3.1. Methodology and Description of the Technique
The methodological basis of the research presented by us is the following: system theory, a systematic approach to managing a company’s sustainable development, theory and practice of modeling, strategic management, and investment design. The theoretical and methodological basis of the study was the works of foreign and domestic scientists in the field of economics, investment, and strategic management, including the management of Russian enterprises. Based on the ambiguity and variability of the conditions of enterprises, we analyzed the works, which examined the possibility of using dynamic models aimed at solving the macroeconomic problems of modern enterprises.
In the framework of this study, the synergy of two approaches is considered—sustainable enterprise management and investment analysis. Moreover, competent investment, on the one hand, positively affects the sustainable development of the enterprise, and on the other hand, directly depends on the current stability of the company (M.L. Tseng et al. 2019) [
21]. This two-sided dependence necessitates the development of methodological approaches to the management of investment activities of industrial enterprises in the context of increasing the sustainability of their development.
Analysis of the studies on the theory of systems, unstable state of industrial facilities, and consideration of the specifics of industrial enterprises has shown that in the field of large-scale industrial production enterprises should be considered as stochastic nonlinear dynamic systems [
7].
As a tool for quantitative and qualitative assessment of the sustainability of industrial enterprises, based on the study of the works of V.V. Leontyev, L.B. Senetskaya, A.V. Schmidt, and T.A. Khudyakova, it is proposed a simulation model of control. This model allows you to simulate the processes of strategic management and formulate strategies in the state of system instability based on the analysis of financial, economic, technical, and other indicators. As the main parameters of the model, we have considered the parameters proposed by V.V. Leontiev [
22]. Leontyev’s macroeconomic model is very convenient for our study since it includes interrelated indicators: capital investments, production assets, gross and final products, labor resources, etc.
An important task of management, taking into account the assessment of the state of the enterprise, is making the right decision sequence that allows overcoming crisis phenomena [
23].
Adequate assessments of the current situation and timely management decisions help an enterprise to implement a sustainable development strategy if a mechanism for regulating unstable business systems is established (K. Waren, 2002) [
24].
The mechanism of sustainable development of industrial enterprises can be represented in the form of a clear system of sequential impacts of the management subsystem on the microeconomic system of a company, which allows the company to fulfill its mission. This approach is observed in N.L. Zaitsev and B. Sharp, D. Bergh, and L. Ming researches [
25,
26]. At the same time, it enables the company to extend the life cycle of the organization within the framework of the implementation of the relevant business strategy.
As the analysis of theoretical sources and business practices shows, the firm’s sustainable development mechanism necessarily includes the fundamental blocks of actions that reflect the management function, the controlling system, the main parameters of management decision making, feedback elements (B. Sharp, D. Bergh, L. Ming, 2013) [
26]. All this allows the company management to predict and adequately respond to the challenges of the external environment, respectively, to accurately determine the possibilities of investing and implementing the strategy.
In the modern realities of socio-economic relations, the environmental uncertainty of a company, the achievement of sustainable development of an industrial enterprise is determined by the positive dynamics of quantitative and qualitative transformations of elements and business processes at various stages of the company’s life cycle. We tried to take into account this provision, based on the research of I. Becker, who proposed algorithms for solving the problem of adapting an enterprise when the situation in the external environment changes, and also considered the criteria for the effectiveness of the company’s business processes [
27].
Also of interest are studies in which it is proposed to use a balanced scorecard in evaluating and shaping an enterprise strategy, which allows making adjustments to the change management process in the industrial company, characterized by upgrading the production base, releasing a new product, introducing innovations, modernizing and reconstructing the technological base (P. Horvath, R. Gleich, M. Seiter) [
28].
The sustainability of a firm is largely determined by the level of investment and innovation potential of the enterprise, which is a fundamental factor, especially in conditions of sharply increased competition among countries [
29]. According to the principles of a systems approach, an enterprise is an open, dynamic system, as it is in constant development, interacting with the external environment, subject to significant fluctuations (Ž. Mateljak, D. Mihanović) [
30]. The company receives from the external environment resources in the form of raw materials and materials, fuel and energy, capital and information, labor resources, equipment, and other assets, which later become part of its internal environment. Some resources are processed, converted into products and services, which are then returned back to the external environment (O.M. Orlovtseva) [
31].
