Abstract
In Europe, a broad variety of agricultural landscape types have originated as a result of traditional farming activities and landscape diversity maintenance over centuries. The rapid development of socio-economic activities during the twentieth century caused significant loss of traditional rural landscapes. Traditional/historical European agricultural landscape types (EALs) represent a type of cultural landscape with many specific unique cultural, historical, and biodiversity patterns. Despite their high value, maintenance in practice is lacking. European farmers and landowners need to learn how to implement innovative multifunctional farming techniques within these landscapes. An online interactive educational tool of the ERASMUS+ FEAL project (FEAL: multifunctional Farming for the sustainability of European Agricultural Landscapes) deals with these topics. Case studies from the FEAL project showed the best examples of sustainable agricultural management practices in different types of EALs. The aim of this article was to evaluate case studies within coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) Land Cover (CLC) 2012 classes representing traditional land use forms, nature and landscape protection areas, and ecologically important areas, as well as High Nature Value (HNV) farmland. Results based on 28 case studies from five European countries interpreted the positive external effects of farms on values of EALs. A prevailing number of farms exhibited a coincidence between CLC 2012 classes with traditional land use forms and HNV farmland and protected areas. Regarding land cover classes with traditional land use forms, key words selected by farmers gave importance to recreation and tourism, furthering of biodiversity, direct sale, social farming, renewable energy, and traditional building. The highest frequencies of the key words were achieved in CLC 2012 classes concerning (to some degree) natural and semi-natural ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Over several thousand years the landscape has been influenced by agriculture. In Europe, a broad variety of agricultural landscape types have originated as a result of traditional farming activities and landscape diversity maintenance [1]. Such traditional landscapes usually represent the surviving remnants of landscape heritage going back to a remote past. They are characterized by a man-made features with irreplaceable ecological, cultural, and historical value [2]. A broad range of European agricultural landscape types (EALs) represent a specific time-limited pattern of landscapes that express a unique sense or spirit of place. They are also cherished due to their biological or anthropogenic values [3,4,5].
The massive socioeconomic changes of the twentieth century caused serious loss of unique rural ecosystem habitats. Agriculture has become oriented towards maximum profit, requiring strict specialization of agricultural production. Specialized agricultural systems brought higher economic income for farmers. On the other hand, typical EALs with mixed farming structures bearing historically-, culturally-, and regionally-specific characteristics have become rare and, in many regions, have disappeared. In the European Eastern Bloc countries, EALs were influenced by collectivization or land consolidation, mostly for arable and pastoral landscapes. The more marginal ones in the mountains changed less, and traditional land use forms have persisted to date [6]. In Central Europe, traditional farming practices have been significantly influenced by current innovative technologies, intensification of agriculture, industry, transport development, and collectivization [7,8,9]. The present-day character of the agricultural landscape in Europe has been significantly influenced by several processes but in a number of places a dominant rural character remains, delivering cultural, recreational, habitat, and supporting services [10,11,12]
Despite the above-mentioned exceptional value of the historical rural landscape, its conservation practice is very poor. The unique features of EALs are becoming rare and more valuable. Considering the disappearance and ongoing abandonment of historical rural landscapes in Europe, the preservation of these landscapes is an issue of growing importance [13].
Multifunctional and sustainable farming activities emerged as a concept that contributes to the preservation of rural landscape's heritage. Multifunctionality is one of the most important aspects of sustainable rural development [14]. In the scientific literature there is no generally accepted understanding of the essence of multifunctionality. There are essentially two approaches. The first one interprets multifunctionality as a characteristic of an economic activity. The second one refers to the multiple roles assigned to agriculture [15]. Even the most commonly cited definition, the working definition of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (2001), does not reflect the essence of the phenomenon, but rather its two main characteristics. According to this definition, “the key elements of multifunctionality are the existence of numerous market and non-market results that are jointly produced in agriculture” [16].
Rural identity expressed in the knowledge and perception of both local land users and rural entrepreneurs plays a crucial role in historical EAL maintenance and sustainable rural development. Raising awareness on landscape values for farmers and stakeholders should improve the quality of landscape and bring added value to the landscape. The concept of multifunctional and sustainable farming should be disseminated and should become a philosophy for product trademark [6]. The main problem is weak knowledge of people living in a territory with respect to a particular EAL. Residents, including farmers and other inhabitants, usually underestimate cultural, historical, and environmental value [17]. Moreover, they have no idea of how to implement landscape values into their farm business plans.
Due to the lack of EAL maintenance, preservation status, and farmer awareness of landscape values we aimed to deliver comprehensive research findings on the relationship between multifunctional and/or sustainable farming practices of small farms and EALs particularly embedding traditional features in land use. The FEAL project (FEAL: multifunctional Farming for the sustainability of European Agricultural Landscapes) aimed at the development of online vocational and educational training material (VET) for small, family, and young farmers living in the rural environment. The training material explained how to apply knowledge on landscape values in different landscape types and to implement it into daily farming activities through case studies. Further, it clarified how multifunctional and sustainable farming practices aiming at protecting the heritage of European agricultural landscapes lead to win–win situations. The FEAL research was grounded in material collected from farmers/promoters of good practices through questionnaires.
The article's objective was to evaluate data gathered from case studies of the FEAL project. We evaluated the frequency of farm locations within coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) 2012 Land Cover (CLC) classes with traditional land use forms, nature and landscape protection areas/ecologically important areas, and High Nature Value (HNV) farmland. Attitudes of farmers to the multifunctional and sustainable agriculture mirrored in key words which were selected by the farmers and collected during a questionnaire survey. The presence of key words within CLC 2012 classes with traditional land use forms documented preferences of farmers characterizing a certain land cover class. Results interpreted positive external effects of farms on values of European agricultural landscapes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The selection of case studies depends on certain factors and criteria considered during the process of the selection. Case studies can be set up according to literature review [18], through a questionnaire survey [19,20], or according to criteria based on experimental work to verify a model and its functions (e.g., using the example of 18 farmers in Sweden [21]). The selection of case studies always depends on a target topic. On the one hand, innovation, research, and new technologies can be the main aspects promoted in case studies [22]. On the other hand, preserving a revitalization of traditional rural agri-techniques motivated researchers to perform long-term observation (2010–2014) and deep field investigation in five villages in the Eastern provinces of China [23].
