Abstract
Soil microorganisms play important roles in the plant health and agricultural production. However, little is known about the complex responses of microbial communities and interaction networks to different agricultural management practices in tea plantation soils. In the present study, Illumina Miseq high-throughput sequencing technology and molecular ecological network (MEN) analysis were used to investigate the soil microbial diversity, community structure and composition, interaction networks of organic tea plantation (OTP), non-polluted tea plantation (NPTP) and conventional tea plantation (CTP). Alpha-diversity indices, Chao1 and richness, of OTP soil were significantly higher than those of NPTP and CTP soils. The beta-diversity analysis showed there were significant differences among bacterial community structures of OTP, NPTP and CTP soils. Composition analysis showed that Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria and Chloroflexi were the most dominant bacteria in all tea plantation soil samples under different management practices, and the beneficial community compositions of OTP soil were significantly different from NPTP and CTP soils at the phylum and genus levels. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) and mantel test revealed that TOC and NO3-N contents as well as pH values were the key soil factors to affect the bacterial community structures of tea plantation soils. Furthermore, network analysis showed that the network of OTP soil possessed more functionally interrelated microbial modules than NPTP and CTP soils, indicating that OTP soil possessed the higher ecosystem multi-functionality. These results provided the theoretical basis and reference for improving soil microbial diversity and enhancing community multi-functionality in tea plantation soil ecosystems through effective agricultural management practices.
1. Introduction
As the world’s largest tea (Camellia sinensis) producer and exporter, China is the first country to discover, utilize and cultivate tea plants in the world [1]. The tea plantation in China covers a total area of 3680 hectares, and its tea yield is 2609 million tons by the end of 2017, accounting for 60% and 40% of world’s total tea plantation area and total tea production, respectively. As an important cash crop, tea plays a critical role in adjusting the structure of agricultural industry, promoting the development of efficient agriculture, increasing the farmers’ incomes and developing the rural economy in China.
The traditional intensive agricultural management practices with high inputs of synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers not only lead to serious damage to the ecological environment of the tea plantation [2,3], but also cause the excessive pesticide residues in tea [4,5], which affect the quality and value of tea. It is well known that organic agricultural management practices have significant positive effects on improving the soil structure with the increase of soil organic matter content [6,7], consequently decreasing the soil erosion and soil nutrient loss [8]. However, one of the major challenges for organic agricultural management practice is to enhance the soil nutrient availability by improving soil physicochemical properties [9]. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the quality of tea and enhance the soil fertility to achieve sustainable development of tea production through the application of effective agricultural management practices [10].
Soil microorganisms play the essential roles in soil formation and development, farmland material circulation, fertility evolution, degradation and purification of toxic substances [11,12]. Soil is an excellent culture medium for the growth and development of various microorganisms due to the availability of nutrients, water, organic and inorganic matter [13]. Plant roots and soil microorganisms interact with each other in the rhizosphere, significantly affecting growth, development and health of plants [14]. The bulk soil microbiota are the main bank of the plant rhizosphere and endophytic microbiota, and they are driven by different plant genotypes and migrated into plant endophytic microbiota through niche utilization and interactions with the host [15,16]. The endophytic bacteria may be microbial symbionts or recessive pathogens of root and stem tissues [17]. Therefore, the bulk soil microorganisms play an important role in enhancing soil fertility, improving plant nutrient absorption, enhancing plant stress resistance and resisting soil-borne pathogens [18,19]. In addition, at present, the study on soil microbial community and composition of tea plantation has become an important topic in current agricultural production [20,21].
