The Effects of Fast Food Restaurant Attributes on Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation Using DINESERV Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Background
2.1. Service Quality
2.2. Food Quality
2.3. Atmosphere
2.4. Price
2.5. Customer Satisfaction
2.6. Revisit Intention and Recommendation
3. Research Model and Methodology
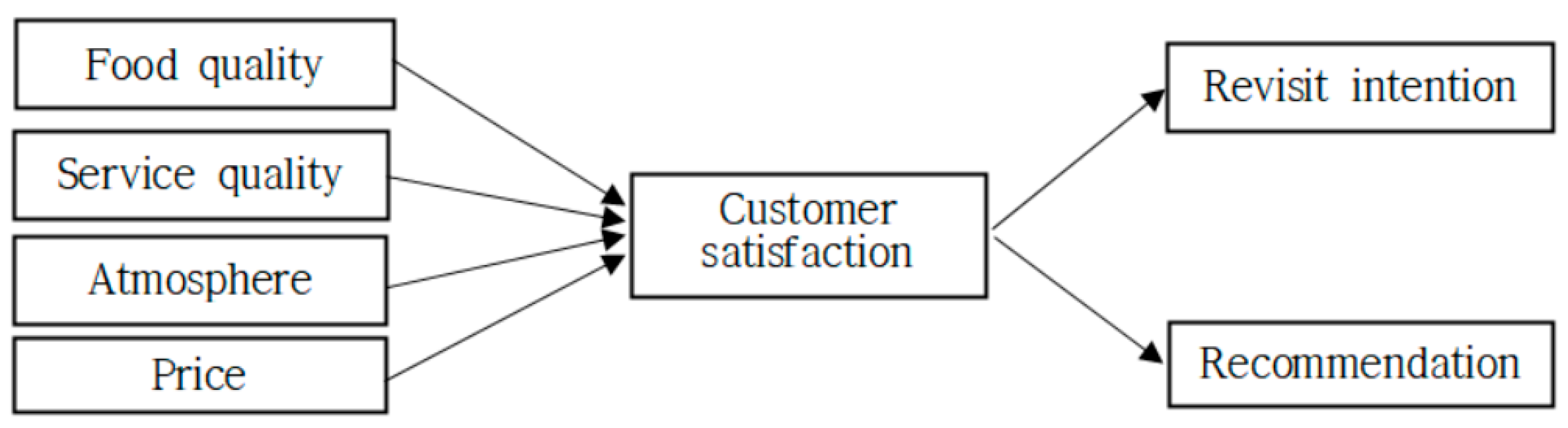
3.1. Research Model
- Research Question 1: Which institutional DINESERV factors will have greater impacts on customer satisfaction?
- Research Question 2: Which institutional DINESERV factors will have greater impacts on revisit intention?
- Research Question 3: Which institutional DINESERV factors will have greater impacts on recommendations?
- Research Question 4: Do DINESERV factors and the customers’ overall satisfaction levels differ with respect to different restaurants (between global restaurants and local restaurants)?
- Research Question 5: Are there any significant relationships among customer satisfaction, revisit intention, and likelihood of recommendation?