All of the above and analysis of the practice of the activities of Russian companies imply a very careful attitude to the selection process, formation, and implementation of industrial enterprise strategies, the use of proven algorithms for implementing strategic management, described, in particular, by S.G. Kalinin and V.H. Tribushnaya, reflecting the specifics of the activities of Russian enterprises [
32].
In the process of implementation by the company’s management innovation and investment projects aimed at maintaining the real economic sustainability of the industrial enterprise, there is a need to design a mechanism and model of strategic management for the development, selection, and implementation of investment scenarios for the development of the company. Algorithms for modeling this process are considered in the work of V.I. Shiryaev and E.V. Shiryaev [
33].
Improving the parameters of the strategic management model for the sustainable development of an industrial enterprise, we took into account that the amount of invested capital and investment activities depend on the type of the enterprise—whether it rents capital or is engaged in investing in another organization’s business [
34].
Besides, it is provided for the need to analyze the magnitude of the costs per unit of capital leased to the firm for a certain period of time. It also revealed, on the basis of the analysis of the theory and practice of the activities of Russian enterprises, that investment in the development of a company depends on the marginal product of the organization’s capital, the number of costs per unit of capital, and the amount of retired capital. The result of our research has been the improvement of the strategic management model of the formation of the industrial enterprise strategy, the optimization of the firm’s investment capital structure, the mechanism for developing, and managing the implementation of the investment strategy of the industrial company.
The focus has been on the process of forming the investment capital of a company. The works of G. Kokins, B. Sharp, N. Kotova, and other scientists were considered as basic sources for determining the directions and methods of forming the structure of the investment capital of the company. We were attracted by the work of G. Kokins, who drew attention to the possible gaps in the implementation of the strategy associated with the discrepancy between the investment needs of the company and its real possibilities [
