Evaluation of Sustainable Development Management in EU Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
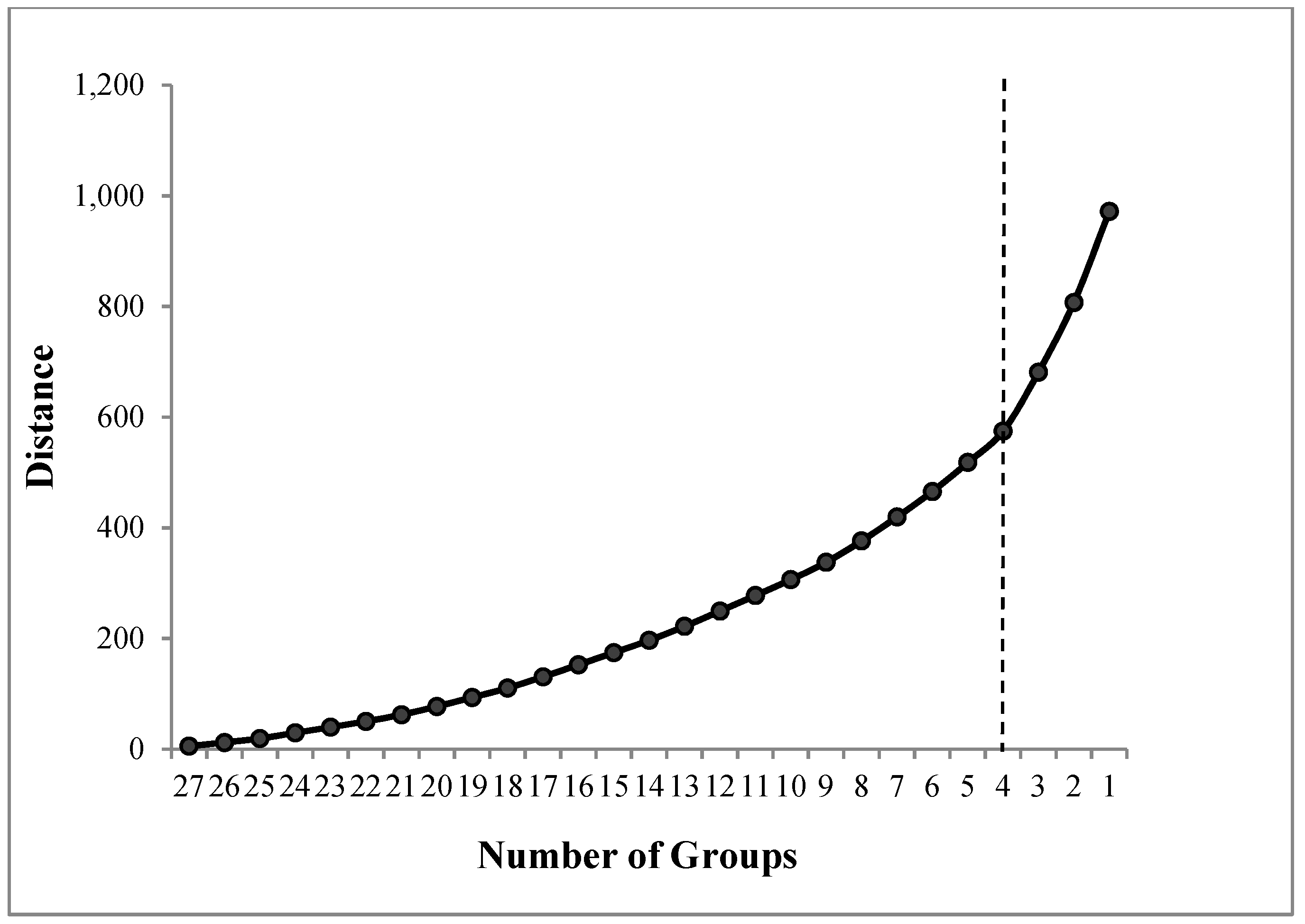
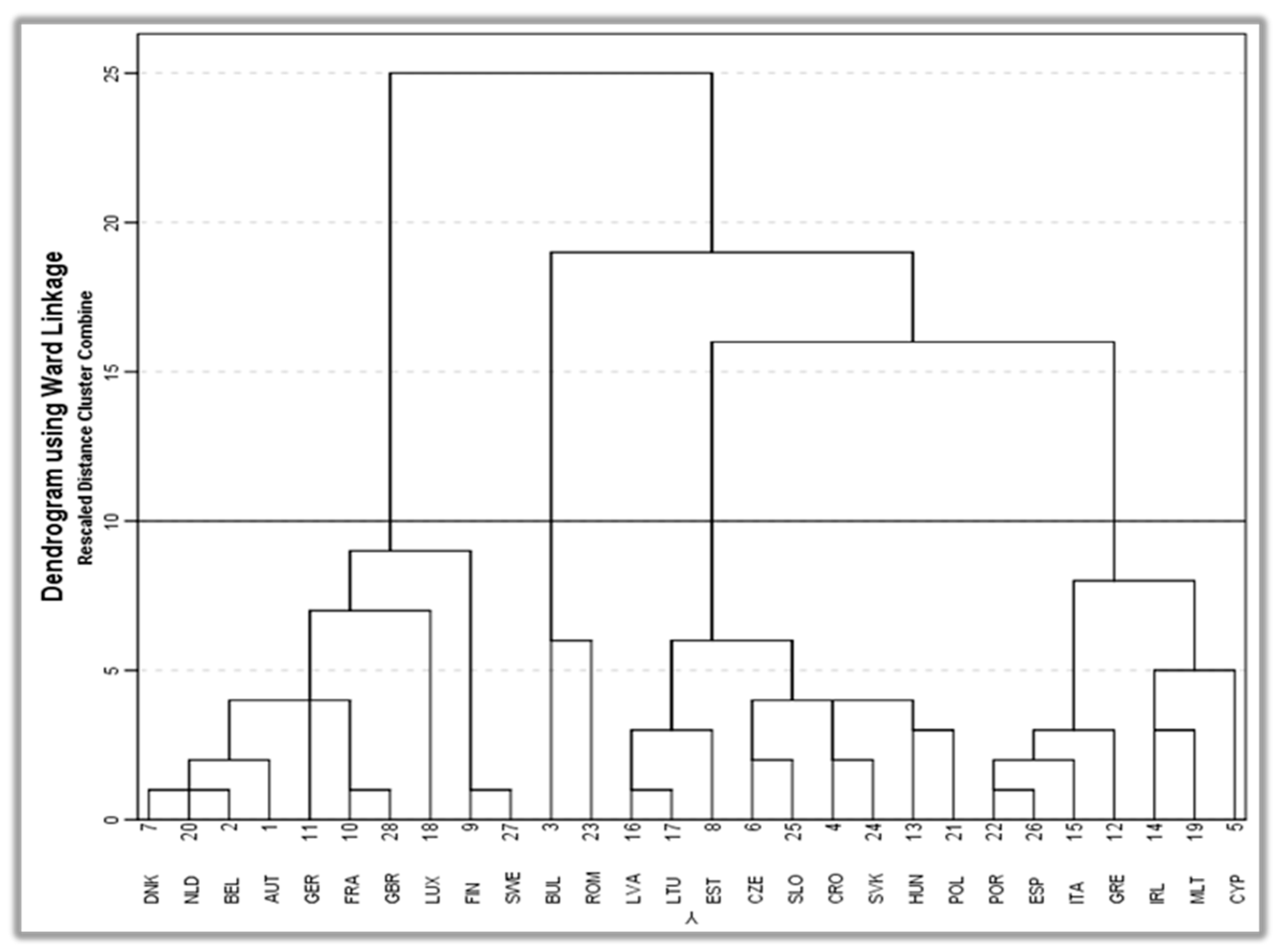
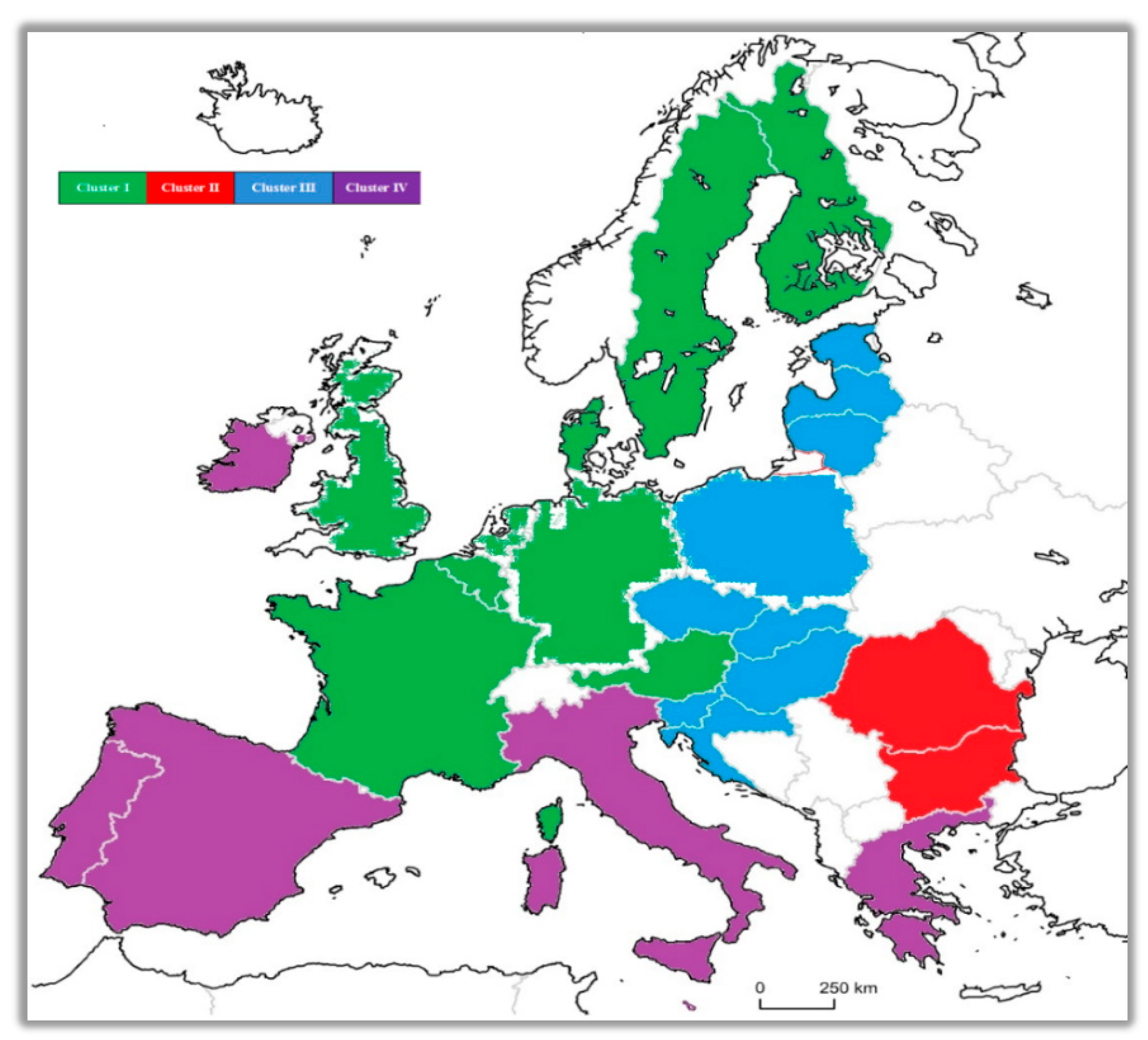
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szopik-Depczyńska, K.; Kędzierska-Szczepaniak, A.; Szczepaniak, K.; Cheba, K.; Gajda, W.; Ioppolo, G. Innovation in sustainable development: An investigation of the EU context using 2030 agenda indicators. Land Use Policy 2018, 79, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.; Azeiteiro, U.; Alves, F.; Pace, P.; Mifsud, M.; Brandli, L.; Caeiro, S.S.; Disterheft, A. Reinvigorating the sustainable development research agenda: The role of the sustainable development goals (SDG). Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2018, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Pouw, N.R.M.; Ros-Tonen, M.A.F. Towards an elaborated theory of inclusive development. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 2015, 27, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.A.; Herman, E. Productive Employment for Inclusive and Sustainable Development in