Impact of Research and Development Strategy on Sustainable Growth in Multinational Pharmaceutical Companies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Analysis
3. Results
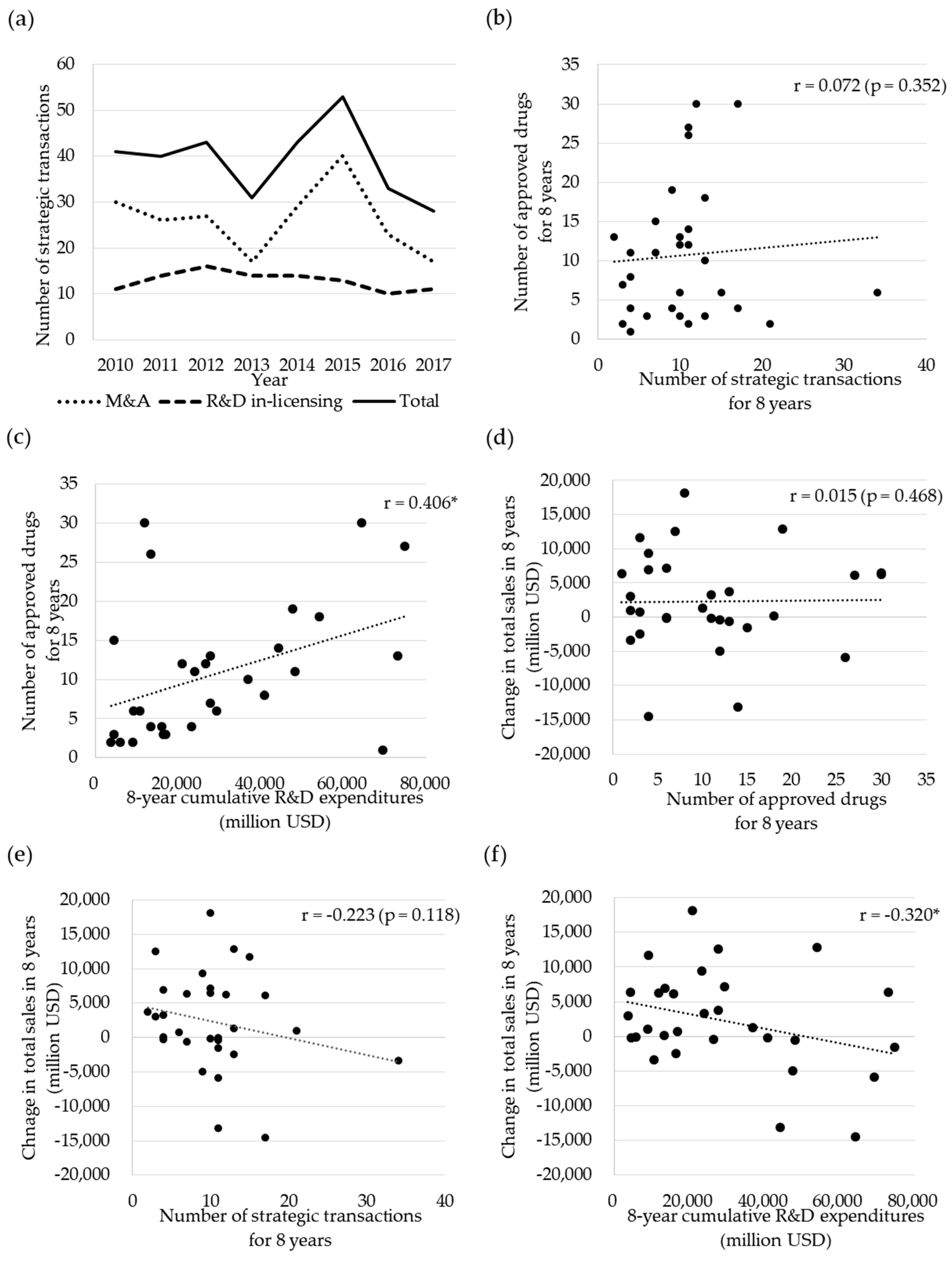
3.1. Trends in Strategic Transactions and R&D Productivity within the Pharmaceutical Industry
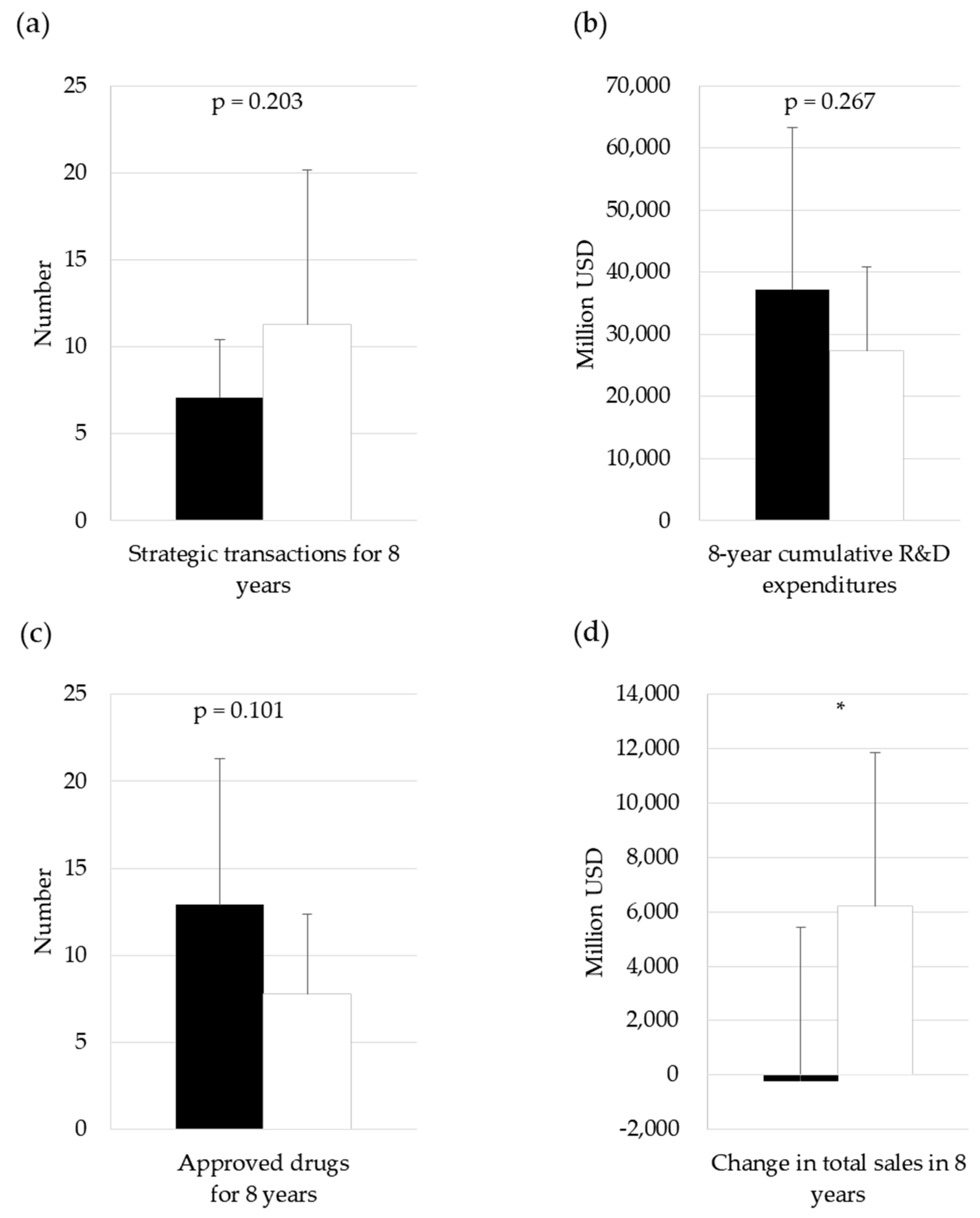
3.2. Comparison between Global Companies and Home-Region-Oriented Companies in Terms of R&D Productivity
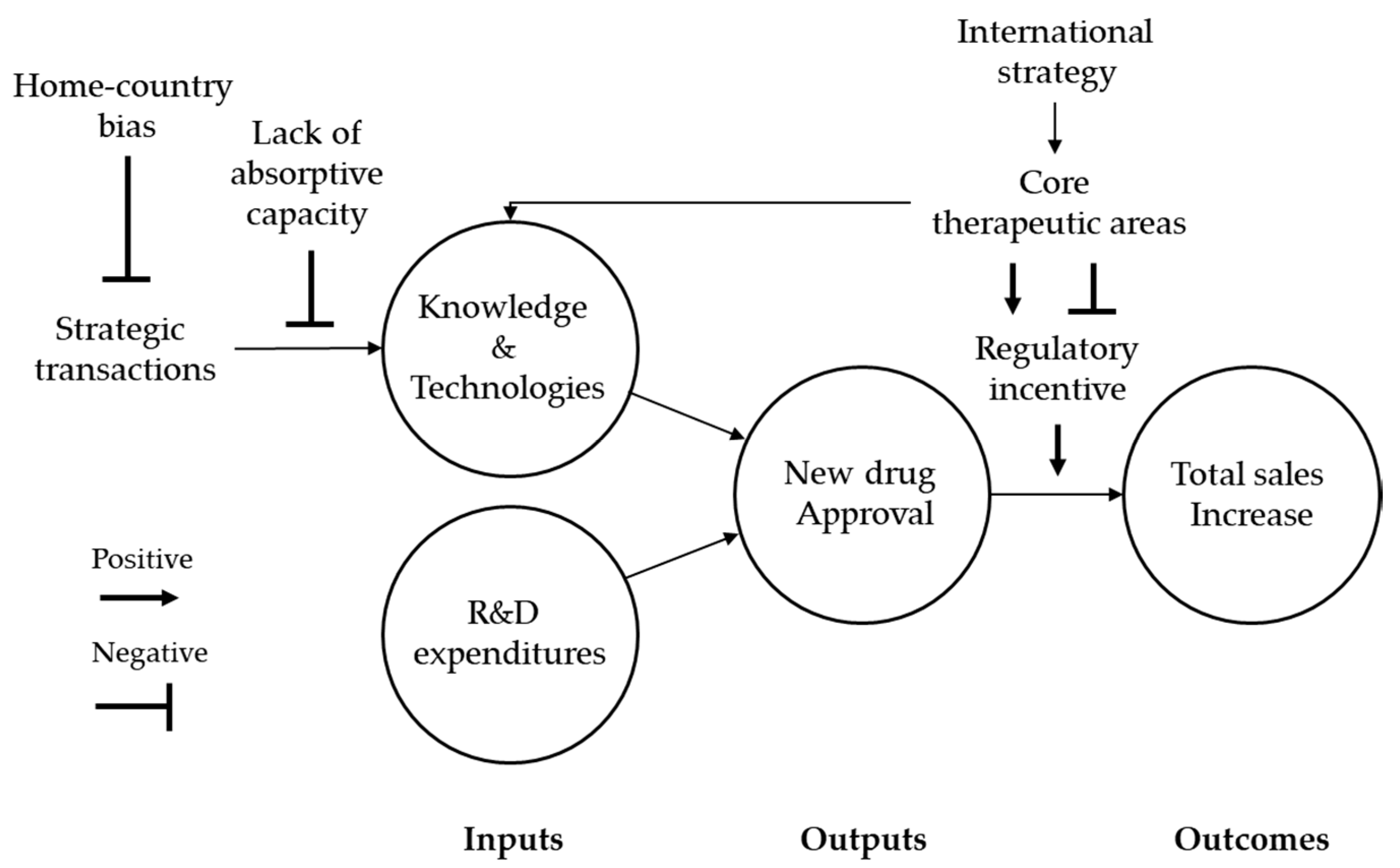
3.3. Relationship between Inputs, Outputs, and Outcomes in Terms of R&D Productivity
3.4. Factors Impacting on R&D Productivity in the Pharmaceutical Industry
4. Discussion and Implications
5. Conclusions, Limitation, and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kessel, M. The problems with today’s pharmaceutical business—An outsider’s view. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.M.; Mytelka, D.S.; Dunwiddle, C.T.; Persinger, C.C.; Munos, B.H.; Lindborg, S.R.; Schacht, A.L. How to improve R&D productivity: The pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munos, B. Lessons from 60 years of pharmaceutical innovation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scannell, J.W.; Blanckley, A.; Boldon, H.; Warrington, B. Diagnosing the decline in pharmaceutical R&D efficiency. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smietana, K.; Siatkowski, M.; Moller, M. Trends in clinical success rates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 379–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammolli, F.; Magazzini, L.; Riccaboni, M. The productivity crisis in pharmaceutical R&D. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 428–438. [Google Scholar]
- DiMasai, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. Innovation in the pharmaceutical industry: New estimates of R&D costs. J. Health Econ. 2016, 47, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Angelis, A.; Lange, A.; Kanavos, P. Using health technology assessment to assess the value of new medicines: Results of a systematic review and expert consultation across eight European countries. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2018, 19, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramae, F.; Yamaguchi, N.; Makino, T.; Sengoku, S.; Kodama, K. Holistic cost-effectiveness analysis of anticancer drug regimens in Japan. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, D.; Tsuyuki, A.; Suzuki, T. Drugs targeted for price cutting in Japan: The case of price revisions based on the divergence of official versus delivery prices. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2017, 51, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneller, R. The importance of new companies for drug discovery: Origins of a decade of new drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, S.; Helmstädter, A. Market entry, power, pharmacokinetics: What makes a successful drug innovation. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khann, I. Drug discovery in pharmaceutical industry: Productivity challenges and trends. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 1088–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafols, I.; Hopkins, M.H.; Hoekman, J.; Siepel, J.; O’Hare, A.; Perianes-Rodriguez, A.; Nightingale, P. Big pharma, little science? A bibliometric perspective on big pharma’s R&D decline. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2014, 81, 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, B.; Zemmel, R. Prospects for productivity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Plump, A.; Ringel, M. Racing to define pharmaceutical R&D external innovation models. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gautam, A.; Pan, X. The changing model of big pharma: Impact of key trends. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraça, J.; Lundvall, B.A.; Mendonça, S. The changing role of science in the innovation process: From Queen to Cinderella? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2009, 76, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramae, F.; Makino, T.; Lim, Y.; Sengoku, S.; Kodama, K. International strategy for sustainable growth in multinational pharmaceutical companies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guennif, S.; Ramani, S.V. Explaining divergence in catching-up in pharma between India and Brazil using the NSI framework. Res. Policy 2012, 41, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, Y.; Shenkar, O.; Raveh, A. National and corporate cultural fil in mergers/acquisitions: An exploratory study. Manag. Sci. 1996, 42, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkar, O. Cultural distance revisited: Towards a more rigorous conceptualization and measurement of cultural differences. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2012, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Contactor, F.J. Choosing an appropriate alliance governance mode: The role of institutional, cultural and geographical distance in international research & development (R&D) collaborations. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2016, 47, 210–232. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.T.; Lovas, B. How do multinational companies leverage technological competencies? Moving from single to interdependent explanations. Strateg. Manag. J. 2004, 25, 801–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambos, B.; Schlengelmilch, B.B. The use of international R&D teams: An empirical investigation of selected contingency factors. J. World Bus. 2004, 39, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Schuhmacher, A.; Germann, P.G.; Trill, H.; Gassmann, O. Models for open innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, E.; Bruccoleri, M.; Perrone, G. Open innovation and firms’ performance: State of the art and empirical evidences from the bio-pharmaceutical industry. Int. J. Technol. Manag. 2016, 70, 109–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olk, P.; West, J. The relationship of industry structure to open innovation: Cooperative value creation in pharmaceutical consortia. R D Manag. 