35]. Having also studied the practice of industrial enterprises in Russia and the theoretical sources of domestic and international researchers, we proposed to change the approach to the formation of investment capital and investment reserves of the enterprise. We propose to use this acceptable for the company and its owners the range of reducing the size of dividends of the main owners of the company.
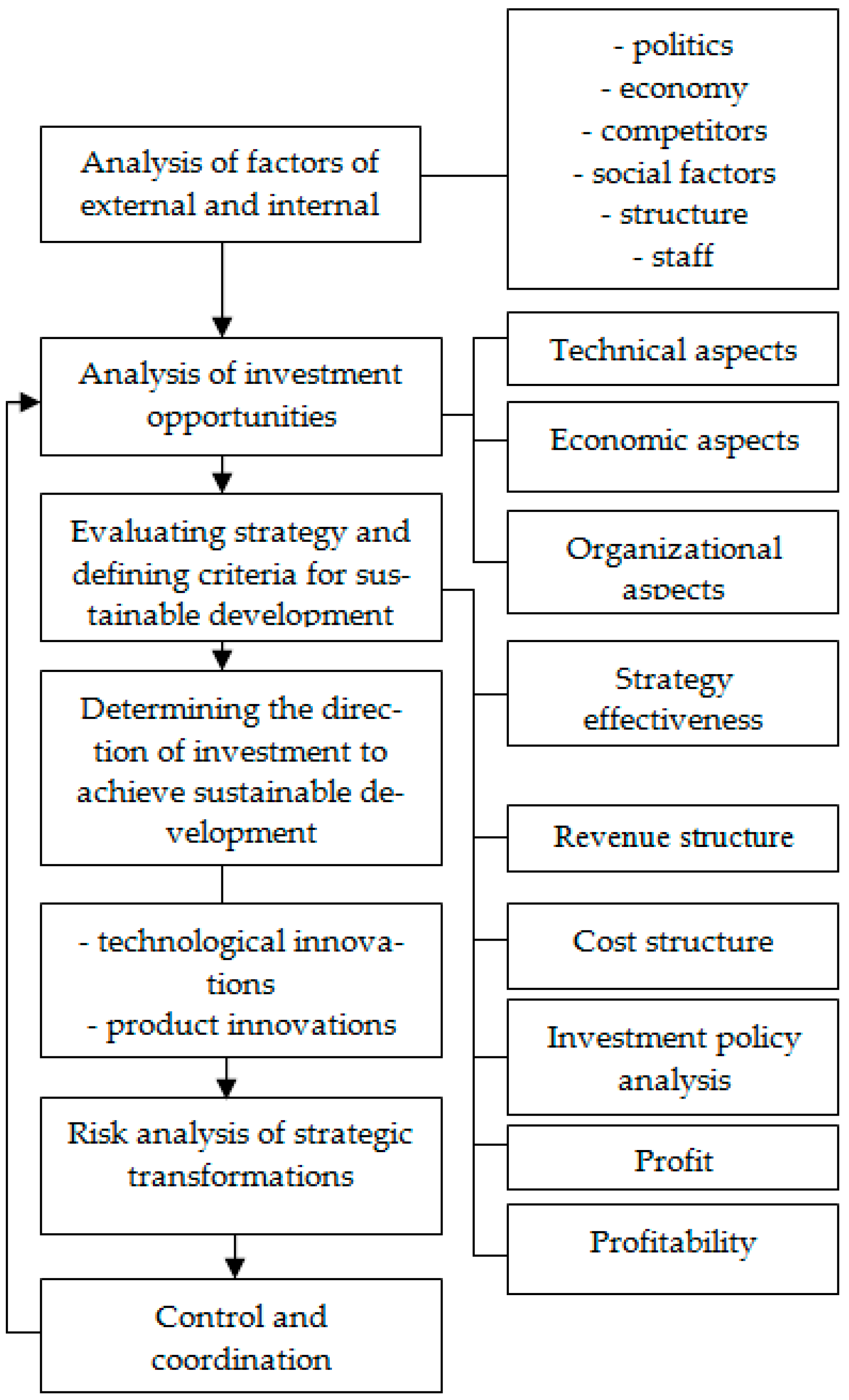
In order to improve strategic management, the strategy selection process, and the definition of investment opportunities, appropriate tools for assessing business risks were also proposed. At the same time, we relied on the theoretical studies of O.V. Rostova, S.G. Kalinin, V.I. Shiryaev, and A.I. Izotov. We are interested in research I.A. Becker, who singled out methods for risk assessment in the conditions of unsustainable economic development [
27]. Studies on the implementation of automated information systems in the process of risk assessment and the adjustment of the strategy implemented by the company allowed us to outline the prospects for further work to achieve the objectives of this study (F. Mousavifard, A. Ayoubi, M.S. Sanie, 2016) [
36].
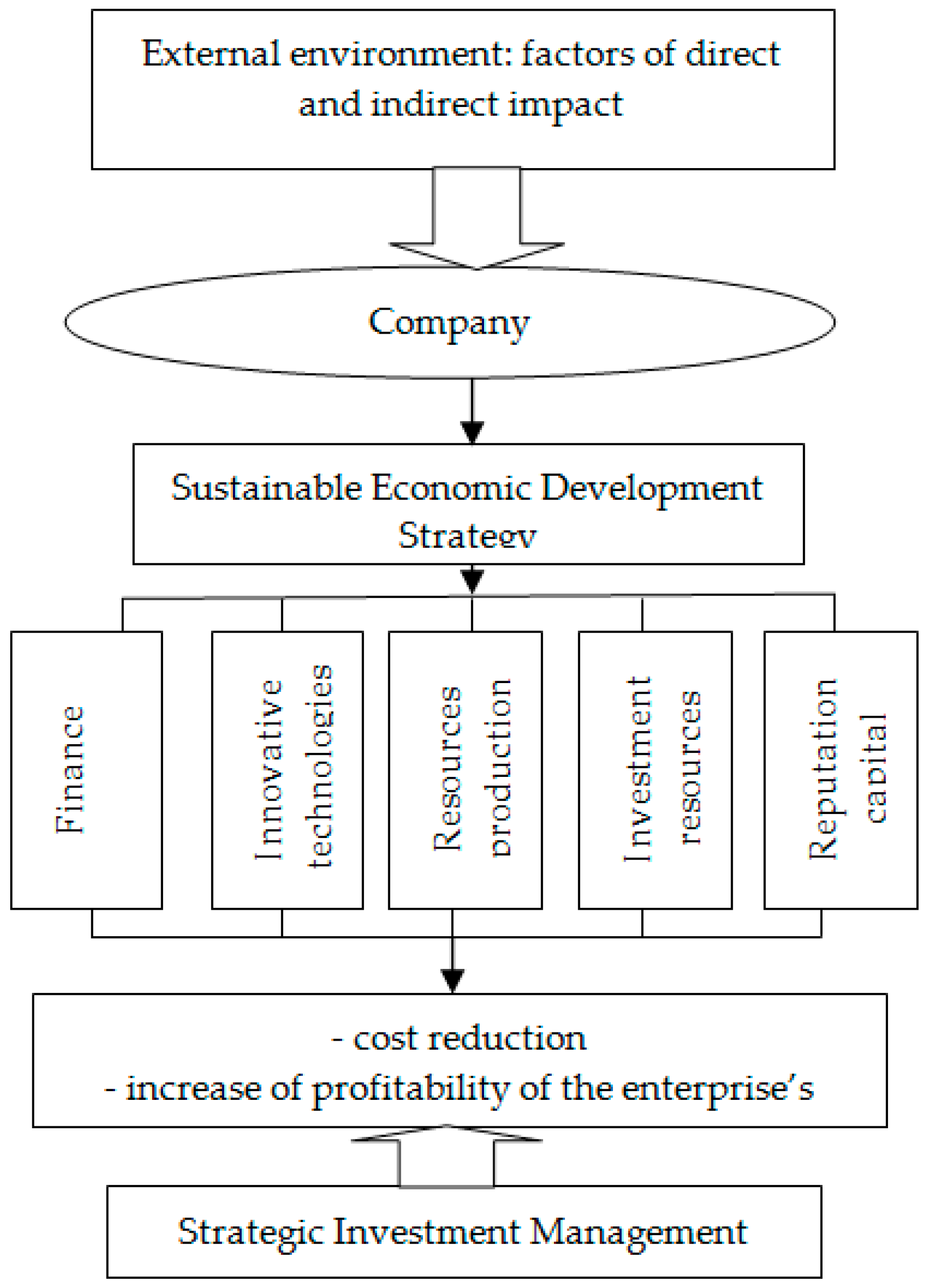
Thus, the management of an industrial enterprise needs to develop and comply with a certain mechanism for implementing the strategic management of the company’s investment activities. The main elements of the mechanism developed by us are presented in the following sections of the article, where graphic and economic-mathematical models are also proposed, which describe the corresponding control processes.
In this study, we relied on the principles of modeling the mechanisms of the stable development of an enterprise. The practice of enterprises in the Russian Federation, global trends in economic development, and the analysis of theoretical research require the most careful consideration of identifying, evaluating, and developing measures to achieve the leveling of the negative effects of objective and subjective factors that impede the sustainable development of a business.