European Union Countries: A Multivariate Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, G. Inclusive Growth: What Future for the European Social Model; IZA Policy Paper No. 82; Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA): Bonn, Germany, 2014; Available online: http://ftp.iza.org/pp82.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2018).
- Islam, R.; Islam, I. Employment and Inclusive Development; Routledge: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978041582596. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Science. A Guide to SDG Interactions: From Science to Implementation; ICSU: Paris, France, 2017; Available online: https://council.science/cms/2017/05/SDGs-Guide-to-Interactions.pdf. (accessed on 28 July 2019).
- Lange Salvia, A.; Leal Filho, W.; Londero Brandli, L.; Sapper Griebeler, J. Assessing research trends related to Sustainable Development Goals: Local and global issues. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlouhá, J.; Henderson, L.; Kapitulčinová, D.; Mader, C. Sustainability-oriented higher education networks: Characteristics and achievements in the context of the UN DESD. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4263–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Indicators of Sustainable Development: Guidelines and Methodologies, 3rd ed.; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/guidelines.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- United Nations. Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 21 December 2012—Implementation of Agenda 21, the Programme for the Further Implementation of Agenda 21 and the outcomes of the World Summit on Sustainable Development and of the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development. 27 February 2013. Available online: https://www.un.org/ga/search/view_doc.asp?symbol=A/RES/67/203&Lang=E (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Janković Šoja, S.; Anokić, A.; Bucalo Jelić, D.; Maletić, R. Ranking EU Countries According to Their Level of Success in Achieving the Objectives of the Sustainable Development Strategy. Sustainability 2016, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Resolution Adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017. Available online: https://undocs.org/A/RES/71/313 (accessed on 16 July 2019).
