Influence of Aged Biochar Modified by Cd2+ on Soil Properties and Microbial Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil and Biochar
2.2. Characterization of Biochar
2.2.1. Specific Surface Area and Porosity
2.2.2. Elemental Analysis
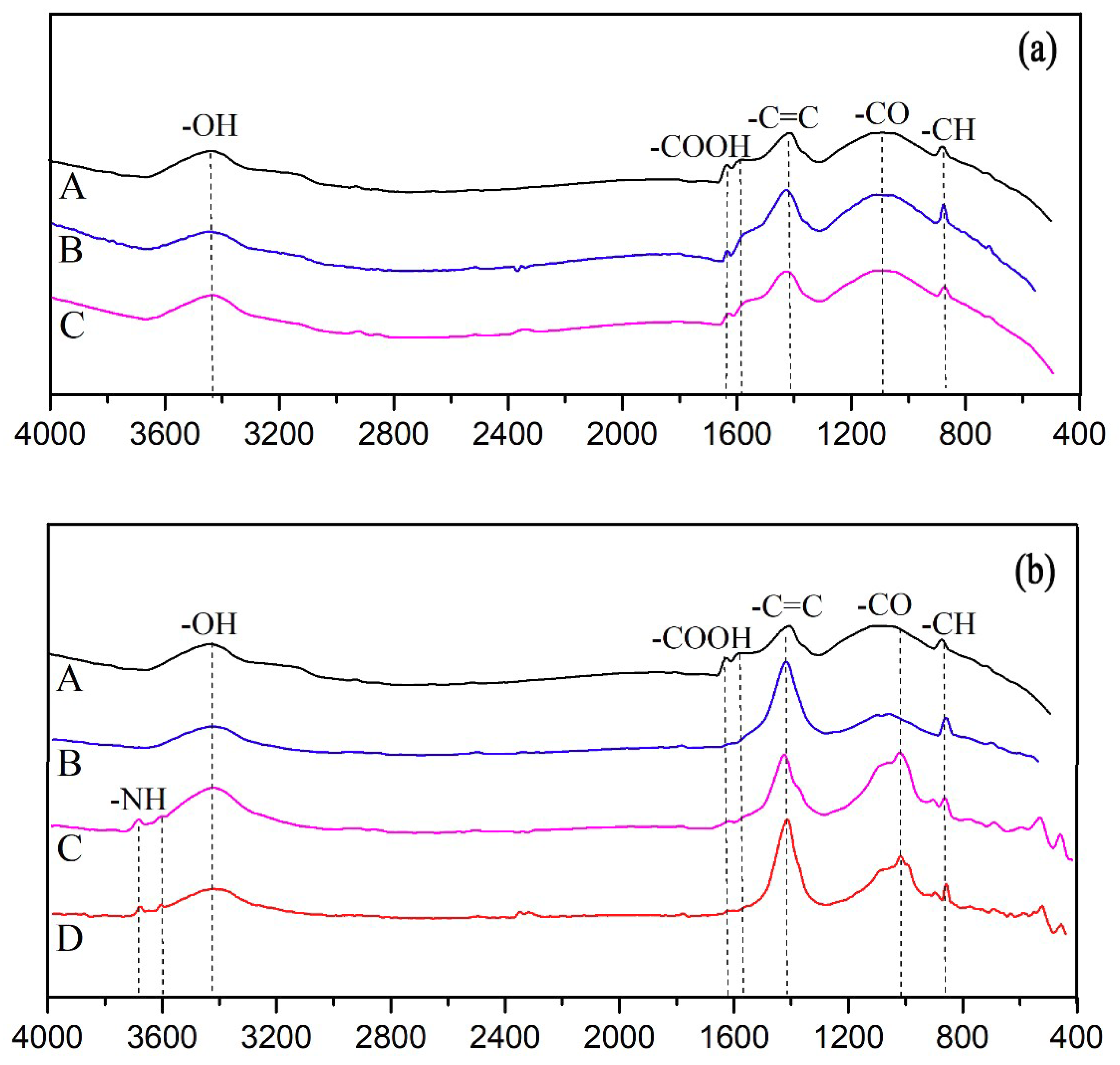
2.2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.2.4. Boehm Titration
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Short-Term Incubation Experiment
2.5. Soil Characteristics
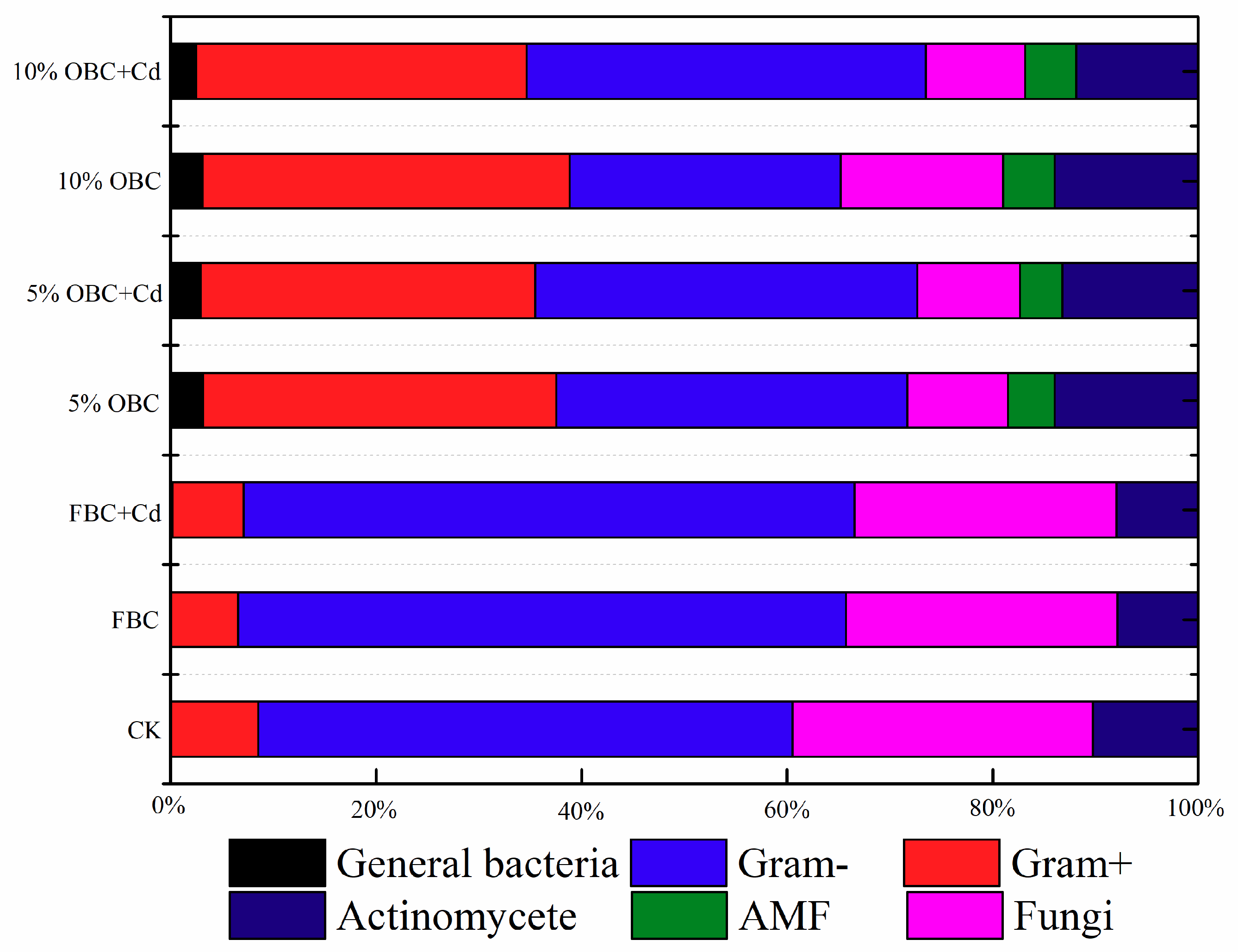
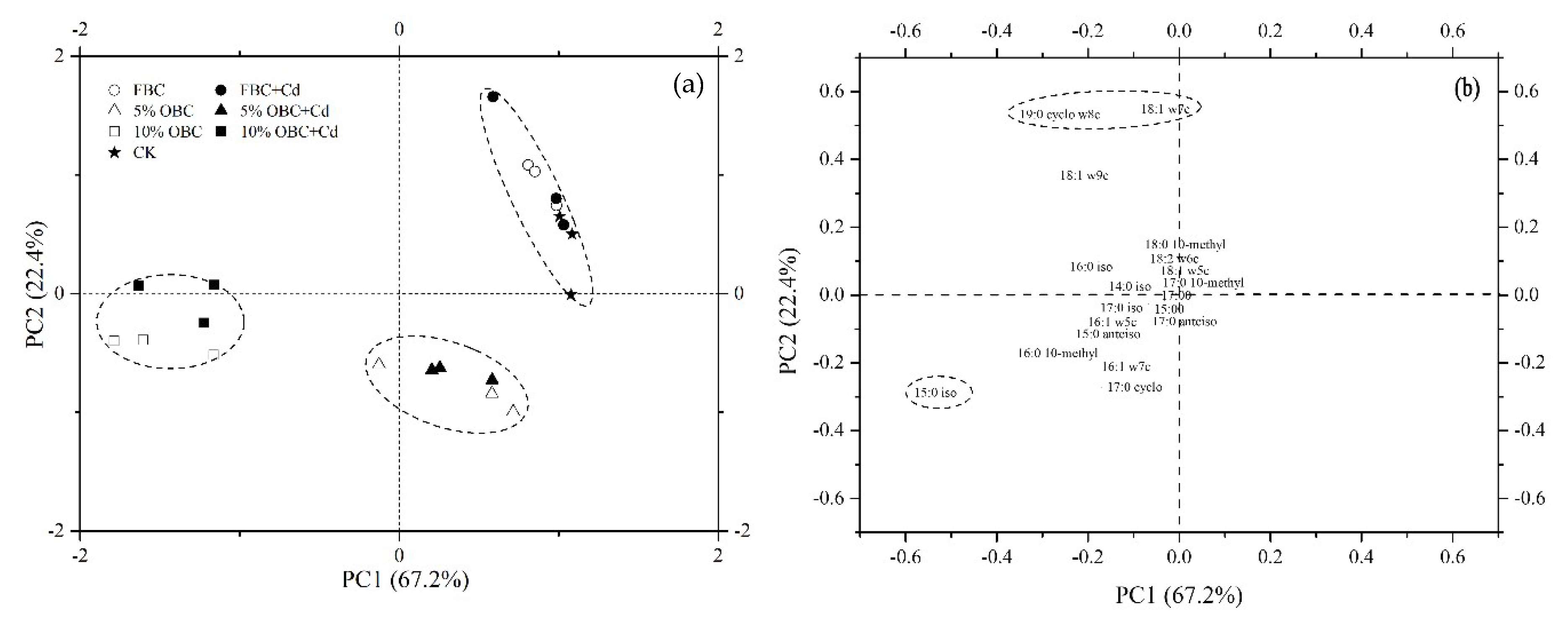
2.6. Soil Microbial Community
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Biochar Characteristics during Aging
3.1.1. Physical and Chemical Property Changes
3.1.2. Cadmium Adsorption of Aged Biochar
3.2. Changes in Soil Properties by Aged Biochar
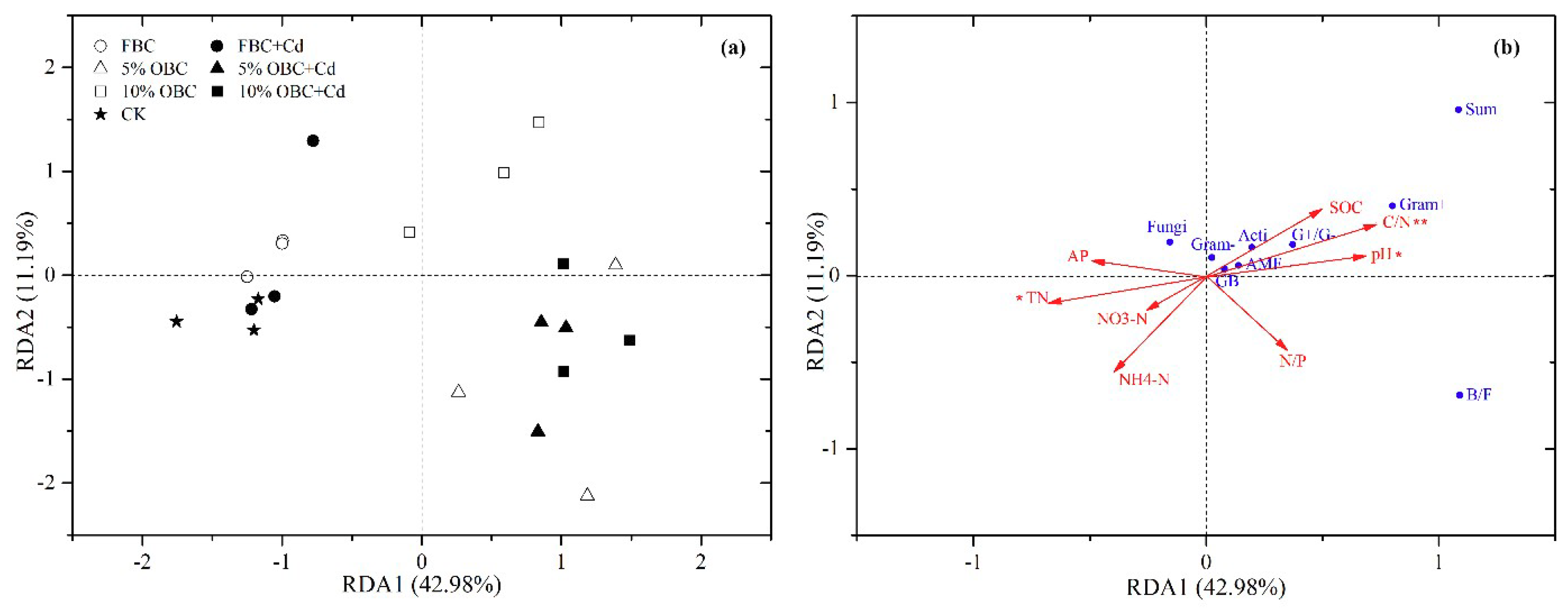
3.3. Interactions of Aged Biochar and Soil Microbiota
3.3.1. Changes in the Microbial Community
3.3.2. Relationship between Microbiota and Soil Properties
3.4. Influence of Cadmium Adsorption on Soil Properties and Microbiota
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International BI, Standardized Product Definition and Product Testing Guidelines for Biochar That is Used in Soil. IBI Biochar Standards. 2012. Available online: http://www.biochar-international.org/characterizationstandard (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- O’Connor, D.; Peng, T.; Zhang, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Alessi, D.S.; Shen, Z.; Bolan, N.S.; Hou, D. Biochar application for the remediation of heavy metal polluted land: A review carof in situ field trials. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.D.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Lin, Y.; Munroe, P.; Chia, C.H.; Hook, J.; van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.; Cowie, A.; Singh, B.P.; et al. An investigation into the reactions of biochar in soil. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronsse, F.; van Hecke, S.; Dickinson, D.; Prins, W. Production and characterization of slow pyrolysis biochar: Influence of feedstock type and pyrolysis conditions. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, W.; Harsh, J.B.; Abu-Lail, N.I.; Fortuna, A.-M.; Dallmeyer, I.; Garcia-Perez, M. Influence of feedstock source and pyrolysis temperature on biochar bulk and surface properties. Biomass Bioenerg. 