Exploring the Impact of Responsible Leadership on Organizational Citizenship Behavior for the Environment: A Leadership Identity Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
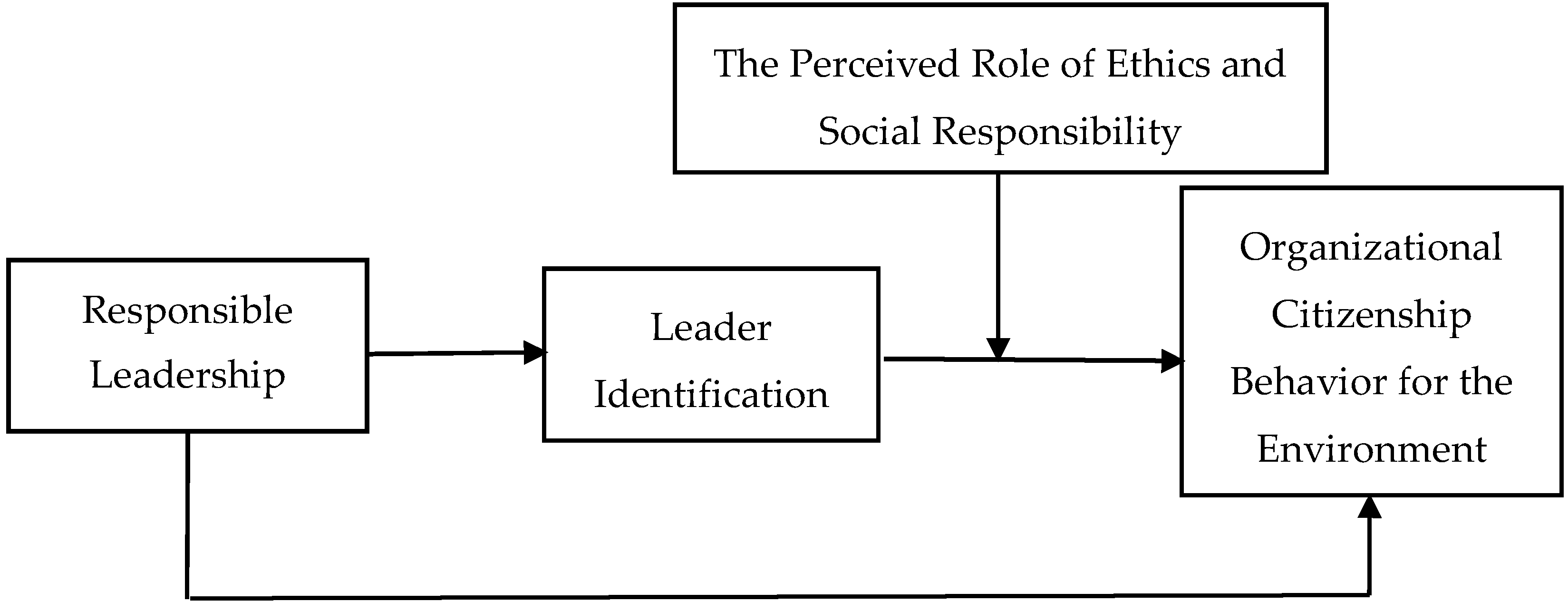
2. Theory and Hypotheses
2.1. Responsible Leadership and OCBE
2.2. The Mediating Role of Leader Identification
2.3. The Moderating Role of PRESOR
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample and Procedure
3.2. Measurement of Variables
4. Results
4.1. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
4.2. Descriptive Statistics
4.3. Hypothesis Testing
4.3.1. Direct Effect Hypothesis
4.3.2. Mediation Analyses
4.3.3. Moderation Analyses
5. Discussion
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Implications
5.3. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manaktola, K.; Jauhari, V. Exploring consumer attitude and behavior towards green practices in the lodging industry in India. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. M. 2007, 19, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdanowicz, P. European hoteliers’ environmental attitudes: Greening the business. Cornell. Hotel. Rest. A. 2005, 46, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, W.G.; Choi, H.M.; Phetvaroon, K. The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees’ eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 76, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.C.; Crane, A. The greening of organizational culture: Management views on the depth, degree and diffusion of change. J. Organ. Change. Manag. 2002, 15, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, B.F.; Bishop, J.W.; Govindarajulu, N.A. Conceptual model for organizational citizenship behavior directed toward the environment. Bus. Soc. 2009, 48, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiral, O.; Paillé, P. Organizational citizenship behavior for the environment: Measurement and validation. J. Bus. Ethics. 2012, 109, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temminck, E.; Mearns, K.; Fruhen, L. Motivating employees towards sustainable behaviour. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2015, 24, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.J.; Boiral, O.; Paillé, P. Pursuing quality and environmental performance: Initiatives and supporting processes. Bus. Process. Manag. J. 2013, 19, 30–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; O’Sullivan, T. Environmentally responsible behaviour in the workplace: An internal social marketing approach. J. Market. Manag. 2012, 28, 469–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egri, C.P.; Herman, S. Leadership in the North American environmental sector: Values, leadership styles, and contexts of environmental leaders and their organizations. Acad. Manage. J. 2000, 43, 571–604. [Google Scholar]
- Ramus, C.A. Organizational support for employees: Encouraging creative ideas for environmental sustainability. Calif. Manage. Rev. 2001, 43, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramus, C.A.; Steger, U. The roles of supervisory support behaviors and environmental policy in employee “Ecoinitiatives” at leading-edge European companies. Acad. Manage. J. 2000, 43, 605–626. [Google Scholar]
- Maak, T. Responsible leadership, stakeholder engagement, and the emergence of social capital. J. Bus. Ethics. 2007, 74, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maak, T.; Pless, N.M. Responsible leadership in a stakeholder society—A relational perspective. J. Bus. Ethics. 2006, 66, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pless, N.M. Understanding responsible leadership: Role identity and motivational drivers. J. Bus. Ethics. 2007, 74, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kets de Vries, M.F.; Vrignaud, P.; Florent-Treacy, E. The global leadership life inventory: Development and psychometric properties of a 360-degree feedback instrument. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Man. 2004, 15, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Moorman, R.H.; Fetter, R. Transformational leader behaviors and their effects on followers’ trust in leader, satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behaviors. Leadership. Quart. 1990, 1, 107–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Law, K.S.; Hackett, R.D.