Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Biomass Growth and Species Diversity among Various Grassland Types of the Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Experiment Design
2.2. Data Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
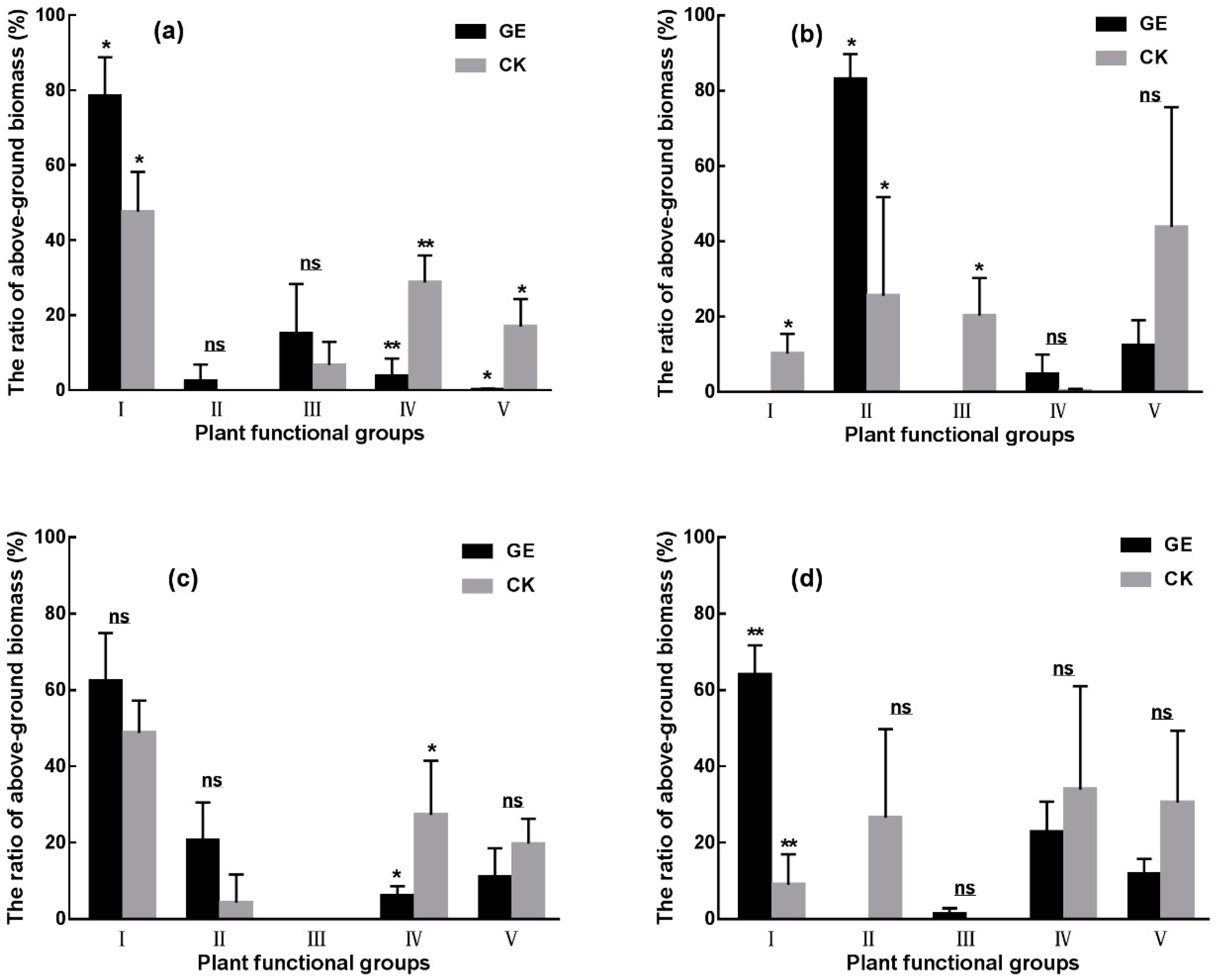
3.1. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Vegetation Ecological Characteristics
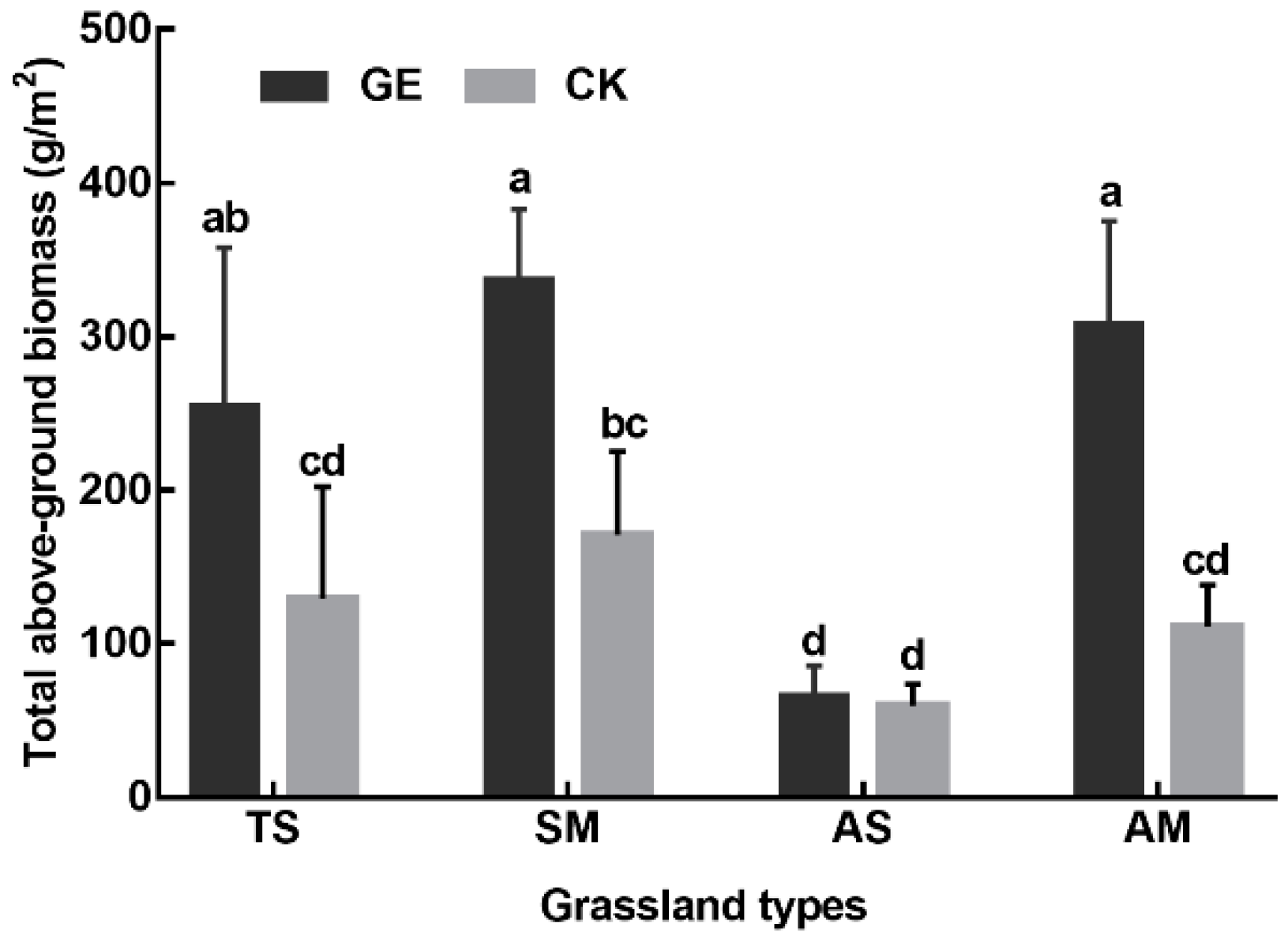
3.2. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Vegetation Biomass
3.3. Comparison of Grazing Exclusion Effects in the Different Grassland Types
4. Discussion
4.1. The Responses of Vegetation Characteristics and Species Diversity to Grazing Exclusion
4.2. The Responses of Biomass Growth to Grazing Exclusion
4.3. Implications for Sustainable Grassland Management Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Temperate Steppe Site | Swamp Meadow Site | Alpine Steppe Site | Alpine Meadow Site | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | 35°39′ N, 100°21′ E | 33°12′ N, 96°37′ E | 35°06′ N, 97°58′ E | 32°50′ N, 96°57′ E |
| Annual precipitation/mm | 380.92 | 556.41 | 544.01 | 535.50 |
| Annual mean temperature/°C | 2.27 | −0.16 | 1.91 | −0.28 |
| Climate type | Plateau continental climate | Plateau continental climate | Plateau continental climate | Plateau continental climate |
| Annual evaporation/mm | 1378.5 | 1110 | 1215 | 1110 |
| Soil type | Castanozems | Frigid calcic soils | Bog soils | Felty soils |
| Annual sunshine hour/h | 2664.9 | 2578.4 | 2600 | 2578.4 |
References
- Klein, J.A.; Harte, J.; Zhao, X.Q. Experimental warming, not grazing, decreases rangeland quality on the Tibetan plateau. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, E.; Pedersen, C. Opposing plant community responses to warming with and without herbivores. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12353–12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavlu, V.; Hejcman, M.; Pavlu, L.; Gaisler, J. Restoration of grazing management and its effects on vegetation in an upland grassland. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2007, 10, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isselstein, J.; Griffith, B.A.; Pradel, P.; Venerus, S. Effects of livestock breed and grazing intensity on biodiversity and production in grazing systems, 1: Nutritive value of herbage and livestock performance. Grass Forage Sci. 2007, 62, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proulx, M.; Mazumder, A. Reversal of grazing impact on plant species richness in nutrient-poor vs. nutrient-rich ecosystems. Ecology 1998, 79, 2581–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Q.; Chai, L.R.; Hou, F.J.; Chang, S.H.; Ma, Y.S.; Tsunekawa, A.; Cheng, Y.X. Quantifying grazing intensity using remote sensing in Alpine meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, M.T.; Venhaus, H.C.; Windhager, S. Exploiting the attributes of regional ecosystems for landscape design: The role of ecological restoration in ecological engineering. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Ru, W.M.; Li, B. Relationships between vegetation and climate on the Loess Plateau in China. Folia Geobot. 2006, 41, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.M.; Li, S.G.; Guo, Q.; Niu, S.L.; Li, N.H.; He, N.P. A synthesis of the effect of grazing exclusion on carbon dynamics in grasslands in China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Okayasu, T.; Jamsran, U.; Takeuchi, K. Threshold changes in vegetation along a grazing gradient in Mongolian rangelands. J. Ecol. 2008, 96, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.A.; Kuns, M.M.; Guido, D.R. Consumer control of grassland plant production. Ecology 2002, 83, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Fan, J.W.; Yu, H.L. The effects of different restoration practices on temperate grassland ecosystems in the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Control Project. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2018, 27, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.T.; Dong, Y.R. Factors affecting species diversity of plant communities and the restoration process in the loess area of China. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.P.; Han, X.G.; Yu, G.R.; Chen, Q.S. Divergent changes in plant community composition under 3-decade grazing exclusion in continental steppe. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, W.; Liu, W. Comparing the effect of naturally restored forest and grassland on carbon sequestration and its vertical distribution in the Chinese Loess Plateau. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.W.; Zhong, H.P.; Harris, W.; Yu, G.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Hu, Z.M.; Yue, Y.Z. Carbon storage in the grasslands of China based on field measurements of above—And below-ground biomass. Clim. Chang. 2008, 86, 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F.; Riahi, M. The influence of grazing exclosure on soil c stocks and dynamics, and ecological indicators in upland arid and semi-arid rangelands. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and cause. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q. Alpine Meadow Ecosystem and Global Change; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H.K.; Xu, S.X.; Dong, Q.M.; Wu, G.L.; He, Y.X. Using balance of seasonal herbage supply and demand to inform sustainable grassland management on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2018, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.P.; Shi, P.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zou, C.B. Effects of grazing exclusion on carbon sequestration and plant diversity in grasslands of China—A meta-analysis. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.Z.; Li, Y.L.; Cui, H.Y.; Zhao, W.Z. Influences of continuous grazing and livestock exclusion on soil properties in a degraded sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, norther China. Catena 2005, 59, 267–278. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, G.H.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. Vegetation traits and soil properties in response to utilization patterns of grassland in Hulun Buir City, Inner Mongolia, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engemann, K.; Sandel, B.; Boyle, B.; Enquist, B.J.; Jorgensen, P.M.; Kattge, J.; Mcgill, B.J.; Morueta-Holme, N.; Peet, R.K.; Spencer, N.J.; et al. A plant growth form dataset for the New World. Ecology 2016, 97, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, W.Y.; Ren, H.Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cobb, A.B.; Wilson, G.W.T.; Sun, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G.W. Plant functional group influences arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal abundance and hyphal contribution to soil CO2 efflux in temperate grasslands. Plant Soil 2018, 432, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, J.; Dwyer, J.M.; Andrey, A.; Arlettaz, R. Impacts of nitrogen addition on plant biodiversity in mountain grasslands depend on dose, application duration and climate: A systematic review. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, H.; Keller, M.; Porret, N.; Dietz, H.; Edwards, P.J. The effect of slug grazing on vegetation development and plant species diversity in an experimental grassland. Funct. Ecol. 2005, 19, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, Z.B.; Cheng, J.M.; Chen, A. Assessment of vegetative ecological characteristics and the succession process during three decades of grazing exclusion in a continental steppe grassland. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 7, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, E.C. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1996, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.Z.; Dong, S.K.; Liu, S.L.; Wang, X.X.; Su, X.K.; Li, Y.Y.; Tang, L.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhao, H.D. Effects of grazing and climate warming on plant diversity, productivity and living state in the alpine rangelands and cultivated grasslands of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Rangel. J. 2014, 37, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, W.X.; Wang, J.L.; Li, X.L.; Xu, C.L.; Shi, S.L. Effects of grazing regime on vegetation structure, productivity, soil quality, carbon and nitrogen storage of alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmartin, M.