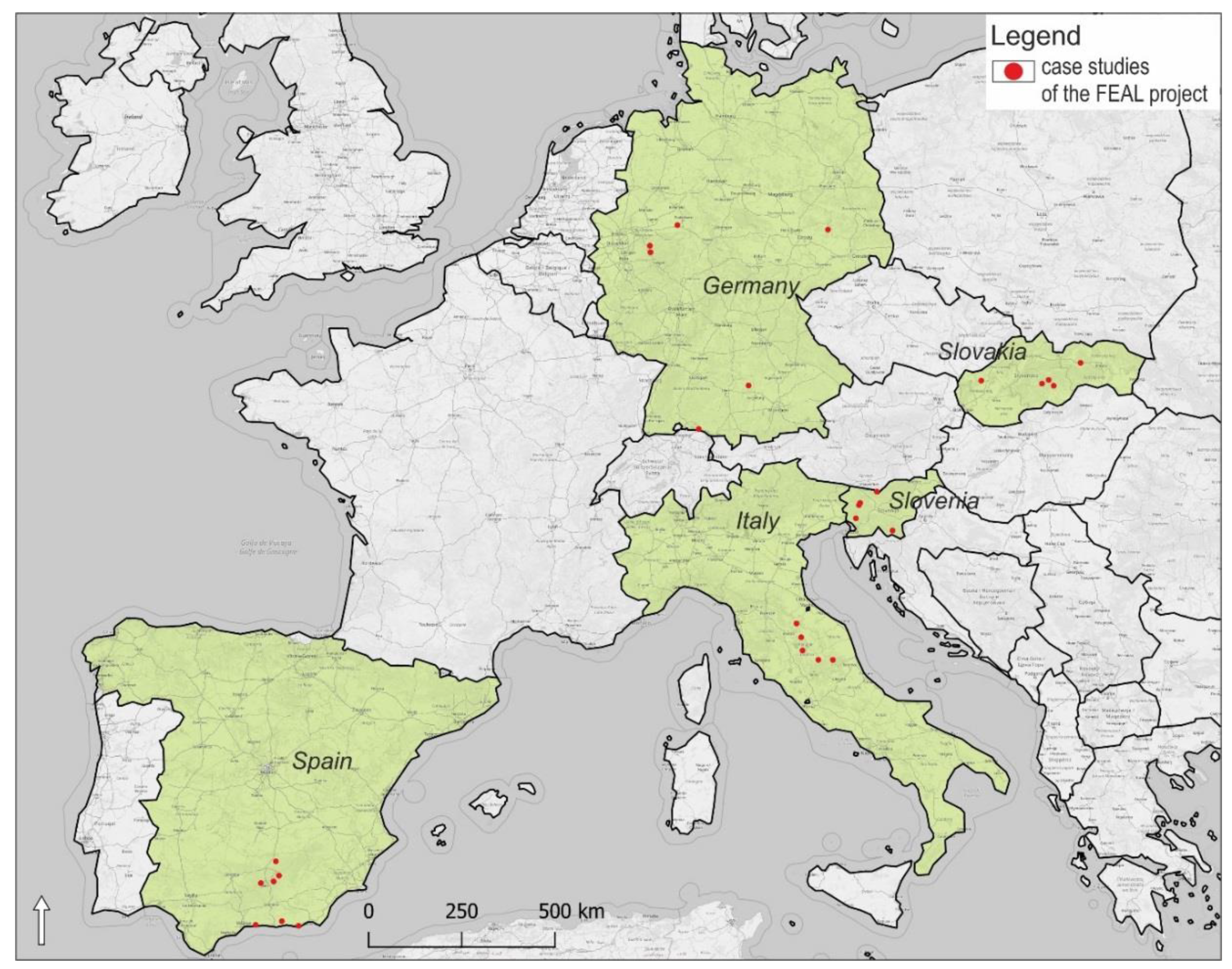
Case studies presented in the article were selected from countries involved in the FEAL project under ERASMUS+ program, Key Action 2. Exchange of good practices was expected to demonstrate possible solutions for problems of multifunctional farms existing in different geographical regions across Europe. Research was conducted from case studies in Germany, Italy, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Spain, covering Eastern European, Mediterranean, and Western European countries in order to obtain a diversity of geographic, geomorphological, and environmental factors, as well as different socio-economic and cultural situations (Figure 1). A similar approach in a wider research context focused on demonstration activities at commercial farms is shown in the PLAID project (PLAID: Peer-to-peer Learning: Accessing Innovation through Demonstration) under Horizon 2020 program (2017–2019) [24] where consortium of partners presented 24 case studies from distinctive European regions.
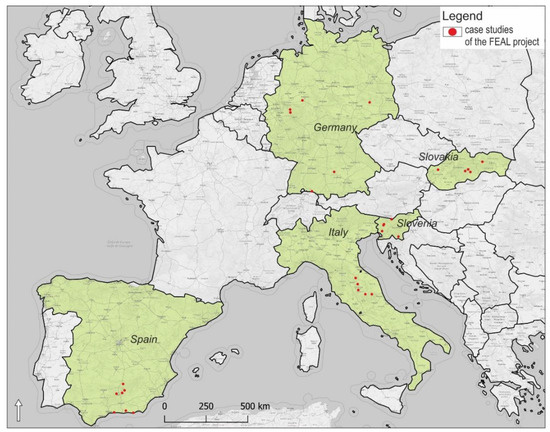
Figure 1.
Case studies (28) of the FEAL project (FEAL: multifunctional Farming for the sustainability of European Agricultural Landscapes) located in five European countries (Germany, Italy, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Spain).
Landscape types classified according to national landscape typologies are specified in Table 1 and in Supplementary Material 1 (S1). They are characterized in interactive files in a portable document format (pdf) at the FEAL website (https://www.cs.feal-future.org/en/case-studies2) in more detail. The FEAL case studies were situated in mountainous, sub-mountainous, or hill areas (17), some were in rivers valleys or in lakes alluvial plains (10), and one had a coastal position.

Table 1.
Natural and cultural landscape types classified at a national level of the FEAL case studies of the FEAL project (FEAL: multifunctional Farming for the sustainability of European Agricultural Landscapes).
2.2. Approach and Methods
Our survey implemented the bottom-up approach based on the field and questionnaire survey of small- and medium-sized farms performing sustainable and multifunctional agriculture, which is welcome and very important for future management plans of EALs. Landscape studies and plans should be understood as an instrument to diffuse knowledge about landscape and to involve rural populations in the process of identifying, assessing, and managing the landscape [25]. Recent studies handled socially oriented semi-structured interviews from farmers and tourists visiting farms [26]. The most prevalent group of farmers does not wish to intensify landscape cultivation. A majority of farmers wished to maintain the cultivated landscape. Tourists favored cultivated landscapes, with elements of traditionality within built infrastructure, and had an interest in undertaking nature-based activities [26,27].
We performed interviews with 28 farmers from five European countries (Germany (6), Italy (5), Slovakia (5), Slovenia (5), and Spain (7)). Learning through examples of good practices is very constructive and motivating, especially for adult learners. We conducted two questionnaire surveys using semi-structured questionnaires with expected outputs: free text and exact answers. Formulation of answers with free text fields was a result of dialog between a farmer and a surveyor. The first semi-structured questionnaire was performed at the farm and farmers were asked to answer three groups of questions on (1) promoter data, (2) farm data, and (3) and multifunctional and sustainable farming and EALs. From the article's research perspective the following points of the third group of questions were important: characteristics of the agricultural landscape, contribution of multifunctional and sustainable farming activities to landscape maintenance, and the added value of an agricultural landscape in helping a farm in its farming activities.
The second questionnaire survey contained the following groups of questions: introduction; farm profile; multifunctional and sustainable farming and EALs; considerations, competences, skills involved and queries or/and questions; and key words. The final result of the questionnaire survey was text of interactive case studies published at the FEAL project web site (Figure 2). Farmers characterized their farms using key words which were arranged into three groups. Firstly, keywords describing landscape types corresponded with the locations of farms in 15 EALs (“dehesas”, “delta landscapes”, “farmland”, “heathland”, “highland”, “huertas”, “meadow”, “open fields”, “orchards”, “pasture”, “rural area”, “semi bocage”, “terraced landscape”, “vineyard”, and “wooded landscape”, with another keyword being “protected area”). EALs were characterized in detail in the E-Atlas at the FEAL website (https://www.feal-future.org/eatlas/en; the E-Atlas was developed by the Institute for Research on European Agricultural Landscapes e.V. with co-operation of the FEAL consortium. Secondly, a group of keywords characterizing farming activities highlighted some specific agricultural activities of farms (“almond”, “alpaca”, “avocado”, “beekeeping”, “cattle”, “cherries”, “dairy farming”, “field crops”, “fighting bulls” (the Spanish Fighting Bull is a specific cattle breed with aggressive behavior when it is unable to escape at risk), “forestry”, “fruit”, “goats”, “grasslands/pasture”, and “greenhouses”). Thirdly, 11 keywords (KWs 1–11) characterizing multifunctional and sustainable farming were defined by farmers and these KWs were applied in the article: “avoid soil erosion” (KW 1), “biodiversity” (KW 2), “cooperation” (KW 3), “direct sales” (KW 4), “quality organics” (KW 5), “certified production” (KW 6), “renewable energy” (KW 7), “social farming” (KW 8), “tourism and recreation related to EALs” (KW 9), “traditional building” (KW 10), and “traditional land use” (KW 11).