3.2. Data Collection and Methods
4. Results of the Study and Implications
4.1. Demographic Profile of Respondents
4.1.1. Frequency of Visits of Respondents to Fast Food Restaurants
4.1.2. Comparison of Mean for Each Item (t-Test)
4.2. Factor Analysis
4.3. Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation
4.3.1. Customer Satisfaction
4.3.2. Revisit Intention
4.3.3. Recommendation
4.3.4. Comparison of Two Restaurants
4.4. The Relationship between Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation
4.5. Discussion and Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grand View Research. Fast Food & Quick Service Restaurant Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Type (Chain, Independent), by Cuisine (American, Turkish & Lebanese), by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2020–2027. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/fast-food-quick-service-restaurants-market (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Abdelkafi, N.; Täuscher, K. Business Models for Sustainability from a System Dynamics Perspective. Organ. Environ. 2015, 29, 74–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; McLaughlin, E.; Gomez, M. Guest Satisfaction and Restaurant Performance. In The Next Frontier of Restaurant Management: Harnessing Data to Improve Guest Service and Enhance the Employee Experience; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 33–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mongolian Business Sectors. Available online: http://www.mse.mn/uploads/files/mongolian%20business%20sectors%201_compressed.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Mongolia GDP Growth Rate YoY. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/mongolia/gdp-growth (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Zhu, Z. Burger King Opens in Mongolia, Bringing Burgers to Their Birthplace. Available online: https://asiamattersforamerica.org/articles/burger-king-opens-in-mongolia-bringing-burgers-to-their-birthplace (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Great Food Comes First. Available online: http://www.burgerking.mn (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Yonhap, S. Korean Fast-Food Chain Lotteria Opens in Mongolia. Available online: http://www.koreaherald.com/view.php?ud=20180625000515 (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Gikonyo, L.; Berndt, A.; Wadawi, J. Critical Success Factors for Franchised Restaurants Entering the Kenyan Market. SAGE Open 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, S.; Raspor, S.; Sergaric, K. Does restaurant performance meet customers’ expectations? An assessment of restaurant service quality using a modified DINESERV approach. Tour. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 16, 81–195. [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. SERVQUAL: A Multiple-Item Scale for Measuring Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality. J. Retail. 1988, 64, 12–40. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, P.; Knutson, B.; Patton, M. Dineserv: A Tool for Measuring Service Quality in Restaurants. Cornell Hotel. Restaur. Adm. Q. 1995, 36, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H. Determinant Factors and Choice Intention for Chinese Restaurant Dining. J. Restaur. Foodserv. Mark. 1997, 2, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettijohn, L.S.; Pettijohn, C.E.; Luke, R.H. An Evaluation of Fast Food Restaurant Satisfaction. J. Restaur. Foodserv. Mark. 1997, 2, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, I.; Abdullah, M. The impact of service quality and customer satisfaction on customer’s loyalty: Evidence from Fast Food restaurant of Malaysia. Int. J. Inf. Bus. Manag. 2015, 7, 784–793. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, M.K.; Cronin, J.J. Customer Orientation. J. Serv. Res. 2001, 3, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namin, A. Revisiting customers’ perception of service quality in fast food restaurants. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2017, 34, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, Y.; Jang, S. Does Food Quality Really Matter in Restaurants? Its Impact on Customer Satisfaction and Behavioral Intentions. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2007, 31, 387–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Jang, S. The effects of dining atmospherics on behavioral intentions through quality perception. J. Serv. Mark. 2012, 26, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.; Han, H. Influence of the Quality of Food, Service, and Physical Environment on Customer Satisfaction and Behavioral Intention in Quick-Casual Restaurants: Moderating Role of Perceived Price. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2009, 34, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, C. The universe of food quality. Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, I.; Garg, R.; Rahman, Z. Influence of retail atmospherics on customer value in an emerging market. Great Lakes Her. 2010, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Singhania, S. Determinants of Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intentions and Word of Mouth in the Restaurant Industry–Study Conducted In Selective Outlets of South Kolkata. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Invent. 2018, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Andaleeb, S.S.; Conway, C. Customer satisfaction in the restaurant industry: An examination of the transaction-specific model. J. Serv. Mark. 2006, 20, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. A Cognitive Model of the Ancedents and Consequences of Satisfaction Decisions. J. Mark. Res. 1980, 17, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C. A national customer satisfaction barometer: The Swedish experience. J. Mark. 1992, 56, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Chau, M. Customer revisit intention to restaurants: Evidence from online reviews. Inf. Syst. Front. 2013, 17, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H. Diners’ Perceptions of Quality, Value, and Satisfaction. Cornell Hotel. Restaur. Adm. Q. 2000, 41, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.; Feinstein, A.H.; Dalbor, M. Customer Satisfaction of Theme Restaurant Attributes and Their Influence on Return Intent. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2004, 7, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-T.; Hu, H.-H. How determinant attributes of service quality influence customer-perceived value: An empirical investigation of the Australian coffee outlet industry. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2010, 22, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-J.; Choi, K. Bridging the Perception Gap between Management and Customers on DINESERV Attributes: The Korean All-You-Can-Eat Buffet. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, S.; Komsic, J.; ve Stifanic, M. Measuring Service Quality in City Restaurant Settings Using DINESERV Scale. 2013. Available online: http://www.wseas.us/elibrary/conferences/2013/Dubrovnik/MATREFC/MATREFC-27.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2017).
