Abstract
Information security management (ISM) has emerged as a major challenge to sustainable management of companies that highly rely on information technology (IT). To achieve organizational sustainability for managing assets, it is critical for all members of the organization to be assimilated into ISM. An important consideration of ISM assimilation is sustainable IT capabilities. However, so far, there are limited empirical studies on ISM assimilation, particularly those focusing on importance of the organization’s sustainable IT capabilities. Therefore, this study proposes three sustainable IT capabilities (viz., IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance) with their antecedents based on the existing research, and attempts to empirically prove the impact of these sustainable IT capabilities on ISM assimilation for sustainable management of assets. Additionally, this study proposes policy-to-technology balance as a moderator on the relationships between the three sustainable IT capabilities and ISM assimilation to examine the impact of the non-technical aspect. Responses from 232 upper-management-level employees at various firms currently implementing ISM were collected. Structural equation analysis was run using AMOS 22.0. The results show that the three sustainable IT capabilities were found to have a positive effect on ISM. Furthermore, policy-to-technology balance was found to strengthen the relationship between two IT capabilities (IT infrastructure and IT business spanning capability) and ISM assimilation. However, it emerges that the policy-to-technology balance does not impact IT proactive stance and assimilation. The findings provide meaningful information for future research on sustainable IT capabilities and ISM along with key guidance for the organization to establish a complementary strategy for sustainable assets.
1. Introduction
Several present-day businesses rely heavily on information technology (IT) as a crucial tool to ensure productivity and efficiency across their activities. However, as the use of IT increases, the problem of redressing security risk—which is a possibility that certain threats can damage organizational systems—to information and systems is intensifying [1]. With the fast-growing Internet technology, it is easy to acquire advanced hacking technology. Moreover, information leakage, targeting not only individuals but also the organization, frequently occurs. While adoption of a wide range of information technologies has resulted in higher productivity and efficiency, companies are constantly exposed to security risks, which pose a potential threat to the organization’s sustainability [2].
In addition, as the organization’s data and information infrastructure become more sophisticated, the variety of data and information increases; therefore, efficient management of these resources becomes a major goal of corporate management activities and IT. Security management in response to the ever-increasing proportion of data privacy issues and the leakage of confidential data has emerged as one of the major issues to be addressed in management [3,4,5]. Accordingly, the demand for information security management (ISM) that includes various activities to protect organizational information from several risks and ensure business continuity and opportunities is gradually increasing [4]. Companies are, thus, focusing on the ISM to maintain a higher level of business sustainability. This is because security risks, that is, the risk of loss of integrity, privacy, or accessibility of information in any form due to ineffectual management or unplanned events, are likely to cause tremendous damages, both tangible and intangible, such as a decline in corporate brand value, a decrease in corporate credibility, and financial damage [6].
As there is greater awareness of the potential risks in organizational assets, investment in ISM is increasing, and several approaches have evolved to mitigate the risk depending on the scope of application. In this regard, Bishop [7] claimed that security of IT depends on three elements: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. In general, judgments on information security have led to extensive research on these three elements. In addition, due to the proliferation of IT, the purpose of information security itself is described as securing three elements of information [8,9,10]. However, an organization’s information system might be exposed to security risks because of technical failures, system vulnerabilities, human error, or external factors. It is necessary to prepare in advance a management base to prevent such risks and even act after an accident. That is, a company-wide security management policy and system introduction becomes crucial for sustainable security management.
However, majority of the existing studies on organizational information security focuses on technical aspects, but few address the organizational aspects that limit the ability to explain the company’s internal strategy on information security. In this respect, Sanderson and Forcht [11] claimed that the studies on information security should not be limited to the technical part alone because various security risks arise from users using technologies in an organization. Thus, it is necessary to consider information security as a social and organizational issue because not only do security-related problems change over time, but also most IT operations are performed by humans [12]. Furthermore, Doherty and Fulford [13] argued that because technology-driven information security studies focus on external threats such as hackers and viruses, there is a lack of preparation for violations or risks from within the organization, and that organizational research is important for continuity of information security. In other words, to explain an organization’s ISM, the non-technical matters that organizations and members must follow should not be overlooked [14].
Although ISM is meant to protect valuable assets and mitigate various risks arising from all factors in the organization’s environment, corporate efforts for information security generally focus only on weaknesses in technical assets such as hardware, software, and networking. This can be seen as a consequence of sacrificing the cost of managing weaknesses for other sources such as people, processes, and culture [14,15,16]. Thus, focusing on technical solutions for ISM is not sufficient for firms to mitigate security risks and increase sustainability of protecting assets [6,17,18].
In addition, as the significance of the organization’s information security system is increasingly emphasized, organizations are making efforts to implement the correct information security strategy through the support of the information system and IT technology. However, it is difficult to ensure a security solution only with technical support, because security-related technology is a necessary condition, but not sufficient for successful security management. In other words, security products, such as hardware and software, cannot protect an organization’s information without good policy and management [19]. Actual information security problems are not only caused by technical reasons but also by non-technical reasons in many cases [10,16]. Thus, empirical studies reflect that two perspectives are required, rather than separately addressing technical or non-technical elements in ISM.
Based on the rationales of the study, and important implications for and limitations of ISM in the existing research, the main purpose of this study is to propose and verify a research model that explains the effects of three dimensions of IT capabilities (IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance) on the ISM assimilation. In addition, the proposed research model includes the policy-to-technology balance as an enhancing factor for the relationships between IT capability and ISM assimilation. The data were collected from members in various organizations to empirically test the proposed research model using the structural equation modeling (SEM) approach. Findings of the study may have both academic and practical contributions, in that this study takes a new approach, considering both technical and non-technical factors in explaining the assimilation of organizational ISM for sustainable management of assets within organizations.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Resource-Based View (RBV)
Resource-based view (RBV) has a major impact on current business-related discussions, because it is appropriate to describe an organization’s internal sources to maintain competitive advantage and sustainability. RBV proposes that if a company wants to maintain its competitive advantage and sustainability, it must acquire and manage unique, inimitable, and irreplaceable resources and abilities, and at the same time must build an organization that can absorb and apply these resources and abilities [20]. In other words, a resource-based perspective is a discussion of the resources owned by a company that preempts its competitive advantage and allows it to achieve better long-term performance [21,22]. In this regard, earlier studies [23,24] claimed that a company’s performance originates from its specific capabilities and assets that are sustainable and help in establishing and maintaining a competitive advantage. In a rapidly changing environment, such as the experience of rapid technology transfer, dynamic competency is essential to enhance internal business capabilities. Bhatt and Grover [25] described a company’s empowerment as one of the unique strategic mechanisms for strengthening the influence of corporate resources, because resources are unique and inimitable, deeply located within the enterprise. In this study, the characteristics of RBV with regard to competitive advantage and sustainability for managing information security within an organization are classified into three abilities: value, competitive, and dynamic.
Investment in the IT infrastructure is classified as a value capability. IT management capabilities, including IT business experience and relationships, are classified as competitive capabilities, while dynamic capabilities include knowledge sharing and accumulation or organizational learning. This classification aims to differentiate the source of IT-based competitive advantage, which can guide organizational-level capabilities. In general, value and uniqueness are prerequisites for preemptive advantage, while irreplaceable organizational knowledge is a prerequisite for maintaining competitive advantage and increasing sustainability [25]. The present study considers that information security can be managed based on the organization’s sustainable resources when establishing a security strategy. Therefore, by focusing on sustainable IT capabilities related to information protection and security management systems among the resources in the organization, the study proposes a method to establish and strengthen ISM within the organization.