Economic stability is understood as the internal state of a manufacturing entity, which is developed under the influence of many factors [
37,
38].
The analysis of scientific researches shows that, in general, the economic stability of an industrial enterprise is determined by three main factors: (1) economic growth as a determining factor, (2) economic balance (the state of the internal and external environment of an industrial enterprise), ensuring the functioning of enterprise subsystems, (3) the level of management that ensures the full development of the enterprise in the process of its activities (A.G. Chofreh et al., 2020) [
39].
As we said earlier, in many respects, the economic sustainability of Russian enterprises and their development depend on the introduction of innovative production technologies, which requires optimization of the strategic management model and improvement of investment policy [
40,
41]. The need for long-term investments involves the unification of small enterprises into larger companies, which will allow to pay closer attention to the economic aspects of activity, reduce costs, identify additional reserves and new sources of investment.
Similar conclusions are made by Korean researchers W. Park, C.S. Sung, and C.G. Byun in their article [
42].
In this paper, the main problem that needs to be addressed immediately is the improvement of the mechanism for the strategic management of the investment policy of companies whose sustainable development will inevitably be inhibited without ensuring the correct adaptation of the investment strategy to rapidly changing external and internal environment variables.
According to the theoretical principles of a systematic approach, any enterprise is a dynamic, open, variable, goal-oriented system [
4]. This approach means a systematic change in all components of the system, which ensures the creation of conditions for updating the state of the company, its internal components, and also allows the owners to form new quality characteristics of the updated system that are really necessary to ensure the competitiveness of the company. Sustainable development of an enterprise depends on the correct actions of the management, on the optimally structured mechanism for making managerial decisions based on the methods of economic and mathematical modeling.