Figure 2.
Structure of the FEAL case studies of the FEAL project (FEAL: multifunctional Farming for the sustainability of European Agricultural Landscapes) presented on the FEAL website. General introduction about the farm (a), its location, history, and natural settings (b); characteristics of European agricultural landscapes and national landscape types (c); personal skills and knowledge of a farmer and SWOT analysis (SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) of a farm (d); and keywords, which are applied also as filters on the case studies website (e).
Each surveyor visited more farms and collected more questionnaires in the first survey round that is presented in the article. After field visits of farms experts from the FEAL consortium excluded some farms during the transnational project meeting. Some farmers also step down from the co-operation and did not enter the second questionnaire survey. Thus, we collected 28 questionnaires completely characterizing farms and data from these farms were applied in the article.
Considering the content of both questionnaires, the criteria for the selection of case studies were as follows:
- (1)
- Multifunctional farms
- (2)
- Sustainable land use management performed by farmers
- (3)
- Presence of specific-traditional land use techniques which are relevant to a given European landscape
- (4)
- Preserved indigenous knowledge system
We excluded farms (besides ES.06) with a pure agri-industrial production because as pointed out in [28] these farms were not expected to be multifunctional. Farms involved in sustainable rural development and providing social and economic capital and environmental benefits tend to be multifunctional [28]. A meaningful relationship between productivism and multi-business farms has been clarified [29]. While production-oriented farms obtain their main income from primary agricultural production and demand for services, multi-business farms provide these services and products. Only one case study, a farm in Spain (ES.06) represented agriculture in greenhouses (the so-called “plastic landscape”) and met only the second criteria because farmers applied sustainable agri-techniques. However, we decided to include this case study because this kind of agriculture has become widespread over the last decades and we would like to promote positive examples of greenhouse farming practices through the project.
Geographical location of farms strongly influences their multi-functional potential and decisions of farmers to choose adequate multifunctional activities [30]. Therefore, we characterized geographic units or regions and basic geomorphological distinctives.
Cultural landscapes are “combined works of nature and of man” as stipulated by Article 1 of the World Heritage Conservation (1992). Specific techniques of sustainable land use are applied with respect to limits of the natural environment and a specific spiritual relation to a cultural landscape. Thus, modern techniques of sustainable land use which follow traditional practices can maintain or enhance natural values in the landscape [31].
The identity of farmers is mirrored in landscape maintenance and awareness of its features and heritage. Indigenous knowledge is held by local inhabitants or is locally unique to a given culture or society [32]. Particularly, rural landscapes have inherited complex constructions resulting from steps of maintenance carried out by many single individuals and dispersed through lengthy periods of time. Therefore, it is necessary to achieve awareness and management of the materials and building techniques represented by historical objects or landforms (terraces, boundary hedges, etc.) [27]. The authors of [33] presented a comparable qualitative survey in order to get better understanding of the local practices of traditional farming, and they interpreted traditional practices and the role of traditional farming in sustaining the area’s resources and enhancing its adaptability to environmental changes [34]. In particular, the product designated “original food” incorporates unique features from local resources, both material and immaterial, and this highly differentiates and characterizes local foods in the market [32].
The following CLC 2012 classes indicating traditional land uses were adopted from the CLC 2012 maps. The presence of traditional landscapes was indicated according to well-known literature sources, taking into consideration the following:
- Agroforestry systems, recognized worldwide to be a traditionally cultivated agro-ecosystems [35];
- Heterogeneous agricultural areas and land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation containing typical traditional land uses because of traditional farming practices including livestock grazing and forest management, resulting in highly heterogeneous and spatially structured cultural landscape mosaics [36];
- Olive groves [37];
- Heterogeneous agricultural areas, which have a complex cultivation pattern [38];
- Agricultural areas, permanent crops, fruit trees, and berry plantations created by semi-subsistence farms maintaining the species-rich mosaic of arable fields, grasslands, and forests, as shown by the example of Transylvania in Romania [39];
- Land principally occupied by agriculture with significant areas of natural vegetation. This land cover class is usually rich in biodiversity and provides habitat for many species [40]. However, from the economic point of view, this land use class contributes the most to marginal agricultural lands [41].
Agriculture has created distinctive features in agricultural landscapes over the world. During its history a number of semi-natural habitats, land cover heterogeneity, and many distinctive biophysical features have been created [17]. Photo documentation of distinctive features mirroring traditional land use forms in European agricultural landscapes is illustrated in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Distinctive features of landscapes where traditional land use forms prevail (adapted to coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) 2012 Land Cover classes).
The selection of these categories does not mean that that traditional land use does not occur in other CLC 2012 classes. The classes that we considered to be traditional had distinctive visible features indicating traditional land use activities and these were applied in the survey.
The concept of HNV farmland ties together biodiversity to the continuation of farming on certain types of land and the maintenance of specific farming systems [42]. Therefore, the presence of HNV farmland was also evaluated in case studies.
2.3. Data Collection and Processing
Data on farms were collected from October 2017 to April 2018 within the workflow on the second output of the FEAL project. Farms were geotagged in Google maps on the FEAL web site where case studies are published. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) coordinates were inserted into geographic information system (GIS), and thus the position of the farms was geotagged in maps presented in the article.
Datasets on CLC 2012 [43] were used for the comparison of land cover classes at European level among five countries—Germany, Italy, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Spain. The CLC 2012 has 44 classes distinguished according to details into three levels. In the article we applied characteristics of land cover classes from the second and the third level. In total, we analyzed 15 CLC 2012 classes from the third-level class (highlighted in cursive in Table 3). “Agricultural areas” (non-irrigated arable land; arable land; permanently irrigated land; pastures; heterogeneous agricultural areas; land principally occupied by agriculture with significant areas of natural vegetation; heterogeneous agricultural areas—complex cultivation patterns; olive groves; agroforestry areas; permanent crops; fruit trees and berry plantations), “Forest and semi natural areas” (coniferous forest; broad-leaved forest; mixed forest; scrub and/or herbaceous vegetation associations; sclerophyllous vegetation), and “Artificial surfaces” (discontinuous urban fabric). National CLC 2012 datasets that were used in the article and web links for a GIS connector are cited in Table 2.

Table 2.
National datasets and coordinate systems related to case studies.
Geodata were processed in Quantum GIS 3.6.3. (QGIS). Maps were downloaded from online web map servers using a web map service (WMS) a protocol developed by the Open Geospatial Consortium and national reference systems were applied (Table 2). The quantitative data of farm distribution and keyword (multifunctional and sustainable farming) frequencies within specified categories of CLC 2012, protected landscape areas, ecologically important areas, and HNV farmland were processed and evaluated using a contingency table and a graph in MS ExcelTM.