- Dlouhá, J.; Pospíšilová, M. Education for Sustainable Development Goals in public debate: The importance of participatory research in reflecting and supporting the consultation process in developing a vision for Czech education. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4314–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Vegelin, C. Sustainable development goals and inclusive development. Int. Environ. Agreem. Polit. Law Econ. 2016, 16, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, G.; Tamás, P.; Harder, M.K. Can we improve indicator design for complex sustainable development goals? A Comparison of a Values-Based and Conventional Approach. Sustainability 2016, 8, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, F.; Poyatos, J.A. Designing a Sustainable Development Goal Index through a Goal Programming Model: The Case of EU-28 Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 20 April 2019).
- United Nations, Department of of Economic and Social Affairs. Global Indicator Framework for the Sustainable Development Goals and Targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/indicators/Global%20Indicator%20Framework%20after%202019%20refinement_Eng.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Eichler, G.M.; Schwarz, E.J. What Sustainable Developments Goals Do Social Innovations Address? A Systematic Review and Content Analysis of Social Innovation Literature. Sustainability 2019, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcilovic-Souminen, S.; Pülzl, H. Sustainable development—A ‘selling point’ of the emerging EU bioeconomy policy framework? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4170–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Database. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/indicators/database/ (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- World Bank Data. Database. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/ (accessed on 23 March 2019).
- Eurostat. Database. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database (accessed on 24 March 2019).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Database. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 24 March 2019).
- United Nations. Tier Classification for Global SDG Indicators 31 December 2018. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/files/Tier%20Classification%20of%20SDG%20Indicators_31%20December%202018_web.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- The World Bank. WDI and the Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: http://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/wdi-and-the-sustainable-development-goals.html (accessed on 5 March 2019).
- Chen, R.; Yin, P.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Ross, J.A.; Tse, L.A.; Kan, H.; Zhou, M. Fine particulate air pollution and daily mortality: A nationwide analysis in 272 Chinese cities. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.; Strader, R.; Davidson, C. Airborne reduced nitrogen: Ammonia emissions from agriculture and other sources. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.; Guo, X.; Li, G. Impacts of air pollution wave on years of life lost: A crucial way to communicate the health risks of air pollution to the public. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodny, J.; Tutak, M. Analysis of the diversity in emissions of selected gaseous and particulate pollutants in the European Union countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatios, N.; Skordoulis, M.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Arabatzis, G.; Chalikias, M.; Galatsidas, S.; Batzios, A.; Katsarou, A. Renewable Energy and Economic Growth: Evidence from European Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bointner, R. Innovation in the energy sector: Lessons learnt from R&D expenditures and patents in selected IEA countries. Energy Policy 2014, 73, 733–747. [Google Scholar]
- Boons, F.; Montalvo, C.; Quist, J.; Wagner, M. Sustainable innovation, business models and economic performance: An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, M.; Ivanicova, Z.; Surmanova, K. Cluster analysis of selected world development indicators in the fields of agriculture and the food industry in European Union countries. Agric. Econ. Czech 2018, 64, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, A.; Bruggeman, E. The highly variable economic performance of European agriculture. Land Use Policy 2015, 45, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, Ľ.; Grznár, M. Agriculture in the EU and position of the Slovak Republic. Agric. Econ. Czech. 2015, 61, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.L. Segmenting farms in the European Union. Agric. Econ. Czech. 2013, 59, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, M.; Bastianoni, S.; Gagliardi, F.; Gigliotti, M.; Riccaboni, A.; Betti, G. Sustainable Development Goals Indicators: A Methodological Proposal for a Multidimensional Fuzzy Index in the Mediterranean Area. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, D.; Busch-Casler, J.; Haberstroh, M.M.; Pinkwart, A. National health innovation systems: Clustering the OECD countries by innovative output in healthcare using a multi indicator approach. Res. Policy 2019, 48, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reibling, N. Healthcare systems in Europe: Towards an incorporation of patient access. J. Eur. Soc. Policy 2010, 20, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, C. Mapping European healthcare systems: A comparative analysis of financing, service provision and access to healthcare. J. Eur. Soc. Policy 2009, 19, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Cluster Analysis. In Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 415–475. ISBN 978-0138132637. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačić, Z. Analiza grupisanja. In Multivarijaciona Analiza; Ekonomski fakultet Univerziteta u Beogradu: Belgrade, Serbia, 1994; pp. 255–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojičić, Z.; Išljamović, S.; Petrović, N.; Jeremić, V. A novel approach to evaluating sustainable development. Probl. Ekorozw. Probl. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 7, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Alestalo, M.; Hort, S.E.O.; Kuhnle, S. The Nordic Model: Conditions, Origins, Outcomes, Lessons. 2009. Available online: http://edoc.vifapol.de/opus/volltexte/2013/4255/pdf/41.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2019).
