Influence of Extreme Events in Electric Energy Consumption and Gross Domestic Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Presentation
2.2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
Analysis of Extreme Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Paraná
4.1.1. 1979 to 1987
4.1.2. 2000s
4.1.3. 2009
4.2. Brazil
4.2.1. 1979 to 1987
4.2.2. 2000s
4.2.3. 2009
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Epstein, G.A. Financialization and the World Economy; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hobsbawm, E.J. Age of Extremes: The Brief Century XX, 1914–1991, 2nd ed.; Letter Company: São Paulo, Brazil, 1995; 598p, ISBN 857164468-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brener, J. 1929: The Crisis that Changed the World, 1st ed.; Ática, 20th Century Retrospective Collection: São Paulo, Brazil, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- ANEEL—National Agency of Energy Electricity. ANEEL: Brasília, Brazil, 2002; 153p. Available online: http://www2.aneel.gov.br/arquivos/pdf/livro_atlas.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Heffernan, J.E.; Stephenson, A.G. Ismev: An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values. 2018. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ismev/ismev.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Bak, P.; Tang, C.; Wiesenfeld, K. Self-organized criticality. Phys. Rev. A 1998, 38, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, P.; Tang, C.; Wiesenfeld, K. Self-organized criticality: An explanation of the 1/f noise. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, P.; Chen, K. Self-organized criticality. Sci. Am. 1991, 264, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirlant, J.; Goegebeur, Y.; Segers, J.; Teugels, J.L. Statistics of Extremes: Theory and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, J.T. Statistical Extremes and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, R.W. Statistics of extremes in climate change. Clim. Chang. 