Sanitation Network Sulfide Modeling as a Tool for Asset Management. The Case of the City of Murcia (Spain)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hydraulic Model of Reference
2.2. Experimental Field Campaign in the City of Murcia
2.3. Equations and Algorithm That Conform the EMU-SANETSUL Code
2.3.1. Reaction Equations Based on the Empirical Model Proposed by Matos et al.
2.3.2. Discrete Volume Element Method (DVEM)
2.4. Workflow of the EMU-SANETSUL Code
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calibration of Nodes Comparison with Experimental Measurements
3.2. Asset Management Information from Sulfide Modeling
4. Conclusions
- Pipes located downstream of a pump station;
- Overloaded pipes where the gas phase represents a low surface;
- Higher values of slope or a combination of these.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jiang, G.; Sun, J.; Sharma, K.; Yuan, Z. Corrosion and odor management in sewer systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Environmental Research Information. Odor and Corrosion Control in Sanitary Sewerage Systems and Treatment Plants: Design Manual; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1985.
- Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Vollertsen, J.; Nielsen, A.H. Sewer Processes: Microbial and Chemical Process Engineering of Sewer Networks; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- García, J.T.; Ruiz-Martínez, D.; Vigueras-Rodríguez, A.; Castillo, L.G.; Carrillo, J.M.; Solano, P.D.; Santos, S.N. Análisis de sensibilidad en la generación de sulfuros en redes de saneamiento. Caso de la ciudad de Murcia. In Proceedings of the Jornadas de Ingeniería del Agua JIA Coruña, Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros de Caminos, A Coruña, Spain, 25–26 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Romanova, A.; Mahmoodian, M.; Alani, A. Influence and interaction of temperature, H2S and pH on concrete sewer pipe corrosion. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Struct. Constr. Archit. Eng. 2014, 8, 621–624. [Google Scholar]