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.X. Leader-member exchange as a mediator of the relationship between transformational leadership and followers’ performance and organizational citizenship behavior. Acad. Manage. J. 2005, 48, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, B.; House, R.J.; Arthur, M.B. The motivational effects of charismatic leadership: A self-concept based theory. Organ. Sci. 1993, 4, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Huang, J.C.; Farh, J.L. Employee learning orientation, transformational leadership, and employee creativity: The mediating role of employee creative self-efficacy. Acad. Manage. J. 2009, 52, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeli, A.; Gilat, G.; Waldman, D.A. The role of perceived organizational performance in organizational identification, adjustment and job performance. J. Manage. Stud. 2007, 44, 972–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walumbwa, F.O.; Hartnell, C.A. Understanding transformational leadership—Employee performance links: The role of relational identification and self-efficacy. J. Occup. Organ. Psych. 2011, 84, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.D.; Vitell, S. A general theory of marketing ethics. J. Macromarketing. 1986, 6, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitell, S.J.; Paolillo, J.G. A cross-cultural study of the antecedents of the perceived role of ethics and social responsibility. Bus. Ethics. 2004, 13, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhapakdi, A.; Karande, K.; Rao, C.P.; Vitell, S.J. How important are ethics and social responsibility?—A multinational study of marketing professionals. Eur. J. Marketing. 2001, 35, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pless, N.M.; Maak, T. Responsible leadership: Pathways to the future. J. Bus. Ethics. 2011, 98, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, K. Integrating leadership development and succession planning best practices. Eng. Manag. Rev. 2011, 39, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegtlin, C. Development of a scale measuring discursive responsible leadership. J. Bus. Ethics. 2011, 98, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, R.G.; Brown, D.J. Leadership, values, and subordinate self-concepts. Leadership. Quart. 2001, 12, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, E.; Tosti-Kharas, J.; Williams, E.G. Read this article, but don’t print it: Organizational citizenship behavior toward the environment. Group. Organ. Manage. 2013, 38, 163–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiral, O.; Baron, C.; Gunnlaugson, O. Environmental leadership and consciousness development: A case study among Canadian SMEs. J. Bus. Ethics. 2011, 123, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, W.M.; Halbesleben, J.R.; Paul, J.R. If you are close with the leader, you must be a brownnose: The role of leader-member relationships in follower, leader, and coworker attributions of organizational citizenship behavior motives. Hum. Resour. Manage. R. 2010, 20, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaffe, T.; Kark, R. Leading by example: The case of leader OCB. J. Appl. Psychol. 2011, 96, 806–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.R.; Corman, S.R.; Cheney, G. Development of a structurational model of identification in the organization. Commun. Theor. 1998, 8, 298–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.M. Traditional Chinese leadership and employee voice behavior: A cross-level examination. Leadership. Quart. 2015, 26, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, G.; Scherer, A.G. Corporate social responsibility, democracy, and the politicization of the corporation. Acad. Manage. Rev. 2008, 33, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, D.A.; Galvin, B.M. Alternative perspectives of responsible leadership. Organ. Dyn. 2008, 37, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cremer, D.; Van Knippenberg, D. How do leaders promote cooperation? The effects of charisma and procedural fairness. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Knippenberg, D.; Van Knippenberg, B.; De Cremer, D.; Hogg, M.A. Leadership, self, and identity: A review and research agenda. Leadership. Quart. 