2020, 50, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, H.; Kyle, M. Mergers and alliances in pharmaceuticals: Effects on innovation and R&D productivity. In The Economics of Corporate Governance and Mergers; Gugler, K., Yurtoglu, B.B., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2008; pp. 262–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ringel, M.S.; Choy, M.K. Do large mergers increase or decrease the productivity of pharmaceutical R&D? Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1749–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Ornaghi, C. Mergers and innovation in big pharma. Int. J. Ind. Organ. 2009, 27, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanor, W.S.; Scherer, F.M. Mergers and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. J. Health Econ. 2013, 32, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geringer, J.M.; Beamish, P.W.; Dacosta, R.C. Diversification strategy and internationalization: Implications for MNE performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 1989, 10, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Khoury, T.; Peng, M.; Qian, Z. The performance implications of intra- and inter-regional geographic diversification. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 31, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, R.C. How much growth can a firm afford? Financ. Manag. 1977, 6, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, H.; Masuda, S.; Kimura, H. Research and development productivity map: Visualization of industry status. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciotti, J.; Clinton, P. Pharma Exec’s Top 50 Companies 2010. Available online: https://www.slideshare.net/healthcaremanas/top-50-pharmaceutical-companies-2010-pharma-exec-report (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Christel, M. Pharma Exec’s Top 50 Companies 2018. Available online: http://www.pharmexec.com/pharm-execs-top-50-companies-2018?pageID=2 (accessed on 11 January 2020).
- Crunchbase. Available online: https://www.crunchbase.com/discover/organization.companies (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- Informa Pharma Intelligence. Biomedtracker. Available online: https://www.biomedtracker.com/ (accessed on 3 February 2020).