In the present study, we aimed to (i) investigate the microbial diversity, community composition and structure of tea plantation soils, such as conventional tea plantation (CTP), non-polluted tea plantation (NPTP) and organic tea plantation (OTP), under different long-term management practices; (ii) study the effects of different long-term management practices on the physicochemical properties of tea plantation soils, and establish the correlation between soil properties and microbial community structure; and (iii) analyze the networks of interactions among resident microbes and differences of ecological functional modules of tea plantation soil communities under different management practices through network analysis. We found that there were differences in bacterial diversity, community structure and composition, network structure and ecological functional groups in bulk soils of tea plant under different management practices. Our findings provided data support and theoretical basis for improving the quality and microecological environment of tea plantation soil and promoting sustainable development of tea industry through effective agricultural practice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Soil Sampling
A long-term experimental site is located in Changsha County of Changsha city with subtropical monsoon climate, Hunan Province, China, which is established in 2003. The type of tea plantation soils is a typical red soil. Three management practices were designed in this experiment as follows: OTP (organic inputs), NPTP (organic-chemical combined inputs) and CTP (chemical inputs). A detailed description of three management practices was as follows: OTP, commercial organic fertilizer + cow manure + pig manure + insect, disease and weed management as approved for organic farming insecticides (Bacillus thuringiensis, nucleopolyhedrovirus, Beauveria bassiana, matrine, kasugamycin, valienamineand so on; manual weeding or mowing); NPTP, commercial organic fertilizer + cow manure + pig manure + urea + ammonium sulfate + potassium sulfate + calcium magnesium + phosphate fertilizer + calcium superphosphate + insect, disease and weed management as approved for organic farming insecticides (Bacillus thuringiensis, nucleopolyhedrovirus, Beauveria bassiana, matrine, kasugamycin, valienamine and so on; manual weeding or mowing) + herbicides, fungicides and insecticides were used as recommended insecticides (phoxim, cypermethrin, diflubenzuron, buprofezin, carbendazim, chlorothalonil, sulfonylurea herbicides and so on); CTP, urea + ammonium sulfate + potassium sulfate + calcium magnesium + phosphate fertilizer + calcium superphosphate + herbicides, fungicides and insecticides were used as recommended insecticides (phoxim, cypermethrin, diflubenzuron, buprofezin, carbendazim, chlorothalonil, sulfonylurea herbicides and so on). There were three experimental plots for each management practice, with a size of larger than 1200 m2. In order to minimize fertilizer and pesticide drift, the experimental plots were separated by 10-m alleyways of camphor trees.
Soil samples were randomly collected from the bulk soils of tea plants at the depths of 0–20 cm. A total of 50 soil cores were taken from each experimental plot of each management practice by using the checkerboard sampling method in September 2017. Five soil cores were pooled to form a composite sample, and 10 bulk soils from tea plantation under each management practice were randomly collected from 50 tea plants. Moreover, a total of 30 soil samples were collected and stored at −80 °C until DNA extraction. One part of soil samples was assigned for detecting the physicochemical properties, while the other part was used to perform molecular analysis.
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of Soils
The following physicochemical properties of collected soil samples were determined: pH, total organic carbon (TOC), nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N), ammonia nitrogen (NH4-N), total nitrogen (TN), available phosphorus (AP), moisture and total phosphorus (TP). The soil properties were determined by the previously reported methods [22].
2.3. DNA Extraction and Amplicon Sequencing
DNA extraction of soil samples and amplicon sequencing were performed by previously described methods [23]. The purified DNA was used as a template to amplify the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene by using the 515F (5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA-3′)/806R(5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) primers. PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification was performed on a SelectCycler II (Select BioProduct). E.Z.N.A. TM Gel Extraction Kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, USA) was used to purify the PCR products. The purified amplicons were quantified by using a Qubit fluorometer (Life Technologies Holdings Pte Ltd., Singapore), and the library was constructed with VAHTSTM Nano DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). The samples were sequenced by Miseq sequencing machine (Illumina) at Central South University, China.
2.4. Sequence Preprocessing and Bioinformatic Approaches
The barcodes were assigned to the raw reads (with one mismatch allowance). After removal of barcodes and primers, pair-ended sequences were quality-filtered by using Flash program [24]. UPARSE algorithm [25] was used to remove chimeras and generate OTU (operational taxonomic unit) table at a similarity level of 97% without discarding any singletons. All the sequence preprocessings were performed in an in-house pipeline (http://mem.rcees.ac.cn:8080) with a series of bioinformatic tools (e.g., Btrim program, UPARSE, FLASH).
2.5. Ecological and Statistical Analysis
The Chao1 [26] and richness indices were calculated to analyze the alpha-diversity of microbial community in tea plantation soils under different management practices. Principal components analysis (PCA) plot based on UniFrac distances was performed to evaluate the differences in microbial community structure [27]. The canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) and mantel test were applied to correlate the soil properties and microbial community structure. The significant difference tests of the microbial community between different samples were conducted by two different statistical approaches, including analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) and non-parametric permutational multivariate analysis of variance of the Adonis function (PERMANONA).
2.6. Network Analysis
To explore microbial interactions of soil communities in tea plantation soils under different management practices, the phylogenetic Molecular ecological networks (pMENs) were constructed through Random Matrix Theory (RMT)-based approach in MEN analysis pipeline (MENA, http://ieg2.ou.edu/MENA/) [28,29]. The detailed operation process was consistent with a previously described method [28]. First, only OTUs that were observed in more than eight soil samples were obtained without log-transferring prior to obtaining Spearman rank correlation matrix (r value). The threshold values ranging from 0.01 to 0.99 with 0.01 intervals were used in the Spearman’s rank correlation. The optimal threshold value was kept for calculating the network eigenvalues when the nearest-neighbor spacing distribution followed the Poisson distribution well, which is associated with characteristic nonrandom properties in the complex ecosystem [30]. Furthermore, the appropriate consistent threshold value (0.91) was applied to construct networks to compare the different networks under the same conditions. Further network topological properties (R2 of power law, average connectivity, average path length, average clustering coefficient and modularity) were all analyzed and shown in Table S3. The constructed networks of soil communities for tea plantation soils under different management practices were visualized by Cytoscape 3.3.0 software [31].