2004, 15, 825–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluss, D.M.; Ashforth, B.E. How relational and organizational identification converge: Processes and conditions. Organ. Sci. 2008, 19, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, E.R.; Branzei, O. “On time and on budget”: Harnessing creativity in large scale projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiral, O.; Talbot, D.; Paillé, P. Leading by example: A model of organizational citizenship behavior for the environment. Bus. Strat. Env. 2015, 24, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhapakdi, A.; Vitell, S.J.; Rallapalli, K.C.; Kraft, K.L. The perceived role of ethics and social responsibility: A scale development. J. Bus. Ethics. 1996, 15, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhapakdi, A.; Gopinath, M.; Marta, J.K.; Carter, L.L. Antecedents and consequences of perceived importance of ethics in marketing situations: A study of Thai businesspeople. J. Bus. Ethics. 2008, 81, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D. Organisational virtue, moral attentiveness, and the perceived role of ethics and social responsibility in business: The case of UK HR practitioners. J. Bus. Ethics. 2008, 148, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettijohn, C.; Pettijohn, L.; Taylor, A.J. Salesperson perceptions of ethical behaviors: Their influence on job satisfaction and turnover intentions. J. Bus. Ethics. 2008, 78, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. The role of idealism and relativism as dispositional characteristics in the socially responsible decision-making process. J. Bus. Ethics. 2005, 56, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mael, F.; Ashforth, B.E. Alumni and their alma mater: A partial test of the reformulated model of organizational identification. J. Organ. Behav. 1992, 13, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, B.; Zakay, E.; Breinin, E.; Popper, M. Correlates of charismatic leader behavior in military units: Subordinates’ attitudes, unit characteristics, and superiors’ appraisals of leader performance. Acad. Manage. J. 1998, 41, 387–409. [Google Scholar]
- Paillé, P.; Chen, Y.; Boiral, O.; Jin, J. The impact of human resource management on environmental performance: An employee-level study. J. Bus. Ethics. 2014, 121, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etheredge, J.M. The perceived role of ethics and social responsibility: An alternative scale structure. J. Bus. Ethics. 1999, 18, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.M.; Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. How transformational leadership and employee motivation combine to predict employee pro-environmental behaviors in China. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.; Miao, Q.; Hofman, P.S.; Zhu, C.J. The impact of socially responsible human resource management on employee’s organizational citizenship behavior: The mediating role of organizational identification. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Man. 2016, 27, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zientara, P.; Zamojska, A. Green organizational climates and employee pro-environmental behaviour in the hotel industry. J. Sustain. Tour. 2018, 26, 1142–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwepker, C.H., Jr. Ethical climate’s relationship to job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention in the salesforce. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preacher, K.J.; Rucker, D.D.; Hayes, A.F. Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2007, 42, 185–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paillé, P.; Mejía-Morelos, J.H. Antecedents of pro-environmental behaviours at work: The moderating influence of psychological contract breach. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 38, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillé, P.; Boiral, O.; Chen, Y. Linking environmental management practices and organizational citizenship behaviour for the environment: A social exchange perspective. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Man. 2013, 24, 3552–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, B.; Bauer, T.N.; Taylor, S. Management commitment to the ecological environment and employees: Implications for employee attitudes and citizenship behaviors. Hum. Relat. 2015, 68, 1669–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, T.A.; McShane, L.; Webster, J. Green information technologies and systems: Employees’ perceptions of organizational practices. Bus. Soc. 2011, 50, 266–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, D.M.; DeRue, D.S. The convergent and discriminant validity of subjective fit perceptions. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.H.; Peters, G.J.Y.; Kok, G. A review of determinants of and interventions for proenvironmental behaviors in organizations. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2012, 42, 2933–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Models | X2 | df | RMSEA | SRMR | CFI | TLI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-factor model (responsible leadership, leader identification, PRESOR, OCBE) | 287.17 | 146 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| 3-factor model 2 (responsible leadership and leader identification were combined into one factor) | 430.05 | 149 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 0.90 |
| 3-Factor model 1 (responsible leadership and PRESOR were combined into one factor) | 871.69 | 149 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 0.73 |
| 2-factor model (responsible leadership, PRESOR, and leader identification were combined into one factor) | 1011.47 | 151 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.72 | 0.68 |
| 1-factor model (all variables were combined into one factor) | 1138.15 | 152 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.68 | 0.64 |
| Variable | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Gender | 1.49 | 0.50 | - | |||||||
| 2. Age | 23.75 | 4.27 | −0.08 | - | ||||||
| 3. Tenure | 1.56 | 3.07 | −0.11 * | 0.71 ** | - | |||||
| 4. Organizational ethical climate | 3.71 | 0.80 | −0.10 | 0.04 | −0.05 | - | ||||
| 5. Responsible leadership | 3.71 | 0.83 | −0.07 | −0.05 | −0.18 ** | 0.63 ** | - | |||
| 6. Leader identification | 3.97 | 0.75 | −0.04 | −0.03 | −0.10 | 0.66 ** | 0.60 ** | - | ||
| 7.OCBE | 3.82 | 0.76 | −0.08 | 0.00 | −0.14 * | 0.68 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.64 ** | - | |
| 8. PRESOR | 2.44 | 1.30 | −0.13 * | 0.13 * | 0.18 ** | 0.14 * | 0.61 | −0.03 | 0.04 | - |
| Effects | Estimate | S.E. | Est./S.E. | P-Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
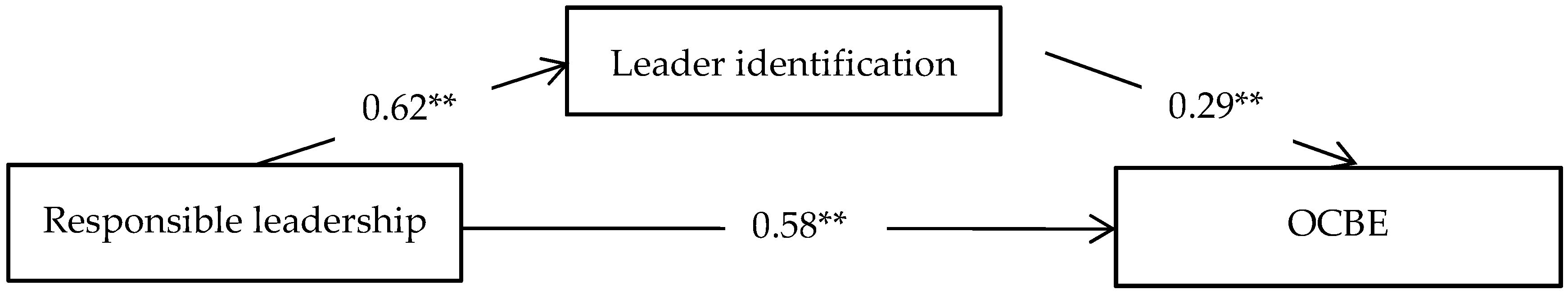
| Responsible leadership → OCBE | 0.33 ** | 0.11 | 3.00 | 0.00 | [0.13, 0.56] |
| Responsible leadership → Leader identification | 0.74 ** | 0.08 | 9.19 | 0.00 | [0.59, 0.90] |
| Leader identification → OCBE | 0.35 ** | 0.09 | 3.84 | 0.00 | [0.17, 0.54] |
| Responsible leadership → Leader identification → OCBE | 0.26 ** | 0.07 | 3.78 | 0.00 | [0.14, 0.41] |
| Variables | OCBE | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | |
| Control variables | |||
| Gender | −0.04 | −0.04 | −0.03 |
| Age | 0.11 * | 0.11 * | 0.11 * |
| Tenure | −0.18 ** | −0.18 ** | −0.18 ** |
| Organizational Ethical Climate | 0.45 ** | 0.45 ** | 0.44 ** |
| Independent variable | |||
| Leader identification | 0.32 ** | 0.32 ** | 0.12 |
| Moderated variable | |||
| PRESOR | −0.01 | −0.65 * | |
| Interaction | |||
| Leader identification × PRESOR | 0.68 * | ||
| R2 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.55 |
| ΔR2 | 0.54 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| F | 69.68 ** | 57.88 ** | 51.47 ** |
| ΔF | 69.68 ** | 0.02 | 6.52 * |
| Dependent Variable | Mediator | Moderator | Level | Mean | Effect Size | Boot SE | LL 95% CI | UL 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCBE | Leader identification | PRESOR | Low (−1 SD) | 1.14 | 0.02 | 0.03 | −0.02 | 0.09 |
| High (+1 SD) | 3.74 | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.16 | |||
| PRESOR | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Zhou, Q. Exploring the Impact of Responsible Leadership on Organizational Citizenship Behavior for the Environment: A Leadership Identity Perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11040944
Zhao H, Zhou Q. Exploring the Impact of Responsible Leadership on Organizational Citizenship Behavior for the Environment: A Leadership Identity Perspective. Sustainability. 2019; 11(4):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11040944
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hongdan, and Qiongyao Zhou. 2019. "Exploring the Impact of Responsible Leadership on Organizational Citizenship Behavior for the Environment: A Leadership Identity Perspective" Sustainability 11, no. 4: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11040944
APA StyleZhao, H., & Zhou, Q. (2019). Exploring the Impact of Responsible Leadership on Organizational Citizenship Behavior for the Environment: A Leadership Identity Perspective. Sustainability, 11(4), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11040944