2.2. Sustainable Information Technology Capability
Various definitions of sustainable IT capability have been proposed based on the RBV. For example, Bharadwaj [26] defined sustainable IT capability as a firm’s ability to develop and mobilize IT-based resources that appear or combine with other resources and capabilities. Tippins and Sohi [27] conceptualized sustainable IT competency as a degree of knowledge about using IT efficiently to manage and sustain assets in the company. Furthermore, they classified sustainable IT capability into three dimensions: knowledge, operations, and objects. This classification not only includes tangible and intangible elements of IT skills, but also introduces the effects of IT operations and IT knowledge work. Based on these classifications, Li et al. [28] defined IT knowledge as a firm’s extent of technical knowledge about IT objects such as system-based computers, while IT operation refers to the extent that a firm uses IT to manage and sustain customer information and markets. Finally, IT objects include hardware/software (HW/SW), network, user supports, and others as a part of an ongoing IT policies. The value of IT is revealed when sustainable IT capabilities are aligned with business strategies and used to increase innovation [29].
Another perspective of sustainable IT capability is related to the technical and organizational competency [30]. IT technology capability implies physical assets such as HW/SW, network, and database that can facilitate a company’s functionality in terms of scope and accessibility to share information [26,31]. In addition, a firm’s IT technological capability, including IT infrastructure, can be a source of competitive advantage when it can realize business objectives such as improved cycle times and streamlined business processes [32]. The strength of an organization’s technical capabilities reduces the complexity of integration and enables IT departments to deliver new technologies quickly and efficiently [33].
Studies exist on sustainable IT capability from an organizational management perspective. For example, Teece et al. [34] and Sambamurthy et al. [35] described organization-level capabilities based on resource-based theory. Organizational management skills include organizational leadership skills and ability to promote technology integration and coordinate organizational planning [26]. With rapid change in technology and uncertain future competition and markets, timing has become an important issue because innovative responses require a quicker time to market. Therefore, it is crucial for a firm to build organizational management skills to properly apply, integrate, and transform technologies and resources inside and outside the organization, and to develop a functional and dynamic capability to meet the needs of the changing environment. This dynamic ability not only updates the organization’s diverse resources, but also explains that core competencies can change dynamically. Dynamic ability can be applied to various fields that describe organizational management capabilities such as product and process development, technology transfer, intellectual capital, manufacturing, and organizational learning [28].
Teece et al. [34] explained organizational management capabilities by defining a company’s distinctive and dynamic capabilities from three perspectives: process, position, and path. Process is related to the approach that companies follow to carry out their day-to-day operations, or what they are currently engaged in, and what they want to learn. Position is related to a firm’s current specific capabilities, including its assets such as technical, complementary, reputation, financial, structural, and market. Finally, path indicates the specific direction of competency development that the company should adopt. In general, firms that have a competitive advantage operate according to the organizational processes formed by the possible directions and the status of specific assets. In addition, other studies have presented organizational management capabilities in three categories: process capital, agility, and corporate boundaries [28,35].
Based on earlier studies, this study conceptualized sustainable IT competency as an ability to strengthen competitiveness for changing technologies among organizational capabilities in terms of IT flexibility. In other words, a firm’s sustainable IT capabilities can include improved ISM. A company’s ability to provide quick and efficient technical solutions lies in integrating new IT innovations within its current infrastructure [30]. Consistently strengthening IT capabilities reduces the cost of developing new technologies and enables companies to earn financial and productivity gains. Furthermore, this study proposes sustainable IT capabilities as a company-specific ability to integrate and deploy valuable resources that are distinct from other companies to measure performance, despite the similar internal and external resources [26,30]. Therefore, flexible and sustainable IT capabilities will enable quick adaptation and response in organizational security management and be an indicator of successful security management development.
2.3. Policy-to-Technology Balance
To undertake ISM, the company’s IT must be well integrated with the security management system. Integrating existing systems with the new information technologies is easier and offers more opportunities for organizations to benefit from the integration [36]. If the new system harmonizes with the organizational IT structure and strategy, the satisfaction of the users increases [37]. In this context, task–technology fit is a concept similar to policy–technology balance, referring to the extent to which new IT can support various tasks by enabling smooth business processes within the organization [38].
Earlier studies [39] claimed that task–technology fit is the degree of agreement between IT supported for specific tasks undertaken by members of the organization, and the functions required to perform such a task. Therefore, a high task–technology fit leads to a positive attitude and positive results for the technology [40]. Similar to the characteristics of task–technology fit, the unit of security management in ISM is a matter of the entire organization, so the performance or behavior of the ISM of the organization can be determined according to the level of balance between the organization’s security policy and the appropriate technology. That is, it can be assumed that the harmonization between the IT supported by the organization and its security policy for ISM will affect the organization’s ISM [3,5].
Earlier studies described harmonization of policy and technology as the level of IT that can interact with various divisions in the organization, which implies the harmonization with technology that can accommodate changes in specific areas such as IT strategy [41]. For example, past studies [42,43] related to electronic data interchange (EDI) adoption claimed that differences and inconsistencies between standards or policies and technologies not only result in several obstacles, but also serve as a major inhibitor to the use and expansion of EDI between enterprises. This difficulty is compounded because the standards and technical elements adopted by EDI differ from the organization’s existing information system [44]. In other words, the integrated EDI following diverse standards and policies further exacerbates the complexity of applying various internal applications and databases because of the uniqueness of individual enterprise technology environments [41].
In the case of an IT venture company, when framing a technology development strategy, strategies such as technology innovation, upgrade strategy, and resource utilization are important factors depending on the external environment. Since venture companies are sensitive to technology development and the environment, its results can be obtained through harmonization of strategy development and technology [45]. To adopt a new information security policy for managing information security, the technical infrastructure, composition, and operation of the existing information system must be considered. As new or strengthened policies may change how organizations handle business, managers will be passive in establishing and adopting better policies if implementation is laborious and adaptation is time-consuming [46]. Therefore, if the current information systems are compatible with the technological infrastructure, the policy and decision-making on information security at the organization level will be more efficient.
2.4. Prior Studies in Information Security Management Assimilation
Research on ISM has been conducted in two directions: technology and management innovation. Prior studies that dealt with security as a technology innovation research generally defined computer security as a basic concept. For example, Cavusoglu et al. [6] studied the value of IT security architecture, and Gordon and Loeb [47] explored the economic implications of organizational capital expenditure for information security. However, this research, as regards technological innovation on information security, does not provide sufficient and adequate explanation when the organizational structure stands out and the organization becomes more organic [17]. However, Ransbotham and Mitra [5] defined ISM as focusing on management activities that promote a secure environment. Therefore, ISM assimilation includes continuous improvement of and changes in its management to adapt to various environmental changes, which is consistent with the organizational-environmental view of management innovation.