3. Results
3.1. Microbial Diversity
A total of 549,196 high-quality reads (OTP soil, 169, 251; NPTP soil, 164, 928; CTP soil, 215, 017) were obtained from 30 samples by utilizing high-throughput sequencing analysis. The rarefaction curves of OTUs tended to approach the saturation plateau, indicating that the range of sequencing coverage was enough for downstream data analysis (Figure S1). Richness (Figure 1a) and Chao1 (Figure 1b) indices were used to compare the alpha-diversity of microbial communities in tea plantation soils under different management practices. The results showed that the alpha-diversity of soil community was ranked as follows: OTP > NPTP > CPT, indicating that there were significant differences for bacterial diversity among OTP, CTP and NPTP soils (p < 0.05). In addition, we further analyzed the beta-diversity of microbial communities in tea plantation soils under different management practices, and PCA of microbial communities revealed a clear separation between CTP soil and both of OTP and NPTP soils, while a partial overlap between OTP and NPTP soils was observed (Figure 2). The dissimilarity tests of bacterial communities in tea plantation soils under different management practices were carried out using ANONISM and MRPP based on Bray-Curtis distance, and the results showed that there were significant differences in soil bacterial communities among OTP, NPTP and CTP soils (Table S1). In brief, we concluded that there were significant differences for alpha and beta diversity among OTP, CTP and NPTP soil bacterial communities.
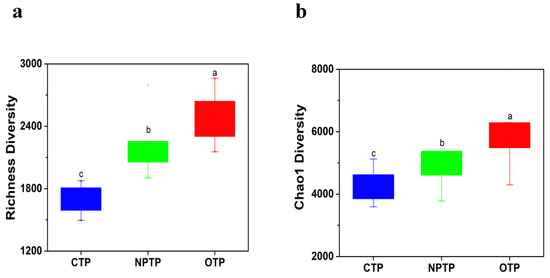
Figure 1.
Diversity indices based on 16S rRNA gene of bacterial community in tea plantation soils under different management practices. (a) richness index; (b) Chao1 index. Different letters represent the significant difference among soils at p < 0.05. OTP: organic tea plantation, NPTP: non-polluted tea plantation, CTP: conventional tea plantation, similarly hereinafter.
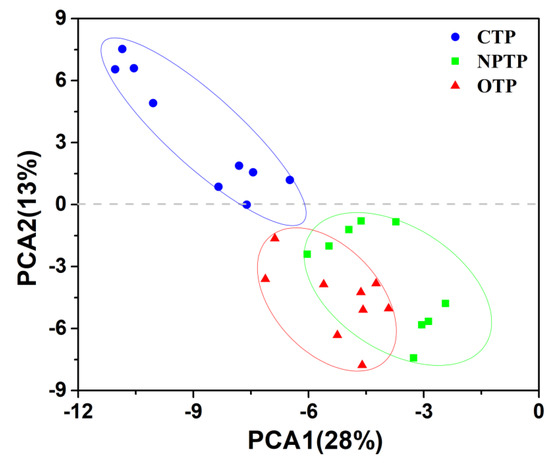
Figure 2.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of bacterial community structures in tea plantation soils under different management practices.
3.2. Microbial Community Composition
All OTUs of samples were identified as 36 phyla and 652 genera, and the cladogram indicated the phylogenetic distribution of bacterial lineages in tea plantation soils under different agricultural management practices (Figure 3a), showing that there were significant differences for the microbial community components of OTP, CTP and NPTP soils from phylum to genus levels (p < 0.05). The 13 dominant phyla (relative sequence abundance >1%) across all samples were Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, Thaumarchaeota, Verrucomicrobia, Bacteroidetes, Candidate division Wps-2, Planctomycetes, Nitrospirae, Woesearchaeota and unclassified bacteria (Figure 3b). The relative abundances (Table S2) of phyla Verrucomicrobia (8.66%), Bacteroidete (3.19%) and Planctomycetes (2.92%) in OTP soil were significantly higher than those of CTP and NPTP soils (p < 0.05), while the lowest abundances of Proteobacteria (16.78%), Nitrospirae (0.07%), Verrucomicrobia (1.97%), Bacteroidete (1.67%) and Planctomycetes (1.06%) were significantly observed in CTP soil (p < 0.05).