Effectively, the ongoing development of enterprises in modern conditions is determined by the availability of affordable investments. The analysis of the practice of Russian companies indicates a close relationship between the value of investments and the quality of developing a development strategy, updating production assets, and reproducing the resource base of enterprises. The optimal investment policy, strategically well-managed investment project management in the conditions of overcoming the crisis allows achieving sustainable development of enterprises.
It is necessary to distinguish between such concepts as “stable development” and “sustainable development”. As a rule, sustainable development is understood to mean the ability of a certain system to maintain its current state, which characterizes the organization’s static position. Stable development means the development of a system over a certain period of time [
4]. The stable development of an organization is a process consisting of certain stages, specific steps, operations of an activity. Each stage involves the use of a clear algorithm of managerial decisions, a set of methods, tools, forms of management, accounting for macro and microeconomic environmental factors (R.S. Kaplan D.P. Norton, 2004) [
43].
During the research, the main static theories of the capital structure were considered: traditional approach, Miller-Modigliani theory, compromise approach. According to the traditional concept and approach of Miller-Modigliani, strategic decisions to the sources of financing should be made, focusing on the optimal capital structure. The compromise theory considers the optimal structure as a compromise between the tax preferences of debt financing and the costs of possible bankruptcy [
44].
The Miller-Modigliani model is proposed for a sustainable market, indicates that the value of the firm does not depend on the method of financing, it does not take into account the risks of bankruptcy and does not allow to make optimal decisions in crises, which must be taken into account in the situation of unstable development typical of many modern Russian companies [
45].
In their study, Ahmad and Murray confirm the close dependence between the sustainability of the enterprise and its investment opportunities. Their research once again proves the relevance of this topic [
46].
The compromise theory considers the possibility of maximizing the value of the firm. The company’s management is aimed at choosing the perfect capital structure based on the precise definition of the benefits and costs using the type, form, and size of the investment. The increase in costs when using external investments affects the increase in the level of financial instability of the business. At the same time, internal sources of financing and the use of potential opportunities of the enterprise are not sufficiently considered.
Taking into account the gaps in these concepts, the article focuses on the following proposals in the development of the methodology of strategic investment management and the formation of the capital structure of the company. Analysis of business practice shows the need for targeted application and inclusion in the management model of an industrial company tool to minimize the range of dividends of the owners of the company, adequate to the existing conditions of economic activity of the enterprise. The implementation of these proposals will create a fairly significant amount of insurance reserves of the company, reduce financial risks, determine the optimal range of investment, in which it is possible to ensure the sustainability of the company during the implementation of relevant business projects.
The most important factors affecting the stability of the enterprise include: accurate determination of possible production volumes, qualifications of employees, the technical base of the enterprise, optimal utilization of production assets.
In recent years, the main problem of inhibiting entrepreneurial activity is an insufficiently perfect mechanism and model of strategic management of investment activities of companies.
It is known that the firm’s capital structure includes resources allocated to the organization’s fixed assets, enterprise’s working capital, and assets that are used in the implementation of investment projects. When a company does not have enough financial resources, management begins to reduce the number of investments in working capital, which very quickly leads first to financial and then production problems of the enterprise
The management of most domestic enterprises is trying to solve these problems by the usual, many times tested, way, attracting new loans and credits. This, in turn, usually leads to additional costs, increases the total cost of projects, reduces efficiency, and negatively affects the sustainable development of companies.
The application of the proposed model will help to predict the likelihood of a risk of a decrease in the solvency of the enterprise, as well as the risk of changes in shareholder income. This will allow senior managers to use preventive management, which allows, in the face of variability of external and internal factors, on the one hand, to find the optimal ratio between changes in the stability of the enterprise and the level of investor income, and on the other hand, to minimize the likelihood of a potential decrease in the stability of the company. In addition, this model can be used as a part of both tactical and strategic management.
3.4. The Economic and Mathematical Model of Strategic Investment Management of a Company
The current socio-political and economic situation requires Russian enterprises to be able to adequately respond to changes in the conditions of economic activity, to make decisions in a regime of constraints, conflict environment, and increasing risks.
Minimizing the level of risk can be achieved by diversifying the forms of attracted capital, optimizing the structure of the sources of its formation, applying the best methods of analysis and accounting for financial risks.
