Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land-Use and Ecosystem Services Valuation in the Belt and Road Initiative
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
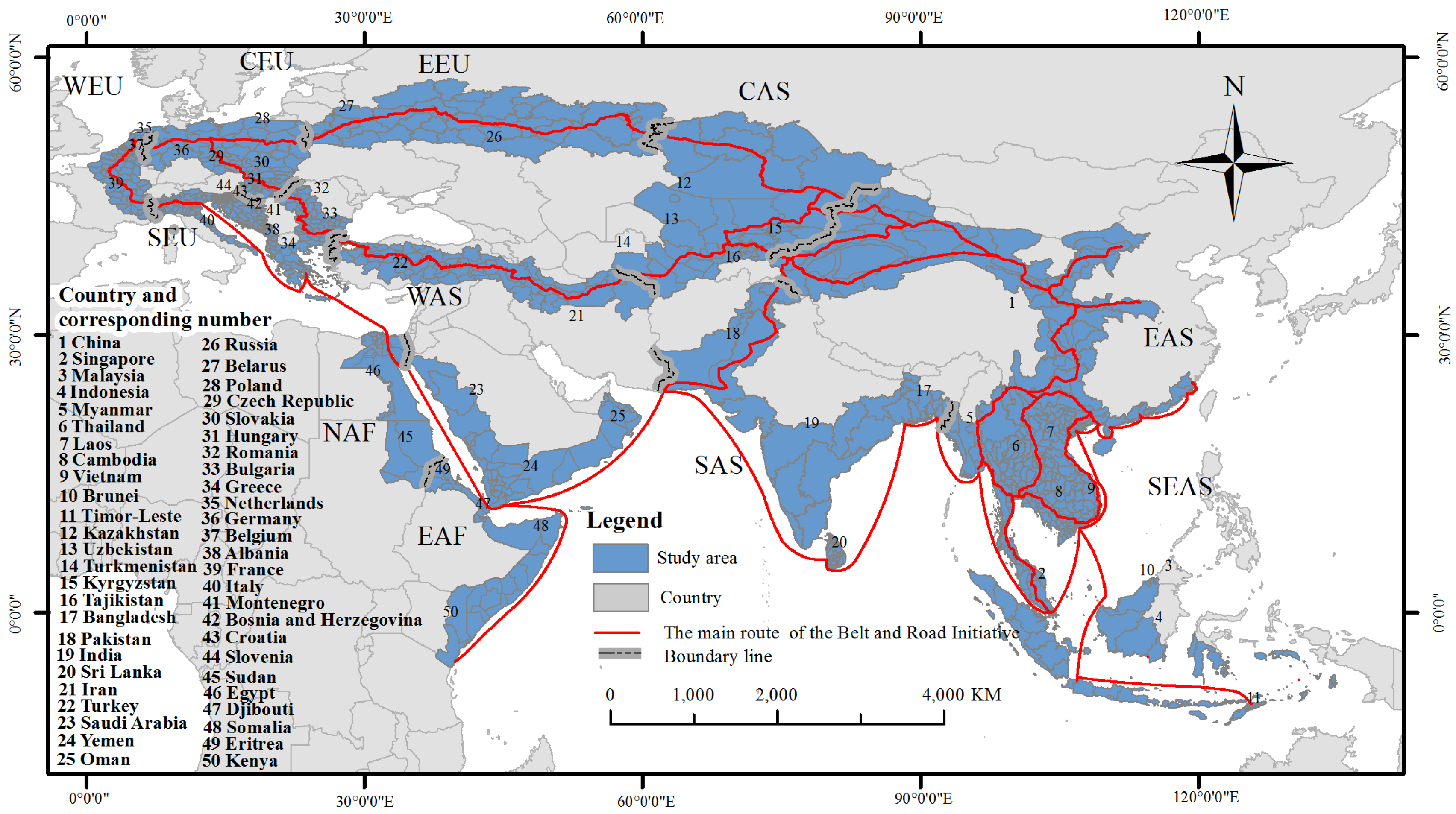
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Basis and Method for Classifying Land-Use Types
2.3.2. Calculation of Land-Use Dynamics
2.3.3. Land-Use Transfer Matrix
2.3.4. Comprehensive Index of Land-Use Degree
2.3.5. Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Services
3. Results
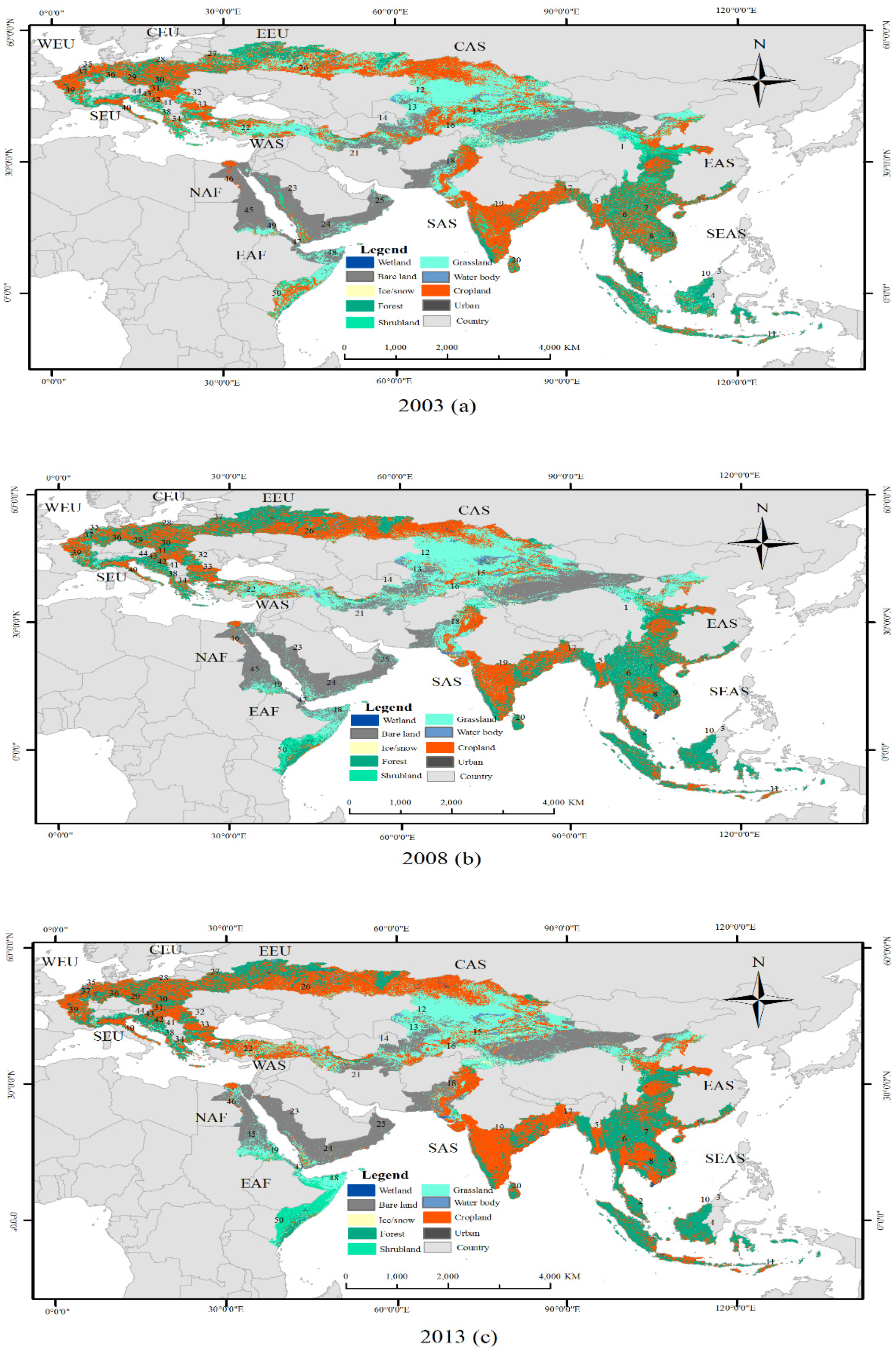
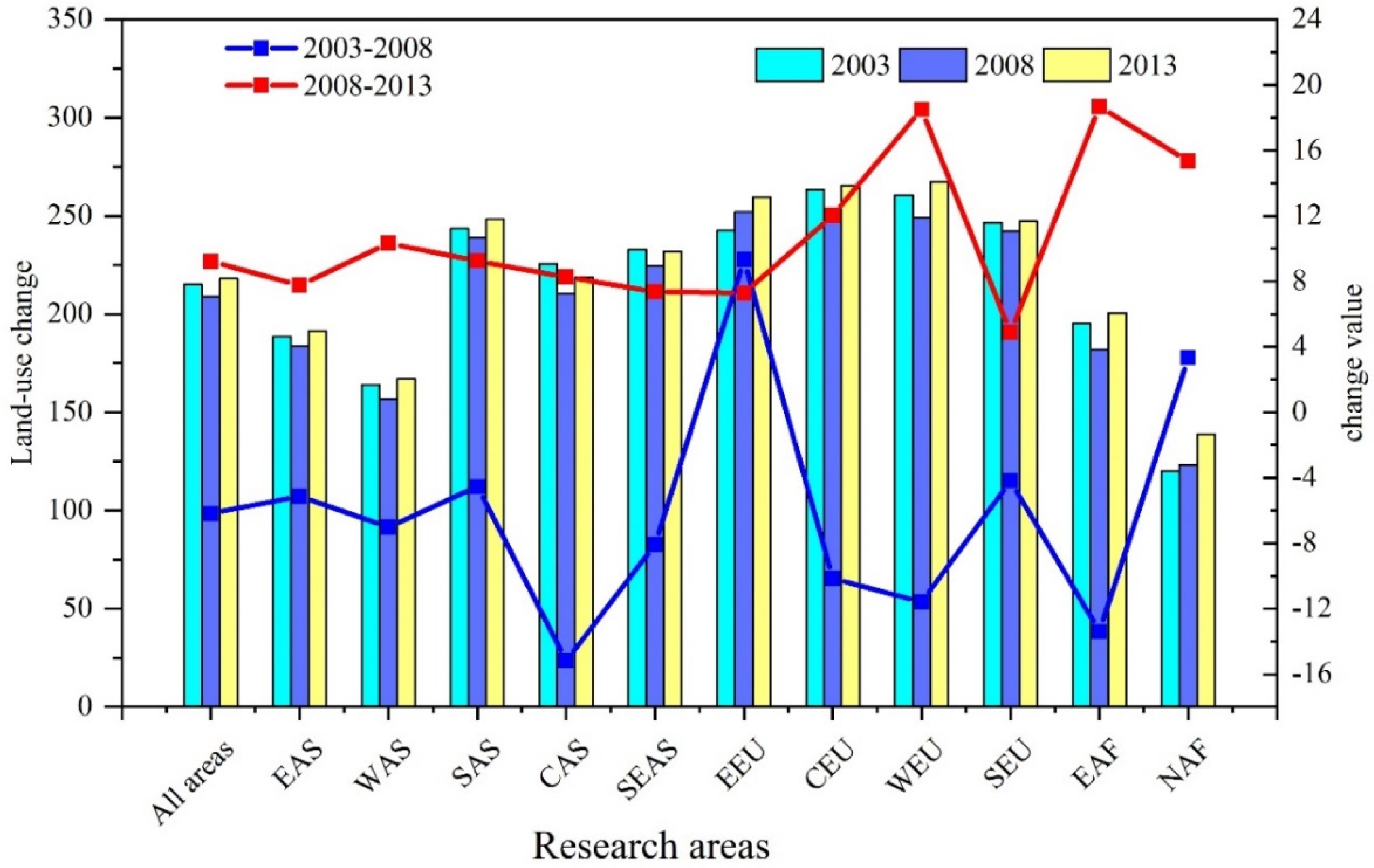
3.1. Land-Use Distribution Pattern of the Belt and Road Areas
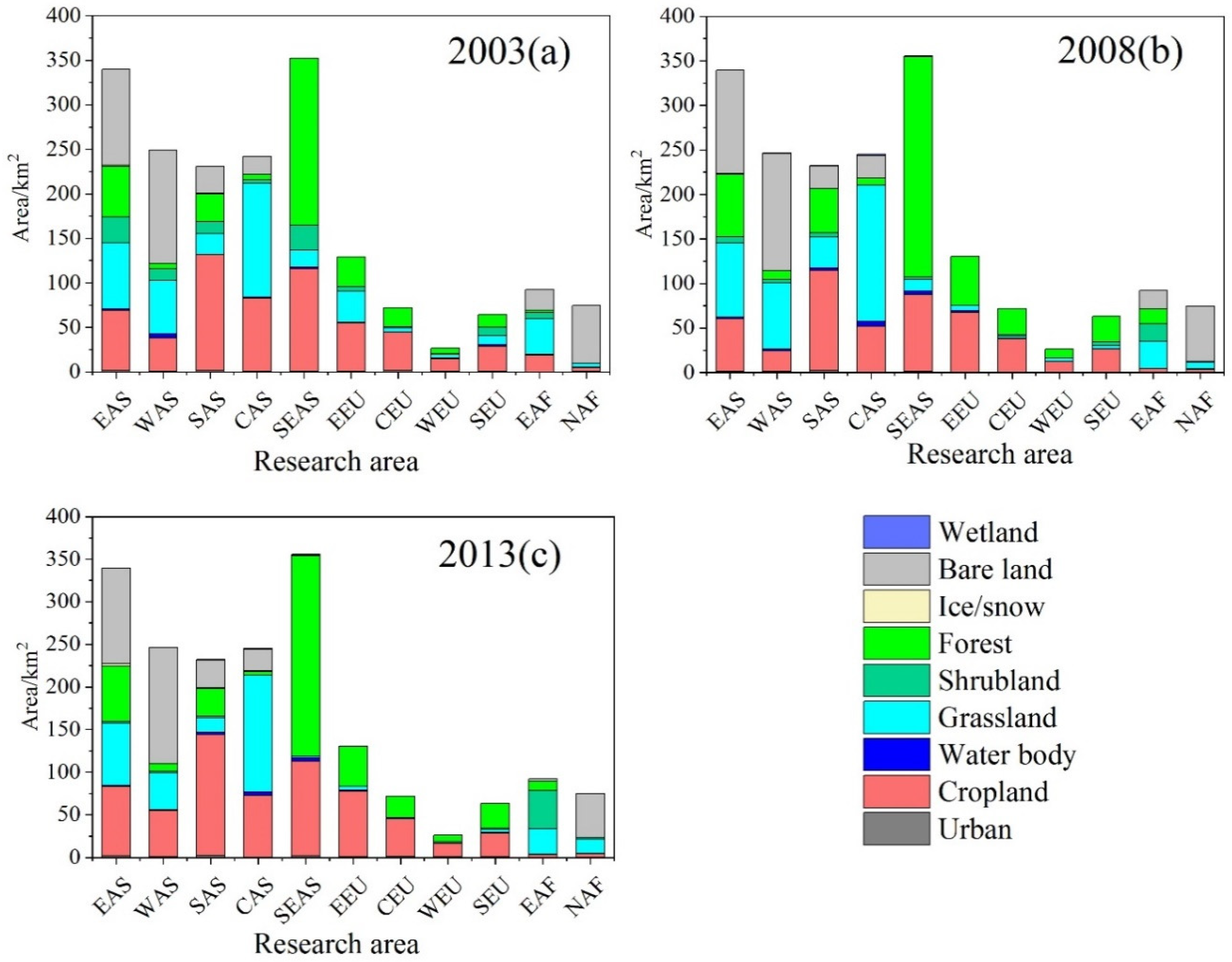
3.2. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land-Use in the Belt and Road Areas
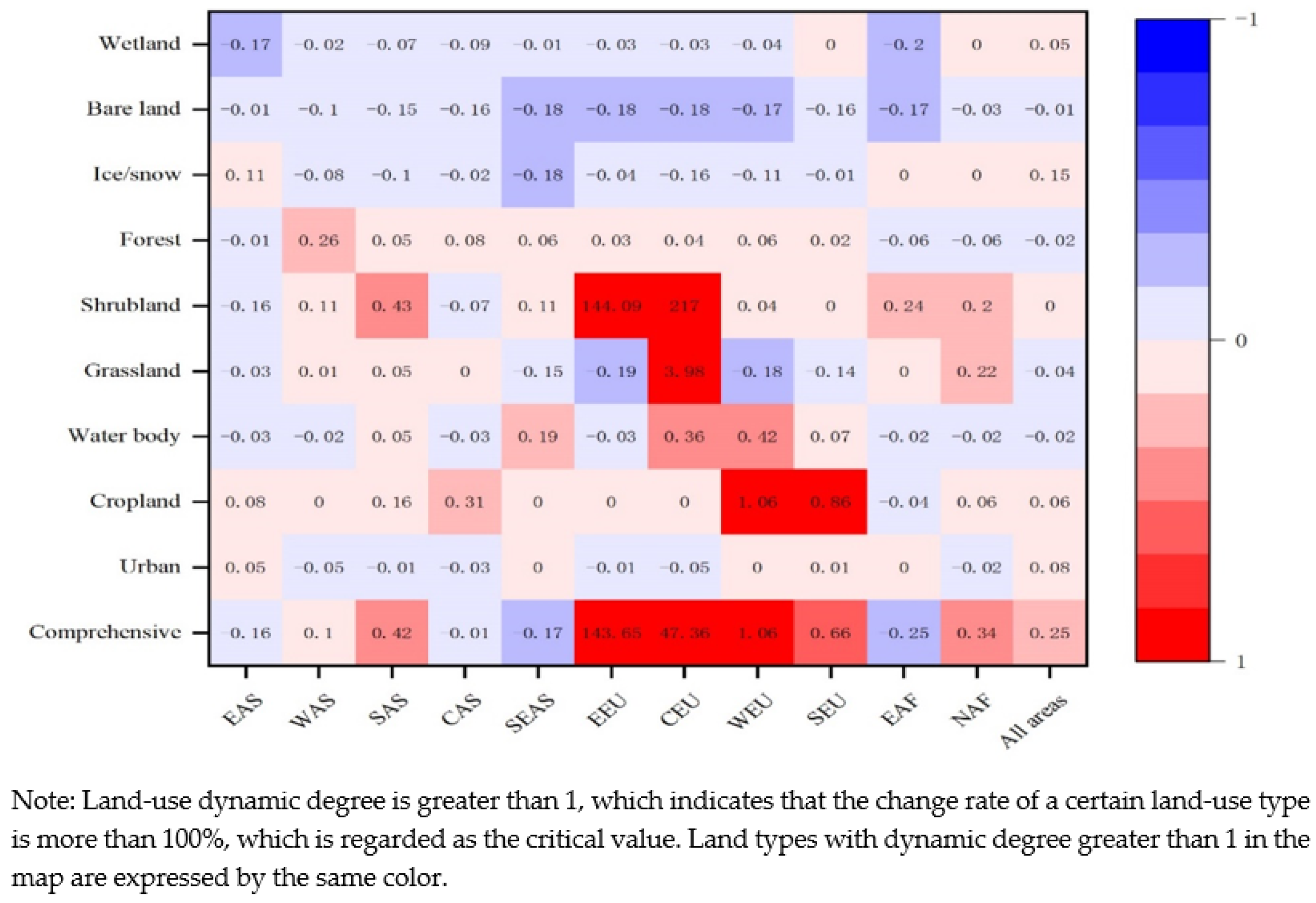
3.2.1. Dynamic Changes in Land-Use in the Belt and Road Areas
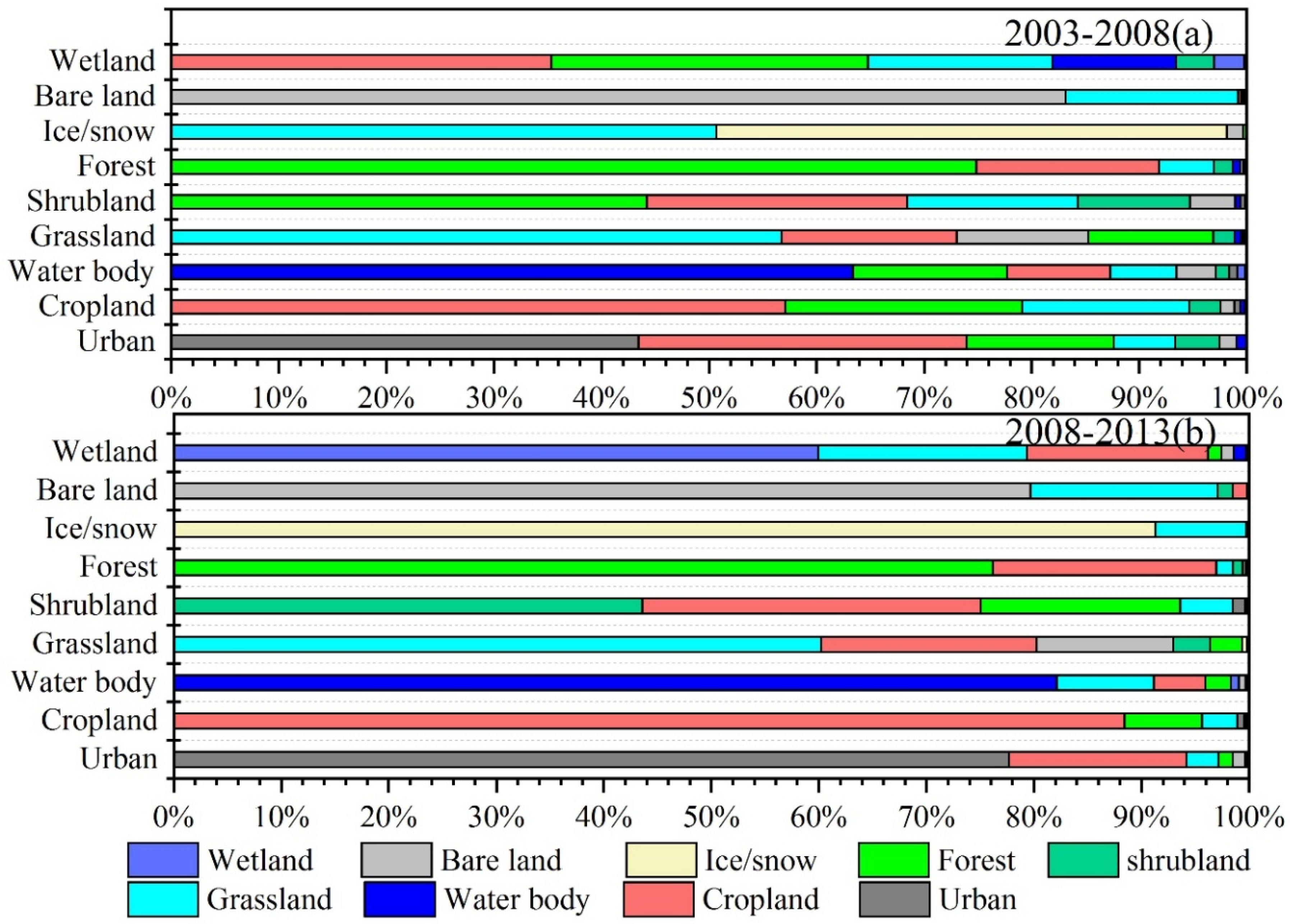
3.2.2. Land-Use Transfer Characteristics of the Belt and Road Areas
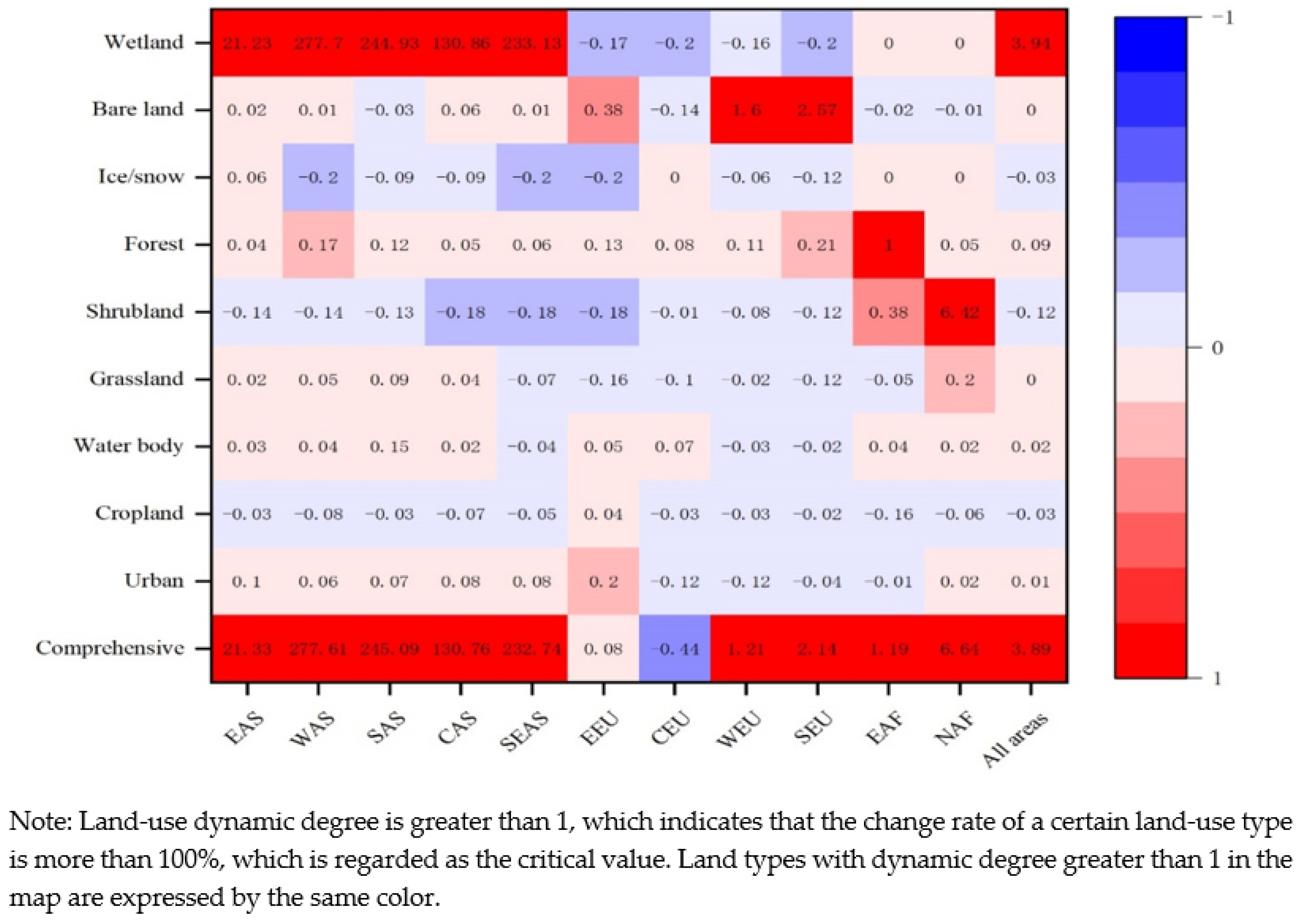
3.2.3. General Change Characteristics of Land-Use Degree in Study Area
3.3. Changes in Ecosystem Services during the Period 2003–2013
4. Discussions
4.1. Land-Use Change Analysis
4.2. Ecosystem Services
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Ministry of Commerce. Vision and Action to Promote the co Construction of the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road [N]. People’s Daily, 2015-03-29 (004). Available online: http://zhs.mofcom.gov.cn/article/xxfb/201503/20150300926644.shtml (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Huang, Y. Understanding China’s Belt & Road Initiative: Motivation, framework and assessment. China Econ. Rev. 2016, 40, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.J.; Duan, N.; Shu, J.M.; Zhang, H.Y.; Jiaerheng, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.B.; Qiao, Q.; Yin, W.L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Ecological Civilization Construction Strategies in the Tianshan Mountain Northern Slope Economic Belt. Strateg. Study Chin. Acad. Eng. 2017, 19, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H. Motivation behind China’s ‘One Belt, One Road’ Initiatives and Establishment of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank. J. Contemp. China 2016, 26, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Shen, Y. Water and ecological security: Dealing with hydroclimatic challenges at the heart of China’s Silk Road. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.; Chunhui, Y.; Strohmaier, D.; Ahmed, M.; Jie, L. Does finance affect environmental degradation: Evidence from One Belt and One Road Initiative region? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9579–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianhong, L.; Wenkai, L.; Zhenghan, Q. Variations in ecosystem service value in response to land use changes in Shenzhen. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Valdéz, V.; Ruiz-Luna, A.; Ghermandi, A.; Nunes, P.A.L.D.; Ruiz-Luna, A. Valuation of ecosystem services provided by coastal wetlands in northwest Mexico. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 78, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Chuai, X.; Dai, C.; Lai, L.; Zhang, M. The impact of land use change on the temporospatial variations of ecosystems services value in China and an optimized land use solution. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, A.; Konteh, W. Autonomy, ambiguity and symbolism in African politics: The development of forest policy in Sierra Leone. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, A.; Fresco, L. Reconstructing land use drivers and their spatial scale dependence for Costa Rica (1973 and 1984). Agric. Syst. 1997, 55, 19–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Luo, D.; Wang, J. Housing Development and Urbanisation in China. World Econ. 2013, 37, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelmans, L.; Van Rompaey, A. Complexity and performance of urban expansion models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2010, 34, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.D.; Kasischke, E.S. Change vector analysis: A technique for the multispectral monitoring of land cover and condition. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Miyamoto, A.; Hasegawa, S.F. Derivation of a yearly transition probability matrix for land-use dynamics and its applications. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 25, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Zhuang, D.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Deng, X.Z. Study on spatial pattern of land-use change in China during 1995-2000. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 46, 373–384. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Aswal, P.; Tanzeem, M.; Saini, S.S. Land Use Land Cover Change Detection using Remote Sensing and GIS in Srinagar, India. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2019, 178, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, Z.X. Land-use/land-cover changes in the Yellow River basin. J. Tsinghua Univ. 2004, 44, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, H.A.; Duraiappah, A.; Larigauderie, A. Evolution of natural and social science interactions in global change research programs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.; Skole, D.; Sanderson, S.; Fischer, G.; Fresco, L. Land-Use and Land-Cover Change: Science/research plan. Glob. Chang. Rep. 1995, 43, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, S.M.; Ducharne, A.; Polcher, J. The impact of global land-cover change on the terrestrial water cycle. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 3, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.; Mendoza, G.; Regetz, J.; Polasky, S.; Tallis, H.; Cameron, D.; Chan, K.M.A.; Daily, G.C.; Goldstein, J.; Kareiva, P.M.; et al. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, B.; Kroll, F.; Nedkov, S.; Müller, F. Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasky, S.; Nelson, E.; Pennington, D.; Johnson, K.A. The Impact of Land-Use Change on Ecosystem Services, Biodiversity and Returns to Landowners: A Case Study in the State of Minnesota. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2010, 48, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Ye, X.; Lee, J.; Lu, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, K. Effects of urbanization on ecosystem service values in a mineral resource-based city. Habitat Int. 2015, 46, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiszewski, I.; Costanza, R.; Anderson, S.J.; Sutton, P.C. The future value of ecosystem services: Global scenarios and national implications. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.; Schulp, C.J.; Verburg, P.H. Mapping ecosystem services demand: A review of current research and future perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 55, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Yan, H.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X. Impacts of urbanization-induced land-use changes on ecosystem services: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, U.P.; Harris, H.G.; Matlock, M.D.; Lacey, R.E. Change in ecosystem service values in the San Antonio area, Texas. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.-Q.; Dong, M.; Cui, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.-L.; Cui, Q.-G.; He, W.-M. Quantification of the Impact of Land-Use Changes on Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in Pingbian County, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 128, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubiszewski, I.; Costanza, R.; Dorji, L.; Thoennes, P.; Tshering, K. An initial estimate of the value of ecosystem services in Bhutan. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 3, e11–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, I.J.; Harwood, A.R.; Mace, G.; Watson, R.T.; Abson, D.J.; Andrews, B.; Binner, A.; Crowe, A.; Day, B.H.; Dugdale, S.; et al. Bringing Ecosystem Services into Economic Decision-Making: Land Use in the United Kingdom. Science 2013, 341, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, J.J.; Lewis, D.J.; Nelson, E.; Plantinga, A.J.; Polasky, S.; Withey, J.C.; Helmers, D.P.; Martinuzzi, S.; Pennington, D.; Radeloff, V.C. Projected land-use change impacts on ecosystem services in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Rao, E.; Jiang, L.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Han, C.H.; Hao, L.G.