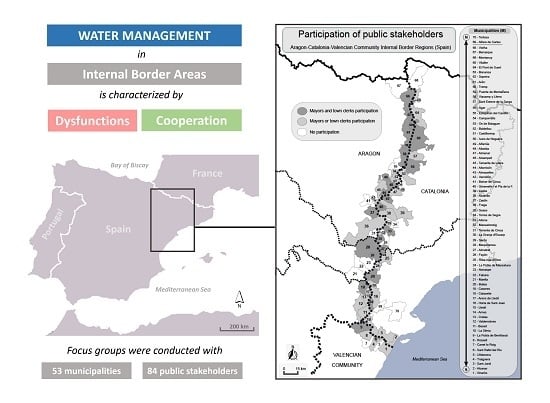
Furthering Internal Border Area Studies: An Analysis of Dysfunctions and Cooperation Mechanisms in the Water and River Management of Catalonia, Aragon and the Valencian Community (Spain)
Abstract
1. Introduction
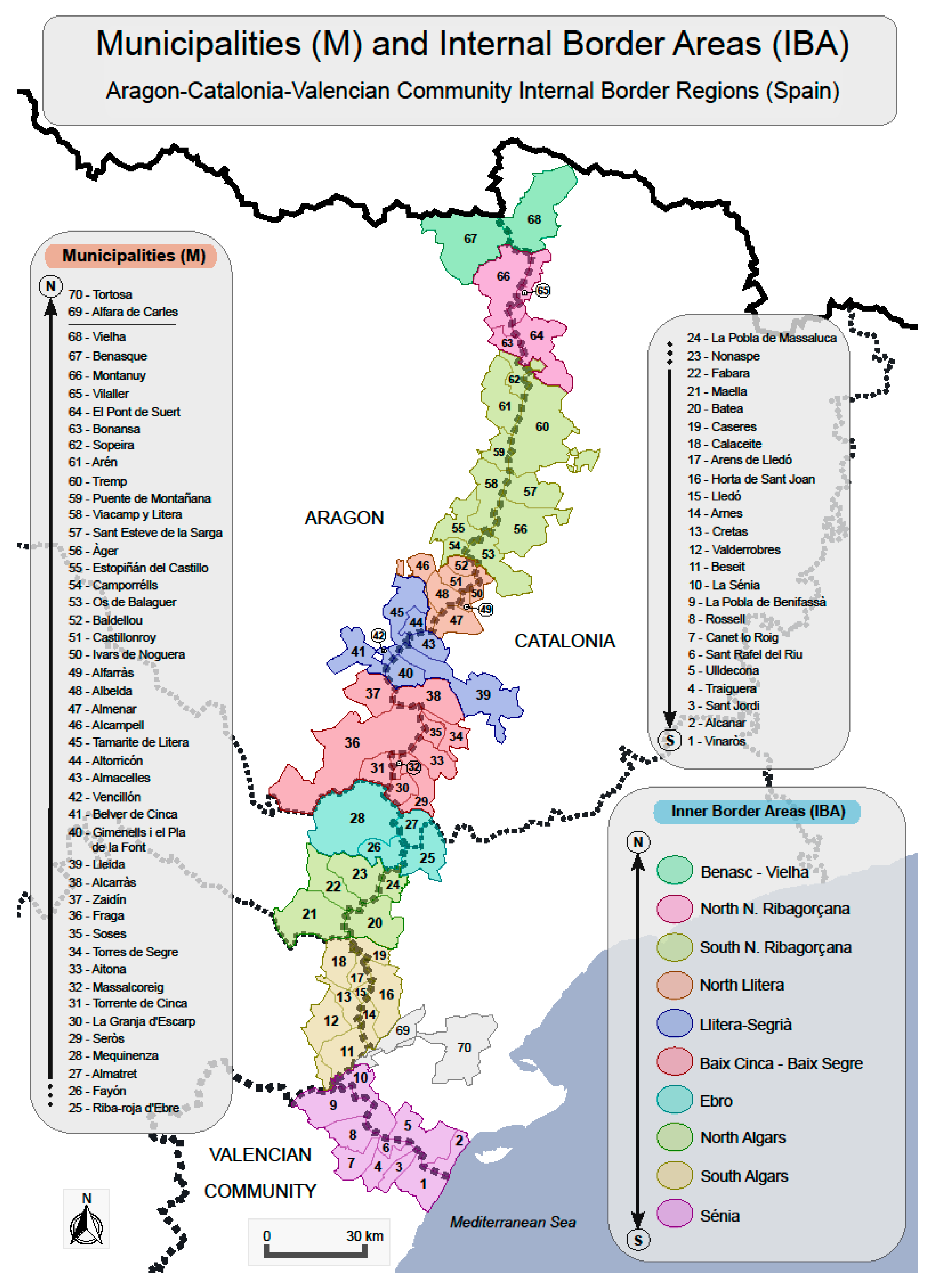
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dysfunctional Water Management
3.2. Water Policies: Matarranya River Contract and Sénia River Commonwealth (Taula del Sénia)
3.3. Tres Territoris River Tourism Project
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paasi, A. Generations and the ‘development’ of border studies. Geopolitics 2005, 10, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Jones, R.; Paasi, A.; Amoore, L.; Mountz, A.; Salter, M.; Rumford, C. Interventions on rethinking ‘the border’ in border studies. Polit. Geogr. 2011, 30, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.M.; Donnan, H. A Companion to Border Studies; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, N.C. The Changing Economics of International Borders and Border Regions. In Borders and Border Regions in Europe and North America; Ganster, P., Sweedler, A., Scott, J., Dieter-Eberwein, W., Eds.; San Diego University: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton, T.M. Recent trends in border economics. Soc. Sci. J. 2003, 40, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; O’Dowd, L.; Wilson, T.M. New Borders for a Changing Europe: Cross-Border Cooperation and Governance; Frank Cass: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Williams, N. Borders, Territory, Law. Int. Polit. Sociol. 2008, 2, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naples, N. Borderlands Studies and Border Theory: Linking Activism and Scholarship for Social Justice. Sociol. Compass 2010, 4, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.; van Assche, K. Understanding Empirical Boundaries: A Systems-Theoretical Avenue in Border Studies. Geopolitics 2014, 19, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillo Santamaría, J.M.; Pires, I. Fronteras en la investigación peninsular: temáticas y enfoques contemporáneos; Universidade de Santiago de Compostela: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2016. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D. Contemporary Research Agendas in Border Studies: An Overview. In The Ashgate Companion to Border Studies; Wastl-Walter, D., Ed.; Ashgate Publishing: Furnham, UK, 2011; pp. 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D. On borders and power: A theoretical framework. J. Borderl. Stud. 2003, 18, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paasi, A. Bounded spaces in a ‘borderless world’: border studies, power and the anatomy of territory. J. Power 2009, 2, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolossov, V.; Scott, J. Selected Conceptual Issues in Border Studies. Belgeo. Revue belge de géographie. 2013. Available online: https://journals.openedition.org/belgeo/10532 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Grygiel, J. Great Powers and Geopolitical Change; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Haselsberger, B. Decoding borders. Appreciating border impacts on space and people. Plan. Theory Pract. 2014, 15, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Jones, R. Where is the Border. In Placing the Border in Everyday Life; Jones, R., Johnson, C., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Brambilla, C.; Laine, J.; Scott, J.W.; Bocchi, G. Borderscaping: Imaginations and Practices of Border Making; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J.W. Borders, border studies and EU enlargement. In The Routledge Research Companion to Border Studies; Wastl-Walter, D., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2016; pp. 145–164. [Google Scholar]