- Hartmann-Hirsch, C. The State of the Luxembourg’s Welfare State: The Effects of the Crisis on a Corporatist Model Shifting to a Universalistic Model. CEPS/INSTEAD Working Papers. 2010. Available online: http://www.statistiques.public.lu/catalogue-publications/working-papers-CEPS/2010/44-2010.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2016).
- Djuran, J.; Golušin, M.; Munitlak, I.O.; Jovanović, L.; Andrejević, A. Renewable energy and socio-economic development in the European Union. Probl. Ekorozw. 2013, 8, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, F. Economic openness and welfare state attitudes: A multilevel study across 67 countries. Int. J. Soc.Welf. 2013, 21, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megyesiova, S.; Lieskovska, V. Analysis of the Sustainable Development Indicators in the OECD Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttmanová, E. Sustainable Development and Sustainability Management in the European Union Countries. Eur. J. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 5, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Target | Target Description | Indicators | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goal 1 | End poverty in all its forms everywhere | 1.1 People at risk of poverty or social exclusion (% of total population) | Eurostat |
| Goal 2 | End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture | 2.1 Proportion of local breeds classified as known being at risk (%) | FAO |
| 2.2 Proportion of local breeds classified as known being not at risk (%) | |||
| 2.3 Proportion of local breeds classified as being at unknown level of risk of extinction (%) | |||
| Goal 3 | Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages | 3.1 Under-five mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 1000 live births) | United Nations |
| 3.2 Neonatal mortality rate (deaths per 1000 live births) | |||
| 3.3 Tuberculosis incidence (per 100,000 population) | |||
| 3.4 Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical diseases (number) | |||
| 3.5 Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease (probability) | |||
| 3.6 Suicide mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 100,000 population) | |||
| 3.7 Age-standardized mortality rate attributed to ambient air pollution (deaths per 100,000 population) | |||
| 3.8 Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, unsafe sanitation and lack of hygiene (deaths per 100,000 population) | |||
| 3.9 Proportion of the target population with access to 3 doses of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP3) (%) | |||
| Goal 4 | Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all | 4.1 Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills (%) | United Nations |
| 4.2 Participation in early childhood education | Eurostat | ||
| Goal 5 | Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls | 5.1 Proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments (% of total number of seats) | United Nations |
| 5.2 Proportion of women in managerial positions (%) | |||
| Goal 6 | Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all | 6.1 Water body extent (permanent) (% of total land area) | United Nations |
| Goal 7 | Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all | 7.1 Proportion of population with primary reliance on clean fuels and technology (%) | United Nations |
| Goal 8 | Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all | 8.1 GDP per capita growth (annual %) | the World Bank |
| 8.2 Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person (%) | United Nations | ||
| 8.3 Domestic material consumption per unit of GDP, by type of raw material (kilograms per constant 2010 United States dollars) | United Nations | ||
| 8.4 Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate) | the World Bank | ||
| 8.5 Share of youth not in education, employment or training, total (% of youth population) | the World Bank | ||
| Goal 9 | Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation | 9.1 Manufacturing, value added (% of GDP) | the World Bank |
| 9.2 Manufacturing employment as a proportion of total employment (%) | United Nations | ||
| 9.3 Research and development expenditure (% of GDP) | the World Bank | ||
| 9.4 Carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP | United Nations | ||
| Goal 10 | Reduce inequality within and among countries | 10.1 Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP) | the World Bank |
| Goal 11 | Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable | 11.1 PM2.5 air pollution, mean annual exposure (micrograms per cubic meter) | the World Bank |
| Goal 14 | Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development | 14.1 Terrestrial and marine protected areas (% of total territorial area) | the World Bank |