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, J.X. The main route and water resource areas of the Belt and Road Initiative. Resour. Sci. 2018, 40, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi, R.; Uriyangqai, B.; Al-Bilbisi, H.; Ghar, M.A.; Tsend-Ayush, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Kasimu, A.; Hoan, N.T.; Shalaby, A.; Alsaaideh, B.; et al. Production of global land cover data—GLCNMO. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 4, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, R.; Hoan, N.T.; Kobayashi, T.; Alsaaideh, B.; Tana, G.; Phong, D.X. Production of Global Land Cover Data—GLCNMO2008. J. Geogr. Geol. 2014, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Tateishi, R.; Alsaaideh, B.; Sharma, R.C.; Wakaizumi, T.; Miyamoto, D.; Bai, X.L.; Long, B.D.; Gegentana, G.; Maitiniyazi, A.; et al. Production of Global Land Cover Data—GLCNMO2013. J. Geogr. Geol. 2017, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer resolution observation and monitoring of global land cover: First mapping results with Landsat TM and ETM+ data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, B.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.; Wen, Q.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.; Hu, S. A 2010 update of National Land Use/Cover Database of China at 1:100000 scale using medium spatial resolution satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, P.; Yu, L.; Hu, L.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Towards a common validation sample set for global land-cover mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4795–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Feng, Z.M.; Jiang, L.G. Progress on studies of land use/land cover classification systems. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Niu, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, Y. Land use changes and its driving forces in hilly ecological restoration area based on gis and rs of northern china. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Chen, J.-F.; Qiu, H.-L.; Römkens, M.; Yang, X.; Jiang, S.-F.; Li, B.-C. Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Driving Forces of Land Use Changes in Xiamen. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y. Macro Survey and Dynamic Research of China’s Resources and Environment Remote Sensing; Science and Technology of China Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Haines-Young, R.H.; Potschin, M.; Kienast, F. Indicators of ecosystem service potential at European scales: Mapping marginal changes and trade-offs. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, I.J.; Mace, G.; Fezzi, C.; Atkinson, G.; Turner, K. Economic Analysis for Ecosystem Service Assessments. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2010, 48, 177–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.; Teluguntla, P.G.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Giri, C.; Pyla, V.; Dixit, S.; Whitbread, A. Agricultural cropland extent and areas of South Asia derived using Landsat satellite 30-m time-series big-data using random forest machine learning algorithms on the Google Earth Engine cloud. GIScience Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Knox, J.W.; Ozdogan, M.