2010, 100, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L. Threshold methods for sample extremes. In Statistical Extremes and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 621–638. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, F.J.; Menéndez, M.; Luceño, A.; Losada, I.J. Estimation of the long-term variability of extreme significant wave height using a time-dependent peak over threshold (pot) model. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE. Country Information. Available online: https://paises.ibge.gov.br/#/pt/pais/brasil/info/sintese (accessed on 27 October 2017).
- ANEEL. Map of the National Electric Power Transmission System. Available online: http://www.aneel.gov.br/transmissao5 (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- COPEL—Company Paranaense of Energy. Available online: www.copel.com (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Word Bank. Country Database. Available online: http://databank.worldbank.org/data/reports.aspx?source=2&series=SP.POP.TOTL&country=# (accessed on 25 June 2017).
- Fix, B. Energy and institution size. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trintin, J.G. The New Economy of Paranaense: 1970 to 2000; Eduem: Maringá, Brazil, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, D. Urbanization and Industrialization in Paraná; SEED: Curitiba, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Leão, I.Z.C.C. Paraná in the Seventies; IPARDES/CONCITEC: Curitiba, Brazil, 1989.
- Volaco, G.; Baggio, E.C.; Shibata, E.K.; Lourenço, G.M. Paraná Economy: Recent Performance and Short-Term Scenarios; Conjunctural Analysis; IPARDES: Curitiba, Brazil, 1991.
- Magalhães Filho, F.B.B. The New Economic Profile of Paraná. FEE Econ. Indic. 1993, 21. Available online: https://revistas.fee.tche.br/index.php/indicadores/article/view/588/827 (accessed on 20 September 2017).