2016, 84, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, L. Effects of feedstock type, production method, and pyrolysis temperature on biochar and hydrochar properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 240, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, J.M.; de Rosado, M.; Paneque, M.; Miller, A.Z.; Knicker, H. Effects of aging under field conditions on biochar structure and composition: Implications for biochar stability in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechberger, M.V.; Kloss, S.; Wang, S.-L.; Lehmann, J.; Rennhofer, H.; Ottner, F.; Wriessnig, K.; Daudin, G.; Lichtenegger, H.; Soja, G.; et al. Enhanced Cu and Cd sorption after soil aging of woodchip-derived biochar: What were the driving factors? Chemosphere 2019, 216, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmelpfennig, S.; Glaser, B. One Step Forward toward Characterization: Some Important Material Properties to Distinguish Biochars. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Bird, M.I.; Wurster, C.; Saiz, G.; Goodrick, I.; Barta, J.; Capek, P.; Santruckova, H.; Smernik, R. Rapid degradation of pyrogenic carbon. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, I.C.; Leuschner, C. Variation of soil and biomass carbon pools in beech forests across a precipitation gradient. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 16, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, B. Competitive adsorption of cadmium and aluminum onto fresh and oxidized biochars during aging processes. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusz, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Dobrowolski, R. Application of laboratory prepared and commercially available biochars to adsorption of cadmium, copper and zinc ions from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Sun, J.; Chu, L.; Cui, L.; Quan, G.; Yan, J.; Hussain, Q.; Iqbal, M. Effects of chemical oxidation on surface oxygen-containing functional groups and adsorption behavior of biochar. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Chen, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q. A study of cadmium remediation and mechanisms: Improvements in the stability of walnut shell-derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Seshadri, B.; Sarkar, B.; Wang, H.; Rumpel, C.; Sparks, D.; Farrell, M.; Hall, T.; Yang, X.; Bolan, N. Biochar modulates heavy metal toxicity and improves microbial carbon use efficiency in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Changes of bacterial community compositions after three years of biochar application in a black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Fu, S.; Méndez, A.; Gascó, G.; Paz-Ferreiro, J. Effect of Biochar in Cadmium Availability and Soil Biological Activity in an Anthrosol Following Acid Rain Deposition and Aging. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Tang, J.; Xi, X.; Zhang, S.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X. Responses of soil nutrients and microbial activities to additions of maize straw biochar and chemical fertilization in a calcareous soil. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2018, 84, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.; Kuhn, T.K.; Macdonald, L.M.; Maddern, T.M.; Murphy, D.V.; Hall, P.A.; Singh, B.P.; Baumann, K.; Krull, E.S.; Baldock, J.A. Microbial utilisation of biochar-derived carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.; Torn, M.S.; Bird, J.A. Biological degradation of pyrogenic organic matter in temperate forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 51, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Bogomolova, I.; Glaser, B. Biochar stability in soil Decomposition during eight years and transformation as assessed by compound-specific 14C analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frišták, V.; Friesl-Hanl, W.; Wawra, A.; Pipíška, M.; Soja, G. Effect of biochar artificial ageing on Cd and Cu sorption characteristics. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, Z.; Han, L.; Du, P.; Wang, X.; Xing, B. Effects of chemical oxidation on phenanthrene sorption by grass-and manure-derived biochars. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.; Sohi, S.P. A method for screening the relative long-term stability of biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, M.D.; Lee, J.W. Biochar-surface oxygenation with hydrogen peroxide. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 165, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrinenko, M.; Laird, D.A.; Johnson, R.L.; Jing, D. Accelerated aging of biochars: Impact on anion exchange capacity. Carbon 2016, 103, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, S.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Singh, B. Chapter One—Long-term aging of biochar: A molecular understanding with agricultural and environmental implications. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yue, X.; Li, F.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, D. Preparation of rice straw-derived biochar for efficient cadmium removal by modification of oxygen-containing functional groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, H.P. Surface oxides on carbon and their analysis: A critical assessment. Carbon 2002, 40, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Han, Y.; Li, B.; Yan, H.; Yang, W. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of soil nitrogen mineralization in a Picea stand and its relation to soil physicochemical factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q. Large-scale spatial variability of eight soil chemical properties within paddy fields. Catena 2020, 188, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Zhao, X. Quantity and quality changes of biochar aged for 5 years in soil under field conditions. Catena 2017, 159, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Xie, Y.; Qiu, Y. Natural oxidation of a temperature series of biochars: Opposite effect on the sorption of aromatic cationic herbicides. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2015, 114, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, C.; Spokas, K.A.; Cox, L.; Koskinen, W.C. Influence of soil biochar aging on sorption of the herbicides MCPA, nicosulfuron, terbuthylazine, indaziflam, and fluoroethyldiaminotriazine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10855–10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Demisie, W.; Zhang, M. Simulated degradation of biochar and its potential environmental implications. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 179, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lou, Z.; Yi, P.; Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, J.; et al. Improving abiotic reducing ability of hydrothermal biochar by low temperature oxidation under air. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 172, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Raghavan, V.G.S.; Orsat, V.; Ngadi, M. Surface characterisation and classification of microwave pyrolysed maple wood biochar. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 131, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.K.; Sandle, N.K. Effect of different oxidizing agent treatments on the surface properties of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, S.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Singh, B. Aging Induced Changes in Biochar’s Functionality and Adsorption Behavior for Phosphate and Ammonium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8359–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, N.; Joseph, S.