3. Results
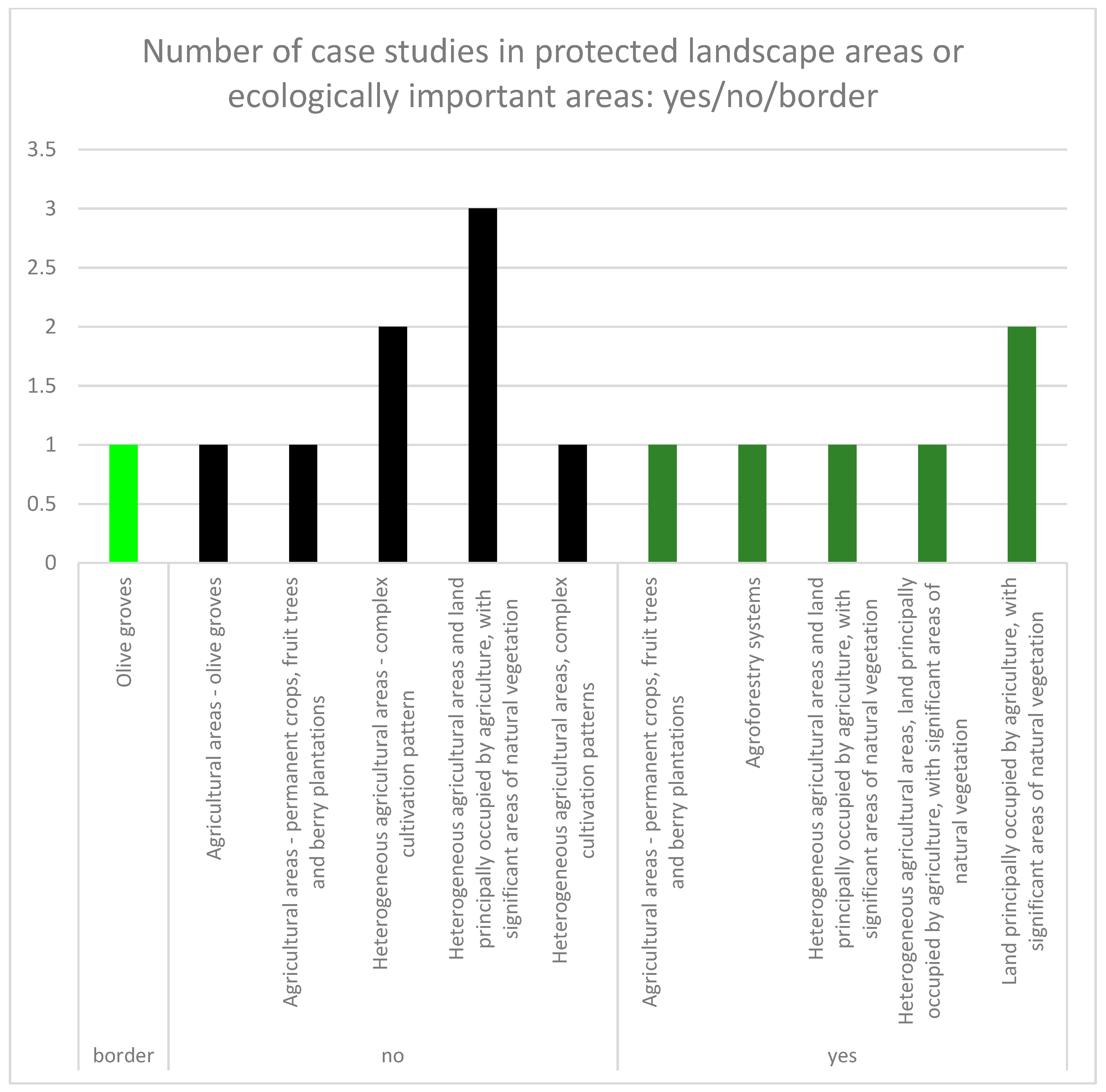
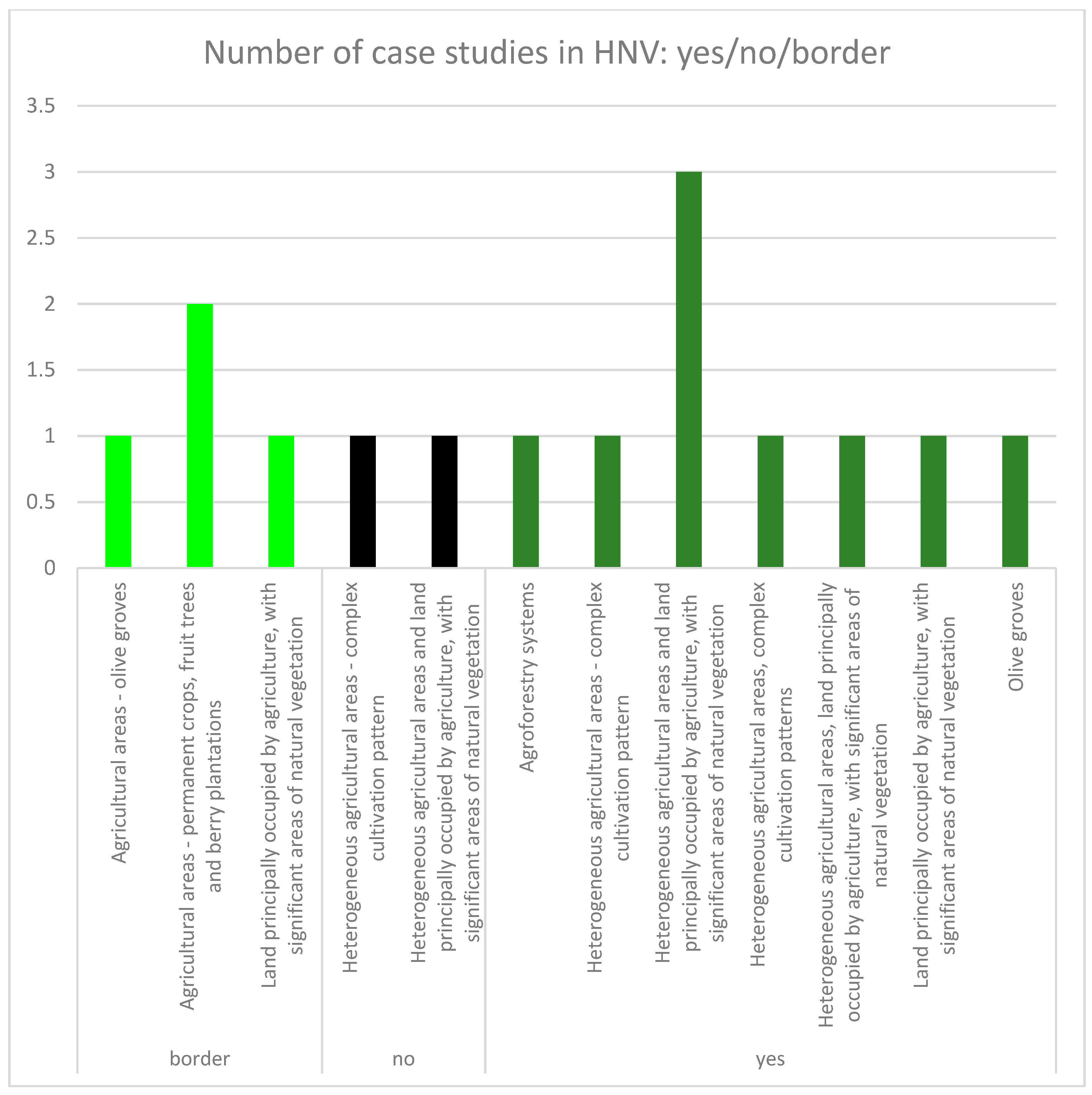
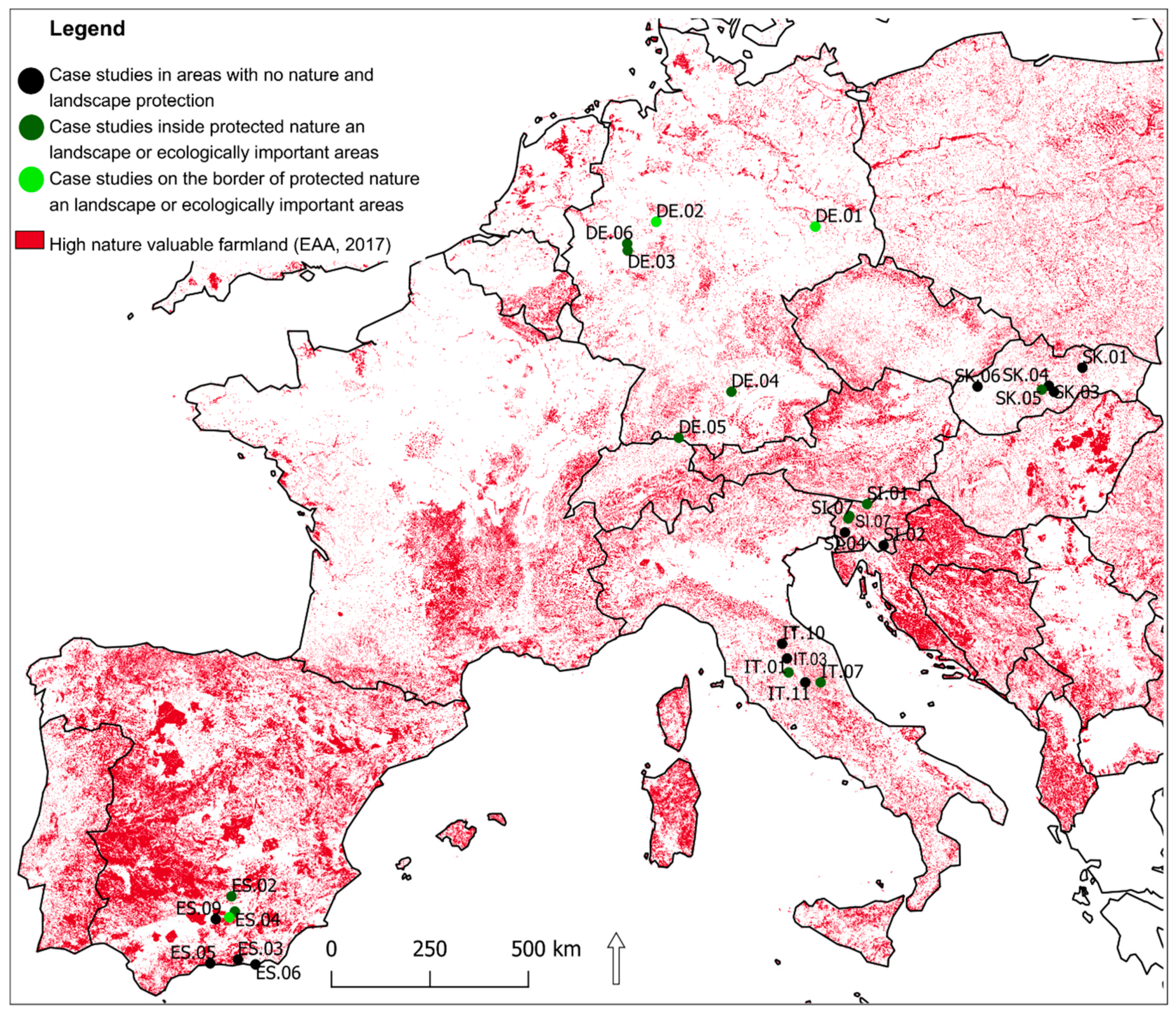
Twelve case studies out of 28 were located inside areas with a protection status or inside ecologically important areas and three were on the border. Eleven case studies had position inside HNV farmland, and nine were on the border (Table 3). Nearly half (15 of 28) case studies met criteria selected in methodology and exhibited a presence of CLC 2012 class with traditional land use forms and cultivation (Figure 4). The frequency of the distribution of case studies (from the selected 15) in protected and ecologically important landscape areas was nearly equal inside and outside of these areas; eight case studies were outside of these areas, one was located on the border, and six were inside (Figure 5, Figure 7). Other results brought evaluation of the frequency of case studies in HNV farmland (Figure 6, Figure 7). Four case studies (DE.05; SK.05; SI.05; ES.02) showed full coincidence among traditional land use, a position inside a protected or an ecologically important area, and location inside HNV farmland. Partial coincidence was present in seven case studies (IT.10; SK.03; SK.04; SI.04; SI.07; ES.01; ES.04) and no coincidence was found in three case studies (IT.01; IT.11; SK.06).

