Behavior of Rejects from a Biological-Mechanical Treatment Plant on the Landfill to Laboratory Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
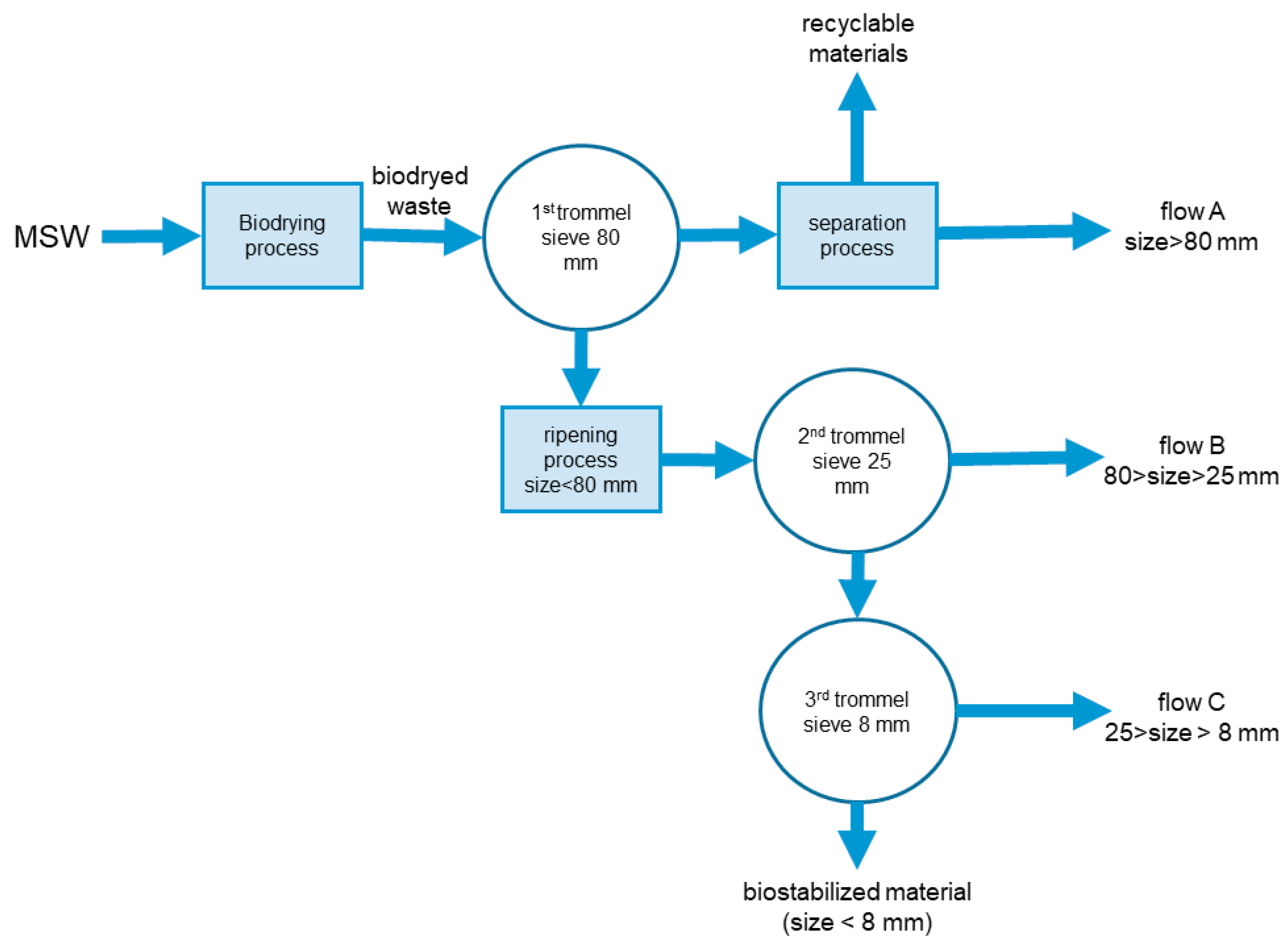
2.1. Sample Collection and Physical Characterisation
2.2. Initial Determination of Rejects’ Properties
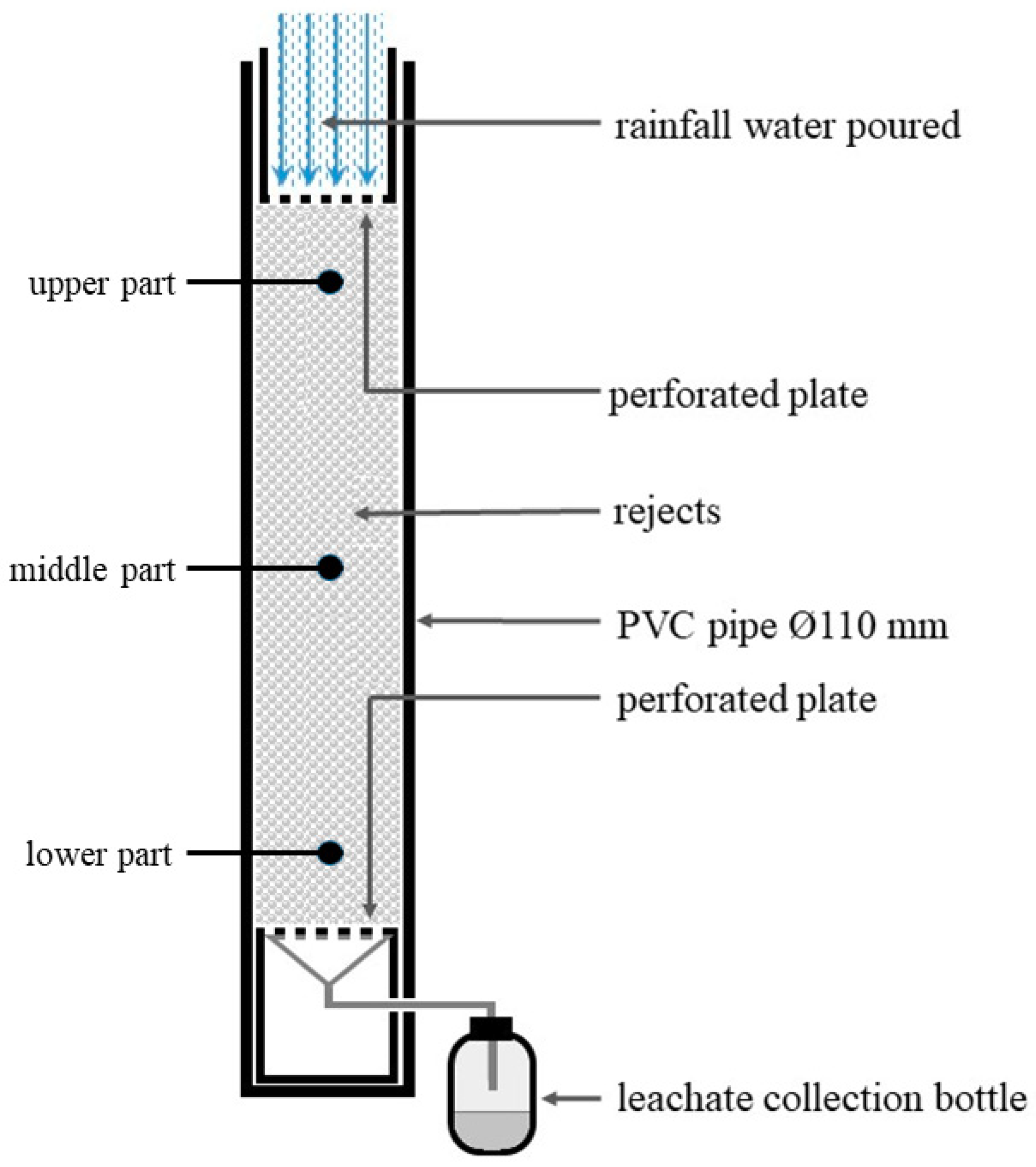
2.3. Construction and Filling of the Four Lysimeters
2.4. Experimental Phase
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterisation of the Initial Reject
3.2. Determination of the FC of Rejects
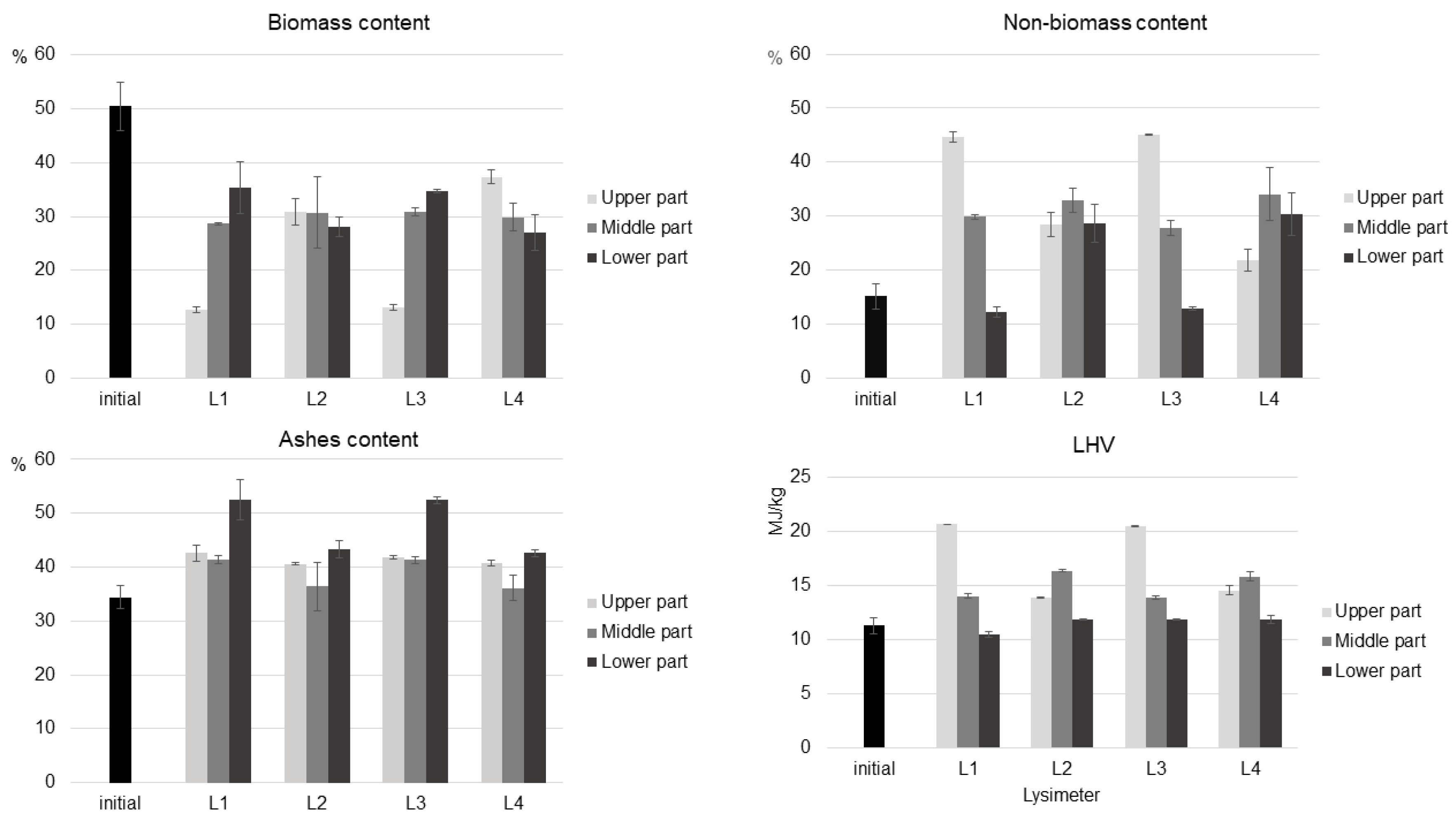
3.3. Influence of Recirculation on Rejects’ Properties
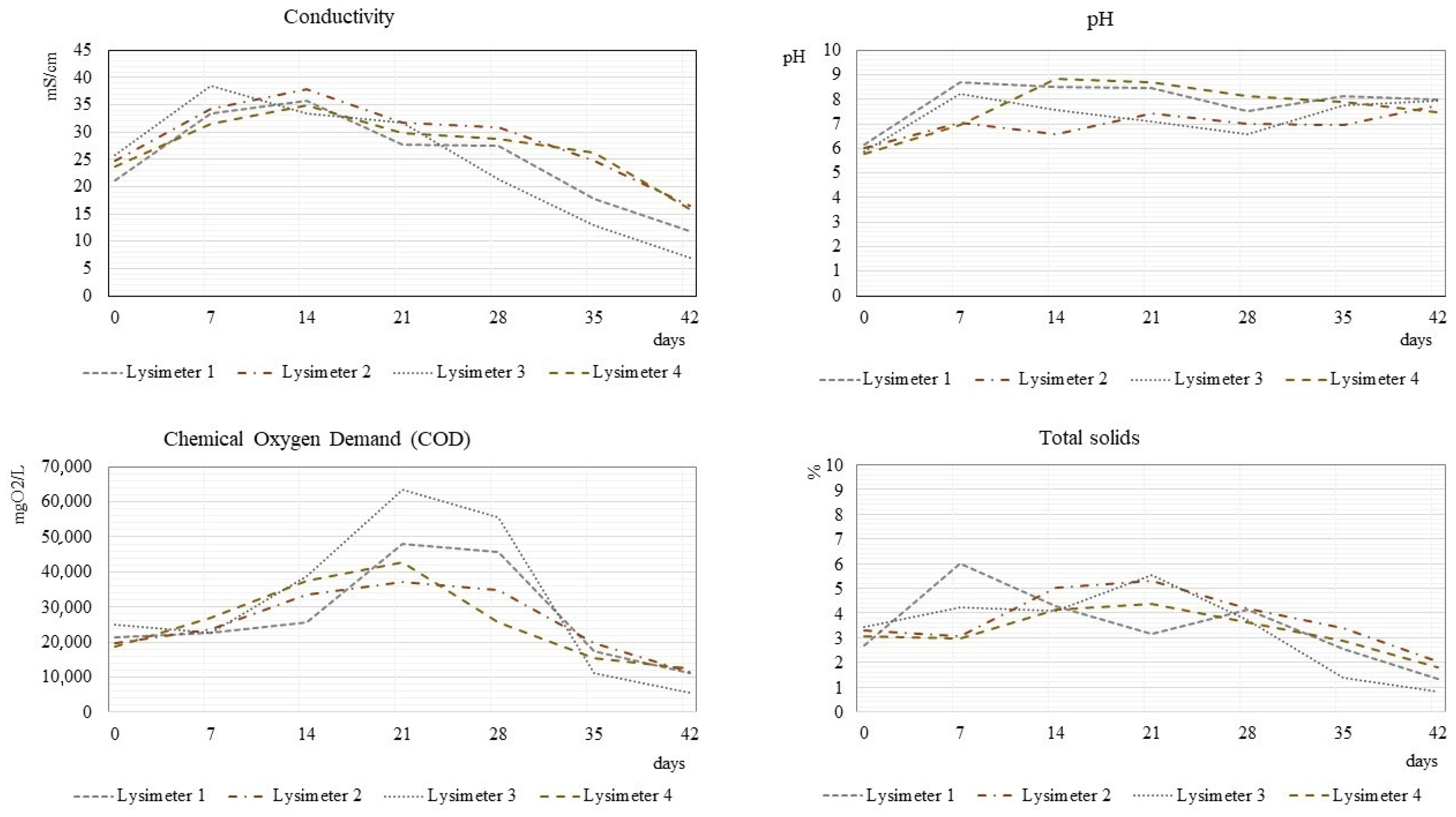
3.4. Properties of Leachate Evolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the Landfill of Waste. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31999L0031&from=ENN (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Paoli, L.; Corsini, A.; Bigagli, V.; Vannini, J.; Bruscoli, C.; Loppi, S. Long-term biological monitoring of environmental quality around a solid waste landfill assessed with lichens. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaro, A.; Russo, L.; Farina, A.; Belgiorno, V. Organic fraction of municipal solid waste from mechanical selection: Biological stabilization and recovery options. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Altabella, J.; Colomer-Mendoza, F.J.; Gallardo-Izquierdo, A. Simulation of the behavior of a refuse landfill on a laboratory scale. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edo-Alcón, N.; Gallardo, A.; Colomer-Mendoza, F.J. Characterization of SRF from MBT plants: Influence of the input waste and of the processing technologies. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 153, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, A.; Carlos, M.; Bovea, M.D.; Colomer, F.J.; Albarrán, F. Analysis of refuse-derived fuel from the municipal solid waste reject fraction and its compliance with quality standards. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montejo, C.; Costa, C.; Ramos, P.; Márquez, M.C. Analysis and comparison of municipal solid waste and reject fraction as fuels for incineration plants. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krook, J.; Svensson, N.; Eklund, M. Landfill mining: A critical review of two decades of research. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Z.Y.; Bilitewski, B.; Zhu, N.; Chai, W.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y. Environmental impacts of a large-scale incinerator with mixed MSW of high water content from a LCA perspective. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlaz, M.A.; Ham, R.K.; Schaefer, D.M. Methane production from municipal refuse: A review of enhancement techniques and microbial dynamics. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1990, 19, 557–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, B.S.; Anto, C.A.; Singh, D.N. Simulation of municipal solid waste degradation in aerobic and anaerobic bioreactor landfills. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialowiec, A.; Siudak, M.; Jakubowski, B.; Wisniewski, D. The influence of leachate recirculation on biogas production in a landfill bioreactor. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2017, 43, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbelkacem, H.; Bayard, R.; Abdelhay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Gourdon, R. Effect of leachate injection modes on municipal solid waste degradation in anaerobic bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5206–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkare, T.J.; Palmroth, M.R.T.; Rintala, J.A. Screening biological methods for laboratory scale stabilization of fine fraction from landfill mining. Waste Manag. 2015, 60, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öman, C.; Hynning, P.A. Identification of organic compounds in municipal landfill leachates. Environ. Pollut. 1991, 80, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šan, I.; Onay, T.T. Impact of various leachate recirculation regimes on municipal solid waste degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 87, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledakowicz, S.; Kaczorek, K. Laboratory simulation of anaerobic digestion of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2004, 39, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.Y.S.; Chu, L.M.; Wong, M.H. Effects of leachate recirculation on biogas production from landfill co-disposal of municipal solid waste, sewage sludge and marine sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 118, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Jung, S.; Chang, S. The Influence of Waste Composition on Landfill Gas Generation in a Pilot-Scale Lysimeter. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaradin, M.; Persson, K.M. The emission potential from municipal solid waste landfill in Jordan. J. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 17, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godio, A.; Arato, A.; Chiampo, F.; Ruggeri, B.; Di Addario, M.; Fischetti, M.; Perissinotto, E. Liquid injection to enhance biogas production in landfills for pretreated municipal solid wastes—BIO-LEAR Project (LIFE Plus Program). Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnolo, M.C.; Grossule, V.; Raga, R. Innovative dual-step management of semi-aerobic landfill in a tropical climate. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.F.; Shimaoka, T.; Nakayama, H.; Komiya, T.; Chai, X.L. Stimulation of waste decomposition in an old landfill by air injection. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slezak, R.; Krzystek, L.; Ledakowicz, S. Degradation of municipal solid waste in simulated landfill bioreactors under aerobic conditions. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowska, D.; Sołtysiak, M.; Biniecka, P.; Michalska, J.; Wasilkowski, D.; Nowak, A.; Nourani, V. Application of hydrogeological and biological research for the lysimeter experiment performance under simulated municipal landfll condition. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2019, 21, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Turnhout, A.G.; Brandstätter, C.; Kleerebezem, R.; Fellner, J.; Heimovaara, T.J. Theoretical analysis of municipal solid waste treatment by leachate recirculation under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, T.; Lu, W. Evolution of unsaturated hydraulic properties of municipal solid waste with landfill depth and age. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthasil, N.; Chiemchaisri, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Wangyao, K.; Towprayoon, S.; Endo, K.; Yamada, M. Comparison of solid waste stabilization and methane emission from anaerobic and semi-aerobic landfills operated in tropical condition. Environ. Eng. Res. 2014, 19, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.L.; Nobrega, B.M.A.; Sousa, R.B.A.; Melo, M.C.; Paiva, W.; Monteiro, V.E.D. Statistical Modeling of Municipal Solid Waste Settlement from a Lysimeter. Soils Rocks 2017, 40, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, M.C.; Caribe, R.M.; Ribeiro, L.S.; Sousa, R.B.A.; Monteiro, V.E.D.; de Paiva, W. Settlement behavior of municipal solid waste due to internal and external environmental factors in a lysimeter. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2016, 51, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, R.; Lai, T.; Pivnenko, K. Waste washing pre-treatment of municipal and special waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 207–208, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Methodology for the Analysis of Solid Waste (SWA-Tool); iC consuleten ZT Gmbh: Kaiserstrasse, Austria, 2004; Available online: https://www.wien.gv.at/meu/fdb/pdf/swa-tool-759-ma48.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Hemidat, S.; Saidan, M.; Al-Zu’bi, S.; Irshidat, M.; Nassour, A.; Nelles, M. Potential Utilization of RDF as an Alternative Fuel to be Used in Cement Industry in Jordan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, D.; Martin-Marroquin, J.M.; Corona, F. A multi-waste management concept as a basis towards a circular economy model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 11, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drudi, K.C.R.; Drudi, R.; Martins, G.; Antonio, G.C.; Leite, J.T.C. Statistical model for heating value of municipal solid waste in Brazil based on gravimetric composition. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.P.; Veksha, A.; Lei, J.; Oh, W.D.; Dou, X.; Gianis, A.; Lisak, G.; Lim, T.T. A novel real-time monitoring and control system for waste-to-energy gasification process employing differential temperature profiling of a downdraft gasifier. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearse, L.F.; Hettiaratchi, J.P.; Kumar, S. Towards developing a representative biochemical methane potential (BMP) assay for landfilled municipal solid waste—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chen, Y.M.; Zhan, L.T.; Bian, X.C. Engineering properties for high kitchen waste content municipal solid waste. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 7, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orta de Velásquez, M.T.; Cruz-Rivera, R.; Rojas-Valencia, N.; Monje-Ramírez, I. Determination of field capacity of municipal solid waste with surcharge simulation. Waste Manag. Res. 2003, 21, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, R.A. Determinación De Los Parámetros Hidrológicos En Rellenos Sanitarios En México. In Caso De Estudio: Tlalnepantla. Estado De México. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico, Mexico City, México, 2008; p. 106. Available online: http://132.248.52.100:8080/xmlui/bitstream/handle/132.248.52.100/2183/aguilarvera.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 8 January 2019).
