blogs | −0.184 | 0.156 | 0.239 | 0.012 | 0.174 | 0.947 | 0.124 | 0.192 | 0.520 | −0.188 | 0.170 | 0.270 | |
| Social Media | −0.189 | 0.138 | 0.173 | −0.025 | 0.129 | 0.846 | 0.043 | 0.139 | 0.756 | 0.199 | 0.129 | 0.123 | |
| P2P Media | 0.163 | 0.173 | 0.345 | 0.038 | 0.157 | 0.810 | 0.014 | 0.176 | 0.938 | −0.185 | 0.157 | 0.239 | |
| e-Buzzword | −0.168 | 0.120 | 0.160 | −0.042 | 0.139 | 0.762 | −0.030 | 0.139 | 0.830 | −0.147 | 0.131 | 0.261 | |
| ACM | −0.085 | 0.145 | 0.558 | 0.313 | 0.133 | 0.019 | 0.283 | 0.167 | 0.090 | 0.382 | 0.155 | 0.014 | |
| constant | 0.963 | 0.765 | 0.208 | 0.655 | 0.740 | 0.376 | 1.309 | 0.736 | 0.075 | 2.957 | 0.723 | 0.000 | |
| Trust effect | chi2(7) | 24.497 | 0.000 | 25.611 | 0.000 | 40.947 | 0.000 | 51.866 | 0.000 | ||||
| Media effect | chi2(8) | 11.999 | 0.151 | 7.837 | 0.450 | 3.666 | 0.886 | 7.136 | 0.522 | ||||
| Education effect | chi2(3) | 12.295 | 0.006 | 3.338 | 0.342 | 7.539 | 0.057 | 4.401 | 0.221 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, C.; Simeone, M.; Perito, M.A. Educated Millennials and Credence Attributes of Food Products with Genetically Modified Organisms: Knowledge, Trust and Social Media. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208534
Russo C, Simeone M, Perito MA. Educated Millennials and Credence Attributes of Food Products with Genetically Modified Organisms: Knowledge, Trust and Social Media. Sustainability. 2020; 12(20):8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208534
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Carlo, Mariarosaria Simeone, and Maria Angela Perito. 2020. "Educated Millennials and Credence Attributes of Food Products with Genetically Modified Organisms: Knowledge, Trust and Social Media" Sustainability 12, no. 20: 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208534
APA StyleRusso, C., Simeone, M., & Perito, M. A. (2020). Educated Millennials and Credence Attributes of Food Products with Genetically Modified Organisms: Knowledge, Trust and Social Media. Sustainability, 12(20), 8534. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208534