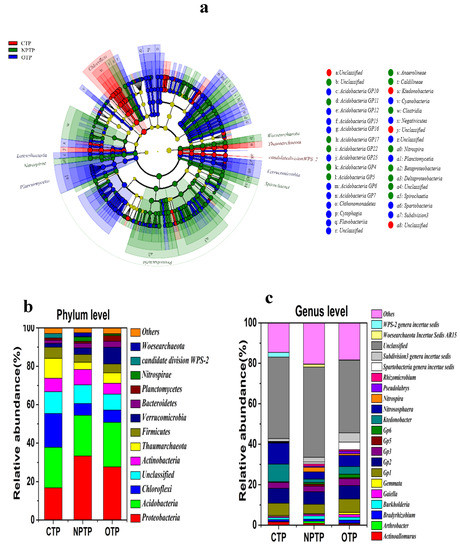
Figure 3.
Comparison of microbial community compositions in tea plantation soils under different management practices. (a) Cladogram showing the phylogenetic distribution of the most differentially abundant taxa in tea plantation soils under different management practices. Each circle’s diameter is relative to the abundance of taxa in different tea plantation soil communities, different colors represent the differences of the most differentially abundant taxa in different tea plantation soil communities (blue indicates OTP, red indicates CTP, green indicates NPTP), circles represent phylogenetic levels from domain to genus; (b) comparison of the soil community composition at phylum level (relative abundance higher than 1%); (c) comparison of the soil community composition at genus level (relative abundance higher than 1%).
The 21 dominant genera (relative sequence abundance >1%) across all samples were Ktedonobacter, Gp2, Gp1, Gp2, Gp3, Gp5, Gp6, Subdivision 3 genera incertae sedis, Spartobacteria genera incertae sedis, Burkholderia, Bradyrhizobium, Nitrospira, Actinoallomurus, WPS-2 genera incertae sedis, Gaiella, Rhizomicrobium, Pseudolabrys, Gemmata, Arthrobacter, AR15 and unclassified bacteria (Figure 3c). The relative abundances (Table S2) of genera Gemmata (1.03%), Gaiella (1.3%), GP6 (1.76%), Bradyrhizobium (1.47%), Pseudolabrys (1.29%), Spartobacteria genera incertae sedis (3.71%) and Subdivision3 genera incertae sedis (4.65%) in OTP soil were significantly higher than those of CTP and NPTP soils (p < 0.05), and the lowest relative abundances of genera Bradyrhizobium (0.94%), Gemmata (0.47%), Nitrospira (0.07%), Pseudolabrys (0.14%), Rhizomicrobium (0.28%) and Spartobacteria genera incertae sedis (0.28%) were observed in CTP soil. Overall, the microbial composition and relative abundance of bacterial phyla and genera were significantly different in OTP, CTP and NPTP soils.
3.3. Correlation Analysis between Soil Properties and Bacterial Community Structures
Table 1 shows the physicochemical properties of tea plantation soils under different long-term management practices. The TOC and NO3-N contents and pH values in OTP soil were significantly higher than those in NPTP and CTP soils. No significant difference in TP content was observed among OTP, NPTP and CTP soils. The CCA plots of microbial community structures and soil properties showed that pH as well as TOC and NO3-N contents were the three longest vectors (Figure 4a). Furthermore, a partial Mantel test (Figure 4b) based on both Bray-Curtis and Jaccard distances also demonstrated that pH as well as TOC and NO3-N contents were key physicochemical factors in assembling the microbial communities of tea plantation soils under different long-term management practices (pH, p < 0.001; TOC, p < 0.01; NO3-N, p < 0.01).

Table 1.
Soil properties of tea plantation soils under different management practices.
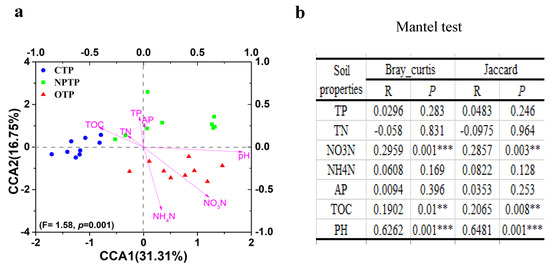
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis between soil properties and bacterial community structures. (a) Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA); (b) Mantel test. Asterisks denote the p-value for the difference: ** Difference is significant at 0.01 level. *** Difference is significant at 0.001 level.