- Pikaar, I.; Sharma, K.; Hu, S.; Gernjak, W.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Reducing sewer corrosion through integrated urban water management. Science 2014, 345, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, T.; Melchers, R.E.; Bond, P. Factors involved in the long term corrosion of concrete sewers. In Australasian Corrosion Association Proceedings of Corrosion and Prevention, Coffs Harbour, Australia; Semantic Scholar: Seattle, WA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, G.H.; Brongers, M.P.; Thompson, N.G.; Virmani, Y.P.; Payer, J.H. Corrosion Cost and Preventive Strategies in the United States 2002 (No. FHWA-RD-01-156, R315-01); Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tscheikner-Gratl, F.; Caradot, N.; Cherqui, F.; Leitão, J.P.; Ahmadi, M.; Langeveld, J.G.; Le Gat, Y.; Scholten, L.; Roghani, B.; Rodríguez, J.P.; et al. Sewer asset management—State of the art and research needs. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Fan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Kodagoda, S.; Cunningham, D. Predictive Analytics Toolkit for H2S Estimation and Sewer Corrosion; OZWater: St Leonards, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Caradot, N.; Sonnenberg, H.; Kropp, I.; Ringe, A.; Denhez, S.; Hartmann, A.; Rouault, P. The relevance of sewer deterioration modelling to support asset management strategies. Urban Water J. 2017, 14, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodian, M.; Alani, A. Sensitivity analysis for failure assessment of concrete pipes subjected to sulfide corrosion. Urban Water J. 2016, 13, 637–643. [Google Scholar]
- Sydney, R.; Esfandi, E.; Surapaneni, S. Control concrete sewer corrosion via the crown spray process. Water Environ. Res. 1996, 68, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.T.; Vigueras-Rodriguez, A.; Castillo, L.G.; Carrillo, J.M. Evaluation of sulfide control by air-injection in sewer force mains: Field and laboratory study. Sustainability 2017, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oviedo, E.R.; Johnson, D.; Shipley, H. Evaluation of hydrogen sulfide concentration and control in a sewer system. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland-Stacey, L.; Corrie, S.; Neethling, A.; Johnson, I.; Gutierrez, O.; Dexter, R.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J.; Hamilton, G. Continuous measurement of dissolved sulfide in sewer systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sharma, K.; Fluggen, M.; O’Halloran, K.; Murthy, S.; Yuan, Z. Online dissolved methane and total dissolved sulfide measurement in sewers. Water Res. 2015, 68, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, O.; Sudarjanto, G.; Sharma, K.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. SCORe-CT: A new method for testing effectiveness of sulfide-control chemicals used in sewer systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Vollertsen, J.; Tanaka, N. Wastewater quality changes during transport in sewers—An integrated aerobic and anaerobic model concept for carbon and sulfur microbial transformations. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 257–264, Printed in errata of 39(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollertsen, J.; Nielsen, A.H.; Jensen, H.S.; Rudelle, E.A.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. Modeling the corrosion of concrete sewers. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Urban Drainage, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 11–16 September 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, J.S.; De Sousa, E.R. The forecasting of hydrogen sulfide gas build-up in sewerage collection systems. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, R.D.; Parkhurst, J.D. The forecasting of sulfide build-up rates in sewers. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Water Pollution Research, Sydney, Australia, 17–22 October 1976; pp. 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, A.; Lister, A. Formation of sulfide in rising main sewers and its prevention by injection of oxygen. Prog. Wat. Tech. 1975, 7, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Elmaleh, S.; Delgado, S.; Álvarez, M.; Gómez, L.E.R.; Aguiar, E. Forecasting of HS build-up in a reclaimedwastewater pipe. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongsiri, C.; Vollertsen, J.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. Hydrogen sulfide emission in sewer networks: A two-phase modeling approach to the sulfur cycle. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongsiri, C.; Vollertsen, J.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. Air-water transfer of hydrogen sulfide—An approach for application in sewer networks. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2002, 2002, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, O.; Lu, Y.; Shavit, U.; Loewenthal, R.E. Modeling hydrogen sulfide emission rates in gravity sewage collection systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2004, 130, 1382–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, A.H.; Vollertsen, J.; Jensen, H.S.; Madsen, H.I.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. Aerobic and anaerobic transformations of sulfide in a sewer system—Field study and model simulations. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.H.; Yongsiri, C.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Vollertsen, J. Simulation of sulfide buildup in wastewater and atmosphere of sewer networks. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marleni, N.; Park, K.; Lee, T.; Navaratna, D.; Shu, L.; Jegatheesan, V.; Feliciano, A. A methodology for simulating hydrogen sulfide generation in sewer network using EPA SWMM. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollertsen, J.; Revilla, N.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Nielsen, A.H. Modeling sulfides, pH and hydrogen sulfide gas in the sewers of San Francisco. Water Environ. Res. 2015, 87, 1980–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, N.; Matos, R.V.; Ferreira, F.; Vollertsen, J.; Matos, J.S. Release of hydrogen sulfide under intermittent flow conditions—The potential of simulation models. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 77, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; de Haas, D.W.; Corrie, S.; O’Halloran, K.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Predicting hydrogen sulfide formation in sewers: A new model. Water 2008, 35, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- InfoSewer Pro Suite INNOVIZE®. Available online: https://www.innovyze.com/en-us/products/infosewer (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Sun, X.; Jiang, G.; Bond, P.L.; Keller, J. Impact of fluctuations in gaseous H2S concentrations on sulfide uptake by sewer concrete: The effect of high H2S loads. Water Res. 2015, 81, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teplý, B.; Rovnaníková, M.; Řoutil, L.; Schejbal, R. Time-variant performance of concrete sewer pipes undergoing biogenic sulfuric acid degradation. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pr. 2018, 9, 04018013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, S.; Hur, J.; Shafieezadeh, A. A high-fidelity computational investigation of buried concrete sewer pipes exposed to truckloads and corrosion deterioration. Eng. Struct. 2020, 221, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodian, M.; Li, C. Service life prediction of underground concrete pipes subjected to corrosion. In Concrete Solutions; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2011; pp. 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, M.; Melchers, R.E. Probabilistic analysis of underground pipelines subject to combined stresses and corrosion. Eng. Struct. 1997, 19, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A.; Boulos, P.F.; Altman, T. Discrete volume-element method for network water-quality models. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1993, 119, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossman, L.A.; Clark, R.M.; Grayman, W.M. Modeling chlorine residuals in drinking-water distribution systems. J. Environ. Eng. 1994, 120, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossman, L.A.; Boulos, P.F. Numerical methods for modeling water quality in distribution systems: A comparison. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1996, 122, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.T.; Espín-Leal, P.; Vigueras-Rodriguez, A.; Castillo, L.G.; Carrillo, J.M.; Martinez-Solano, P.; Nevado-Santos, S. Urban runoff characteristics in combined sewer overflows (CSOs): Analysis of storm events in southeastern Spain. Water 2017, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.T.; Espín-Leal, P.; Vigueras-Rodriguez, A.; Carrillo, J.M.; Castillo, L.G. Synthetic pollutograph by prediction indices: An evaluation in several urban sub-catchments. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Solano, P.; Leal, P.E.; Santos, S.N.; Bermejo, J.T.G. Dimensionado de depósitos de retención de contaminación mediante caracterización de las descargas de sistemas unitarios en la ciudad de Murcia. Rev. Recur. Hídricos 2019, 40, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, R. Generation and control of sulfide in filled pipes. Sew. Ind. Wastes 1959, 31, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Pomeroy, R.D.; Parkhurst, J.D. Forecasting of sulfide buildup rates in sewers. Prog. Water Technol. 1977, 9, 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. EPA. Process Design Manual for Sulfide Control and in Sanitary Sewerage Systems; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1974.
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Boyle, D.P.; Bäse, F. Comparison of different efficiency criteria for hydrological model assessment. Adv. Geosci. 2005, 5, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, J.T.; Harrington, J.R. Fine sediment modeling during storm-based events in the River Bandon, Ireland. Water 2019, 11, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