- Cox, J.T.; Yesiller, N.; Hanson, J.L. Implications of variable waste placement conditions for MSW landfills. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, L. Moisture retention of municipal solid waste mixed with sewage sludge and ash in a semi-arid climate. Waste Manag. Res. 2005, 23, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, K.P.K.; Komiya, S.T.T.; Ehler, P. Laboratory determination of water retention characteristics and pore size distribution in simulated MSW landfill under settlement. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, A.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. A field investigation of the quantity and quality of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill in a Mediterranean climate (Thessaloniki, Greece). Adv. Environ. Res. 2002, 6, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-J.; Shu, H.-Y.; Yang, H.-S.; Chen, W.-C. Characteristics of landfill leachates in central Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 361, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, Z.; Hamouri, K.; Djemaa, R.; Allia, K. Evaluation of landfill leachate pollution and treatment. Desalination 2008, 220, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salam, M.M.A.; Abu-Zuid, G.I. Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: A case study in Egypt. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, B.P.; Mahapatra, D.M.; Sitharam, T.G.; Sivapullaiah, P.V.; Ramachandra, T.V. Physico-chemical and biological characterization of urban municipal landfill leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisey, E.; Aleya, L. Prolonged aerobic degradation of shredded and pre-composted municipal solid waste: Report from a 21-year study of leachate quality characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 800–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.C.; Sacks, J.; Senior, E. Irrigation of soil with synthetic landfill leachate—Speciation and distribution of selected pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 106, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsi, A.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Coagulation–flocculation pretreatment of sanitary landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes de Morais, J.; Peralta Zamora, P. Use of advanced oxidation processes to improve the biodegradability of mature landfill leachates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 123, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Qi, X.D.; Liu, Z.G. Landfill leachate production, quality and recirculation treatment in northeast China. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 625–628. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Chen, W.; Wen, P.; Jiang, G.; Li, Q. Impact of leachate recirculation frequency on the conversion of carbon and nitrogen in a semi-aerobic bioreactor landfill. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 13354–13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltz, G.; Gourc, J.P.; Oxarango, L. Liquid and gas permeabilities of unsaturated municipal solid waste under compression. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 118, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.J.; Cao, B.Y.; Xie, H.J. Modelling of leachate recirculation using spraying-vertical well systems in bioreactor landfills. Int. J. Geomech. 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, M.S.; Demir, A.; Özkaya, B. Influence of leachate recirculation on aerobic and anaerobic decomposition of solid wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Physical Composition Dirty Material % | Dirt in the Waste (%) | Physical Composition Clean Material% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | |||
| Organic waste | 12.95 | --- | --- | 25.53 * |
| Wood | 2.85 | 15.16 | 5.19 | 2.42 |
| Paper and cardboard | 25.12 | 9.77 | 2.21 | 22.67 |
| Plastic | 29.21 | 11.23 | 1.95 | 25.93 |
| Glass | 3.76 | 7.59 | 2.01 | 3.48 |
| Textile | 16.02 | 13.49 | 2.03 | 13.86 |
| Metals | 3.55 | 10.76 | 4.56 | 3.17 |
