Do Ecosystem Service Value Increase and Environmental Quality Improve due to Large–Scale Ecological Water Conveyance in an Arid Region of China?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
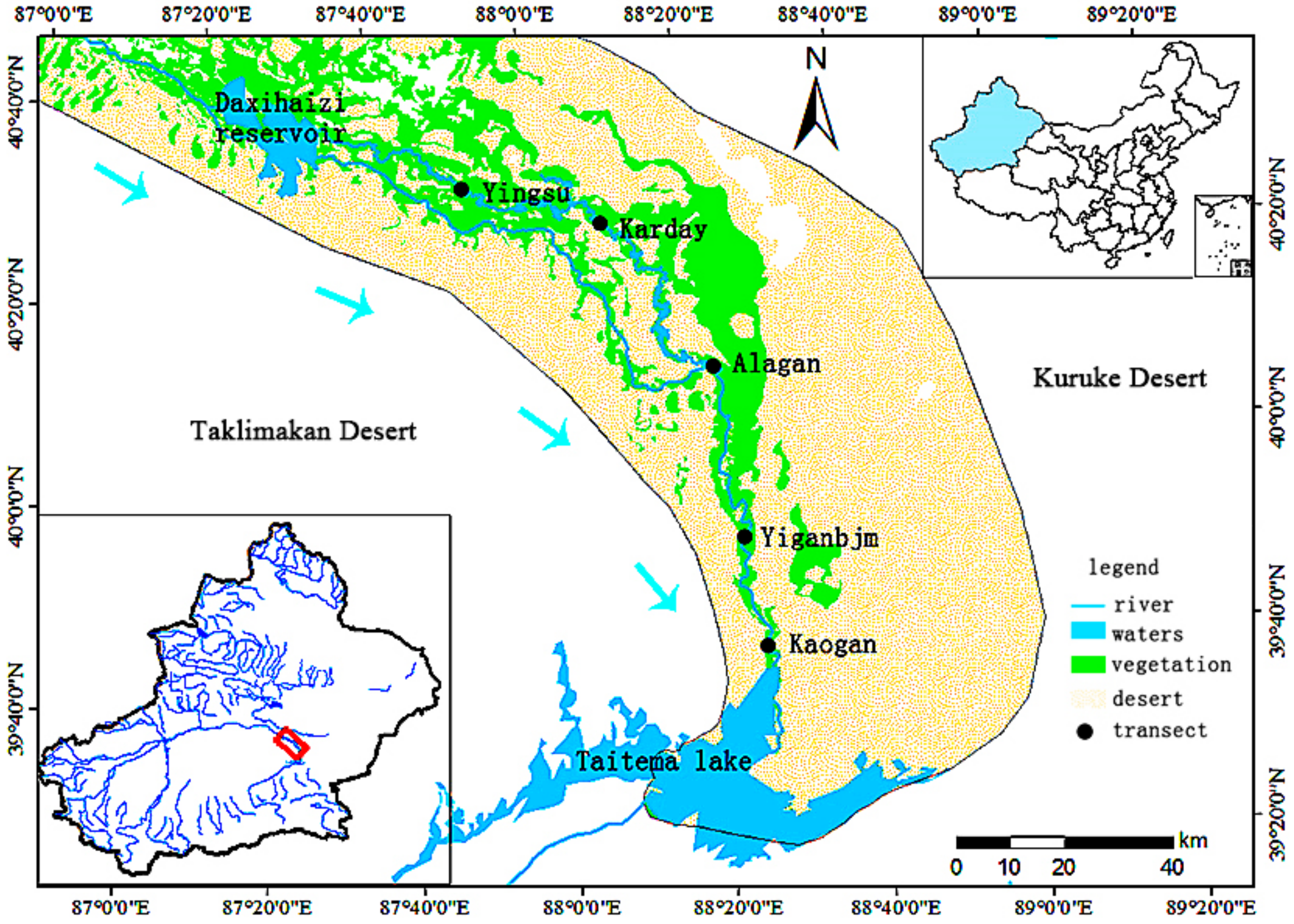
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Image Interpretation and Classification
2.2.2. Analysis Methods of Land Coverage
2.2.3. Methods for Evaluating Ecosystem Service Values
2.3. Calculation of the Ecological Environment Index (EI)
3. Results and Analysis
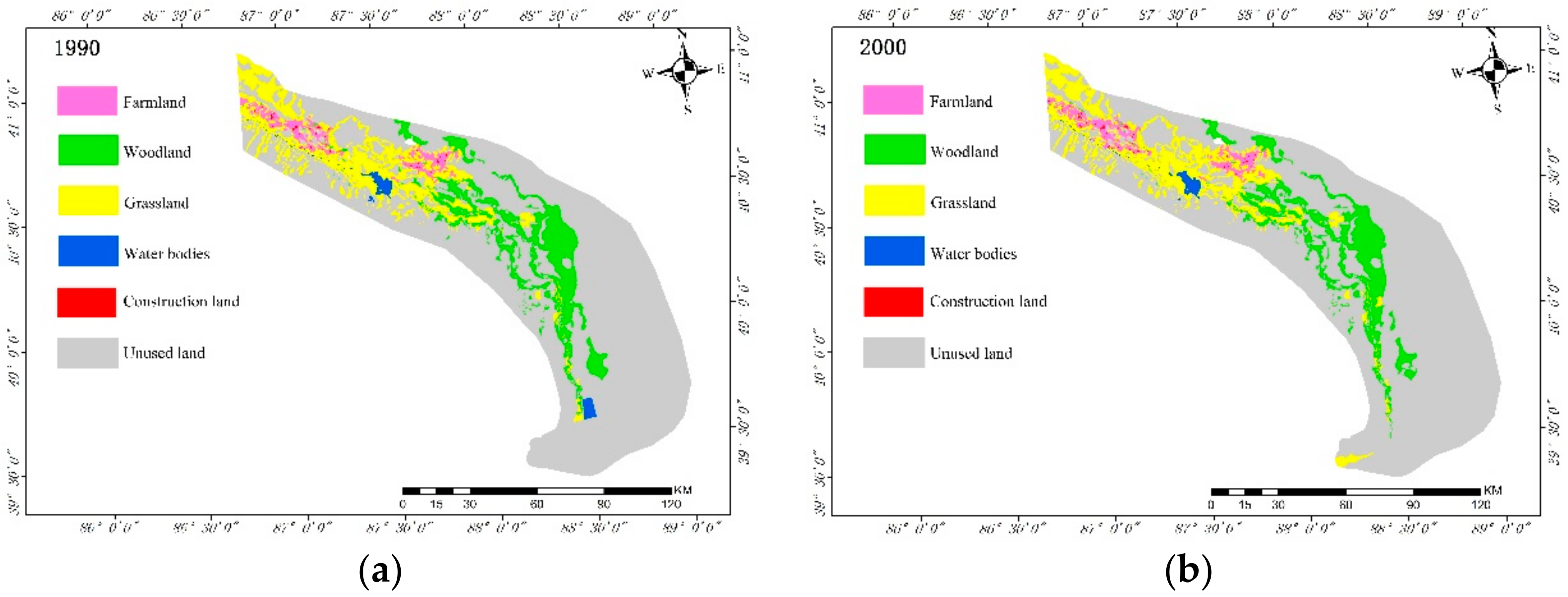
3.1. Changes in Land-Use Types Before and After Ecological Water Conveyance
3.2. Changes in the Ecosystem Service Value Before and After Ecological Water Conveyance
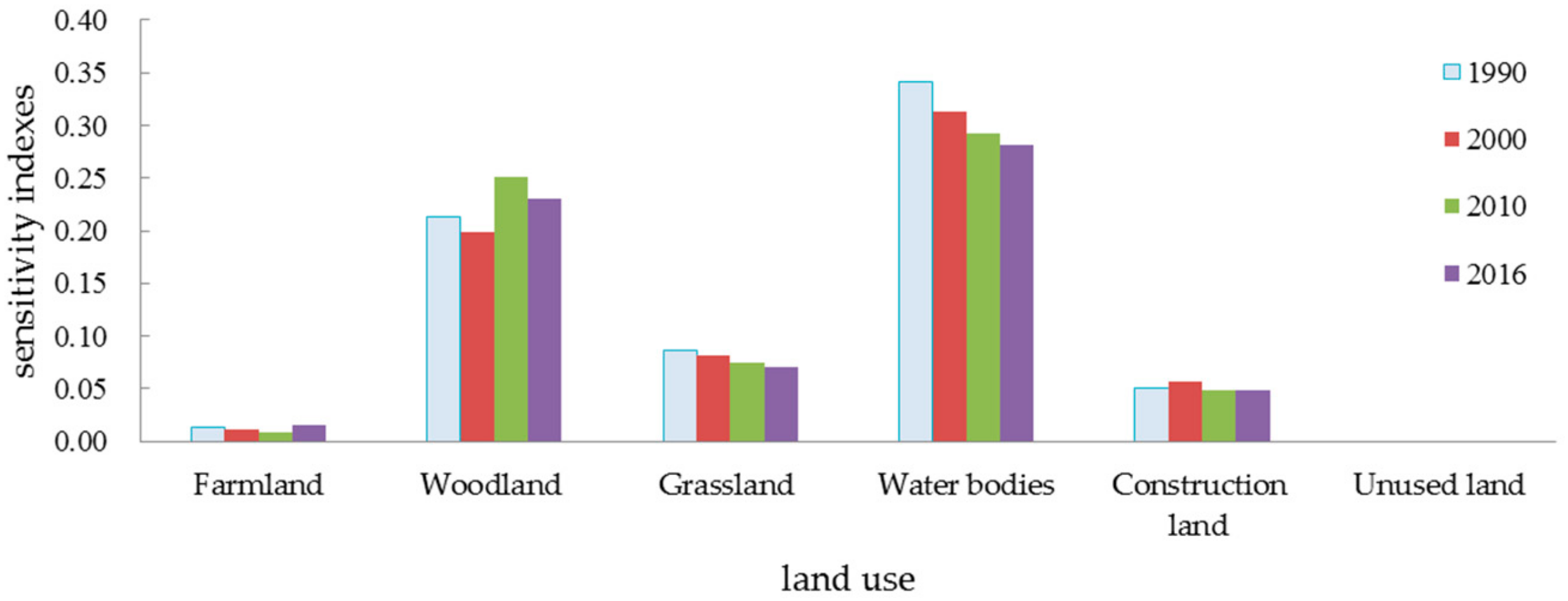
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Ecosystem Services
3.4. Characteristics of Ecological Environment in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River
4. Discussion
4.1. Reasons for a Change in Ecosystem Service Value in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River
4.2. Measures for Environmental Quality Restoration in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River
4.3. Some Recommendations for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muntadas, A.; Silvia, D.J.; Demestre, M. Integrating the provision of ecosystem services and trawl fisheries for the management of the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ola, U.; Eva, L. Rendering global change problematic: The constitutive effects of Earth System research in the IGBP and the IHDP. Environ. Politics 2014, 23, 339–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hansjürgens, B.; Droste, N.; Tockner, K. Neglected Values of Major Water Engineering Projects: Ecosystem Services, Social Impacts, and Economic Valuation. Society-Water-Technology; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Grilli, G.; Ciolli, M.; Garegnani, G.; Geri, F.; Sacchelli, S.; Poljanec, A.; Vettorato, D.; Paletto, A. A method to assess the economic impacts of forest biomass use on ecosystem services in a National Park. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 98, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.E.; Chen, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Parajuli, P. Dynamics of ecosystem service values in response to landscape pattern changes from 1995 to 2005 in Guangzhou, Southern China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2015, 13, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vallet, A.; Locatelli, B.; Levrel, H.; Brenes, P.C.; Lmbach, P.; Estraba, C.N.; Manlay, R.; Oszwald, J. Dynamics of Ecosystem Services during Forest Transitions in Reventazón, Costa Rica. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harclerode, M.A.; Lal, P.; Miller, M.E. Quantifying Global Impacts to Society from the Consumption of Natural Resources during Environmental Remediation Activities. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfeddine, L.; Al–Malk, A.Y.; Korbi, K.A. Is it possible to improve environmental quality without reducing economic growth: Evidence from the Qatar economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreen, S.; Anwar, S.; Ozturk, I. Financial stability, energy consumption and environmental quality: Evidence from South Asian economies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 1105–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.R.; Dutta, P.B. Tourism development, environmental pollution and economic growth: A theoretical analysis. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2017, 27, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, W. How much are nature’s services worth. Science 1977, 197, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Service: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems. Pac. Conserve. Biol. 1997, 6, 220–221. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimental, D.; Wilson, C.; Gomez, M.C.; Huang, R.; Dwen, P.; Flack, J.; Tran, Q.; Saltman, T.; Cliff, B. Economic and environmental benefits of biodiversity. BioScience 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Chai, P.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Gu, M.; Lu, H.; Shen, P.; Jin, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Association of PM2.5 pollution with the pattern of human activity: A case study of a developed city in eastern China. Air Repair 2016, 66, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, Z.R.; Preiss, P.; Van, G.T.; Dingenen, R.; Huijbregts, M. Regionalized life cycle impact assessment of air pollution on the global scale: Damage to human health and vegetation. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 134, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Darbalaeva, D.A.; Mikheeva, A.S. The Baikal Basin as a Transboundary Ecological and Economic System. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2015, 03, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mcintyre, O. Benefit–sharing and upstream/downstream cooperation for ecological protection of transboundary waters: Opportunities for China as an upstream state. Water Int. 2015, 40, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Deng, X.Z.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, D.D. Projections of Future Land Use in Bangladesh under the Background of Baseline, Ecological Protection and Economic Development. Sustainability 2017, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houska, M.L. The conversion of cost and benefit criteria in the TOPSIS method. Int. J. Appl. Decis. Sci. 2012, 5, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bian, X.M.; Cao, L.; Xu, Z.S. The Evaluation Method of Surface Roughness Degree for Long–Term Operating Conductors Based on Gray Value Matrix. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 30, 1641–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svärd, H. Interior value extrapolation: A new method for stress evaluation during topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2015, 51, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.X.; Liu, M.; Li, L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Metro Project Bidding Risk Based on Entropy Value Method and Fuzzy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Technology and Management Science, Tianjin, China, 27–28 March 2015; Qingdao Technological University: Qingdao, China, 2015; pp. 