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Kammann, C.I.; Harter, J.; Borch, T.; Young, R.B.; Varga, K.; Taherymoosavi, S.; Elliott, K.W.; et al. Organic coating on biochar explains its nutrient retention and stimulation of soil fertility. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, D.; Evrard, L.; Sonnet, P. Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempster, D.N.; Jones, D.L.; Murphy, D.V. Clay and biochar amendments decreased inorganic but not dissolved organic nitrogen leaching in soil. Soil Res. 2012, 50, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, R.; Shen, G.; Zhang, J.; Meng, G.; Zhang, J. Effects of biochar on nutrients and the microbial community structure of tobacco-planting soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2017, 17, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Bayou, W.D.; Tang, H.J. Effects of biochar’s application on active organic carbon fractions in soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 26, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, S.; Kammann, C.I.; Shepherd, J.G.; Conte, P.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Hagemann, N.; Rich, A.M.; Marjo, C.E.; Allen, J.; Munroe, P.; et al. Microstructural and associated chemical changes during the composting of a high temperature biochar: Mechanisms for nitrate, phosphate and other nutrient retention and release. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Joseph, S.; Tsechansky, L.; Privat, K.; Schreiter, I.J.; Schüth, C.; Graber, E.R. Biochar aging in contaminated soil promotes Zn immobilization due to changes in biochar surface structural and chemical properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrishamkesh, S.; Gorji, M.; Asadi, H.; Bagheri-Marandi, G.H.; Pourbabaee, A.A. Effects of rice husk biochar application on the properties of alkaline soil and lentil growth. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Schumacher, T.E.; McDonald, L.M.; Clay, D.E.; Malo, D.D.; Papiernik, S.K.; Clay, S.A.; Julson, J.L. Phosphorus Sorption and Availability from Biochars and Soil/Biochar Mixtures. Clean-Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, Z. Field-aged biochar stimulated N2O production from greenhouse vegetable production soils by nitrification and denitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, W.; Riby, P.; Waterson, J. Effects of three different biochars on aggregate stability, organic carbon mobility and micronutrient bioavailability. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Amonette, J.E.; Lin, Z.; Liu, G.; Ambus, P.; Xie, Z. How does biochar influence soil N cycle? A meta-analysis. Plant. Soil 2018, 426, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K.; Thomas, B.W.; Sachdeva, V.; Deng, H. Physico-chemical properties and microbial responses in biochar-amended soils: Mechanisms and future directions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 206, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Gutiérrez, E.; Floch, C.; Ziarelli, F.; Albrecht, R.; Le Petit, J.; Augur, C.; Criquet, S. Characterization of a Mediterranean litter by 13C CPMAS NMR: Relationships between litter depth, enzyme activities and temperature. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Subbotina, I.; Chen, H.; Bogomolova, I.; Xu, X. Black carbon decomposition and incorporation into soil microbial biomass estimated by 14C labeling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Motta, A.C.; Reeves, D.W.; Burmester, C.H.; van Santen, E.; Osborne, J.A. Soil microbial communities under conventional-till and no-till continuous cotton systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jing, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, H. Responses of soil microbial community structure changes and activities to biochar addition: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.; Gleixner, G. Soil organic matter in soil depth profiles: Distinct carbon preferences of microbial groups during carbon transformation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, L. Reduced carbon sequestration potential of biochar in acidic soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.L.; Williams, M.A.; Bottomley, P.J.; Myrold, D.D. Microbial community dynamics associated with rhizosphere carbon flow. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 6793–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, S.K.; Williams, M.A.; Bottomley, P.J.; Myrold, D.D. Dynamics of microbial communities during decomposition of carbon-13 labeled ryegrass fractions in soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-J.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, H.; Yao, H.-Y.; Su, J.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-G. Biochar impacts soil microbial community composition and nitrogen cycling in an acidic soil planted with rape. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9391–9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, G.