- Word Bank. GDP per Capita (Current US$). Available online: https://datamarket.com/data/list/?q=gdp+spain+provider%3Aworld-bank (accessed on 25 June 2017).
- Walter, A.W. Governing Finance; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Fidrmuc, J.; Korhonen, I. The impact of the global financial crisis on business cycles in Asian emerging economies. J. Asian Econ. 2010, 21, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Wei, S.-J. The composition matters: Capital inflows and liquidity crunch during a global economic crisis. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2011, 24, 2023–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Word Bank. Unemployment, Total (Modeled ILO Estimate). Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SL.UEM.TOTL.ZS (accessed on 25 June 2017).
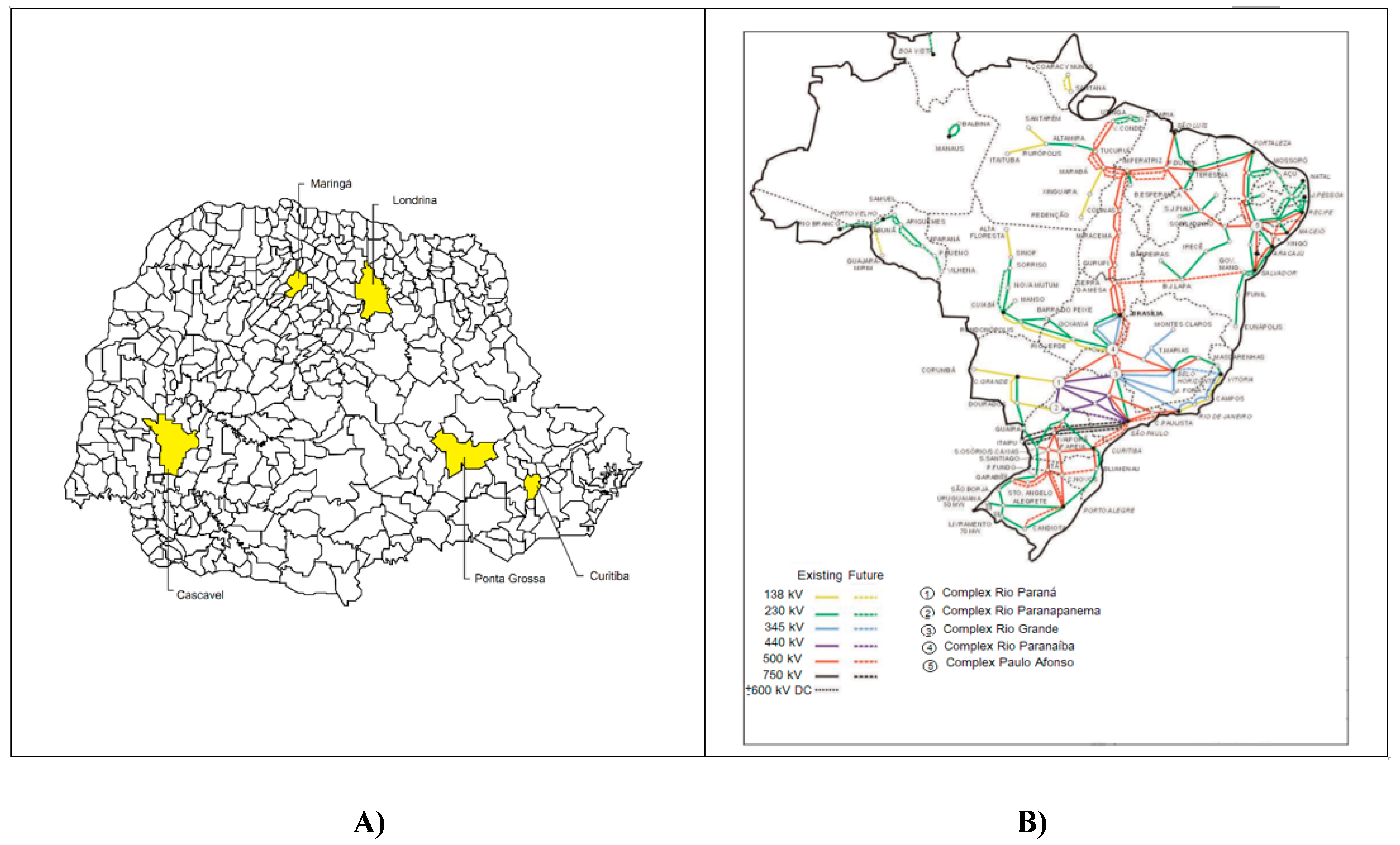



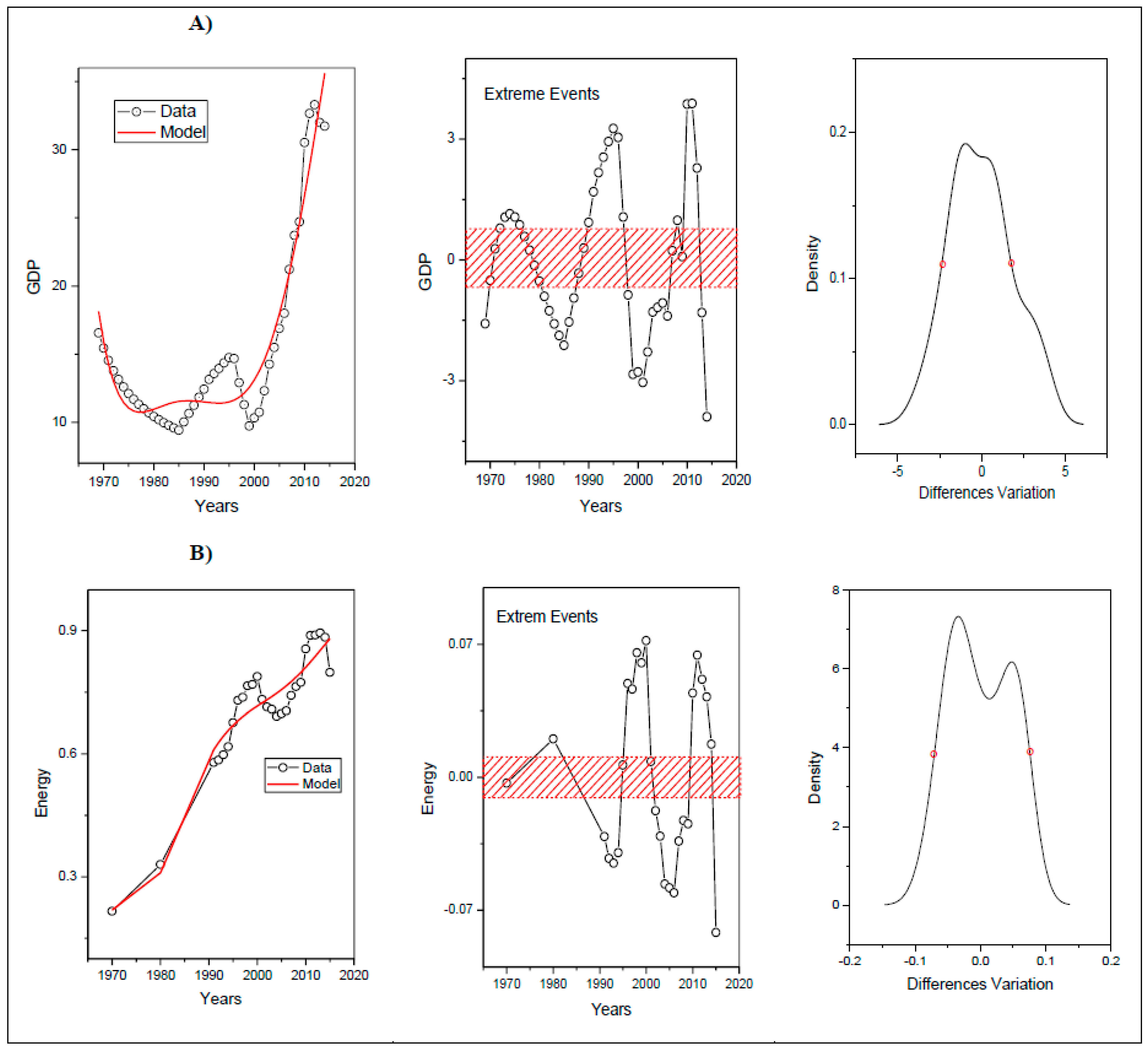
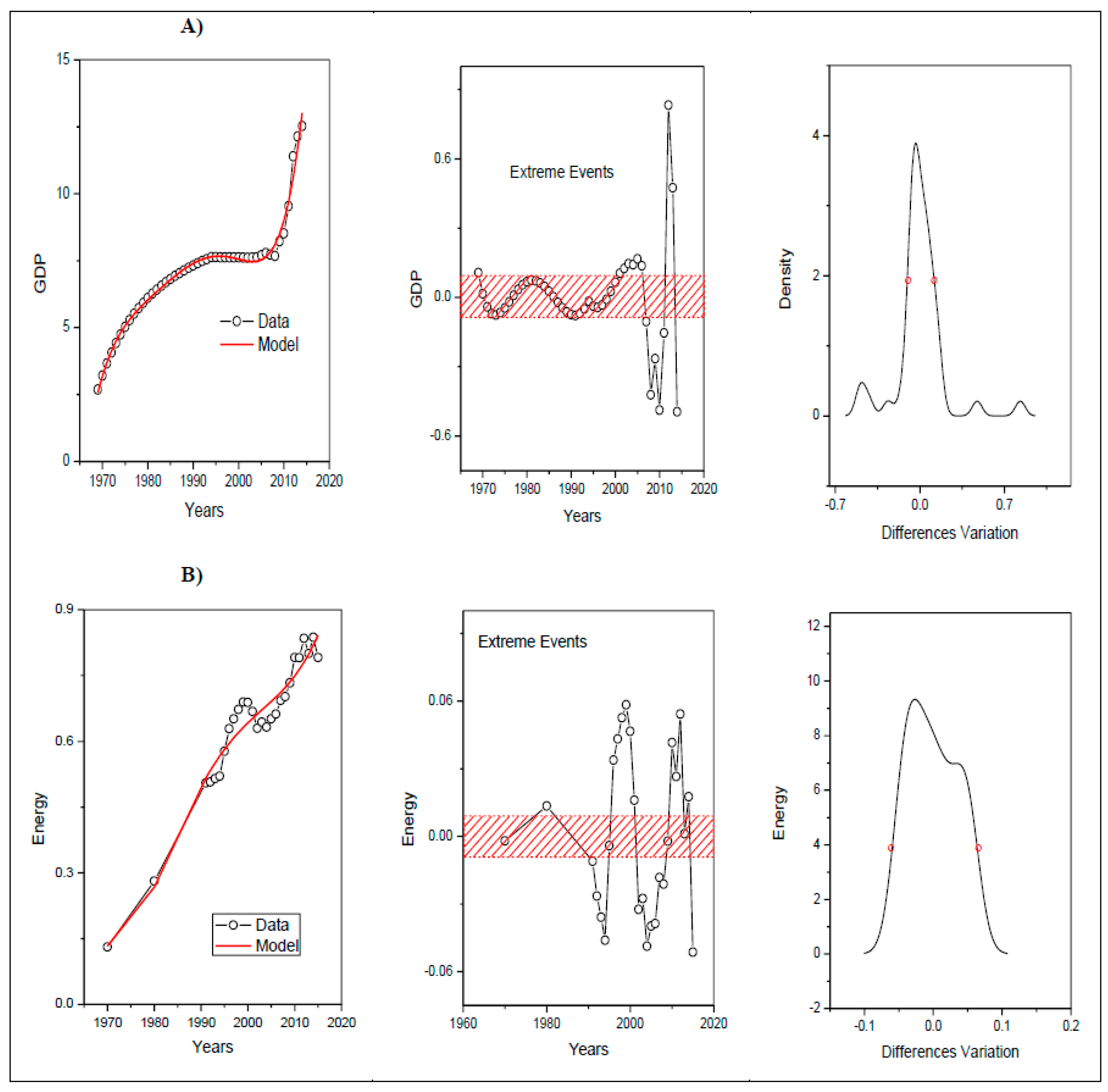
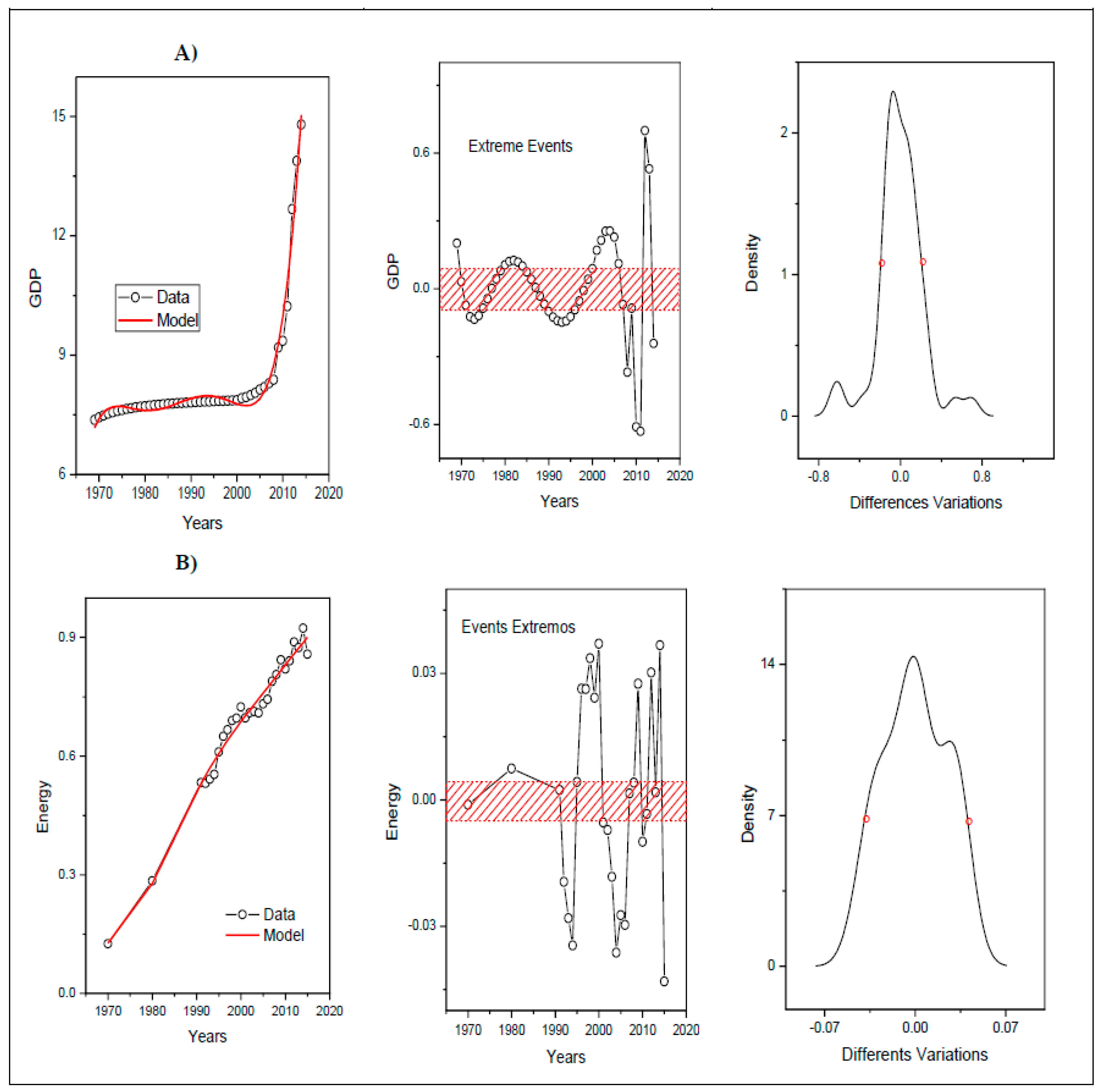


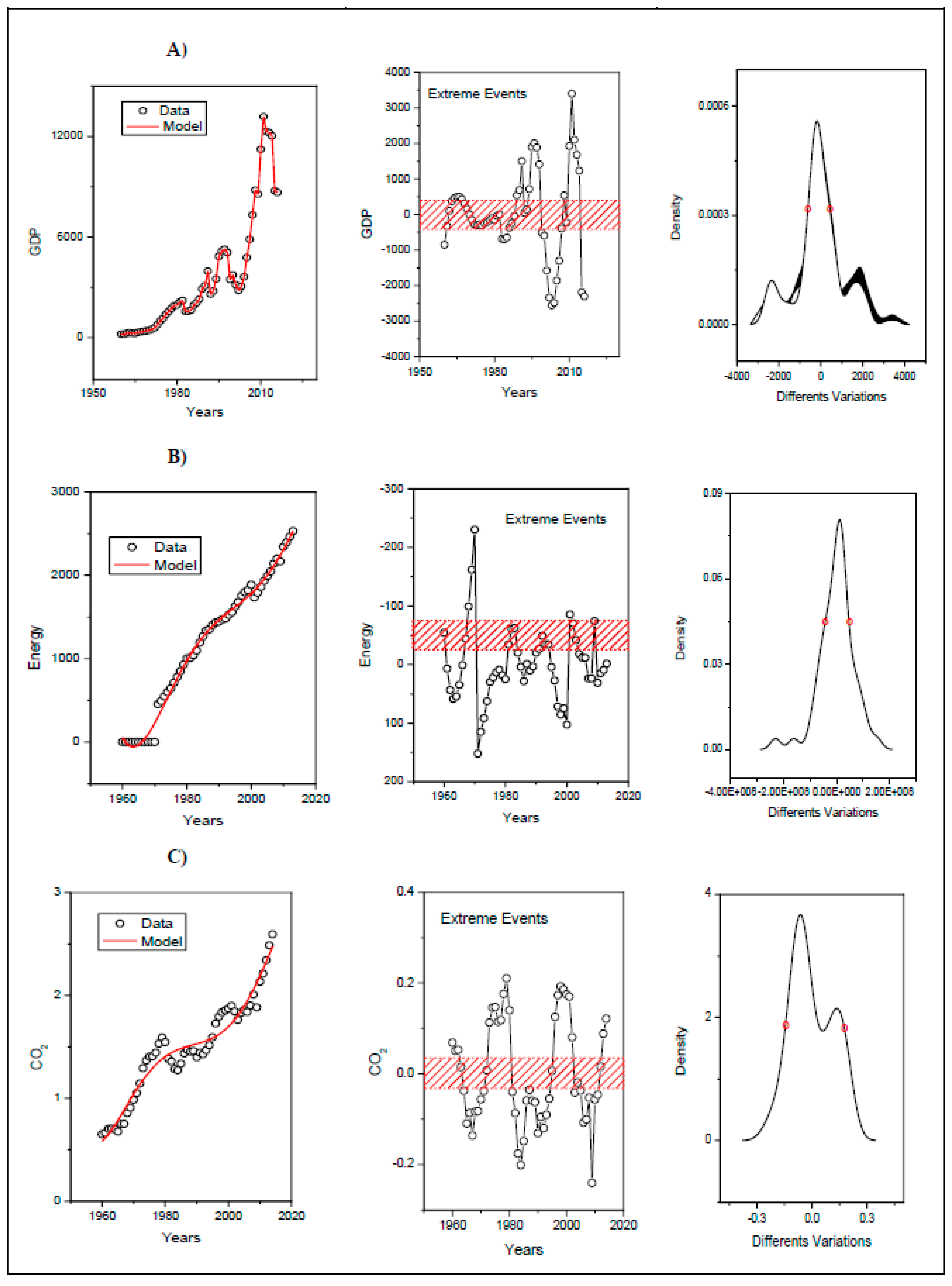
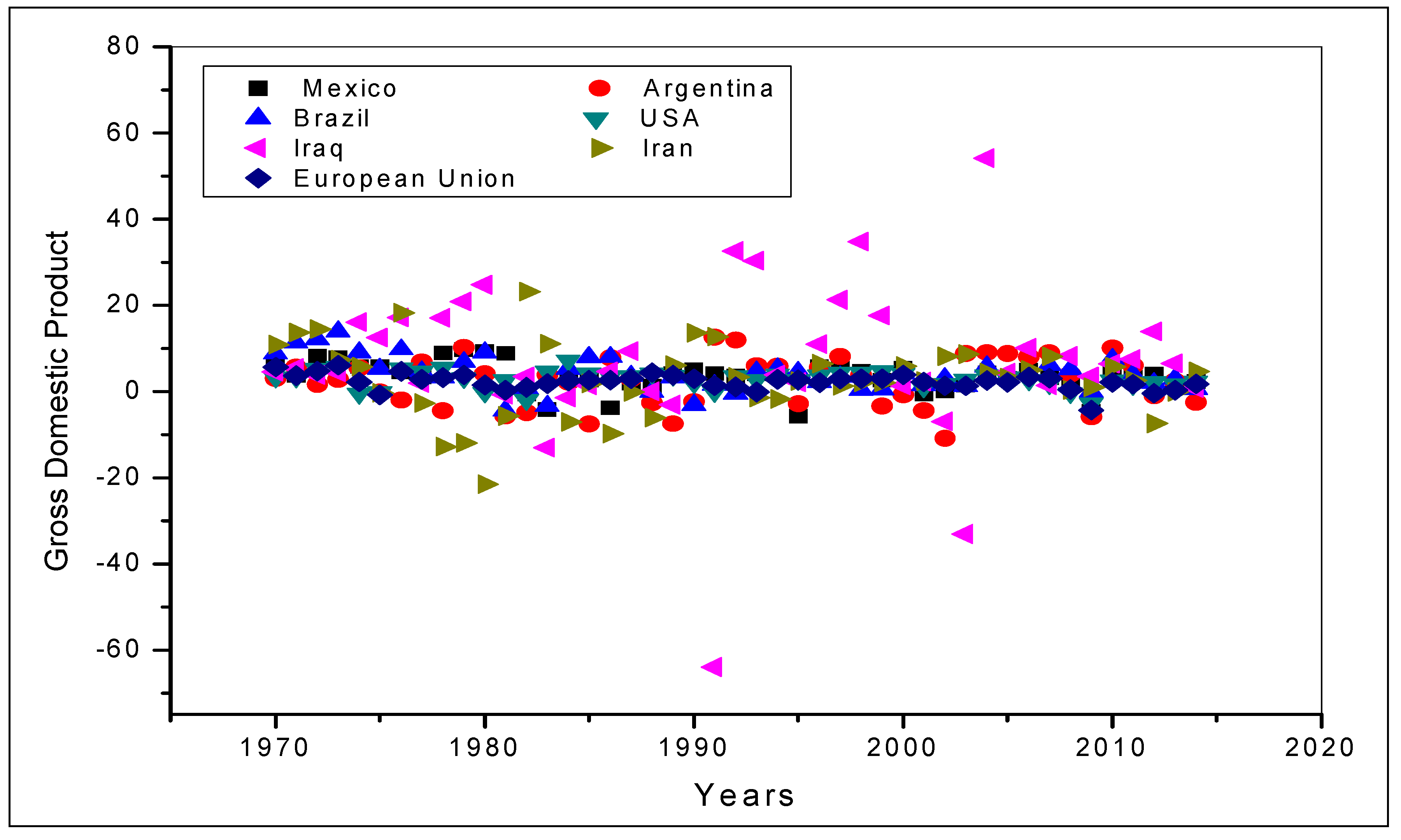
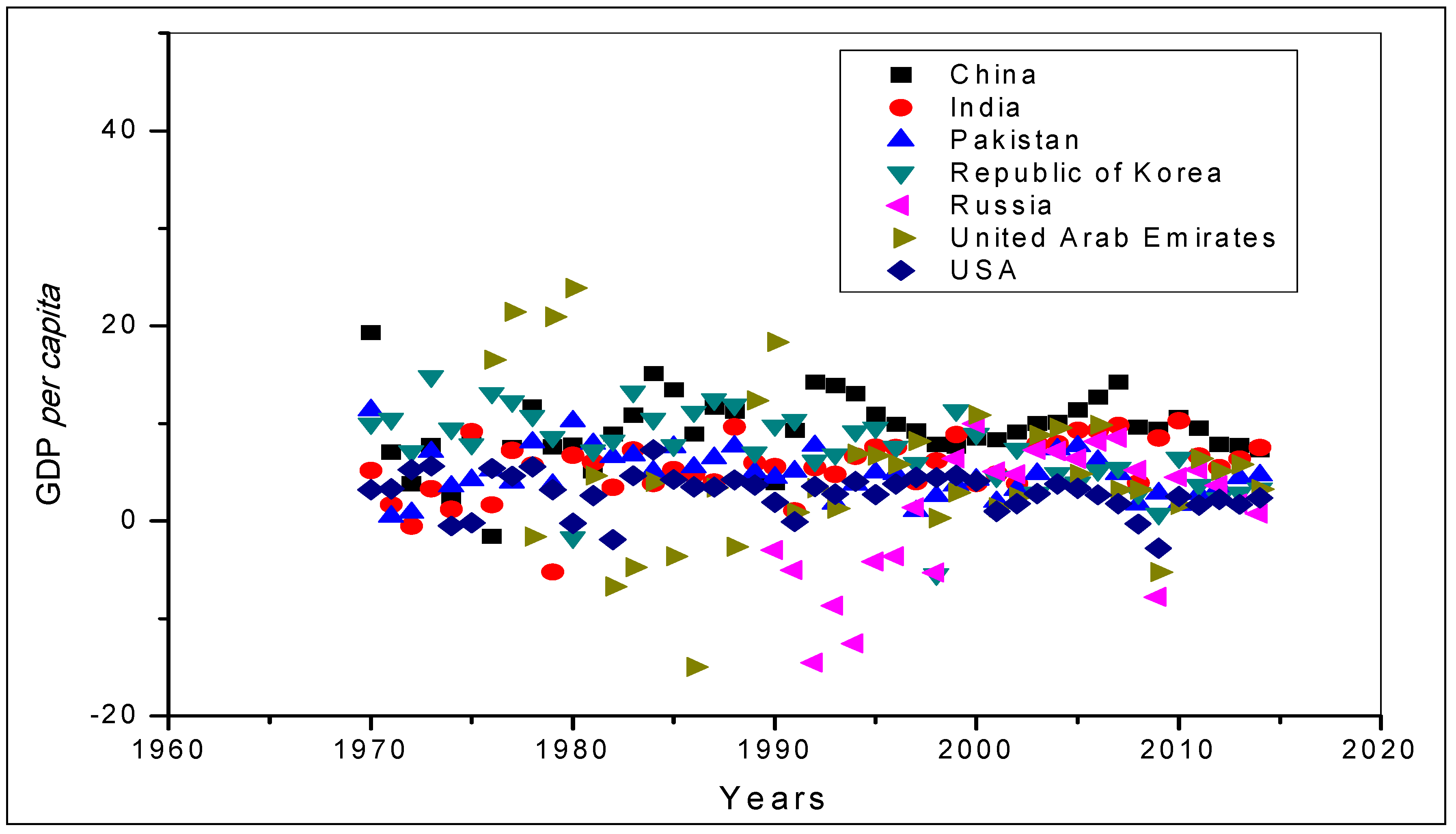
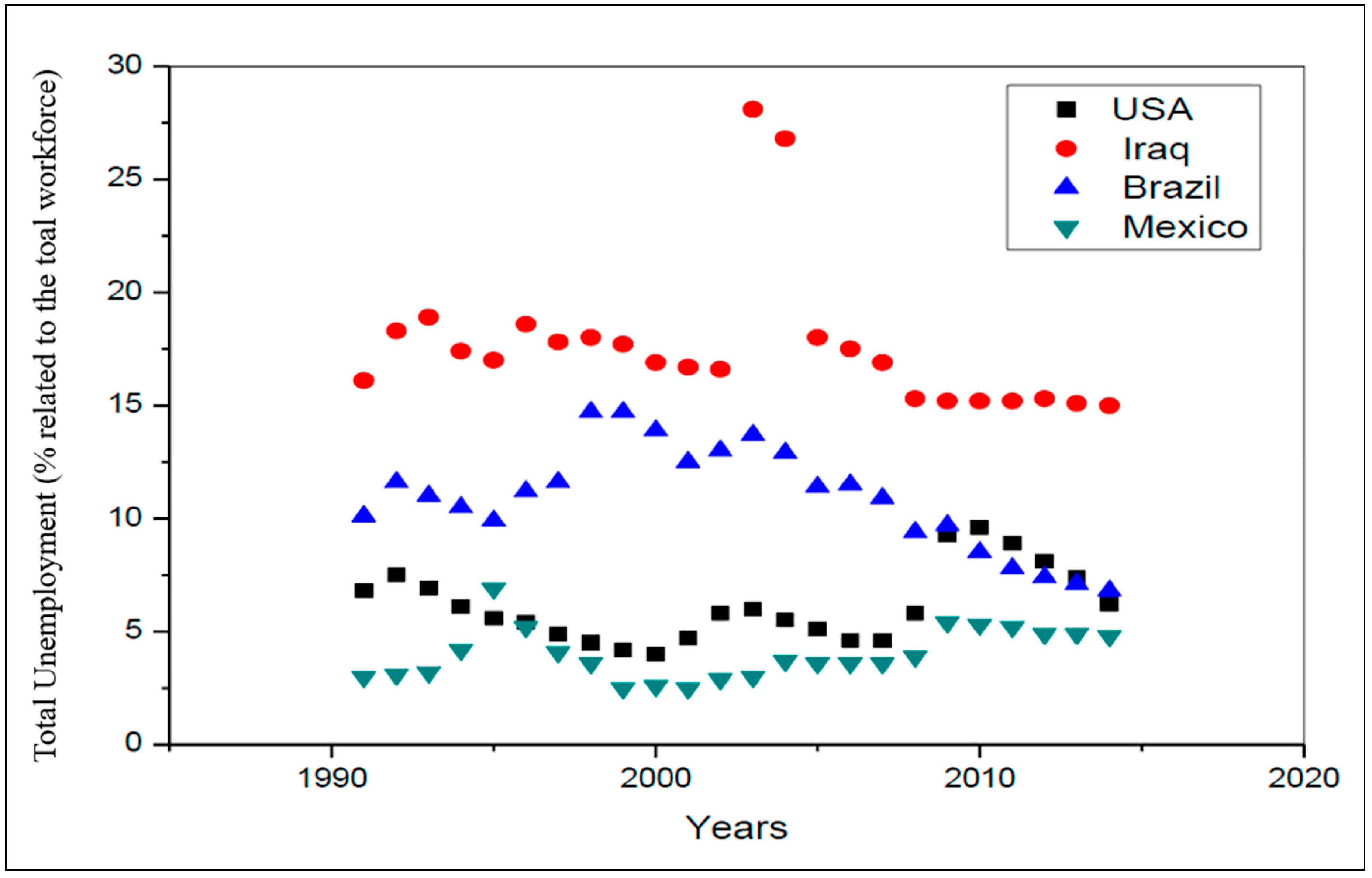
| Locality | Extreme Events (EE) x Variable | Years that Presented EE above the Width at Half Height: | Years that Presented EE below the Width at Half Height: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curitiba | EE(Extreme Events) GDP | 1991–1996 | 1970, 1982–1986, 199–2006, 2013–2014 |
| EE electricity consumption | 1995–2000, 2010–2013 | 1991–1995, 2004–2008 | |
| Londrina | EE GDP | 1970, 1980–1985 (discreet), 2002–2007 (strong), 2012–2013 (strong) | 1972–1975 (leve), 1990–1995 (leve), 2008–2011 (strong), 2014 (strong) |
| EE electricity consumption | 1995–1999, 2009–2011 | 1991–1993, 2002–2008, 2014 | |
| Maringá | EE GDP | 1970, 1979–1985 (discreet), 2000–2007 (strong), 2013–2014(strong) | 1973–1976, 1990–1997, 2010–2011, 2015 |
| EE electricity consumption | 1997–2000, 2007, 2009 | 1992–1995, 2004–2007, 2015 | |