- Adeinat, I. Measuring Service Quality Efficiency Using Dineserv. Int. J. Qual. Res. 2019, 13, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, B.J.; Stevens, P.; Patton, M. DINESERV. J. Hosp. Leis. Mark. 1996, 3, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; McCahon, C.; Miller, J. Assessing Service Quality in Korean Casual-Dining Restaurants Using DINESERV. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2003, 6, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougoure, U.-S.; Neu, M.-K. Service Quality in the Malaysian Fast Food Industry: An Examination Using DINESERV. Serv. Mark. Q. 2010, 31, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Lin, I.H.; Tsai, J.Y. Combining fuzzy integral and GRA method for evaluating the service quality of fast-food restaurants. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2018, 21, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, N.K.; Simmers, C.S. Measuring Service Quality Perceptions of Restaurant Experiences: The Disparity Between Comment Cards and DINESERV. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2011, 14, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyorat, K.; Sophonsiri, S. The influence of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in the chain restaurant context: A Thai case. J. Glob. Bus. Technol. 2010, 6, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, K.V. Development of SERVQUAL and DINESERV for Measuring Meal Experiences in Eating Establishments. Scand. J. Hosp. Tour. 2014, 14, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukanja, M.; Planinc, T. Toward cost-effective service excellence: Exploring the relationship between managers’ perceptions of quality and the operational efficiency and profitability of restaurants. Qual. Manag. J. 2020, 27, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.G.; Ng, C.Y.N.; Kim, Y.-S. Influence of institutional DINESERV on customer satisfaction, return intention, and word-of-mouth. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2009, 28, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Oriade, A.; Fallon, P. Service quality and customer satisfaction in Chinese fast food sector: A proposal for CFFRSERV. Adv. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2014, 2, 30–53. [Google Scholar]
- DiPietro, R. Restaurant and foodservice research. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 1203–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinković, V.; Senic, V.; Mimovic, P.M. Factors affecting choice and image of ethnic restaurants in Serbia. Br. Food J. 2015, 117, 1903–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewole, P. Multiattribute Dimensions of Service Quality in the All-You-Can-Eat Buffet Restaurant Industry. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2013, 22, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-C.; Mohi, Z. Assessment of Service Quality in the Fast-Food Restaurant. J. Foodserv. Bus. Res. 2015, 18, 358–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulkhaq, M.M.; Nartadhi, R.L.; Akshinta, P.Y. Evaluating Service Quality of Korean Restaurants: A Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Approach. Ind. Eng. Manag. Syst. 2016, 15, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factors | Items | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Food quality | Taste of food | [43] [44] [42] [45] |
| Freshness of food | ||
| Menu variety | ||
| Good portions | ||
| Service quality | Kindness | [15] [46] [19] |
| Good attitude | ||
| Quick service response | ||