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Wu, Z.T.; Milesi, C.; Finkral, A.; Marshall, M.; Mariotto, I.; et al. Assessing Future Risks to Agricultural Productivity, Water Resources and Food Security: How Can Remote Sensing Help? Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 773–782. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Lu, M.; Wu, W.; Ru, Y. Multiple factors influence the consistency of cropland datasets in Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 89, 102087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, J.; Wong, C.M.; ChinLiew, S. 500M spatial resolution land cover map in insular Southeast Asia. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; pp. III-314–III-317. [Google Scholar]
- Andreas, B.B.; Hugh, D.E. The potential use of high-resolution Landsat satellite data for detecting land-cover change in the Greater Horn of Africa. Afr. Geogr. Rev. 2015, 33, 209–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ricaurte, L.F.; Olaya-Rodríguez, M.H.; Cepeda-Valencia, J.; Lara, D.; Arroyave-Suárez, J.; Finlayson, C.M.; Palomo, I. Future impacts of drivers of change on wetland ecosystem services in Colombia. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2017, 44, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Harms, M.J.; Balvanera, P. Methods for mapping ecosystem service supply: A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2012, 8, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, Z.; Gibson, J. A review on trade-off analysis of ecosystem services for sustainable land-use management. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J. Analysis on spatial-temporal characteristics and driving force of land-use change in Hainan island. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS 2003, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 2644, pp. 2641–2643. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K. The Routledge Handbook of Urbanization and Global Environmental Change; Informa UK Limited: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.A.; Pfautsch, S. Grand Challenges: Forests and Global Change. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2018, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. State of the World’s Forests 2016. Forests and agriculture: Land-use challenges and opportunities. Food Agric. Organ. U. N. Rome 2016, 105–107. [Google Scholar]
