Abstract
In contrast to the efforts made to develop functioning fishways for upstream migrants, the need for effective downstream migration facilities has long been underestimated. The challenge of developing well-performing bypasses for downstream migrants involves attracting the fish to the entrance and transporting them quickly and unharmed into the tailrace. In this study, the acceptance of different opening sizes of a surface bypass as well as the injuries which fish experience during the passage were examined. Overall bypass acceptance was low compared to the turbine passage. There was no significant difference in the number of downstream moving fish between the small and the large bypass openings. Across all fish species, no immediate mortality was detected. Severe injuries such as amputations or bruises were only rarely detected and at low intensity. Scale losses, tears and hemorrhages in the fins and dermal lesions at the body were the most common injuries, and significant species-specific differences were detected. To increase bypass efficiency, it would likely be useful to offer an alternative bottom bypass in addition to the existing surface bypass. The bypass injury potential could be further reduced by structural improvements at the bypass, such as covering protruding components.
1. Introduction
In order to meet the rising global energy demand and to increase the percentage of renewable energies, there is a huge global effort to push ahead the expansion of hydropower [1,2]. The construction of dams and hydropower plants can result in reduced serial continuity and habitat changes in streams, mainly from the fragmentation and the change in the hydrological conditions of the affected river systems [3,4,5]. As a result, upstream and downstream fish migrations are often impaired or even impossible [6,7], which can lead to population declines or extinctions, particularly in migratory fish populations [8,9].
In contrast to the efforts made to develop functioning fishways for upstream migrants, the need for effective facilities for downstream migration has long been underestimated [10,11]. During their downstream migration, fish usually tend to follow the main current [12] and are therefore often directed to the turbine inlet at many hydropower plants. Since the turbine passage is generally considered the route that most likely harms fish, it is important to develop strategies to bypass or protect fish at power plants to minimize turbine entrainment and associated fish mortality [13,14,15]. One option would be to use less harmful turbine types, which reduce the injury potential and increase the survival rate [13,16]. Alternatively, physical (e.g., vertical/horizontal bar screens) or behavioural barriers (e.g., louvers, sound/light/electrical screens) are often installed upstream of the turbine inlet to prevent fish from swimming through the turbine and guiding them via alternative corridors into the tailrace [17,18]. Such alternative corridors include spillways, undershot sluice gates, surface and bottom bypasses and nature-like fishways [7,19,20]. The challenge of developing functioning bypasses for downstream migrants involves attracting the fish to the entrance and transporting them quickly and unharmed into the tailrace [15]. Critical points that need to be considered for a successful downstream passage include adequate dimensioning of the bypass, the location of the bypass (top, middle, bottom), proper hydraulic conditions at the entrance and a low fish injury risk of the bypass itself [12,18,21]. However, even state-of-the-art downstream migration corridors can cause unexpected problems such as poor fish attraction, inappropriate location of entrances or an increased risk of injury [22,23]. Therefore, it is important to provide alternative corridors and to examine these in light of their functionality with a properly designed monitoring [24], analogous to evidence-based concepts in stream restoration (e.g., [25]). There are already several studies dealing with the acceptance of various downstream migration corridors (e.g., [26,27]), but studies that also investigate the injury potential of such alternative corridors in a standardized way with a broad range of fish species are rare.
In this study, the acceptance of differently sized openings of a surface bypass, installed in the flap gate of a movable power-plant as well as the injury potential to which fish are exposed during the passage of this route were examined. Specifically, we hypothesized that (i) fish can find the surface bypass and especially large fish that do not fit through the fish protection screen of the turbine are successfully guided to the tailrace, (ii) the percentage of inflow used for surface bypass attraction is proportional to the percentage of downstream moving fish and (iii) fish do not get injured while passing the surface bypass and sliding down to the tailrace.
2. Materials and Methods
The animal experiments in this study were carried out following national animal care laws and regulations, and all procedures were approved for appropriate animal care by the ethics commission of the Bavarian government (permit number ROB–55.2–2532.Vet_02–15–31). Discomfort or pain of the fish was minimized according to European standards [28] and national guidelines for the use of aquatic animals in scientific experiments [29].