- Nail, T. Theory of the Border; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Evrard, E.; Nienaber, B.; Sommaribas, A. The Temporary Reintroduction of Border Controls Inside the Schengen Area: Towards a Spatial Perspective. 2018. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08865655.2017.1415164 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Parker, N.; Vaughan-Williams, N. Lines in the Sand? Towards an Agenda for Critical Border Studies. Geopolitics 2009, 14, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M. Rethinking borders. In Planning Across Borders in a Climate of Change; Steele, W., Alizadeh, T., Eslami-Andargoli, L., Serrao-Neumann, S., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014; pp. 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Klatt, M.; Herrmann, H. Half Empty or Half Full? Over 30 Years of Regional Cross-Border Cooperation Within the EU: Experiences at the Dutch-German and Danish-German Border. J. Borderl. Stud. 2011, 26, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R. Deriving collaborative aims and outcomes: A case-study of cross-border cooperation in Central and Eastern Europe. Evaluation 2011, 17, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, K.; Magennis, E. The Business of Building Peace: Private Sector Cooperation across the Irish Border. Ir. Polit. Stud. 2014, 29, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf, B.; Raeymaekers, T. Violence on the Margins. States, Conflict and Borderlands; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kurowska-Pysz, J.; Castanho, R.A.; Naranjo-Gómez, J.M. Cross-border cooperation: the barriers analysis and the recommendations. Pol. J. Manag. Stud. 2018, 17, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knotter, A. The Border Paradox. Uneven Development, Cross-Border Mobility and the Comparative History of the Euregio Meuse-Rhine. 2003. Available online: https://popups.uliege.be/1374-3864/index.php?id=237 (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- Hataley, T.; Leuprecht, C. Determinants of Cross-Border Cooperation. J. Borderl. Stud. 2018, 33, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, L. The Changing Significance of European Borders. Reg. Fed. Stud. 2002, 12, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braverman, I.; Blomley, L.; Delaney, D.; Kedar, A. The Expanding Spaces of Law: A Timely Legal Geography; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Holder, J.; Harrison, C. Law and Geography; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Raustiala, K. The Geography of Justice. Fordham Law Rev. 2005, 73, 2501–2560. [Google Scholar]
- Decoville, A.; Durand, F. Establishing cross-border spatial planning. In European Territorial Cooperation; Medeiros, E., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2018; pp. 229–244. [Google Scholar]
