Urban Expansion and Growth Boundaries in an Oasis City in an Arid Region: A Case Study of Jiayuguan City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
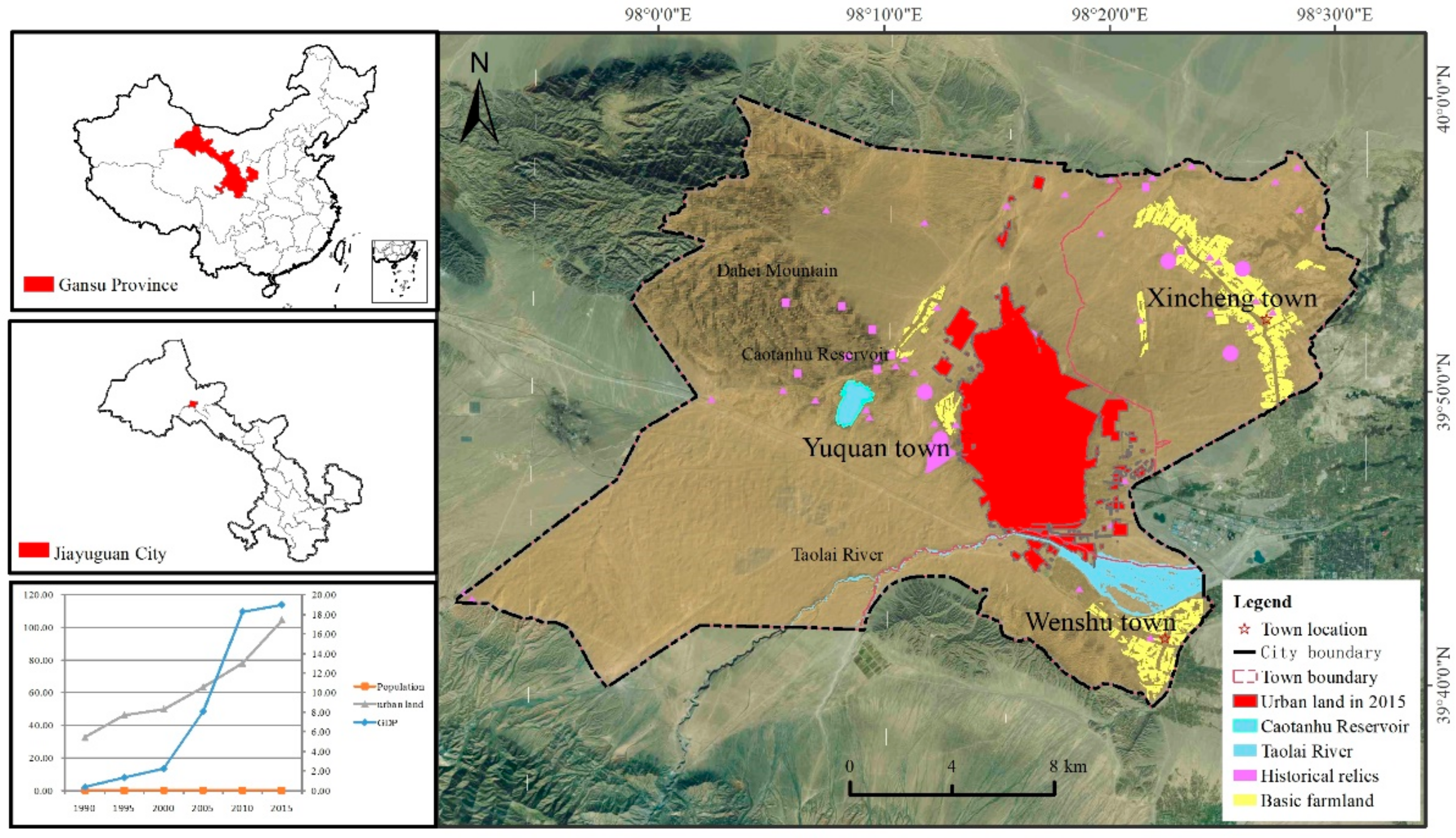
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Landsat Image Processing and Derivation of Land Use Map
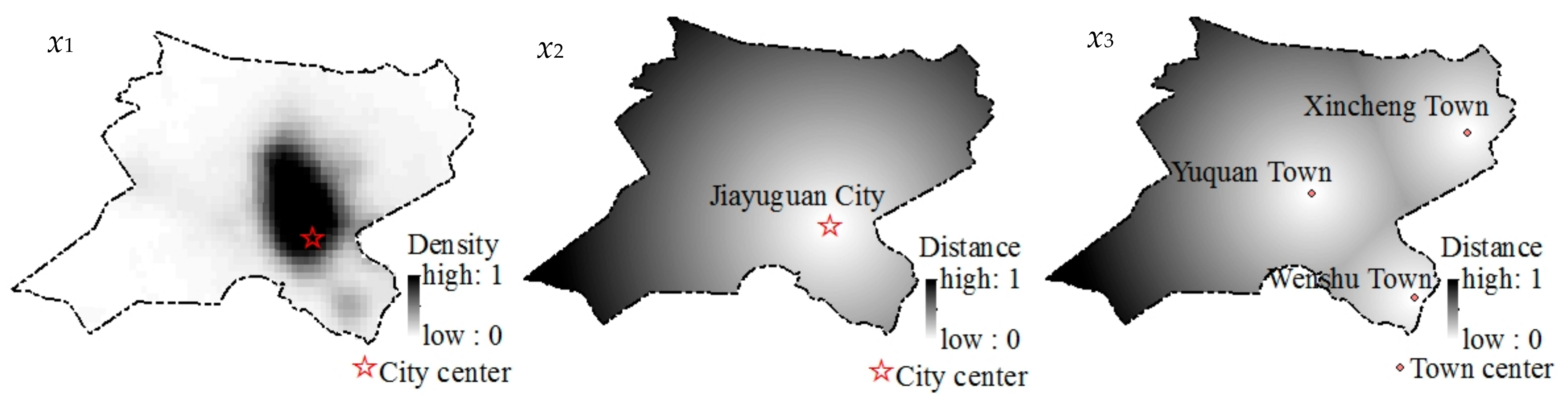
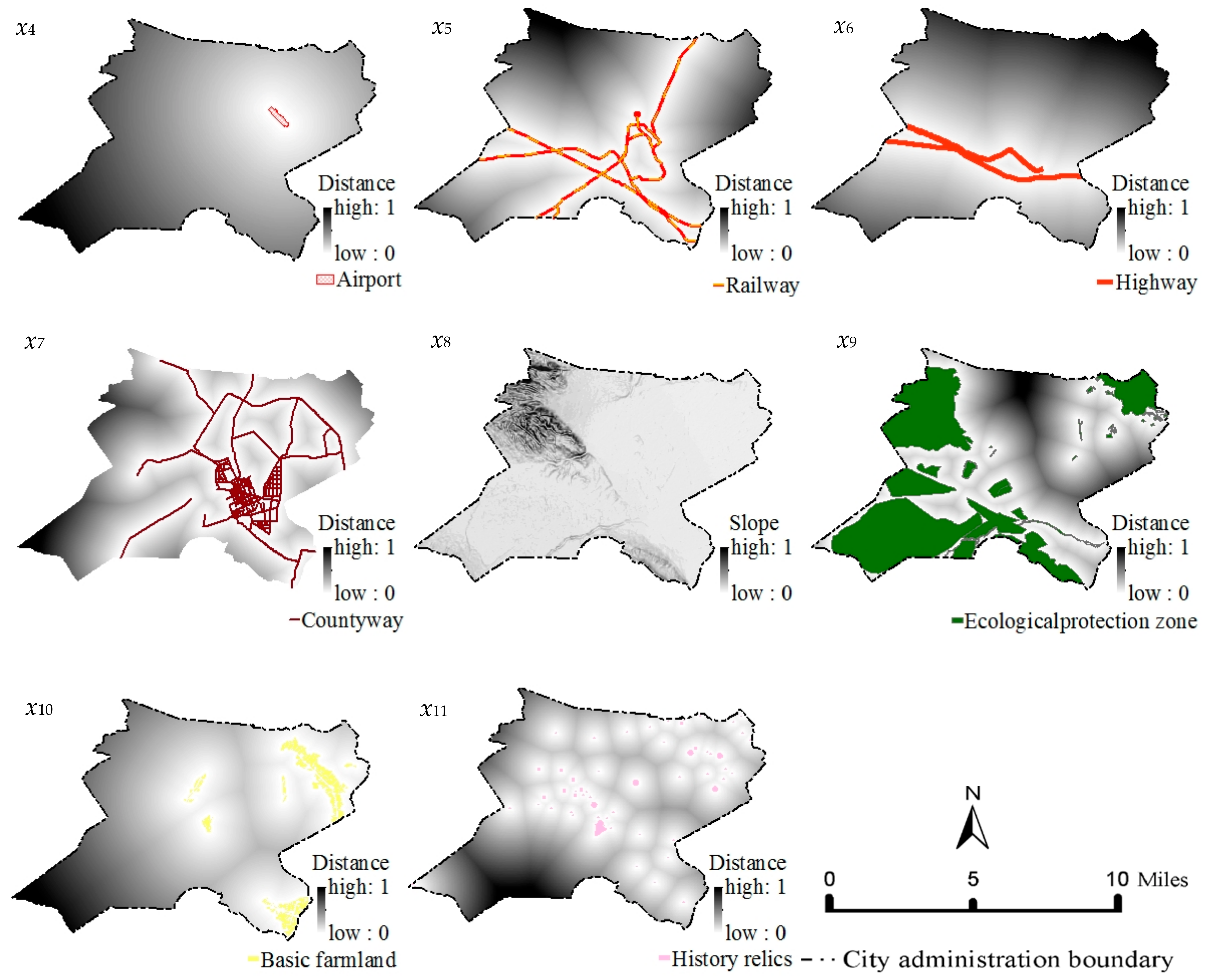
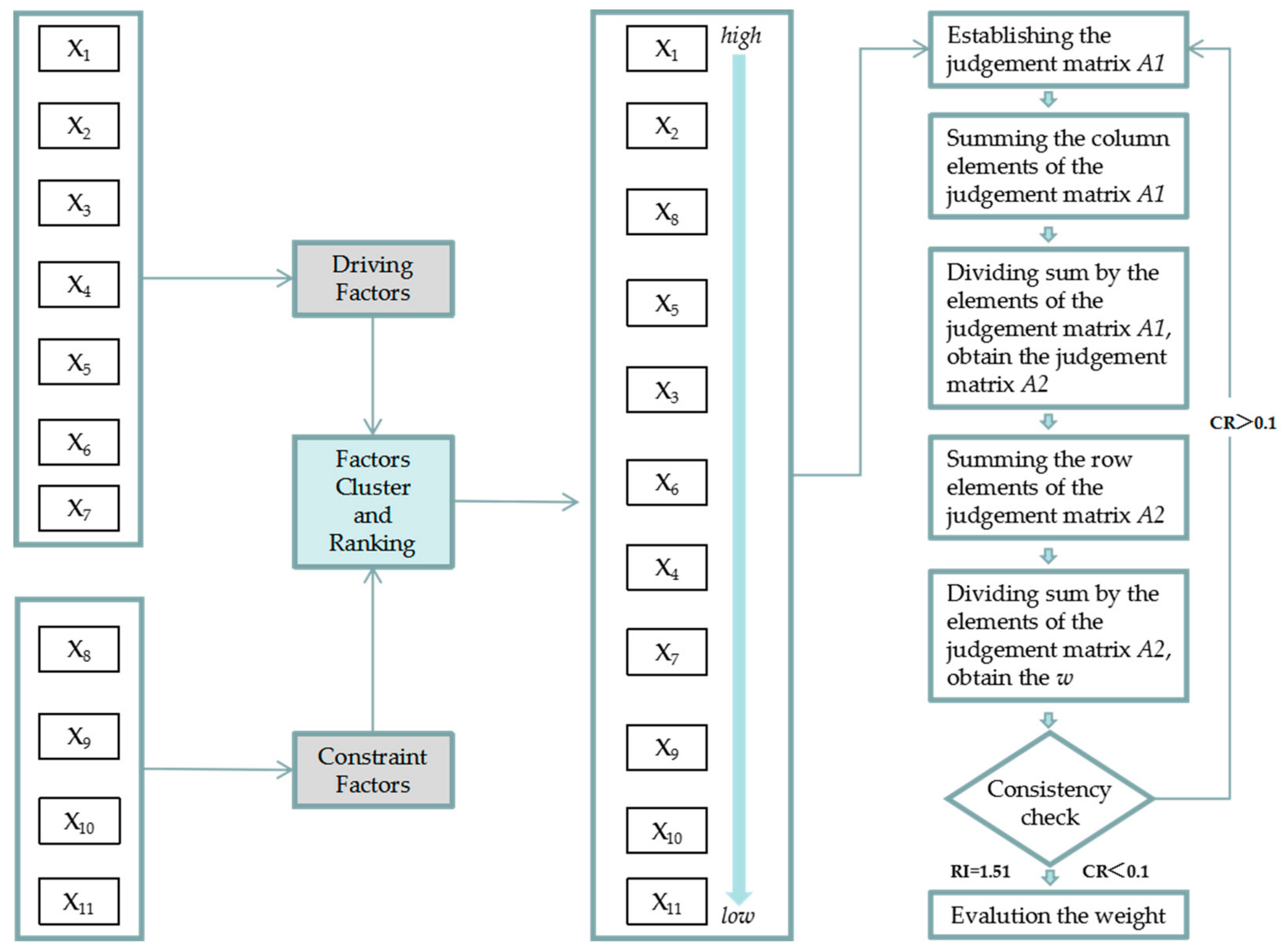
2.2.2. Spatial Variables Selection and Expression
3. Methodology
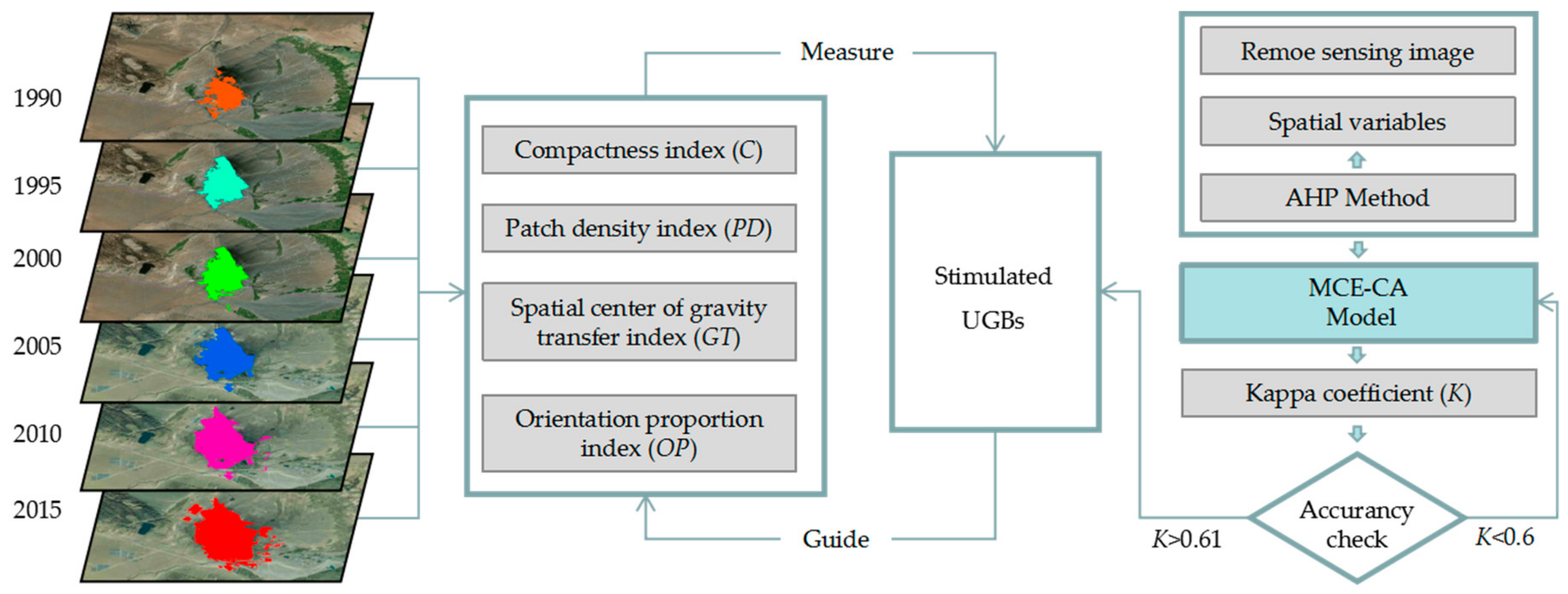
3.1. Morphological Index of Urban Spatial Expansion
- (1)
- The Compactness Index (C)
- (2)
- The Patch Density Index (PD)
- (3)
- The Spatial Center of Gravity Transfer Index (GT)
- (4)
- The Orientation Proportion Index (OP)
3.2. MCE-CA Model
3.3. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Method
3.4. Kappa Coefficient
4. Results
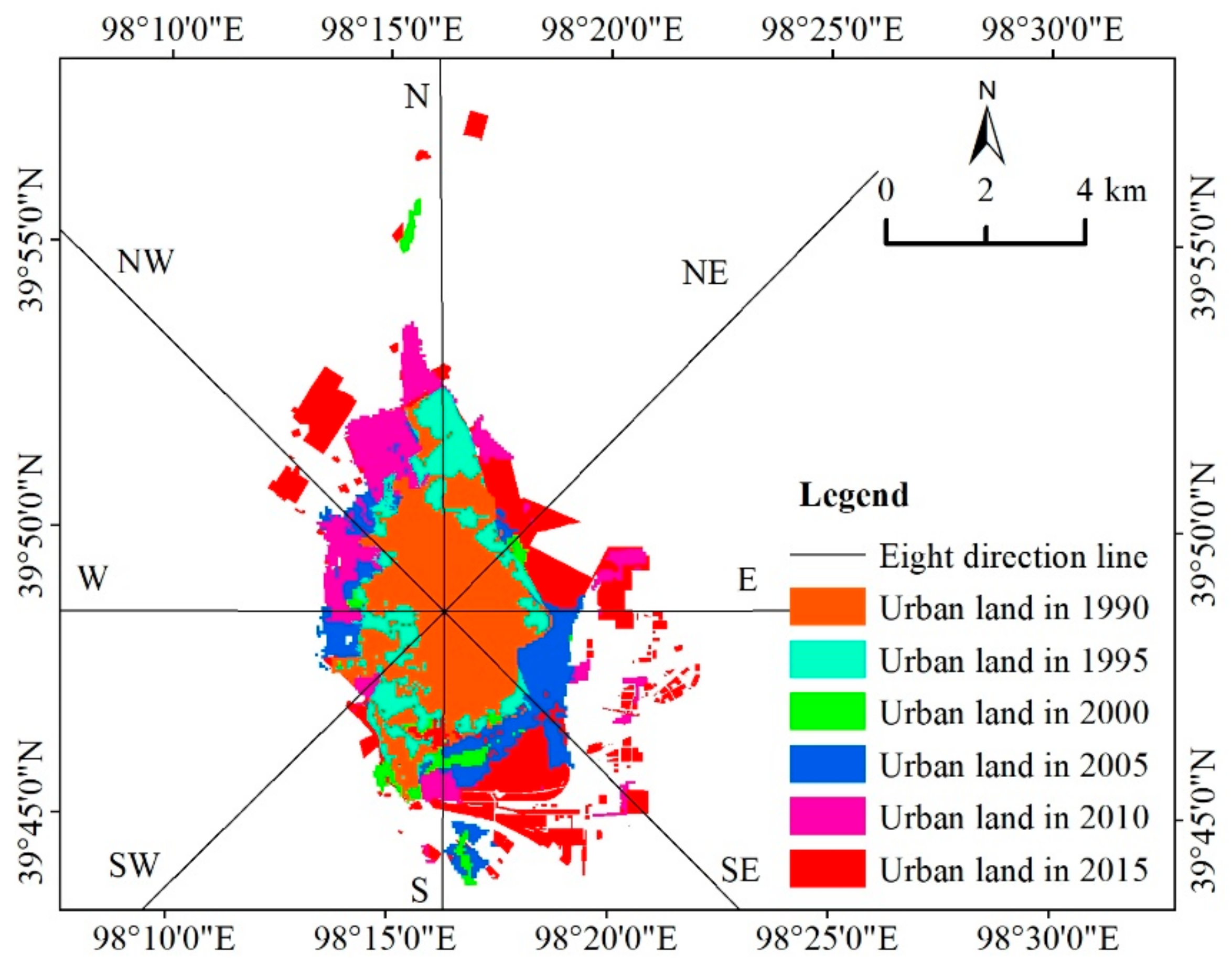
4.1. Characteristics of Urban Land Use Spatiotemporal Expansion
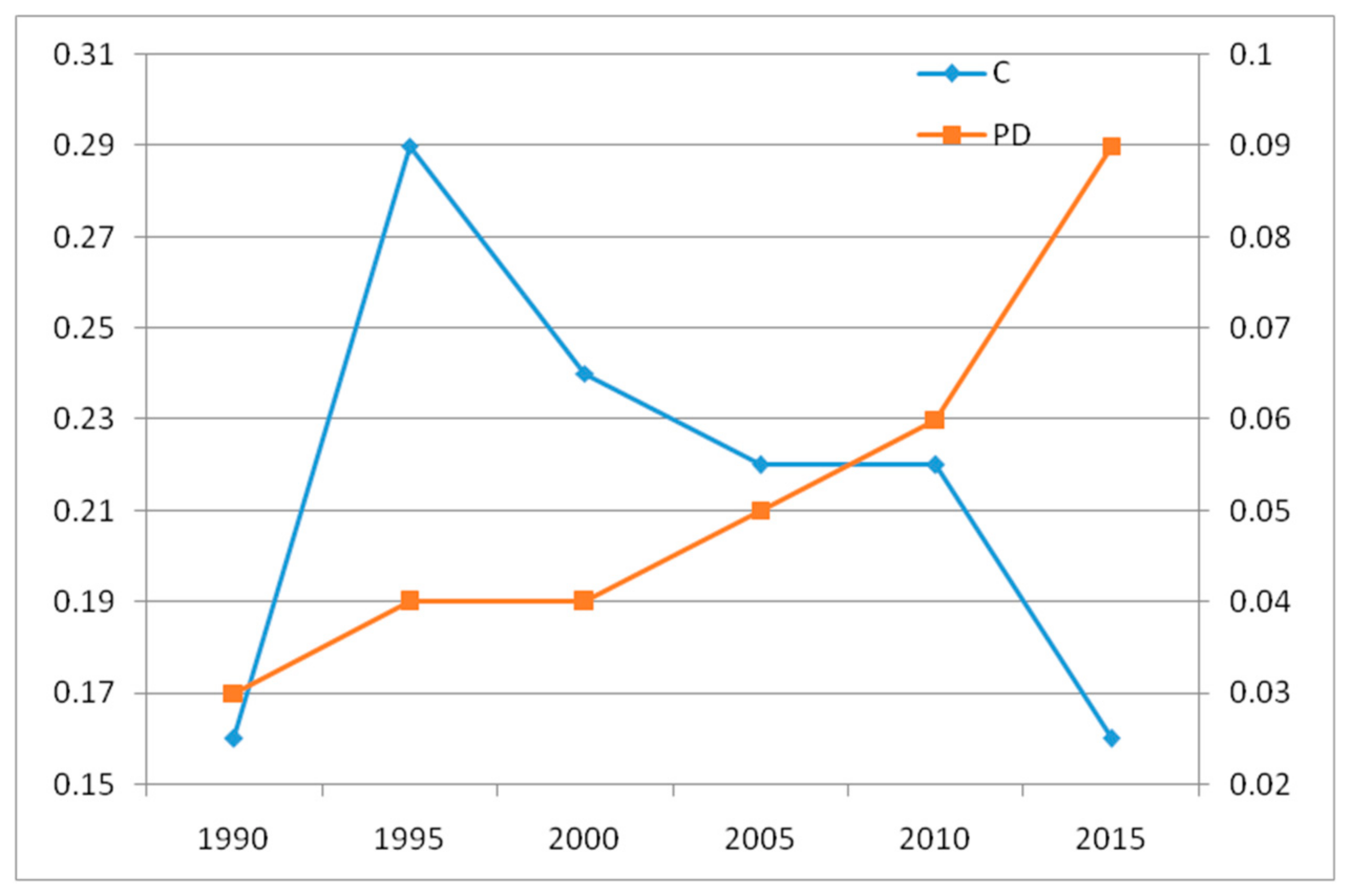
4.1.1. Characteristics of Urban Morphological Change
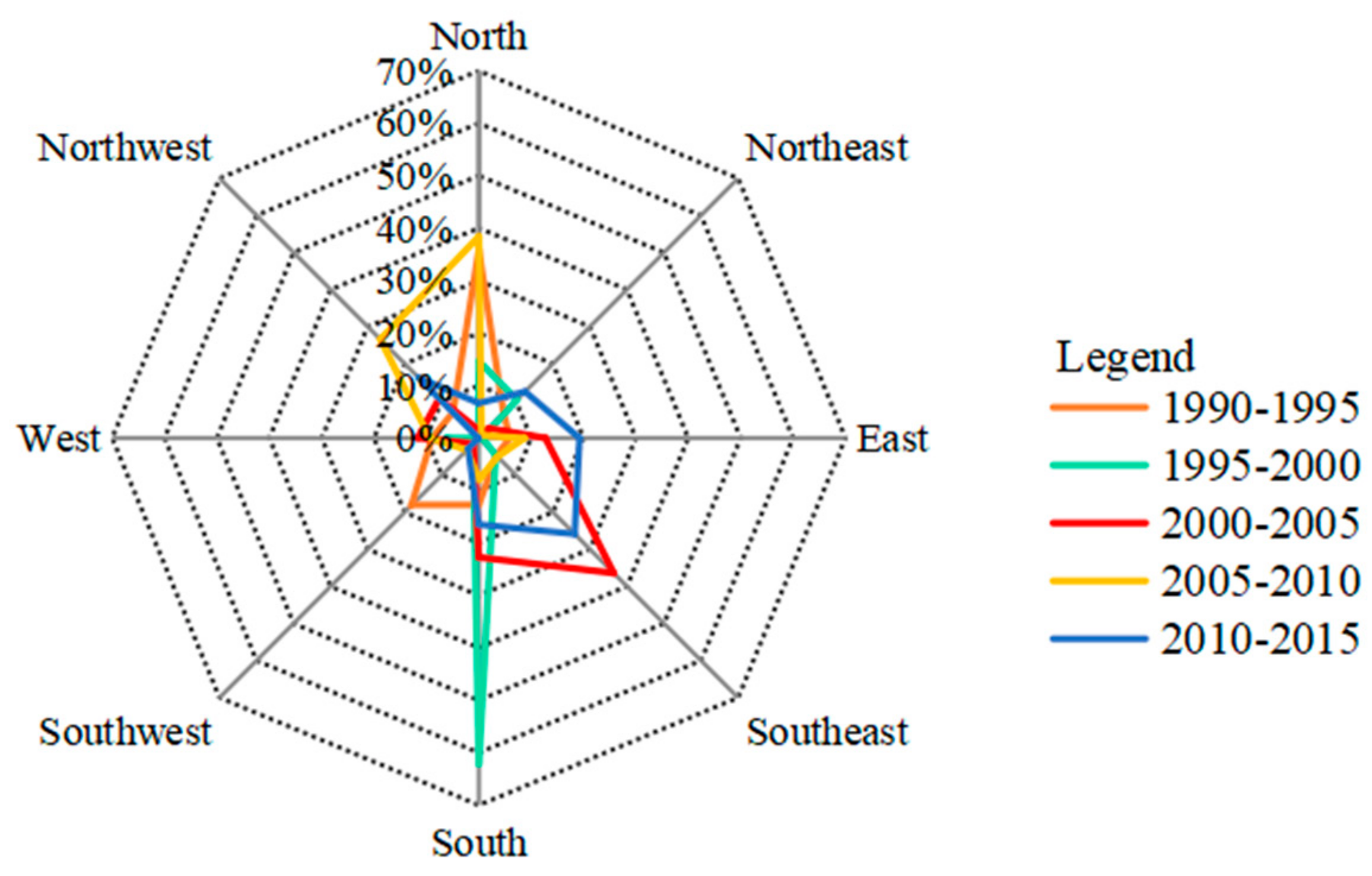
4.1.2. The Spatial Center of Gravity Transfer and Orientation Proportion Analysis
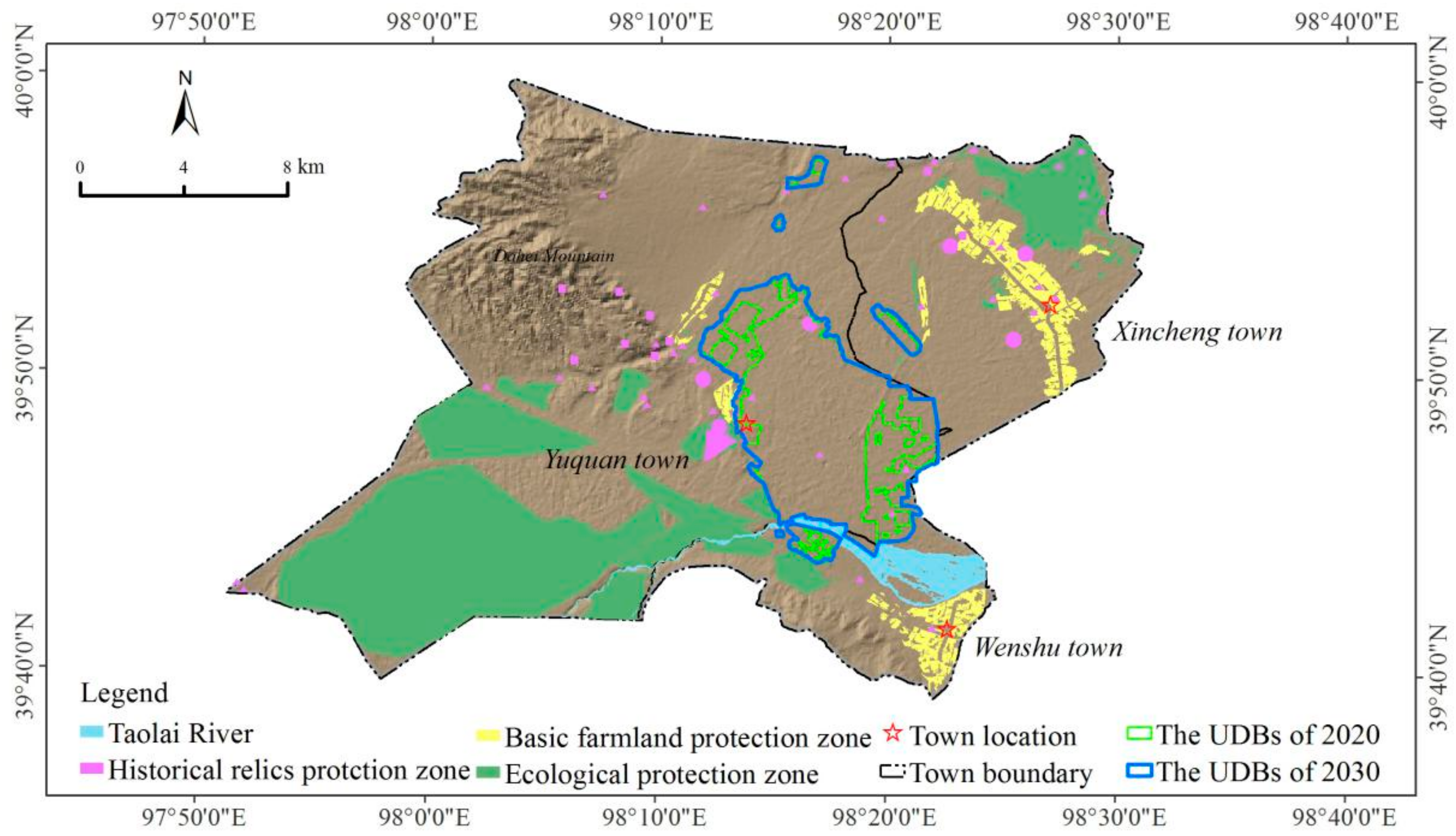
4.2. Delimiting the Urban Development Boundaries Based on the MCE-CA Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatial Characteristic of Urban Land
5.2. Technical Methods of Delimitation UGBs
5.3. Suggestions on UGBs
5.4. Research Prospects of UGBs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.X.; Liu, W.D.; Lu, D.D. Challenges and the way forward in China’s new-type urbanization. Land Use Policy 2015, 55, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, A.; David, P. Anti-sprawl policies in a system of congested cities. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2008, 38, 408–423. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.Z.; Huang, J.K.; ScottRozelle, R.; Emi, U. Growth, population and industrialization, and urban land expansion of China. J. Urban Econ. 2008, 63, 96–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, Y.H.; Li, T.T. The spatiotemporal patterns of urban–rural development transformation in China since 1990. Habitat Int. 2016, 53, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.J.; Chen, D.X.; Wu, S.H.; Mao, L.J.; Tong, G.J.; Yan, D.H. Urban sprawl decreases the value of ecosystem services and intensifies the supply scarcity of ecosystem services in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Wei, Y.D.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.L. Economic transition and urban land expansion in Provincial China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Dong, J.W.; Chi, W.F.; Zhang, C. The rapid and massive urban and industrial land expansions in China between 1990 and 2010: A CLUD based analysis of their trajectories, patterns, and drivers. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 145, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Gong, Y.H.; Lu, D.D.; Ye, C. Build a people-oriented urbanization: China’s new-type urbanization dream and Anhui model. Land Use Policy 2019, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.L.; Wang, Z.B. Quantitative diagnoses and comprehensive evaluations of the rationality of Chinese urban development patterns. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3859–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Kuang, W.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.C.; Moore, T. Assessing Urban Growth Management: The Case of Portland, Oregon, the USA’s Largest Urban Growth Boundary. Land Use Policy 1993, 10, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Chen, Z.; Yen, S.T.; Eastwood, D.B. Estimating Effects of an Urban Growth Boundary on Land Development. J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2006, 38, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Planning Association. Growing Smart Legislative Guidebook: Model Statutes for Planning and the Management of Change; American Planning: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, A.C.; Duncan, J.B. Growth Management: Principles and Practice; American Planning Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, M.J. The Effects of Portland’s Urban Growth