Sustainability and Environmental Inequality: Effects of Animal Husbandry Pollution in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Estimation Method of Pollutant Discharged from the Animal Husbandry
2.2. Environmental Inequality Measures
2.2.1. Equitable Distribution Index
2.2.2. Economic Efficiency Index
2.3. Panel Threshold Model
3. Study Area and Data
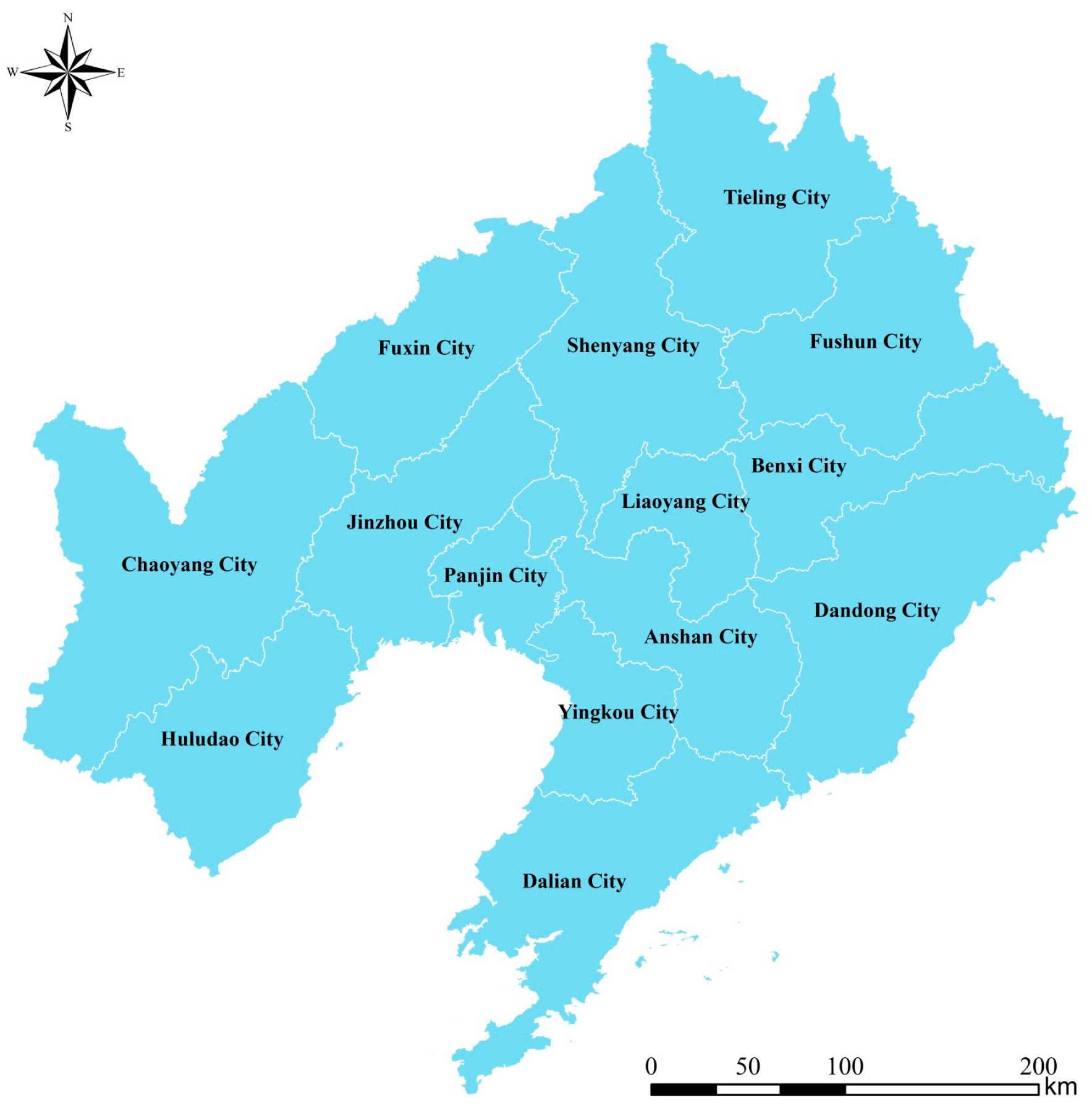
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Sources
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Estimation of COD Discharges of the Animal Husbandry
4.2. Spatial–Temporal Differentiation of COD discharge Inequality
4.3. Threshold Model of Determinants of COD discharge Inequality
4.3.1. Threshold Effect Testing
4.3.2. Threshold Recognition and Estimate
4.3.3. Panel Threshold Model Estimation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WWF. Living Planet Report. 2014. Available online: http://wwf.panda.org/knowledge_hub/all_publications/living_planet_report_timeline/lpr_2014/ (accessed on 8 December 2018).