The above allows you to achieve the financial equilibrium of an industrial company in the process of its development. This balance is determined primarily by the high level of economic stability, the solvency of the organization and is ensured by the formation of an optimal capital structure. In addition, financial equilibrium can be ensured by rationalization of the composition of the formed capital over the period of its attraction. It is desirable to achieve the creation of a mixed capital structure of the company, the optimal ratio of equity and debt, which allows you to minimize the weighted average cost of capital and maximize the market value of the company.
The main problem that arises in determining the optimal capital structure, as the practice of industrial enterprises shows, is the need to take into account a significant number of various factors that can directly or indirectly affect the efficiency of such a structure, creating risks for the sustainable development of companies [
48].
At present, the capital formation and capital management system has a large arsenal of advanced technologies and tools to minimize risks and solve the strategic goal of the organization’s development, namely, to increase the welfare of the owners based on the increase in the market value of the enterprise.
In Russia, business practices have evolved, in which the owners of enterprises, wishing to profitably use the available resources of the company, preferred to invest less in their own funds by attracting borrowed resources. At the same time, many companies tried to obtain loans abroad, looking for external borrowing. This led to an increase in debts of Russian enterprises. Gradually, the risk of bankruptcy increased, especially in cases where creditors demanded the return of large borrowed funds during the crisis period for the company, when there were not enough working capital to pay for creditors’ claims. This led to an increase in the cost of borrowed capital and increased financial risks.
Credit organizations prefer to cooperate with firms that have a large share, namely, equity. This implies that one of the main criteria affecting the capital structure and investment risks is the criterion for the ratio of borrowed and own funds. The dynamics of this indicator reflects the change in the dependence of the firm on external investors.
A significant increase in the share of borrowed funds may indicate an irrational structure of the company’s capital, considered as a negative trend, which indicates an increase in the company’s dependence on external loans.
An analysis of theoretical sources has shown that static theories of capital structure have gained greater popularity and serious distribution in business practices. It is these theories that justify the existence of an optimal financial structure of the company, which allows you to maximize the valuation of capital. Within the framework of these concepts, it is recommended to make decisions on the choice of investment sources, based on the optimal capital structure. When the optimal structure is specified precisely, then it is necessary to achieve the optimal proportions in the components of capital, which will eventually improve the management of the investment strategy of the enterprise and reduce financial risks. This article pays close attention to the possibility of Russian industrial companies using such a financial instrument as the range of accrual of dividends to owners of an enterprise, which showed itself quite positively in the process of forming investment policy at gold mining enterprises [
49].
Since the 1990s of the last century, the owners of Russian enterprises have preferred to receive income by increasing the size of dividends on the organization’s securities. Currently, in connection with the above problems in the field of industrial production, business owners are trying to use a variety of tools to improve the competitiveness of the enterprise.
Therefore, within the framework of optimization of the mechanism for developing and implementing the process of strategic management of the company’s investment activities, we can turn to the practice of using the range of reducing the number of dividends of the company’s main owners acceptable to the company and its owners. This tool was proposed by us to the management of a number of mining companies in Sakha-Yakutia, in particular, Zapadnaya Group of Companies, Vitim Group, which allowed them to optimize the investment policy and solve a number of important tasks. Specifically, we managed to do the following.
To determine the boundaries of the interval of investments in projects of the enterprise.
To accurately determine the number of investments, to achieve maximum profitability of financial resources.
To reduce the number of unreasonable investment costs.
The reduction of dividends will allow the company to create a fairly significant amount of insurance reserves of the company (Equation (1)).
where
is the insurance cash reserve formed from the company’s own financial reserves,
is the value of equity,
is the number of dividends that the company offers to its shareholders.
The investment strategy involves the use of the firm along with its own and borrowed capital. The practice of Russian business shows that enterprises often tried to attract borrowed funds more than was actually necessary. Thus, in a peculiar way, the management of industrial companies tried to insure the company against a possible shortage of funds, and credit institutions, on the contrary, sought to issue loans that would be really secured by the main assets of the enterprise (Equation (2)).
where
is the limited amount of borrowed capital offered by the bank,
are the company’s assets that can provide guarantees of the bank.
The practice of the activities of Russian companies shows that the formation of a reserve of borrowed funds, in most cases, costs the company much more, therefore the firm should take measures to reduce the number of loan resources borrowed from the bank (Equation (3)).
where
is the value of the reserve of financial assets, which is formed on the basis of loans from a credit institution,
is the maximum amount of investment attracted within the project.