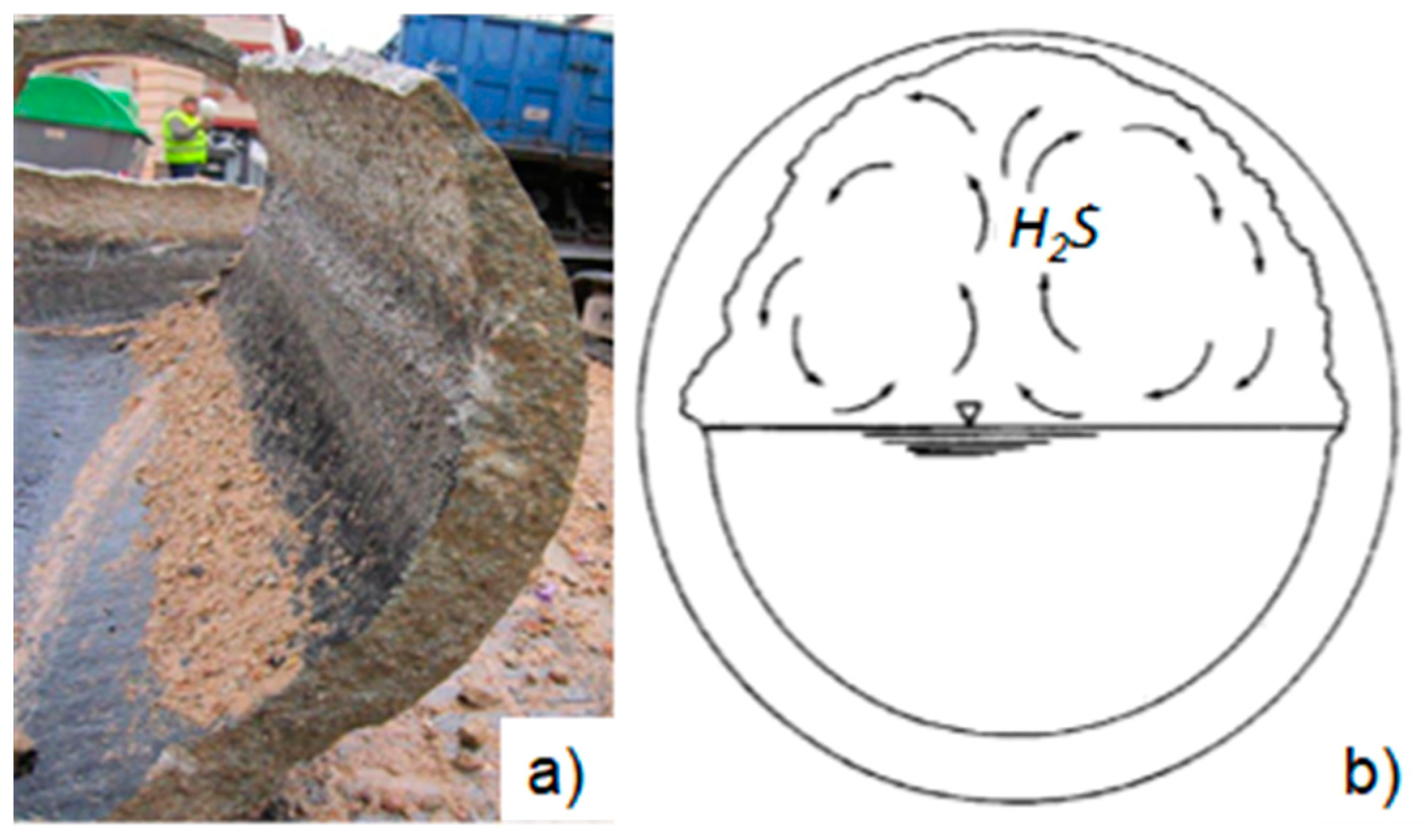

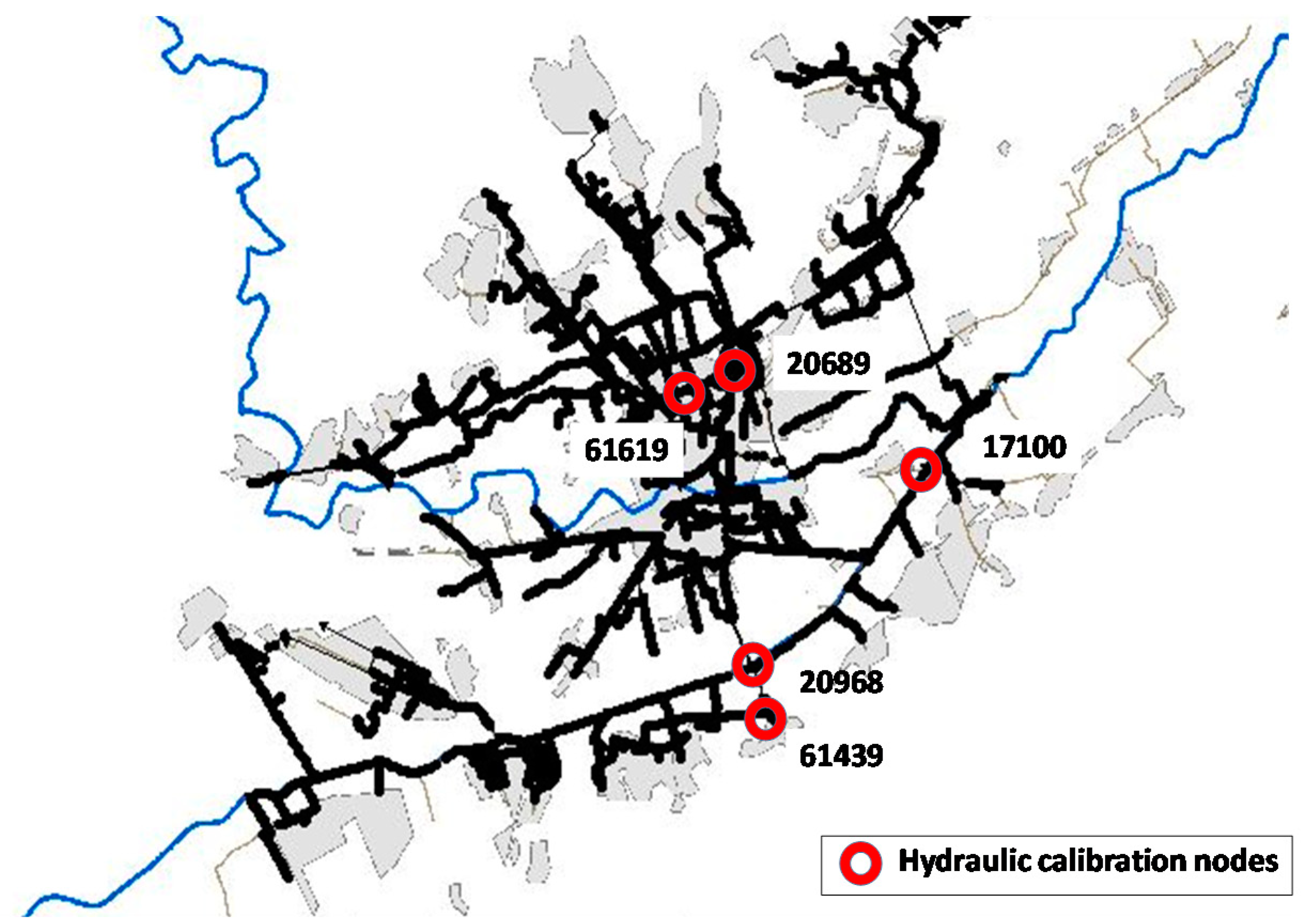
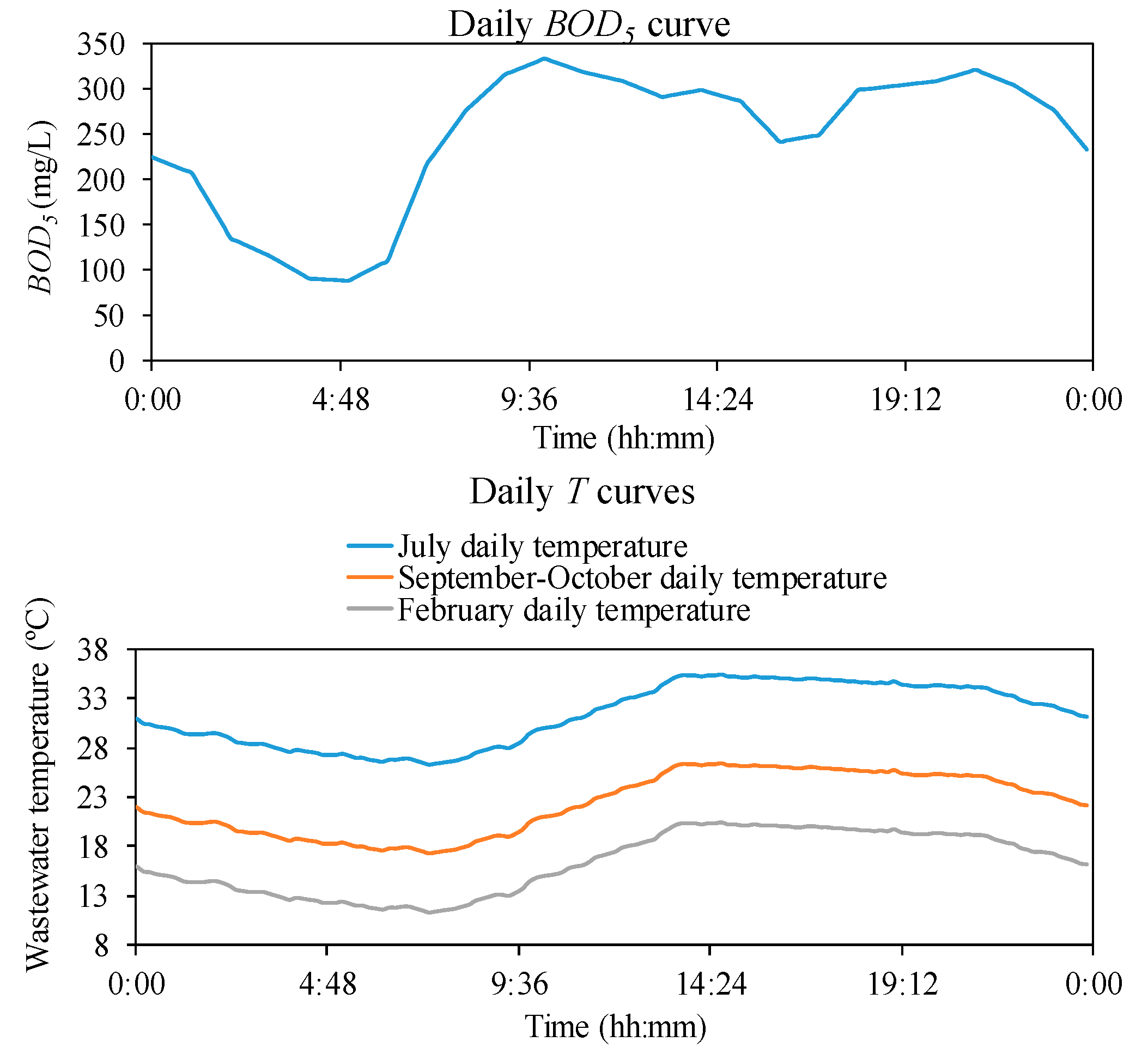
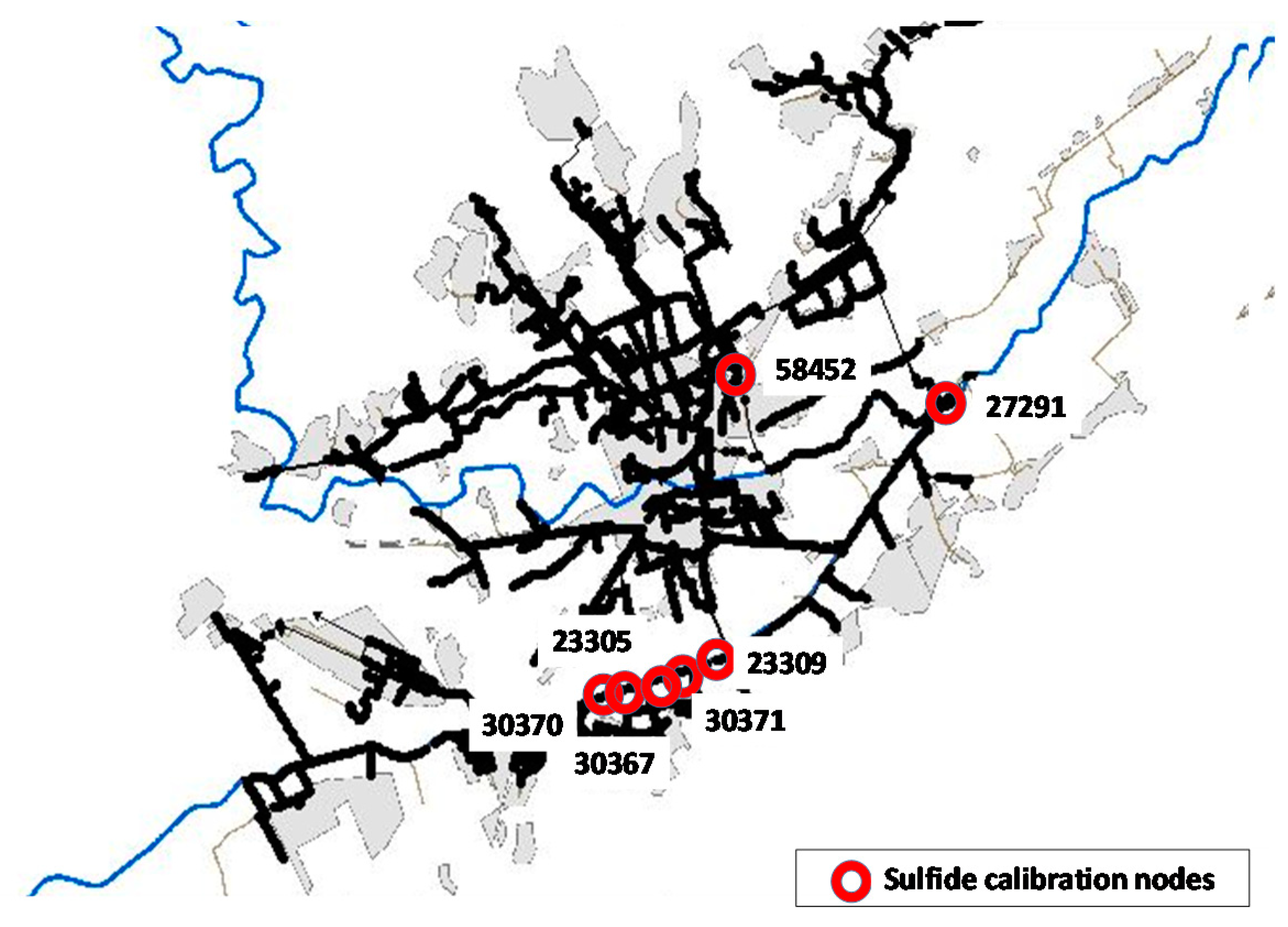

| Description | Element | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulics | Nodes | 6656 |
| Outfalls | 65 | |
| Tanks | 65 | |
| Links | 6655 | |
| Pump stations | 39 |
| Calibration Node | Temporal Period | M | m | fp | s | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m/h) | (-) | (-) | (%) | (m) | ||
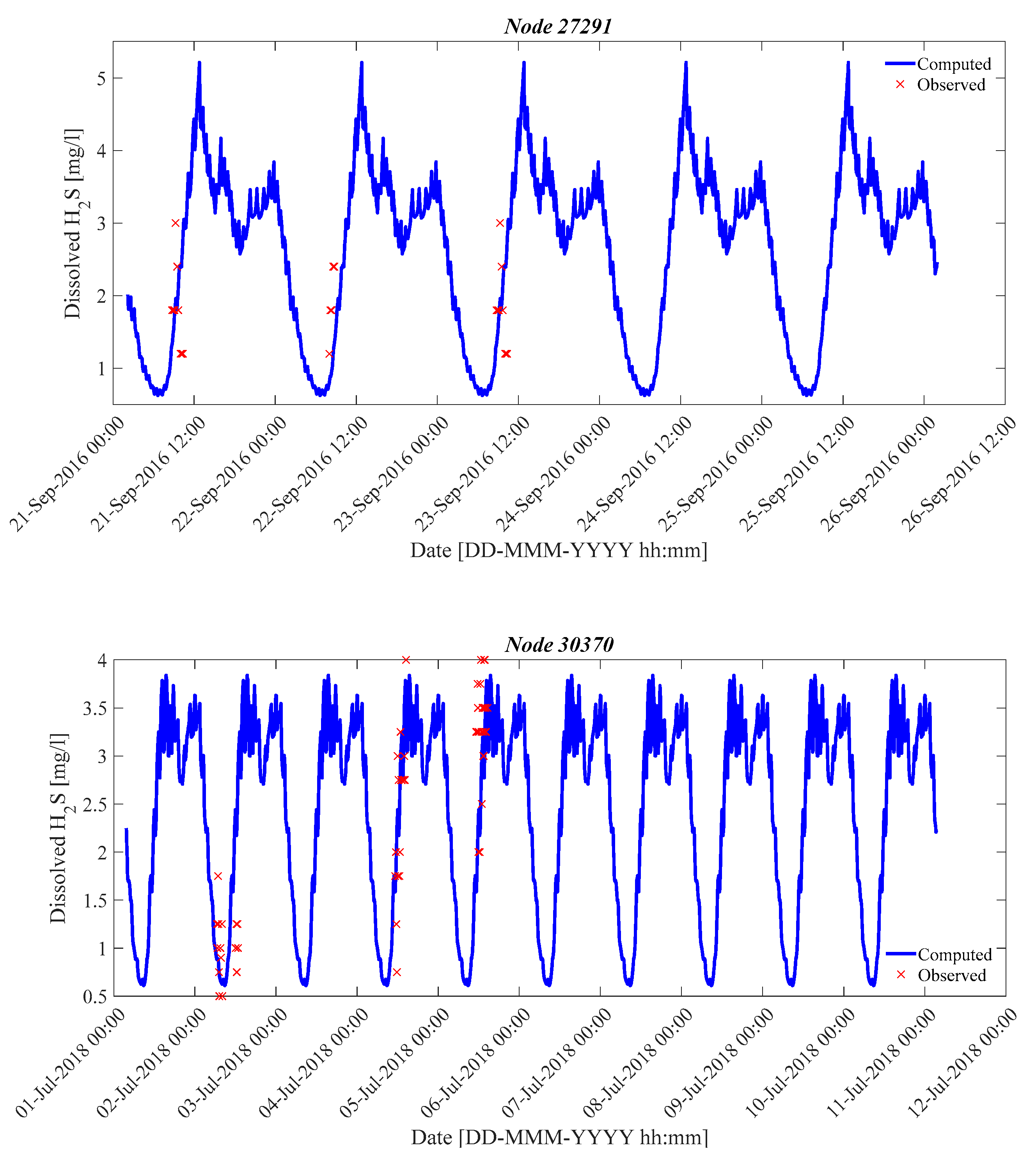
| 27,291 | September 2016 | 0.006 | 0.7 | 0.99 | 0.38 | 2.00 |
| 58,452 | October 2016 | 0.001 | 0.7 | 0.96 | 0.39 | 2.80 |
| 30,370 | July 2018 | 0.004 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.6367 | 0.90/0.60 |
| 30,371 | July 2018 | 0.0017 | 0.7 | 0.97 | 0.12 | 1.20/0.80 * |
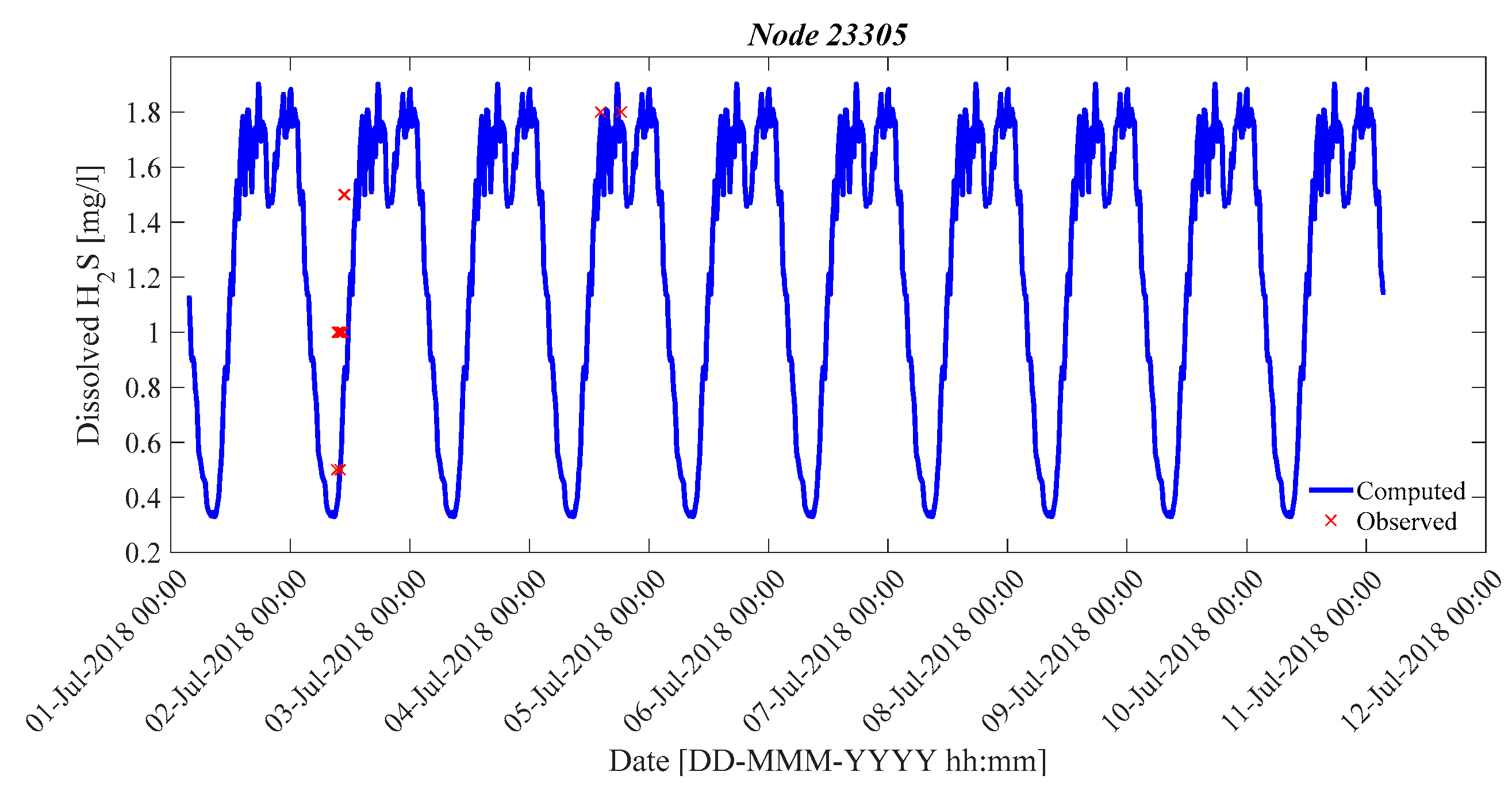
| 23,305 | July 2018 | 0.0045 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.1093 | 1.20/0.80 |
| 23,305 | March 2019 | 0.0028 | 0.7 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 1.20/0.80 * |
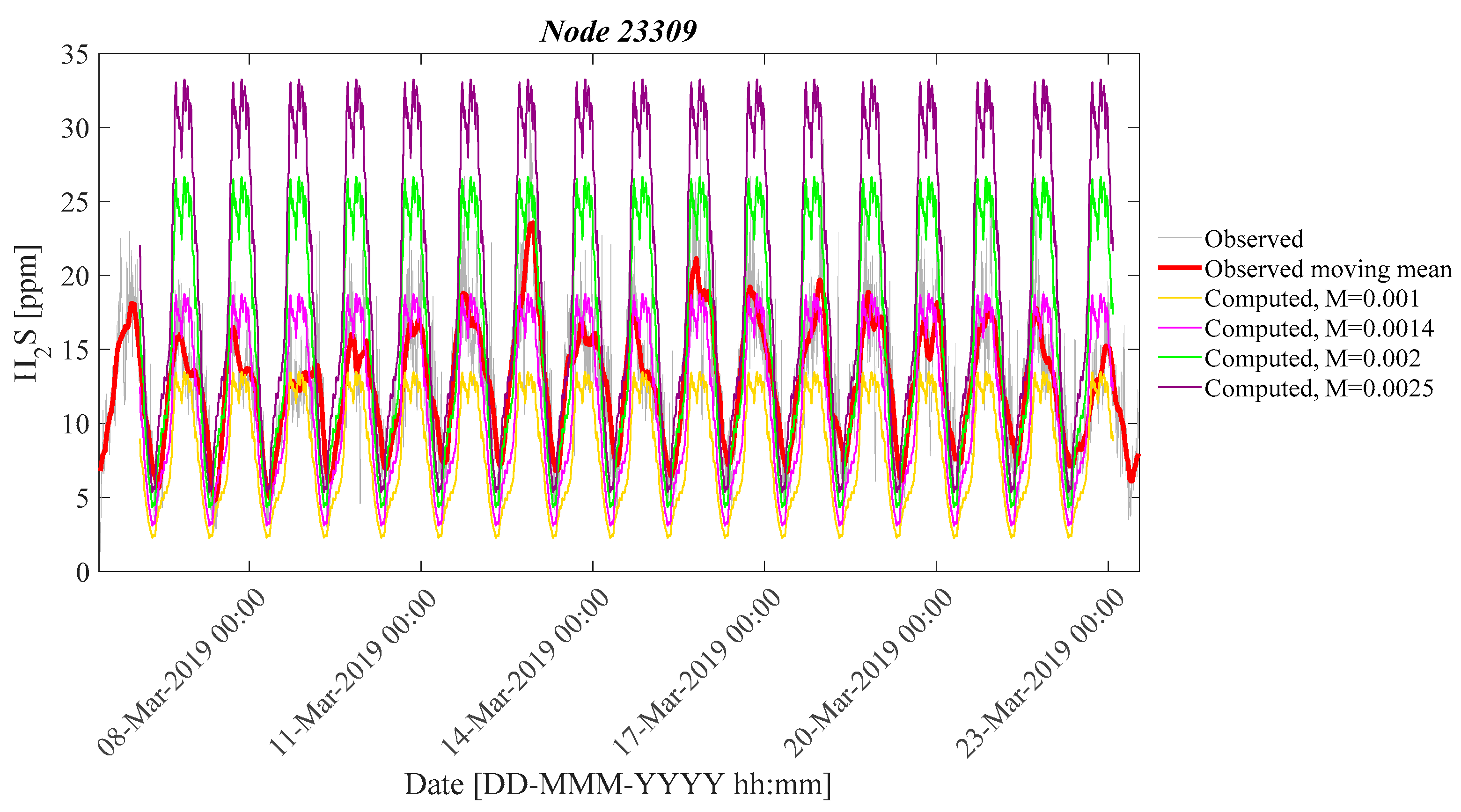
| 23,309 | March 2019 | 0.0014 | 0.7 | 0.97 | 0.18 | 1.20/0.80 * |
| 30,367 | March 2019 | 0.0011 | 0.7 | 0.97 | 0.06 | 0.90/0.60 * |
| 30,370 | March 2019 | 0.006 | 0.7 | 0.97 | 0.63 | 0.90/0.60 * |
| Node Name | Period | AI (%) | Er (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23,305 | March 2019 | 22.55 | 4.21 |
| 23,305 | July 2018 | 37.42 | 1.61 |
| 23,309 | March 2019 | 28.09 | 13.79 |
| 30,367 | March 2019 | 28.35 | 2.11 |
| 30,370 | March 2019 | 31.20 | −5.09 |
| 30,370 | July 2018 | 40.31 | −2.75 |
| 30,371 | July 2018 | 35.27 | 5.42 |
| 27,291 | September 2016 | 33.26 | −5.82 |
| 58,452 | October 2016 | 29.04 | 8.01 |
| Node Name | M | AI (%) | Er (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23,309 | 0.001 | 41.64 | 37.8 |
| 0.0014 | 28.04 | 13.79 | |
| 0.002 | 45.58 | −22.23 | |
| 0.0025 | 75.09 | −52.24 |
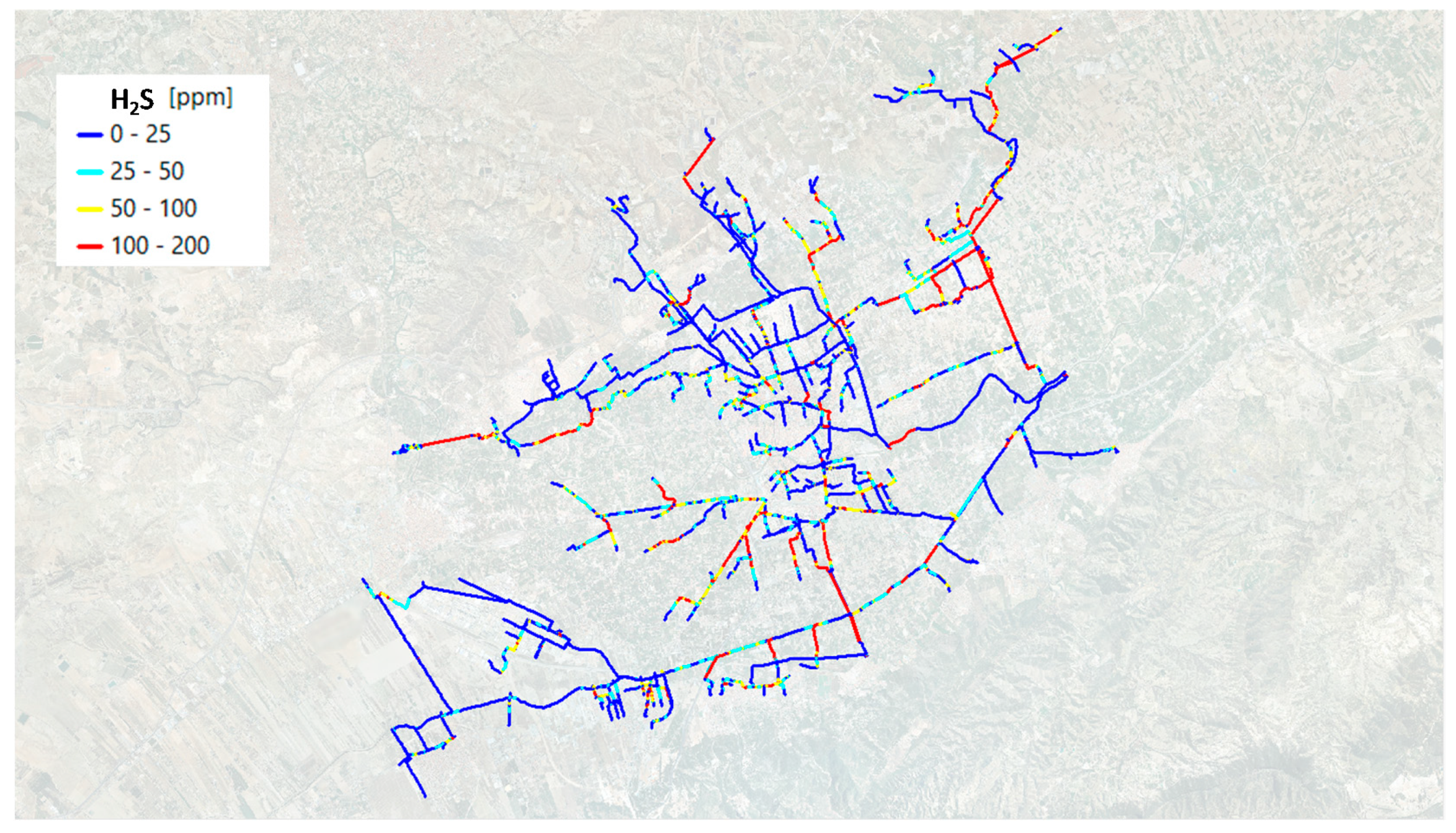
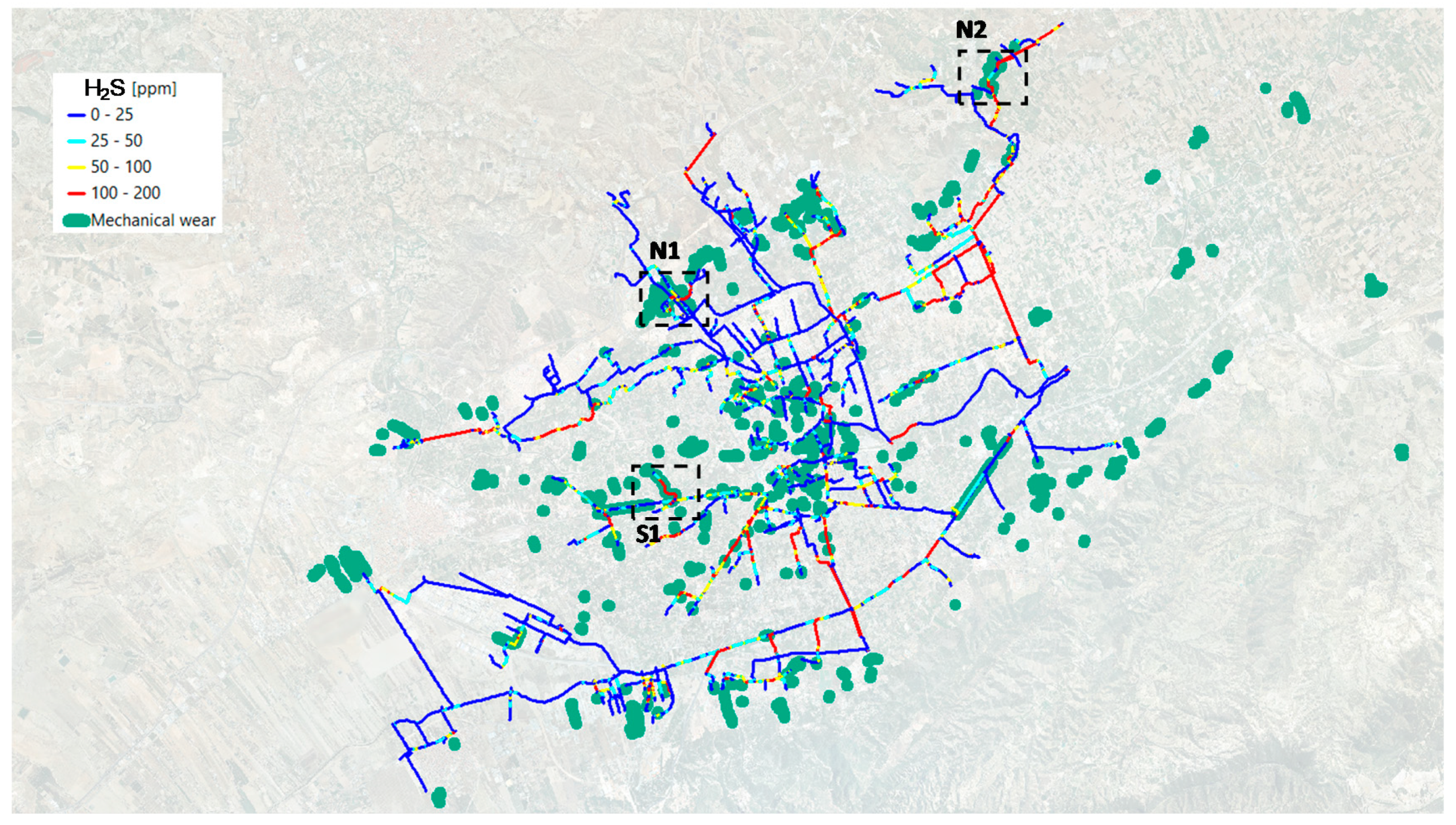