| Well trained | ||
| Chef’s knowledge | ||
| Atmosphere | Good interior and decoration | [43] [47] [48] |
| Clean dining areas and restroom | ||
| Comfortable seats | ||
| Comfortable temperature | ||
| Music and pleasant feeling | ||
| Price | Valuable price | [46] [42,44] |
| Discount | ||
| Satisfaction | Overall satisfaction | [10] |
| Revisit | Revisit | [27,29] |
| Recommendation | Recommendation | [30] |
| Items | Frequency | Percent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Country of residence | Mongolia | 90 | 59.6% |
| South Korea | 61 | 40.4% | |
| Gender | Male | 70 | 46.4% |
| Female | 81 | 53.6% | |
| Age | 18–25 | 64 | 42.4% |
| 26–40 | 78 | 51.7% | |
| 41–60 | 9 | 6% | |
| 61 and above | 0 | 0% | |
| Marital status | Married | 61 | 40.4% |
| Single | 90 | 59.6% | |
| Occupation | Student | 61 | 40.4% |
| Civil servant | 12 | 7.9% | |
| Private sector | 61 | 40.4% | |
| Others | 17 | 11.3% | |
| Income (tugruk) | <500,000 | 12 | 7.9% |
| 500,000–1,000,000 | 40 | 26.5% | |
| 1,000,000–1,500,000 | 41 | 27.2% | |
| >1,500,000 | 58 | 38.4% | |
| Frequency of Visit | Burger King | Berlin Burger | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Respondents | Percent | No. of Respondents | Percent | |
| Once a week | 27 | 22.5 | 46 | 7.3 |
| Once every two weeks | 32 | 13.2 | 16 | 10.6 |
| Once a month | 66 | 37.1 | 11 | 30.5 |
| Total | 125 | 72.8 | 73 | 48.3 |
| System (missing) | 26 | 27.2 | 78 | 51.7 |
| Total | 151 | 100 | 151 | 100 |
| Factors | Items | Burger King vs. Berlin Burger | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residence (Mongolia) n = 90 | Residence (Korea) n = 61 | Total n = 151 | ||
| Food quality | Taste of food | 3.4889 vs. 2.6556 * | 3.6721 vs. 3.3443 ** | 3.5629 vs. 2.9338 * |
| Freshness | 3.4111 vs. 2.6111 * | 3.5410 vs. 3.2787 *** | 3.4636 vs. 2.8808 * | |
| Menu variety | 3.2360 vs. 2.8000 * | 3.6885 vs. 3.3770 ** | 3.4200 vs. 3.0331 * | |
| Good Portions | 3.1910 vs. 2.8000 ** | 3.6885 vs. 3.3607 ** | 3.3933 vs. 3.0265 * | |
| Service quality | Kindness | 3.4889 vs. 2.6222 * | 3.6230 vs. 2.9836 * | 3.5430 vs. 2.7682 * |
| Good attitude | 3.4778 vs. 2.6333 * | 3.6393 vs. 3.0000 * | 3.5430 vs.2.7815 * | |
| Quick service | 3.3778 vs. 2.6111 * | 3.5902 vs. 3.0656 * | 3.4636 vs. 2.7947 * | |
| Well trained | 3.4000 vs. 2.6333 * | 3.6066 vs. 2.9508 * | 3.4834 vs. 2.7616 * | |
| Chef’s knowledge | 3.3778 vs. 2.6556 * | 3.5738 vs. 3.0000 * | 3.4570 vs. 2.7947 * | |
| Atmosphere | Interior/decoration | 3.4000 vs. 2.5111 * | 3.6885 vs. 3.0000 * | 3.5166 vs. 2.7086 * |
| Clean dining areas | 3.3556 vs. 2.5333 * | 3.6230 vs. 2.9016 * | 3.4636 vs. 2.6821 * | |
| Comfortable seats | 3.4444 vs. 2.5333 * | 3.6885 vs. 3.0328 * | 3.5430 vs. 2.7351 * | |
| Temperature | 3.4889 vs. 2.7111 * | 3.7213 vs. 3.0164 * | 3.5828 vs. 2.8344 * | |
| Music and feeling | 3.2333 vs. 2.4000 * | 3.6721 vs. 2.9016 * | 3.4106 vs. 2.6026 * | |
| Price | Valuable price | 3.0222 vs. 2.7333 ** | 3.6230 vs. 3.1311 * | 3.2649 vs. 2.8940 * |
| Discount | 2.7333 vs. 2.3333 * | 3.5246 vs. 2.7705 * | 3.0530 vs. 2.5099 * | |
| Satisfaction | 3.2111 vs. 2.5111 * | 3.5410 vs. 3.0000 * | 3.3444 vs. 2.7086 * | |
| Revisit intention | 3.1444 vs. 2.4333 * | 3.6557 vs. 3.1148 * | 3.3510 vs. 2.7086 * | |
| Recommendation | 3.0333 vs. 2.3000 * | 3.5574 vs. 3.0000 * | 3.2450 vs. 2.5828 * | |
| Items | Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Quality (SQ) | Atmosphere (A) | Food Quality (FQ) | Price (P) | Cronbach’s Alpha | |
