Accident Trend Prediction of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Heshangshan Drinking Water Source Area Based on Integrating a Two-Dimensional Water Quality Model and GIS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
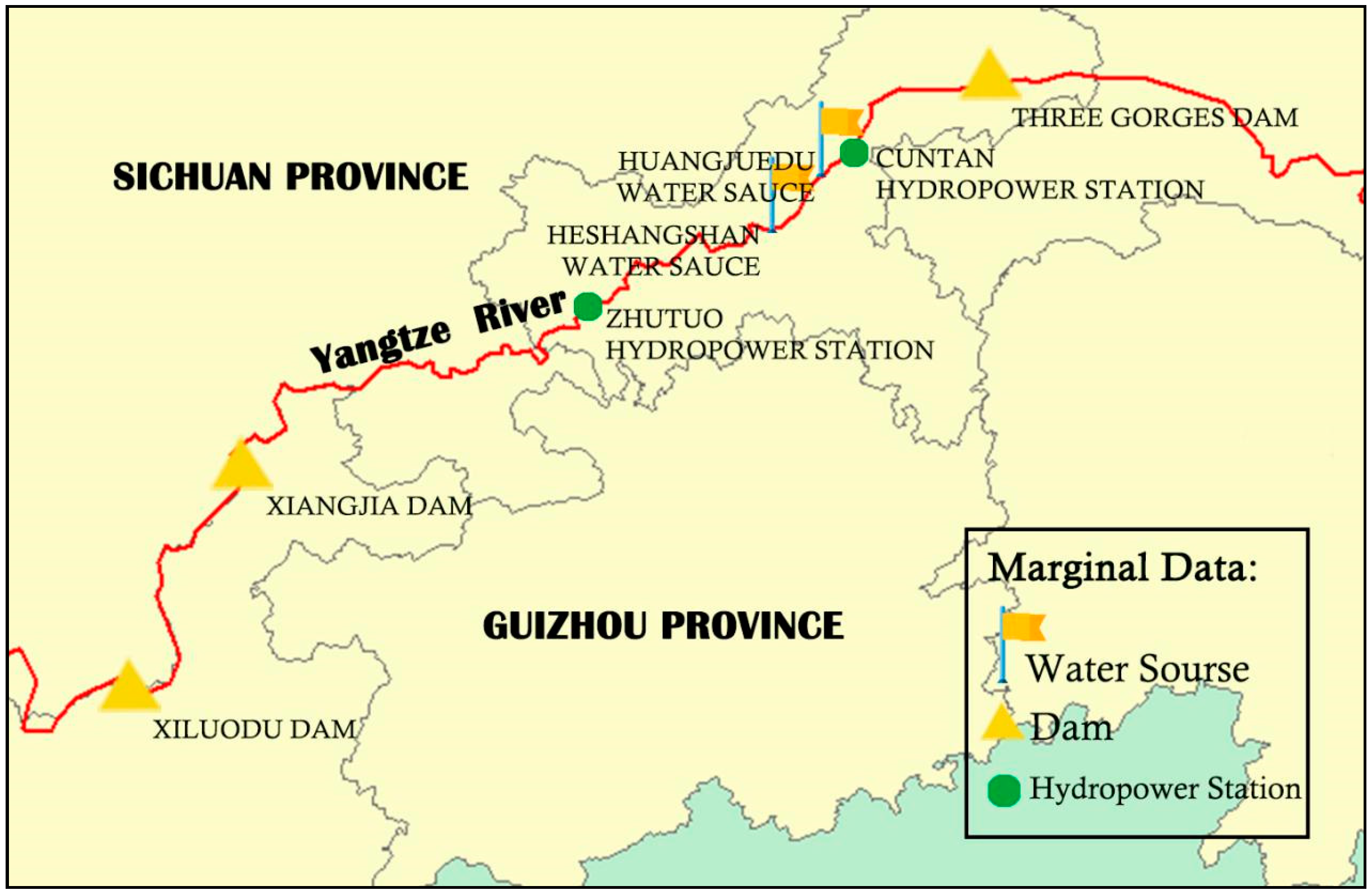
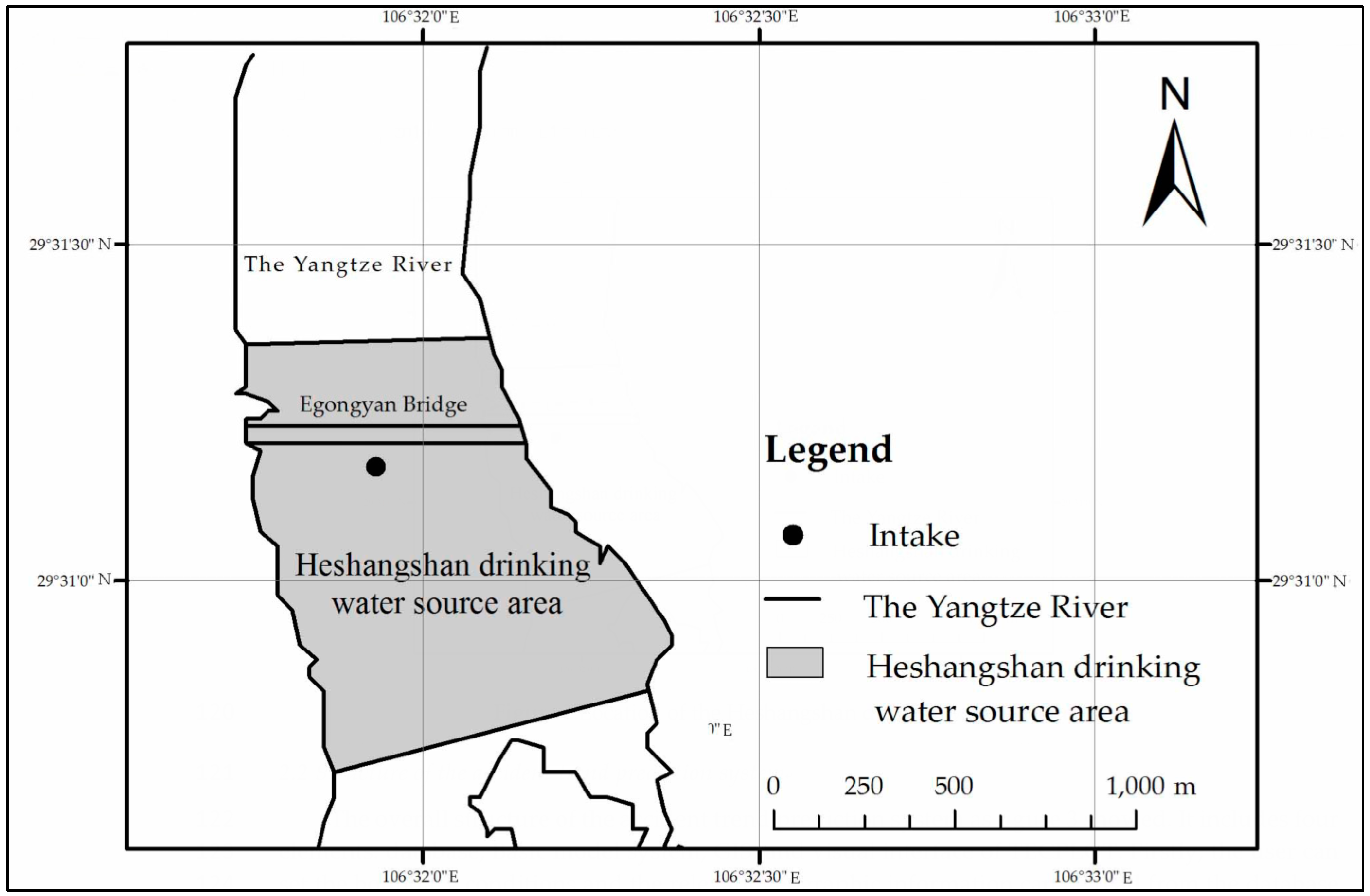
2.1. Research Area
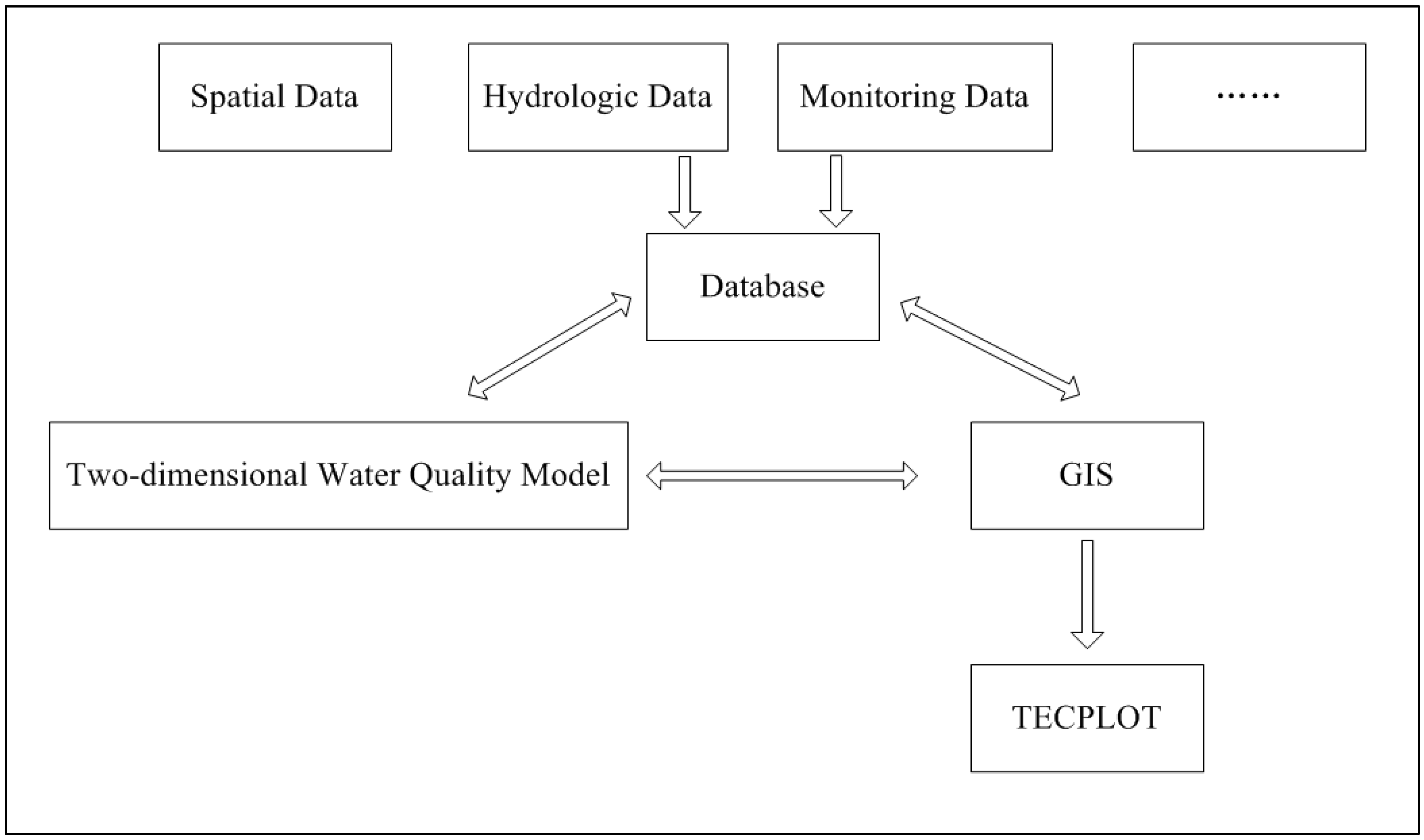
2.2. Structure of the Accident Trend Prediction System
