Integrated Software Development and Case Studies for Optimal Operation of Cascade Reservoir within the Environmental Flow Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cascade Reservoir Optimal Operation Model under the Constraint of Environmental Flow
3. Methodology
3.1. Improved Minimum Monthly Average Runoff Method (IMMR)
3.1.1. Divide into Different Years
3.1.2. Division of Different Periods in One Year
3.1.3. IMMR for Environmental Flow
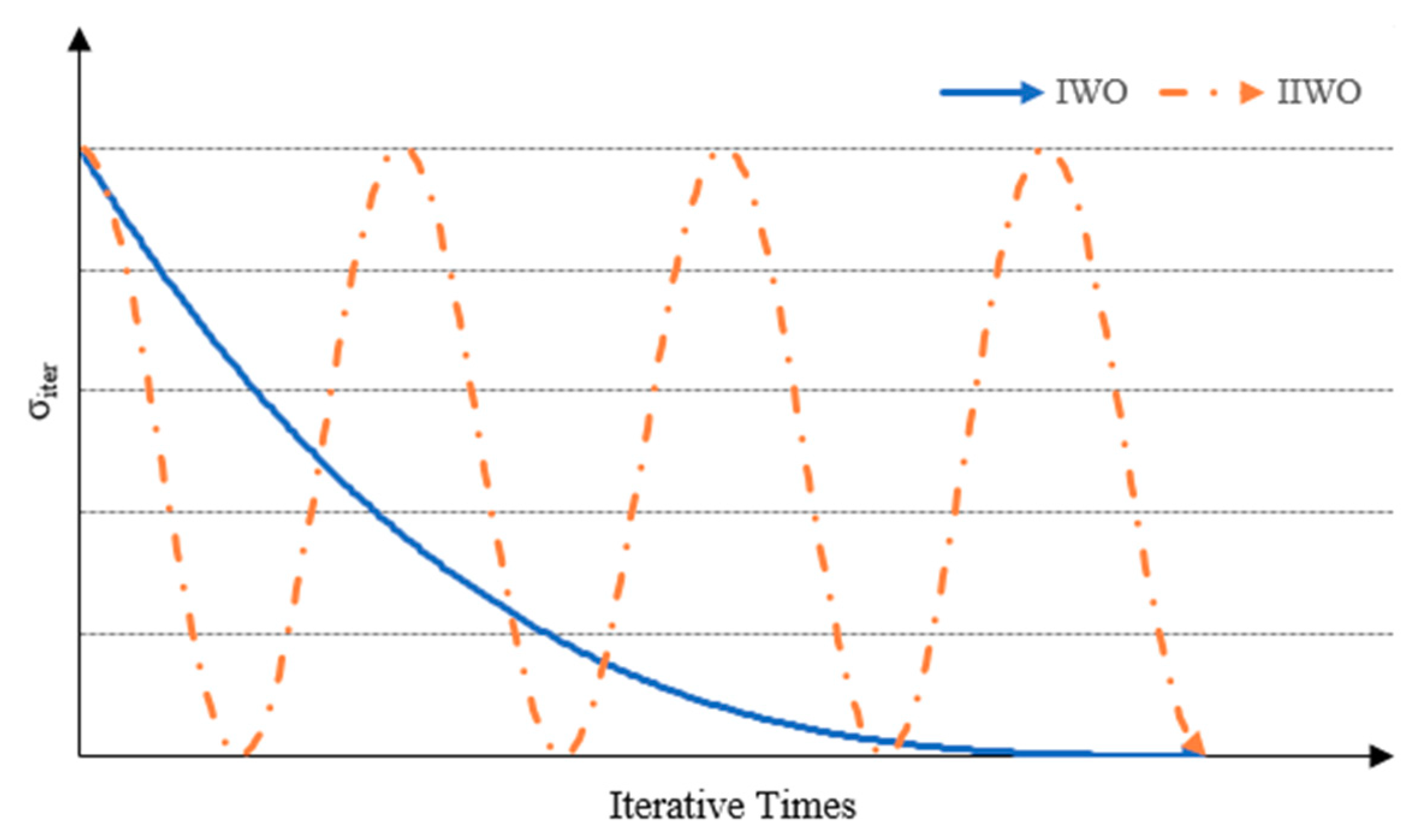
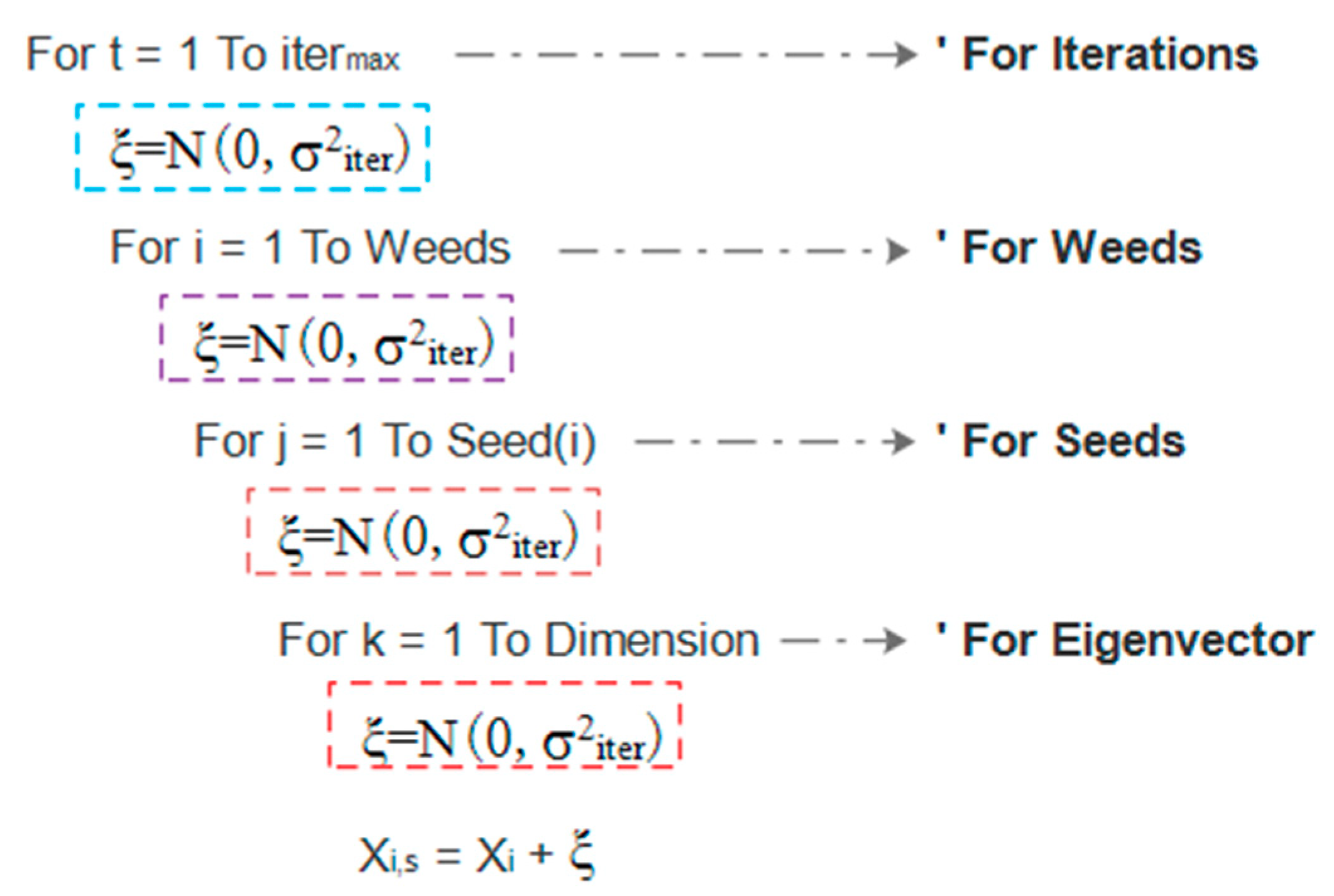
3.2. Improved Invasive Weed Optimization Algorithm (IIWO)
3.2.1. Invasive Weed Optimization Algorithm (IWO)
3.2.2. Improvement from IWO to IIWO
Improvement of Spatial Dispersal Formula
Selection of Spatial Dispersal Rules
3.3. Development of Integrated Software
3.3.1. IIWO Convergence Test Module
3.3.2. Environmental Flow Calculation Module
3.3.3. Cascade Reservoir Operation Module
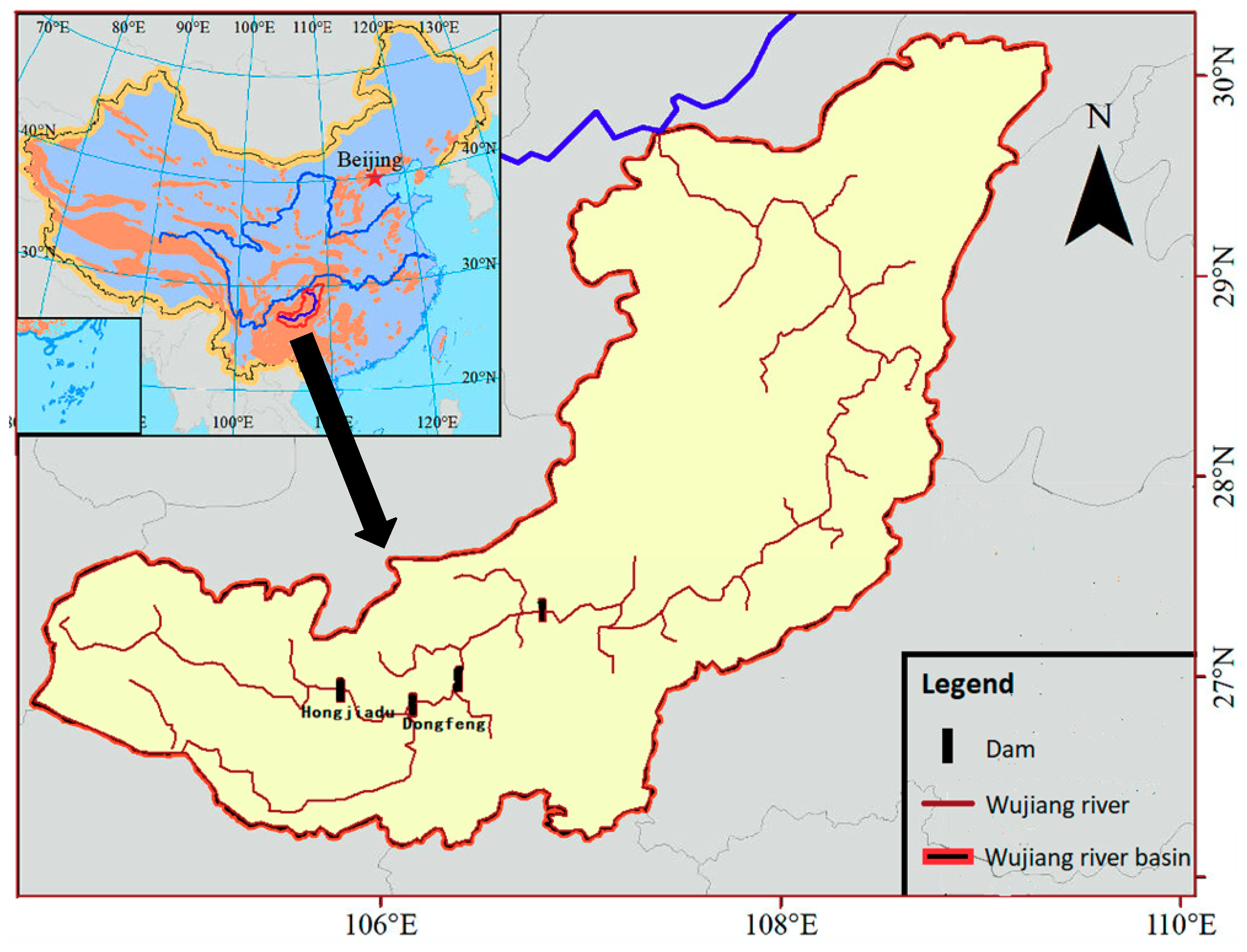
4. Case Studies
5. Results and Discussion
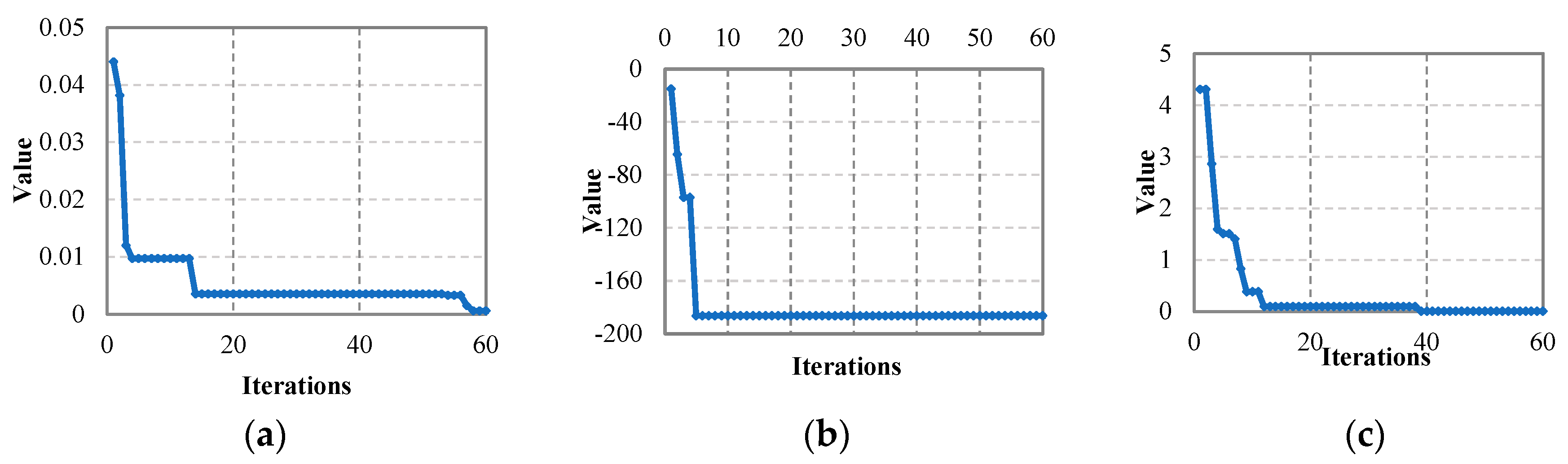
5.1. IIWO Convergence Test
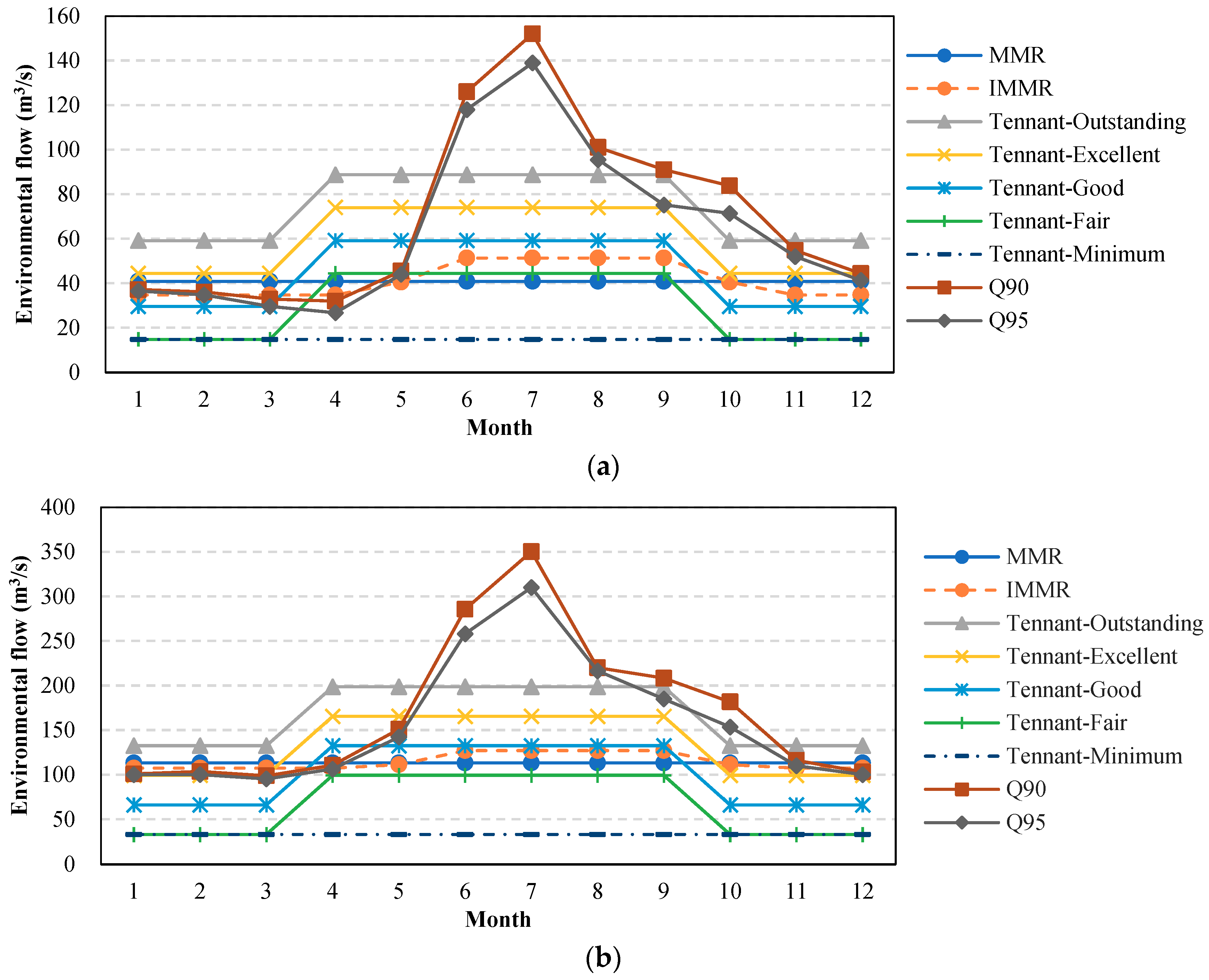
5.2. Environmental Flow Calculation
5.3. Single Reservoir and Cascade Reservoir Optimal Operation
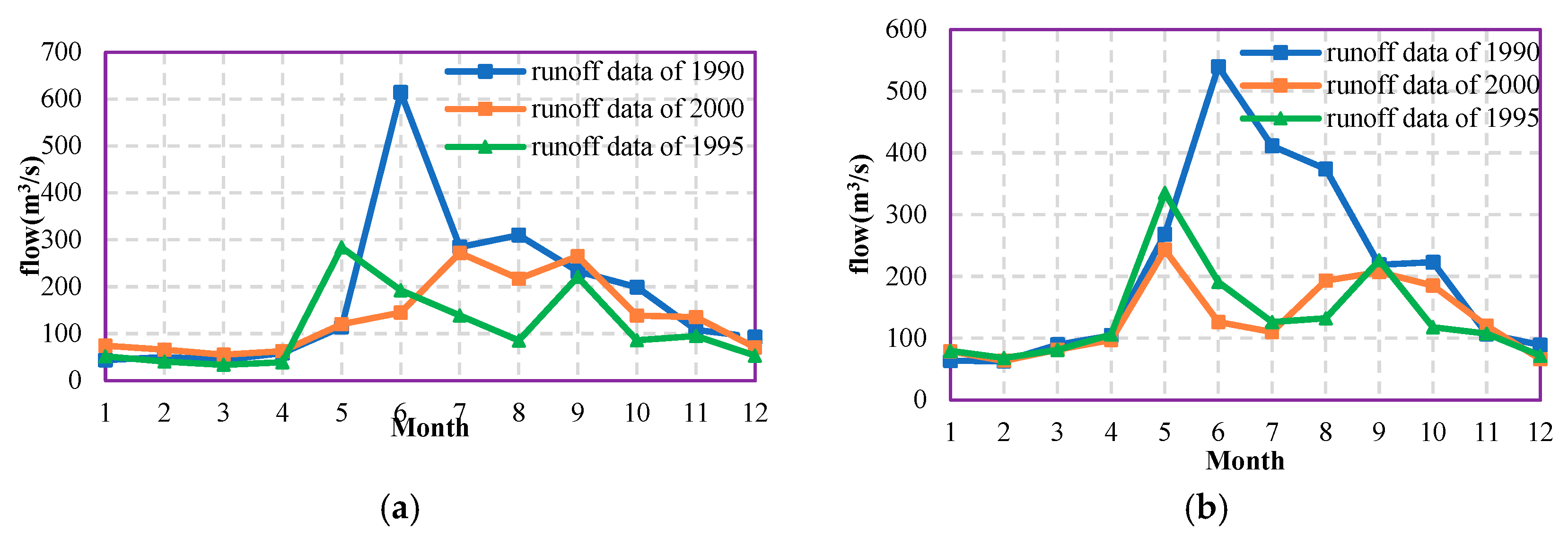
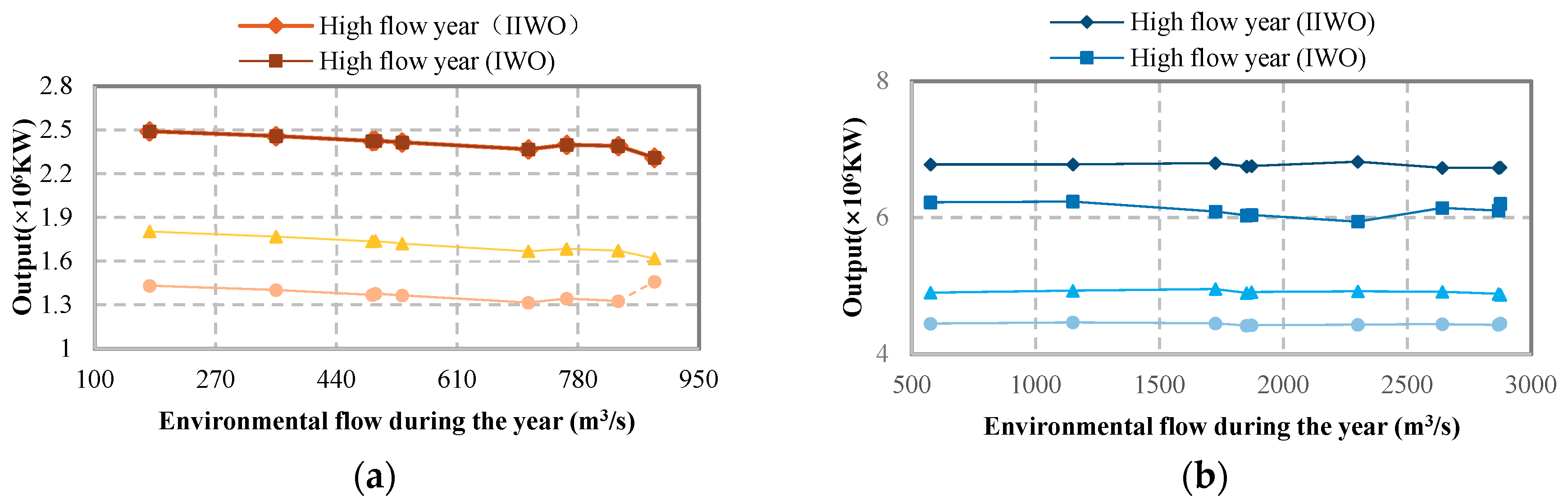
5.3.1. Operation Results in Different Years
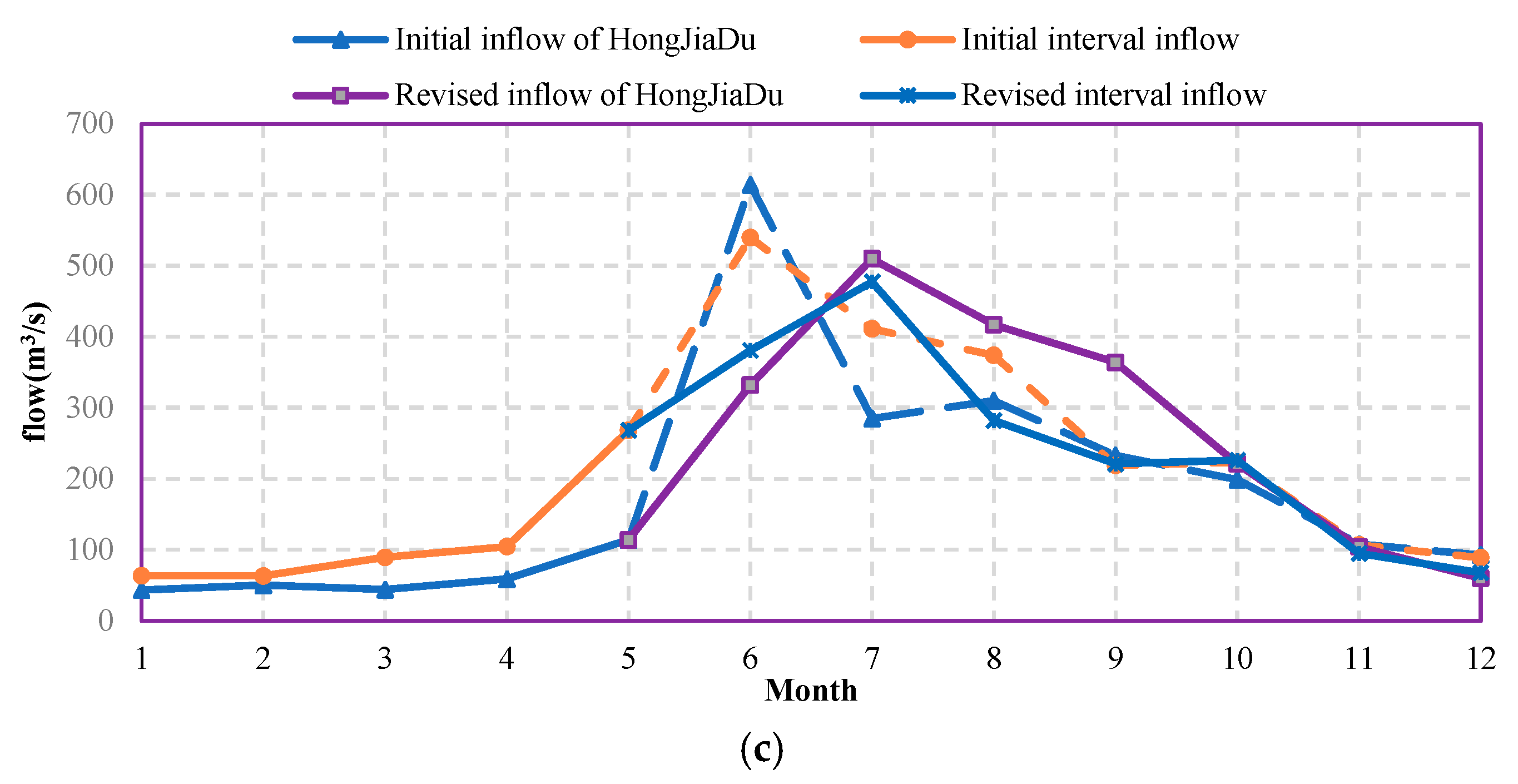
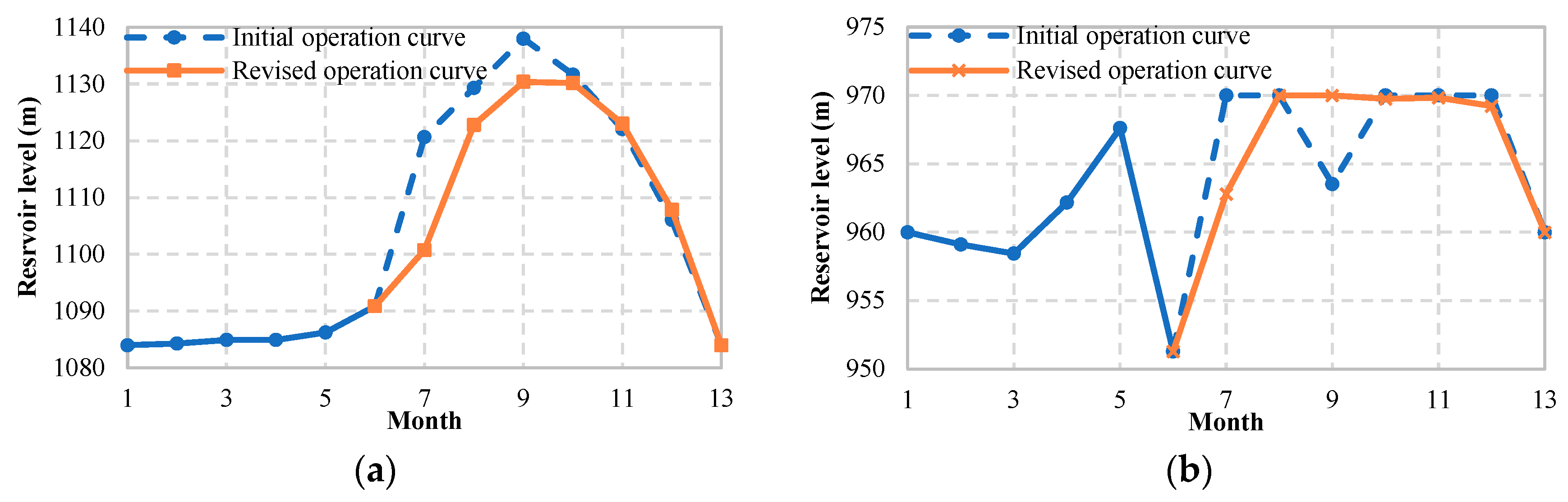
5.3.2. Rolling Correction of Cascade Reservoir Operation Curves