| Well trained (SQ4) Attitude (SQ2) Availability (SQ3) Staff knowledge (SQ5) Kindness (SQ1) | 0.823 | 0.379 | 0.282 | 0.210 | 0.977 |
| 0.808 | 0.396 | 0.245 | 0.257 | ||
| 0.805 | 0.375 | 0.311 | 0.216 | ||
| 0.795 | 0.312 | 0.338 | 0.227 | ||
| 0.776 | 0.367 | 0.304 | 0.250 | ||
| Temperature (A4) Comfortable seats (A3) Interior (A1) Cleanliness (A2) Music (A5) | 0.331 | 0.796 | 0.392 | 0.159 | 0.969 |
| 0.383 | 0.783 | 0.351 | 0.218 | ||
| 0.428 | 0.771 | 0.224 | 0.252 | ||
| 0.397 | 0.752 | 0.263 | 0.316 | ||
| 0.403 | 0.721 | 0.235 | 0.361 | 0.931 | |
| Fresh (FQ2) Tasty (FQ1) Variety of menus (FQ3) Good portions (FQ4) | 0.301 | 0.406 | 0.767 | 0.175 | |
| 0.441 | 0.346 | 0.736 | 0.196 | ||
| 0.283 | 0.277 | 0.704 | 0.429 | ||
| 0.298 | 0.199 | 0.693 | 0.457 | ||
| Discount (P2) Value (P1) | 0.246 | 0.287 | 0.264 | 0.839 | 0.897 |
| 0.295 | 0.302 | 0.362 | 0.757 | ||
| KMO | 0.942 | ||||
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Chi-square | 3368.902 | |||
| df (sig.) | 120 (0.000) | ||||
| Items | Component | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Quality (SQ) | Atmosphere (A) | Food Quality (FQ) | Price (P) | Cronbach’s Alpha | |
| Staff knowledge (SQ5) | 0.779 | 0.358 | 0.318 | 0.329 | 0.983 |
| Availability (SQ3) | 0.776 | 0.351 | 0.402 | 0.240 | |
| Attitude (SQ2) | 0.774 | 0.388 | 0.373 | 0.202 | |
| Well trained (SQ4) | 0.755 | 0.374 | 0.427 | 0.242 | |
| Kindness (SQ1) | 0.733 | 0.389 | 0.450 | 0.202 | |
| Variety of menu (FQ3) | 0.362 | 0.842 | 0.266 | 0.180 | 0.968 |
| Tasty (FQ1) | 0.334 | 0.798 | 0.340 | 0.240 | |
| Good portions (FQ4) | 0.332 | 0.782 | 0.329 | 0.243 | |
| Fresh (FQ2) | 0.340 | 0.765 | 0.346 | 0.288 | |
| Music (A5) | 0.381 | 0.211 | 0.779 | 0.302 | 0.967 |
| Comfortable seats (A3) | 0.339 | 0.438 | 0.769 | 0.208 | |
| Cleanliness (A2) | 0.418 | 0.335 | 0.742 | 0.250 | |
| Interior (A1) | 0.406 | 0.426 | 0.725 | 0.232 | |
| Temperature (A4) | 0.425 | 0.389 | 0.621 | 0.304 | |
| Discount (P2) Value (P1) | 0.271 | 0.259 | 0.428 | 0.767 | 0.871 |
| 0.366 | 0.489 | 0.244 | 0.687 | ||
| KMO | 0.941 | ||||
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Chi-square | 3964.552 | |||
| df (sig.) | 120(0.000) | ||||
| Factors | Customer Satisfaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | t-Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Constant | 3.347 | 0.041 | 82.217 * | 0.000 | |
| Food quality | 0.543 | 0.041 | 0.457 | 13.295 * | 0.000 |
| Service quality | 0.394 | 0.041 | 0.332 | 9.646 * | 0.000 |
| Atmosphere | 0.653 | 0.041 | 0.550 | 15.989 * | 0.000 |
| Price | 0.539 | 0.041 | 0.454 | 13.205 * | 0.000 |
| Factors | Customer Satisfaction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | t-Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Constant | 2.709 | 0.044 | 61.204 * | 0.000 | |
| Food quality | 0.498 | 0.044 | 0.441 | 11.217 * | 0.000 |
| Service quality | 0.566 | 0.044 | 0.502 | 12.752 * | 0.000 |
| Atmosphere | 0.468 | 0.044 | 0.415 | 10.544 * | 0.000 |
| Price | 0.446 | 0.044 | 0.395 | 10.042 * | 0.000 |
| Factors | Revisit Intention | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | t-Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Constant | 3.353 | 0.051 | 65.243 * | 0.000 | |
| Food quality | 0.502 | 0.052 | 0.407 | 9.730 * | 0.000 |
| Service quality | 0.339 | 0.052 | 0.275 | 6.567 * | 0.000 |
| Atmosphere | 0.585 | 0.052 | 0.475 | 11.352 * | 0.000 |
| Price | 0.651 | 0.052 | 0.528 | 12.624 * | 0.000 |
| Factors | Revisit Intention | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | t-Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Constant | 2.709 | 0.050 | 54.321 * | 0.000 | |