1170–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B. Evaluation Method of R&D Investment Value of Intelligent Manufacturing Enterprise Based on Growth Option. Procedia Eng. 2017, 174, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.X. Luxury Brand Value Evaluation Method Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. International Conference on Robots & Intelligent System. IEEE Comput. Soc. 2017, 1, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.G.; Xu, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.M.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Zhou, K.F.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.H.; Liu, J.Z.; Wang, T. Response of groundwater chemistry to water deliveries in the lower reaches of Tarim River, Northwest China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhu, X.M.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, H.L.; Zhang, H.F.; Chen, Y.P. Analysis on the ecological benefits of the stream water conveyance to the dried–up river of the lower reaches of Tarim River, China. Sci. China 2004, 47, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.G.; Mi, A.J.; Wu, Y.G. Application of Tetra–Water Balance Model in Utilization and Protection of Water Resources in the Bosten Lake Basin. Res. Sci. 2005, 27, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.F.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Si, J.H.; Xi, H.Y.; Chen, L.J. Soil water and salinity in response to water deliveries and the relationship with plant growth at the lower reaches of Heihe River, Northwestern China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 7009–7017. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.J.; Yang, P.N.; Zhou, H.Y.; Xu, H.L. Water Conversion and Strategy of Ecological Water Conveyance in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 717–726. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Feng, Q.; Li, J. Environmental changes after ecological water conveyance in the lower reaches of Heihe River, northwest China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Yu, J.J.; Qiao, M.Y.; Yang, H.W. Effects of eco–water transfer on changes of vegetation in the lower Heihe River basin. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 42, 757–765. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.W.; Wang, G.S. Reconstruction of historic spatial pattern for water resources utilization in the Heihe River basin. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1977–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.L.; Bao, C. The Coupling Model of Water–Ecology–Economy Coordinated Development and Its Application in Heihe River Basin. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2004, 59, 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, Y.N.; Pan, B.R. Distribution and floristics of desert plant communities in the lower reaches of Tarim River, southern Xinjiang, People’s Republic of China. J. Arid Environ. 2005, 63, 772–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Xu, C.C.; Ye, Z.