Boundary on Urban Development Patterns and Commuting. Urban Stud. 2004, 41, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.R.; Gerrit, J.K.; Lewis, D.H. Managing urban growth with urban growth boundaries: A theoretical analysis. J. Urban Econ. 1998, 46, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, G.K. Urban growth controls: Transitional dynamics of development fees and growth boundaries. J. Urban Econ. 2004, 55, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Pijanowski, B.C.; Pekin, B. Two rule-based Urban Growth Boundary Models applied to the Tehran Metropolitan Area, Iran. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Plantinga, A.J. How well do urban growth boundaries contain development? Results for Oregon using a difference-in-difference estimator. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2013, 43, 996–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennaio, M.P.; Hersperger, A.M.; Bürgi, M. Containing urban sprawl—Evaluating effectiveness of urban growth boundaries set by the Swiss Land Use Plan. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaap, G.J.; Hopkins, L.D. The Inventory Approach to Urban Growth Boundaries. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2001, 67, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, R.A. Land use-transport interaction modelling: A review of the literature and future research directions. J. Transp. Land Use 2015, 8, 11–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kill, M.; Moeckel, R.; Thill, J.C. Land use, transport, and environment interactions: WCTR 2016 contributions and future research directions. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 77, 101335. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Mao, Q.Z.; Dang, A.R. Beijing urban development model: Urban growth analysis and simulation. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2009, 14, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.Y.; Tu, Y.C.; Shu, X.F. Evaluating the effectiveness of urban growth boundaries using human mobility and activity records. Cities 2015, 46, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Zhang, G.; Zhuang, Z.Z.; Cheng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, N. A new perspective for urban development boundary delineation based on SLEUTH-InVEST model. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, G.S.; Wang, H.M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, M.; Yi, L. Study on the Delimitation of the Urban Development Boundary in a Special Economic Zone: A Case Study of the Central Urban Area of Doumen in Zhuhai, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.F.; Li, X.; Cai, Y. Delimiting the urban growth boundaries with a modified ant colony optimization model. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 62, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Han, H.Y.; Lai, S.K.; Mao, Q.Z. Urban growth boundaries of the Beijing Metropolitan Area: Comparison of simulation and artwork. Cities 2012, 31, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.G.; Lu, S.Y.; Tian, T. Some preliminary exploration of UGB establishment management system. Planners 2009, 8, 11–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Liu, X.P.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, H.; Yao, Y. Delineating multiscenario urban growth boundaries with a CA based FLUS model and morphological method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 177, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Hu, Y.M.; Long, X.Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Analysis of the Effectiveness of Urban Land-Use-Change Models Based on the Measurement of spatiotemporal, Dynamic Urban Growth: A Cellular Automata Case Study. Sustainability 2017, 5, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Li, X.; Li, X.P.; Liu, X.; Ai, B.; Li, S. Capturing the varying effects of driving forces over time for the simulation of urban growth by using survival analysis and cellular automata. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 152, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.J.; Li, H.L.; Li, D.H. The negative approach and ecological infrastructure: The smart preservation of natural system in the process of urbanization. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 937–958. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.J.; Li, D.H.; Li, N.Y. The evolution of greenways in China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 14, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Planning an ecological network of Xiamen Island (China) using landscape metrics and network analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 78, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Ai, B.; Li, S.; He, Z. Simulating urban growth by integrating landscape expansion index (LEI) and cellular automata. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 1, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Cheng, Q.; Gong, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, D. Using Urban Development Boundaries to Constrain Uncontrolled Urban Sprawl in China. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2016, 106, 1321–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Shi, P.J.; Tong, H.L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, X. Characteristics and driving forces of spatial expansion of oasis cities and towns in Hexi Corridor, Gansu Province, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 2, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Dong, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Sterr, T. Interactions between water-land resources and oasis urban development at the northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2012, 2, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Jin, N.; Du, H.R.; Ma, W.W. Spatial difference features and organization optimization of cities and towns in Tarim River Basin. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Song, W.; Deng, X.Z. Understanding the spatiotemporal variation of urban land expansion in oasis cities by integrating remote sensing and multi-dimensional DPSIR-based indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiayuguan City Bureau of Statistic of China (JCBSC). Jiayuguan City Statistical Yearbook; Jiayuguan City Bureau of Statistic of China (JCBSC): Jiayuguan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bumairiyemu, M.; Ding, J.L.; Bibula, S.; Alimujiang, K. Characterizing urban expansion of Korla City and its spatial-temporal patterns using remote sensing and GIS methods. J. Arid Land 2017, 3, 458–470. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.Z.; Liu, Y.S.; Xia, B.C.; Zhao, G.W. Urban ecological security assessment and forecasting, based on a cellular automata model: A case study of Guangzhou, China. Ecol. Model. 2017, 24, 3612–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Zang, S.Y.; Wu, C.S.; Liu, W.; Na, X. Analyzing and modeling land use land cover change (LUCC) in the Daqing City, China. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 2, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Wang, X.S.; Zhuang, D.F. Application of convex hull in identifying the types of urban land expansion. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 6, 885–892. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.B.; Luo, K.; Song, J.; Xu, J. Characteristics of change and strategic considerations of the structure of urban functional divisions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt since 2000. Prog. Geogr. 2015, 11, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, G.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Xie, Y.C.; Yang, Z.; Zhuang, D.; Niu, Z. Analysis of spatiotemporal dynamic pattern and driving forces of urban land in China in 1990s using TM images and GIS. Cities 2005, 6, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.M.; Mao, L.F.; Liu, Y.L. Multiorder landscape expansion index: Characterizing urban expansion dynamics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 37, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns of urban land-use change in four cities of china with time series landscape metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 7, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. Compact city, urban sprawl, and subjective well-being. Cities 2019, 92, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Exploring urban green spaces in China: Spatial patterns, driving factors and policy implications. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, F. Vector analysis theory on landscape pattern in Sanjiang plain marsh, China. Wetl. Sci. 2004, 9, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, C.D.; Nancy, L.G.; Gorge, E.P.; Paula, R.; Wilson, A.V. Spatiotemporal dynamics of urban growth in Latin American cities: An analysis using nighttime light imagery. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103640. [Google Scholar]
- WU, F.; Webster, C.J. Simulation of land development through the integration of cellular automata and multicriteria evaluation. Environ. Plan. B 1998, 25, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, Q.G.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, F.H. Simulation and prediction of land use change in Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on MCE-CA-Markov. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 268–277. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; He, J. Concepts, methodologies, and tools of an integrated geographical simulation and optimization system. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 633–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lao, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y. Coupling urban cellular automata with ant colony optimization for zoning protected natural areas under a changing landscape. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2011, 25, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, D.; Liu, X.P. Geographical simulation and optimization system (GeoSOS) and its cuttingedge researches. Adv. Earth Sci. 2009, 8, 899–907. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector necessary. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 145, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Y. Rehabilitation in Beijing. Habitat Int. 1991, 15, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Communist Party of China Central Committee and the State Council. National New Urbanization Planning of China (2014–2020). 2014. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2014/content_2644805.htm (accessed on 16 March 2014).