3.4. Molecular Ecology Networks
pMENs analysis was applied to reveal the influence of different agricultural practices on the microbial interactions of tea plantation soils. Three networks analyses with the same threshold (0.91) were performed for the OTP, NPTP and CTP soils, respectively (Table S3). The OTP, NPTP and CTP networks consisted of 493, 387 and 210 nodes as well as 756, 637 and 452 links, respectively, suggesting that OTP network possessed a more complex structure and a higher number of microbial interactions compared with NPTP and CTP networks. The CTP network had the highest values of average degree (avgK, 4.305), average path distance (GD, 7.126) and average clustering coefficient (avgCC, 0.333) compared to NPTP (avgK, 3.292; GD, 6.042; avgCC, 0.208) and OTP (avgK, 3.067; GD, 6.803; avgCC, 0.177) networks, indicating that the interaction relationship among resident species of the CTP soil communities was more close. In addition, the avgCC (0.177–0.333) of empirical networks was higher than that of the corresponding random networks (0.008–0.035), suggesting that our three networks had the typical small-world characteristics [32]. The modularity (M) values (0.666–0.749) of OTP, NPTP and CTP networks were all significantly higher than the M values (0.456–0.618) in corresponding randomized networks, indicating that all the networks had the characteristic of modular topology [33]. In order to provide an intuitionistic exhibition of interaction relationship among resident microorganisms within tea plantation soils, the visualized networks of OTP, NPTP and CTP were shown in Figure 5a–c, respectively. The network structure of OTP soil had a greater number of topological modules (22 modules) than that of NPTP network (17 modules) and CTP network (9 modules). Overall, these results indicated that the topological structures of OTP, NPTP and CTP networks were significantly different.

Figure 5.
The networks of interactions among resident species of bacterial communities in tea plantation soils under different management practices. (a) OTP Network; (b) NPTP Network; (c) CTP Network. A module consists of larger than 5 nodes. Each node represents an OTU of bacteria. Different colors of node belong to different bacterial phyla. Blue links stand for positive interactions between nodes and red links stand for negative interactions.
4. Discussion
The microorganisms are involved in a variety of important biochemical processes for soil ecosystem functions [34]. Moreover, the microbial community structure and composition can directly affect the stability and balance of soil microecosystem, thereby impairing the plant growth, development, health and productivity [19]. Soil microorganisms mainly consist of bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes, among which bacteria are the most abundant species playing important roles in various biological processes of soils (such as ammoniating reaction and organic degradation) [35]. Massive inputs of chemical fertilizers and synthetic pesticides can lead to the decline of the populations of soil microorganisms, leading to the soil degradation, which is similar to the overuse of antibiotics in humans [36]. Previous studies have shown that different long-term management practices affect the microbial diversity and community structure of plant soils [7,37]. The organic management practice of tea plantation relies on a series of farming practices that do not use synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers to meet the needs of plant nutrition and control of pests and diseases in the production process [38]. Long-term application of organic fertilizers has positive influence on aspects of biology, physics and chemistry of soil fertility, as well as the soil microbial diversity and function [39]. However, most of pesticides largely have negative effects on soil microorganisms and reduce the numbers of soil microorganisms and soil microbial biomass [40,41,42]. Some studies have shown that application of biopesticides has fewer negative effects on the microbial diversity and community structure compared with chemical pesticides [43]. The effects of long-term organic management practices on microbial communities have been well evaluated in alternative farming systems that it can improve the diversity and stability of soil microbial community across different climatic and soil conditions [7,44]. Our results indicated that the organic management practices (OTP) could improve the microbial diversity of tea plantation soils compared with the chemical-inputs (CTP) and chemical-organic combined inputs (NPTP). Different long-term agricultural management practices could markedly alter the soil microbial community structure. The PCA results showed the clear separation of bacterial community structures of OTP, NPTP and CTP (Figure 3). In combination with the results of dissimilarity test of soil communities (Table S2), we showed that the different long-term agricultural management practices resulted in the differences in the microbial community structures.
Different long-term agricultural management practices affected the microbial community composition and function of tea plantation soils. The relative abundances of phyla Verrucomicrobia, Bacteroidetes and Planctomycetes in OTP soil were significantly higher than those of NPTP and CTP soils (Table S1). Previous studies have showed that phyla Verrucomicrobia and Bacteroidetes can play important roles in effectively degrading organic matter and increasing the general level of plant resistance [45]. The phylum Planctomycetes is involved in the absorption of plant nutrients, especially in the utilization of carbon and nitrogen sources [46]. The genera Nitrospira (phylum Nitrospirae) and Rhizomicrobium are regarded as the nitrifier and have the ability to change nitrite to nitrate. Crucially, their relative abundances are the lowest in the CTP soil [47,48], which can explain the fact that the NO3-N content in CTP soil was lower compared with OTP and NPTP soils. The highest relative abundances of genera Gemmata, Pseudolabrys and Bradyrhizobium were observed in OTP soil, while their lowest values were observed in CTP soil. Genus Gemmata can increase the enzymatic activity of urease with the ability of degrading organic matter through enzymatic reaction [49], which can improve the utilization efficiency of organic matter for tea plants. Genus Pseudolabrys has been reported as a beneficial biocontrol microorganism in plant rhizosphere soils [50]. In addition, the pesticides can significantly decrease mycorrhizal and rhizobial performance in soybean and adversely affect nitrogen fixation and overall plant growth as well [51]. Furthermore, the pesticides can decrease the recruitment of rhizobia bacteria to host plant roots, resulting in less production of root nodules [52]. These finding can explain well that the CTP soil has the lowest relative abundances of Bradyrhizobium. Beneficial root-colonizing microbes can promote the plant growth and development under stressed and normal conditions [53]. However, applications of synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers can affect the functions of these microbes. Taken together, different management practices could lead to the changes in the bacterial community compositions in the bulk soils of tea plants. Organic agricultural management practice significantly increased the relative abundances of beneficial bacteria, which was of great significance for promoting the absorption of nutrients, improving the utilization efficiency of organic matter and enhancing the resistance against diseases.
