Characteristics of Atmospheric Deposition during the Period of Algal Bloom Formation in Urban Water Bodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
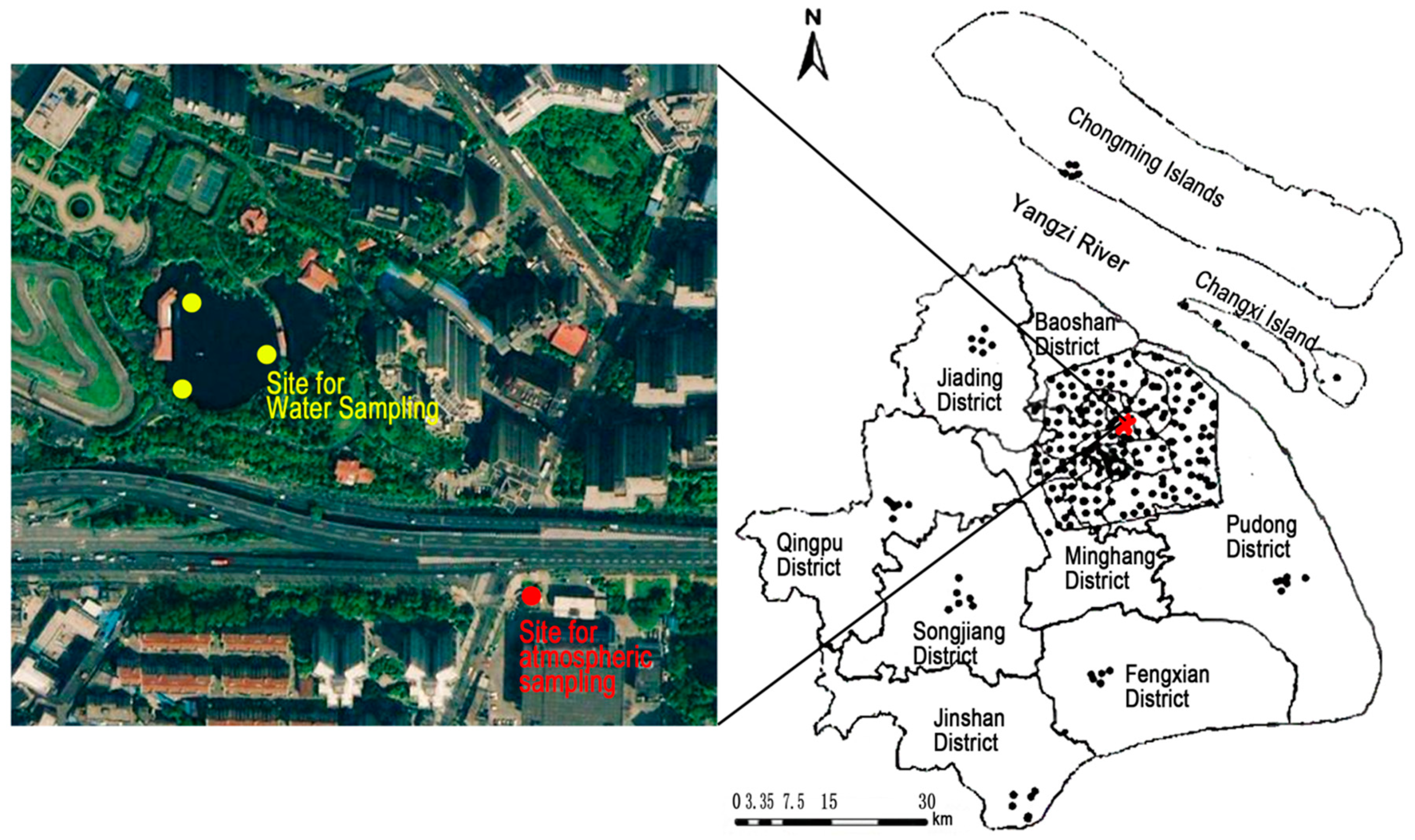
2.1. Sampling Site
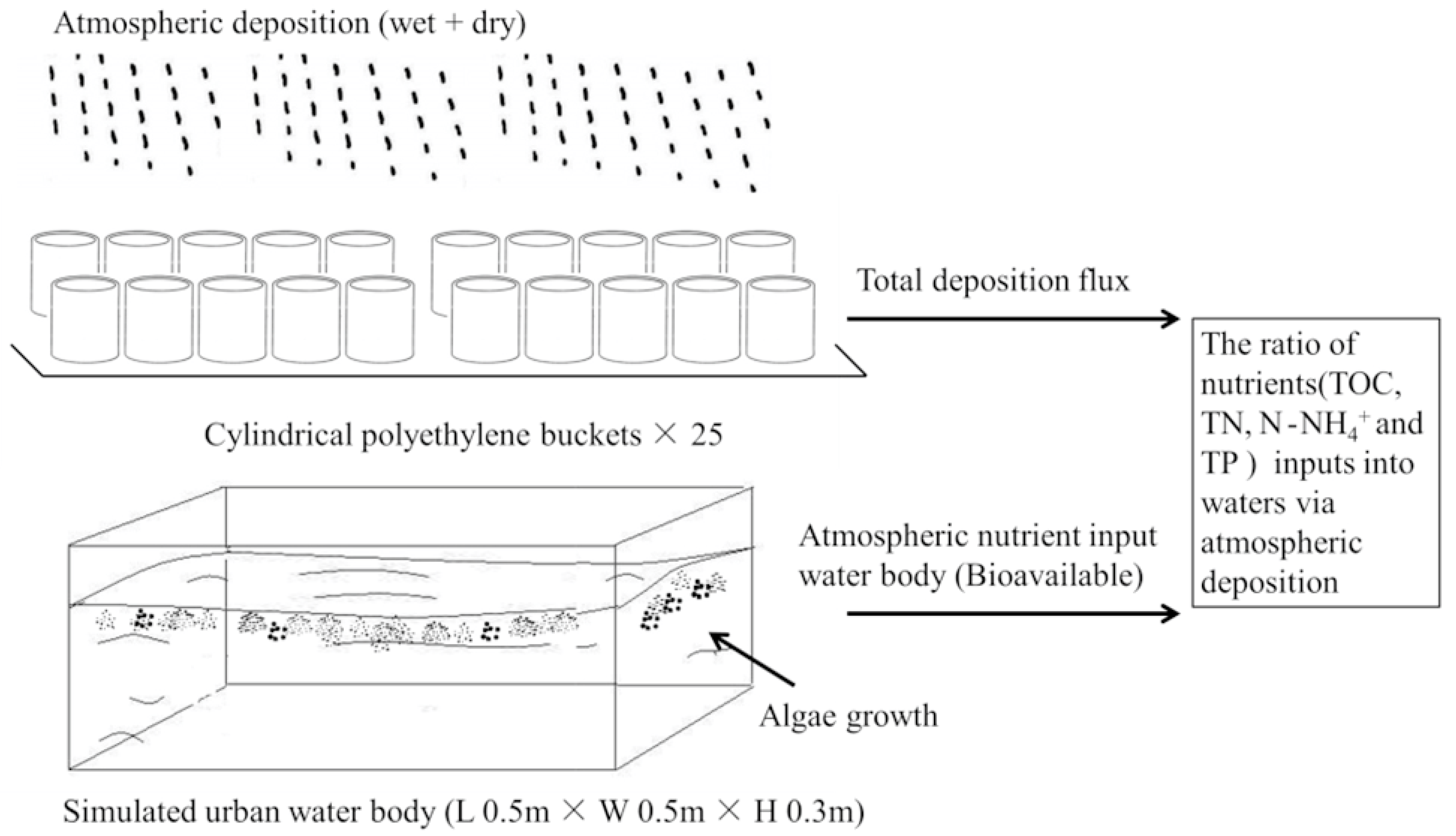
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Sample Testing Method
2.4. Calculation and Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
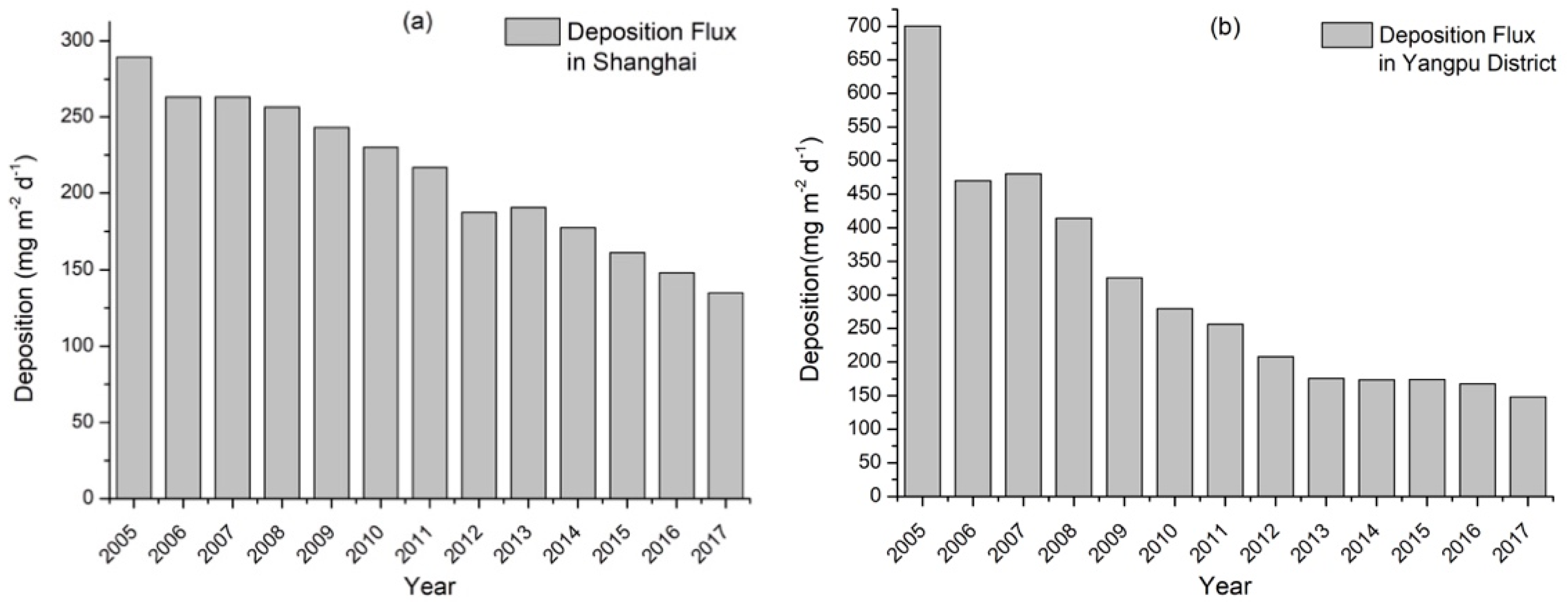
3.1. Deposition Rates of Atmospheric TOC, Nitrogen and Phosphorus
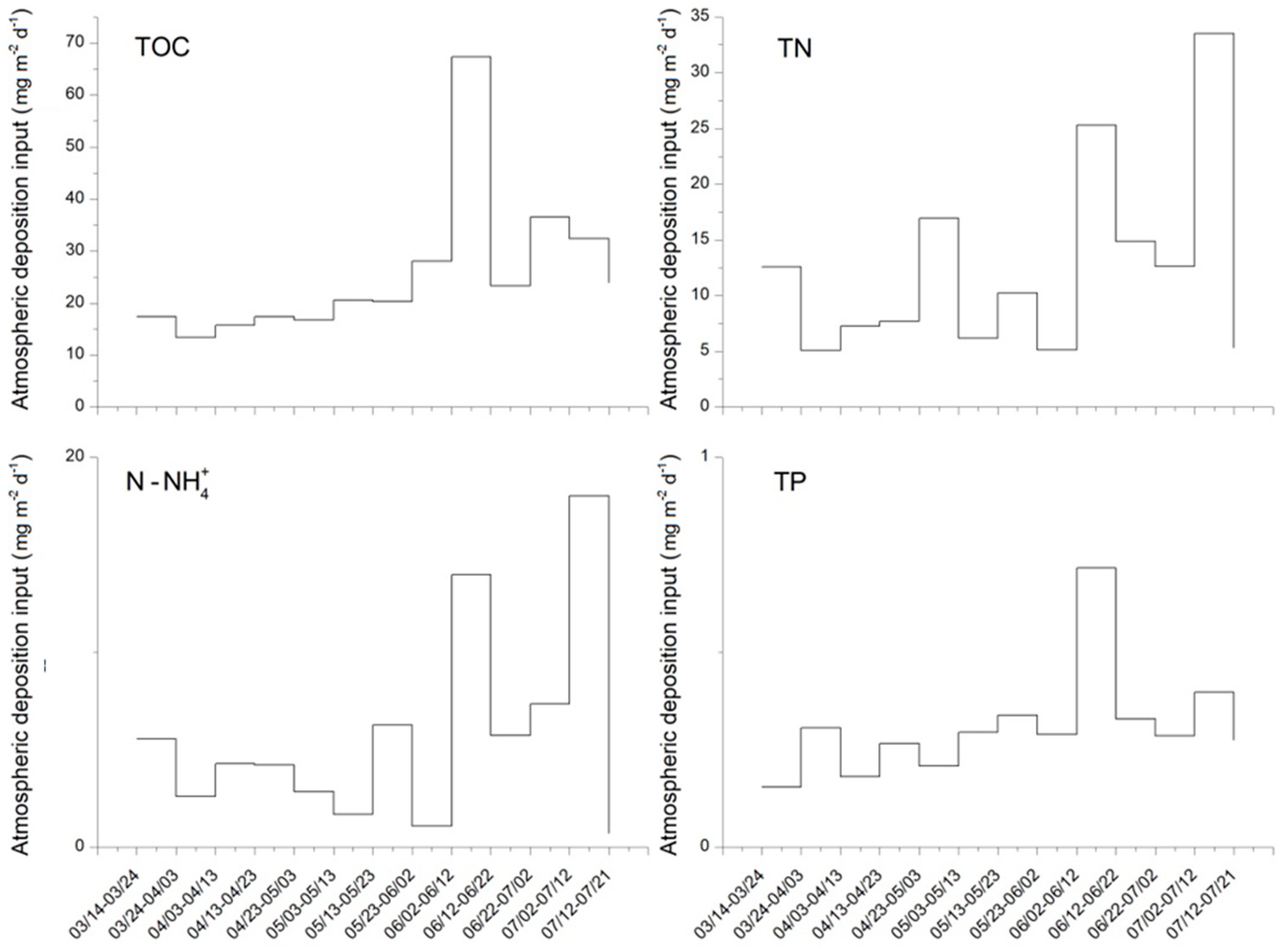
3.2. Estimation of Atmospheric Nutrient Input Loading to Shallow Urban Water Body
3.3. Potential Impacts of Nitrogen Deposition to Primary Production in the Lake