2.1. Study Site
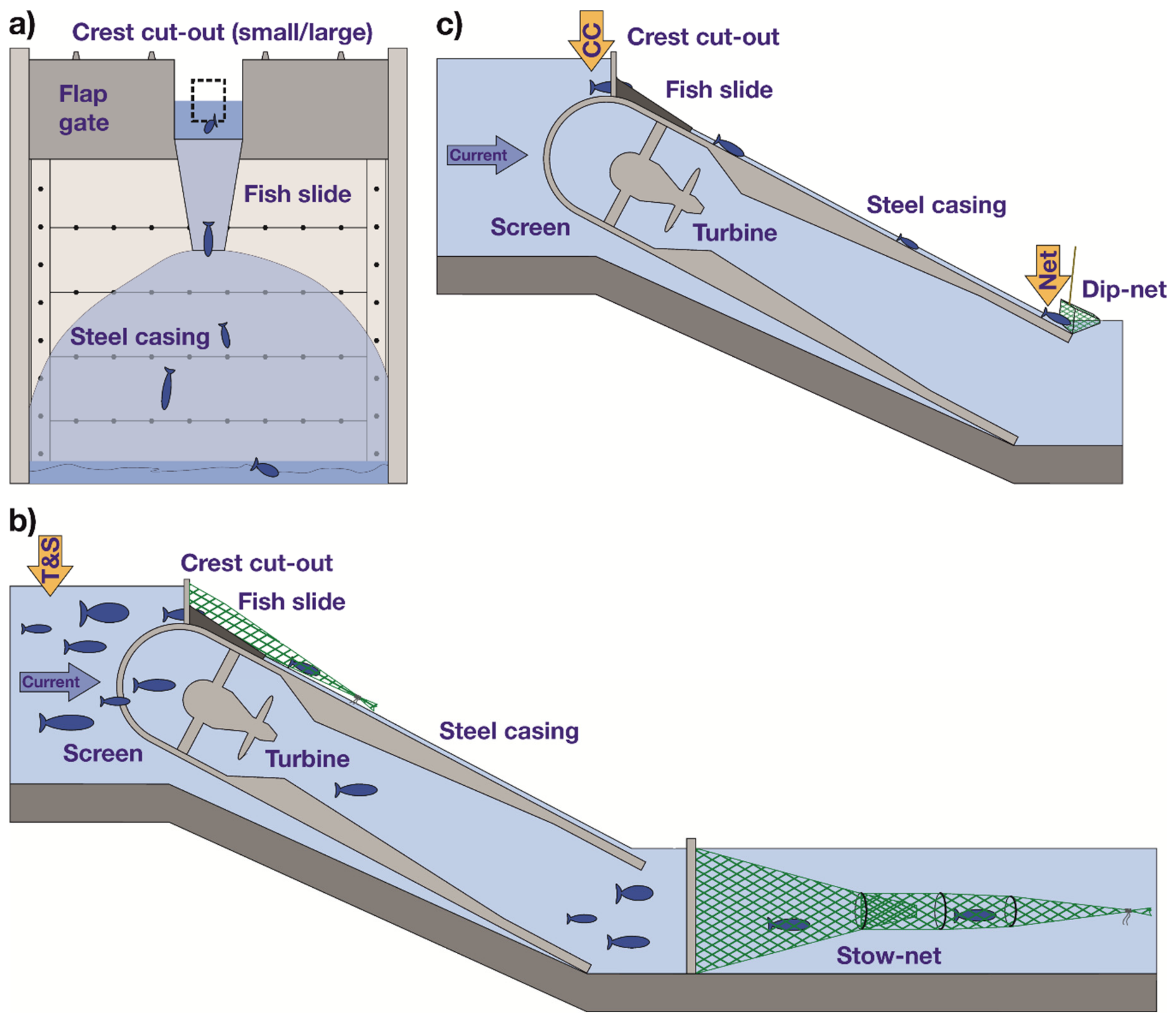
The study was carried out at an innovative movable run-of-the-river hydropower plant in Bavaria, Germany. The power plant is located at the dam of an artificial reservoir (approx. 100 ha) at the river Schwarzach near the city of Rötz (N 49.3396, E 12.4799). The 4.8 m high dam separates the site into a main reservoir and a pre-storage basin. The moveable power plant was installed in winter 2016/2017. It is equipped with a four-bladed Kaplan turbine with 190 kW of installed power at a head of 5.0 m and a maximum flow of 4.5 m³/s (diameter = 1.0 m, drive = 333 rpm). The Kaplan turbine, which is housed in a swiveling steel casing, can be lifted by a hydraulic device, in order to allow sediment transport and downstream movement of aquatic organisms during high flow conditions. As a fish protection device, a round screen with a bar spacing of 20 mm, is installed in front of the 2.64 m wide turbine inlet. To pass the power plant downstream, surface-orientated fish can swim through a permanently opened crest cut-out (CC) in the middle of the flap gate and slide on top of the steel casing into the tailrace (fish slide; Figure 1).
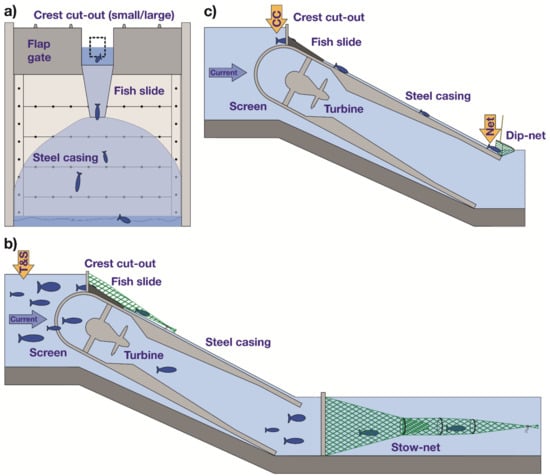
Figure 1.
Schematic of the hydropower plant and experimental design. Orange arrows = release point of hatchery-reared fish; blue arrows = flow direction; T&S = upstream of the fish protection screen, CC = crest cut-out, Net = entrance of the dip-net. (a) View of the hydropower plant from the tailrace. The dotted rectangle symbolizes the small CC. (b) Schematic cross-section of the movable power plant. To assess the acceptance of different sized CCs, fish were caught with stow-nets at the fish slide and at the turbine outlet. (c) For the assessment of potential injuries, fish of the treatments CC and Net were caught with a dip-net at the bottom of the steel casing.
2.2. Experimental Design
To assess the acceptance and the fish injury risk of the downstream migration corridor CC, eight hatchery-reared fish species were used, which were transported from the fish hatcheries to the hydropower plant one day before the experiments started. Fish were transferred into rectangular tanks (300 cm × 70 cm × 70 cm, Aquacultur Fischtechnik GmbH, Nienburg, Germany) after being adapted to reservoir temperature and water chemistry. Fresh water from the tailrace was permanently supplied to the tanks by a submersible motor pump (Easy-Mix-U20, Aquacultur Fischtechnik GmbH, Nienburg, Germany).
2.2.1. Acceptance of Different Sized Crest Cut-Outs
In April 2018, two different opening sizes of the CC installed in the middle of the flap gate were comparatively examined for their acceptance as a downstream migration corridor. The mean flow rate through the small CC (27.6 cm x 36.0 cm) is approx. 26 L/s (0.6% of the turbine flow) at a water depth of 9.0 cm in the CC and a maximum turbine flow rate of 4.5 m³/s. About 160 L/s (3.6% of the turbine flow) flow through the large CC (59.0 cm × 71.0 cm) at a water depth of 18.5 cm in the CC and a maximum turbine flow rate of 4.5 m³/s. The different opening sizes were the two construction options provided by the power plant operator. The small opening was designed according to the operator’s ideal conception (low loss of turbine discharge) and the larger opening complies with the minimum requirements according to Ebel [30]. There were almost no variations in physical and chemical water parameters, which were measured three times a day during the investigation period of the small and the large CC (Table 1).

Table 1.
Arithmetic mean, standard deviation (±), minimum and maximum values (in parentheses) for the measured physical and chemical parameters during the investigation period of the small and the large crest cut-out. Discharge = total discharge through turbine and crest cut-out. Current speed was measured in the headrace channel.
In order to determine the downstream movement rate through the turbine corridor and the two different sized CCs, a total of 6,888 individuals of the fish species grayling (Thymallus thymallus, L.), brown trout (Salmo trutta, L.) and barbel (Barbus barbus, L.; Table 2) were released directly into the headrace channel of the hydropower plant. Fish were transferred into a 40 L bucket and carefully stocked about 5 m upstream of the power plant over a period of four consecutive days, while both the small and the large CC were installed at the same position in the flap gate on two days each. Fish passing through the turbine and the CC were caught with knotless stow-nets of decreasing mesh size and narrowing diameter, applying 1 h emptying intervals (8 am–6 pm) to minimize the catch-related damage to fish [31]. The rectangular opening of the stow-nets was knotted to a metal frame with each mesh, allowing the fixation in u-profiles and covering 100% of the flow-through. To recover the fish, the cod-end was opened, the trapped fish were transferred into a large water-filled bin and supplied with oxygen. Each individual was identified to species level and total length was measured.

Table 2.