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld/ (accessed on 8 December 2018).
- Boyce, J.K.; Zwickl, K.; Ash, M. Measuring environmental inequality. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 124, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szasz, A.; Meuser, M. Environmental inequalities: Literature review and proposals for new directions in research and theory. Curr. Sociol. 1997, 45, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellow, D.N.; Weinberg, A.; Schnaiberg, A. The environmental justice movement: Equitable allocation of the costs and benefits of environmental management outcomes. Soc. Justice Res. 2001, 14, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Li, W.Q. On environmental equity, environmental efficiency, and sustainable development. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2003, 13, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.F.; Yao, Z.C.; Li, Y.W. An overview and progress of the study of environmental equity. Adv. Earth Sci. 2009, 24, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Boer, J.T.; Pastor, M.; Sadd, J.L.; Snyder, L.D. Is there environmental racism? The demograhics of hazardous waste in losangeles county. Soc. Sci. Q. 1997, 78, 793–810. [Google Scholar]
- Hird, J.A.; Reese, M. The distribution of environmental quality: An empirical analysis. Soc. Sci. Q. 1998, 79, 693–716. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, H.; Colvin, J. Addressing environmental inequalities in UK policy: An action research perspective. Local Environ. 2005, 10, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulle, R.J.; Pellow, D.N. Environmental justice: Human health and environmental inequality. Ann. Rev. Public Health 2006, 27, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.C.; Wu, J. Assessing environmental inequalities in the city of santiago (chile) with a hierarchical multiscale approach. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 74, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedron, P. Identifying the geographic extent of environmental inequalities: A comparison of pattern detection methods. Can. Geogr. 2016, 60, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, S.F.; Fan, C.Y. Environmental externality and inequality in China: Current Status and future choices. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.C.; Yan, W.J. Research frame and survey of environmental equity issue. China Populat. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Heerink, N.; Mulatu, A.; Bulte, E. Income inequality and the environment: Aggregation bias in environmental Kuznets curves. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 38, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, J.K. Inequality as a cause of environmental degradation. Ecol. Econ. 1994, 11, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.D. Environmental inequality: Air pollution exposures in california’s south coast air basin. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5499–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, C.; Liam, D. Inter-Neighborhood Migration, Race, and Environmental Hazards: Modeling Micro-Level Processes of Environmental Inequality. Am. J. Sociol. 