| Goal 15 | Protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss | 15.1 Average proportion of Terrestrial Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) covered by protected areas (%) | United Nations |
| 15.2 Forest area certified under an independently verified certification scheme (thousands of hectares) | |||
| 15.3 Red List Index | |||
| Goal 17 | Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development | 17.1 Volume of remittances (in United States dollars) as a proportion of total GDP (%) | the World Bank |
| 17.2 Internet users per 100 inhabitants |
| Indicators | Min. | Max. | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| People at risk of poverty or social exclusion (%) | 13.30 | 40.40 | 23.78 | 6.88 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as known being at risk (%) | 0.00 | 99.12 | 56.81 | 30.34 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as known being not at risk (%) | 0.00 | 34.00 | 8.21 | 8.79 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as being at unknown level of risk of extinction (%) | 0.00 | 100.00 | 34.98 | 33.36 |
| Under-five mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 1000 live births) | 2.30 | 8.50 | 4.23 | 1.51 |
| Neonatal mortality rate (deaths per 1000 live births) | 1.20 | 4.50 | 2.41 | 0.79 |
| Tuberculosis incidence (per 100,000 population) | 3.70 | 64.00 | 12.34 | 13.72 |
| Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical diseases (number) | 0.00 | 272.00 | 31.14 | 55.68 |
| Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease. cancer. diabetes or chronic respiratory disease (probability) | 9.10 | 23.60 | 13.98 | 4.61 |
| Suicide mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 100,000 population) | 5.00 | 31.90 | 14.12 | 5.54 |
| Age-standardized mortality rate attributed to ambient air pollution (deaths per 100,000 population) | 7.00 | 53.00 | 21.25 | 11.81 |
| Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, unsafe sanitation and lack of hygiene (deaths per 100,000 population) | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Proportion of the target population with access to 3 doses of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP3) (%) | 87.00 | 99.00 | 95.25 | 3.00 |
| Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills (%) | 38.50 | 78.60 | 57.81 | 9.51 |
| Participation in early childhood education | 75.10 | 100.00 | 92.54 | 6.61 |
| Proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments (% of total number of seats) | 10.10 | 43.55 | 26.59 | 10.08 |
| Proportion of women in managerial positions (%) | 17.74 | 47.25 | 32.99 | 6.31 |
| Water body extent (permanent) (% of total land area) | 0.14 | 9.91 | 1.96 | 2.43 |
| Proportion of population with primary reliance on clean fuels and technology %) | 86.00 | 95.00 | 94.29 | 2.03 |
| GDP per capita (in United States dollars) | 8311.93 | 107,865.27 | 35,144.33 | 22,244.17 |
| GDP per capita growth (annual %) | 0.36 | 5.40 | 2.41 | 1.28 |
| Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person (%) | −1.80 | 5.60 | 1.13 | 1.78 |
| Domestic material consumption per unit of GDP, by type of raw material (kilograms per constant 2010 United States dollars) | 0.58 | 6.95 | 1.92 | 1.58 |
| Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate) | 3.95 | 23.54 | 8.65 | 4.45 |
| Share of youth not in education, employment or training, total (% of youth population) | 4.57 | 19.54 | 10.99 | 4.11 |
| Manufacturing, value added (% of GDP) | 4.57 | 32.14 | 14.69 | 5.90 |
| Manufacturing employment as a proportion of total employment (%) | 4.24 | 27.80 | 15.33 | 5.63 |
| Research and development expenditure (% of GDP) | 0.44 | 3.25 | 1.53 | 0.86 |
| Carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.08 |
| Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP) | −7.39 | 76.96 | 10.99 | 18.46 |
| PM2.5 air pollution, mean annual exposure (micrograms per cubic meter) | 5.20 | 25.65 | 14.84 | 5.57 |
| Terrestrial and marine protected areas (% of total territorial area) | 1.69 | 55.09 | 21.31 | 11.77 |
| Average proportion of Terrestrial Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) covered by protected areas (%) | 56.26 | 99.40 | 81.24 | 11.85 |
| Forest area certified under an independently verified certification scheme (thousands of hectares) | 0.00 | 23,571.47 | 3547.96 | 5828.02 |
| Red List Index | 0.79 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.05 |
| Volume of remittances (in United States dollars) as a proportion of total GDP (%) | 0.17 | 4.45 | 1.52 | 1.33 |
| Internet users per 100 inhabitants | 59.50 | 98.10 | 80.06 | 10.43 |
| Cluster I | Cluster II | Cluster III | Cluster IV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | Bulgaria | Latvia | Cyprus |