2.3. Database
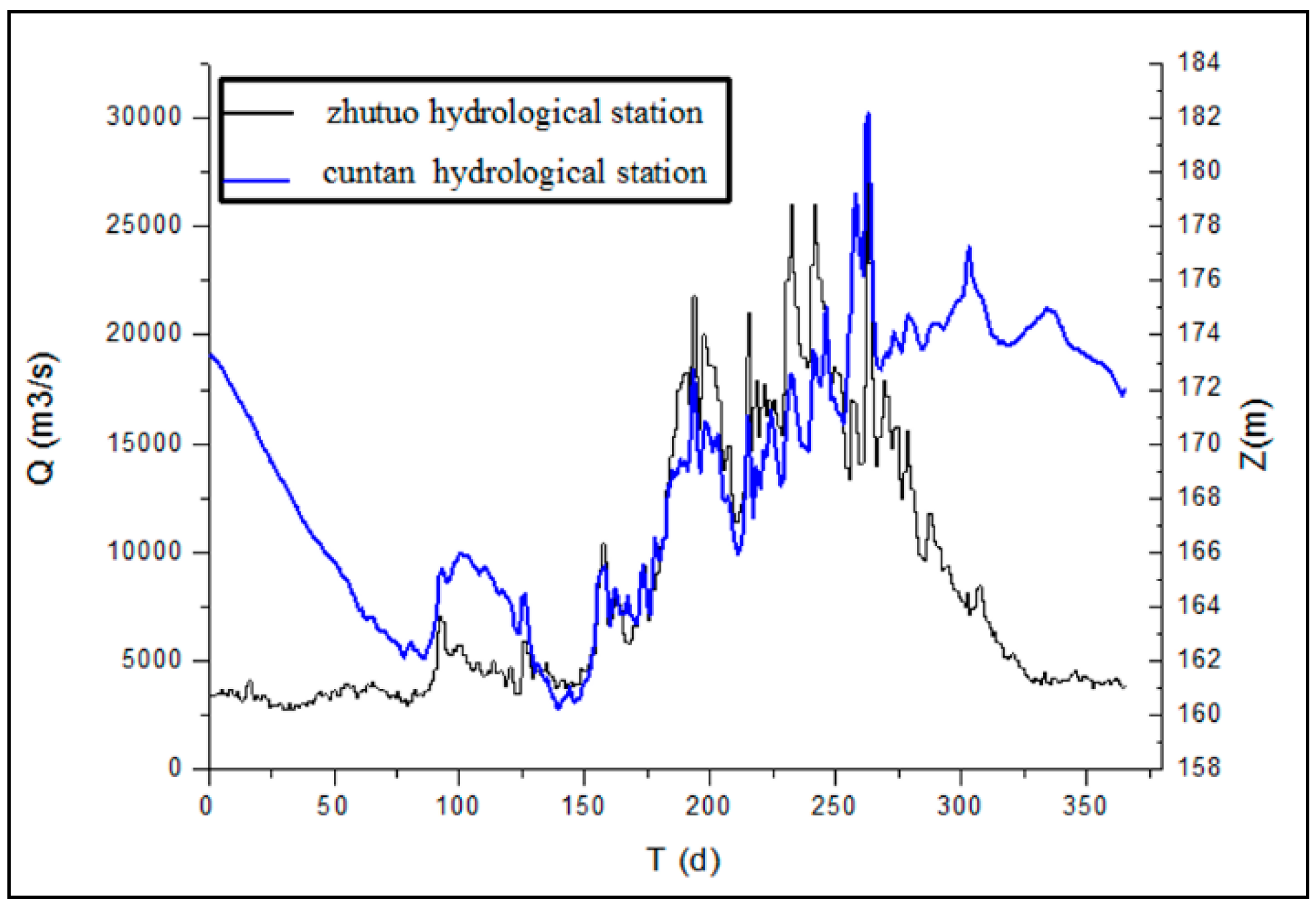
2.3.1. Boundary Conditions
2.3.2. Initial Conditions
3.3. Model Parameter Determination Method
2.4. Basic Model System
2.4.1. Two-dimensional Water Quality Model