Thus, the amount of the company’s safety stock () required for investment activity is obtained by adding up the capital (Equation (4)).
The optimal investment strategy, according to the proposed model of managing the strategic activities of an industrial company, provides for a clear definition of the boundaries of the investment project. In this case, the lower limit of the investment strategy range shows the minimum investment amount at which the project implemented by the company will be above the break-even point and will not lead to possible losses (Equation (5)).
where
is the amount of capital invested in a business project,
is the minimum value of capital invested in a business project,
is the effect on the investment project for the settlement period of the enterprise activity.
In this case, the upper limit of the investment range should be determined on the basis of the maximum allowable amount of funds attracted for the implementation of a business project (Equation (6)).
where
is the amount of capital that is necessary for the implementation of the main, basic activities of the company.
Thus, the optimal range of investment in which you can ensure the sustainability of the company during the implementation of relevant business projects should be in the following boundaries (Equation (7)).
where
C is the capital of the company, which the company attracts to provide financing for a business project.
Therefore, the implementation of the investment strategy by industrial enterprises of Russia involves the targeted use of a tool to reduce the range of dividend size of the company’s shareholders, which is adequate for the business environment of the enterprise in recent years. In this case, you should pay close attention to the risk assessment of the investment projects being implemented.
The Russian economy continues to be in a state of unsustainable development, new sanctions are emerging from the United States and the European Union countries, and there are serious fluctuations in the ruble exchange rate against the dollar. All this affects the investment policy of industrial enterprises, reduces the efficiency of operations, and contributes to increased risks.
We reviewed the theory and practice of risk management and came to the following. There are two main approaches to objectively measuring probable risk. This is a priori deduction, and a posteriori method, which provides a statistical analysis of available data. In a crisis economy, unsustainable business development, one of the main criteria for a strategic decision is the estimated cost, which can be calculated using the following formula (Equation (8)).
where
is estimated cost,
is the value of the
i-th recoil,
is the probability of the
i-th recoil, equal to the probability of the
i-th variant.
According to the presented formula, the estimated cost of the chosen strategy is considered as a weighted average cost, which uses the probabilities of return as weighting factors. If the strategy of an enterprise is used several times with similar options, one can expect to receive an average return that is equal to the estimated cost. Let us assume that it is necessary to evaluate several development strategies with the same value of investments. Then it is the estimated cost that will be the basic criterion in the process of comparing the available options for investment projects. It is logical that, most likely, the management of the company will choose a strategy that has a high estimated cost.
Often, enterprise management faces a situation where alternative strategies have virtually the same estimated value. In this case, you should use another criterion for choosing a strategy—the degree of risk. The degree of risk, in this case, should be understood as the degree of deviation of possible returns from the estimated cost of the company’s strategy [
50,
51,
52]. The farther from the average the actual return is, the riskier the chosen strategy will be. This means that in order to measure risk, it is necessary to make calculations of the scope, by which we mean the difference between the extreme values of the return on the value of the strategy being implemented.
Unfortunately, when calculating the scope, as shown by our research, only the extreme values of return on the project are identified, whereas the values that are between them are not taken into account. In order to more accurately calculate the possible risks, one should assume that there is a normal distribution of the probability of an event occurring and refer to the standard deviation σ, which shows the magnitude of the deviation of return from the estimated cost of the strategy. The standard deviation demonstrates the rigidity of the probability distribution. The higher the σ, the higher the risk for the project. To calculate the standard deviation, you must first determine the estimated cost (the weighted arithmetic average).
In order to obtain a number of deviations from the estimated cost of the project, it is necessary to subtract the estimated cost from each result obtained (Equation (9)).
where
is the deviation from the estimated cost of the project.
In order to determine the mean squared deviation (σ2), each deviation from the estimated cost should be squared. Then multiply it by the probability of the result associated with it (Equation (10)).
After the calculations, we take the square root of the variance (σ2) and obtain the standard deviation σ, (Equation (11)).