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Chaneton, E.J. Grazing history effects on above- and below-ground litter decomposition and nutrient cycling in two co-occurring grasses. Plant Soil 2008, 303, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo, J.; Steudler, P.A.; Abler, J.D.; Newkirk, K.; Lux, H.; Bowles, F.P.; Catricala, C.; Magill, A.; Ahrens, T.; Morrisseau, S. Soil warming and carbon-cycle feedbacks to the climate system. Science 2002, 298, 2173–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, C.P.H. Vertebrate herbivores and plants in the Arctic and Subarctic: Effects on individuals, populations, communities and ecosystems. Perspect. Plant Ecol. 1999, 2, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, J.P. Plant Strategies and Vegetation Processes; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Z.H.; Ma, Y.S.; Long, R.J.; Ding, L.M. Effect of fencing, artificial seeding and abandonment on vegetation composition and dynamics of “black soil land” in the headwaters of the Yangtze and the Yellow Rivers of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2008, 19, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.; Kaufmann, R.; Vorhauser, K.; Erschbamer, B. Effects of grazing exclusion on species composition in high-altitude grasslands of the Central Alps. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2009, 10, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautier, Y.; Niklaus, P.A.; Hector, A. Competition for light causes plant biodiversity loss after eutrophication. Science 2009, 324, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Zeng, X.Y.; Schumann, M.; Chen, H. Effectiveness of exclosures on restoration of degraded alpine meadow in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2011, 25, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Santors, B.; Putwain, P.D.; Fernandez-Gomez, M.J. Natural and man-induced revegetation on mining wastes: Changes in the floristic composition during early succession. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 30, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.J. Study on the timely adjustment of the grazing prohibition policy: Ban or lift? Empirical research from local government managers. Sustainability 2019, 10, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.A.; Harte, J.; Zhao, X.Q. Experimental warming causes large and rapid species loss, dampened by simulated grazing, on the Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Yu, J.B.; Zhou, D.; Dong, H.F.; Li, Y.Z.; Lin, Q.X.; Guan, B.; Wang, Y.L. Vegetative ecological characteristics of restored reed (Phragmites australis) wetlands in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Manag. 2012, 49, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.P.; Wei, X.R.; Zhang, X.C.; Cheng, J.M. Ecosystem carbon and nitrogen accumulation after grazing exclusion in semiarid grassland. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.Q.; Cao, W.; Fan, J.W.