Short-Term Effects of Eco-Friendly Fertilizers on a Soil Bacterial Community in the Topsoil and Rhizosphere of an Irrigated Agroecosystem
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.2. Determination of Cabbage Growth Characteristics and Soil Properties
2.3. Extraction of DNA, PCR and Sequencing
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cabbage Growth Characteristics and Soil Properties
3.2. Bacterial Community Diversity and Richness
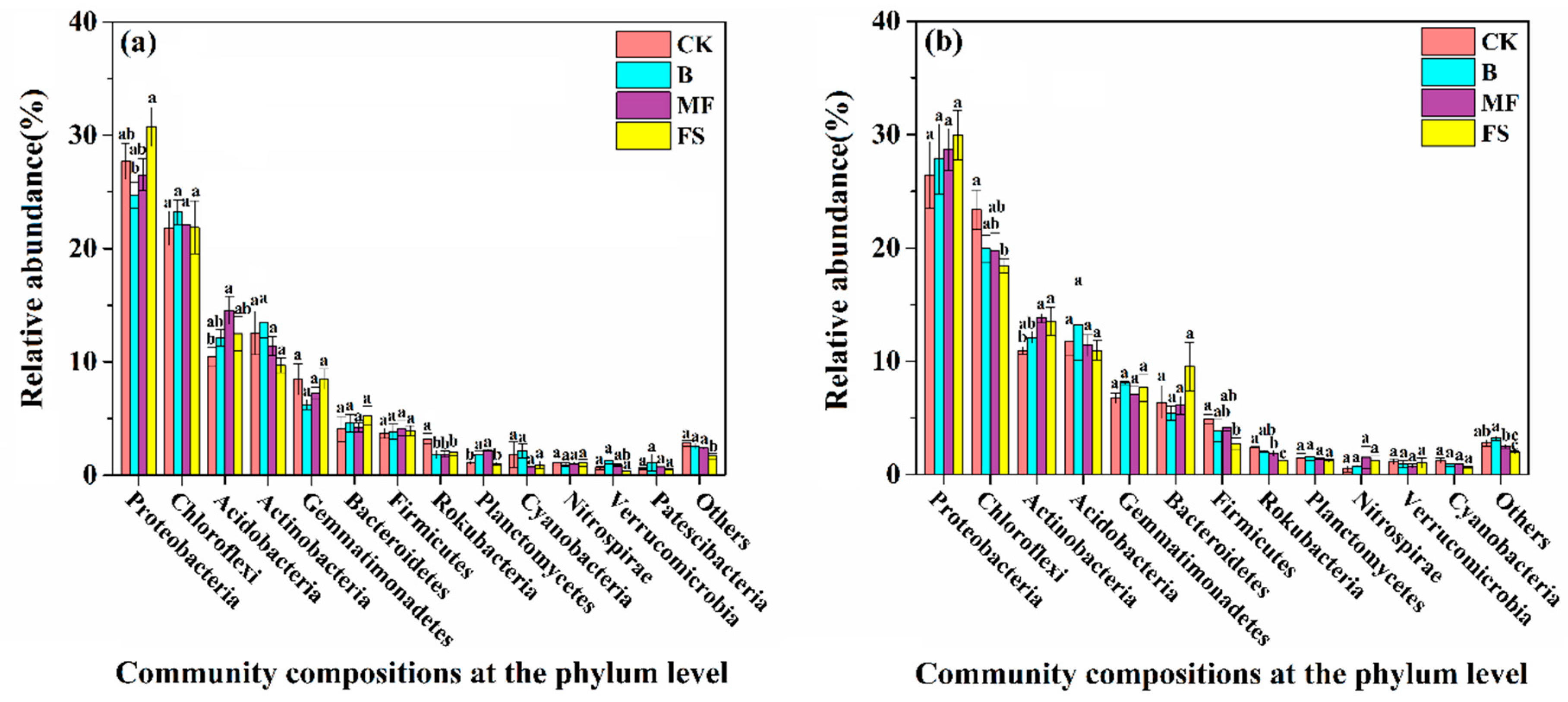
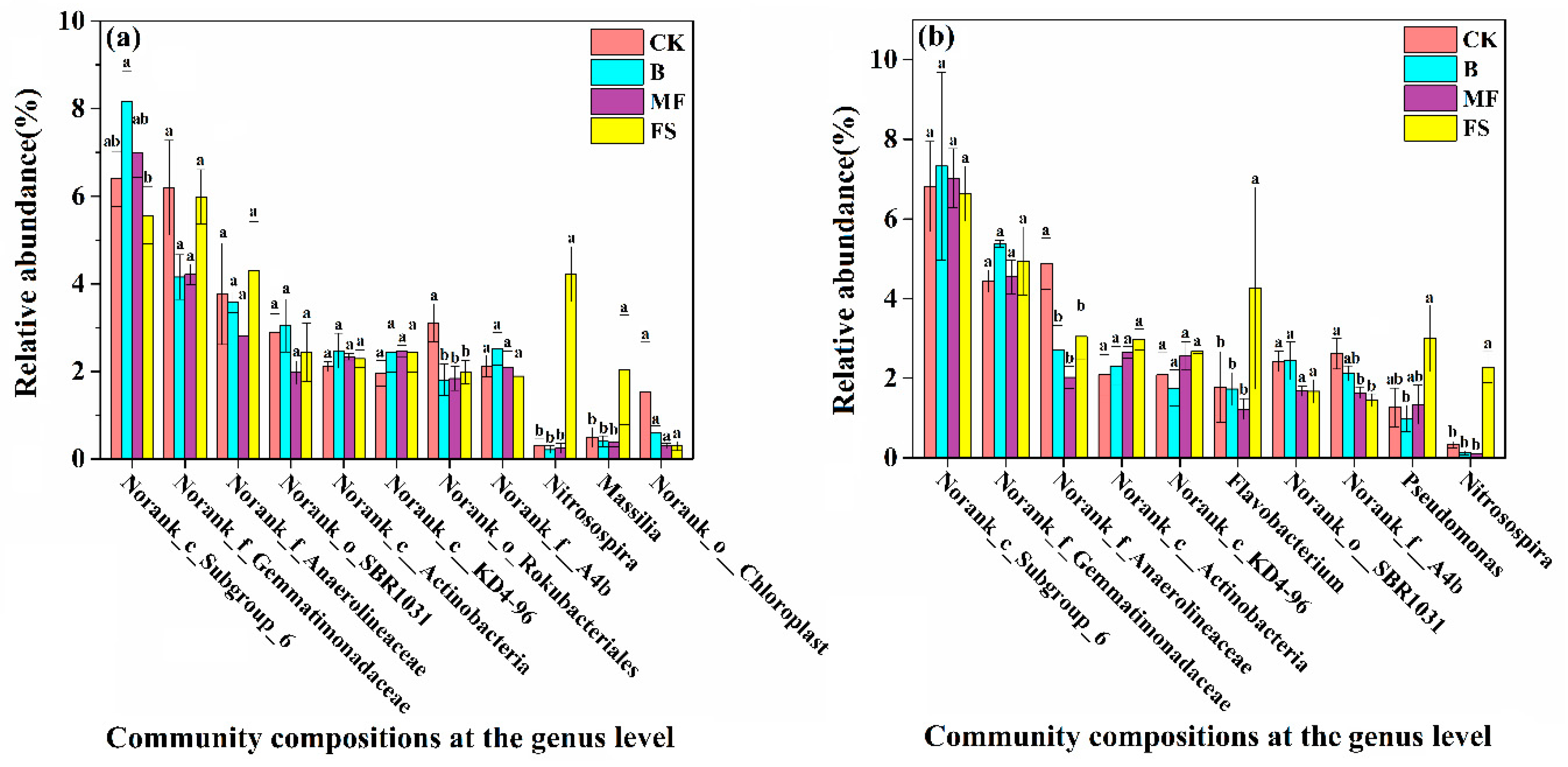
3.3. Bacterial Community Composition
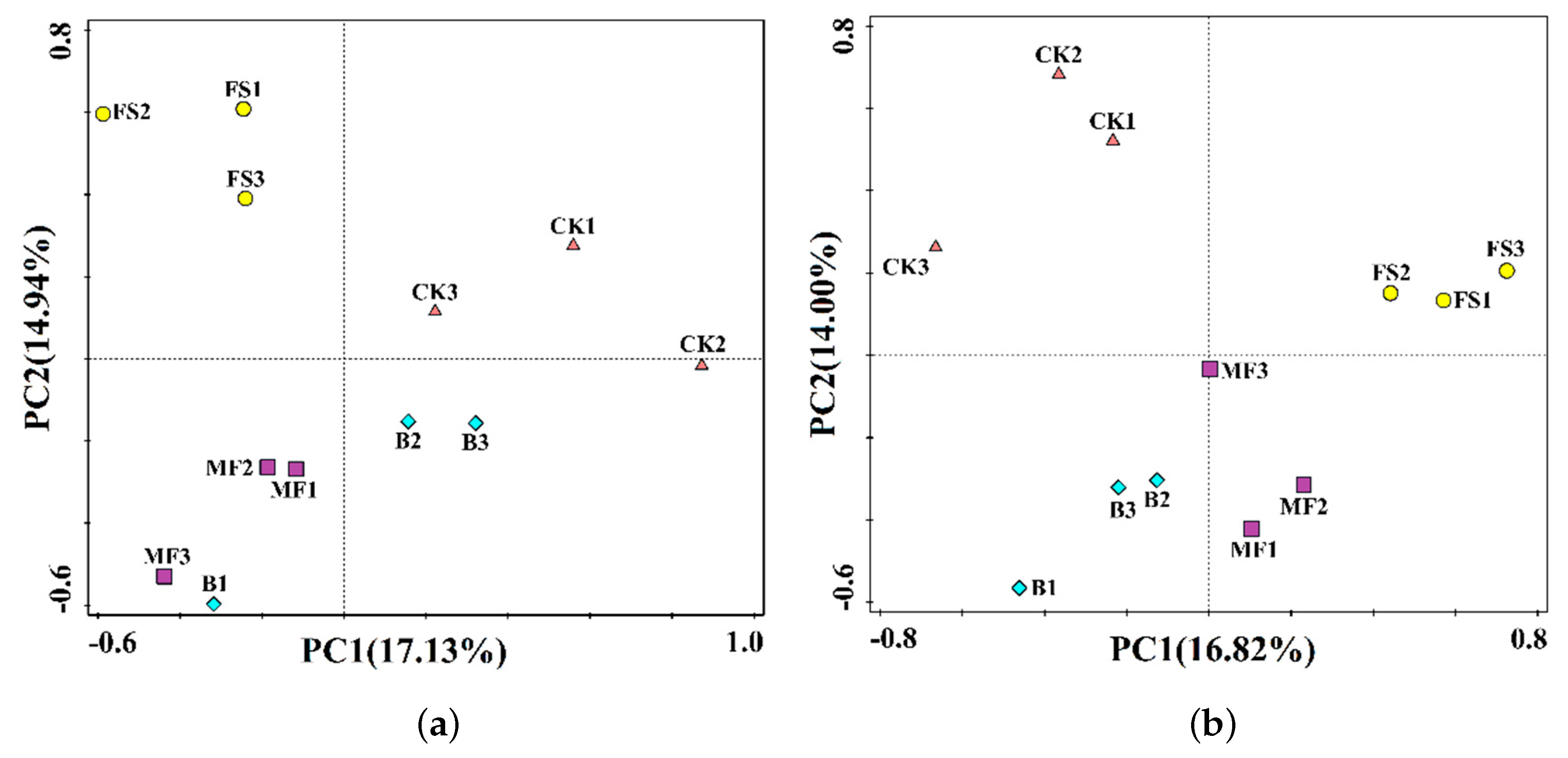
3.4. Relationship Between Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Properties
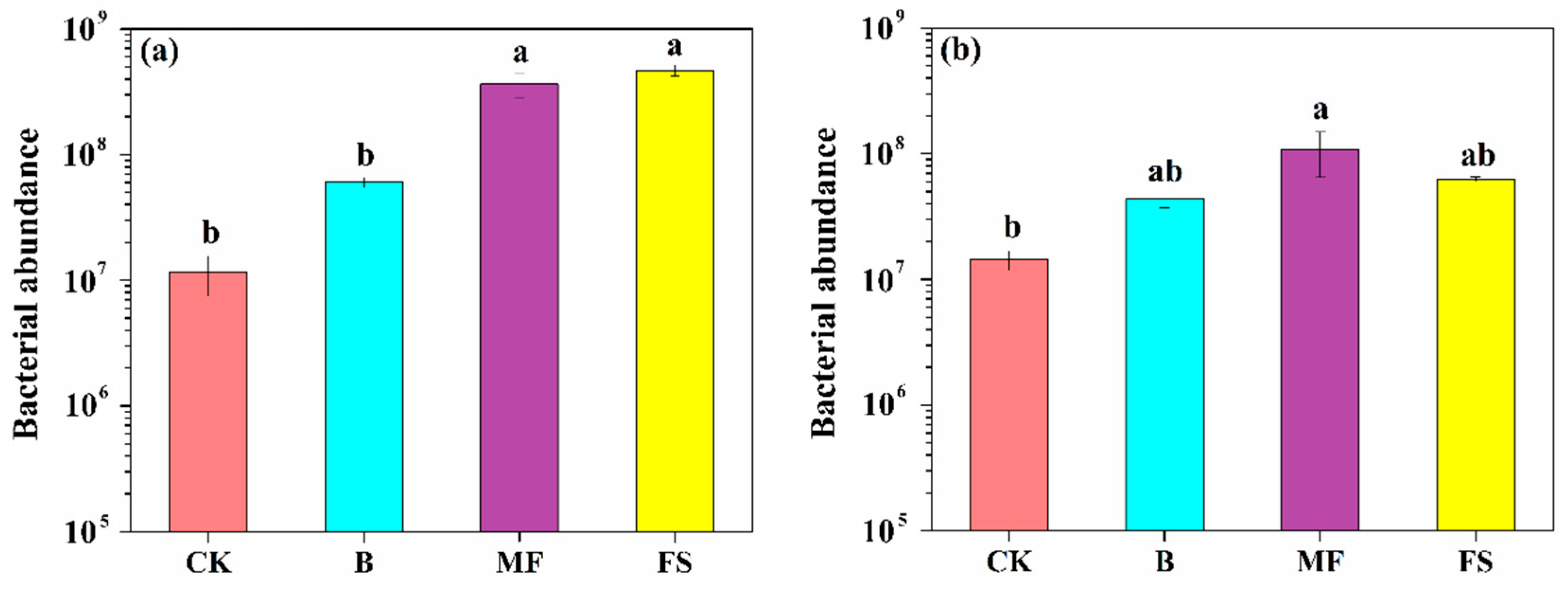
3.5. Quantification of Bacterial Abundance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Samples | Sequence Numbers | Base Numbers | Mean Length | Minimum Length | Maximum Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 66282 | 27658924 | 417.3 | 312 | 512 |
| CK2 | 72067 | 30124601 | 418.0 | 220 | 476 |
| CK3 | 62105 | 25882367 | 416.8 | 204 | 488 |
| CK Even | 66818 | 27888631 | 417.4 | 245 | 492 |
| B1 | 64158 | 26764080 | 417.2 | 245 | 514 |
| B2 | 64089 | 26618299 | 415.3 | 238 | 519 |
| B3 | 70792 | 29531375 | 417.2 | 203 | 477 |
| B Even | 66346 | 27637918 | 416.5 | 229 | 503 |
| MF1 | 61112 | 25451186 | 416.5 | 246 | 488 |
| MF2 | 59863 | 24963098 | 417.0 | 306 | 495 |
| MF3 | 54473 | 22681732 | 416.4 | 202 | 500 |
| MF Even | 58483 | 24365339 | 416.6 | 251 | 494 |
| FS1 | 65576 | 27353010 | 417.1 | 232 | 487 |
| FS2 | 63489 | 26484438 | 417.2 | 283 | 509 |
| FS3 | 55129 | 22994710 | 417.1 | 245 | 468 |
| FS Even | 61398 | 25610719 | 417.1 | 253 | 488 |
| Samples | Sequence Numbers | Base Numbers | Mean Length | Minimum Length | Maximum Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK1 | 66593 | 27799418 | 417.5 | 244 | 468 |
| CK2 | 58990 | 24583105 | 416.7 | 265 | 512 |
| CK3 | 74734 | 31215183 | 417.7 | 216 | 512 |
| CK Even | 66772 | 27865902 | 417.3 | 242 | 497 |
| B1 | 64194 | 26781738 | 417.2 | 227 | 498 |
| B2 | 53277 | 22246172 | 417.6 | 245 | 520 |
| B3 | 62480 | 26119546 | 418.0 | 245 | 481 |
| B Even | 59984 | 25049152 | 417.6 | 239 | 500 |
| MF1 | 54659 | 22805944 | 417.2 | 245 | 503 |
| MF2 | 65766 | 27404662 | 416.7 | 222 | 511 |
| MF3 | 58205 | 24298646 | 417.5 | 298 | 468 |
| MF Even | 59543 | 24836417 | 417.1 | 255 | 494 |
| FS1 | 66026 | 27535674 | 417.0 | 211 | 497 |