- International Monetary Fund. International Financial Statistics. Exchange Rates. Available online: http://data.imf.org/?sk=4C514D48-B6BA-49ED-8AB9-52B0C1A0179B&sId=1409151240976 (accessed on 27 September 2018).
- Schuhmacher, A.; Gassmann, O.; Hinder, M. Changing R&D models in research-based pharmaceutical companies. J. Transl. Med. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. New Molecular Entity (NME) Drug and New Biologic Approvals. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/nda-and-bla-approvals/new-molecular-entity-nme-drug-and-new-biologic-approvals (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Glickman, S.W.; McHutchison, J.G.; Peterson, E.D.; Cairns, C.B.; Harrington, R.A.; Califf, R.M.; Schulman, K.A. Ethical and scientific implications of the globalization of clinical research. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiehchen, D.; Espinoza, M.; Hsieh, A. The cooperative landscape of multinational clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvia, R.E.; Amato, A.A.; Guilhem, D.B.; Novaes, M.R.C.G. Globalization of clinical trials: Ethical and regulatory implications. Int. J. Clin. Trials 2016, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugman, A.M.; Verbeke, A. A perspective of regional and global strategies of multinational enterprises. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Building theories from case study research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1989, 14, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahalad, C.K.; Doz, Y.L. The Multinational Mission: Balancing Local Demands and Global Vision; NY Free Press & Collier Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, M.R.; Yadav, S. Motivations, capability handicaps, and firm responses in the early phase of internationalization: A study in the Indian pharmaceutical industry. J. Glob. Mark. 2015, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 28 April 2020).