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhu, C.G.; Ma, X.D. Effects of ecological water conveyance on groundwater dynamics and riparian vegetation in the lower reaches of Tarim River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyimu, M.; Halik, Ü.; Kurban, A. Estimation of water consumption of riparian forest in the lower reaches of Tarim River, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.M.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.G.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.Q. Assessing the effect of EWDP on vegetation restoration by remote sensing in the lower reaches of Tarim River. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bao, A.M.; Wang, S.F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Duan, Y.B. Eco–environmental change in the lower Tarim River under the influence of intermittent water transport. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Xu, H.L.; Ling, H.B.; Fu, J.Y. Analysis on Land Use Changes and Ecosystem Services Value in the Area along the Tarim River. J. Desert Res. 2013, 33, 1912–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Z.F.; Hu, R.D.; Lin, S.Q. Spatial econometric analysis of Kuznets’ relationship between environmental quality and economic growth. Geogr. Res. 2009, 28, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, A.H.; Li, W.H.; Chen, Y.N. The Factors Affecting the Stem Water Potential of Tamarix ramosissima in the Extremely Arid Regions. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 800, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Song, Y.D.; Chen, Y.N. The Natural Vegetation Responses to the Groundwater Change Resulting from Ecological Water Conveyances to the Lower Tarim River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Tang, D.S. The influence of water conveyances on restoration of vegetation to the lower reaches of Tarim River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.H.; Xu, C.C.; Ye, Z.X.; Chen, Y.P. Desert riparian vegetation and groundwater in the lower reaches of the Tarim River basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.; Li, S.C. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Res. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.S. Preliminary Research on Construction and Application of Ecosystem Services Value Evaluation System on the Landscape Scale in Arid Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Xinjiang University, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.C.; Shi, X.J.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Wan, H.Y. Comparison on methods and results of urban ecological system service value in Lanzhou City. China Popul. Res. Environ. 2013, 23, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.L.; Wang, W. Modification of Costanza’s model of valuing ecosystem services and its application in China. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 5, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, H.L.; Du, Q.; Ling, H.B.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X.F. Change of Ecological Conditions in the Mainstream Area of the Tarim River based on RS and GIS during the Period of 1990–2010. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 416–422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.M.