2.4.2. Discretization Mathematical Model of Water Quality
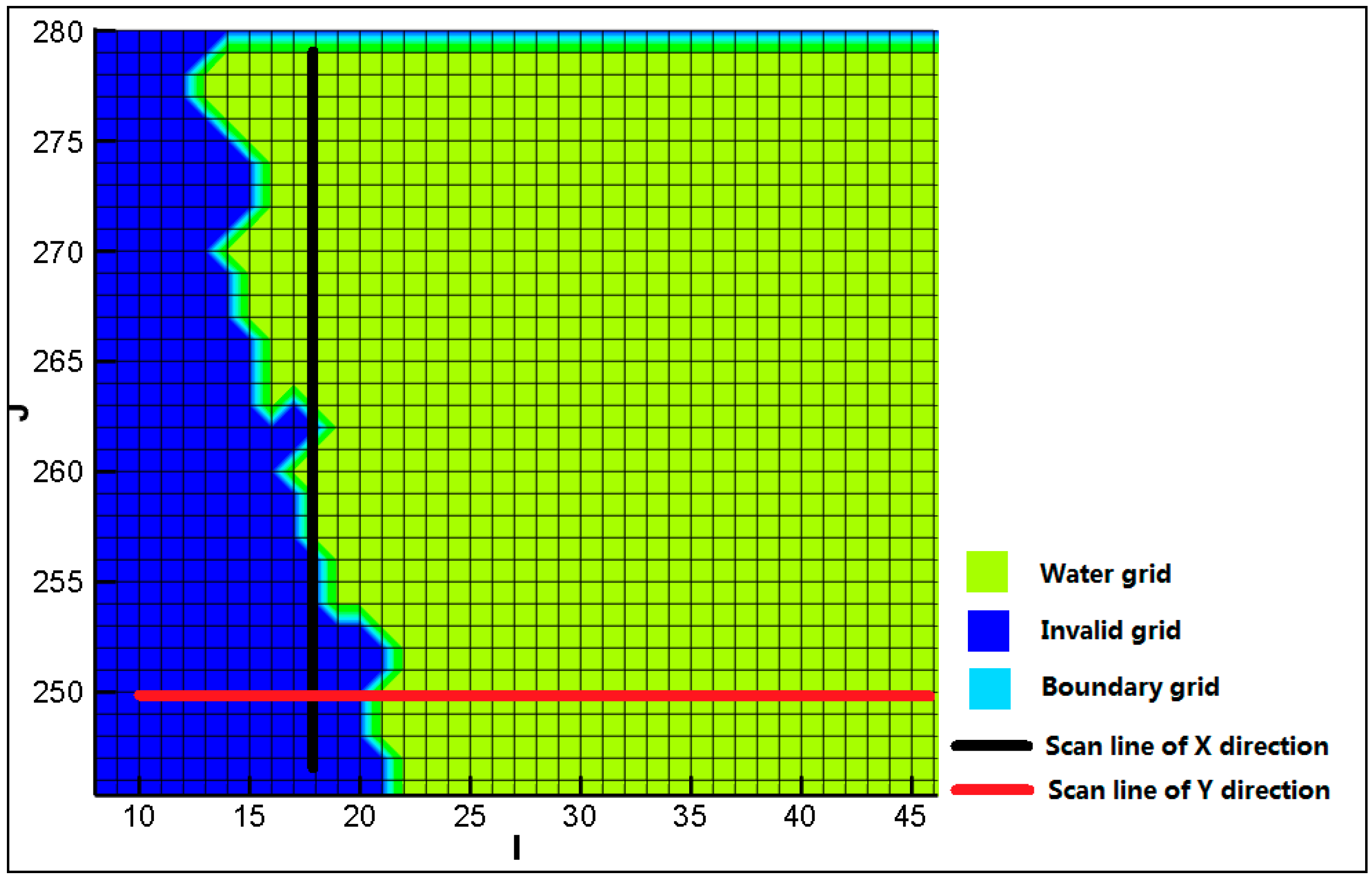
2.4.3. Grid Division of Complex Boundaries
2.4.4. Parameter Calibration
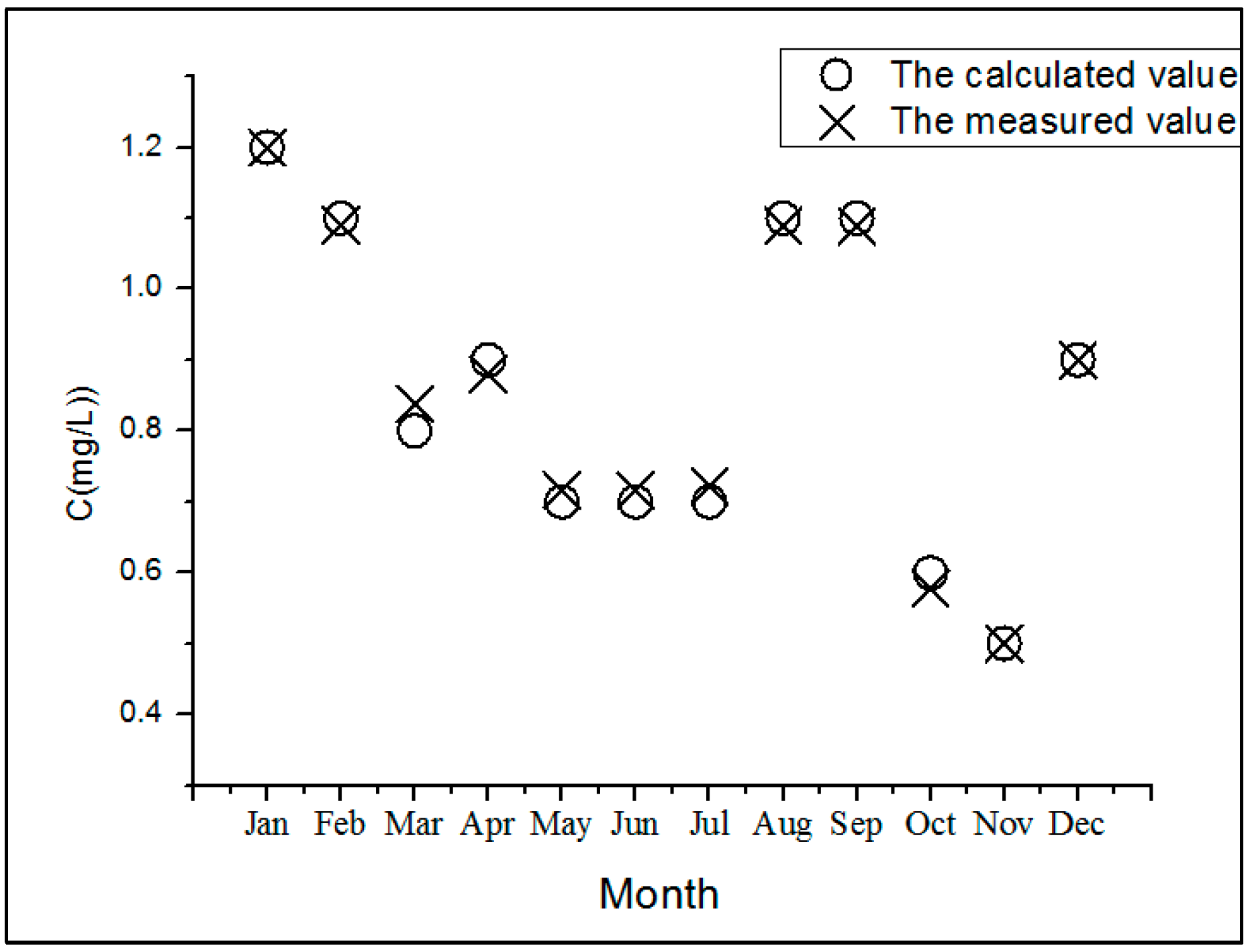