- Heron, M. Deaths: Leading causes for 2017. Nation Vital Stat. Rep. 2019, 68, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kuemmerle, W. Foreign direct investment in industrial research in the pharmaceutical and electronics industries—Results from a survey of multinational firms. Res. Policy 1999, 28, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerybadze, A.; Reger, G. Globalization of R&D: Recent changes in the management of innovation in transnational corporations. Res. Policy 1999, 28, 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Achilladelis, B.; Antonakis, N. The dynamics of technological innovation: The case of the pharmaceutical industry. Res. Policy 2001, 30, 535–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belderbos, R.; Leten, B.; Suzuki, S. How global is R&D? Firm-level determinants of home-country bias in R&D. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2013, 44, 765–786. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, K. Pharma’s Broken Business Model: An Industry on the Brink of Terminal Decline. Endpoints News. Available online: https://endpts.com/pharmas-broken-business-model-an-industry-on-the-brink-of-terminal-decline/ (accessed on 23 December 2019).
- Lubatkin, M.; Florin, J.; Lane, P. Learning together and apart: A model of reciprocal interfirm learning. Hum. Relat. 2001, 54, 1353–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Wagner, M. The influence of exploratory versus exploitative acquisitions on innovation output in the biotechnology industry. Small Bus. Econ. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, R.C. R&D alliances and firm performance: The impact of technological diversity and alliance organization on Innovation. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 364–386. [Google Scholar]
- de Leeuw, T.; Lokshin, B.; Duysters, G. Returns to alliance portfolio diversity: The relative effects of partner diversity on firm’s innovative performance and productivity. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yeniyurt, S. Contingency distance factors and international research and development (R&D), marketing, and manufacturing alliance formations. Int. Bus. Rev. 2015, 24, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, W.N.; Levinthal, D.A. Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation. Adm. Sci. Q. 1990, 35, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Vega, M. Patterns of internationalisation of corporate techinology: Location vs. home country advantage. Res. Policy 1999, 28, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaister, K.W.; Buckley, P.J. Strategic motives for international alliance formation. J. Manag. Stud. 1996, 33, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.J. Liability of foreignness and entry mode choice: Taiwanese firms in Europe. J. Bus. Res. 2006, 59, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijssen, R.J.W. Internationalisation of pharmaceutical R&D: How globalised are Europe’s largest multinational companies? Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2009, 21, 859–879. [Google Scholar]
- Doz, Y.; Santos, J.; Williamson, P. From Global to Metanational: How Companies Win in the Knowledge Economy; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Teece, D.J. A dynamic capabilities-based entrepreneurial theory of the multinational enterprise. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2014, 45, 8–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B. Orphan drugs and their impact on pharmaceutical development. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, L.; Goldsmith, J.C.; Temple, R. Challenges of developing and conducting clinical trials in rare disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 176, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalban, M.; Sakinç, M.E. Financialization and productive models in the pharmaceutical industry. Ind. Corp. Chang. 2013, 22, 981–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Lechevalier, S. Why some firms persistently out-perform others: Investigating the interactions between innovation and exporting strategies. Ind. Corp. Chang. 2010, 19, 1997–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, S.; Pereira, T.S.; Godinho, M.M. Trademarks as an indicator of innovation and industrial change. Res. Policy 2004, 33, 1385–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Company | Home Region | Internationalization 1 |
|---|---|---|