So, at present, industrial enterprises in Russia, in particular, mining companies, are simply obliged to apply the best methods for managing business risks. In this case, two aspects of investment risks should be taken into account. This is the risk of the degree of decrease in the solvency of the enterprise and the risk of changes in the income of the shareholders of the enterprise. If a company includes long-term debt in a firm’s capital structure, there is usually a very unpleasant situation when the company’s revenues have to be spent on debt servicing, that is, making payments to fixed assets and paying off interest on loans.
In recent years, there have been frequent cases when Russian industrial companies do not have enough money to service their debts, as a result of which a situation comes close to a crisis and even a bankruptcy situation. The more companies spend money to reduce debt, the less money left that can be sent to dividends to shareholders of the company.
Our proposed improved strategic management model and tools for reducing the range of dividend size for shareholders of an enterprise and taking into account risk probabilities should help define the organization’s strategy more accurately, take into account various aspects of business and financial risks, and prevent the situation of uncertainty and the possibility of the company becoming bankrupt. Of course, our recommendations, despite their practical implementation, are still far from perfect. However, they indicate the direction for further research in the field of strategic management of investment policies of industrial companies.
The economic and mathematical model in our study is presented on the basis of the integration of the economic development of the organization and the state of investment activity.
In the context of the war of sanctions, the transition to new conditions of world economic activity, changes in market factors and dynamic models should be applied and focused on solving macroeconomic problems. Our studies show that it is possible to successfully apply Leontief’s open dynamic model with one product, which means that gross investments are fully spent on fixed assets growth during a calendar year and depreciation charges.
In a discrete form, this relation is as follows (Equation (12)).
where
is the increase in fixed assets in
year,
is the model parameter,
is depreciation charges.
In the continuous form, the analog of this equation is as follows (Equation (13)):
Combining these equations, we obtain the model of one product in the discrete form (Equation (14)):
where
is output growth,
is production costs in the year
,
is non-productive consumption in the year
.
Our study showed that the macroeconomic model of a single product, based on the Leontiev’s and Loon’s models, was logical and easy to use and could be modified for most enterprises in Russia. This model provided that the company produced homogeneous products using homogeneous means of production and a single workforce. At any time during the implementation of the project, only a finite number of operations can be used. During the project, the technology of work remains constant [
35]. All this allows us to simplify the task of increasing the value of the enterprise and optimizing its investment policy.
The Loon’s model focuses management’s attention on two main areas: production activity is labor-intensive and capital-intensive [
20]. This restriction in no way reduces the quality of the simulation model, the adequacy of management decisions and does not upset the balance of labor and the distribution of capital in the organization. We assume that the production process is linear, and products are manufactured using labor resources and enterprise capital in fixed proportions.
Given the above, trying to achieve integration of the economic development of the company and investment policy, we proposed to link the methods, technologies of development and the capital structure of the company. We proposed to determine the level of output by the following formula (Equation (15)):
where
is the level of output,
is the sum of the fixed capital,
is the efficiency of the use of the company’s fixed capital.
The level of employment is determined by Equation (16):
where
is the level of employment of the company,
is gross capital investments.
The amount of fixed capital has been represented by the following expression (Equation (17)):
Equations (15)–(17) indicated a direct relationship between the structure of the enterprise’s finances and the way of production (Equation (18)):
where
is gross investment, and
is the final product.
It is usually assumed that an increase in equity should be due to retained earnings and acquired investment subsidies [
24]. It is assumed that the level of investment subsidies should be proportional to the level of gross investment. Then, to determine the cost of equity, we can propose a differential equation (Equation (19)):
where
is the profit tax,
is the volume of sales,
is labor compensation,
is the depreciation capital,
is the interest for the loan,
is the dividend, and
is the investment subsidy rate.
In addition to modeling the management of the company’s business processes, in order to achieve a steady increase in the value of the enterprise in the Russian Federation, it is necessary to create an insurance stock, the source of which is the company’s own and borrowed funds as part of strategic investment management. Directions for the use of own funds are investments, as well as dividends of the company’s shareholders.
In order to improve the strategic management of investment projects, we propose using a range of dividends for business owners that is acceptable to the enterprise and shareholders, which will amount to a certain value of the company’s insurance stock, its reserve—
(Equation (20)):
where
is the reserve of funds, which is formed from the company’s own funds,
is the size of the firm’s equity,
is the number of dividends that the firm pays to shareholders.
The safety stock allows the company to reduce the number of credit reserves and increase the efficiency of the enterprise.