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.; Meng, L.H. Analysis of Socio–Economic Factors Related to Ecosystem Degradation in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River in the Last 50 Years. Res. Sci. 2008, 30, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, H.H. Response of the accumulation of proline in the bodies of Populus euphratica to the change of groundwater level at the lower reaches of Tarim River. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Li, J.M. The water transfer effects on agricultural development in the lower Tarim River, Xinjiang of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.B.; Zhang, P.; Guo, B.; Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Deng, X.Y. Negative feedback adjustment challenges reconstruction study from tree rings: A study case of response of Populus euphratica to river discontinuous flow and ecological water conveyance. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, W.H.; Ma, J.X. Changes of Value of Ecosystem Services and its Driving Forces in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 260–261, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.G.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, W.H.; Ma, J.X.; Fu, A.H. Effects of groundwater decline on Populus euphratica at hyper–arid regions: The lower reaches of the Tarim River in Xinjiang, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 3326–3337. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, M.; Xu, H.L.; Ren, M. Primary Study on the Rational Time of Ecological Water Conveyance to Lower Reaches of the Tarim River. Arid Land Res. 2012, 29, 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Bao, A.M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Jiang, L.L. Eco–environmental Change in the Main Stream Area of the Tarim River before and after Implementing the Comprehensive Management Project. Arid Zone Res. 2016, 33, 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Teusner, A.; Blandin, G.; Le, C.P. Augmenting water supply by combined desalination/water recycling methods: An economic assessment. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limburg, K.E.; O’Neill, R.V.; Costanza, R.; Farber, S. Complex systems and valuation. Ecol. Econ. 2002, 41, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, I.; Berkhout, B.W.; Ismail, Z. Thermal Change and the Dynamics of Multi–Host Parasite Life Cycles in Aquatic Ecosystems. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Yu, L.; Li, C.C.; Wang, J.; Liang, L.; Li, X.C.; Ji, L.Y.; Bai, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z.L. New research paradigm for global land cover mapping. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 20, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignet, D. The impacts of pollution and exposure pathways on home values: A stated preference analysis. Ecol. Econ. 2012, 82, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konarska, K.M.; Sutton, P.C.; Castellon, M. Evaluating scale dependence of ecosystem service valuation: A comparison of NOAA–AVHRR and Landsat TM datasets. Ecol. Econ. 2004, 41, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.X.; Zhang, X.S. The value of chinese ecological system. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, K.G. Changes in the value of ecosystem services along a rural–urban gradient: A case study of Greater Manchester, UK. Landsc. Urb. Plan. 2013, 109, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Service Function | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water Bodies | Construction Land | Unused Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Production | 1.00 | 0.80 | 1.24 | 4.74 | 0.76 | 0.00 |