- Jiayuguan City Bureau of Planing of China. Land Use Master Plan of Jiayuguan City (2006–2020); Jiayuguan City Bureau of Planing of China: Jiayuguan, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jiayuguan City Bureau of Planing of China. Master Plan of Jiayuguan City (2018–2030); Jiayuguan City Bureau of Planing of China: Jiayuguan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Jiayuguan City. The 13th Five Year National Social-Economic Plan of Jiayuguan City (2016–2020); Government of Jiayuguan City: Jiayuguan, China, 2016.
- Dietzel, C.; Clarke, K.C. Toward optimal calibration of the SLEUTH land use change model. Trans. GIS 2007, 1, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, A.; Pijanowski, B.; Tayyebi, A.H. An urban growth boundary model using neural networks, GIS and radial parameterization: An application to Tehran, Iran. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 100, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Deng, Y. A solution to the conflicts of multiple planning boundaries: Landscape functional zoning in a resource-based city in China. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekade, W. Defificits of formal urban land management and informal responses under rapid urban growth, an international perspective. Habitat Int. 2000, 24, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Tochen, R.; Wang, C. Exploration of the streamlined urban growth boundary method in Oregon and its potential application to China. Urban Dev. Study 2017, 33, 88–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, Q.K.; Dan, X.W.; Wang, S.H. Comparison on Multi-Scale Urban Expansion Derived from Nightlight Imagery between China and India. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type | Variable | Description | Value | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driving factors | x1 | Population density | 0–1 | Night-time light data from the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (https://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/ngdc.html) |
| x2 | Distance from the city center | 0–1 | City center data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x3 | Distance from the town center | 0–1 | Town center data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x4 | Distance from the airport | 0–1 | Airport data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x5 | Distance from the railway | 0–1 | Railway data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x6 | Distance from the highway | 0–1 | Highway data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x7 | Distance from the county road | 0–1 | County road data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| Constraint factors | x8 | Slope | 0–1 | Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data from Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn) |
| x9 | Ecological protection zone | 0–1 | Ecological protection zone data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x10 | Basic farmland protection zone | 0–1 | Basic farmland protection zone data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning | |
| x11 | Historical relics protection zone | 0–1 | Historical relics protection zone data from Gansu Academy of Natural Resources Planning |
| N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| RI | 0 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 1.24 | 1.32 | 1.41 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.51 |
| Year | Area/km2 | C | PD | X | Y | D/m | OP | β/Degree Minute Second |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 32.51 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 98°16′16″ | 39°48′34″ | |||
| 1995 | 46.47 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 98°16′16″ | 39°48′45″ | 348.92 | N | 103°41′31″ |
| 2000 | 49.90 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 98°16′16″ | 39°48′40″ | 138.91 | S | 92°16′50″ |
| 2005 | 63.41 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 98°16′23″ | 39°48′24″ | 559.79 | SE | 63°30′1″ |
| 2010 | 77.94 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 98°16′23″ | 39°48′42″ | 580.96 | N | 106°32′29″ |
| 2015 | 104.58 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 98°16′35″ | 39°48′36″ | 501.53 | SE | 23°10′35″ |
| xn | x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | x6 | x7 | x8 | x9 | x10 | x11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wn | 0.163 | 0.126 | 0.096 | 0.083 | 0.105 | 0.088 | 0.073 | 0.112 | 0.065 | 0.051 | 0.038 |
| Year | Area/km2 | C | PD | X | Y | D/m | OP | β/Degree Minute Second |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 104.58 | 0.16 | 0.09 | 98°16′35″ | 39°48′36″ | |||
| 2020 | 110.73 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 98°16′42″ | 39°48′33″ | 359.66 | SE | 70°47′32″ |
| 2030 | 152.63 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 98°17′36″ | 39°47′35″ | 470.28 | SE | 35°44′26″ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Mao, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, R. Urban Expansion and Growth Boundaries in an Oasis City in an Arid Region: A Case Study of Jiayuguan City, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010210
Ren J, Zhou W, Liu X, Zhou L, Guo J, Wang Y, Guan Y, Mao J, Huang Y, Ma R. Urban Expansion and Growth Boundaries in an Oasis City in an Arid Region: A Case Study of Jiayuguan City, China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(1):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010210
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jun, Wei Zhou, Xuelu Liu, Liang Zhou, Jing Guo, Yonghao Wang, Yanjun Guan, Jingtian Mao, Yuhan Huang, and Rongrong Ma. 2020. "Urban Expansion and Growth Boundaries in an Oasis City in an Arid Region: A Case Study of Jiayuguan City, China" Sustainability 12, no. 1: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010210
APA StyleRen, J., Zhou, W., Liu, X., Zhou, L., Guo, J., Wang, Y., Guan, Y., Mao, J., Huang, Y., & Ma, R. (2020). Urban Expansion and Growth Boundaries in an Oasis City in an Arid Region: A Case Study of Jiayuguan City, China. Sustainability, 12(1), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010210