2010, 115, 1110–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.; Mitchell, G.; Fairburn, J.; Smith, G. Industrial pollution and social deprivation: Evidence and complexity in evaluating and responding to environmental inequality. Local Environ. 2005, 10, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, C.M.; Kihal-Talantikite, W.; Vieira, V.M.; Rossello, P.; Le Nir, G.; Zmirou-Navier, D.; Deguen, S. Air quality and social deprivation in four French metropolitan areas—A localized spatio-temporal environmental inequality analysis. Environ. Res. 2014, 134, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüttenauer, T. Neighbours matter: A nation-wide small-area assessment of environmental inequality in Germany. Soc. Sci. Res. 2018, 70, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.P. Study on the fairness of resource-environment system of Jiangxi Province based on different methods of Gini coefficient. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 6431–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.J.; Chen, H.M. Review on the Inequality of Carbon Emissions. Resour. Sci. 2013, 35, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.S.; Xu, J. Inequality in the Distribution of Environmental Benefit and Its Transfer Mechanism. Econ. Res. J. 2016, 51, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Druckman, A.; Jackson, T. Measuring resource inequalities: The concepts and methodology for an area-based gini coefficient. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 65, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.M.; Bitacola, L.M.; Janes, L.M.; Esses, V.M. Intergroup ideology and environmental inequality. Anal. Soc. Issues Public Policy 2013, 13, 327–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Kochan, B.; Bellemans, T.; Wets, G.; Panis, L.I. Modeling personal exposure to air pollution with ab2c: Environmental inequality. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 32, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liévanos, R.S.; Greenberg, P.; Wishart, R. In the shadow of production: Coal waste accumulation and environmental inequality formation in Eastern Kentucky. Soc. Sci. Res. 2018, 71, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Cheng, S.K.; Yu, H.L.; Yang, D.W. Waste from livestock and poultry industry and its potential assessment of biogas energy in rural china. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 126, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Xu, Z.C.; Wu, G.Y.; Yang, J. Construction of pollutants producing and discharging coefficient accounting system for livestock and poultry industry. Environ. Monit. China 2013, 2, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Guo, A.D.; Li, X.M.; Huang, T. Study of the Impact of a High-Speed Railway Opening on China’s Accessibility Pattern and Spatial Equality. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.M. Farm animal welfare and food policy. Food Policy. 1997, 22, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R. The value of farm animal welfare. J. Agric. Econ. 1995, 46, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, M.; Cardinale, D.; Lucia, P.; Faraone, D. Influence of different information presentation formats on consumer acceptability: The case of goat milk presented as obtained from different rearing systems. J. Sens. Stud. 2015, 30, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, M.; Cardinale, D.; Lucia, P.; Faraone, D. Creating public awareness of how goats are reared and milk produced may affect consumer acceptability. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2016, 19, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Luan, W.X.; Kang, M.J. COD pollution load of social and economic activities in Liaohe River Basin, China. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment, the People’s Republic of China. The 2018 Report on the State of the Ecology and Environment in China. 2019. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/zghjzkgb/lnzghjzkgb/201905/P020190619587632630618.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Wang, C.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J.K. Evaluation of pollution source of the bays in Fujian province. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Guan, Y.Y.; Xia, J.H.; Jin, C.; Li, X.M. Spatiotemporal variations in greenspace ecosystem service value at urban fringes: A case study on Ganjingzi District in Dalian, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Ge, Q.S.; Li, X.M. Assessing the Impacts of Urbanization-Associated Green Space on Urban Land Surface Temperature: A Case Study of Dalian, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Dai, L.; Cheng, Z.G.; Li, Y. Spatio-temporal scale analysis on the equality of energy consumption carbon emission distribution in china. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.X.; Gao, Z.Q.; Ning, J.C. Model building discussions on the provincial differences of carbon emissions in china based on fairness for 2010. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 998–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.X.; Gao, Z.Q.; Ning, J.C. Model-based assessment of the pattern differences and the equity of national carbon emissions in China during 2000–2010. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, L.Y. Environmental regulation, upgrading of industrial structure and economic fluctuation: An empirical study of dynamic panel threshold. J. Environ. Econ. 2019, 4, 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.Z.; Chen, Z.; Hou, L. Research on the threshold effect of local government scale and economic growth. Rev. Econ. Manag. 2019, 4, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, B.E. Threshold effects in non-dynamic panels: Estimation, testing, and inference. J. Econ. 1999, 93, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Luan, W.X. Industrial Structure and COD Emission of Livestock and Poultry Breeding in Liaoning Province, NE China: Empirical Research on the Panel Threshold Model. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference of Green Buildings and Environmental Management, Qingdao, China, 23–25 August 2018; Volume 186. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, C.; Esen, Ö. Does the level of energy intensity matter in the effect of energy consumption on the growth of transition economies? Evidence from dynamic panel threshold analysis. Energy Econ. 2018, 69, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
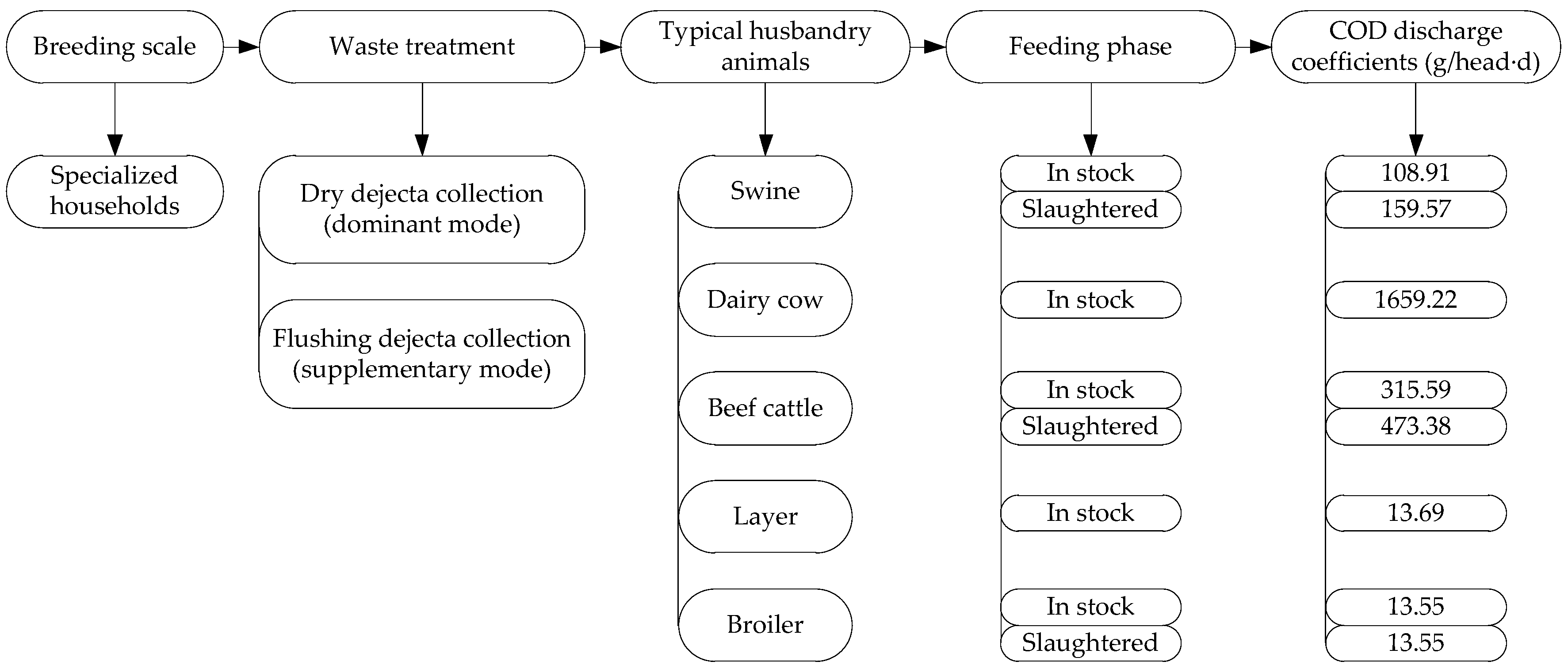


| Variable | Description | Mean | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equitable distribution index (EDI) | COD discharge inequality in distribution | 1.216 | 0.246 | 4.096 |