- Braunerhielm, L.; Olsson, E.A.; Medeiros, E. The importance of the Swedish-Norwegian border citizens’ perspectives for bottom-up cross-border planning strategies. Nor. J. Geogr. 2019, 73, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E. Cross-border cooperation in inner Scandinavia: A territorial impact assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2017, 62, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E. Spatial Planning, Territorial Development and Territorial Impact Assessment. J. Plan. Lit. 2019, 34, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E. Is there a new ‘trust’ in inner Scandinavia? Evidence from cross-border planning and governance. Geogr. Ann. 2014, 4, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E. Territorial impact assesment and cross-border cooperation. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2015, 2, 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz, D.; DeJong, D.N. Russia’s internal border. Reg. Sci. Urban Eco. 1999, 29, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topaloglou, L.; Kallioras, D.; Manetos, P.; Petrakos, G. A border regions typology in the enlarged European Union. J. Borderl. Stud. 2011, 20, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Woude, M.; van der Leun, J. Crimmigration cheks in the internal border areas of the EU: Finding the discretion that matters. Eur. J. Criminol. 2017, 14, 27–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mosley, H.; Schütz, H. The implementation of active policies in the German regions: decentralization and cooperation. In Labour Market Policy and Unemployment. Impact and Process Evaluations in Selected European Countries; De Koning, J., Mosley, H., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Northampton, UK, 2001; pp. 178–218. [Google Scholar]
- Thoenig, J.C. Territorial Administration and Political Control: Decentralization in France. Pub. Adm. 2005, 83, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, P.; Swales, K. Economics of devolution/decentralization in the UK: Some questions and answers. Reg. Stud. 2010, 39, 477–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L. Decentralization in Spain. Reg. Stud. 2002, 36, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.; Obydenkova, A. Federalization in Russia and Spain: The Puzzle of Reversible and Irreversible Outcomes. Reg. Fed. Stud. 2013, 23, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Huerta, J. Spanish Decentralization and Fiscal Federalism. In Principles and Practices of Fiscal Autonomy. Experiences, Debates and Prospects; Pola, G., Ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2016; pp. 185–201. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C. New directions in binational water resource management in the U.S.-Mexico borderlands. Soc. Sci. J. 2003, 40, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maganda, C. Border water culture in theory and practice: political behavior on the Mexico-U.S. border. J. Polit. Eco. 2012, 19, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, L.J.; Oughton, E.A.; Donaldson, A.; Cook, B.; Forresrer, J.; Spray, C.; Cinderby, D.; Passmore, D.; Bissett, N. Flood risk management, an approach to managing cross-border hazards. Nat. Hazards 2016, 82, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, S.; Shaw, D. Reconceptualizing Territory and Spatial Planning: Insights from the Sea. Plan. Theory Pract. 2013, 14, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, M. Landscapes, water policy and the evolution of discourses on hydropower in Spain. Landsc. Res. 2010, 35, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, N.; Subirats, J. Water Management in Spain: The Role of Policy Entrepreneurs in Shaping Change. 2010. Available online: https://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol15/iss2/art25/ (accessed on 19 August 2019).