- MacDicken, K.G.; Sola, P.; Hall, J.E.; Sabogal, C.; Tadoum, M.; De Wasseige, C. Global progress toward sustainable forest management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 352, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.F.; Ge, C.Z.; Wang, J.N.; Yan, X.D.; Cheng, C.Y. The strategic implementation framework of “The Belt and Road” green development. China Environ. Manag. 2016, 8, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H. Towards Sustainable Land Use in China: A Collection of Empirical Studies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; He, Y.; Xie, X. Exploring the factors influencing ecological land change for China’s Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region using big data. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Lu, H. Impact of land fragmentation and non-agricultural labor supply on circulation of agricultural land management rights. Land Use Policy 2017, 68, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Yang, D.G.; Shi, J.J.; Cai, W.C. Analysis on Land Use Change and Driving Force in Urumqi. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2007, 21, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H. Land use policy in China: Introduction. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, W.F. Reflections on the tropical deforestation crisis. Biol. Conserv. 1999, 91, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catinot, R. Tropical silviculture in dense African forest (Part 1). Bois Forets Trop. 2018, 336, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; De Groot, R.; Sutton, P.C.; Van Der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoke, T.; Steinbeis, O.-E.; Bösch, M.; Roman-Cuesta, R.M.; Burkhardt, T. Cost-effective compensation to avoid carbon emissions from forest loss: An approach to consider price–quantity effects and risk-aversion. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1139–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Lu, N.; Xu, Z.; Ren, J.; Xing, K. Linking land use change, ecosystem services and human well-being: A case study of the Manas River Basin of Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 27, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Changes of ecosystem service values in response to land use/land cover dynamics in Munessa–Shashemene landscape of the Ethiopian highlands. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 547, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| FAO/UNEP LCCS Classification System | Land-Use Types |
|---|---|
| Wetland | Wetland |
| Bare area, consolidated (gravel, rock); Bare area, unconsolidated (sand) | Bare area |
| Ice/Snow | Ice/snow |
| Broadleaf Evergreen Forest, Broadleaf Deciduous Forest, Needleleaf Evergreen Forest, Needleleaf Deciduous Forest, Mixed Forest, Tree Open, Mangrove | Forest |
| Shrub, Sparse vegetation | Shrubland |
| Herbaceous, Herbaceous with Sparse Tree/Shrub | Grassland |
| Water body | Water body |
| Cropland, Paddy field, Cropland/Other Vegetation Mosaic | Cropland |
| Urban | Urban |
| Land-Use Types | Classification Types of Land-Use | Graded Index | Equivalent Biomes | Ecosystem Services Coefficient (US $ ha−1 year−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wetland | Unused land grade | 1 | Wetland | 14785 |