From this perspective, IT capabilities are essential for the ISM of the organization and should be considered [46]. For example, Chang and Ho [10] found a positive relationship between ISM and business IT management skills. Furthermore, Hsu et al. [48] demonstrated how external economic efficiency and internal organizational capabilities work between the pressure on institutional unity and ISM, based on the institutional theory of organizational information system innovation.
3. Research Model and Hypotheses
3.1. Research Model
As there is growing interest in corporate information security management, the importance of developing and strengthening ISM has been emphasized, while the awareness or investment in corporate ISM is insufficient. Therefore, theoretical research is needed to make decisions on the organization’s ISM or to provide solutions for security problems, such that organizations are able to sustain their information security assets. In addition, earlier studies on ISM underlined the need for security management, and majority of the studies focused on defining concepts or technical emphasis and presenting a security management model and the necessary factors [49,50]. Therefore, this study empirically verifies the factors that affect the assimilation of ISM by members to maintain the continuity of information security. In particular, with the focus on sustainable IT capabilities as a key determinant among the various resources within the organization, this study examines the relationship between sustainable IT capabilities and ISM assimilation to establish and strengthen ISM within the organization. Based on past literature [10], an organization’s sustainable IT capabilities are grouped into three dimensions: IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance. Each dimension has antecedent variables. Therefore, this study suggests data management, network, and HW/SW capability as the antecedents of IT infrastructure, while IT management, IT vision, and IT plan are suggested as the antecedents of IT business spanning capability. Finally, IT learning culture, IT investment, and IT innovation are the proposed antecedents of IT proactive stance [15].
In addition to the direct effects, the proposed research model includes policy-to-technology balance as a moderator between sustainable IT capability and ISM assimilation. To increase the sustainability of an organization’s information security, the organization’s policies must be harmonized with the technologies in use. In particular, in the environment in which an organization increases its ISM assimilation with sustainable IT capabilities, the harmony between policy and technology creates greater synergy in ISM [15,16]. Therefore, in the ISM study, this variable was included to verify its role in the organization’s information security sustainability. Figure 1 describes the research model with the proposed hypotheses.
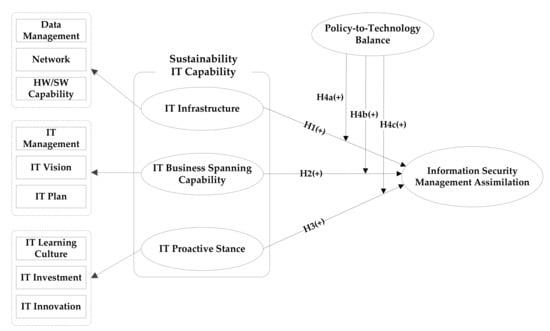
Figure 1.
Research model and proposed hypotheses. IT: information technology; HW/SW: hardware/software.
3.2. Hypotheses Development
3.2.1. Sustainable IT Capabilities
IT infrastructure reflects the diversity and harmonization of the IT components needed to support business applications. An organization’s well-established IT infrastructure not only provides an integrated platform for data and process integration and standardization, but also enables accurate and timely information collection and information sharing [51]. In addition, the organization’s IT infrastructure enables real-time shareable and comprehensive information to facilitate efficient decision-making [52]. This real-time access to information supports an expanded environmental footprint to collect, track, and distribute information to change customer needs, competitors, technology, or regulatory development [53].
The integrated IT infrastructure provides a platform for creating digital choices to support companies to enable access, integration, and development of knowledge and to improve the richness and reach of their processes and knowledge [35]. For example, IT infrastructure establishes a network where members at a firm can share data and information for managing knowledge. Through this network, it is possible to simultaneously adopt various IT-enabled approaches, such as automatically modifying and storing knowledge that is shared and reused through a database [54]. A state-of-the-art IT infrastructure enables internal judgment to cope with changes in market demand or supply disruptions and frequent or unexpected rapid changes.
IT infrastructure plays a key role in enterprise-wide applications, databases, and collaborative systems to perform quickly, intensively, and innovatively; rapidly change processes; and provide the best support initiatives for demand [55,56]. Underlining the importance of IT infrastructure as a firm’s sustainable technology asset, Weill and Broadbent [57] suggested an association between IT infrastructure and IT assimilation for increasing sustainability of ISM. In other words, a mature IT infrastructure allows organizations to develop higher levels of technical knowledge, which promotes better innovation and IT assimilation [58,59]. In addition, Sambamurthy and Zmud [60] claimed that IT infrastructure strengthens the ability and willingness of business managers to shape innovative IT applications, which creates compatible advantages in managing information security. ISM develops a higher level of security knowledge based on a mature IT infrastructure and improves the ability and willingness of business managers to promote better ISM assimilation to increase the sustainability of the organization’s information security [59]. Based on these claims, the following hypothesis was proposed:
Hypothesis 1. (H1):
IT infrastructure will have a positive effect on ISM assimilation.
Another sustainable IT capability is the IT business spanning capability, referring to an organization’s ability to plan and develop IT resources that strengthen and support the purpose of business activities [60,61]. This ability to connect with IT creates synergies between the organization’s IT and business partnerships, thus enabling them to frame effective IT strategies combined with organizational decisions [62,63]. In addition, close interaction and collaboration between IT and business fosters long-term maturity of trust and respect that encourages knowledge sharing and exchange between IT and managers. This shared knowledge not only influences the organization’s IT use, IT assimilation, and IT–business alliance level, but also allows the organization to focus more on strategic IT use for ongoing ISM [64,65,66,67].
The synergy between IT and business activities enables quick, efficient, and innovative responses in ISM, and redesigns business processes and information systems to increase the continuity of organizational information resource protection. Mitchell and Zmud [68] claimed that IT-related strategies are beneficial for innovative and rapid process changes. During uncertain times, such as ISM, the organization’s sustainable IT and business links are very useful for informal and impromptu decision-making [69]. In other words, close collaboration between IT and business enables business processes to be flexible and responsive [70]. Therefore, the synergy between the organization’s IT and business enables quick and efficient decision-making on ISM and effective security management strategies to facilitate the assimilation of security management within the organization. Based on these claims, hypothesis 2 was established.
Hypothesis 2. (H2):
IT business spanning capability will have a positive effect on ISM assimilation.
IT’s proactive stance refers to a company’s characteristics in seeking methods for R&D in IT resources to exploit and create business opportunities [71]. Companies seeking a comprehensive understanding of critical IT innovation tend to identify, select, and implement IT innovation after considering the probability that the innovation will be suitable. Companies have the ability to foresee uncertainty about the benefits of using innovation and the cost of innovation development, and exercise caution while testing the potential for new IT innovation [72]. In addition, companies can predict related changes because of the advanced nature of IT, and they get the opportunity to be more creative by emerging technologies. Zaheer and Zaheer [73] argued that proactive use of information networks allows not only more proactive information retrieval, but also advanced information for a balanced and accurate perception of trends. In addition, Galliers [74] claimed that IT proactive stance allows companies to quickly identify and select opportunities for IT innovation to deal with changes in business strategy and information needs. IT proactive stance allows companies to quickly leverage the opportunities and preempt market opportunities.