| Economic efficiency index (EEI) | COD discharge inequality in economic efficiency | 1.069 | 0.391 | 4.237 |
| Economic development level (PGDP) | Gross domestic product/city population | 33,212 | 2461 | 110,682 |
| Industrial structure of agriculture (ISA) | Gross output value of animal husbandry/gross output value of agriculture (ratio) | 0.378 | 0.104 | 0.601 |
| Public fiscal support level for science and technology (FST) | Science & research expenditure/public finance expenditure (ratio) | 0.009 | 0.001 | 0.045 |
| Model | Threshold Forms | F-Value | p-Value | Bootstrap Times | Critical Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% | 5% | 10% | |||||
| EDI | Single threshold | 47.674 *** | 0.004 | 500 | 37.149 | 24.095 | 18.933 |
| Double threshold | 63.335 ** | 0.020 | 500 | 71.090 | 40.405 | 8.104 | |
| Triple threshold | 20.913 | 0.106 | 500 | 47.810 | 29.176 | 21.910 | |
| EEI | Single threshold | 4.569 | 0.230 | 500 | 40.659 | 17.120 | 12.129 |
| Double threshold | 69.828 *** | 0.002 | 500 | 49.742 | 21.276 | 10.348 | |
| Triple threshold | 4.742 | 0.102 | 500 | 9.266 | 6.370 | 4.860 | |
| Threshold Forms | Threshold Estimate | 95% Confidence Intervals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDI | Single threshold | 8.532 | [8.532,8.682] | |
| Double threshold | Ito1 | 11.608 | [11.608,11.608] | |
| Ito2 | 8.532 | [8.532,8.532] | ||
| Triple threshold | 10.053 | [9.839,10.514] | ||
| EEI | Single threshold | 11.375 | [8.532,11.375] | |
| Double threshold | Ito1 | 10.027 | [8.532,11.163] | |
| Ito2 | 11.608 | [11.608,11.608] | ||
| Triple threshold | 10.118 | [8.532,11.360] |
| Model | EDI | EEI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic development level | Lower | Higher | Lower | Medium | Higher | |
| Threshold variable (lnPGDP) | ≤8.532 | >8.532 | ≤10.027 | (10.027, 11.608] | >11.608 | |
| lnISA | −0.561 *** | 0.149 | 0.0333 | −0.185 * | −0.574 *** | |
| (−7.20) | (1.87) | (1.26) | (−2.17) | (−7.89) | ||
| lnFST | 0.0527 ** | 0.0253 | 0.0222 | 0.0464 ** | 0.0133 | |
| (2.65) | (1.16) | (1.26) | (−2.27) | (0.94) | ||
| _cons | 0.329 ** | 0.362 ** | 0.0966 | 0.0156 | 0.0285 | |
| (3.26) | (2.85) | (1.12) | (0.16) | (0.39) | ||
| Fixed region effect | controlled | controlled | controlled | controlled | controlled | |
| Time trend effect | controlled | controlled | controlled | controlled | controlled | |
| F Stat | 70.06 | 55.20 | 88.60 | 84.01 | 109.29 | |
| Prob. F Stat. | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Luan, W.; Xue, Y. Sustainability and Environmental Inequality: Effects of Animal Husbandry Pollution in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174576
Yang Y, Luan W, Xue Y. Sustainability and Environmental Inequality: Effects of Animal Husbandry Pollution in China. Sustainability. 2019; 11(17):4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174576
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yujie, Weixin Luan, and Yunan Xue. 2019. "Sustainability and Environmental Inequality: Effects of Animal Husbandry Pollution in China" Sustainability 11, no. 17: 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174576
APA StyleYang, Y., Luan, W., & Xue, Y. (2019). Sustainability and Environmental Inequality: Effects of Animal Husbandry Pollution in China. Sustainability, 11(17), 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174576