Total number of test fish (N total), number of caught fish in the crest cut-out (N caught CC) and in the turbine (N caught TU), arithmetic mean (AM), standard deviation (SD), minimum (MIN) and maximum (MAX) of the total fish length (TL) in cm as well as ratio of the percentage of captured fish to the percentage of inflow for the crest cut-out (N CC (%)/inflow CC (%)) and the turbine (N TU (%)/inflow TU (%)) during the investigation period of the small and the large crest cut-out.
2.2.2. Fish Injury Risk of the Downstream Migration Corridor Crest Cut-Out
For the assessment of potential injuries that fish may experience during the passage of the CC, 660 individuals of eight hatchery-reared fish species (grayling, brown trout, barbel, eel (Anguilla anguilla, L.), perch (Perca fluviatilis, L.), Danube salmon (Hucho hucho, L.), nase (Chondrostoma nasus, L.), roach (Rutilus rutilus, L.); Table 3) were tested in a standardized experiment in which individuals were introduced at specific parts of the power plant. The eight fish species tested were chosen according to their ecological relevance in Bavarian streams and covered different morphological types [31,32].

Table 3.
List of species and number (N) of fish used to assess the fish injury risk of the downstream migration corridor crest cut-out as well as arithmetic mean (AM), minimum (MIN) and maximum (MAX) of the total length (TL) in cm.
To quantify fish damage caused by the passage of the CC (fish pass through the opening of the bypass and subsequently slide on top of the steel casing into the tailrace), hatchery-reared fish were used. To account for injuries related to aquaculture, transportation, handling and catching them with the net, two different treatments were applied (CC, Net; Figure 1). For the treatment CC, each individual was investigated for its pre-damage first (injuries related to aquaculture, transportation and other handling such as touching and taking them out of the fish tanks) and then introduced directly in front of the entrance of the CC. After passing the CC and the fish slide, every fish was caught individually with a large dip-net at the bottom part of the Kaplan turbine steel casing and then re-evaluated for its injuries by the same person. For the treatment Net, the pre-damage was also evaluated as described above and afterwards every fish was released individually directly into the dip-net and then immediately re-evaluated for its injuries by the same person. Fish injury assessment was carried out as described in Mueller et al. [32] using a detailed protocol comprising 86 combinations of injury types at different body parts as well as five general fish health criteria. The intensity of a single injury type can vary between 0 (not injured) and 5 (severely injured). The number of injuries per individual fish can reach a maximum of 86, and the injury intensity a maximum of 430 (meaning each injury can be found at each body part with the highest intensity level 5). Staff was intensively trained on the use of the protocol and the scoring system. The same evaluation procedure was followed for all species and treatments. After evaluation, fish were kept in fish tanks with fresh water and oxygen supply for 96 h. to account for potential delayed mortality.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
To examine the acceptance of the two different sized bypass openings, recapture rates, downstream movement rates per hour and the ratio of the percentage of captured fish passing the surface bypass to the percentage of inflow used for surface bypass attraction were calculated.
For the injury risk assessment of the surface bypass, the number of injuries and the injury intensity of every individual fish were calculated (cf., [32]). To compare the number of injuries and the injury intensity between treatments and the total lengths of fish passing the turbine or the different sized CCs, univariate statistics were used (software R 3.4.1, [33]). Normality was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk-test and homogeneity of variances was checked using Levene’s-test. Exclusively non-parametric tests were used since normality and homogeneity of variances did not apply to any of the data (Mann-Whitney-U-tests for comparison of two groups, Kruskal-Wallis-tests and Bonferroni-corrected post-hoc pairwise Mann-Whitney-U-tests for comparison of more than two groups).
To test for relations between the total lengths of specimens from the tested fish species with the number and intensity of the injuries, mixed effects models were applied using the function “lmer” in R [33] package “lme4” [34]. Response variables were number of injuries and injury intensity. Total length and fish species were set as fixed effects with treatment as a random effect. For model selection, the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) based on the restricted maximum likelihood (REML) was chosen. The lower the AIC value, the better the fit of the model [35]. A similar amount of deviation of the residuals from the predicted values indicates homoscedasticity. Wald chi-square tests were performed to obtain p-values for predictor variables of the best fitting model.
To analyze differences in fish injury patterns between treatments and between species, a multivariate approach was used. For all multivariate analyses, raw data on fish injury intensity were transformed into a resemblance matrix containing similarity values for each comparison of samples (fish individuals). As similarity measure, the Bray-Curtis coefficient was used [36]. If variables among samples happened to be entirely zero, a zero-adjusted Bray-Curtis coefficient, including a virtual dummy variable being one for all objects, was used as suggested by Clarke et al. [37].
Differences between multivariate injury patterns of different treatments were analyzed using one-way analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) based on Bray-Curtis similarities [38].
To identify the most common and steadily occurring injury patterns in the different treatments, a one-way similarity percentage analysis (SIMPER, [39]) was carried out to determine the average intensity of injuries and the contribution to the between group-dissimilarity between treatments. All multivariate analyses were carried out using the statistic software PRIMER v7 (PRIMER-e, Massey University, Auckland, NZ). For all statistical analyses, significance was accepted at p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Acceptance of Different Sized Crest Cut-Outs
Out of a total of 6888 fish from three species that were released directly upstream of the hydropower plant, 2236 (32%) individuals were recaptured. Most of the non-recaptured fish presumably remained in the headrace, swam upstream or moved downstream after completion of the investigation. The recapture rate was highest for the grayling with 49%, followed by the barbel with 42% and the brown trout with 16%. During the investigation period of the small CC, a total of 92.6% of the recaptured individuals passed the 20 mm screen and the turbine to reach the tailrace, and 7.4% of the fish moved downstream via the surface bypass (Table 2). The percentage of fish using the small CC as downstream migration corridor was highest for brown trout at 25.6%. Only 0.7% of the barbels and 5.7% of the graylings moved downstream via the small CC. During the investigation period of the large CC, 90.3% of the recaptured individuals used the turbine corridor for downstream movement and 9.7% the surface bypass. More brown trout (32.6%) and graylings (8.0%) used the large CC than the small CC as downstream migration corridor. However, no barbels moved downstream via the large CC (Table 2). There was no significant difference in the number of downstream moving fish per hour between the small CC and the large CC (Mann-Whitney-U-test: W = 85; p > 0.05). The ratio of the percentage of captured fish passing the surface bypass to the percentage of inflow used for surface bypass attraction was almost five times higher for the small CC than for the large CC (Table 2).