| FS2 | 56562 | 23617658 | 417.6 | 287 | 469 |
| FS3 | 59166 | 24732261 | 418.0 | 277 | 511 |
| FS Even | 60585 | 25295198 | 417.5 | 258 | 492 |
| Depth | Sample | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species | OTUs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | CK | 39 | 111 | 311 | 519 | 952 | 1947 | 5892 |
| B | 39 | 110 | 310 | 511 | 966 | 2007 | 6146 | |
| MF | 39 | 109 | 306 | 516 | 974 | 1991 | 6228 | |
| FS | 37 | 107 | 284 | 474 | 900 | 1791 | 5024 | |
| Rhizosphere | CK | 39 | 105 | 294 | 495 | 921 | 1932 | 5865 |
| B | 39 | 108 | 302 | 509 | 966 | 1979 | 5903 | |
| MF | 38 | 105 | 302 | 518 | 976 | 2029 | 5950 | |
| FS | 37 | 104 | 290 | 484 | 917 | 1853 | 5202 |
References
- Lin, Y.; Ye, G.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Liu, D.; Fan, J.; Ding, W. Long-term manure application increases soil organic matter and aggregation, and alters microbial community structure and keystone taxa. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Wei, W.; He, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Hu, R. Soil organic matter priming and carbon balance after straw addition is regulated by long-term fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Li, L.; Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Coulter, J.A.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Effect of long-term nitrogen addition on wheat yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and residual soil nitrate in a semiarid area of the Loess Plateau of China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yu, W.; Yao, H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chu, H. Suppressed N fixation and diazotrophs after four decades of fertilization. Microbiome 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Effects of organic-inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice-wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L. Change of soil microbial community under long-term fertilization in a reclaimed sandy agricultural ecosystem. PeerJ 2019, 2019, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen fertilizer induced greenhouse gas emissions in China. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustainability 2011, 3, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Wehmeyer, H.; de Guia, A.H.; Connor, M. Reduction of fertilizer use in South China—Impacts and implications on smallholder rice farmers. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhu, P.; Cui, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Soil bacterial communities under different long-term fertilization regimes in three locations across the Black Soil region of Northeast China. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Casey, P.; Muster, T.; Gill, H.; Adhikari, B. Enhanced efficiency fertilisers: A review of formulation and nutrient release patterns. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritika, B.; Utpal, D. Biofertilizer, a way towards organic agriculture: A review. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 2332–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C.; Muhammad, N.; Wu, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Potential role of biochars in decreasing soil acidification—A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameloot, N.; Sleutel, S.; Das, K.C.; Kanagaratnam, J.; de Neve, S. Biochar amendment to soils with contrasting organic matter level: Effects on N mineralization and biological soil properties. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Whalen, J.K. Biochemical cycling of nitrogen and phosphorus in biochar-amended soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aseri, G.K.; Jain, N.; Panwar, J.; Rao, A.V.; Meghwal, P.R. Biofertilizers improve plant growth, fruit yield, nutrition, metabolism and rhizosphere enzyme activities of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) in Indian Thar Desert. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 117, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosro, M.; Yousef, S. Bacterial Biofertilizers for Sustainable Crop Production: A Review. J. Agric. Bol. Sci. 2012, 7, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Ansari, M.W.; Sahoo, R.K.; Tuteja, N. Biofertilizers function as key player in sustainable agriculture by improving soil fertility, plant tolerance and crop productivity. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, P.; Chi, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, P.; Liu, N.; Cai, D.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, N. Controlling the hydrolysis and loss of nitrogen fertilizer (urea) by using a nanocomposite favors plant growth. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2068–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamminger, C.; Zaiser, N.; Zinsser, P.; Lamers, M.; Kammann, C.; Marhan, S. Effects of biochar, earthworms, and litter addition on soil microbial activity and abundance in a temperate agricultural soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, S.; Gao, S.; Duan, Y.; Wang, D. Soil microbial community structure affected by biochar and fertilizer sources. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 150, 103452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Cao, Z.H.; Li, Z.G.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, M.H. Effects of biofertilizer containing N-fixer, P and K solubilizers and AM fungi on maize growth: A greenhouse trial. Geoderma 2005, 125, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.; Ortega, R.; Barrientos, L.; Moya, M.; Reyes, G.; Kramm, V. Development of a biofertilizer based on filamentous nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria for rice crops in Chile. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Crowley, D. Effect of biochar amendment on yield and methane and nitrous oxide emissions from a rice paddy from Tai Lake plain, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locey, K.J.; Lennon, J.T. Scaling laws predict global microbial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5970–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eo, J.; Park, K.C. Long-term effects of imbalanced fertilization on the composition and diversity of soil bacterial community. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Vose, J.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Geron, C.D.; Walker, J.T. Evaluation of the effectiveness of riparian zone restoration in the southern Appalachians by assessing soil microbial populations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2004, 26, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Rott, M.; Schlaeppi, K.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Ahmadinejad, N.; Assenza, F.; Rauf, P.; Huettel, B.; Reinhardt, R.; Schmelzer, E.; et al. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 2012, 488, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.D.; Martiny, J.B.H. Resistance, resilience, and redundancy in microbial communities. Light Evol. 2009, 2, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Han, M.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Tian, Q.; Jiao, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Effects of continuous cropping of sweet potato on the fungal community structure in rhizospheric soil. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, L.E.; Nelson, D.W. Determination of total phosphorus in soils: A rapid perchloric acid digestion procedure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanos, D.S.; Kapoulas, V.M. A rapid method for the determination of organic nitrogen and phosphorus based on a single perchloric acid digestion. Anal. Chim. Acta 1966, 34, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Song, G.; Hui, R.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Development of bacterial communities in biological soil crusts along a revegetation chronosequence in the Tengger Desert, northwest China. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 3801–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, L.M.; Yang, M.; He, J.Z. Long-term fertilization regimes affect bacterial community structure and diversity of an agricultural soil in northern China. J. Soils Sediments 2008, 8, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Q.; Yu, Y.N.; Gao, R.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Long, X.H.; Shen, Q.R.; Chen, W.; Cai, F. High-throughput absolute quantification sequencing reveals the effect of different fertilizer applications on bacterial community in a tomato cultivated coastal saline soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Knight, R. Comparative metagenomic, phylogenetic and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.T.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Caporaso, J.G.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Examining the global distribution of dominant archaeal populations in soil. ISME J. 2011, 5, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Boer, W.; Laanbroek, H.J. Ureolytic nitrification at low pH by Nitrosospira spec. Arch. Microbiol. 1989, 152, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yao, H.; Huang, C. Microbial biomass, N mineralization and nitrification, enzyme activities, and microbial community diversity in tea orchard soils. Plant. Soil 2006, 288, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Muhammad, N.; Yu, X.; Xiao, K.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C. The effects and mechanisms of soil acidity changes, following incorporation of biochars in three soils differing in initial pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1606–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.N.L.