2.4.5. Model Verification
2.5. GIS
2.6. Model Application
2.6.1. Accident Source Design
2.6.2. Accident Scenarios Design
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulation Results of Pollution Accident in Scenario 1
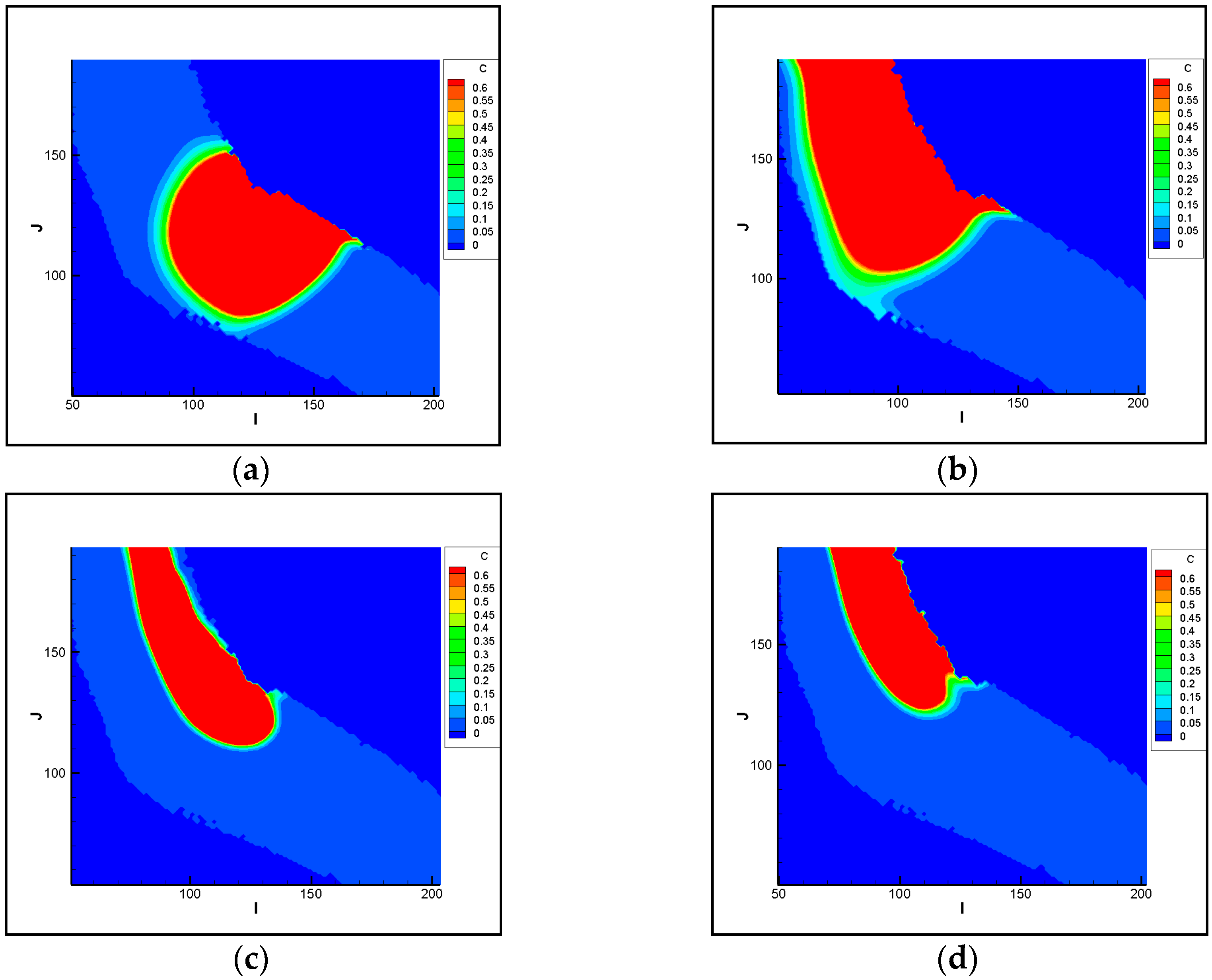
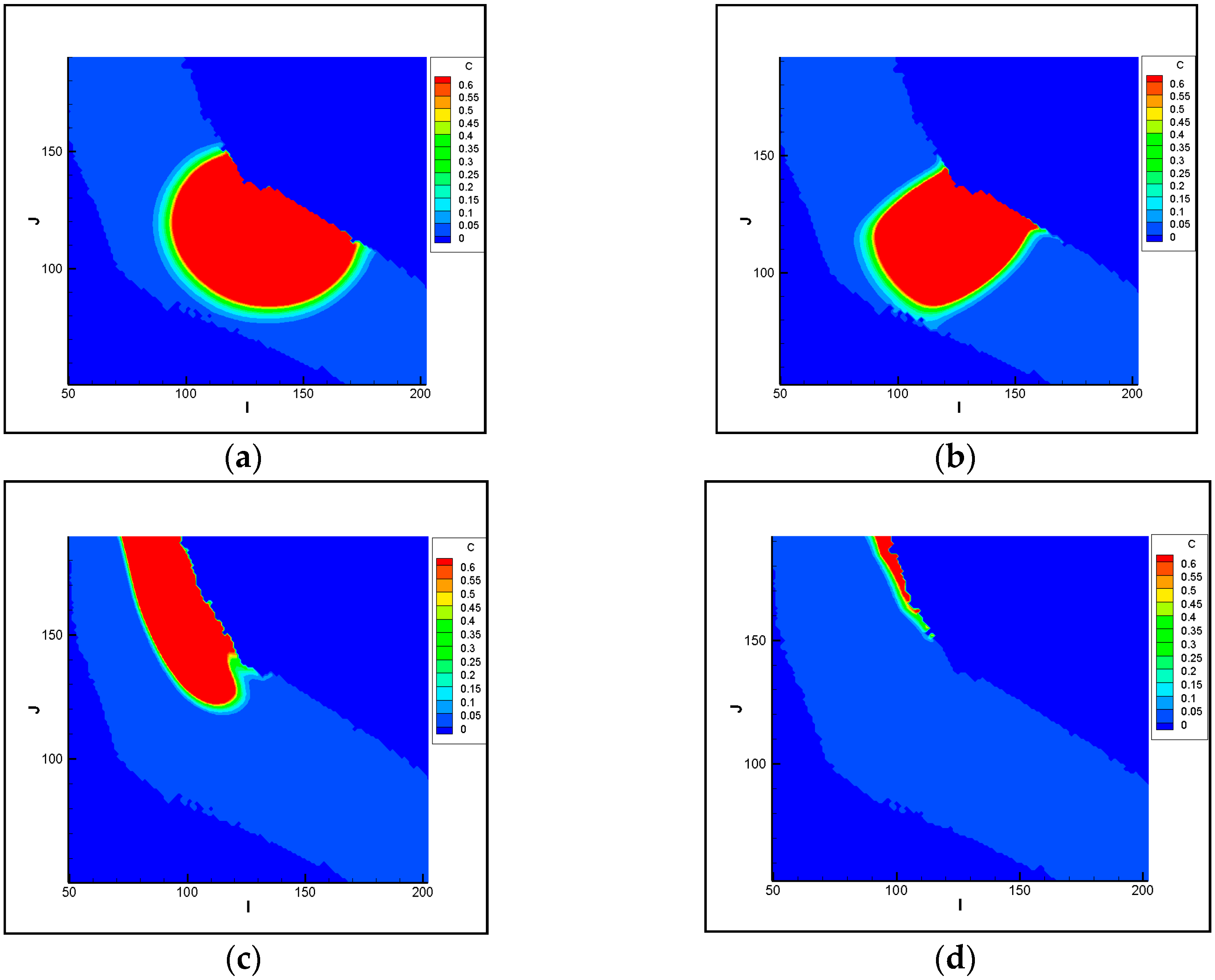
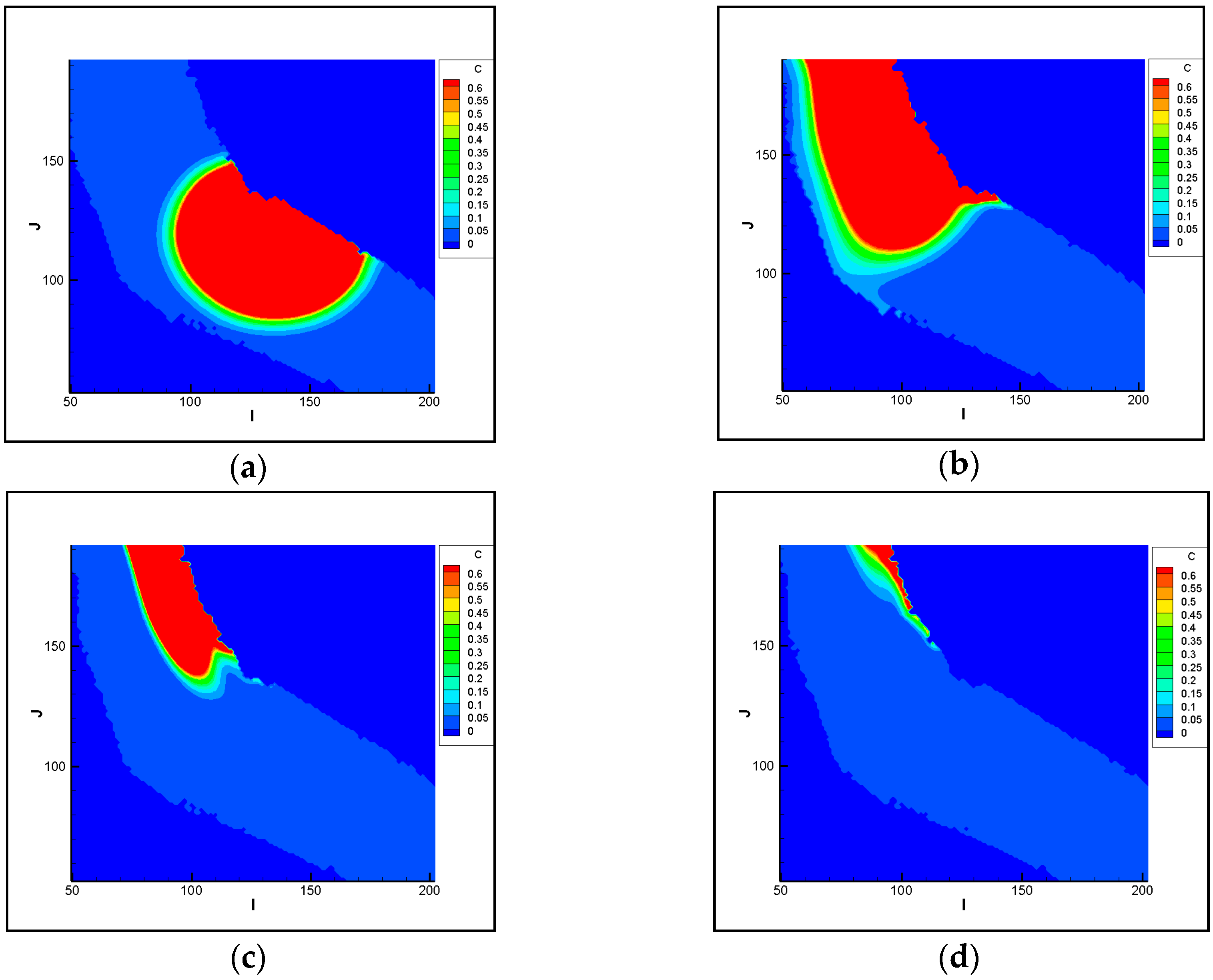
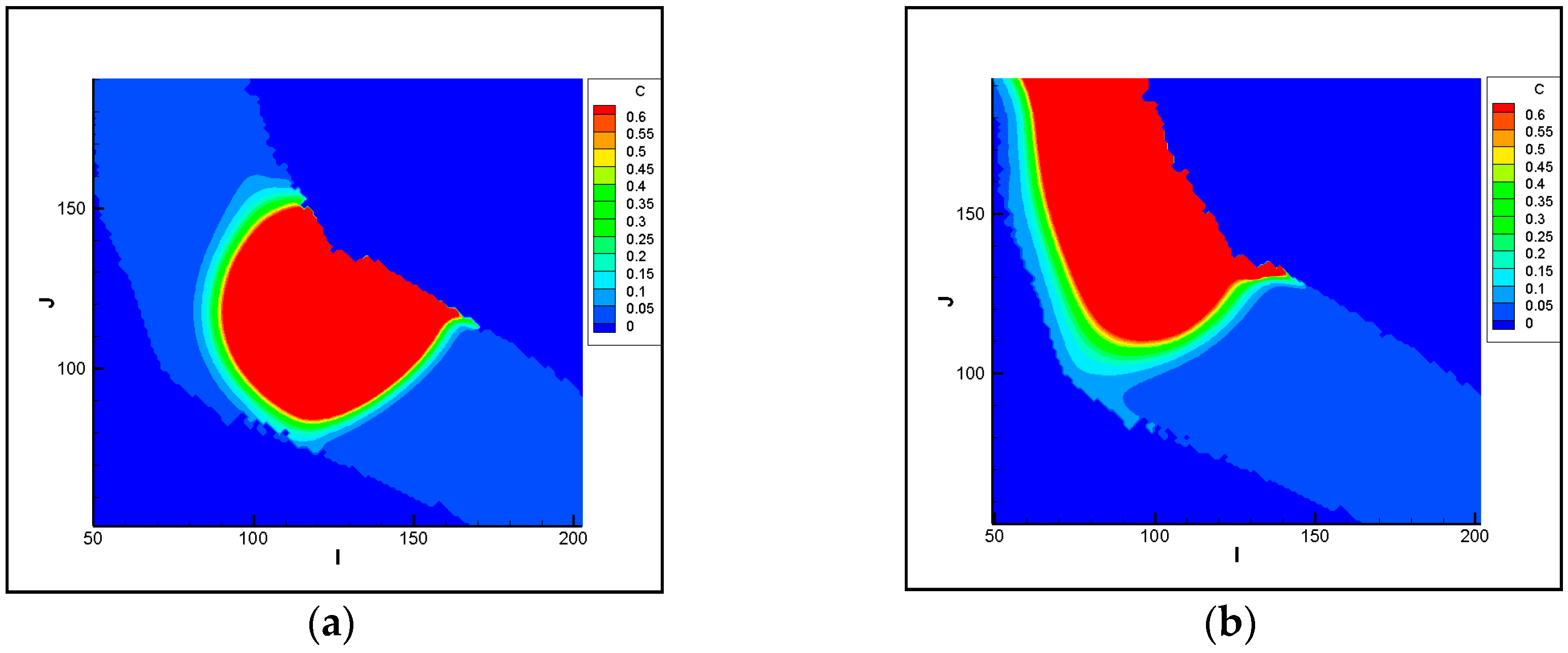
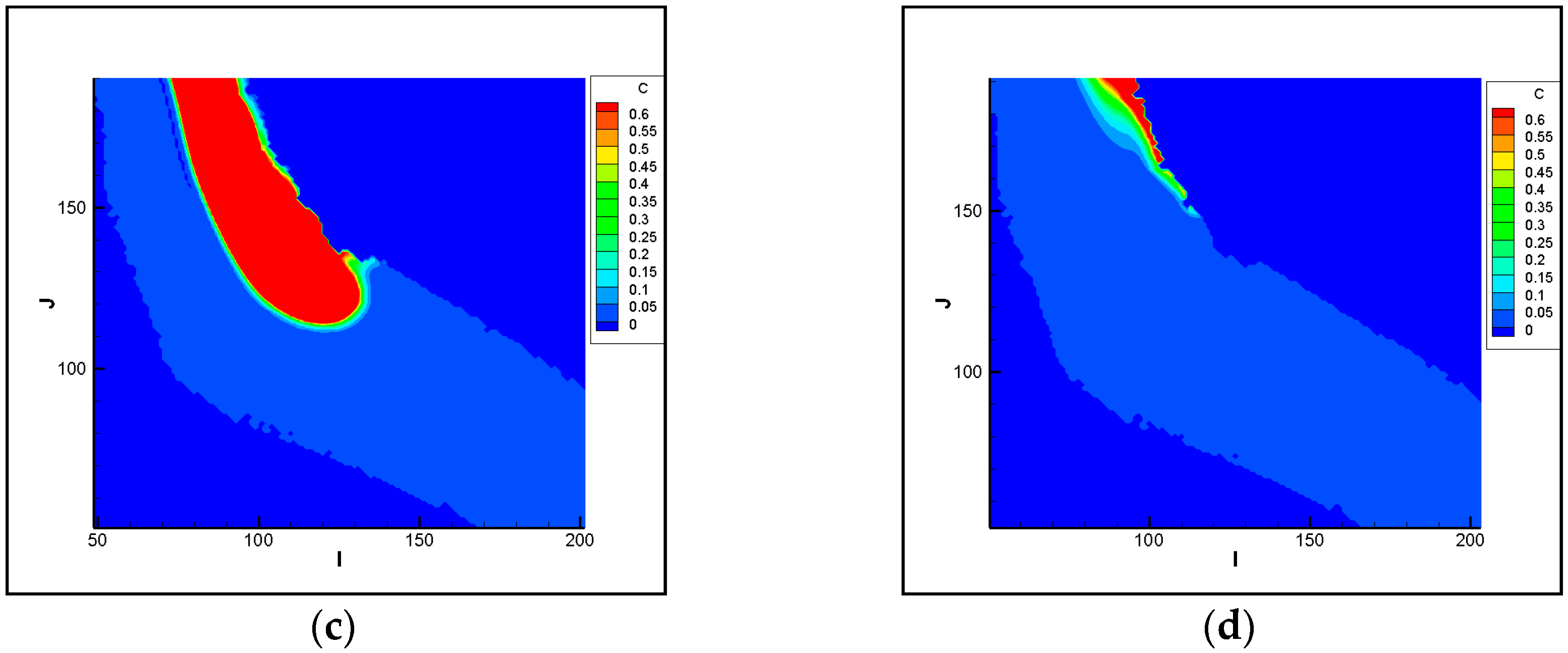