Different long-term management practices affect the physical and chemical properties of soils, which may directly or indirectly impact the microbial community structure of tea plantation soils. Our results showed that long-term organic management practices could improve soil pH value as well as TOC and NO3-N contents (Table 1), and these soil factors were key physical and chemical factors to affect the microbial community structure of tea plantation soils (Figure 4). Some studies have indicated that available carbon content in soils is significantly higher in soils under organic management practices, and carbon is a key soil factor to affect soil communities [54,55]. Ammonium fertilizers can decrease soil pH and subsequently lead to a negative effect on soil microbial community [56]. In addition, pesticides are closely related to metabolic activity of soil microorganisms and soil enzyme activity [57]. Our results also showed that the organic management practice improved the abundances of beneficial microbes which played key roles in biochemical reactions in soils. Therefore, we concluded that different management practices altered the soil properties related to the microbial community structure, and these microbes, in return, in combination with soil enzyme activity might alter soil properties of tea plantation.
The microorganism–microorganism interactions are of great significance for the functions of soil ecosystems [58]. At present, pMENs analysis is increasingly used to explore the potential microbial interactions in different ecosystems [59]. However, the studies on the soil microorganism interaction of tea plantation under different management practices have been rarely reported. In the present study, we used network analysis to quantify and visualize the microbial interaction in tea plantation soils under different management practices. This study offered a new perspective for the interaction mechanism of microbial species and helped us understand the responses of ecological functions of microbial communities in tea plantation soils to different management practices. Different long-term management practices altered the network structure of soil microbial community in tea plantation. Non-synthetic pesticides and non-chemical fertilizers had a significant positive effect on the interaction network of soil microbial community in OTP soil. Compared with NPTP (17 modules) and CTP soils (9 modules), OTP network had a more complex structure and a higher number of modules (22 modules) with topological characteristics (Figure 5). Since highly connected microbial communities within a single module may have unique ecological functions [60], the structure of soil microbial network in organic tea gardens has more diverse ecological function groups, which is of great significance for improving the versatility of soil ecosystem [61]. On the contrary, the common tea garden soil network has the minimum number of topological modules (9 modules), which may lead to the hindrance of the exchange of information, energy and nutrients between microbial communities [60].
5. Conclusions
Our results highlighted the responses of microbial diversity, community structure and interaction network to different management practices in tea plantation soils. The organic management practice (OTP) improved the soil microbial diversity, increased the abundances of beneficial soil microbes, and altered the interaction network structure compared with conventional (CTP) and non-polluted (NPTP) management practices. This study provided the theoretical basis and reference for improving soil microbial diversity and enhancing community multi-functionality in tea plantation soil ecosystems through effective agricultural management practices.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/16/4428/s1. Figure S1: Rarefaction curves of soil bacteria from different tea plantations, Table S1: Dissimilarity test of bacterial community structure in tea plantation soils under different management practices based on Bray-Curtis distance, Table S2: Relative abundance of dominant phyla in tea plantation soil bacterial community under different management practices, Table S3: The topological properties of networks in microbial communities of tea plantation soils under different management practices.
Author Contributions
L.T., Q.H. and S.G. performed the main experiments and analyzed data; L.T. and Q.H. planned and designed the research, wrote the manuscript, with substantial input from S.L., Z.R., Y.D., Z.L., Z.G. and W.X.
Funding
This research was supported by the key Project of the Education Department of Hunan Province, China (No. 18A090), the Key Research and Development Program of Hunan Province, China (No. 2018NK2033), Science and Technology Plan Project of Changsha Science and Technology Bureau, Hunan Province, China (No. kq1701038 and No. kq1801023), and the project of Key laboratory of environmental biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS, kf2018008).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of financial interest.