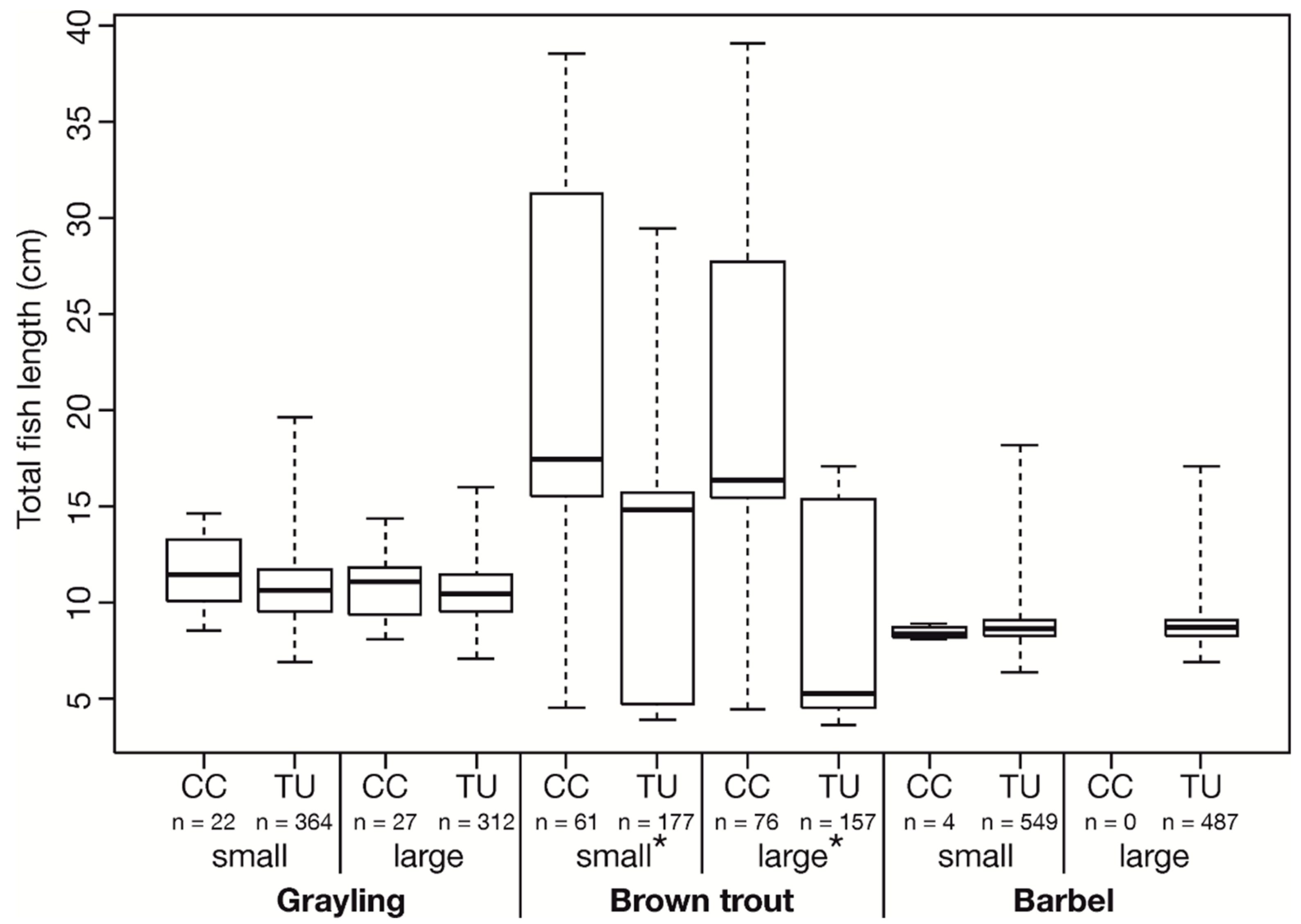
The entire range of fish sizes of the examined grayling (maximum total length 19.6 cm) and barbel (maximum total length 18.2 cm) was able to swim through the vertical round screen of the turbine inlet with a bar spacing of 20 mm. Regarding the brown trout, only individuals up to a total length of 29.4 cm passed the screen and moved downstream through the turbine. According to Ebel [30] the examined species have a relative body width (= width/total length) of about 0.1 and only individuals with a total length of less than 20 cm should be able to pass the 20 mm vertical screen. Larger brown trout were exclusively detected in the surface bypass (Figure 2).
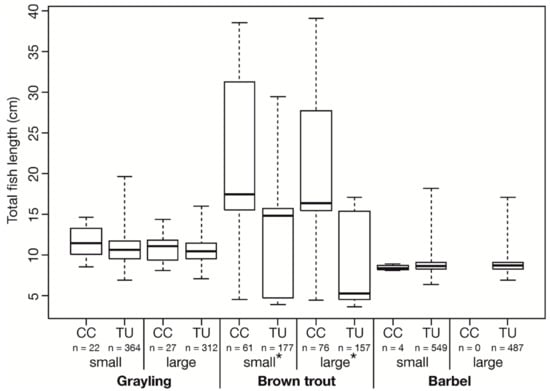
Figure 2.
Total fish length (cm) of the three test species after the passage of the crest cut-out (CC) and the turbine (TU) during the investigation period of the small and the large CC. Box: 25% quantile, median, 75% quantile; whisker: minimum, maximum values. Asterisks indicate significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in the total length between CC and TU; n = number of individuals.