3.4. Water Quality Maintenance, HAB Early Warning and Emergency Measures in Urban Water Bodies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. The development of a multi-species algal ecodynamic model for urban surface water systems and its application. Ecol. Model. 2017, 221, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakanov, A.I. Assessment of water and sediment quality in fresh water bodies based on characteristics of benthic communities. Russ. J. Ecol. 2004, 35, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Greve, T.M.; Nielsen, K. Eelgrass as a bioindicator under the European Water Framework Directive. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ni, J.; Yang, C.; Feng, M.; Li, Z.; Xie, D. Efficient Ammonium Removal by Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas Isolated from Natural Landscape Water: China Case Study. Water 2018, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.L. Research on Potential Largest Photosynthetic Efficiency of Algae of Urban Landscape Water and the Purification Technology of Microbubble. Master’s Thesis, Tongji University, Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, B.; He, N.; Yu, G.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Tian, J. Phosphorus and carbon competitive sorption–desorption and associated non-point loss respond to natural rainfall events. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Li, C.H. Wet deposition of atmospheric nitrogen and its eutrophication effect on Xihu Lake, Huizhou City. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2008, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Qin, B.Q.; Hu, W.P.; Luo, L.C.; Song, Y.Z. The Atmospheric Deposition of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Nutrients in Taihu Lake. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2007, 38, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Whitall, D.R. Anthropogenically-derived atmospheric nitrogen deposition, marine eutrophication and harmful algal bloom expansion: Is there a link? Ambio 1999, 28, 307–311. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Environmental Bulletin. Available online: http://www.sepb.gov.cn/fa/cms/shhj/shhj2143/shhj2144/index_show.shtml (accessed on 2 July 2018).