| Ponta Grossa | EE GDP | 1970, 1980–1984, 2000–2005, 2013–2014 | 1971–1975, 1989–1996 (discreet), 2008–2010 (strong), 2015 |
| EE electricity consumption | 1995–2000, 2011–2014 | 1992–1994, 2004–2009, 2015 | |
| Cascavel | EE GDP | 2005–2010, 2015 | 1998–2002 (discreet), |
| EE electricity consumption | 1996–2000, 2012 | 1991–1993, 2004–2006, 2015 | |
| Brazil | EE GDP | 1986, 1989–1992, 2010–2014, | 1961–1963, 1973–1986, 1991–1992, 2005–2010, 2015–2016 |
| EE electricity consumption | 1960, 1967–1970, 1980–1982, 2000–2002, 2010 | 1962–1965, 1971–1976, 1996–2000, 2007–2010 | |
| EE Emissions of CO2 | 1973–1980, 1997–2003, 2011–2012 | 1965–1969, 1982–1985, 1990–1993, 2006–2009 |
| Location/Year | 1970–1975 | 1975–1980 | 1980–1985 | 1985–1990 | 1990–1995 | 1995–2000 | 2000–2005 | 2005–2010 | 2010–2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curitiba | EE GDP: 1970 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1982–1985 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1986 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1991–1995 EE electricity consumption: 1991–1995 | EE GDP: 1995–1996, 1999–2000 EE electricity consumption: 1995–2000 | EE GDP: 2000–2005 EE electricity consumption: 2004–2005 | EE GDP: 2005–2006 EE electricity consumption: 2005–2008 | EE GDP: – EE electricity consumption: 2010–2013 |
| Londrina | EE GDP: 1970, 1972–1975 EE electricity consumption: | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1980–1985 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1990–1995 EE electricity consumption: 1991–1993 | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: 1995–1999 | EE GDP: 2002–2005 EE electricity consumption: 2002–2005 | EE GDP: 2005–2007, 2008–2010 EE electricity consumption: 2005–2008, 2009–2010 | EE GDP: 2010–2011, 2012–2013 EE electricity consumption: 2010–2011, 2014 |