- De Stefano, L.; Hernandez-Mora, N. Multi-level interactions in a context of political decentralization and evolving water-policy goals: the case of Spain. Reg. Environ. Change 2018, 18, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Flores, J. La metodología de investigación mediante grupos de discusión. Enseñanza 1993, 10–11, 199–214. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Kitzinger, J. The methodology of Focus Groups: the importance of interaction between research participants. Soc. Health Illn. 1994, 16, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyumba, T.O.; Wilson, K.; Derrick, C.J.; Mujerjee, N. The use of focus groups discussion methodology: Insights from two decades of application in conservation. Methods Eco. Evol. 2018, 9, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheer, D.P. Dysfunctional Water Management: Causes and Solutions. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2009, 136, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, A. Arguments for involving the public in water management: evidence from local and regional plans in the Netherlands. Water Policy 2016, 18, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, D.E. Privatization and Commodification of the Resource. In Water Resource Management. Sustainability in an Era of Climate Change; McNabb, D.E., Ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2017; pp. 307–327. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchis-Ibor, C.; Boelens, R.; García-Mollá, M. Collective irrigation reloaded. Re-collection and re-moralization of water management after privatization in Spain. Geoforum 2017, 87, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Borghgraef, K.; Vinckier, C. Causes of Water Supply Problems in Urbanised Regions in Developing Countries. Water Res. Manag. 2009, 24, 1885–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, D. National Scenario of Rural Water Supply: Problems and Prospects. In Water and Sanitation in the New Millenium; Narth, K., Sharma, V., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2017; pp. 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Arana, V. Governance, Planning, Capacities and Management Models. In Water and Territory in Latin America. Trends, Challenges and Opportunities; Arana, V., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2016; pp. 123–143. [Google Scholar]
- La Jeunesse, I.; Rounsevell, M.; Vanclooster, M. Delivering a decision support system tool to a river contract: a way to implement the participatory approach principle at the catchment scale? Phys. Chem. Earths, Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillon, F. Valley Landscape management: the context of a ‘river contract’ in the Semois valley, Belgium. Landsc. Res. 2004, 29, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mees, H.; Suykens, C.; Crabbé, A. Evaluating Conditions for Integrated Water Resource Management at Sub-basin Scale. A Comparison of the Flemish Sub-basin Boards and Walloon River Contracts. Environ. Policy Gov. 2017, 27, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Allain, S. Social Participation in French Water Management: Contributions to River Basin Governance and New Challenges. In Water Governance and Management. Critical and Global Perspectives; Berry, K., Mollard, E., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; pp. 95–113. [Google Scholar]