- Mizerkowski, B.D.; Hesse, K.J.; Ladwig, N.; Machado, E.D.; Rosa, R.; Araujo, T.; Koch, D. Sources, loads and dispersion of dissolved inorganic nutrients in Paranagua Bay. Ocean Dynam. 2012, 62, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulaki, S.; Petihakis, G.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Tsiaras, K.; Triantafyllou, G. Atmospheric deposition in the Eastern Mediterranean. A driving force for ecosystem dynamics. J. Mar. Syst. 2013, 109, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Yang, L.; Hu, W. Observations of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus deposition during the period of algal bloom formation in Northern Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, A.F.; Ingall, E.D.; Diaz, J.M.; Oakes, M.; King, L.E.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Violaki, K.; Avila, A.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R. P-NEXFS analysis of aerosol phosphorus delivered to the Mediterranean Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4043–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sickman, J.O.; Melack, J.M.; Clow, D.W. Evidence for nutrient enrichment of high-elevation lakes in the Sierra Nevada, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicars, W.C.; Sickman, J.O.; Ziemann, P.J. Atmospheric phosphorus deposition at a montane site: Size distribution, effects of wildfire, and ecological implications. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2813–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, L. Nutrients in the wet deposition of Shanghai and ecological impacts. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opening Information of Government. Available online: http://www.shyp.gov.cn/zwgk/Home/List?parentModuleId=009300020009 (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Akkoyunlu, B.O.; Tayanç, M. Analyses of wet and bulk deposition in four different regions of Istanbul, Turkey. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3571–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.M.; Santos, E.B.H.; Duarte, A.C. Dissolved organic and inorganic matter in bulk deposition of a coastal urban area: An integrated approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Yu, J.Z.; Yang, L.; Qin, B. Atmospheric phosphorus in the northern part of Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.J.; Zhang, G.L.; Ruan, X.L.; Zhao, W.J.; Yang, J.L.; Zhou, L.X. The flux and pollution character of dust-fall in different functional zones of Nanjing. China Environ. Sci. 2007, 1, 2–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Imboden, A.S.; Christoforou, C.S.; Salmon, L.G. Determination of atmospheric nitrogen input to lake Greenwood, South Carolina-1. PM measurements. J. Air Waste Manag. 2002, 52, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jung, J.; Jang, Y.; Arimoto, R.; Uematsu, M.; Lee, G. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition and its impact to Lake Sihwa in South Korea from January 2004 to September 2005. Geochem. J. 2009, 43, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, A.N.; Hastings, M.G.; Sigman, D.M.; Lipschultz, F.; Galloway, J.N. The flux and isotopic composition of reduced and total nitrogen in Bermuda rain. Mar. Chem. 2010, 120, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Koba, K.; Makabe, A.; Li, X.D.; Yoh, M.; Liu, C.Q. Ammonium first: Natural mosses prefer atmospheric ammonium but vary utilization of dissolved organic nitrogen depending on habitat and nitrogen deposition. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.; Kremer, J.N. Estimating direct and episodic atmospheric nitrogen deposition to a coastal waterbody. Mar. Environ. Res. 2005, 59, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mills, S.; Street, J.; Golan, D.; Post, A.; Jacobson, M.; Paytan, A. Estimates of atmospheric dry deposition and associated input of nutrients to Gulf of Aqaba seawater. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Nitrogen Fixation Rate and Its Influencing Factors in Surface Waters of Shanghai. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Isabell, K.; Stefano, B.; Volker, B.; Helle, P. Aerobic and anaerobic nitrogen transformation processes in N2-fixing cyanobacterial aggregates. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, L.M.; Landolfi, A.; Oschlies, A.; Hansell, D.A.; Dietze, H.; Dentener, F. Atmospheric deposition of nutrients and excess N formation in the North Atlantic. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 777–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.A.; Clough, J.S.; Wellman, M.C. AQUATOX: Modeling environmental fate and ecological effects in aquatic ecosystems. Ecol. Model. 2008, 213, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnay, L.; Gertler, A.W.; Blank, R.R.; Taylor, G.E. Preliminary measurements of summer nitric acid and ammonia concentrations in the Lake Tahoe Basin air-shed: Implications for dry deposition of atmospheric nitrogen. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 113, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.K.; Smith, V.H. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Almanac 2017. Available online: http://www.shanghai.gov.cn/nw2/nw2314/nw24651/nw43437/nw43442/u21aw1311502.html (accessed on 25 September 2018).