References
- Liu, Z.H.; Gao, L.Z.; Chen, Z.M.; Zeng, X.X.; Huang, J.A.; Gong, Y.S.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Lin, Y.; Cai, S.X.; et al. Leading progress on genomics, health benefits and utilization of tea resources in China. Nature 2019, 7742, e566. [Google Scholar]
- Adesemoye, A.O.; Torbert, H.A.; Kloepper, J.W. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savci, S. An agricultural pollutant: Chemical fertilizer international. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2012, 3, 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nafees, M.; Jan, M.R. Residues of cypermethrin and endosulfan in soils of Swat valley. Soil Environ. 2009, 28, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, A.; Pradhan, S.; Saha, M.; Sanya, N. Impact of pesticides on soil microbiological parameters and possible bioremediation strategies. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, M.; Frey, B.; Mayer, J.; Maeder, P.; Widmer, F. Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Tu, C.; Hoyt, G.D.; DeForest, J.L.; Hu, S.J. Long-term no-tillage and organic input management enhanced the diversity and stability of soil microbial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, D.; Schulz, E.; Lentendu, G.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T. Mineral vs. organic amendments: Microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, e1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H.L.; Hodge, I.D.; Riordan, P.; Macdonald, D.W. Does organic farming reduce environmental impacts? A meta-analysis of European research. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.W.; Feng, H.X.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Z.D.; Hu, X.D.; Wei, C.Y.; Liang, T.; Li, H.T.; Geng, Y.B. Does dual reduction in chemical fertilizer and pesticides improve nutrient loss and tea yield and quality? A pilot study in a green tea garden in Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2019, 26, 2464–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Wei, G.S.; Tian, R.M.; Li, C.P.; Wang, B.; Lin, R.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Chi, X.L.; Zhou, B.; et al. The occurrence of potato common scab correlates with the community composition and function of the geocaulosphere soil microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raaijmakers, J.M.; Mazzola, M. Soil immune responses. Science 2016, 352, 1392–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisi-Johnson, M.A.; Obi, C.L.; Ekosse, G.E. Microbiological and health related perspectives of geophagia: An overview. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 5784–5791. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, W.A.; Jin, Z.; Youngblut, N.; Wallace, J.G.; Sutter, J.; Zhang, W.; González-Peña, A.; Peiffer, J.; Koren, O.; Shi, Q.J.; et al. Large-scale replicated field study of maize rhizosphere identifies heritable microbes. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7368–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, L.W.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; De Hollander, M.; Mendes, R.; Tsai, S.M. Influence of resistance breeding in common bean on rhizosphere microbiome composition and function. ISME J. 2018, 12, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lareen, A.; Burton, F.; Schafer, P. Plant root-microbe communication in shaping root microbiomes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, B.J.E.; Boyle, C.J.C.; Sieber, T.N. Microbial Root Endophytes; Springer: Dordercht, NL, USA; Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, L.W.; Kuramae, E.E.; Navarrete, A.A.; van Veen, J.A.; Tsai, S.M. Taxonomical and functional microbial community selection in soybean rhizosphere. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, R.; Garbeva, P.; Raaijmakersm, J.M. The rhizosphere microbiome: Significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 634–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.F.; Wu, Z.D.; You, Z.M.; Yi, X.Y.; Ni, K.; Guo, S.W.; Ruan, J.Y. Effects of organic substitution for synthetic N fertilizer on soil bacterial diversity and community composition: A 10-year field trial in a tea plantation. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 268, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Li, T.X.; Zheng, Z.C.; Chen, H.Y.H. Soil aggregate-associated bacterial metabolic activity and community structure in different aged tea plantations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Jin, D.C.; Jin, S.L.; Wang, Z.G.; Yin, H.Q.; Xu, M.Y.; Deng, Y. Responses of bacterial community to dibutyl phthalate (DBP) pollution in a soil-vegetable ecosystem. J. Hazar. Mater. 2018, 353, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, Z.J.; Cai, W.W.; Liu, W.Z.; Xu, M.Y.; Yin, H.Q.; Wang, A.J.; He, Z.L.; Deng, Y. Biodiversity and species competition regulate the resilience of microbial biofilm community. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6170–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric Estimation of the Number of Classes in a Population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.F.; He, Z.L.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J.Z. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.L.; Yang, Y.F. Phylogeneticmolecular ecological network of soil microbial communities inresponse to elevated CO2. MBIO 2011, 2, e00122-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhong, J.X.; Gao, H.; Khan, L.; Thompson, D.K.; Zhou, J.Z. Constructing gene co-expression networks andpredicting functions of unknown genes by random matrix theory. BMC Bioinformatics 2007, 8, e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and community structure in networks. Pro. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.S.; Gupta, V.K. Soil microbial biomass: A key soil driver in management of ecosystem functioning. Sci. Total Enviro. 2018, 634, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.Y.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.L.; Mu, X.Y.; Liu, K.; Li, C.H. Effects of deep tillage and straw teturning on soil microorganism and enzyme activities. Sci. World J. 2014, e451493. [Google Scholar]