| Raw Material Production | 0.00 | 2.56 | 0.00 | 1.96 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Gas Regulation | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 2.46 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Climate Regulation | 0.00 | 2.65 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Hydrologic Regulation | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.00 |
| Waste Disposal | 0.00 | 1.61 | 1.61 | 0.08 | 12.31 | 0.00 |
| Soil Conservation | 0.00 | 8.65 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Maintenance of Biodiversity | 0.70 | 0.33 | 0.89 | 5.63 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Provide Aesthetic Landscape | 0.00 | 1.26 | 0.04 | 26.94 | 4.26 | 0.00 |
| Total | 1.70 | 17.95 | 4.53 | 42.24 | 17.47 | 0.00 |
| Normalization Constant | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| Biological abundance index | 400.62 |
| Vegetation cover index | 355.24 |
| River length | 46.63 |
| Lake area | 17.88 |
| Water resources | 61.42 |
| Land degradation index | 146.33 |
| SO2 | 0.06 |
| COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) | 0.33 |
| Solid waste | 0.77 |
| Type of Land-Use | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | 337.39 | 355.02 | 458.38 | 510.50 |
| Woodland | 1493.93 | 1404.67 | 1350.29 | 1280.89 |
| Grassland | 1704.77 | 1704.84 | 557.36 | 1568.18 |
| Water bodies | 119.23 | 72.44 | 1404.53 | 410.83 |
| Constrution land | 13.86 | 14.84 | 15.29 | 17.71 |
| Unused land | 9828.96 | 9946.35 | 9718.2 | 9715.84 |
| Type of Land-Use | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2016 | 1990–2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variation of Area (km2) | Change Rate (%) | Variation of Area (km2) | Change Rate (%) | Variation of Area (km2) | Change Rate (%) | Variation of Area (km2) | Change Rate (%) | |
| Farmland | 17.63 | 5.23 | 103.36 | 29.11 | 52.12 | 11.37 | 173.11 | 51.31 |
| Woodland | −89.25 | −5.97 | −54.38 | −3.87 | −69.40 | −5.14 | −213.03 | −14.26 |
| Grassland | 0.07 | 0.004 | −1147.48 | −67.31 | 1010.82 | 181.36 | −136.59 | −8.01 |
| Water Bodies | −46.79 | −39.24 | 1332.09 | 1838.89 | −993.70 | −70.75 | 291.60 | 244.57 |
| Constrution Land | 0.98 | 7.071 | 0.45 | 3.03 | 2.42 | 15.86 | 3.85 | 27.81 |
| Unused Land | 117.39 | 1.19 | −228.15 | −2.29 | −2.36 | −0.024 | −113.12 | −1.15 |
| Year | Types of Land-Use | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water Bodies | Construction Land | Unused Land | |
| 1990 | 0.72 | 12.00 | 2.79 | 28.98 | 13.22 | 0 |
| 2000 | 0.70 | 11.11 | 2.60 | 26.77 | 12.11 | 0 |
| 2010 | 0.87 | 12.98 | 3.07 | 31.18 | 13.95 | 0 |
| 2016 | 0.94 | 13.99 | 3.56 | 33.41 | 15.62 | 0 |