IT proactive performance, an organization’s sustainable capacity, allows continuous learning and renewal of IT, thus improving the organization’s ability to quickly change processes to adapt to change and promoting the significance and awareness of ISM [75]. Swanson and Ramiller [71] argued that companies with high IT proactive stance can thoroughly manage the introduction, assimilation, and performance of IT innovations, and avoid falling into fixed technical rigidity. In addition, companies can secure appropriate opportunities by reusing or adapting existing IT resources for rapid innovation and radical business activities. In other words, IT proactive stance can increase the awareness of ISM among organizational members through preemptive activities to protect the organization’s information resources, thereby increasing its sustainability [22]. Past literature shows that an organization’s IT proactive performance has a positive impact on the organization’s ISM assimilation by adapting to rapidly changing information-security-related technologies and enabling rapid security response, thus suggesting hypothesis 3.
Hypothesis 3. (H3):
IT proactive stance will have a positive effect on ISM assimilation.
3.2.2. Impacts of Policy-to-Technology Balance
To revitalize and internalize the sustainability of ISM within the organization, the importance of security policy, which is a significant factor of security management and sustainable IT capabilities, must be emphasized. While past research emphasizes the importance of balanced security policies and technologies, there is a lack of empirical research on the role that policies play between organizations’ sustainable IT capabilities and ISM assimilation [43,45]. Thus, this study includes policy elements in ISM as a moderating effect consistent with the argument that information-security-related policies would further strengthen the relationship between the organization’s sustainable IT capabilities and ISM assimilation. However, O’Callaghan [76] argued that an organization’s information security policy could change or influence the IT environment within the organization. Therefore, to conceptualize policies related to information security technology, policy–technology balance is used as a moderating variable in this study.
Balance or harmony can be defined as the extent that organizational values, prior experience, and current needs and innovations match [77]. A balance between organizational policy and technology innovation is preferred, because it enables organizations to be more effective and understand organizational innovation from a desirable perspective. Therefore, balance with policies is important when designing new information systems or introducing new technologies [46]. Furthermore, it must be ensured that the goals of the new IT do not contradict the tried and tested. Knowledge of what kind of strategic objectives lead to inconsistencies with policies, or what specific systems are in use, allows one to design useful systems with actionable policies [76].
Introduction or adoption of a new security policy is challenging if the new policy requires more technical functions and complex changes to the existing information system. Moreover, to adopt the new information security policy, the technical infrastructure, composition, and method of operation of the existing information system must be considered. As new or strengthened policies may change how organizations handle business, managers will be passive in establishing and adopting better policies if changing from the existing IT is laborious and time-consuming. Therefore, if the existing information system can be well integrated with the technical infrastructure, the organization’s policy on information security and decision-making will be higher [24]. Choi [78] found that mature organizations with strong information security policies are more harmoniously integrated with policy-IT technologies than those that do not. In addition, Han et al. [30] concurred that when a firm continues to invest in IT or develop security policy to manage or strengthen its sustainable IT capability, then its members tend to be assimilated in ISM. However, Dehning and Stratopoulos [39] emphasized that because policy-to-technology balance is a crucial factor in explaining the relationship between IT capability and ISM, we should not focus only on IT capability in the context of ISM.
Based on these claims, policy–technology balance is considered to be a more powerful motivation for the organization’s ISM assimilation. The following hypotheses were developed to empirically demonstrate how the balance between an organization’s information security policy and IT plays a key role between sustainable IT capabilities and ISM assimilation.
Hypothesis 4a. (H4a):
Policy-to-technology balance will moderate the relationship between IT infrastructure and ISM assimilation.
Hypothesis 4b. (H4b):
Policy-to-technology balance will moderate the relationship between IT business spanning capability and ISM assimilation.
Hypothesis 4c. (H4c):
Policy-to-technology balance will moderate the relationship between IT proactive stance and ISM assimilation.
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Participants and Data Collection
To test the proposed research model, we conducted a survey of employees in organizations that currently and continually implement various information security technologies. For example, some organizations have obtained ISMS 27001 certification, but others have created and implemented internal organizational policies and rules for ISM. By limiting the participants of the survey, we can increase the validity of the results. Furthermore, various companies across different industries were selected to increase the generalizability and validity of the data. Target firms were randomly selected from the two main Korean stock markets: the Korea Composite Stock Price Index (KOSPI) and Korean Securities Dealers’ Automated Quotation (KSDAQ). Questionnaires were sent to employees at different organizational levels. A total of 2000 questionnaires were sent to 103 companies across various industries through email, traditional mail, and visits. As many as 249 responses (response rate: 12.5%) were collected. Among them, the final 232 responses were used for the analysis, excluding 17 incomplete responses. The demographic characteristics of the respondents are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Respondent demographic characteristics (n = 232).
Among the respondents, 171 were males (73.71%) and 61 females (26.29%), implying that there are more males than females in management position. A majority were in the age group 30–40 years, accounting for 75.00%. Respondents included 127 (54.74%) college graduates, followed by 29.31% postgraduates. All the respondents were in management positions, with the highest as head of department (34.05%), followed by 51 managers (21.98%), 49 CEOs (21.12%), and 33 CIO/CFO (14.22).
The industry with the most frequency included 82 companies (35.34%) in finance/banking, followed by 70 firms (30.17%) and 43 firms (18.53%) in IT and manufacturing/service, respectively. Given that information security is a crucial part of daily operation in both finance/banking and IT industry, the higher number of responses from these two industries is obvious. In terms of the period of ISM, 78 participants (33.62%) responded that they have implemented information security for 7–10 years, followed by 5–7 years, and 3–5 years. A total of 23 firms (12.07%) have implemented ISM for more than 10 years, whereas only 17 (7.33%) have implemented for less than 3 years. Finally, participating firms implemented various activities for sustainable ISM. Among them, 86.64% of firms responded that they consistently educated and trained employees for information security. In addition, 79.74% of companies used security-related HW/SWs, while 68.10% respondents control users’ access control and implement monitoring/detection systems for their information assess. These results imply that, regardless of industries, firms are implementing ISM with various activities.
4.2. Measurement Development
We developed items to measure each variable in multiple stages. First, items were adopted by reviewing past studies. For instance, three first-order variables (data management, network, and HW/SW capability) in IT infrastructure were adopted from Bharadwaj [26] and Weill et al. [56]. The items to measure the three antecedents of IT business spanning capability (IT management, IT vision, and IT plan) were developed based on Mata et al. [79] and Overby et al. [51]. In addition, several items were adopted from Mata et al. [79] and Fichman and Kemerer [80] to assess the three antecedents of IT proactive stance (IT learning culture, IT investment, and IT innovation). Items to measure the moderating effect of policy-to-technology balance were adopted from O’ Callaghan et al. [76] and Beatty et al. [81]. Finally, four items developed by Fichman and Kemerer [80] and Ranganathan et al. [80] were adopted to test the sustainability of ISM assimilation. Then, all the items were modified to fit the context of this study.
Second, content validity was tested with five scholars (professors and researchers) in the area of information security for the relevance and accuracy of those modified items. We revised the items that appeared problematic. Finally, the pilot test with a sample of 30 was conducted to exclude statistical issues with measures. Table 2 summarizes all items and related studies.

Table 2.
Variables, measures, and related studies.
5. Analysis Results
5.1. Validity and Reliability: First-Order Hierarchy
Three variables (IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance) in sustainable IT capability were conceptualized as second-order variables. Thus, we conducted the first- and second-order confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) with AMOS 22.0 to analyze the measurement model. We evaluated the first-order measurement model based on several analyses, including overall fitness, individual item loading, composite reliability (CR), average variance extracted (AVE), and Cronbach’s alpha to demonstrate the validity and reliability and to determine if any modification was needed.