Table 3.
Evaluation of case studies in coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) 2012 Land Cover (CLC) classes, protected and ecologically important landscape areas, and High Nature Value (HNV) farmland.
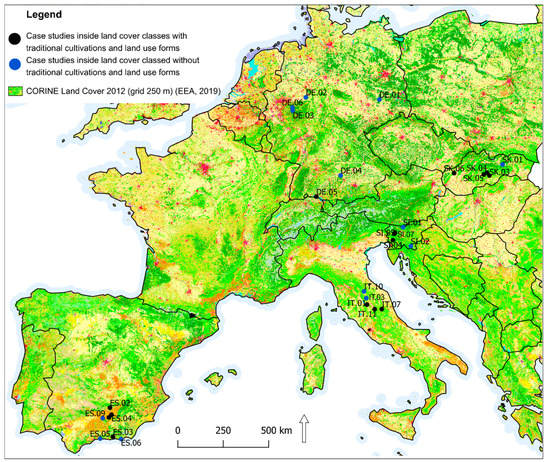
Figure 4.
Position of case studies within with coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) land cover 2012 classes (CORINE) 2012 Land Cover classes with and without traditional cultivation and traditional land use forms.
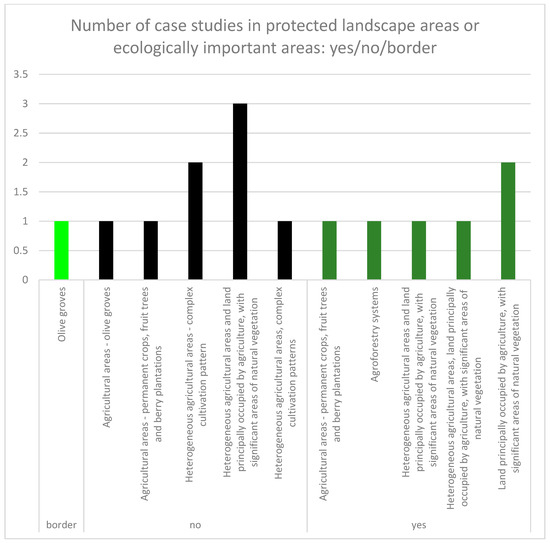
Figure 5.
The evaluation of the case studies frequency (with coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) Land Cover 2012 classes including traditional land uses) within protected and ecologically important landscape areas (yes/no/border).
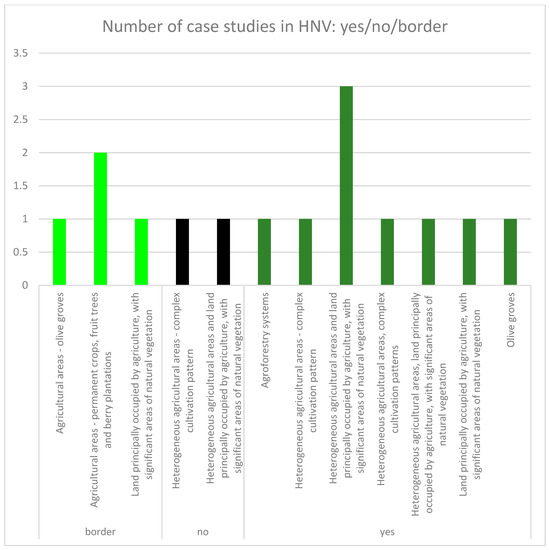
Figure 6.
The evaluation of the case study frequency (with coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) Land Cover 2012 classes including traditional land uses) within High Nature Value farmland (yes/no/border).