| Belgium | Romania | Lithuania | Greece |
| Denmark | Estonia | Ireland | |
| Finland | Croatia | Italy | |
| France | Czech Republic | Malta | |
| Germany | Slovak Republic | Portugal | |
| Netherlands | Slovenia | Spain | |
| Luxembourg | Hungary | ||
| Sweden | Poland | ||
| United Kingdom |
| Indicators | Cluster I | Cluster II | Cluster III | Cluster IV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | R | V | R | V | R | V | R | |
| People at risk of poverty or social exclusion (%) | 18.70 | 1 | 39.60 | 4 | 23.21 | 2 | 27.26 | 3 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as known being at risk (%) | 71.72 | 1 | 44.44 | 3 | 56.18 | 2 | 39.84 | 4 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as known being not at risk (%) | 5.66 | 2 | 3.47 | 1 | 6.20 | 3 | 15.80 | 4 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as being at unknown level of risk of extinction (%) | 22.62 | 1 | 52.08 | 4 | 37.62 | 2 | 44.36 | 3 |
| Under-five mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 1000 live births) | 3.60 | 1 | 8.20 | 4 | 4.20 | 3 | 4.03 | 2 |
| Neonatal mortality rate (deaths per 1000 live births) | 2.23 | 1 | 3.95 | 4 | 2.26 | 2 | 2.44 | 3 |
| Tuberculosis incidence (per 100,000 population) | 6.44 | 1 | 42.00 | 4 | 15.61 | 3 | 8.09 | 2 |
| Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical diseases (number) | 28.00 | 3 | 142.50 | 4 | 13.56 | 1 | 26.43 | 2 |
| Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, Cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease (probability) | 10.82 | 2 | 22.50 | 4 | 18.10 | 3 | 10.76 | 1 |
| Suicide mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 100,000 population) | 14.61 | 3 | 10.95 | 2 | 18.58 | 4 | 8.60 | 1 |
| Age-standardized mortality rate attributed to ambient air pollution (deaths per 100,000 population) | 12.40 | 1 | 46.50 | 4 | 29.89 | 3 | 15.57 | 2 |
| Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water. unsafe sanitation and lack of hygiene (deaths per 100,000 population) | 0.22 | 3 | 0.25 | 4 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.13 | 2 |
| Proportion of the target population with access to 3 doses of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP3) (%) | 94.90 | 3 | 90.50 | 4 | 95.67 | 2 | 96.57 | 1 |
| Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills (%) | 66.10 | 1 | 49.45 | 4 | 56.83 | 2 | 49.60 | 3 |
| Participation in early childhood education | 96.27 | 1 | 87.35 | 4 | 89.06 | 3 | 93.17 | 2 |
| Proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments (% of total number of seats) | 35.01 | 1 | 17.07 | 4 | 21.47 | 3 | 23.86 | 2 |
| Proportion of women in managerial positions (%) | 30.72 | 3 | 35.74 | 2 | 37.18 | 1 | 30.06 | 4 |
| Water body extent (permanent) (% of total land area) | 3.21 | 1 | 1.00 | 4 | 1.43 | 2 | 1.15 | 3 |
| Proportion of population with primary reliance on clean fuels and technology (%) | 95.00 | 1 | 87.50 | 4 | 94.56 | 3 | 94.86 | 2 |
| GDP per capita (in United States dollars) | 55,407.57 | 1 | 9622.13 | 4 | 18,475.7 | 3 | 34,919.9 | 2 |
| GDP per capita growth (annual %) | 1.19 | 4 | 5.04 | 1 | 3.04 | 2 | 2.59 | 3 |
| Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person (%) | 1.04 | 2 | 4.70 | 1 | 0.93 | 3 | 0.50 | 4 |
| Domestic material consumption per unit of GDP by type of raw material (kilograms per constant 2010 United States dollars) | 0.94 | 1 | 5.22 | 4 | 2.91 | 3 | 1.12 | 2 |
| Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate) | 6.71 | 1 | 6.74 | 2 | 7.81 | 3 | 13.07 | 4 |
| Share of youth not in education, employment or training, total (% of youth population) | 7.92 | 1 | 17.79 | 4 | 10.61 | 2 | 13.93 | 3 |
| Manufacturing, value added (% of GDP) | 12.62 | 1 | 17.31 | 3 | 17.42 | 4 | 13.41 | 2 |
| Manufacturing employment as a proportion of total employment (%) | 11.82 | 1 | 19.22 | 3 | 20.48 | 4 | 12.62 | 2 |
| Research and development expenditure (% of GDP) | 2.46 | 1 | 0.63 | 4 | 1.12 | 2 | 1.01 | 3 |
| Carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP | 0.17 | 1.5 | 0.25 | 4 | 0.24 | 3 | 0.17 | 1.5 |
| Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP) | 11.93 | 2 | 3.13 | 4 | 9.29 | 3 | 14.07 | 1 |
| PM2.5 air pollution, mean annual exposure (micrograms per cubic meter) | 12.09 | 1 | 22.36 | 4 | 18.28 | 3 | 12.20 | 2 |
| Terrestrial and marine protected areas (% of total territorial area) | 23.51 | 3 | 25.43 | 2 | 28.06 | 1 | 8.33 | 4 |
| Average proportion of Terrestrial Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) covered by protected areas (%) | 78.21 | 3 | 86.42 | 2 | 87.93 | 1 | 75.49 | 4 |
| Forest area certified under an independently verified certification scheme (thousands of hectares) | 6481.71 | 1 | 1542.70 | 3 | 2994.72 | 2 | 641.14 | 4 |