- Scaduto, M.L. River Contracts and Integrated Water Management in Europe; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brun, A. France’s Water policy: The Interest and Limits of River Contracts. In Globalized Water. A Question of Governance; Schneier-Madanes, G., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, M. River Tourism in the South Asian Subcontinent. In River Tourism; Prideaux, B., Cooper, M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 23–40. [Google Scholar]
- Prideaux, B.; Cooper, M. River Tourism; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Timothy, D.J. River-based Tourism in the USA: Tourism and Recreation on the Colorado and Mississipi Rivers. In River Tourism; Prideaux, B., Cooper, M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Deiminiat, A.; Shojaee-Siuki, H.; Eslamian, S. Tourism and River Environment. In Handbook of Engineering Hydrology. Environmental Hydrology and Water Management; Eslamian, S., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2014; pp. 401–419. [Google Scholar]
- Laws, E.; Semone, P. The Mekong: Developing a New Tourism Region. In River Tourism; Prideaux, B., Cooper, M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Arlt, W.G.; Feng, G. The Yangzi River Tourism Zone. In River Tourism; Prideaux, B., Cooper, M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2009; pp. 117–129. [Google Scholar]
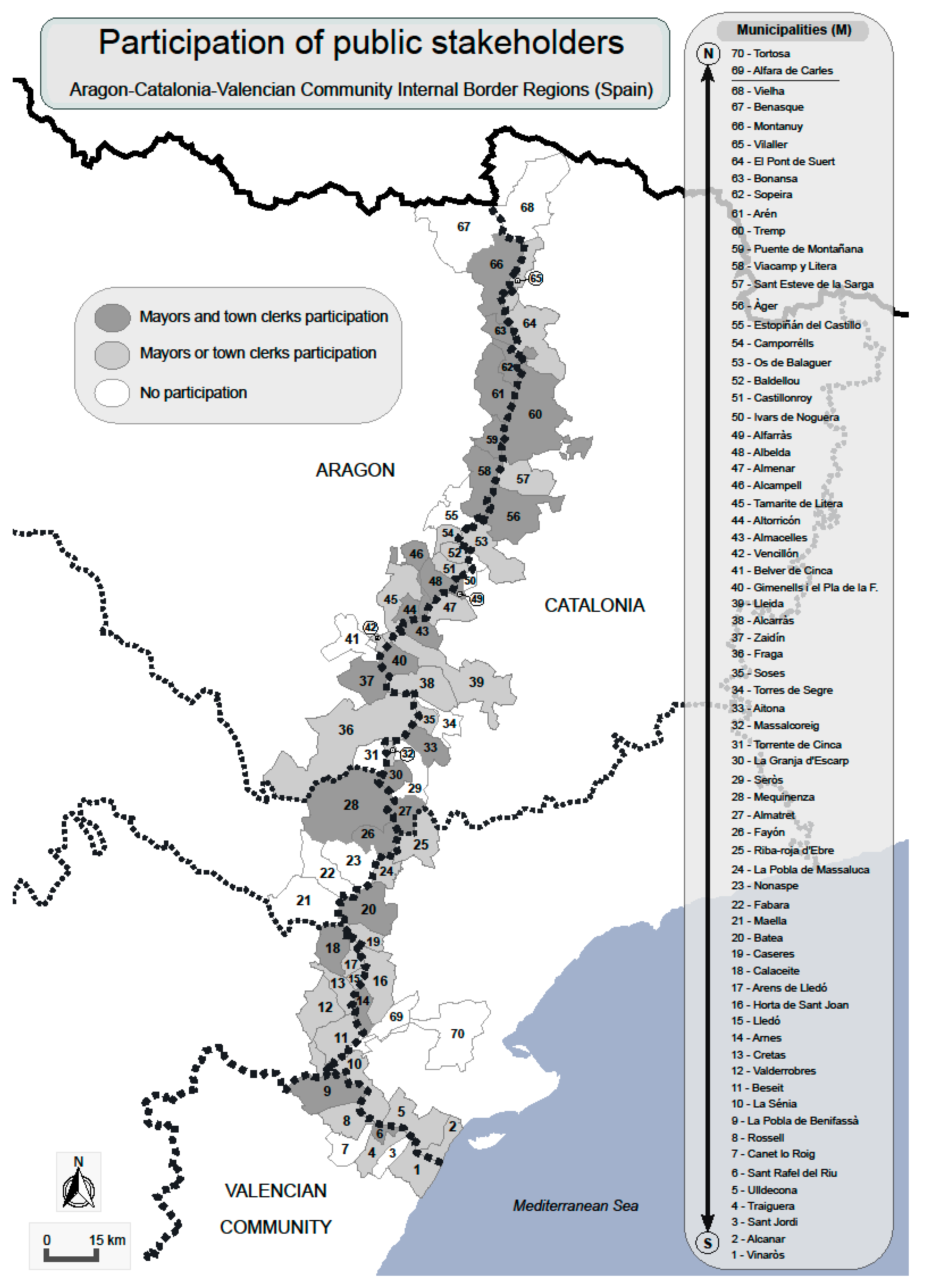
| N | IBA 1 | TM 2 | A/C/V 3 | NS 4 | SM 5 | DL 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Noguera Ribagorçana | PM = 4 TM = 4 | 2/2/0 2/2/0 | PS = 4M/4TC TS = 4M/3TC | M = 63A, 64C, 65C, 66A TC = 63A, 65C, 66A | 2017/05/30 64C |
| 2 | South Noguera Ribagorçana | PM = 10 TM = 9 | 6/4/0 5/4/0 | PS = 10M/10TC TS = 8M/6TC | M = 54C, 56C, 57C, 58A, 59A, 60C, 61A, 62A TC = 53C, 56C, 58A, 59A, 61A, 62A | 2017/05/29 61A |
| 3 | North Llitera | PM = 7 TM = 5 | 4/3/0 3/2/0 | PS = 7M/7TC TS = 4M/5TC | M = 46A, 47C, 48A, 49C TC = 46A, 47C, 48A, 49C, 52A | 2017/05/23 49C |
| 4 | Llitera-Segrià | PM = 7 TM = 6 | 4/3/0 3/3/0 | PS = 7M/7TC TS = 5M/4TC | M = 40C, 42A, 43C, 44A, 45A C = 39C, 40C, 43C, 44A | 2017/05/10 43C |
| 5 | Baix Cinca–Baix Segre | PM = 10 TM = 7 | 3/7/0 2/5/0 | PS = 10M/10TC TS = 4M/6TC | M = 30C, 33C, 36A, 37A TC = 30C, 32C, 33C, 35C, 37A, 38C | 2017/05/09 33C, 37A |
| 6 | Ebro | PM = 4 TM = 4 | 2/2/0 2/2/0 | PS = 4M/4TC TS = 3M/4TC | M = 26A, 27C, 28A TC = 25A, 26A, 27C, 28A | 2017/04/26 28A |
| 7 | North Algars | PM = 5 TM = 1 | 3/2/0 0/1/0 | PS = 5M/5TC TS = 1M/1TC | M = 20C TC = 20C | 2017/03/27 18V |
| 8 | South Algars | PM = 9 TM = 9 | 6/3/0 6/3/0 | PS = 9M/9TC TS = 8M/7TC | M = 11V, 12V, 13V, 14C, 16C, 17V, 18V, 19C TC = 13V, 14C, 15V, 16C, 17V, 18V, 19C | 2017/03/27 18V |
| 9 | Sénia | PM = 10 TM = 8 | 0/3/7 0/3/5 | PS = 10M/10TC TS = 6M/5TC | M = 1V, 4V, 5C, 6V, 8V, 9V TC = 1V, 2C, 6V, 9V, 10C I 7 = Taula del Sénia Clerk | 2017/01/30 10C, 6V |