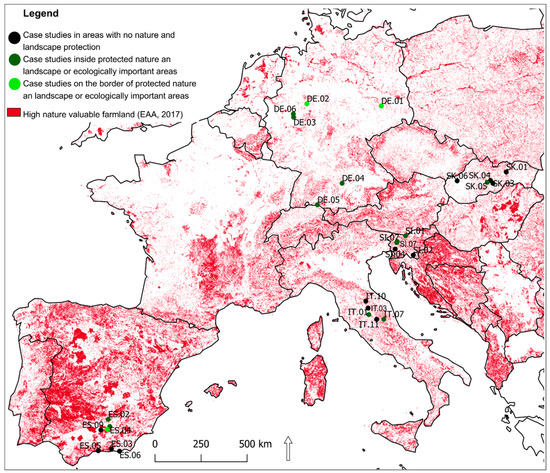
Figure 7.
Position of case studies within High Nature Value (HNV) farmland and status of their nature and landscape protection and ecological importance.
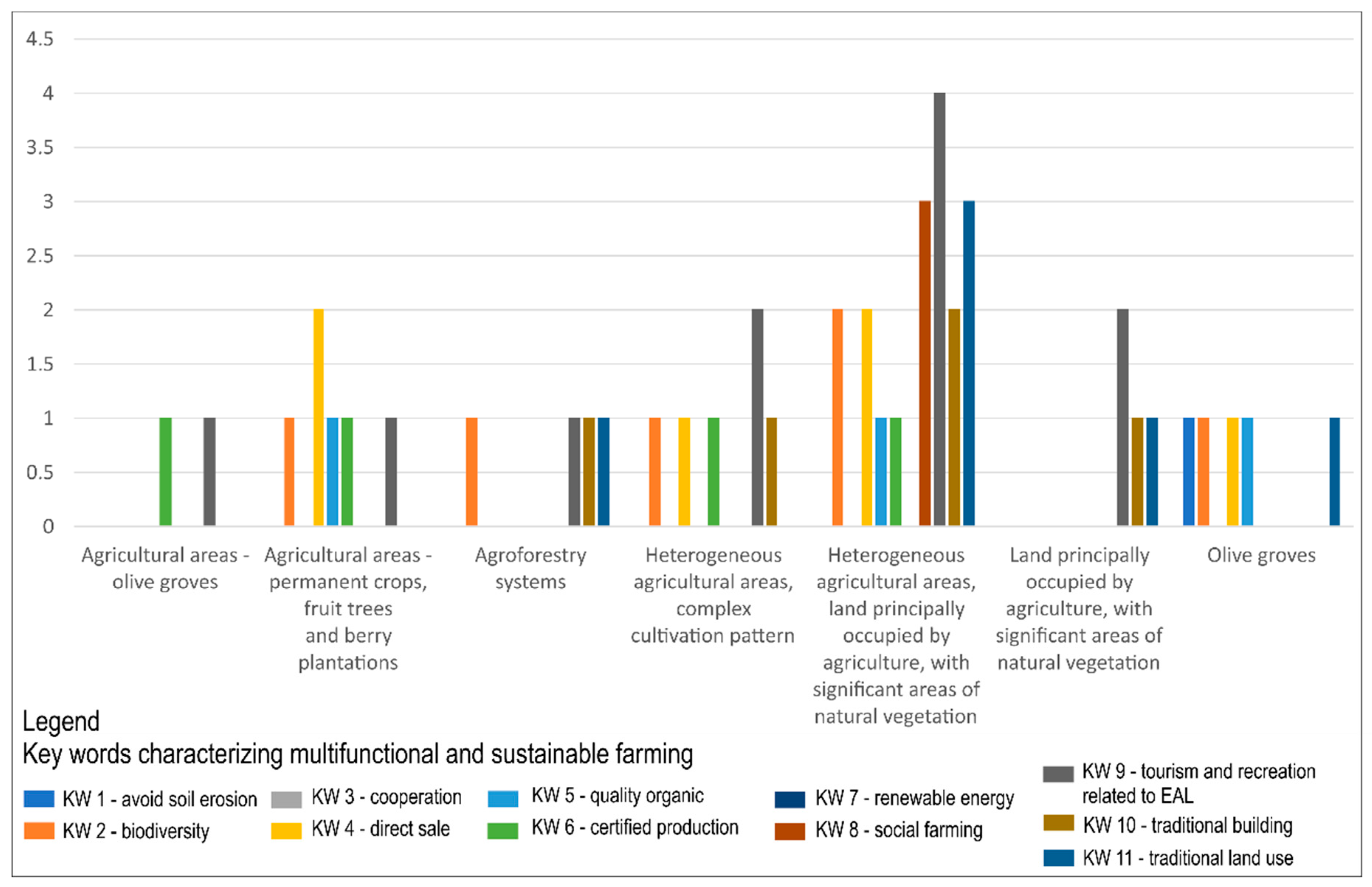
The highest frequency (of 11 KWs) in CORINE Land Cover 2012 classes was for “tourism and recreation related to EALs” (KW 9). KW 9 was found in heterogeneous agricultural areas, land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation (4); in heterogeneous agricultural areas, complex cultivation pattern (2); and in land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation (2). These land cover classes contained a certain proportion of natural or semi-natural eco-systems and thus constituted clean, healthy, and pleasant natural environments for agritourism activities. Further, farmers frequently marked “biodiversity” (KW 2) and “direct sale” (KW 4) as important for multifunctional and sustainable EALs. Higher frequencies (3) were found for “renewable energies” (KW 8), “social farming” (KW 9), and “traditional building” (KW 10) within the CLC 2012 class of heterogeneous agricultural areas, land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation (Figure 8).
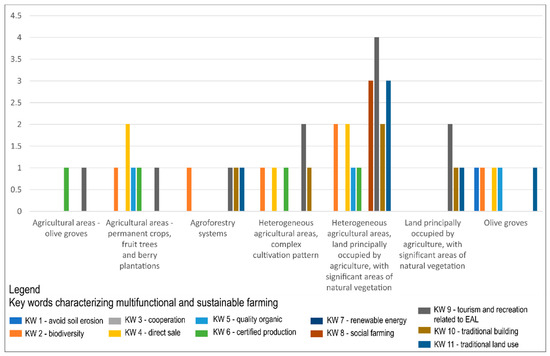
Figure 8.
The evaluation of key words (related with multifunctional and sustainable farming) frequencies within coordination of information on the environment (CORINE) Land Cover 2012 classes representing traditional land use forms in a contingency graph.
4. Discussion and Conclusion
An agricultural landscape as a cultural landscape is a result of interactions between the human population and the natural environment. Here, preserved historical structures, traditional agricultural technologies, and/or ecologically-friendly farming constitute a significant part of European cultural heritage. The main risks for their preservation are mostly extensification and land abandonment on the one hand, and land use development and intensive agriculture on the other. As a response to global trends in agriculture at the European level causing degradation of the agricultural landscapes and the loss of biodiversity, new solutions are being considered for their optimal multifunctional land use [7]. Traditional agricultural landscapes support biocultural diversity and ecotourism [33]. Our results confirmed a coincidence between CLC 2012 classes representing traditional land uses (in total 15 from 28) and HNV farmland, and protected natural areas or ecologically important areas; four case studies were located in both categories, and seven case studies were present in at least one of the categories. Cultural landscapes require maintaining both habitats and functional connections between human society and natural environment. Only then does landscape protection add to landscape value [44].