First, the overall fitness of first-order measurement model was evaluated using several fit indices, including the relative chi-square (χ2/df), normal fit index (NFI), goodness-of-fit index (GFI), adjusted goodness-of-fit index (AGFI), comparative fit index (CFI), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) as suggested in the literature [83]. The results showed that one item (hsc3) designed to measure HW/SW capability in fact loaded to other first-order variables. Thus, this item was removed, and then the first-order fitness was revaluated. Then, the results demonstrated the overall fitness of the first-order variables because the value of all indices (χ2/df = 1.674, NFI = 0.949, GFI = 0.937, AGFI = 0.901, CFI = 0.958, and RMSEA = 0.041) exceeded the threshold (χ2/df < 1.674, NFI, GFI, and CFI ≥ 0.90, AGFI ≥ 0.80, RMSEA ≤ 0.05).
Second, the convergent validity and reliability of the first-order variables was evaluated with individual loading, CR, AVE, and Cronbach’s alpha. To demonstrate the convergent validity, the loading and CR should be greater than 0.7, while AVE should be greater than 0.5 [84]. Moreover, the value of Cronbach’s alpha should be greater than 0.7 to confirm the reliability [85]. The results confirmed both convergent validity and reliability of the first-order variables as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Validity and reliability of first-order variables.
Finally, the discriminant validity of the first-order variables was evaluated by comparing the square root of the AVE for first-order variables with the Pearson’s correlations between those variables. As shown in Table 4, all square roots of the AVEs exceed the correlations, thus confirming that the discriminant validity of the first-order variables was not of concern in this study.

Table 4.
Results for discriminant validity.
5.2. Validity and Reliability: Second-Order Hierarchy
The second-order variables, including IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, IT proactive stance, policy-to-technology balance, and ISM assimilation, were assessed for validity and reliability. Similar to the evaluation of the first-order variables, these variables were analyzed for overall fitness, individual item validity along with CR and AVE, and Cronbach’s alpha for the reliability test. The analysis results confirmed the overall fitness of the second-order variables because the values of all indices (χ2/df = 1.950, NFI = 0.951, GFI = 0.940, AGFI = 0.912, CFI = 0.944, and RMSEA = 0.028) exceeded the threshold. Individual item loadings ranged from 0.737 to 0.885, demonstrating convergent validity. Furthermore, CR and AVE value exceeded the recommended value for all the variables. Finally, Cronbach’s alpha ranged from 0.819 to 0.901, implying that the second-order measurement model demonstrated the reliability. Table 5 summarizes the results of the reliability and convergent validity test.

Table 5.
Reliability and validity of second-order variables.
Finally, the discriminant validity of the second-order latent variables was tested using a similar approach as the first-order-factor discriminant validity test. The square root of the AVE for all the second-order latent variables exceeded the correlation of other latent variables. Therefore, the discriminant validity of the second-order latent variables is not a concern in this study. Table 6 describes the results of the discriminant validity test for the second-order variables.

Table 6.
Results for discriminant validity of second-order latent variables.
5.3. Structural Model Assessment (Direct Model)
The proposed research model was evaluated by considering structural equation modeling (SEM) with AMOS 22.0. First, we built the SEM with three variables in sustainable IT capability and ISM assimilation to test H1 to H3. Then, the moderating effects (H4a to H4c) were tested using moderated multiple regression (MMR) suggested by Carte and Russell [86]. The SEM analysis yielded two important outputs—the standardized coefficient (β) and the squared multiple correlation (R2)—to determine the significance of each path. The standardized coefficient indicates the strength of the causal relationship between two variables [87], while the squared multiple correlations (R2) explain the variance in endogenous variable accounted by exogenous variables in the research model. The path coefficients between IT infrastructure and ISM assimilation was 0.311 (t-value = 4.458), which was significant at p < 0.01, hence H1 was supported. IT business planning capability showed a significant positive effect on ISM assimilation (H2: β = 0.469, t-value = 7.483, p < 0.01), supporting H2. H3 stated the positive effect of IT proactive stance on ISM assimilation, and the result showed that H3 was also supported with the path coefficient 0.427 (t-value = 5.071, p < 0.01). Finally, R2 of endogenous variable (ISM assimilation) was 0.613, implying that the three exogenous variables (IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance) explained 61.3% of the variance in ISM assimilation. Figure 2 illustrates the results of the direct effects along with the value of R2, while Table 7 summarizes the test results.
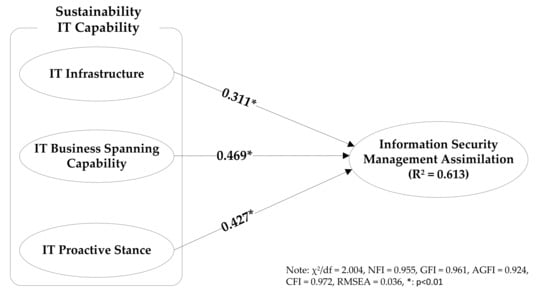
Figure 2.
Results of direct effects (H1 to H3).

Table 7.
Summary of hypotheses tests (Direct Effects).
5.4. Assessment of Moderation Effects (H4a to H4c)
The MMR approach was used to evaluate the impact of a moderator (policy-to-technology balance), based on the difference of two R2 (∆) between two models (interaction and no interaction model) to find the F-value considering degree of freedom (DF or number of input variables) and sample size. First, R2 value () is yielded when independent variable and moderator are the preceding variables in the model (no interaction model). Then, we analyzed another model (interaction model) in which independent variable, moderator, and interaction term are the preceding variables to yield R2 value (). Based on the formula () suggested by Carter and Russell [86], the F-value can be obtained to test the hypotheses. For example, H4a tests the moderating effect of policy-to-technology balance on the relationship between IT infrastructure and ISM assimilation. To test H4a, first (0.217) was obtained when IT infrastructure and policy-to-technology balance are the preceding variable on ISM assimilation. Then, the interaction term (IT infrastructure × policy-to-technology balance) was added in the model to yield (0.249). Then, the difference of two R2 (∆ = 0.032), number of preceding variables (dfa = 2, dfm = 3), and sample size (n = 232) were used to calculate F-value (9.715). Thus, H4a was significantly supported at p < 0.01.
H4b and H4c tested the moderating effect of policy-to-technology balance on the relationship between IT business spanning capability and ISM assimilation, and IT proactive stance and ISM assimilation, respectively. When IT business spanning capability and policy-to-technology balance were the preceding variables on ISM assimilation, (0.252) for H4b was obtained. Then, the interaction term (IT business spanning capability × policy-to-technology balance) was added to yield (0.267). The difference of two R2 (∆) was 0.015, resulting in F-value equals 4.666, significant at p < 0.05. Thus, H4b was supported. Finally, H4c was not supported because the difference of two R2 was 0.008 ( = 0.210 and = 0.218). Figure 3a–f describe the analysis of moderating effects (H4a to H4c). Table 8 summarizes the analysis of the moderating effects.