| Maringá | EE GDP: 1970, 1973–1975 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1975–1976, 1979–1980 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1980–1985 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1990–1995 EE electricity consumption: 1992–1995 | EE GDP: 1995–1997 EE electricity consumption: 1997–2000 | EE GDP: 2000–2005 EE electricity consumption: 2004–2005 | EE GDP: 2005–2007 EE electricity consumption: 2005–2007, 2009 | EE GDP: 2010–2011, 2013–2014, 2015 EE electricity consumption: 2015 |
| Ponta Grossa | EE GDP: 1970, 1971–1975 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1980–1984 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1989–1990 EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: 1990–1995 EE electricity consumption: 1992–1994 | EE GDP: 1996 EE electricity consumption: 1995–2000 | EE GDP: 2000–2005 EE electricity consumption: 2004–2005 | EE GDP: 2008–2010 EE electricity consumption: 2005–2009 | EE GDP: 2013–2014, 2015 EE electricity consumption: 2011–2014, 2015 |
| Cascavel | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: absent | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: 1991–1993 | EE GDP: 1998–2000 EE electricity consumption: 1996–2000 | EE GDP: 2000–2002 EE electricity consumption: 2004–2005 | EE GDP: 2005–2010 EE electricity consumption: 2006 | EE GDP: 2012–2014, 2015 EE electricity consumption: 2012, 2015 |
| Brazil | EE GDP: 1973–1975 EE electricity consumption: 1970, 1971–1975 EE Emissions of CO2: 1973–1975, | EE GDP: 1975–1980 EE electricity consumption: 1976 EE Emissions of CO2: 1975–1980 | EE GDP: 1980–1985 EE electricity consumption: 1980–1982 EE Emissions of CO2: 1982–1985 | EE GDP: 1986, 1989–1990 EE electricity consumption: absent EE Emissions of CO2: absent | EE GDP: 1990–1992 EE electricity consumption: absent EE Emissions of CO2: 1990–1993 | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: 1996–2000 EE Emissions of CO2: 1997–2000 | EE GDP: absent EE electricity consumption: 2000–2002 EE Emissions of CO2: 2000–2003 | EE GDP: 2005–2010 EE electricity consumption: 2007–2010 EE Emissions of CO2: 2006–2009 | EE GDP: 2010–2014, 2015–2016 EE electricity consumption: 2010 EE Emissions of CO2: 2011–2012 |