3.2. Fish Injury Risk of the Downstream Migration Corridor Crest Cut-Out
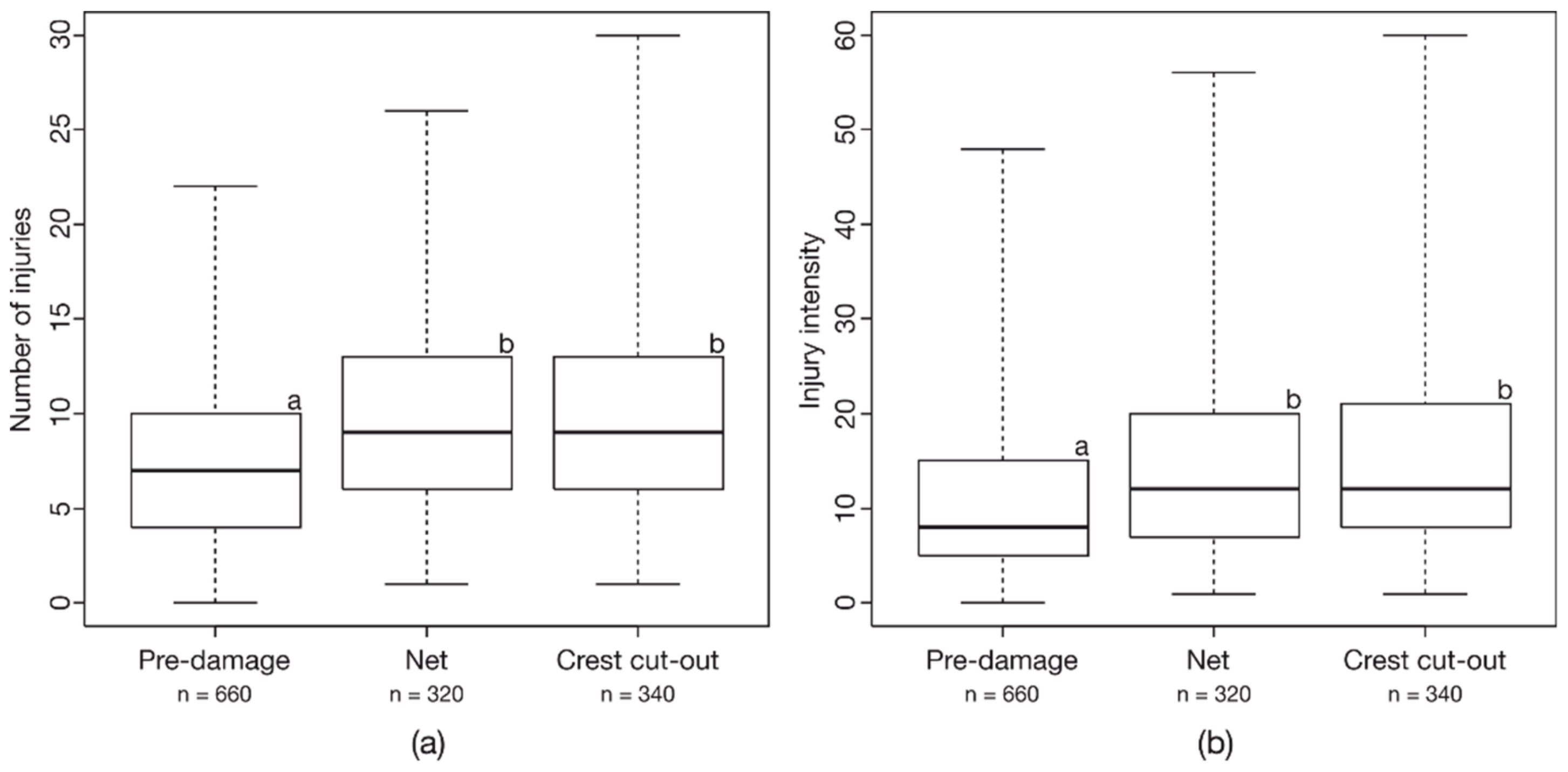
Across all fish species, no immediate mortality was detected in the treatments CC and Net. After an observation period of 96 h, two individuals of roach from the treatment CC and one brown trout from the treatment Net died. Scale losses, tears and hemorrhages in the fins and dermal lesions at the body were the most common injuries of all fish species studied. Severe injuries such as amputations or bruises were only rarely detected and at low intensity. There was no significant difference in the injury patterns between the pre-damage conditions and the treatments Net and CC (ANOSIM: Global R = 0.01, p > 0.05) across all fish species. However, injuries like scale loss, tears in the fins, hemorrhages in the head and fins as well as dermal lesions on the head and body occurred at a higher intensity in the treatment CC than in the pre-damage conditions. These injuries were also detected more frequently in the treatment Net than in the associated pre-damage conditions. Both the number (Kruskal-Wallis-test: X² = 76.8, df = 2, p < 0.001) and the intensity (Kruskal-Wallis-test: X² = 64.2, df = 2, p < 0.001) of all recorded injuries were significantly higher in the treatments CC (post-hoc Mann-Whitney-U-test; number of injuries: p < 0.001; injury intensity: p < 0.001) and Net (post-hoc Mann-Whitney-U-test; number of injuries: p < 0.001; injury intensity: p < 0.001) than in the pre-damage conditions. There was no significant difference in the number and intensity of the injuries between the treatments CC and Net (Figure 3). In addition to the effects of the different treatments, the number of injuries and the injury intensity were significantly affected by the total fish length and the species tested (Table 4). Larger fish usually had more injuries with a slightly higher injury intensity than smaller fish.
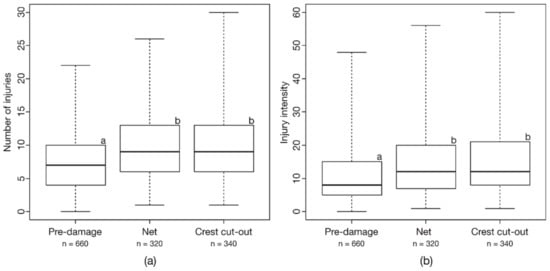
Figure 3.
(a) Number of injuries and (b) injury intensity in the different treatments to assess the fish injury risk of the downstream migration corridor crest cut-out. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) according to Bonferroni-corrected post-hoc pairwise Mann-Whitney-U-tests. Box: 25% quantile, median, 75% quantile; whisker: minimum, maximum values; n = number of individuals.

Table 4.
Test statistics of the best fitting mixed effects models with number of injuries and injury intensity as response variables and treatment as random effect. AIC = Akaike Information Criterion, Residuals = Deviations of the observed values from the predicted values, χ2 = chi-square value, SD = standard deviation, asterisks indicate significance: * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001.