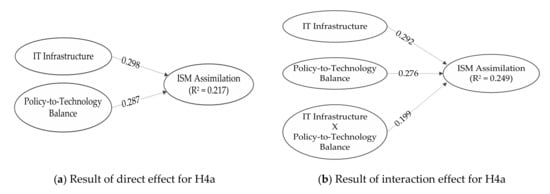
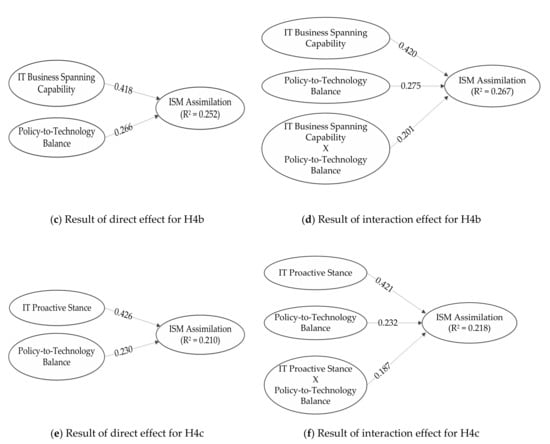
Figure 3.
Results of moderating effects (H4a to H4c).

Table 8.
Summary of moderating effect test.
6. Conclusions
6.1. Summary of Findings and Discussion
This study analyzed and verified the effects of three dimensions of sustainable IT capabilities: IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance on organization’s ISM assimilation. In addition, an empirical analysis was conducted on the effect of harmonization between policy and technology, which is critical in the management environment based on IT, in the relationship between sustainable IT capabilities and ISM. Considering multiple dimensions of sustainable IT capability is a good for understanding the core value of ISM [88]. The empirical results of this study support the underlying concept that each dimension of sustainable IT capability is composed of reflective factors and that IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance are directly related to ISM assimilation for sustainable management of assets. The results of the study are consistent with prior studies [65,69], in that these IT capabilities play a crucial role for managers in assimilation of ISM within the organization. In other words, the organization’s continued investment in IT infrastructure for ISM informs its members how important it is to the organization, thereby increasing their ISM awareness. Rai et al. [89] claimed that all organizations using IT are unlikely to produce any results without continuous investment in the technology. Even in ISM, IT infrastructure such as hardware, software, and network, which are the basic for organization members to maintain continuity of ISM, are essential.
Furthermore, IT policy linked with the business leads to more effective results in ISM. Therefore, if the organization tends toward ISM and creates an environment in which information security is very important, the organization’s ISM will move toward a more active and efficient direction. In this environment, organization members naturally assimilate ISM. Mitchell [90] argued that it is necessary to use IT that is suitable for information-security-related visions, strategies, and activities to foster ISM. Similarly, Ba et al. [91] claimed that IT should be used strategically for business extension. However, if the organization uses technology considering only the performance and excellence of IT while ignoring business linkage, it will result in high investment and low profit. Among the three dimensions of sustainable IT capability, IT business spanning capability (β = 0.469, t-value = 7.483) is shown as the path of greatest significance in relationship with ISM assimilation, compared to IT infrastructure (β = 0.311, t-value = 4.458) and IT proactive stance (β = 0.427, t-value = 5.071).
This study also indicates that the relationships between three sustainable IT capabilities and ISM assimilation are enhanced by different levels of policy-to-technology balance. The effects of IT infrastructure and IT business spanning capability on ISM assimilation were found to be strengthened according to the policy-to-technology balance. These results are consistent with prior studies [91], in that a firm with a stable IT infrastructure can effectively implement and strengthen ISM through the convergence of security policies and technologies. Furthermore, these results imply that organizations can increase the sustainability of information security through IT and business and linkages, but the IT policy that balances with information-security-related policies has a greater impact on information security [28,32]. In other words, the organization’s policy-based sustainable IT capacity building plays a pivotal role in the information security for its members to increase the sustainability of information security.
However, no moderating effect of policy-to-technology balance was found in the relationship between IT proactive stance and ISM assimilation. This result indicated that the organization’s IT proactive stance is often influenced by internal human resources such as members and management. Moreover, the major factors driving the organization’s information-security-related environment are influenced by several external factors. In this regard, Hinton and Lee [46] claimed that policy-to-technology balance has a great potential to work with not only direct impacts related to ISM in business processes and activities, but also uncertain environmental factors and various effects of members in the organization. Based on these findings, organizations need to establish and implement IT strategies and plans considering the policy-to-technology balance that can maximize the effect of assimilation of ISM within an organization by developing sustainable IT infrastructure investments and business-linked IT capabilities.
6.2. Implications and Conclusion
Based on findings of the study, we can highlight several theoretical and practical implications. First, this study provides a theoretical basis for the factors comprising sustainable IT capabilities and affecting ISM assimilation by systematically analyzing and verifying prior studies related to organizational RBV along with information security. Therefore, this study can be used for various dimensions of future studies related to assimilation of ISM and as a theoretical background to explain important influencing factors on corporate decision-making for development and implementation of ISM.
Second, while most of the previous studies on ISM were conducted in the technical context, this study provides a theoretical basis for ISM at the organizational and behavioral level, which is still in its infancy, by conducting research from the organizational resources perspective. Even if the technology offers enormous capabilities to many parts of a firm’s operations, it is the organizational member who actually uses such a technology, thus research on organizational members’ behavior is not only very important, but also must be carried out continuously following the progress of technologies [47,56]. In particular, this study classifies sustainable IT capabilities into multiple dimensions (IT infrastructure, IT business spanning capability, and IT proactive stance) rather than a single dimension to reflect the realistic aspects of rapidly expanding companies’ IT resources. This multi-dimensional research model could provide a more in-depth interpretation of the overall analysis results and provide a theoretical basis for the assimilation of ISM by companies.
Third, by verifying the moderating effect of policy-to-technology balance, we derived a factor that can strengthen the assimilation of sustainable ISM by companies through three sub-dimensions of sustainable IT capabilities. These data can be used for future research. In addition, this study contributes to the research methodology. First, the research items for measuring each variable proposed in this study were developed from the viewpoint of ISM and proved its validity. Second, in the verification of the moderating effect, this study took a remedy approach by Carter and Russell [84] to overcome the limitations of existing moderator test. Thus, we increased the test validity and found the moderating effect of policy-to-technology balance.
Through the findings of this study, some practical guidelines can be presented to the executives and managers who promote ISM. First, in the assimilation of corporate ISM, the sustainable IT capabilities of the organization playing a key role, implying that three dimensions of IT capabilities not only complement each other, but also enhance the assimilation of ISM. A strong IT infrastructure provides a stable and efficient foundation for assimilation of ISM, and the combination of business and IT policy through IT business spanning capability leads to synergy in the corporate ISM assimilation. With all these capabilities, a firm can sustain its assets, which yields high comparative advantages [48,50,56].
In addition, IT proactive stance or leadership attitude not only utilizes the existing IT capabilities, but also has a positive effect on improving ISM capabilities through continuous exploration and attempts on new technologies. The deep association between IT capabilities and ISM assimilation suggests that reexamination of the organization’s IT capabilities is an essential element for today’s companies, which are increasingly dependent on IT throughout their business activities. Thus, findings of this study imply that the executives and managers related to ISM should seek various strategies to improve the IT capabilities of the organization. In particular, it is necessary to focus on the organization’s ability to maintain a strong and flexible technical foundation for the organization’s IT capabilities, consider the link between IT and business strategies, and maintain a meticulous and responsive organizational leadership in IT technology.