The opportunities for the agricultural process to produce a variety of interconnected products and to carry out simultaneously other functions related to our environment are conditions for the successful concept of multifunctionality of agriculture. This concept specifies, to a great extent, the approaches for achieving sustainable development in rural areas [14]. Recreation and tourism potential positively correlates with aesthetic and environmental values of landscape or with land ownership of small parcels [45]. The evaluation of key words selected by farmers in CLC 2012 classes with traditional land use forms confirmed this statement. The highest frequency of the selected 11 key words was for “tourism and recreation”, followed by “biodiversity”, “direct sale”, “renewable energies”, “social farming”, and “traditional building”. It is interesting that the highest frequencies of the key words were achieved in CLC 2012 classes concerning (to some degree) natural and semi-natural ecosystems (heterogeneous agricultural areas, land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation; heterogeneous agricultural areas, complex cultivation pattern; and land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation). Cultural landscapes provide important ecosystem services, contribute to the farmland biodiversity, and cherish their heritage. Nevertheless, they are threatened by intensification on the one hand, and abandonment on the other [46]. Human society provides a cultural capital to deal with ecosystems, biodiversity, and natural resources, involving stakeholders, their knowledge, and human activities shaping the land, enhancing the supply of ecosystem services [27].
A dataset of 28 case studies is not extensive enough to provide relevant statistical results. Therefore, we compared only frequencies of occurrences of farms and key words within selected CLC 2012 classes and other categories related with the landscape protection status or natural value. Perhaps the proposed approach will motivate researches to enrich databases and interpret relevant statistical data in European context. Thus, such a dataset would be used as an argument to force changes in European and in national legislation. Protection-based evaluation methods have been considered to be a useful engine for landscape maintenance action in regions, where EALs are rapidly changing and facing multiple threats [47]. An exceptional example is Italy because it has an old tradition of studies on geography and theory of landscape as well as on the protection of landscape heritage (passing some of the first laws in Europe on this subject). However, the landscape heritage protection theory is less consolidated in the practice of territorial planning [48]. Five Italian case studies represented a purely traditional way of life of small farmers emphasizing their ancestral roots in the landscape, appearing in land use management, architecture, and original farm products as well. The result partially confirmed those of [14] in case studies in the Pralormo municipality in Italy. The farmers, during the interviews, confirmed that qualifying elements that should be valued, in particular historical farms, fishponds, natural elements (hedgerow and woody areas), and the system of paths and roads.
The results confirmed that EALs can be considered as the ones providing a variety of ecosystem services due to their diversified spatial and functional pattern and ecological, cultural, and historical value. There is no consensus on defining and characterizing cultural landscapes. Moreover, mapping the diversity of landscapes in terms of composition or farming practices insufficiently considers the variety of cultural value of these landscapes [49]. Heterogeneous agricultural areas with complex cultivation patterns and with land principally occupied by agriculture, with significant areas of natural vegetation, have been found to be decreasing in area in many European countries over the last decades, with no differences found between the former Eastern Bloc countries or Mediterranean ones [50]. Farmers face very restricted marketing opportunities, and some local farmers are found in an economic deadlock of relying on common agricultural policy (CAP) subsidies as a main source of income [51].
In addition, small-sized farms and young farmers struggle every day with many obstacles (e.g., insufficient capital, education and training opportunities, weak financial support, problems in renting land, complicated food marketing, insufficient and complicated legislation, missing social benefits in some countries, etc.). Traditional agriculture survives mainly as secondary employment. Agricultural work is usually done part-time and the younger generations leave the village. Agriculture becomes dependent on cash income from EU and national agricultural subsidies [27].
Raising awareness on landscape values for farmers and stakeholders and promoting adequate daily maintenance should improve the quality of many exceptional and common European landscapes [6]. This would bring added value to the landscapes and increase the biodiversity and stability of natural systems [52,53]. The training material based on the international exchange of best practices is supposed to represent a baseline form of educational material to be incorporated in the future into training materials for vocational and educational training courses. The approach could be also used in other approaches, i.e., as a base for spatial management, decision support system implementation, climate change actions [54], or in the context of increasing sustainability and resilience [55].
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/21/5966/s1. Figure S1: National landscape types and location of case studies.
Author Contributions
M.S. collected and analyzed the research data, and wrote the paper. I.B. developed the original idea of this study, evaluated the research data, and wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the agency VEGA of the Slovak Republic, Grant No. 1/0868/18.
Acknowledgments
This paper was written within the project ERASMUS+ 2016-1-SK01- KA202-022502, FEAL: Multifunctional Farming for the Sustainability of European Agricultural Landscapes. M.S. and I.B. would like to thank the FEAL project partners for their research data contribution, particularly to Iacopo Benedetti from ON Projects Advising SL (Spain) for material on case studies and the Institut Für Europäische Agrarlandschaftsforschung e.V. (EUCALAND) for material on European Agricultural Landscapes applied in the E-Atlas. Data reused from the FEAL project in the article are available online at: https://www.cs.feal-future.org/en.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Agnoletti, M.; Santoro, A. Cultural values and sustainable forest management: The case of Europe. J. For. Res. 2015, 20, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrop, M. Why landscapes of the past are important for the future. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 70, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoletti, M.; Rotherham, I.D. Landscape and Biocultural Diversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 3155–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špulerová, J.; Petrovič, F.; Mederly, P.; Mojses, M.; Izakovičová, Z. Contribution of Traditional Farming to Ecosystem Services Provision: Case Studies from Slovakia. Land 2018, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechanec, V.; Machar, I.; Pohanka, T.; Opršal, Z.; Petrovič, F.; Švajda, J.; Šálek, L.; Chobot, K.; Filippovova, J.; Cudlín, P.; et al. Effectiveness of Natura 2000 system for habitat types protection: A case study from the Czech Repulic. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 24, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Renes, H.; Gailland, B.; Sigura, M.; Slámová, M.; Belčáková, I.; Ambrožič, A.; Finale, R.; Canalicchio, M.; Rojas Pino, I.; et al. The State of the Art of the relation between sustainable/multifunctional farming practices and European Agriculture Landscapes. In The Summary Report, 1st ed.; Technická univerzita vo Zvolene: Zvolen, Slovakia, 2017; pp. 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Špulerová, J.; Petrovič, F. Historical Agricultural Landscape as a Subject of Landscape Ecological Research. Hrvatski Geografski Glasnik 2011, 73, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprsal, Z.; Harmacek, J.; Pavlik, P.; Machar, I. What Factors Can Influence the Expansion of Protected Areas around the World in the Context of International Environmental and Development Goals? Probl. Ekorozw. 2018, 13, 145–157. [Google Scholar]
- Izakovičová, Z.; Šwiader, M. Building ecological networks in Slovakia and Poland. Ekológia (Bratislava) 2017, 36, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Machar, I. Assessment of management strategy for hardwood floodplain forest ecosystem in protected area. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Silviculurae Mendelianae Brunensis 2014, 62, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, P.; Solecka, I.; Mrozik, K. Driving Forces of Forest Landscape Forest Landscape Change in Ślęża Landscape Park (Southwestern Poland) in Period 1883–2013. Preprints 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machar, I. Local place names as part of landscape memory (Case study from Haná region, Czech Republic). Acta Universitatis Carolinae Geographica 2014, 49, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špulerová, J.; Bezák, P.; Dobrovodská, M.; Lieskovský, J.; Štefunková, D. Traditional agricultural landscapes in Slovakia: Why should we preserve them? Landsc. Res. 2017, 42, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullino, P.; Battisti, L.; Larcher, F. Linking multifunctionality and Sustainability for Valuing Peri-Urban Farming: A Case Study in the Turin Metropolitan Area (Italy). Sustainability 2018, 10, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Coperation and Economic Development (OECD). Multifunctionality: Towards an Analytical Framework. Available online: www.oecd.org/tad/agricultural-policies/40782727.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2017).