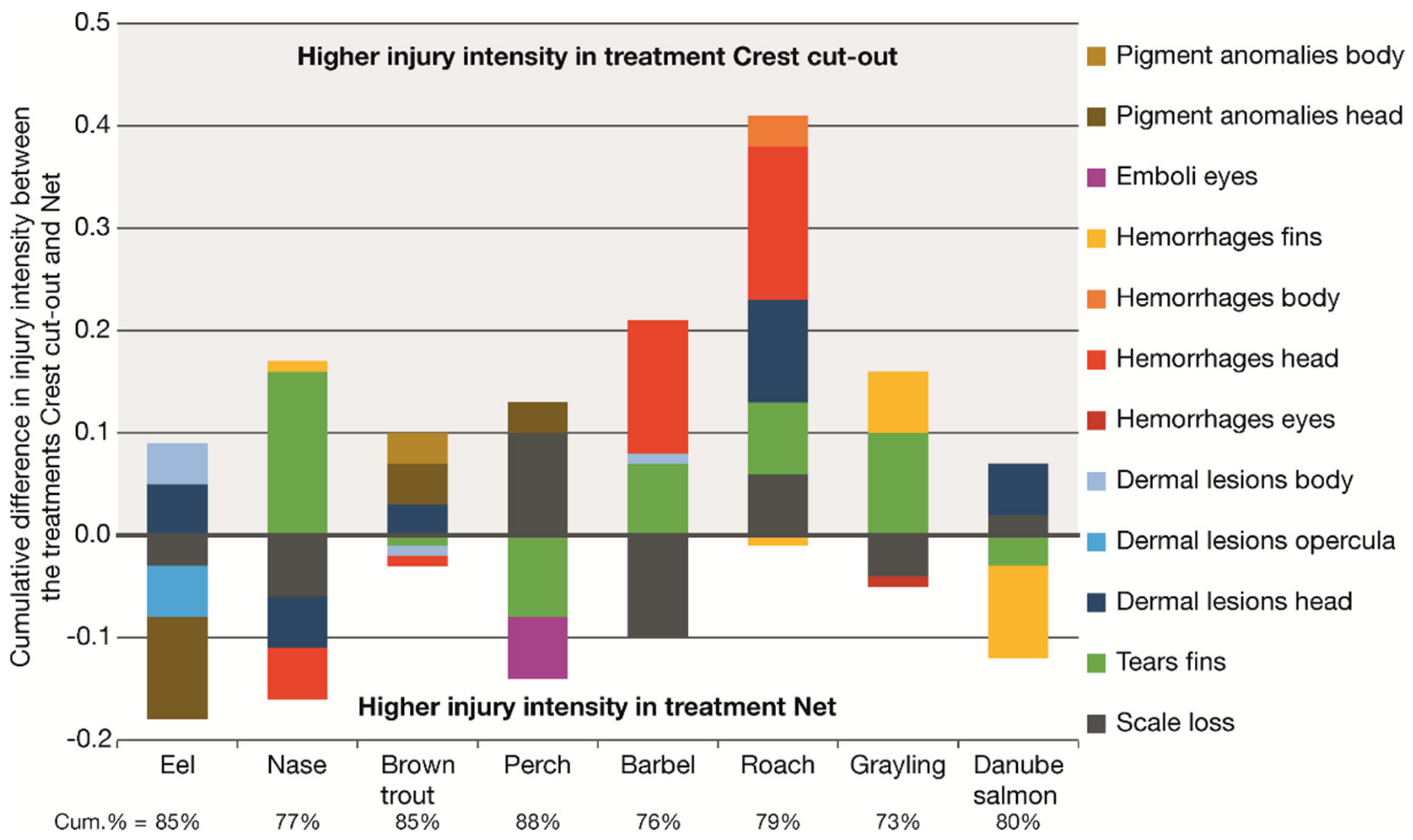
The species-specific consideration of the injury patterns, which were caused by the passage of the CC, revealed significant species-specific differences (Figure 4). Eels had on average a higher intensity of dermal lesions on head and body in the treatment CC than in the treatment Net, in which more pigment anomalies and dermal lesions on the opercula were detected. The species nase had on average more tears in the fins in the treatment CC than in the treatment Net, in which scale losses, dermal lesions on the head and hemorrhages of the head occurred more frequently. For brown trout, especially pigment anomalies and dermal lesions on the head were more frequent in the treatment CC than in the treatment Net. For perch, in particular tears in the fins and emboli in the eyes were detected more frequently in the treatment Net than in the treatment CC, in which primarily the intensity of scale losses was higher. In the treatment CC, barbels had mainly more intense hemorrhages in the head and tears in the fins. However, scale losses were more frequently detected in the treatment Net. For the roach, the differences in the injury patterns between the treatment CC and Net were most pronounced. In particular, hemorrhages of the head and body, dermal lesions on the head, tears in the fins and scale losses were more common after the passage of the CC than in the treatment Net. Typical injuries of the grayling, which were found at a higher intensity after the passage of the CC than in the treatment Net, were tears and hemorrhages of the fins. Danube salmon had on average more scale losses and dermal lesions on the head in the treatment CC than in the treatment Net, in which tears and hemorrhages of the fins occurred more frequently (Figure 4).
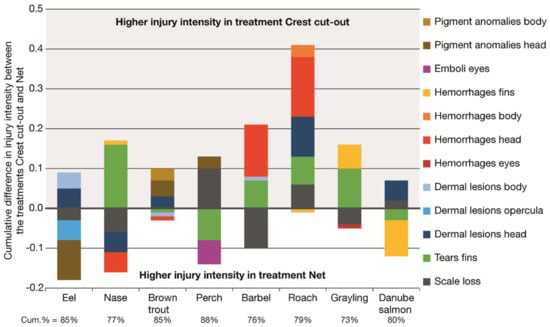
Figure 4.
Absolute differences in the injury intensity for each test species between the treatments Crest cut-out and Net for injuries with a contribution to between-group dissimilarity (Crest cut-out vs. Net) larger than 5% according to similarity percentage analyses (SIMPER). The size of the bar components indicates the delta in intensity values for the respective injury type. Positive values indicate injuries with a larger intensity in the treatment Crest cut-out, negative values indicate injuries with a larger intensity in the treatment Net. Cum.% = cumulative contribution to between-group dissimilarity according to SIMPER. Contribution to between-group dissimilarity of single injury types ranged between 5% and 47%. For the number of replicates within each species and treatment see Table 3.
4. Discussion
There are many studies, in particular for salmon smolts and eels, in which the efficiency of surface bypasses as well as the behavior and migrations in the forebay have been investigated by hydroacoustics and radio-telemetry (e.g., [20,26,27]). However, effects of downstream passage via bypasses on fish health are often only modeled or roughly estimated (e.g., [40,41]). The novelty of the present study is that both the acceptance of two differently sized openings of a surface bypass and detailed injury patterns of different fish species passing that surface bypass were evaluated for eight fish species using a detailed fish injury assessment protocol. The findings suggest that the CC can principally provide a safe downstream passage if carefully constructed (e.g., avoiding open screw heads on the fish slide), but it still needs to be improved concerning dimensioning and position to contribute to a more sustainable hydropower development.
In this study, hatchery-reared fish were used. The advantage is that both the number of test fish and the extent of pre-damage are well known, allowing a clear link between observed post-passage injury patterns against pre-treatment conditions and a reference that accounts for catch-related damage. The assessment of the injury risk of a downstream migration corridor for naturally migrating fish is only possible to a limited extent, if the health condition of the fish before the downstream passage is not well known. We are aware that hatchery-reared fish may not fully represent the natural migratory behavior of fish. Therefore, quantitative studies of bypass efficiency or downstream migration corridor selection should be conducted also using naturally migrating fish. Furthermore, naturally migrating fish can provide important information on seasonal and diurnal variations of downstream fish movement [7,42,43] as well as on fish behavior in front of hydropower plants [19,44].
4.1. Acceptance of Different Sized Crest Cut-Outs
The percentage of fish that moved downstream via the large CC was only slightly higher than via the small CC. However, the ratio of the percentage of captured fish to the percentage of inflow was significantly larger in the small CC than in the large CC (Table 2). It is possible that even the large CC is still too small and fish are prevented from the downstream passage by the dimensions (width and water depth) of the bypass. Larinier and Travade [18], for example, recommended a minimum width and depth of 40 cm for a surface bypass for salmon smolts. Although the bypass discharge of 3.6% in the large CC should be sufficient, the effectiveness of the bypass depends not only on the discharge carried but also on the hydraulic conditions at the entrance [14,18]. Particularly, when the current is very turbulent and fast-changing, fish can be scared away [12].