| Red List Index | 0.94 | 2.5 | 0.94 | 2.5 | 0.96 | 1 | 0.89 | 4 |
| Volume of remittances (in United States dollars) as a proportion of total GDP (%) | 0.89 | 2 | 2.50 | 3 | 2.63 | 4 | 0.70 | 1 |
| Internet users per 100 inhabitants | 90.37 | 1 | 59.65 | 4 | 77.69 | 2 | 74.23 | 3 |
| Indicators | F-Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| People at risk of poverty or social exclusion (%) | 15.73 | 0.000 *** |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as known being at risk %) | 1.79 | 0.175 |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as known being not at risk (%) | 2.87 | 0.058 * |
| Proportion of local breeds classified as being at unknown level of risk of extinction (%) | 0.82 | 0.496 |
| Under-five mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 1,000 live births) | 11.14 | 0.000 *** |
| Neonatal mortality rate (deaths per 1,000 live births) | 3.60 | 0.028 ** |
| Tuberculosis incidence (per 100,000 population) | 6.78 | 0.002 *** |
| Number of people requiring interventions against neglected tropical diseases (number) | 3.99 | 0.019 ** |
| Mortality rate attributed to cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory disease (probability) | 36.50 | 0.000 *** |
| Suicide mortality rate, by sex (deaths per 100,000 population) | 8.02 | 0.001 *** |
| Age-standardized mortality rate attributed to ambient air pollution (deaths per 100,000 population) | 29.28 | 0.000 *** |
| Mortality rate attributed to unsafe water, unsafe sanitation and lack of hygiene (deaths per 100,000 population) | 2.11 | 0.126 |
| Proportion of the target population with access to 3 doses of diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP3) (%) | 2.63 | 0.073 * |
| Proportion of youth and adults with information and communications technology (ICT) skills (%) | 9.22 | 0.000 *** |
| Participation in early childhood education | 2.79 | 0.062 * |
| Proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments (% of total number of seats) | 6.03 | 0.003 *** |
| Proportion of women in managerial positions (%) | 2.88 | 0.057 * |
| Water body extent (permanent) (% of total land area) | 1.45 | 0.252 |
| Proportion of population with primary reliance on clean fuels and technology (%) | 69.18 | 0.000 *** |
| GDP per capita (in United States dollars) | 11.61 | 0.000 *** |
| GDP per capita growth (annual %) | 22.59 | 0.000 *** |
| Annual growth rate of real GDP per employed person (%) | 4.07 | 0.018 ** |
| Domestic material consumption per unit of GDP. by type of raw material (kilograms per constant 2010 United States dollars) | 15.97 | 0.000 *** |
| Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) (modeled ILO estimate) | 4.34 | 0.014 ** |
| Share of youth not in education, employment or training, total (% of youth population) | 9.61 | 0.000 *** |
| Manufacturing, value added (% of GDP) | 1.34 | 0.286 |
| Manufacturing employment as a proportion of total employment (%) | 8.62 | 0.000 *** |
| Research and development expenditure (% of GDP) | 17.34 | 0.000 *** |
| Carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP | 1.99 | 0.143 |
| Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP) | 0.20 | 0.895 |
| PM2.5 air pollution, mean annual exposure (micrograms per cubic meter) | 5.58 | 0.005 *** |
| Terrestrial and marine protected areas (% of total territorial area) | 6.47 | 0.002 *** |
| Average proportion of Terrestrial Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) covered by protected areas (%) | 2.07 | 0.131 |
| Forest area certified under an independently verified certification scheme (thousands of hectares) | 1.64 | 0.207 |
| Red List Index | 2.27 | 0.106 |
| Volume of remittances (in United States dollars) as a proportion of total GDP (%) | 6.74 | 0.002 *** |
| Internet users per 100 inhabitants | 23.31 | 0.000 *** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popović, B.; Janković Šoja, S.; Paunović, T.; Maletić, R. Evaluation of Sustainable Development Management in EU Countries. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247140
Popović B, Janković Šoja S, Paunović T, Maletić R. Evaluation of Sustainable Development Management in EU Countries. Sustainability. 2019; 11(24):7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247140
Chicago/Turabian StylePopović, Blaženka, Svjetlana Janković Šoja, Tamara Paunović, and Radojka Maletić. 2019. "Evaluation of Sustainable Development Management in EU Countries" Sustainability 11, no. 24: 7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247140
APA StylePopović, B., Janković Šoja, S., Paunović, T., & Maletić, R. (2019). Evaluation of Sustainable Development Management in EU Countries. Sustainability, 11(24), 7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247140