| AbbVie | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Alexion | North America | Global |
| Amgen | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Astellas Pharma | Asia-Pacific/Others | Global |
| AstraZeneca | Europe | Global |
| Bayer | Europe | Global |
| Biogen | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Boehringer Ingelheim | Europe | Global |
| Bristol-Myers Squibb | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Celgene | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Daiichi Sankyo | Asia-Pacific/Others | Home-region-oriented |
| Eisai | Asia-Pacific/Others | Home-region-oriented |
| Eli Lilly | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Gilead Sciences | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| GlaxoSmithKline | Europe | Global |
| Johnson & Johnson | North America | Home-region-oriented |
| Merck & Co | North America | Global |
| Merck KGaA | Europe | Global |
| Mylan | North America | Global |
| Novartis | Europe | Global |
| Novo Nordisk | Europe | Host-region-oriented |
| Pfizer | North America | Bi-regional |
| Roche | Europe | Global |
| Sanofi | Europe | Global |
| Shionogi | Asia-Pacific/Others | Bi-regional |
| Shire | Europe | Host-region-oriented |
| Sumitomo Dainippon | Asia-Pacific/Others | Host-region-oriented |
| Takeda | Asia-Pacific/Others | Bi-regional |
| Teva Pharmaceutical | Asia-Pacific/Others | Host-region-oriented |
| UCB | Europe | Bi-regional |
| Independent Variable | B | β | t | p | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 2.968 | 1.211 | 0.241 | ||
| International strategy | −3.416 | −0.240 | −1.542 | 0.140 | 1.207 |
| 8-year cumulative R&D expenditures | 0.000 | 0.701 | 4.755 | 0.000 | 1.085 |
| Strategic transactions | 0.156 | 0.142 | 0.939 | 0.360 | 1.145 |
| R2 (Adjusted R2) | 0.640 (0.580) | ||||
| F | 10.647 *** | ||||
| Independent Variable | B | β | t | p | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 2828.054 | 0.871 | 0.396 | ||
| International strategy | 9099.736 | 0.657 | 3.031 | 0.008 | 1.366 |
| 8-year cumulative R&D expenditures | −0.087 | −0.265 | −0.914 | 0.374 | 2.448 |
| Strategic transactions | −491.310 | −0.462 | −2.274 | 0.036 | 1.201 |
| Approved drugs | 286.722 | 0.295 | 0.955 | 0.353 | 2.775 |
| R2 (Adjusted R2) | 0.640 (0.580) | ||||
| F | 10.647 *** | ||||
| Approved Drug Classification | Global | Home-Region-Oriented | p | V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |||
| Cardiovascular diseases | 0.708 | 0.076 | ||||
| Yes | 2 | 4.7 | 6 | 8.7 | ||
| No | 41 | 95.3 | 63 | 91.3 | ||
| Infectious diseases | 0.001 | 0.321 ** | ||||
| Yes | 25 | 58.1 | 18 | 26.1 | ||
| No | 18 | 41.9 | 51 | 73.9 | ||
| Cancers | 0.004 | 0.272 ** | ||||
| Yes | 2 | 4.7 | 18 | 26.1 | ||
| No | 41 | 95.3 | 51 | 73.9 | ||
| Nervous system diseases | 0.330 | 0.110 | ||||
| Yes | 6 | 14.0 | 5 | 7.2 | ||
| No | 37 | 86.0 | 64 | 92.8 | ||
| Endocrine and metabolic diseases | 0.163 | 0.132 | ||||
| Yes | 3 | 7.0 | 11 | 15.9 | ||
| No | 40 | 93.0 | 58 | 84.1 | ||
| Orphan designation | 0.002 | 0.299 ** | ||||
| Yes | 4 | 9.3 | 25 | 36.2 | ||
| No | 39 | 90.7 | 44 | 63.8 | ||
| Geographic Perspective | Global | Home-Region-Oriented | p | V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |||
| Strategic transactions in their home region | 0.045 | 0.142 * | ||||
| Yes | 30 | 35.3 | 56 | 49.6 | ||
| No | 55 | 64.7 | 57 | 50.4 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teramae, F.; Makino, T.; Lim, Y.; Sengoku, S.; Kodama, K. Impact of Research and Development Strategy on Sustainable Growth in Multinational Pharmaceutical Companies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135358
Teramae F, Makino T, Lim Y, Sengoku S, Kodama K. Impact of Research and Development Strategy on Sustainable Growth in Multinational Pharmaceutical Companies. Sustainability. 2020; 12(13):5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135358
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeramae, Fumio, Tomohiro Makino, Yeongjoo Lim, Shintaro Sengoku, and Kota Kodama. 2020. "Impact of Research and Development Strategy on Sustainable Growth in Multinational Pharmaceutical Companies" Sustainability 12, no. 13: 5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135358
APA StyleTeramae, F., Makino, T., Lim, Y., Sengoku, S., & Kodama, K. (2020). Impact of Research and Development Strategy on Sustainable Growth in Multinational Pharmaceutical Companies. Sustainability, 12(13), 5358. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135358