| Historical context: Paraná: decline of some agrarian activities (coffee cultivation), unemployment, rural exodus, industrialization, extractivism, maté and wood processing, export oriented. | Historical context: Paraná economic instability due to excessive dependence on fossil fuels and because the main oil suppliers are involved in wars. Fall in exports. Brazil: Since the 1970s, the country was influenced by fluctuations in the price of oil, oscillations arising from wars between oil suppliers. Crisis in the American and European stock exchanges (1987). | Historical context: Paraná: prominent in extractivism, agribusiness, and exports. Russian Crisis (1998), North American Crisis (2000), terrorist attacks USA (2001). Brazil: Mexican Crisis (1994). Crisis of the Asian giants (1997). Brazilian exchange rate crisis (1999). NASDAQ Crisis (2000). | Historical context: Paraná: The state maintains among its sources of income the agriculture and the extractivism, being influenced by importing countries that faced economic crises (Europe, USA, etc.). Brazil: Crisis Argentina (2001), American Crisis (2008). European Crisis (2009). Brazilian Crisis (2015). | ||||||
| Curitiba | Londrina | Maringá | Ponta Grossa | Cascavel | Brazil | Historical-Economic Context | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | − | − | + | + | + | North American Crisis | |||||||||||
| 1971 | − | − | |||||||||||||||
| 1972 | − | − | − | ||||||||||||||
| 1973 | − | − | − | − | − | + | Oil Crisis—OPEC | ||||||||||
| 1974 | − | − | − | − | − | + | |||||||||||
| 1975 | − | − | − | − | − | + | |||||||||||
| 1976 | − | − | − | + | |||||||||||||
| 1977 | − | + | |||||||||||||||
| 1978 | − | + | |||||||||||||||
| 1979 | + | − | + | Oil Crisis High in the price of oil barrel | |||||||||||||