Second, there appears to be a difference in the influence of the IT infrastructure and the ability to connect IT on ISM assimilation of the company according to the degree of balance between the company’s technology and policy. Accordingly, to maximize the assimilation effect of corporate information security management, executives and managers who want to settle ISM have established a policy to increase the harmony between the organization’s technology and policies, and various measures that can be continuously implemented. However, the findings of this study imply that an organization or its managers must establish a promotion strategy and an implementation system considering the organizational situation of it, since the policy-to-technology balance plays inadequate impact in the relationship between IT proactive stance and ISM assimilation. Therefore, while organizations prioritize the improvement of IT infrastructure and IT business connection ability, they should consider a strategy that improves IT proactive stance by identifying key determinants such as internal human resources or other external environmental factors, thus strengthening the overall sustainable IT capability.
6.3. Limitations and Future Direction
Despite some important implications suggested by this study, there are some limitations and future research directions that are noteworthy. First, although this was an organization-level study on firms’ ISM, more samples are required to validate the results of the study. Given that most companies have insufficient awareness of ISM and sustainable security management is difficult, it was difficult to secure multiple samples. Thus, in a future study, it will be meaningful to expand the sample and classify the population by company size and industry group to investigate differences according to the company’s situation and industry characteristics. Second, even if this study attempts to generalize the results with data from various industries, the role of IT capabilities in ISM may be different depending on the industry type. Thus, in a future study, we need to focus on a specific industry type to increase the validity of the findings.
Another limitation is related to the research model; this study provides logical supports of focusing on sustainable IT capabilities on ISM assimilation. However, we cannot ignore other factors from various perspectives such as technical, environmental, social, and resource perspectives. In addition, the research model included only the policy-to-technology balance as a key factor in enhancing the ISM assimilation of members within an organization. Therefore, it is necessary to include other factors related to the organization’s monetary or non-monetary interests and various benefits perceived by members of the organization to clearly explain ISM assimilation. Finally, this study has a comprehensive concept of ISM, and the proposed research model was tested in a given period time, which makes the scope of the study quite big and exaggerates the study findings. Thus, we need to focus on a specific security system and conduct longitudinal study to find out how members of organizations perceive or behave with respect to the impact of IT capabilities on ISM assimilation.
Author Contributions
As the main contributors, S.K. and B.K. outlined and collected the data, conducted the first round of analysis and discussion, and performed the literature review. M.S. reorganized the manuscript, conducted an additional literature review, conceptualized the work, research design, and discussion, and completed a reference check. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yoon, H.-S. Internal surveillance and control system for information security and information system asset management. Inf. Syst. Rev. 2007, 9, 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, W.H.; Wallace, L. Is information security under control? Investigating quality in information security management. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2007, 5, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancheau, J.C.; Janz, B.D.; Wetherbe, J.C. Key issues in information systems management: 1994-95 SIM Delphi results. MIS Q. 1996, 20, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmeyer, D.F.; McCrory, J.; Pogreb, S. Managing information security. Mckinsey Q. 2002, 2, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ransbotham, S.; Mitra, S. Choice and chance: A conceptual model of paths to information security compromise. Inf. Syst. Res. 2009, 20, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavusoglu, H.; Cavusoglu, H.; Son, J.Y.; Benbasat, I. Information Security Control Resources in Organizations: A Multidimensional View and Their Key Drivers; Working paper; Sauder School of Business, University of British Columbia: Vancouver, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M. What is computer security? IEEE Secur. Priv. 2003, 1, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.D.; Bordoloi, B. Evaluating security threats in mainframe and client/server environments. Inf. Manag. 1997, 32, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, D.C.; Yen, D.C.; Lin, B.; Cheng, P.H.L. Cyberspace security management. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 1999, 99, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Ho, C.B. Organizational factors to the effectiveness of implementing information security management. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2006, 106, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Forcht, K.A. Information security in business environment. Inf. Manag. Comput. Sec. 1996, 4, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanhalli, A.; Teo, H.H.; Tan, B.C.Y.; Wei, K.K. An integrative study of information systems security effectiveness. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2003, 23, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, N.F.; Fulford, H. Do information security policies reduce the incidence of security breaches: An exploratory analysis. Inf. Res. Manage. J. 2005, 18, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahner, S.; Krcmar, H. Beyond technical aspects of information security: Risk culture as a success factor for IT risk management. In Proceedings of the 11th Americas Conference on Information Systems AMCIS 2005, Omaha, NE, USA, 11–14 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, D.W.; Welke, R. Coping with systems risk: Security planning models for management decision making. MIS Q. 1998, 22, 441–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Solms, B.; von Solms, R. The 10 deadly sins of information security management. Comput. Secur. 2004, 23, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.; Backhouse, J. Current directions in IS security research: Towards socio-organizational perspectives. Inf. Syst. J. 2001, 11, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siponen, M.T. Analysis of modern IS security development approaches: Towards the next generation of social and adaptable ISS methods. Inf. Organ. 2005, 15, 339–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; McCrohan, K. Management’s role in information security in a cyber economy. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2002, 45, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.B. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.M. The resource-based theory of competitive advantage: Implications for strategy formulation. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1991, 33, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernerfelt, B. A resource-based view of the firm. Strat. Manag. J. 1984, 5, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeny, D.; Ives, B. In search of sustainability: Reaping long-term advantage from investment in information technology. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1990, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D. Capturing value from technological innovation: Integration, strategic partnering and licensing decisions. Interfaces 1988, 18, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, G.; Grover, V. Types of information technology capabilities and their role in competitive advantage: An empirical study. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2005, 22, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.S. A resource-based perspective on information technology capability and firm performance: An empirical investigation. MIS Q. 2000, 24, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippins, M.J.; Sohi, R.S. IT competency and firm performance: Is organizational learning a missing link? Strat. Manag. J. 2003, 24, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.Y.; Chen, J.S.; Huang, Y.H. A framework for investigating the impact of it capability and organizational capability on firm performance in the late industrializing context. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2006, 36, 206–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.S.; Hagel, J. Does IT matter? Harv. Bus. Rev. 2003, 81, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.S.; Lee, J.N.; Seo, Y.W. Analyzing the impact of a firm’s capability on outsourcing success: A process perspective. Inf. Manage. 2008, 45, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, P.G. Shaping the Future: Business Design through Information Technology; Harvard Business Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ravichandran, T.; Lertwongsatien, C. Effect of information systems resources and capabilities on firm performance: A resource-based perspective. J. Manag. Inform. Syst 2005, 21, 237–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, T.; Rai, A. Quality management in systems development: An organizational system perspective. MIS Q. 2000, 24, 381–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J.; Pisano, G.; Shuen, A. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strat. Manag. J. 1997, 18, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambamurthy, V.; Bharadwaj, A.; Grover, V. Shaping agility through digital options: Reconceptualizing the role of information technology in contemporary firms. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornatzky, L.G.; Klein, K.J. Innovation characteristics and innovation adoption-implementation: A meta analysis of findings. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 1982, 29, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delone, W.R.; McLean, E.R. Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Inf. Syst. Res. 1992, 3, 60–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhue, D.L.; Thompson, R.L. Task-technology fit and individual performance. MIS Q. 1995, 19, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehning, B.; Stratopoulos, T. Determinants of a sustainable competitive advantage due to an IT-enabled strategy. J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 2003, 12, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, A.P.; Montoya-Weiss, M.; Hung, C.; Ramesh, V. Cultural perceptions of task-technology fit. Commun. ACM 2001, 44, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, K.; Premkumar, G.; Crum, M.R. Organizational and interorganizational determinants of EDI diffusion and organizational performance: A causal model. J. Organ. Comp. Electron. Commer. 1999, 9, 253–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Golhar, D.Y. EDI implementation in JIT and non-JIT manufacturing firms: A comparative study. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1993, 13, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.M.; Hill, N.C. The state of U.S. EDI in 1989. EDI Forum 1989, 2, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, L.; Bergeron, B. EDI success in small and medium sized enterprises: A field study. J. Organ. Comp. Electron. Commer. 1996, 6, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, S.; Bogner, W. Technology strategy and software new ventures’ performance: Exploring the moderating effect of the competitive environment. J. Bus. Ventur. 2000, 15, 135–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, H.M.; Lee, E.S. The compatibility of policies. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Fairfax, VA, USA, 2–4 November 1994; pp. 258–269. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, L.A.; Loeb, M.P. The economics of information security investment. ACM Transa. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2002, 5, 438–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Lee, J.N.; Straub, D.W. Institutional influences on information systems security innovations. Inf. Sys. Res. 2012, 23, 918–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotulic, A.C.; Clark, J.G. Why there aren’t more information security research studies. Inf. Manag. 2004, 41, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, J.L.; Barki, H. User participation in information systems security risk management. MIS Q. 2010, 34, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overby, E.; Bharadwaj, A.; Sambamurthy, V. Enterprise agility and the enabling role of information technology. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2006, 15, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Making fast strategic decisions in high-velocity environments. Acad. Manag. J. 1989, 32, 543–576. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, A.K.; Jaworski, B.J. Market orientation: The construct, research propositions, and managerial implications. J. Mark. 1990, 54, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.T.; Nohria, N.; Tierney, T. What’s your strategy for managing knowledge? Har. Bus. Rev. 1999, 77, 106–116. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, M.; Weill, P.; Neo, B.S. Strategic context and patterns of IT infrastructure capability. J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 1999, 8, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, P.; Subramani, M.; Broadbent, M. Building IT infrastructure for strategic agility. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2002, 44, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Weill, P.; Broadbent, M. Leveraging the New Infrastructure: How Market Leaders Capitalize on Information Technology; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Dewar, R.D.; Dutton, J.E. The adoption of radical and incremental innovations: An empirical investigation. Manag. Sci. 1986, 32, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanpour, F. The adoption of technological, administrative and ancillary innovations: Impact of organizational factors. J. Manag. 1987, 13, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambamurthy, V.; Zmud, R.W. At the heart of success: Organization wide management competencies. In Steps to the Future: Fresh Thinking on the Management of IT-Based Organizational Transformation; Sauer, C., Yetton, P.W., Eds.; Jossey-Bass Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Elbashir, M.Z.; Collier, P.A.; Sutton, S.G. The role of organizational absorptive capacity in strategic use of business intelligence to support integrated management control systems. Account. Rev. 2011, 86, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, M.; Hulland, J. The resource-based view and information systems research: Review, extension and suggestions for future research. MIS Q. 2004, 28, 107–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, P.; Ross, J. IT Governance: How Top Performers Manage IT Decision Rights for Superior Results; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Boynton, A.C.; Zmud, R.W.; Jacobs, G.C. The influence of IT management practice on IT use in large organizations. MIS Q. 1994, 18, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.P.; Sambamurthy, V. Information technology assimilation in firms: The influence of senior leadership and it infrastructures. Inf. Syst. Res. 1999, 10, 304–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, B.H.; Benbasat, I. Factors that influence the social dimension of alignment between business and information technology objectives. MIS Q. 2000, 24, 81–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.; Sabherwal, R.; Thatcher, J.B. Antecedents and outcomes of strategic is alignment: An empirical investigation. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2006, 53, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, V.L.; Zmud, R.W. The effects of coupling IT and work process strategies in redesign projects. Organ. Sci. 1999, 10, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Eisenhardt, K. The art of continuous change: Linking complexity theory and time-paced evolution in relentlessly shifting organizations. Adm. Sci. Q. 1997, 42, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdows, K.; Lewis, M.A.; Machuca, J.A.D. Rapid-fire fulfillment. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2004, 82, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, E.B.; Ramiller, N.C. Innovating mindfully with information technology. MIS Q. 2004, 28, 553–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichman, R.G. Real options and it platform adoption: Implications for theory and practice. Inf. Syst. Res. 2004, 15, 132–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, A.; Zaheer, S. Catching the wave: Alertness, responsiveness and market influence in global electronic networks. Manag. Sci. 1997, 43, 1493–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliers, R. Strategizing for Agility: Confronting Information Systems Inflexibility in Dynamic Environments. In Agile Information Systems; DeSouza, K., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Burlington, Canada, 2007; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Haeckel, S.H. Adaptive Enterprise: Creating and Leading Sense-and-Respond Organizations; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- O’Callaghan, R.; Kaufman, P.J.; Kronsynski, B. Adoption correlates and share effects of electronic data interchange in marketing channels. J. Mark. 1992, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations, 4th ed.; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M. An exploring study on relation between maturity levels of organizations and factors affecting information security policy. Korean J. Bus. Admin. 2009, 22, 1729–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, F.J.; Fuerst, W.L.; Barney, J.B. Information technology and sustained competitive advantage: A resource-based analysis. MIS Q. 1995, 19, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichman, R.G.; Kemerer, C.F. The illusory diffusion of innovation: An examination of assimilation gaps. Inf. Syst. Res. 1999, 10, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, R.C.; Shim, J.P.; Jones, M.C. Factors influencing corporate web site adoption: A time-based assessment. Inf. Manag. 2001, 38, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, C.; Dhaliwal, J.S.; Teo, T.S.H. Assimilation and diffusion of web technologies in supply-chain management: An examination of key drivers and performance impacts. Int. Electron. Commer. 2004, 9, 127–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentler, P.M. Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychol. Bull. 1990, 107, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnally, J.C. Psychometric Theory, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1978; ISBN 9780070474659. [Google Scholar]
- Carte, T.A.; Russell, C.J. In pursuit of moderation: Nine common errors and their solutions. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wixom, B.H.; Watson, H.J. An empirical investigation of the factors affecting data warehousing success. MIS Q. 1981, 25, 17–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, R.; Grover, V. Business value of it: An essay on expanding research directions to keep up with the times. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2008, 9, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Patnayakuni, R.; Seth, N. Firm performance impacts of digitally-enabled supply chain integration capabilities. MIS Q. 2006, 30, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, V.L. Knowledge integration and information technology project performance. MIS Q. 2006, 30, 919–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, S.; Stallaert, J.; Whinston, A.B. Research commentary: Introducing a third dimension in the information systems design—The Case for Incentive Alignment. Inf. Syst. Res. 2001, 12, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).