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Cheng, K.; Jinwei, Z. Biochar decreased microbial metabolic quotient and shifted community composition four years after a single incorporation in a slightly acid rice paddy from southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Capacity and mechanisms of ammonium and cadmium sorption on different wetland-plant derived biochars. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Han, L.; Jin, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Xing, B. Effect of minerals on the stability of biochar. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| C (%) | H (%) | O (%) | N (%) | Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Average Pore Width (Å) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBC | 82.1 | 0.97 | 9.2 | 0.17 | 333.72 | 0.138 | 19.96 |
| 5% OBC | 81.3 | 1.08 | 10.5 | 0.18 | 336.76 | 0.141 | 20.16 |
| 10% OBC | 78.4 | 1.29 | 12.7 | 0.14 | 347.46 | 0.146 | 19.63 |
| Carboxylic | Lactonic | Phenolic | Total Acidic | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBC | 0.14 ± 0.03 a | 0.11 ± 0.04 a | 0.39 ± 0.17 a | 0.64 ± 0.15 a |
| 5% OBC | 0.21 ± 0.18 a | 0.14 ± 0.07 a | 0.69 ± 0.10 b | 1.04 ± 0.67 a |
| 10% OBC | 0.32 ± 0.10 b | 0.21 ± 0.05 b | 1.34 ± 0.15 c | 1.98 ± 0.61 b |
| pH | SOC (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | NH4-N (mg/kg) | NO3-N (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | C/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.60 ± 0.10 a | 11.39 ± 1.90 a | 2.71 ± 0.60 a | 7.27 ± 0.53 a | 19.52 ± 2.08 a | 49.64 ± 9.11 a | 4.48 ± 1.92 a |
| FBC | 6.47 ± 0.06 b | 14.12 ± 2.26 ab | 2.42 ± 0.40 a | 6.13 ± 0.18 bc | 15.72 ± 0.90 b | 31.34 ± 1.90 b | 5.86 ± 0.71 ab |
| FBC + Cd | 6.42 ± 0.02 b | 13.07 ± 2.37 ab | 2.32 ± 0.28 a | 6.32 ± 0.35 bc | 12.77 ± 1.69 c | 33.83 ± 2.24 b | 5.67 ± 1.14 ab |
| 5% OBC | 6.53 ± 0.10 b | 14.41 ± 2.29 ab | 2.08 ± 0.06 a | 6.10 ± 0.27 bc | 15.05 ± 1.38 bc | 32.31 ± 2.94 b | 6.91 ± 0.94 b |
| 5% OBC + Cd | 6.46 ± 0.10 b | 13.20 ± 0.63 ab | 2.29 ± 0.05 a | 6.46 ± 0.25 c | 16.86 ± 0.96 b | 29.50 ± 5.20 b | 5.76 ± 0.34 ab |
| 10% OBC | 6.48 ± 0.16 b | 15.08 ± 0.46 b | 2.01 ± 0.13 a | 5.89 ± 0.17 b | 15.48 ± 1.08 b | 35.67 ± 0.97 b | 7.52 ± 0.53 bc |
| 10% OBC + Cd | 6.44 ± 0.04 b | 14.35 ± 2.08 ab | 1.85 ± 0.22 a | 6.41 ± 0.31 bc | 14.82 ± 0.98 bc | 33.58 ± 3.48 b | 7.89 ± 1.84 c |
| General bacteria | G+ bacteria | G–bacteria | Fungi | AMF | Actinomycetes | Total | G+/G− | B/F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | ND | 0.30 ± 0.04 a | 1.86 ± 0.59 a | 1.00 ± 0.08 a | ND | 0.35 ± 0.04 a | 3.51 ± 0.56 a | 0.17 ± 0.04 a | 2.18 ± 0.72 a |