| 1980 | + | + | + | − | + | + | |||||||||||
| 1981 | + | + | + | − | + | ||||||||||||
| 1982 | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | ||||||||||
| 1983 | − | + | + | + | − | − | |||||||||||
| 1984 | − | + | + | + | − | − | |||||||||||
| 1985 | − | + | + | − | − | ||||||||||||
| 1986 | − | − | |||||||||||||||
| 1987 | Crisis in the American and European stock exchanges | ||||||||||||||||
| 1988 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1989 | − | + | |||||||||||||||
| 1990 | − | − | − | + | − | ||||||||||||
| 1991 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | ||||||||
| 1992 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | ||||||
| 1993 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | |||||||
| 1994 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | Mexican crisis | |||||||||
| 1995 | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | + | |||||||||
| 1996 | + | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | ||||||||
| 1997 | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | − | + | Crisis of the Asian giants | |||||||
| 1998 | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | Russian Crisis | |||||||
| 1999 | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | Brazilian Crisis | ||||||
| 2000 | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | + | + | North American Crisis (NASDAQ) | |||||
| 2001 | − | + | + | − | + | + | Argentina crisis, terrorist attacks on the USA | ||||||||||
| 2002 | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | + | |||||||||
| 2003 | − | + | − | + | + | − | − | + | |||||||||
| 2004 | − | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | ||||||||
| 2005 | − | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | − | − | ||||||
| 2006 | − | − | + | − | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | ||||||
| 2007 | − | + | − | + | + | − | + | − | − | − | |||||||
| 2008 | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | American crisis (biggest crisis since the “Great” crisis of 29) | |||||||