The different recapture rates of the test species in the downstream migration corridors turbine and CC can be attributed to species-specific behavior. The percentage of brown trout using the CC was considerably higher than for grayling and barbel. This is not surprising since brown trout are known to migrate near the surface [45] and thus have a higher chance of finding the CC. The CC was rarely used by the barbel, which can be explained by their bottom-oriented way of life [46] and their migration behavior near the river bed [30]. Due to its position above the turbine inlet, the CC is probably also hard to locate for other bottom-oriented fish species and therefore less efficient. To increase bypass efficiency, it would likely be useful to offer an alternative bottom bypass in addition to the existing surface bypass.
The majority of the test fish used the turbine corridor to get into the tailrace. This route carries a high risk of being injured or killed by a fast-moving Kaplan turbine (333 rpm). The 20 mm fish protection screen in front of the turbine inlet was only an effective barrier for brown trout > 30 cm. For many small and medium-sized fish, such a physical barrier is not very effective as a large part of the population can pass through. These fish species would benefit from the use of less harmful turbine techniques that reduce the mortality and injury risk when passing hydropower plants [13]. Reducing the bar spacing of the screen could also contribute to a higher acceptance of the CC, but would reduce turbine performance and impede the screen cleaning process.
For naturally migratory fish, the effectiveness of the CC may be higher, as they may be searching longer for an alternative corridor than hatchery-reared fish if they cannot pass the fish protection screen in front of the turbine inlet. Nonetheless, most of the naturally downstream migrating fish presumably follow the main current and pass through the turbine to reach the tailrace, if they fit through the fish protection screen.
4.2. Fish Injury Risk of the Downstream Migration Corridor Crest Cut-Out
Several authors have already stated that not only the turbine passage but also the passage of alternative downstream migration corridors can cause injuries [47,48,49]. Injuries at surface bypasses can be caused either by a large head or by structural details of the bypass [18]. The greatest potential for injuries at the investigated CC results from protruding screws and connections of the steel casing that could injure fish while sliding on top of the steel casing into the tailrace.
However, the injury risk of the assessed surface bypass can be classified as low. Fish that passed through the CC did not experience immediate mortality or serious injuries such as amputations or bruises on the body. On the other hand, injuries such as scale loss, tears, hemorrhages and dermal lesions were more common. However, these injuries were also often caused by the catching technique and the handling procedure.
The species-specific differences in injury patterns are mainly due to a different degree of pre-damage and the specific morphological characteristics and sensitivity of the tested species. Considering the individual species, the roach was most sensitive to the passage of the CC. In contrast, almost no effects were detected for rheophilic brown trout and Danube salmon. These species are probably evolutionarily more adapted to live in harsh environments of alpine rivers, where it can be necessary to cross large natural barriers during their migrations.
In general, the injuries caused by the passage of the surface bypass were not severe, as evident from the small difference to the catch-related injuries. However, even less severe injuries such as scale loss or dermal lesions may increase the risk of fungal and bacterial infections [50]. Under unfavorable circumstances, resulting diseases can reduce the vitality and ultimately lead to death [32]. The risk of sublethal and lethal injuries is particularly high for long (e.g., eel) and medium (e.g., barbel, nase) distance migrating fish species. These species are increasingly exposed to cumulative effects of hydropower plants, as they encounter many bypasses and turbines on their downstream migration route. Fish with delayed mortality had no serious external injuries in this study, so they died probably due to stress or unrecognized internal injuries.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the acceptance of the surface bypass was only marginally improved by increasing the flow area by a factor of four, and the mean flow rate by a factor of six (at maximum turbine flow) compared to the original conditions. Overall bypass efficiency was low and ranged between 7.4% (small CC) and 9.7% (large CC). For the bottom-oriented fish species barbel the surface bypass was highly ineffective. Besides a presumably still insufficient dimensioning, the greatest deficit seems to be the position of the bypass itself. To increase bypass acceptance, especially for bottom-oriented fish species, it would likely be useful to offer alternative bypasses near the bottom and in the middle of the water column in addition to the existing surface bypass. The surface bypass and the fish slide at the investigated movable power plant (head 5.0 m) seem to be suitable for passing downstream moving fish into the tailrace without severe injuries. However, the injury potential could probably be further reduced by covering protruding components, such as screw heads and flanges on the power plant steel casing. In addition to the evaluation of the pre-damage, it was crucial for this study also to record the catch-related injuries in order to separate the different effects of handling, catching and passing the CC and to avoid an overestimation of the effects of the downstream migration corridor. For future research, it would also be valuable to examine different positions of the downstream migration bypass in the water column (e.g., middle, bottom), other sizes (> 3.6% of turbine flow) as well as alternative shapes (e.g., round-shaped) to determine the best bypass configuration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K., M.M., J.P. and J.G.; methodology, J.K., M.M., J.P. and J.G.; validation, M.M., J.P. and J.G.; formal analysis, J.K.; investigation, J.K. and M.M.; resources, J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.K.; writing—review and editing, J.K., M.M., J.P. and J.G.