| Hazardous waste | 0.02 | --- | --- | 0.02 |
| Inert | 3.25 | 3.52 | 1.98 | 3.25 |
| Others | 3.27 | 9.56 | 5.21 | 2.96 |
| Start of the Assay | End of the Assay (400 kg/m3) | End of the Assay (500 kg/m3) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Initial Rejects | Lysimeter 1 | Lysimeter 2 | Lysimeter 3 | Lysimeter 4 | ||||||
| ID | Ud | ||||||||||
| Moisture | % | 19.65 | 2.36 | 60.93 | 4.62 | 59.50 | 7.72 | 59.34 | 2.01 | 58.35 | 7.86 |
| Biomass | % | 50.47 | 3.19 | 28.65 | 0.21 | 30.68 | 4.68 | 30.89 | 0.54 | 29.83 | 1.79 |
| Non-biomass | % | 15.17 | 1.67 | 28.92 | 0.67 | 29.99 | 1.55 | 28.60 | 0.14 | 28.75 | 1.38 |
| Ashes | % | 34.36 | 2.16 | 45.52 | 5.74 | 40.10 | 3.77 | 45.20 | 5.62 | 39.82 | 3.19 |
| LHV (d.w.) | MJ/kg | 11.26 | 0.73 | 15.02 | 4.63 | 13.99 | 2.03 | 14.74 | 4.81 | 14.06 | 1.83 |
| LHV (w.w.) | MJ/kg | 9.06 | 0.58 | 5.87 | 0.17 | 5.83 | 0.11 | 5.99 | 0.15 | 5.86 | 0.24 |
| ID | Parameters | Units | Lysimeter 1 | Lysimeter 2 | Lysimeter 3 | Lysimeter 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DR0 | Initial density | kg/m3 | 400 | 400 | 500 | 500 |
| HR0 | Initial moisture | % | 19.65 | 19.65 | 19.65 | 19.65 |
| VR0 | Initial volume of rejects | m3 | 2.68·10 −3 | 2.68·10 −3 | 2.17·10 −3 | 2.17·10 −3 |
| VI1 | Volume of water added on the first day | L | 1.30 | 1.30 | 1.30 | 1.30 |
| VF1 | Volume of leachate on the first day | L | 0.52 | 0.50 | 0.57 | 0.58 |
| FC | Field Capacity (initial) | kgH2O/kgDRY w | 1.15 | 1.17 | 1.09 | 1.08 |
| FC | Field Capacity (final) | kgH2O/kgDRY W | 1.56 | 1.47 | 1.46 | 1.41 |
| Final volume of leachate | L | 1.57 | 1.40 | 1.73 | 1.38 | |
| Lysimeter 1 | Lysimeter 2 | Lysimeter 3 | Lysimeter 4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent (w) | Effluent | Influent (w + l) | Effluent | Influent (w) | Effluent | Influent (w + l) | Effluent | |
| 1st day | 1.300 | 0.520 | 1300 (w) | 0.500 | 1.300 | 0.570 | 1300 (w) | 0.580 |
| 0.500 (l) | 0.280 | 0.580 (l) | 0.400 | |||||
| 1st week | 0.250 | 0.110 | 0.250 (w) | 0.160 | 0.250 | 0.134 | 0.250 (w) | 0.165 |
| 0.440 (l) | 0.317 | 0.565 (l) | 0.350 | |||||
| 2nd week | 0.250 | 0.150 | 0.250 (w) | 0.220 | 0.250 | 0.170 | 0.250 (w) | 0.170 |
| 0.537 (l) | 0.455 | 0.520 (l) | 0.465 | |||||
| 3rd week | 0.250 | 0.175 | 0.250 (w) | 0.245 | 0.250 | 0.180 | 0.250 (w) | 0.220 |
| 0.700 (l) | 0.665 | 0.685 (l) | 0.650 | |||||
| 4th week | 0.250 | 0.180 | 0.250 (w) | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.190 | 0.250 (w) | 0.250 |
| 0.915 (l) | 0.905 | 0.900 (l) | 0.885 | |||||
| 5th week | 0.250 | 0.205 | 0.250 (w) | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.235 | 0.250 (w) | 0.250 |
| 1.155 (l) | 1.150 | 1.135 (l) | 1.130 | |||||
| 6th week | 0.250 | 0.230 | 0.250 (w) | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.250 (w) | 0.250 |
| FINAL BALANCE | 2.800 | 1.570 | 2.800 | 1.400 | 2.800 | 1.729 | 2.800 | 1.380 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esteban-Altabella, J.; Colomer-Mendoza, F.J.; Gallardo, A.; Edo-Alcón, N. Behavior of Rejects from a Biological-Mechanical Treatment Plant on the Landfill to Laboratory Scale. Sustainability 2020, 12, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020499
Esteban-Altabella J, Colomer-Mendoza FJ, Gallardo A, Edo-Alcón N. Behavior of Rejects from a Biological-Mechanical Treatment Plant on the Landfill to Laboratory Scale. Sustainability. 2020; 12(2):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020499
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsteban-Altabella, Joan, Francisco J Colomer-Mendoza, Antonio Gallardo, and Natalia Edo-Alcón. 2020. "Behavior of Rejects from a Biological-Mechanical Treatment Plant on the Landfill to Laboratory Scale" Sustainability 12, no. 2: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020499
APA StyleEsteban-Altabella, J., Colomer-Mendoza, F. J., Gallardo, A., & Edo-Alcón, N. (2020). Behavior of Rejects from a Biological-Mechanical Treatment Plant on the Landfill to Laboratory Scale. Sustainability, 12(2), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020499