| Food quality | 0.484 | 0.050 | 0.416 | 9.674 * | 0.000 |
| Service quality | 0.602 | 0.050 | 0.517 | 12.024 * | 0.000 |
| Atmosphere | 0.439 | 0.050 | 0.377 | 8.767 * | 0.000 |
| Price | 0.448 | 0.050 | 0.385 | 8.953 * | 0.000 |
| Factors | Customer Recommendation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | t-Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Constant | 3.247 | 0.048 | 67.590 * | 0.000 | |
| Food quality | 0.498 | 0.048 | 0.406 | 10.324 * | 0.000 |
| Service quality | 0.371 | 0.048 | 0.302 | 7.689 * | 0.000 |
| Atmosphere | 0.569 | 0.048 | 0.464 | 11.804 * | 0.000 |
| Price | 0.676 | 0.048 | 0.552 | 14.028 * | 0.000 |
| Factors | Customer Recommendation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstandardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficients | t-Value | Sig. | ||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | |||
| Constant | 2.583 | 0.054 | 47.645 * | 0.000 | |
| Food quality | 0.460 | 0.054 | 0.396 | 8.455 * | 0.000 |
| Service quality | 0.539 | 0.054 | 0.464 | 9.907 * | 0.000 |
| Atmosphere | 0.414 | 0.054 | 0.356 | 7.617 * | 0.000 |
| Price | 0.496 | 0.054 | 0.427 | 9.120 * | 0.000 |
| Model | Burger King (p-Value) | Berlin Burger (p-Value) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Satisfaction | Revisit Intention | Customer Recommendation | Customer Satisfaction | Revisit Intention | Customer Recommendation | |
| Constant | 3.347 | 3.353 | 3.247 | 2.709 | 2.709 | 2.583 |
| Food Quality | 13.295 * (0.000) | 9.730 * (0.000) | 10.324 * (0.000) | 11.217 * (0.000) | 9.674 * (0.000) | 8.455 * (0.000) |
| Service Quality | 9.646 * (0.000) | 6.567 * (0.000) | 7.689 * (0.000) | 12.752 * (0.000) | 12.024 * (0.000) | 9.907 * (0.000) |
| Atmosphere | 15.989 * (0.000) | 11.352 * (0.000) | 11.804 * (0.000) | 10.544 * (0.000) | 8.767 * (0.000) | 7.617 * (0.000) |
| Price | 13.205 * (0.000) | 12.624 * (0.000) | 14.028 * (0.000) | 10.042 * (0.000) | 8.953 * (0.000) | 9.120 * (0.000) |
| Pairs | Burger King (p-Value) | Berlin Burger (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer satisfaction vs. revisit intention (r1) | 0.907 *(0.000) | 0.919 *(0.000) |
| Customer satisfaction vs. recommendation (r2) | 0.909 *(0.000) | 0.913 *(0.000) |
| Recommendation vs. revisit intention (r3) | 0.884 *(0.000) | 0.915 *(0.000) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chun, S.-H.; Nyam-Ochir, A. The Effects of Fast Food Restaurant Attributes on Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation Using DINESERV Scale. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7435. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187435
Chun S-H, Nyam-Ochir A. The Effects of Fast Food Restaurant Attributes on Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation Using DINESERV Scale. Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7435. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187435
Chicago/Turabian StyleChun, Se-Hak, and Ariunzaya Nyam-Ochir. 2020. "The Effects of Fast Food Restaurant Attributes on Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation Using DINESERV Scale" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7435. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187435
APA StyleChun, S.-H., & Nyam-Ochir, A. (2020). The Effects of Fast Food Restaurant Attributes on Customer Satisfaction, Revisit Intention, and Recommendation Using DINESERV Scale. Sustainability, 12(18), 7435. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187435