| 2009 | − | + | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | Crisis European Union | |||||||
| 2010 | + | − | + | − | − | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 2011 | + | − | + | − | + | − | + | + | |||||||||
| 2012 | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| 2013 | − | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | |||||||||
| 2014 | − | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | |||||||||
| 2015 | − | − | − | + | − | + | Brazilian Crisis | ||||||||||
 EE (Extreme Events) GDP EE (Extreme Events) GDP |  above the width at half-height above the width at half-height |
 EE electricity consumption EE electricity consumption |  below the width at half-height below the width at half-height |
 EE CO2 emissions EE CO2 emissions |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, F.; Ribeiro, M.A.; Francisco, A.C.d.; Gonçalves Lenzi, G. Influence of Extreme Events in Electric Energy Consumption and Gross Domestic Product. Sustainability 2019, 11, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11030672
Vieira F, Ribeiro MA, Francisco ACd, Gonçalves Lenzi G. Influence of Extreme Events in Electric Energy Consumption and Gross Domestic Product. Sustainability. 2019; 11(3):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11030672
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Fabrício, Maurício Aparecido Ribeiro, Antonio Carlos de Francisco, and Giane Gonçalves Lenzi. 2019. "Influence of Extreme Events in Electric Energy Consumption and Gross Domestic Product" Sustainability 11, no. 3: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11030672
APA StyleVieira, F., Ribeiro, M. A., Francisco, A. C. d., & Gonçalves Lenzi, G. (2019). Influence of Extreme Events in Electric Energy Consumption and Gross Domestic Product. Sustainability, 11(3), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11030672