- Bezák, P.; Dobrovodská, M. Role of rural identity in traditional agricultural landscape maintenance: The story of a post-communist country. Agroecol. Sustain. Food 2019, 43, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzosi, L. Reading and Assessing the Landscape as Cultural and Historical Heritage. Landsc. Res. 2004, 29, 335–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, J.; de Groot, H.L.F.; Rietveld, P.; Verburg, P.H. Manifestations and underlying drivers of agricultural land use change in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 133, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, L.T.; Sluis, T.V.; Giezen, M. The Role of Farm Management Characteristics in Understanding the Spatial Distribution of Landscape Elements: A Case Study in the Netherlands. Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieskovský, J.; Kanka, R.; Bezák, P.; Štefunková, D.; Petrovič, F.; Dobrovodská, M. Driving forces behind vineyard abandonment in Slovakia following the move to a market-oriented economy. Land Use Policy 2013, 32, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlmér, B.; Olson, K.; Brehmer, B. Understanding Farmers’ Decision–Making Processes and Improving Managerial Assistance. Agric. Econ. 1998, 18, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, C.; Klerkx, L.; Nettle, R. Dynamics and distribution of public and private research and extension roles for technological innovation and diffusion: Case studies of the implementation and adaptation of precision farming technologies. J. Rural Stud 2017, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, P.; Liu, Y. What makes better village development in traditional agricultural areas of China? Evidence from long-term observation of typical villages. Habitat Int. 2019, 83, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selecting 24 Case Studies WP5: Case Studies of Demonstration Activities in Commercial Farms. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research/participants/documents/downloadPublic/UGszQjR5TXhld2RDZkhIUGt4NEowTzhQTE8yVmk4RDY1VGJsQUpXUXJjam5KbTJJZlJidE9RPT0=/attachment/VFEyQTQ4M3ptUWVqUTVWU1hsZUxSckpVNW9uU1pubGc= (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- FAO. Landscapes for Life Approaches to Landscape Management for Sustainable Food and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zagari, C.; Schulp, C.J.E.; Kizos, T.; Verburg, P.H. Perspectives of farmers and tourists on agricultural abandonment in east Lesvos, Greece. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018, 18, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, Z.; Berkes, F. Role of traditional ecological knowledge in linking cultural and natural capital in cultural landscapes. In Reconnecting Natural and Cultural Capital, Contributions from Science and Policy, 1st ed.; Paracchini, M.L., Zingari, P.C., Blasi, C., Eds.; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, Germany, 2018; pp. 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kizos, T.; Marin-Guirao, J.I.; Georgiadi, M.E.; Dimoula, S.; Karatsolis, E.; Mpartzas, A.; Mpelali, A.; Papaioannou, S. Survival strategies of farm households and multifunctional farms in Greece. Geogr. J. 2011, 177, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, S. Revisiting agricultural modernisation: Interconnected farming practices driving rural development at the farm level. J. Rural Stud. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.A. From ‘weak’ to ‘strong’ multifunctionality: Conceptualising farm-level multifunctional transitional pathways. J. Rural Stud. 2008, 24, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nation Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). The World Heritage Convention. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/culturallandscape/ (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- Cei, L.; Stefania, G.; Defrancesco, E.; Lombardi, G.V. Geographical indications: A first assessment of the impact on rural development in Italian NUTS3 regions. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Q.X.; Lu, D.J.; Kuo, W.H.J.; Lai, P.H. Traditional Farming and Sustainable Development of an Indigenous Community in the Mountain Area—A Case Study of Wutai Village in Taiwan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.; Kumar, A.; Khan, M.L. Agroforestry: A Sustainable Land Use System for Livelihood Security and Climate Change Mitigation. In Climate Change and Agroforestry, 1st ed.; Pandey, B.C., Gaur, M.K., Goyal, R.K., Eds.; New India Publishing Agency: New Delhi, India, 2017; pp. 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. The cultural landscape as a model for the integration of ecology and economics. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 50, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graaff, J.; Duarte, F.; Fleskens, L.; de Figueiredo, T. The future of olive groves on sloping land and ex-ante assessment of cross compliance for erosion control. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, R.; Brunori, E.; Smiraglia, D.; Salvati, L. Linking traditional tree-crop landscapes and agro-biodiversity in central Italy using a database of typical and traditional products: A multiple risk assessment through a data mining analysis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 3009–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, P.J.; Levers, C.; Kuemmerle, T.; Lindner, M.; Valbuena, R.; Verburg, P.H.; Zudin, S. Mapping wood production in European forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 357, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorresteijn, I.; Nimmo, D.G.; Loos, J.; Hanspach, J.; Moga, C.I.; David, A.; Mernst, L.; Fischer, J. A new world for old landscapes: Land-use intensification and bird conservation in a traditional farming landscape. North-West J. Zool. 2018, 14, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Sallustio, L.; Pettenella, D.; Merlini, P.; Romano, R.; Salvati, L.; Marchetti, M.; Corona, P. Assessing the economic marginality of agricultural lands in Italy to support land use planning. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalej, M. Agricultural land cover changes in metropolitan areas of Poland for the period 1990–2012. Miscellanea Geographica 2016, 20, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- European Environmental Agency (EEA). High Nature Value (HNV) Farmland. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/high-nature-value-farmland#tab-metadata (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- European Environmental Agency (EEA). CORINE Land Cover. Available online: https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- Skoulikidis, N.; Lampou, A.; Karaouzas, I.; Gritzalis, K.; Lazaridous, M.; Zogaris, S. Stream ecological assessment on an Aegean island: Insights from an exploratory application on Samothraki (Greece). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, T.C.; Muhar, A.; Arnberger, A.; Aznar, O.; Boyd, J.W.; Chan, K.M.A.; Costanza, R.; Elmqvist, T.; Flint, C.G.; Gobster, P.H.; et al. Contributions of cultural services to the ecosystem services agenda. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8812–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducci, L.; Roscioni, F.; Carranza, M.L.; Agnelli, P.; Russo, D.; Frate, L.; Loy, A.; Santini, G.; Di Febbraro, M. The role of protected areas in preserving habitat and functional connectivity for mobile flying vertebrates: The common noctule bat (Nyctalus noctula) in Tuscany (Italy) as a case study. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 28, 1569–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peano, A.; Cassatella, C. Landscape Assessment and Monitoring. In Landscape Indicators: Assessing and Monitoring Landscape Quality, 1st ed.; Cassatella, C., Peano, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tieskens, K.F.; Schulp, C.J.E.; Levers, Ch.; Lieskovský, J.; Kuemmerle, T.; Plieninger, T.; Verburg, P.H. Characterizing European cultural landscapes: Accounting for structure, management intensity and value of agricultural and forest landscapes. Land Use Policy 2017, 62, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetzel, T.; Petridisa, P.; Noll, D.; Singh, S.J.; Fischer-Kowalskia, M. Reaching a socio-ecological tipping point: Overgrazing on the Greek island of Samothraki and the role of European agricultural policies. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Llamas, P.; Geijzendorffer, I.R.; García-Niet, A.P.; Calvo, L.; Susana Suárez-Seoane, S.S.; Cramer, W. Impact of land cover change on ecosystem service supply in mountain systems: A case study in the Cantabrian Mountains (NW of Spain). Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucsicsa, G.; Popovici, E.A.; Bălteanu, D.; Grigorescu, I.; Dumitraşcu, M.; Mitrică, B. Future land use/cover changes in Romania: Regional simulations based on CLUE-S model and CORINE land cover database. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 1, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiamonte, G.; Domina, G.; Raimondo, F.M.; Bazan, G. Agricultural landscapes and biodiversity conservation: A case study in Sicily (Italy). Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 3201–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Farm Structure Statics. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Small and large farms in the EU-statistics from the farm structure survey (accessed on 26 June 2019).
- Żmuda, R.; Szewrański, S.; Kowalczy, K.T.; Szarawarski, L.; Kuriata, M. Landscape alteration in view of soil protection from water erosion—An example of the Mielnica watershed. J. Water Land Dev. 2010, 13, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świąder, M. The implementation of the concept of environmental carrying capacity into spatial management of cities: A review. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2018, 29, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).