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. Nitrogen dynamics in soil fertilized with slow release brown coal-urea fertilizers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Hui, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Song, G.; Sun, J. Differences in bacterial community structure between three types of biological soil crusts and soil below crusts from the Gurbantunggut Desert, China. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Gil-Sotres, F.; Leirós, M.C. Thermodynamic parameters of enzymes in grassland soils from Galicia, NW Spain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boveiri Dehsheikh, A.; Mahmoodi Sourestani, M.; Zolfaghari, M.; Enayatizamir, N. Changes in soil microbial activity, essential oil quantity, and quality of Thai basil as response to biofertilizers and humic acid. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Niu, W. Effects of manure fertilizer on crop yield and soil properties in China: A meta-analysis. Catena 2020, 193, 104617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Plant Height (cm) | Crow Width (cm) | Fruit Diameter (cm) | Yield (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 14.73 ± 0.18 c | 33.80 ± 0.75 c | 12.47 ± 0.32 c | 42.65 ± 2.15 b |
| B | 16.10 ± 0.17 b | 37.87 ± 0.35 b | 13.63 ± 0.09 b | 47.88 ± 2.11 ab |
| MF | 16.67 ± 0.09 a | 39.07 ± 0.26 b | 14.57 ± 0.18 a | 49.89 ± 1.34 a |
| FS | 16.77 ± 0.09 a | 40.83 ± 0.24 a | 14.93 ± 0.33 a | 51.56 ± 2.64 a |
| Depth | Sample | pH | EC (μs cm−1) | OM (g kg−1) | TP (mg kg−1) | TN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | CK | 7.80 ± 0.05 b | 342.33 ± 39.82 b | 10.92 ± 1.71 b | 654.43 ± 7.74 b | 641.40 ± 34.48 b | 21.53 ± 5.05 b |
| B | 8.23 ± 0.10 a | 227.27 ± 21.94 b | 12.92 ± 1.09 b | 608.89 ± 25.74 b | 640.06 ± 10.74 b | 22.13 ± 2.22 b | |
| MF | 7.65 ± 0.10 b | 364.67 ± 43.47 b | 11.40 ± 0.21 b | 716.65 ± 36.53 b | 708.35 ± 24.79 b | 34.87 ± 6.37 b | |
| FS | 7.28 ± 0.05 c | 720.00 ± 26.58 a | 17.15 ± 1.22 a | 1316.97 ± 75.85 a | 1044.42 ± 72.03 a | 220.04 ± 89.57 a | |
| Rhizosphere | CK | 7.59 ± 0.03 bc | 405.33 ± 70.76 b | 9.04 ± 0.64 b | 660.20 ± 17.36 b | 618.86 ± 24.45 b | 24.34 ± 8.25 b |
| B | 8.24 ± 0.17 a | 232.10 ± 43.05 b | 14.95 ± 1.49 a | 588.87 ± 49.89 b | 634.99 ± 50.78 b | 24.18 ± 5.26 b | |
| MF | 7.86 ± 0.07 b | 347.33 ± 13.13 b | 11.00 ± 1.69 b | 712.71 ± 22.99 b | 728.80 ± 22.96 b | 34.62 ± 4.28 b | |
| FS | 7.30 ± 0.05 c | 720.67 ± 149.42 a | 16.46 ± 0.37 a | 1093.04 ± 72.78 a | 1135.53 ± 115.27 a | 196.37 ± 36.64 a |