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hadjipaschalis, I.; Poullikkas, A.; Efthimiou, V. Overview of current and future energy storage technologies for electric power applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Shen, J.J.; Su, C.G.; Shen, Q.Q. Trans-regional transmission of large-scale hydropower: Problems and solutions in receiving power grid. Glob. Energy Interconnect. 2019, 2, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lei, X.H.; Wen, X.; Fang, G.H.; Tan, Q.F.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of damming and climatic change on the eco-hydrological system: A case study in the Yalong River, southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Liu, Z.H.; Lei, X.H.; Lin, R.J.; Fang, G.H.; Tan, Q.F.; Wang, C.; Tian, Y.; Quan, J. Future changes in Yuan River ecohydrology: Individual and cumulative impacts of climates change and cascade hydropower development on runoff and aquatic habitat quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Fang, G.H.; Wen, X.; Tan, Q.F.; Huang, X.F.; Lei, X.H.; Tian, Y.; Quan, J. A novel operation chart for cascade hydropower system to alleviate ecological degradation in hydrological extremes. Ecol. Model. 2018, 384, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.D.C. The use of storage water in a hydroelectric system. Oper. Res. 1955, 3, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, A. Optimal short-term hydro scheduling from the principle of progressive optimality. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.W.; Xie, J.C. A new way to solve cascade hydropower reservoirs operation with large scale system analysis. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 1998, 18, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Needham, J.T.; Watkins, D.W.; Lund, J.R.; Nanda, S.K. Linear programming for flood control in the Iowa and Des Moines rivers. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2000, 126, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.S.; Buras, N. Practical estimation of inflows into multi-reservoir system. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2000, 126, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Chow, V.T.; Kokotovi, P.V.; Meredith, D.D. Discrete differential dynamic programing approach to water resources systems optimization. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recep, Y.; Gaplin, S.; Mehmet, A. Hydropower optimization for the lower Seyhan basin system in Turkey using dynamic programming. Water Int. 2006, 31, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howson, H.R.; Sancho, N.G.F. A new algorithm for the solution of multi-state dynamic programming problems. Math. Program. 1975, 8, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E. Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning, 1st ed.; Addison Wesley: Boston, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.W.; Wang, L. Application of a genetic algorithm to optimal operation of hydropower station. Adv. Water Sci. 1997, 8, 275–280. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. Icnn95-Int. Conf. Neural Netw. IEEE. 1995, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Afshar, M.H. Application of an ant colony optimization algorithm for optimal operation of reservoirs: A comparative study of three proposed formulations. Sci. Iran. Trans. A-Civ. Eng. 2009, 16, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian, A.R.; Lucas, C. A novel numerical optimization algorithm inspired from weed colonization. Ecol. Inform. 2006, 1, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, G.G.; Das, S.; Chakraborty, P.; Suganthan, P.N. Design of non-uniform circular antenna arrays using a modified invasive weed optimization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag 2011, 59, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisal, A.K.; Prusty, R.C. Large scale economic dispatch of power systems using oppositional invasive weed optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 29, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, H.R.; Bozorg, H.O.; Pazoki, M.; Loáiciga, H.A. Weed optimization algorithm for optimal reservoir operation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015055.1–04015055.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizipour, M.; Ghalenoei, V.; Afshar, M.H.; Solis, S.S. Optimal Operation of Hydropower Reservoir Systems Using Weed Optimization Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 3995–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.L.; Yu, H.M. Stochastic scheduling strategy of resources in virtual power plant considering wind power dependence structure. Trans. China Electro. Tech. Soc. 2017, 32, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigdeli, B.; Amirkolaee, H.A.; Pahlavani, P. DTM extraction under forest canopy using LiDAR data and a modified invasive weed optimization algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Z.; Yu, W.; Chen, W.; Peng, K.K.; Jia, G.F. Invasive weed optimization for optimizing one-agar-for-all classification of bacterial colonies based on hyperspectral imaging. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2018, 269, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, M.R.; Dutta, S.; Pradhan, S. Hybridizing invasive weed optimization with firefly algorithm for multi-robot motion planning. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 4029–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharme, R.E. A global perspective on environmental flow assessment: Emerging trends in the development and application of environmental flow methodologies for rivers. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 397–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Chen, M.J.; Dong, Z.C. Comments on calculation methods for river ecological water demand. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2004, 32, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, A.; Hong, Y. Using hydrologic and hydraulically derived geometric parameters of perennial rivers to determine minimum water requirements of ecological habitats (case study: Mazandaran Sea basin-Iran). Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 3490–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbins, C.N.; Soulsby, C.; Jeffries, M.J.; Acornley, R. Developing ecologically acceptable river flow regimes: A case study of Kielder reservoir and the Kielder water transfer system. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2001, 8, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, T.K.; Bledsoe, B.; Poff, N.L.; Sanderson, J. Predicting habitat response to flow using generalized habitat models for trout in Rocky Mountain streams. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazvimavi, D.; Madamombe, E.; Makurira, H. Assessment of environmental flow requirements for river basin planning in Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth 2007, 32, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, D.L. Instream fow regimens for fsh, wildlife, recreation, and related environmental resources. Fisheries 1976, 1, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.R.; Cui, S.B.; Li, T.H.; Jin, L. On water demand of river ecosystem. Shui Li Xue Bao 2002, 9, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loar, D.J.; Leonardp, M. Analysis of Environmental Issues Related to Small-Scale Hydroelectric Development; Oak Ridge National Press: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Fang, G.H.; Huang, X.F.; Yuan, Y. Optimized operation of diversion-type hydropower reservoir to alleviate ecological degradation of the de-watered river reach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.N.; Zhao, J.S. Hydropower-ecologic benefits tradeoff analysis of cascade reservoir operation. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2016, 35, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Percentage from Mean | High Flow Year (Flood Season) | Normal Flow Year (Flat Period) | Low Flow Year (Dry Season) |
|---|---|---|---|
| µ | µ > 20% | −20% < µ ≤ 20% | µ ≤ −20% |
| µj | µj > 20% | −20% < µj ≤ 20% | µj ≤ −20% |
| Name | Formula | Sketch |
|---|---|---|
| Schaffer | 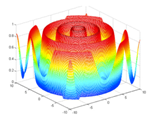 | |
| Shubert |  | |
| Rastrigrin |  |
| Flow Condition | October-March | April-September |
|---|---|---|
| Outstanding | 40% average annual flow | 60% average annual flow |
| Excellent | 30% average annual flow | 50% average annual flow |
| Good | 20% average annual flow | 40% average annual flow |
| Fair or degrading | 10% average annual flow | 30% average annual flow |
| Poor or minimum | 10% average annual flow | 10% average annual flow |
| Name | Hongjiadu | Dongfeng | Location Diagram of the Two Reservoirs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal water level (m) | 1140 | 970 | 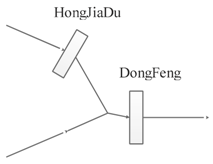 |
| Flood control level (m) | 1138 | 970 | |
| Dead water level (m) | 1076 | 936 | |
| Guaranteed output (MW) | 159.1 | 100 | |
| Installed capacity (MW) | 600 | 695 | |
| Efficiency coefficient | 8.4 | 8.35 |