| FBC | ND | 0.31 ± 0.03 a | 2.76 ± 0.29 a | 1.22 ± 0.03 a | ND | 0.37 ± 0.09 a | 4.66 ± 0.42 a | 0.11 ± 0.004a | 2.50 ± 0.21 a |
| FBC + Cd | 0.01 ± 0.002a | 0.32 ± 0.007a | 2.86 ± 0.86 a | 1.23 ± 0.36 a | ND | 0.38 ± 0.12 a | 4.80 ± 1.36 a | 0.12 ± 0.03 a | 2.62 ± 0.16 a |
| 5% OBC | 0.17 ± 0.03 b | 1.81 ± 0.30 b | 1.92 ± 0.98 a | 0.52 ± 0.16 b | 0.24 ± 0.05 a | 0.74 ± 0.17 b | 5.41 ± 1.67 a | 1.05 ± 0.33 b | 7.49 ± 1.38 b |
| 5% OBC +Cd | 0.16 ± 0.01 b | 1.84 ± 0.30 b | 2.09 ± 0.15 a | 0.57 ± 0.08 b | 0.23 ± 0.02 a | 0.75 ± 0.12 b | 5.64 ± 0.65 a | 0.88 ± 0.10 b | 7.27 ± 0.34 b |
| 10% OBC | 0.25 ± 0.06 c | 2.86 ± 0.77 c | 2.14 ± 0.69 a | 1.27 ± 0.37 a | 0.40 ± 0.11 b | 1.13 ± 0.33 c | 8.05 ± 2.32 b | 1.36 ± 0.12 c | 4.13 ± 0.11 c |
| 10% OBC +Cd | 0.15 ± 0.02 b | 2.05 ± 0.24 b | 2.47 ± 0.37 a | 0.61 ± 0.07 b | 0.31 ± 0.03 c | 0.76 ± 0.13 b | 6.36 ± 0.57 b | 0.84 ± 0.16 b | 7.64 ± 0.81 b |
| Aging | Cadmium | Aging × Cadmium | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Df | F | P | Df | F | P | Df | F | P | |
| General bacteria | 3 | 363.93 | 0.000 | 1 | 12.04 | 0.005 | 2 | 9.06 | 0.005 |
| Gram+ | 3 | 369.47 | 0.000 | 1 | 8.81 | 0.013 | 2 | 3.36 | 0.073 |
| Gram- | 3 | 108.56 | 0.000 | 1 | 21.82 | 0.001 | 2 | 6.91 | 0.011 |
| Fungi | 3 | 205.34 | 0.000 | 1 | 18.06 | 0.001 | 2 | 11.05 | 0.002 |
| AMF | 3 | 616.18 | 0.000 | 1 | 3.87 | 0.075 | 2 | 3.71 | 0.059 |
| Actinomycetes | 3 | 34.66 | 0.000 | 1 | 4.52 | 0.057 | 2 | 1.55 | 0.255 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Yin, G.; Xu, Q.; Yan, J.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Zhu, L.; Lin, Q. Influence of Aged Biochar Modified by Cd2+ on Soil Properties and Microbial Community. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124868
Li K, Yin G, Xu Q, Yan J, Hseu Z-Y, Zhu L, Lin Q. Influence of Aged Biochar Modified by Cd2+ on Soil Properties and Microbial Community. Sustainability. 2020; 12(12):4868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124868
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kun, Guangcai Yin, Qiuyuan Xu, Junhua Yan, Zeng-Yei Hseu, Liwei Zhu, and Qintie Lin. 2020. "Influence of Aged Biochar Modified by Cd2+ on Soil Properties and Microbial Community" Sustainability 12, no. 12: 4868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124868
APA StyleLi, K., Yin, G., Xu, Q., Yan, J., Hseu, Z.-Y., Zhu, L., & Lin, Q. (2020). Influence of Aged Biochar Modified by Cd2+ on Soil Properties and Microbial Community. Sustainability, 12(12), 4868. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124868