| Depth | Sample | DHA (μg h−1 g−1) | AKP (μmol h−1 g−1) | SC (mg h−1 g−1) | CAT (μmol h−1 g−1) | UE (μg h−1 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topsoil | CK | 2.26 ± 0.15 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 c | 0.28 ± 0.01 c | 1.22 ± 0.05 b | 8.09 ± 0.30 b |
| B | 2.11 ± 0.31 a | 0.08 ± 0.00 b | 0.38 ± 0.07 bc | 1.25 ± 0.03 b | 10.42 ± 0.53 a | |
| MF | 2.25 ± 0.31 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 bc | 0.47 ± 0.03 b | 1.73 ± 0.10 a | 9.69 ± 0.67 ab | |
| FS | 2.05 ± 0.36 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.83 ± 0.06 a | 1.13 ± 0.00 b | 8.67 ± 0.33 b | |
| Rhizospherie | CK | 2.57 ± 0.29 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 bc | 0.28 ± 0.02 b | 1.38 ± 0.13 b | 7.71 ± 0.43 d |
| B | 2.08 ± 0.31 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 b | 0.26 ± 0.03 b | 1.44 ± 0.08 b | 11.48 ± 0.30 b | |
| MF | 2.81 ± 0.31 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 c | 0.37 ± 0.02 b | 1.87 ± 0.01 a | 9.00 ± 0.29 c | |
| FS | 2.50 ± 0.25 a | 0.16 ± 0.02 a | 0.95 ± 0.11 a | 1.24 ± 0.05 b | 13.74 ± 0.11 a |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhong, N. Short-Term Effects of Eco-Friendly Fertilizers on a Soil Bacterial Community in the Topsoil and Rhizosphere of an Irrigated Agroecosystem. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124803
Zhang W, Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhao L, Qi J, Wang Y, Zhao P, Zhong N. Short-Term Effects of Eco-Friendly Fertilizers on a Soil Bacterial Community in the Topsoil and Rhizosphere of an Irrigated Agroecosystem. Sustainability. 2020; 12(12):4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124803
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenli, Yubing Liu, Zengru Wang, Lina Zhao, Jinghua Qi, Yansong Wang, Pan Zhao, and Naiqin Zhong. 2020. "Short-Term Effects of Eco-Friendly Fertilizers on a Soil Bacterial Community in the Topsoil and Rhizosphere of an Irrigated Agroecosystem" Sustainability 12, no. 12: 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124803
APA StyleZhang, W., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Zhao, L., Qi, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, P., & Zhong, N. (2020). Short-Term Effects of Eco-Friendly Fertilizers on a Soil Bacterial Community in the Topsoil and Rhizosphere of an Irrigated Agroecosystem. Sustainability, 12(12), 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12124803