Funding
This research was funded by the Bavarian State Ministry of Environmental and Consumer Protection, grant number OelB−0270−45821/2014.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Bavarian State Ministry of Environmental and Consumer Protection, the Bavarian Environmental Agency, the Bayerische Landeskraftwerke GmbH, the Water Authority Weiden, the Fishing Authority Oberpfalz, the fishing association Neunburg vorm Wald and all field volunteers for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Prado, F.A., Jr.; Athayde, S.; Mossa, J.; Bohlman, S.; Leite, F.; Oliver-Smith, A. How much is enough? An integrated examination of energy security, economic growth and climate change related to hydropower expansion in Brazil. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 53, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C.; Lumsdon, A.E.; Berlekamp, J.; Tydecks, L.; Tockner, K. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Lehner, B.; Lumsdon, A.E.; MacDonald, G.K.; Zarfl, C.; Liermann, C.R. An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. The effects of weirs on structural stream habitat and biological communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larinier, M. Dams and fish migration. In Dams, Ecosystem Functions and Environmental Restoration. Thematic Review II.1 prepared as an input to the World Commission on1.TROPICAL ENVIRONMENT41 Dams; Berkamp, G., McCartney, M., Dugan, P., McNeely, J., Acreman, M., Eds.; World Commission on Dams: Cape Town, South Africa, 2000; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, M.C.; Baras, E. Migration of Freshwater Fishes, 47th ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2001; p. 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, M.J.; Grant, J.W.; Jackson, C.D. A quantitative assessment of fish passage efficiency. Fish Fish. 2012, 13, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northcote, T. Migratory behaviour of fish and its significance to movement through riverine fish passage facilities. In Migration and Fish Bypasses; Jungwirth, M., Schmutz, S., Weiss, S., Eds.; Fishing News Books: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Calles, O.; Greenberg, L. Connectivity is a two-way street—the need for a holistic approach to fish passage problems in regulated rivers. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 1268–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larinier, M. Fish passage experience at small-scale hydro-electric power plants in France. Hydrobiologia 2008, 609, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.G.; Armstrong, G.; Katopodis, C.; Larinier, M.; Travade, F. Thinking like a fish: a key ingredient for development of effective fish passage facilities at river obstructions. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čada, G.F. The development of advanced hydroelectric turbines to improve fish passage survival. Fisheries 2001, 26, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, A.; Odeh, M.; Noreika, J.; Castro-Santos, T. Effect of water acceleration on downstream migratory behavior and passage of Atlantic salmon smolts and juvenile American shad at surface bypasses. T. Am. Fish. Soc. 1998, 127, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilt, C.R. Developing fish passage and protection at hydropower dams. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, T.W.; Čada, G.F.; Amaral, S.V. The status of environmentally enhanced hydropower turbines. Fisheries 2014, 39, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egg, L.; Pander, J.; Mueller, M.; Geist, J. Effectiveness of the electric fish fence as a behavioural barrier at a pumping station. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2019, 70, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larinier, M.; Travade, F. Downstream migration: problems and facilities. Bull. Fr. Pêche Piscic. 2002, 364, 181–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egg, L.; Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Knott, J.; Geist, J. Improving European Silver Eel (Anguilla anguilla) downstream migration by undershot sluice gate management at a small-scale hydropower plant. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, C.; Travade, F.; Durif, C.; Rives, J.; Elie, P. Tests of two types of bypass for downstream migration of eels at a small hydroelectric power plant. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katopodis, C. Developing a toolkit for fish passage, ecological flow management and fish habitat works. J. Hydraul. Res. 2005, 43, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scruton, D.A.; McKinley, R.S.; Kouwen, N.; Eddy, W.; Booth, R.K. Use of telemetry and hydraulic modeling to evaluate and improve fish guidance efficiency at a louver and bypass system for downstream-migrating Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolts and kelts. Hydrobiologia 2002, 483, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calles, O.; Karlsson, S.; Hebrand, M.; Comoglio, C. Evaluating technical improvements for downstream migrating diadromous fish at a hydroelectric plant. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 48, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, D.W.; Hinch, S.G. Effectiveness monitoring of fish passage facilities: Historical trends, geographic patterns and future directions. Fish Fish. 2010, 11, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, J.; Hawkins, S.J. Habitat recovery and restoration in aquatic ecosystems: Current progress and future challenges. Aquat. Conserv. 2016, 26, 942–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.E.; Anglea, S.M.; Adams, N.S.; Wik, T.O. Evaluation of a prototype surface flow bypass for juvenile salmon and steelhead at the powerhouse of Lower Granite Dam, Snake River, Washington, 1996–2000. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 2005, 25, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scruton, D.A.; Pennell, C.J.; Bourgeois, C.E.; Goosney, R.F.; Porter, T.R.; Clarke, K.D. Assessment of a retrofitted downstream fish bypass system for wild Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolts and kelts at a hydroelectric facility on the Exploits River, Newfoundland, Canada. Hydrobiologia 2007, 582, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 276, 33–77. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, B.; Schürmann, M.; Schwevers, U. Zum Umgang mit Aquatischen Organismen – Versuchstierkundliche Grundlagen; Springer Spektrum: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2013; p. 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, G. Fischschutz und Fischabstieg an Wasserkraftanlagen – Handbuch Rechen- und Bypasssysteme. Ingenieurbiologische Grundlagen, Modellierung und Prognose, Bemessung und Gestaltung, 1st ed.; Büro für Gewässerökologie und Fischereibiologie: Halle (Saale), Germany, 2013; p. 483. [Google Scholar]
- Pander, J.; Mueller, M.; Knott, J.; Geist, J. Catch-related fish injury and catch efficiency of stow-net-based fish recovery installations for fish-monitoring at hydropower plants. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2018, 25, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. Evaluation of external fish injury caused by hydropower plants based on a novel field-based protocol. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2017, 24, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ineo, E.N.; Walker, N.J.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009; p. 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Somerfield, P.J.; Chapman, M.G. On resemblance measures for ecological studies, including taxonomic dissimilarities and a zero-adjusted Bray-Curtis coefficient for denuded assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 330, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N.; Somerfield, P.J.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 3rd ed.; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2014; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Bickford, S.A.; Skalski, J.R. Reanalysis and interpretation of 25 years of Snake-Columbia River juvenile salmonid survival studies. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 2000, 20, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, W.D.; Smith, S.G.; Williams, J.G.; Sandford, B.P. Survival of juvenile salmonids passing through bypass systems, turbines, and spillways with and without flow deflectors at Snake River dams. N. Am. J. Fish Manag. 2001, 21, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, J.; Mueller, M.; Pander, J.; Geist, J. Seasonal and diurnal variation of downstream fish movement at four small-scale hydropower plants. Ecol. Freshw. Fish. (in press). [CrossRef]
- Pander, J.; Mueller, M.; Geist, J. Ecological functions of fish bypass channels in streams: Migration corridor and habitat for rheophilic species. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travade, F.; Larinier, M.; Subra, S.; Gomes, P.; De-Oliveira, E. Behaviour and passage of European silver eels (Anguilla anguilla) at a small hydropower plant during their downstream migration. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ec. 2010, 398, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnekleiv, J.V.; Kraabøl, M.; Museth, J. Efforts to aid downstream migrating brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) kelts and smolts passing a hydroelectric dam and a spillway. In Developments in Fish Telemetry; Almeida, P.R., Quintella, B.R., Costa, M.J., Moore, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2007; Volume 195, pp. 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottelat, M.; Freyhof, J. Handbook of European Freshwater Fishes; Publications Kottelat, Cornol and Freyhof: Berlin, Germany, 2007; p. 646. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Guensch, G.R.; McKinstry, C.A.; Mueller, R.P.; Dauble, D.D.; Richmond, M.C. Evaluation of fish-injury mechanisms during exposure to turbulent shear flow. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.W.; Sandford, B.P.; Reagan, R.E.; Gilbreath, L.G.; Meyer, E.B.; Ledgerwood, R.D.; Adams, N.S. Bypass system modification at Bonneville Dam on the Columbia River improved the survival of juvenile salmon. T. Am. Fish. Soc. 2007, 136, 1487–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugrath, B.D.; Boys, C.A.; Cathers, B.; Deng, Z.D. Over or under? Autonomous sensor fish reveals why overshot weirs may be safer than undershot weirs for fish passage. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 132, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastjerdi, A.K.; Barthelat, F. Teleost fish scales amongst the toughest collagenous materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2015, 52, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).