| N | IBA 1 | WMD 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | North Noguera Ribagorçana | No dysfunctions detected. |
| 2 | South Noguera Ribagorçana | Problems derived from privatization of water company (ENEL) Conflict of competencies between Ebro Water Agency (CHE) 3 and Catalan Water Agency (ACA) 4 Overexploitation of water derived from a tourist activity (Congost de Mont-Rebei) |
| 3 | North Llitera | Lack of communication with Ebro Water Agency (CHE) Different regulation of fishing between Aragon and Catalonia |
| 4 | Llitera-Segrià | Double taxation: conflict between Catalan Water Agency (ACA) and Ebro Water Agency (CHE) Lack of communication between Ebro Water Agency (CHE) and municipalities in Aragon & Catalonia Canal irrigation management |
| 5 | Baix Cinca – Baix Segre | Double taxation: conflict between Catalan Water Agency (ACA) and Ebro Water Agency (CHE) Lack of communication between Ebro Water Agency (CHE) and municipalities in Aragon & Catalonia Canal irrigation management |
| 6 | Ebro | Different regulation of fishing between Aragon and Catalonia Historical problem: (a) construction of Mequinensa reservoir (1970s) and difficulty of physical communication with towns on the other shore; (b) mismanagement of sludge by Ebro Water Agency (CHE) |
| 7 | North Algars | Different regulation of boat license and fishing between Aragon and Catalonia |
| 8 | South Algars | Difficulty in water supply due to mismanagement of Catalan Water Agency (ACA) |
| 9 | Sénia | Double taxation: conflict between Jucar Water Agency (CHJ) 5 and Ebro Water Agency (CHE) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santasusagna Riu, A.; Galindo Caldés, R.; Tort Donada, J. Furthering Internal Border Area Studies: An Analysis of Dysfunctions and Cooperation Mechanisms in the Water and River Management of Catalonia, Aragon and the Valencian Community (Spain). Sustainability 2019, 11, 4499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164499
Santasusagna Riu A, Galindo Caldés R, Tort Donada J. Furthering Internal Border Area Studies: An Analysis of Dysfunctions and Cooperation Mechanisms in the Water and River Management of Catalonia, Aragon and the Valencian Community (Spain). Sustainability. 2019; 11(16):4499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164499
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantasusagna Riu, Albert, Ramon Galindo Caldés, and Joan Tort Donada. 2019. "Furthering Internal Border Area Studies: An Analysis of Dysfunctions and Cooperation Mechanisms in the Water and River Management of Catalonia, Aragon and the Valencian Community (Spain)" Sustainability 11, no. 16: 4499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164499
APA StyleSantasusagna Riu, A., Galindo Caldés, R., & Tort Donada, J. (2019). Furthering Internal Border Area Studies: An Analysis of Dysfunctions and Cooperation Mechanisms in the Water and River Management of Catalonia, Aragon and the Valencian Community (Spain). Sustainability, 11(16), 4499. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11164499