| Bare land | Unused land grade | 1 | Rock | 0 |
| Ice/snow | Unused land grade | 1 | Ice | 0 |
| Forest | Forest, Grass and Water Land Grade | 2 | Forest | 969 |
| Shrubland | Forest, Grass and Water Land Grade | 2 | Forest | 969 |
| Grassland | Forest, Grass and Water Land Grade | 2 | Grass/rangelands | 232 |
| Water body | Forest, Grass and Water Land Grade | 2 | Lakes/rivers | 8498 |
| Cropland | Agricultural Land Level | 3 | Cropland | 92 |
| Urban | Urban Settlement Land Level | 4 | Urban | 0 |
| Type | Wetland | Bare Land | Ice/Snow | Forest | Shrubland | Grassland | Water Body | Cropland | Urban | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wetland | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.13 |
| Bare land | 0.12 | 291.84 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.61 | 56.34 | 0.60 | 0.93 | 0.29 | 350.96 |
| Ice/snow | 0.00 | 0.05 | 1.44 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 1.54 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.04 |
| Forest | 0.53 | 0.89 | 0.13 | 249.54 | 5.88 | 16.99 | 2.33 | 56.53 | 0.48 | 333.30 |
| Shrubland | 0.16 | 4.49 | 0.00 | 47.18 | 11.15 | 16.93 | 0.54 | 25.8 | 0.43 | 106.68 |
| Grassland | 0.79 | 53.48 | 0.99 | 50.78 | 8.70 | 247.94 | 2.60 | 71.13 | 0.56 | 436.97 |
| Water body | 0.14 | 0.69 | 0.03 | 2.66 | 0.23 | 1.14 | 11.78 | 1.79 | 0.14 | 18.6 |
| Cropland | 1.07 | 7.79 | 0.00 | 136.07 | 17.82 | 96.27 | 2.61 | 352.96 | 3.56 | 618.15 |
| Urban | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 1.26 | 0.38 | 0.53 | 0.09 | 2.80 | 3.99 | 9.99 |
| Total | 2.81 | 359.37 | 2.63 | 487.73 | 44.77 | 437.70 | 20.57 | 511.99 | 9.45 | 1877 |
| Type | Wetland | Bare land | Ice/Snow | Forest | Shrubland | Grassland | Water Body | Cropland | Urban | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wetland | 1.69 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 2.82 |
| Bare land | 0.18 | 286.2 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 5.10 | 62.48 | 0.18 | 4.80 | 0.04 | 359.21 |
| Ice/snow | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.62 |
| Forest | 0.64 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 371.42 | 4.42 | 7.60 | 0.70 | 101.52 | 1.42 | 487.77 |
| Shrubland | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 8.33 | 19.51 | 2.18 | 0.05 | 14.08 | 0.52 | 44.77 |
| Grassland | 0.11 | 55.52 | 2.11 | 12.97 | 15.13 | 263.47 | 0.26 | 87.59 | 0.37 | 437.53 |
| Water body | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.03 | 1.89 | 17.21 | 1.00 | 0.04 | 20.94 |
| Cropland | 0.77 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 36.81 | 0.94 | 16.67 | 0.36 | 452.63 | 3.39 | 511.81 |
| Urban | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 1.56 | 7.35 | 9.46 |
| Total | 3.56 | 342.35 | 4.62 | 430.33 | 45.14 | 355.34 | 18.81 | 663.65 | 13.13 | 1877 |