| Reservoir | IMMR | MMR | Q90 | Q95 | T-O | T-E | T-G | T-F | T-M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hongjiadu | 495 | 491 | 837 | 764 | 888 | 710 | 533 | 355 | 178 |
| Dongfeng | 1376 | 1360 | 2031 | 1877 | 1988 | 1590 | 1193 | 795 | 398 |
| Total | 1871 | 1851 | 2868 | 2641 | 2876 | 2300 | 1726 | 1150 | 576 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Fang, G.; Liao, T.; Huang, X.; Qu, B. Integrated Software Development and Case Studies for Optimal Operation of Cascade Reservoir within the Environmental Flow Constraints. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104064
Wu C, Fang G, Liao T, Huang X, Qu B. Integrated Software Development and Case Studies for Optimal Operation of Cascade Reservoir within the Environmental Flow Constraints. Sustainability. 2020; 12(10):4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104064
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chengjun, Guohua Fang, Tao Liao, Xianfeng Huang, and Bo Qu. 2020. "Integrated Software Development and Case Studies for Optimal Operation of Cascade Reservoir within the Environmental Flow Constraints" Sustainability 12, no. 10: 4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104064
APA StyleWu, C., Fang, G., Liao, T., Huang, X., & Qu, B. (2020). Integrated Software Development and Case Studies for Optimal Operation of Cascade Reservoir within the Environmental Flow Constraints. Sustainability, 12(10), 4064. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104064