3.1.1. Analysis of Pollutant Spatial-Temporal Changes
3.1.2. Analysis of the Polluted Ranges
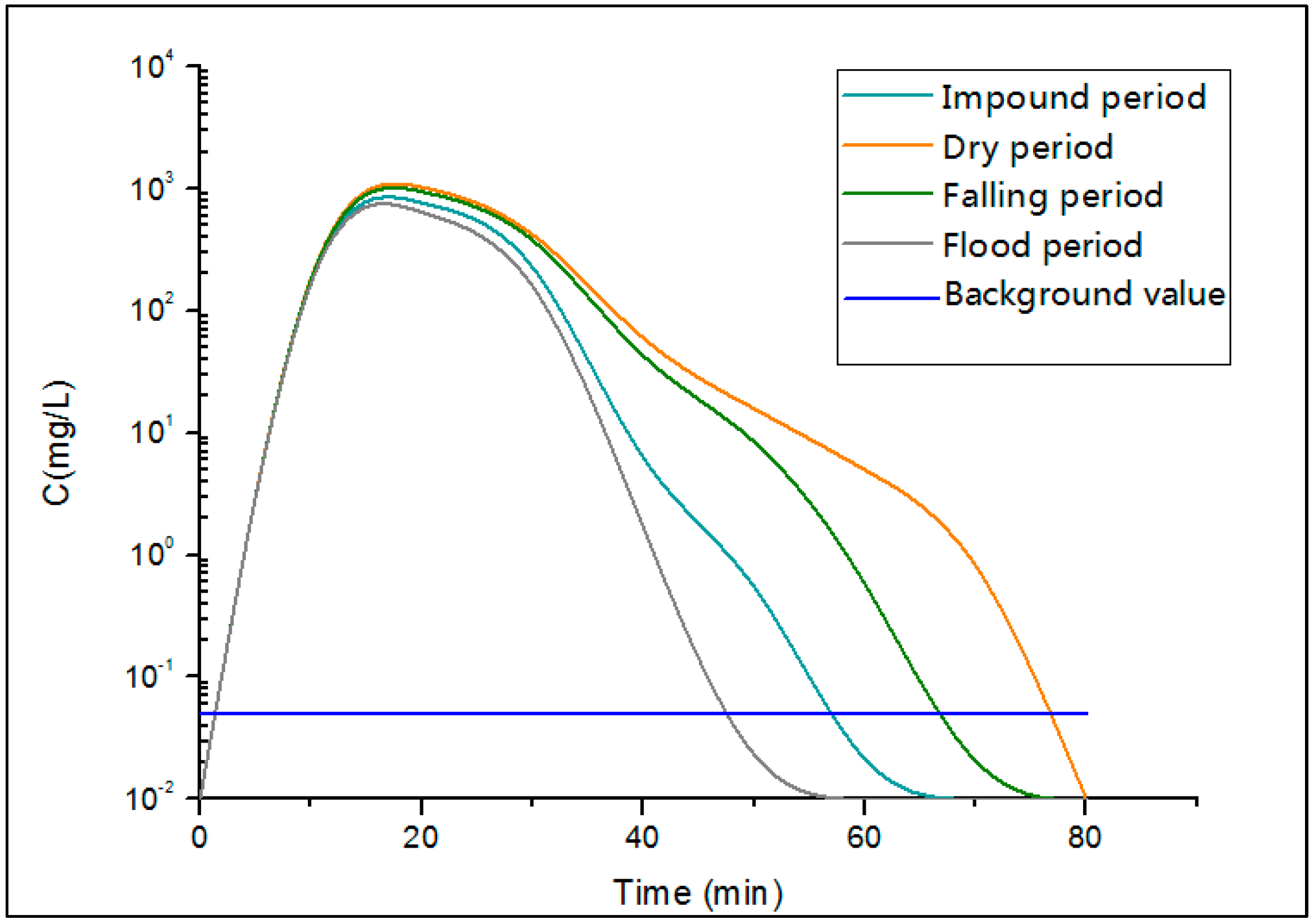
3.1.3. The Change of Maximum Pollution Concentration