| Land-Use Types | ESV (US $ Million) | ESV (US $ Million) Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 2008 | 2013 | 2003–2008 | 2008–2013 | 2003–2013 | |
| Wetland | 0.20 | 4.17 | 5.28 | 3.97 (1985%) | 1.11 (26.62%) | 5.08 (2540%) |
| Bare land | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Ice/snow | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Forest | 32.30 | 47.26 | 41.70 | 14.96 (46.32%) | −5.56 (−11.76%) | 9.40 (29.10%) |
| Shrubland | 10.34 | 4.34 | 4.37 | −6.00 (−58.03%) | 0.04 (0.69%) | −5.97 (−57.73%) |
| Grassland | 10.66 | 10.68 | 8.67 | 0.02 (0.19%) | −2.01 (18.82%) | −1.99 (−18.67%) |
| Water body | 15.79 | 17.46 | 15.99 | 1.67 (10.58%) | −1.47 (−8.42%) | 0.20 (1.27%) |
| Cropland | 5.69 | 4.71 | 6.11 | −0.98 (17.22%) | 1.40 (29.72%) | 0.42 (7.38%) |
| Urban | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Total | 74.98 | 88.62 | 82.12 | 13.64 (18.19%) | −6.50 (−7.33%) | 7.14 (9.52%) |
| Ecosystem Service | ESV2003 | ESV2013 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas regulation | 0.31 | 0.30 | −0.01 |
| Climate regulation | 6.20 | 6.70 | 0.50 |
| Disturbance regulation | 0.15 | 1.72 | 1.57 |
| Water regulation | 10.34 | 10.45 | 0.11 |
| Water supply | 4.12 | 5.48 | 1.36 |
| Erosion control | 5.49 | 5.60 | 0.11 |
| Soil formation | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.03 |
| Nutrient cycling | 15.89 | 17.16 | 1.27 |
| Waste treatment | 8.92 | 9.97 | 1.05 |
| Biological control | 1.96 | 1.82 | −0.14 |
| Food production | 2.58 | 2.50 | −0.08 |
| Raw material | 0.004 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Genetic resource | 8.24 | 8.18 | −0.06 |
| Recreation | 6.07 | 6.60 | 0.53 |
| Cultural | 0.70 | 0.76 | 0.06 |
| Pollution control | 3.43 | 3.85 | 0.42 |
| Habitat/refugia | 0.10 | 0.41 | 0.31 |
| Sum | 74.98 | 82.12 | 7.14 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, Q.; Li, X.; Hao, L.; Hao, M. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land-Use and Ecosystem Services Valuation in the Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6583. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166583
Zuo Q, Li X, Hao L, Hao M. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land-Use and Ecosystem Services Valuation in the Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability. 2020; 12(16):6583. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166583
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Qiting, Xing Li, Lingang Hao, and Minghui Hao. 2020. "Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land-Use and Ecosystem Services Valuation in the Belt and Road Initiative" Sustainability 12, no. 16: 6583. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166583
APA StyleZuo, Q., Li, X., Hao, L., & Hao, M. (2020). Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land-Use and Ecosystem Services Valuation in the Belt and Road Initiative. Sustainability, 12(16), 6583. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12166583