| Annual Average Gas Phase H2S (ppm) | Length (km) | Length (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–25 | 121.7 | 51.9 |
| 25–50 | 38.3 | 16.3 |
| 50–100 | 24.8 | 10.6 |
| 100–200 | 49.7 | 21.2 |
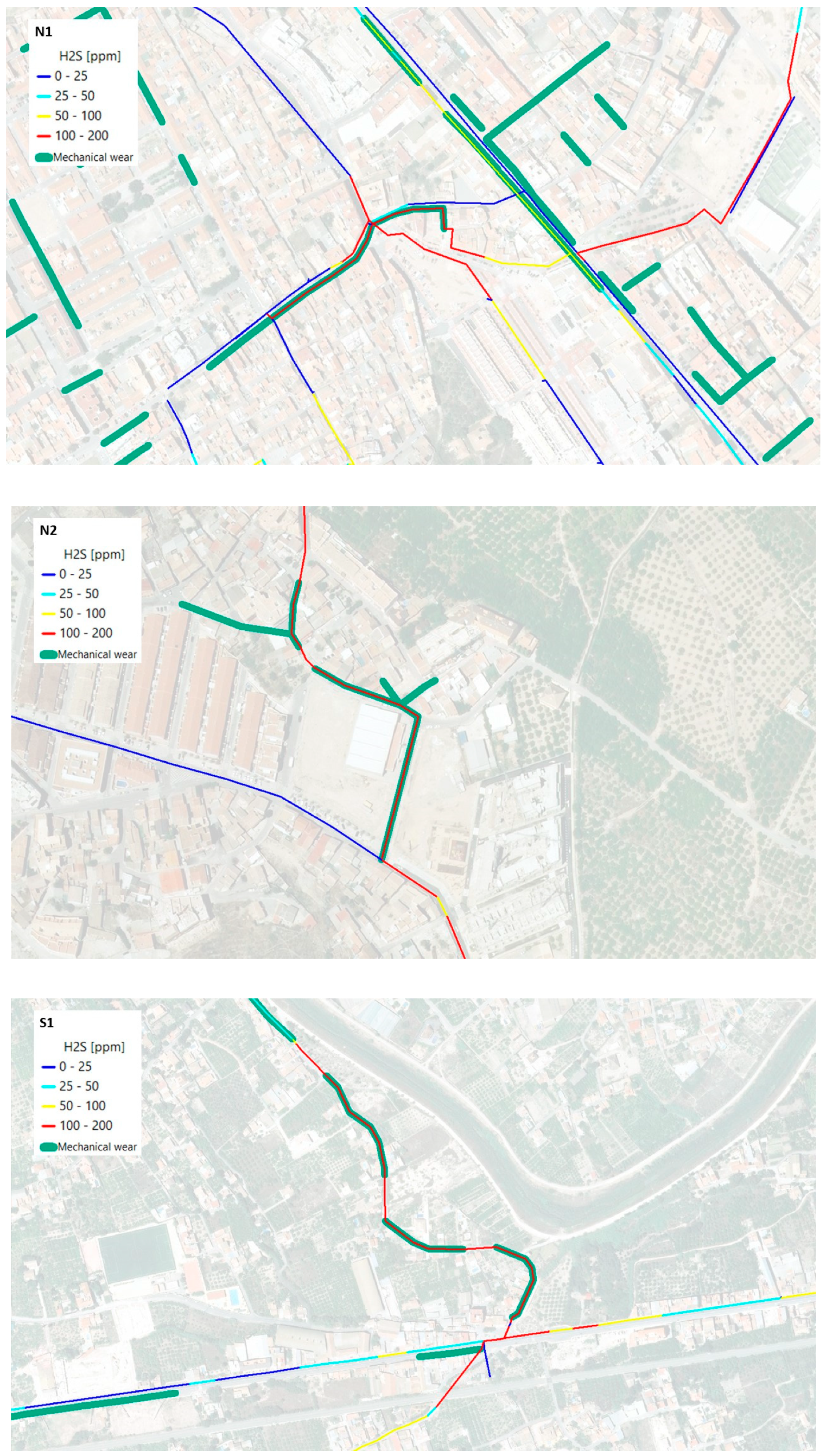
| Selected Zones | Total Length (km) | Length 100–200 ppm Range (km) | Overlap with Mechanical Wear (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 3.68 | 0.87 | 42 |
| N2 | 0.77 | 0.45 | 54 |
| S1 | 2.37 | 0.94 | 57 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, J.T.; García-Guerrero, J.M.; Carrillo, J.M.; Sordo-Ward, Á.; Altarejos-García, L.; Martínez-Solano, P.D.; Pérez de la Cruz, F.-J.; Vigueras-Rodriguez, A.; Castillo, L.G. Sanitation Network Sulfide Modeling as a Tool for Asset Management. The Case of the City of Murcia (Spain). Sustainability 2020, 12, 7643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187643
García JT, García-Guerrero JM, Carrillo JM, Sordo-Ward Á, Altarejos-García L, Martínez-Solano PD, Pérez de la Cruz F-J, Vigueras-Rodriguez A, Castillo LG. Sanitation Network Sulfide Modeling as a Tool for Asset Management. The Case of the City of Murcia (Spain). Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187643
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Juan T., Juan M. García-Guerrero, José M. Carrillo, Álvaro Sordo-Ward, Luis Altarejos-García, Pedro D. Martínez-Solano, Francisco-Javier Pérez de la Cruz, Antonio Vigueras-Rodriguez, and Luis G. Castillo. 2020. "Sanitation Network Sulfide Modeling as a Tool for Asset Management. The Case of the City of Murcia (Spain)" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187643
APA StyleGarcía, J. T., García-Guerrero, J. M., Carrillo, J. M., Sordo-Ward, Á., Altarejos-García, L., Martínez-Solano, P. D., Pérez de la Cruz, F.-J., Vigueras-Rodriguez, A., & Castillo, L. G. (2020). Sanitation Network Sulfide Modeling as a Tool for Asset Management. The Case of the City of Murcia (Spain). Sustainability, 12(18), 7643. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187643