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.L. Effects of an ecological conservation and restoration project in the Three-River Source Region, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.W.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, J.B.; Harris, W.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhong, H.P.; Xu, X.L.; Liu, R.G. Assessment of effects of climate change and grazing activity on grassland yield in the Three Rivers Headwaters Region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 170, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Grassland Type | Treatment | Cover (%) | Height (cm) | Species Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperate steppe | GE | 91.7 ± 6.2ab | 35.0 ± 0.8a | Elymus nutans *, Poa annua L., Trisetum clarkei, Artemisia scoparia |
| CK | 86.7 ± 19.3ab | 10.7 ± 0.9bc | Leymus secalinus *, Pedicularis kansuensis, Artemisia sieversiana, Poa annua L. | |
| Swamp meadow | GE | 100.0 ± 0.0ac | 21.7 ± 2.4ab | Kobresia tibetica Maxim. *, Kobresia humilis, Potentilla anserina L., Pedicularis longiflora var. tubiformis |
| CK | 86.7 ± 11.8ac | 3.8 ± 0.9c | Kobresia parva*, Stipa regeliana, Astragalus membranaceus, Carex parva | |
| Alpine steppe | GE | 66.7 ± 4.7bc | 20.3 ± 0.5b | Stipa purpurea *, Kobresia tibetica Maxim., Carex atrata, Leontopodium nanum, Potentilla bifurca |
| CK | 61.7 ± 6.2b | 13.0 ± 2.2bc | Stipa purpurea *, Leontopodium nanum, Artemisia frigida, Saussurea arenaria | |
| Alpine meadow | GE | 99.3 ± 0.9a | 46.0 ± 9.9abc | Stipa regeliana *, Poa annua L., Elymus nutans |
| CK | 68.3 ± 6.2ab | 5.0 ± 0.8c | Stipa regeliana *, Ligularia virgaurea, Kobresia parva, Potentilla saundersiana |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, L. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Biomass Growth and Species Diversity among Various Grassland Types of the Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061705
Wang S, Fan J, Li Y, Huang L. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Biomass Growth and Species Diversity among Various Grassland Types of the Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability. 2019; 11(6):1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061705
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Suizi, Jiangwen Fan, Yuzhe Li, and Lin Huang. 2019. "Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Biomass Growth and Species Diversity among Various Grassland Types of the Tibetan Plateau" Sustainability 11, no. 6: 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061705
APA StyleWang, S., Fan, J., Li, Y., & Huang, L. (2019). Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Biomass Growth and Species Diversity among Various Grassland Types of the Tibetan Plateau. Sustainability, 11(6), 1705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061705