| Type of Land-Use | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2016 | 1990–2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variation of Value (108 Yuan) | Change Rate (%) | Variation of Value (108 Yuan) | Change Rate (%) | Variation of Value (108 Yuan) | Change Rate (%) | Variation of Value (108 Yuan) | Change Rate (%) | |
| Farmland | 0.008 | 2.48 | 0.21 | 61.29 | 0.11 | 20.25 | 0.33 | 98.76 |
| Woodland | −3.16 | −12.95 | 2.62 | 12.32 | 0.54 | 2.26 | −0.003 | −0.01 |
| Grassland | −0.43 | −6.70 | −3.71 | −61.40 | 5.28 | 226.53 | 1.14 | 17.60 |
| Water bodies | −2.07 | −43.88 | 57.02 | 2158.33 | −40.96 | −68.66 | 13.99 | 297.25 |
| Construction land | −0.004 | −1.64 | 0.045 | 18.33 | 0.09 | 30.05 | 0.13 | 51.37 |
| Unused land | 0.008 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Service Function | Total Value of Ecological Service Value (108 Dollar) | Change Rate (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2016 | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2016 | 1990–2016 | |
| Food Production | 0.97 | 1.06 | 3.60 | 2.48 | 9.87 | 239.15 | −31.25 | 156.42 |
| Raw Material Production | 0.93 | 1.01 | 2.51 | 1.74 | 8.37 | 149.92 | −30.69 | 87.81 |
| Gas regulation | 0.55 | 0.39 | 3.95 | 1.61 | −29.21 | 911.98 | −59.24 | 192.33 |
| Climate Regulation | 4.24 | 3.64 | 4.13 | 4.16 | −14.18 | 13.55 | 0.73 | −1.83 |
| Hydrologic Regulation | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.73 | 0.49 | −16.82 | 190.49 | −31.83 | 65 |
| Waste Disposal | 5.69 | 5.07 | 3.77 | 6.50 | −10.96 | −25.55 | 72.35 | 14.24 |
| Soil Conservation | 14.82 | 12.78 | 13.42 | 13.90 | −13.73 | 4.96 | 3.57 | −6.22 |
| Maintenance of Biodiversity | 3.12 | 2.57 | 10.26 | 5.33 | −17.45 | 298.84 | −48.07 | 71.01 |
| Provide Aesthetic Landscape | 5.57 | 3.76 | 44.34 | 15.72 | −32.60 | 1079.72 | −64.54 | 181.96 |
| Total | 36.18 | 30.52 | 86.70 | 51.76 | −15.63 | 184.04 | −40.30 | 43.06 |
| Grade | Excellent | Good | Commonly | Poor | Very Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range of EI | EI ≥ 75 | 55 ≤ EI < 75 | 35 ≤ EI < 55 | 20 ≤ EI < 35 | EI < 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Ling, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, T. Do Ecosystem Service Value Increase and Environmental Quality Improve due to Large–Scale Ecological Water Conveyance in an Arid Region of China? Sustainability 2019, 11, 6586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236586
Wang X, Peng S, Ling H, Xu H, Ma T. Do Ecosystem Service Value Increase and Environmental Quality Improve due to Large–Scale Ecological Water Conveyance in an Arid Region of China? Sustainability. 2019; 11(23):6586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236586
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiyi, Shuzhen Peng, Hongbo Ling, Hailiang Xu, and Tingting Ma. 2019. "Do Ecosystem Service Value Increase and Environmental Quality Improve due to Large–Scale Ecological Water Conveyance in an Arid Region of China?" Sustainability 11, no. 23: 6586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236586
APA StyleWang, X., Peng, S., Ling, H., Xu, H., & Ma, T. (2019). Do Ecosystem Service Value Increase and Environmental Quality Improve due to Large–Scale Ecological Water Conveyance in an Arid Region of China? Sustainability, 11(23), 6586. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236586