- Fuerhacker, M.; Haile, T.M.; Monai, B.; Mentler, A. Performance of a filtration system equipped with filter media for parking lot runoff treatment. Desalination 2011, 275, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, S.P.; Li, Z.; Guo, W.J.; Zhong, F.; Yin, D.Q. Case study on rehabilitation of a polluted urban water body in Yangtze River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7038–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, M.S.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, F.; Luo, J.H. Ecological restoration by a multistage floating-bed system in a eutrophic urban river, China. In Mechatronics and Applied Mechanics, Pts 1 and 2; Guo, J., Ed.; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 157–158, pp. 945–949. [Google Scholar]
- Cerco, C.F.; Noel, M.R.; Tillman, D.H. A practical application of Droop nutrient kinetics (WR 1883). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4446–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Villada, L.; Rico, M.; Altamirano, M.; Sanchez-Martin, L.; Lopez-Rodas, V.; Costas, E. Occurrence of copper resistant mutants in the toxic cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa: Characterisation and future implications in the use of copper sulphate as algaecide. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Marsh, T.L.; Voice, T.C.; Long, D.T. Loss of seasonal variability in a lake resulting from copper sulfate algaecide treatment. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, Q.; Li, G.; Huang, X. Algae separation from urban landscape water using a high density microbubble layer enhanced by micro-flocculation. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



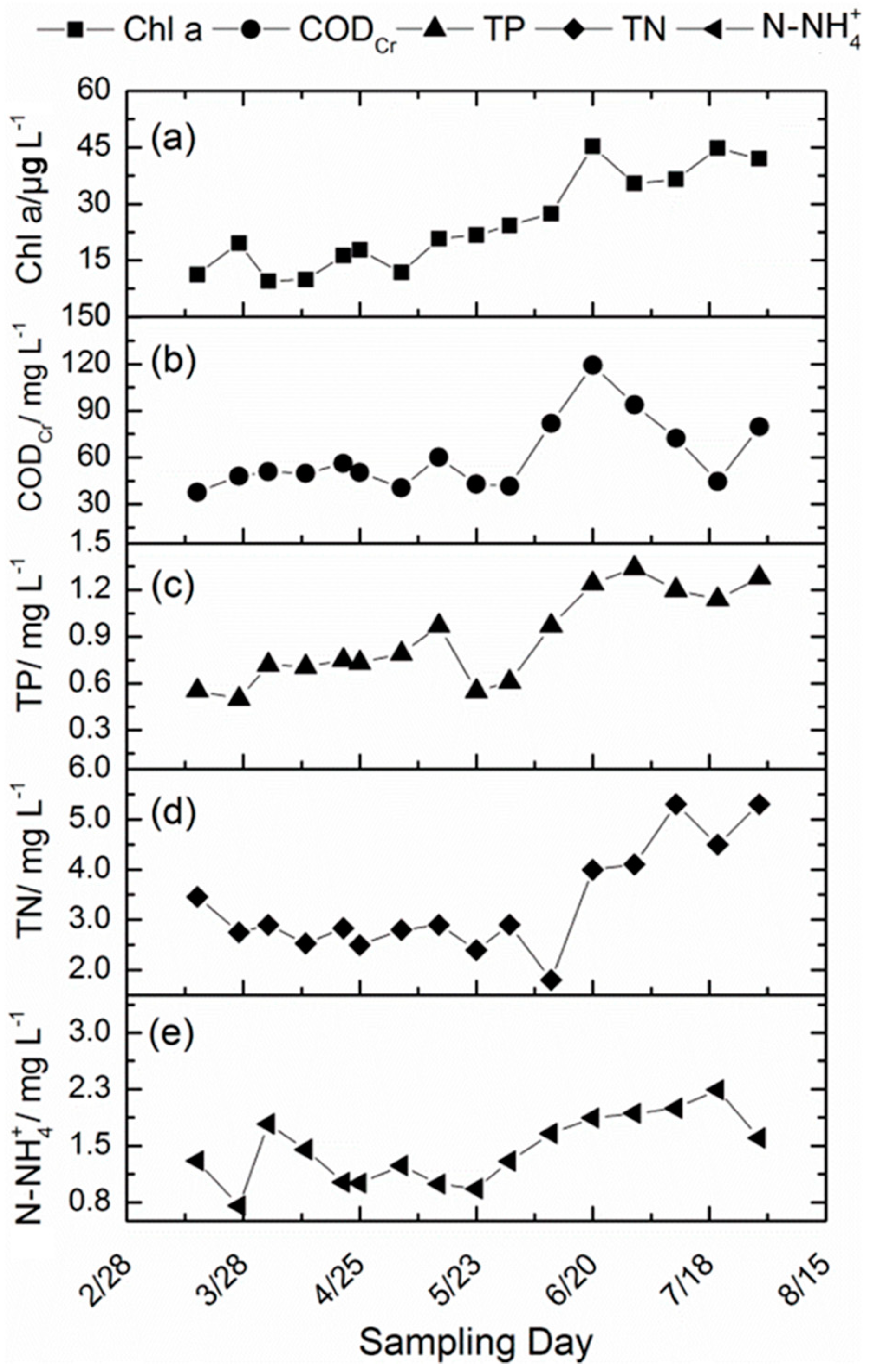
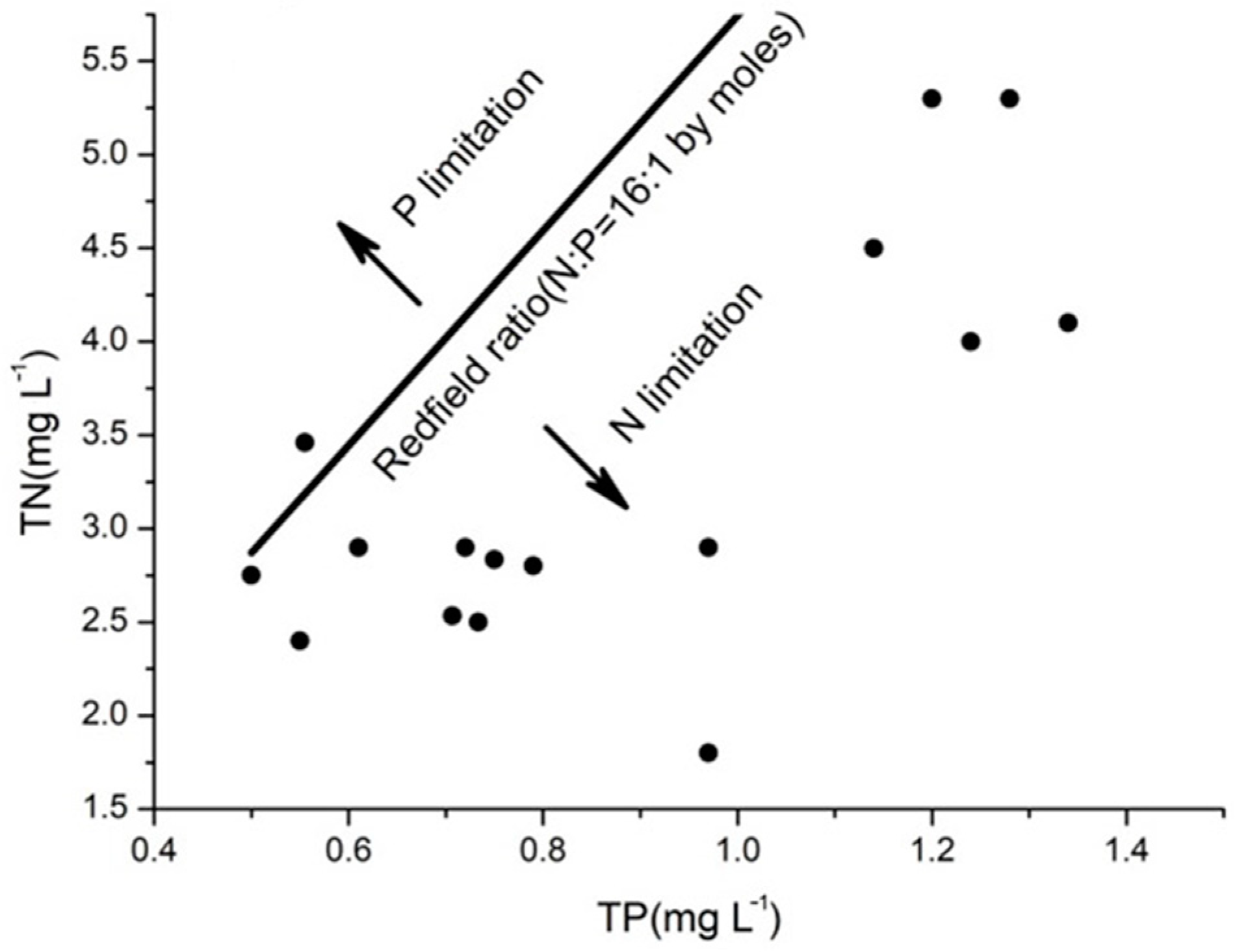
| Sampling Date (M/D) | Calculated New Production of Chl-a (μg L−1) | Measured Chl-a (μg L−1) | Contribution of Atmospheric Nitrogen (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 March–24 March | 9.82 | 62.07 | 15.8 |
| 24 March–3 April | 4.44 | 68.08 | 6.5 |
| 3 April–13 April | 9.10 | 52.37 | 17.4 |
| 13 April–23 April | 6.91 | 54.35 | 12.7 |
| 23 April–3 May | 5.17 | 89.63 | 5.8 |
| 3 May–13 May | 3.65 | 64.69 | 5.6 |
| 13 May–23 May | 12.62 | 114.41 | 11.0 |
| 23 May–2 June | 2.54 | 67.81 | 3.8 |
| 2 June–12 June | 27.69 | 151.68 | 18.3 |
| 12 June–22 June | 9.92 | 150.01 | 6.6 |
| 22 June–2 July | 17.62 | 165.49 | 10.6 |
| 2 July–12 July | 37.98 | 191.15 | 19.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, T.; Cao, H.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Yan, Y.; Lin, X.; Huang, J. Characteristics of Atmospheric Deposition during the Period of Algal Bloom Formation in Urban Water Bodies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061703
Zheng T, Cao H, Liu W, Xu J, Yan Y, Lin X, Huang J. Characteristics of Atmospheric Deposition during the Period of Algal Bloom Formation in Urban Water Bodies. Sustainability. 2019; 11(6):1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061703
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Tao, Haihua Cao, Wei Liu, Jingcheng Xu, Yijing Yan, Xiaohu Lin, and Juwen Huang. 2019. "Characteristics of Atmospheric Deposition during the Period of Algal Bloom Formation in Urban Water Bodies" Sustainability 11, no. 6: 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061703
APA StyleZheng, T., Cao, H., Liu, W., Xu, J., Yan, Y., Lin, X., & Huang, J. (2019). Characteristics of Atmospheric Deposition during the Period of Algal Bloom Formation in Urban Water Bodies. Sustainability, 11(6), 1703. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061703