- Aktar, M.W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdisc. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsborrow, P.; Cooper, J.; Tetard-Jones, C.; Srednicka-Tober, D.; Baraniski, M.; Eyre, M.; Schmidt, C.; Shotton, P.; Volakakis, N.; Cakmak, I.; et al. The effect of organic and conventional management on the yield and quality of wheat grown in a long-term field trial. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 51, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, F.S.; Ho, T.Y.; Chong, K.P.; Jalloh, M.B.; Wong, N.K. Organic versus conventional farming of tea plantation. J. Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Diacono, M.; Montemurro, F. Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.S.F.; Monterio, R.T.R.; Abarkeli, R.B. Effect of glyphosate on the microbial activity of two brazilian soils. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devare, M.H.; Jones, C.M.; Thies, J.E. Effect of Cry3B transgenic corn and tefluthrin on the soil microbial community: Biomass, activity and diversity. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SeVerstraete, W.; Top, E.M. Effect of long-term herbicide applications on the bacterial community structure and function in an agricultural soil. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 46, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, S. Impact of chemical- and bio-pesticides on bacterial diversity in rhizosphere of Vigna radiata. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lori, M.; Symnaczik, S.; Mäder, P.; De Deyn, G.; Gattinger, A. Organic farming enhances soil microbial abundance and activity–a meta-analysis and meta-regression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e018044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S. Network analysis reveals functional redundancy and key stone taxa amongst bacterial and fungal communities during organic matter decomposition in an arable soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Roy, K.S.; Nayak, A.K.; Shahid, M.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Mohapatra, T. Metagenomic assessment of methane production-oxidation and nitrogen metabolism of long term manured systems in lowland rice paddy. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lücker, S.; Wagner, M.; Maixner, F.; Pelletier, E.; Koch, H.; Vacherie, B.; Ratteie, T.; Damstéf, J.S.S.; Spieckg, E.; Paslier, D.L.; et al. A Nitrospira metagenome illuminates the physiology and evolution of globally important nitrite-oxidizing bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13479–13484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.F.; Dong, J.; Shen, Z.Q.; Mou, R.; Zhou, Y.X.; Chen, X.M.; Fu, X.Y.; Yang, C.P. Nitrogen removal of naerobically digested swine wastewater by pilot-scale tidal flow constructed wetland based on in-situ iological regeneration of zeolite. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, R.J.; Gao, J.S.; Ma, X.T.; Yin, H.Q.; Zhang, C.W.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y. Thirty-one years of rice-ricegreen manure rotations shape the rhizosphere microbial community and enrich beneficial bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.E.; Gulledge, J.; Engelhaupt, E.; Burow, M.E.; McLachlan, J.A. Pesticides reduce symbiotic efficiency of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia and host plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10282–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.F.; Silva, C.M.M.S.; Silveira, A.P.D. Soil microbial biomass C and symbiotic processes associated with soybean after sulfentrazone herbicide application. Plant Soil 2007, 300, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampfer, P.; Young, C.C.; Arun, A.B.; Shen, F.T.; Jäckel, U.; Rossello´-Mora, R.; Lai, W.A.; Rekha, P.D. Pseudolabrys taiwanensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an alphaproteobacterium isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2006, 56, 2469–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Fu, S.; Mathew, R.P.; Lawrence, K.S.; Feng, Y. Soil microbial community structure and activity in a 100-year-old fertilization and crop rotation experiment. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 8, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkhofer, K.; Bezemer, T.M.; Bloem, J.; Bonkowski, M.; Christensen, S.; Dubois, D.; Ekelund, F.; Fliessbach, A.; Gunst, L.; Hedlund, K.; et al. Long-term organic farming fosters below and aboveground biota: Implications for soil quality, biological control and productivity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulluck, L.R.; Ristaino, J. Effffect of synthetic and organic soil fertility amendments on southern blight, soil microbial communities, and yield of processing tomatoes. Phytopathology 2002, 92, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunemann, E.K.; Schwenke, G.D.; Van Zwieten, L. Impact of agricultural inputs on soil organisms a review. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2006, 44, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Walker, A. Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 428–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, A.B.; Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Richardson, A.E.; Toscas, P.; Farrell, M.; Macdonald, L.M.; Baker, G.; Wark, T.; Thrall, P.H. Network analysis reveals that bacteria and fungi form modules that correlate independently with soil parameters. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Howe, A.; Hofmockel, K. Demonstrating microbial co-occurrence pattern analyses within and between ecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, e358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qi, G.F.; Luo, T.; Zhang, H.C.; Jiang, Q.K.; Wang, R.; Zhao, X.Y. Continuous-cropping tobacco caused variance of chemical properties and structure of bacterial network in soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4106–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).