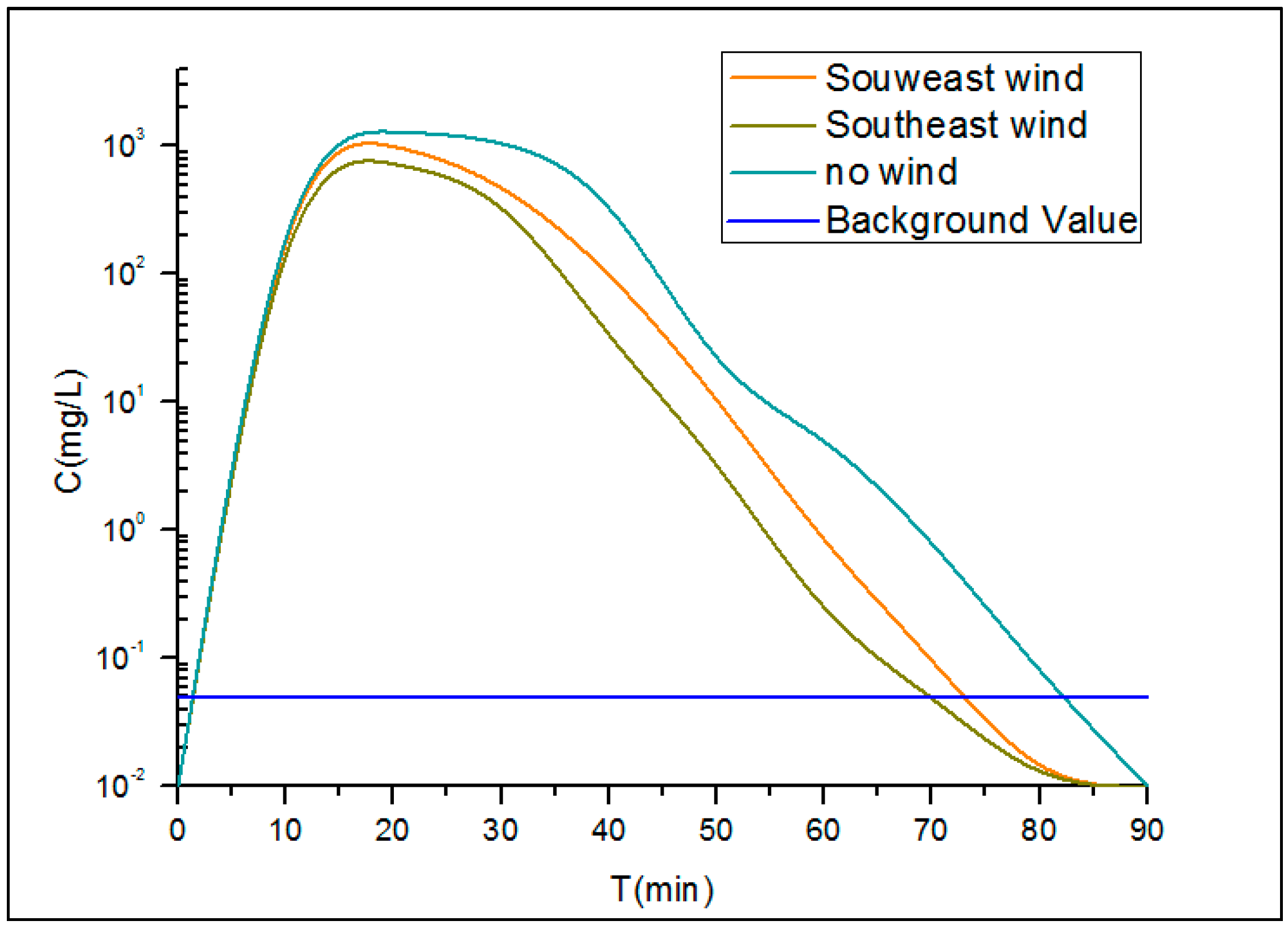
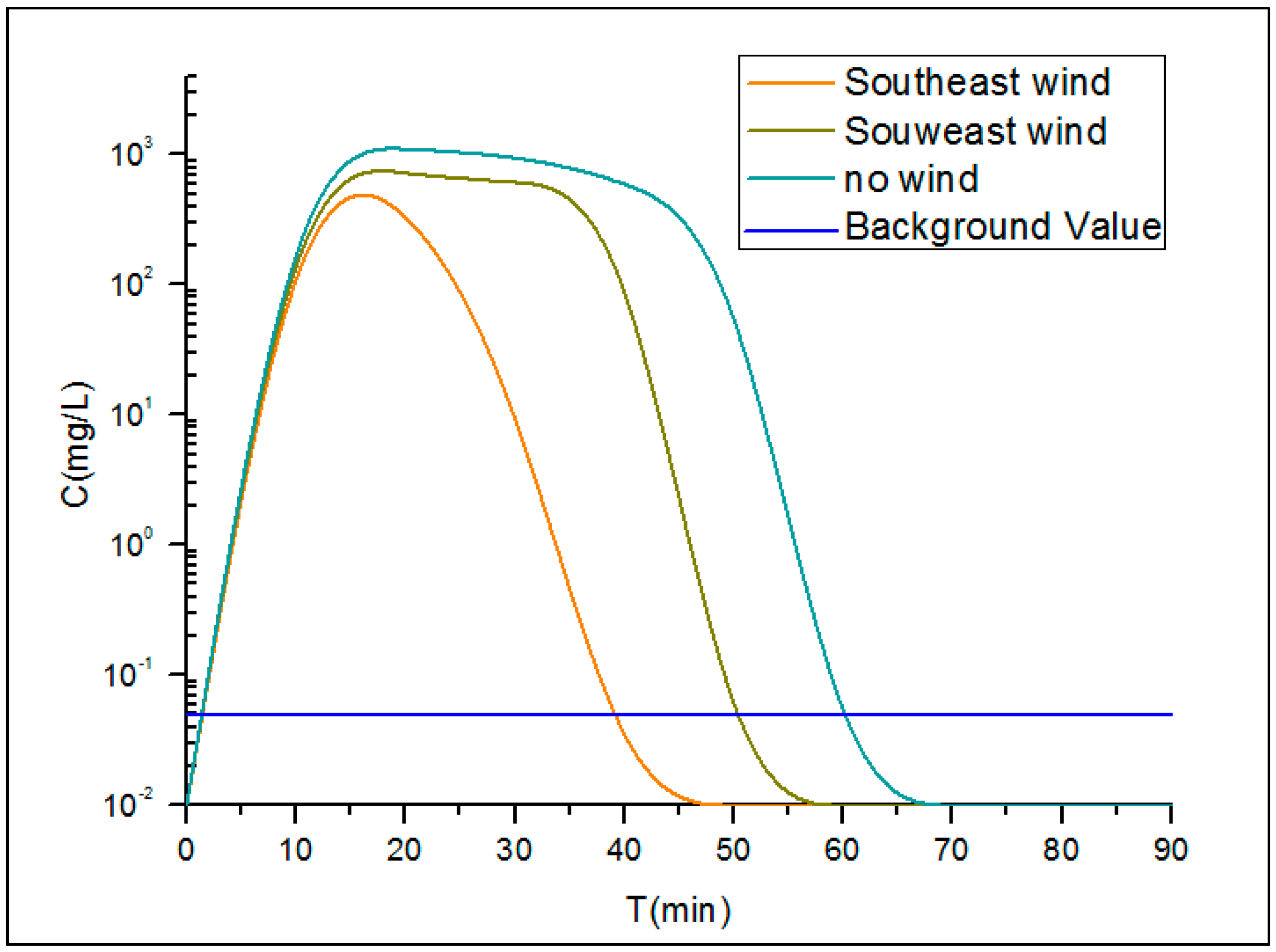
3.1.4. Analysis of the Emergency Response Time
3.2. Simulation Results of the Pollution Accident in Scenario 2
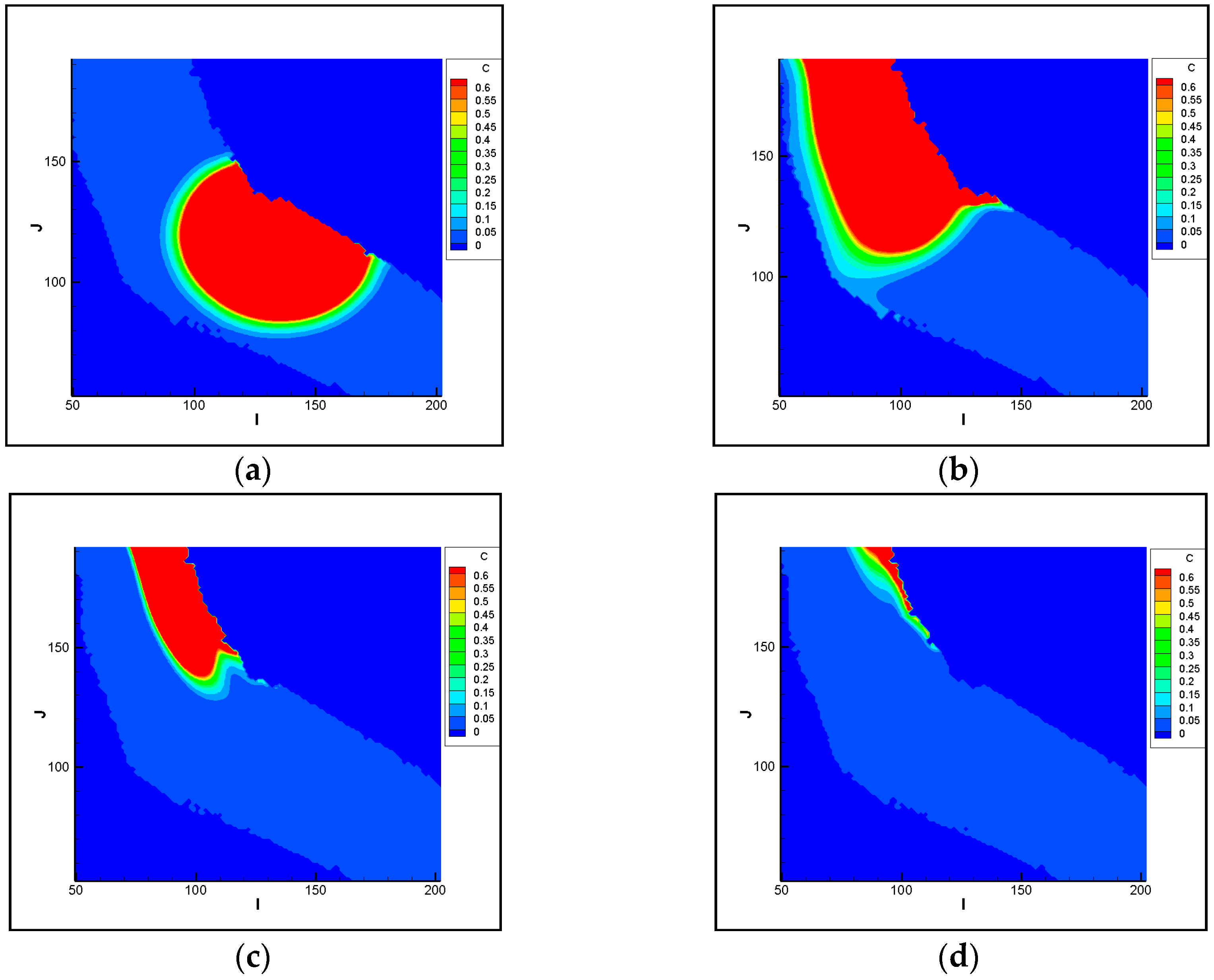
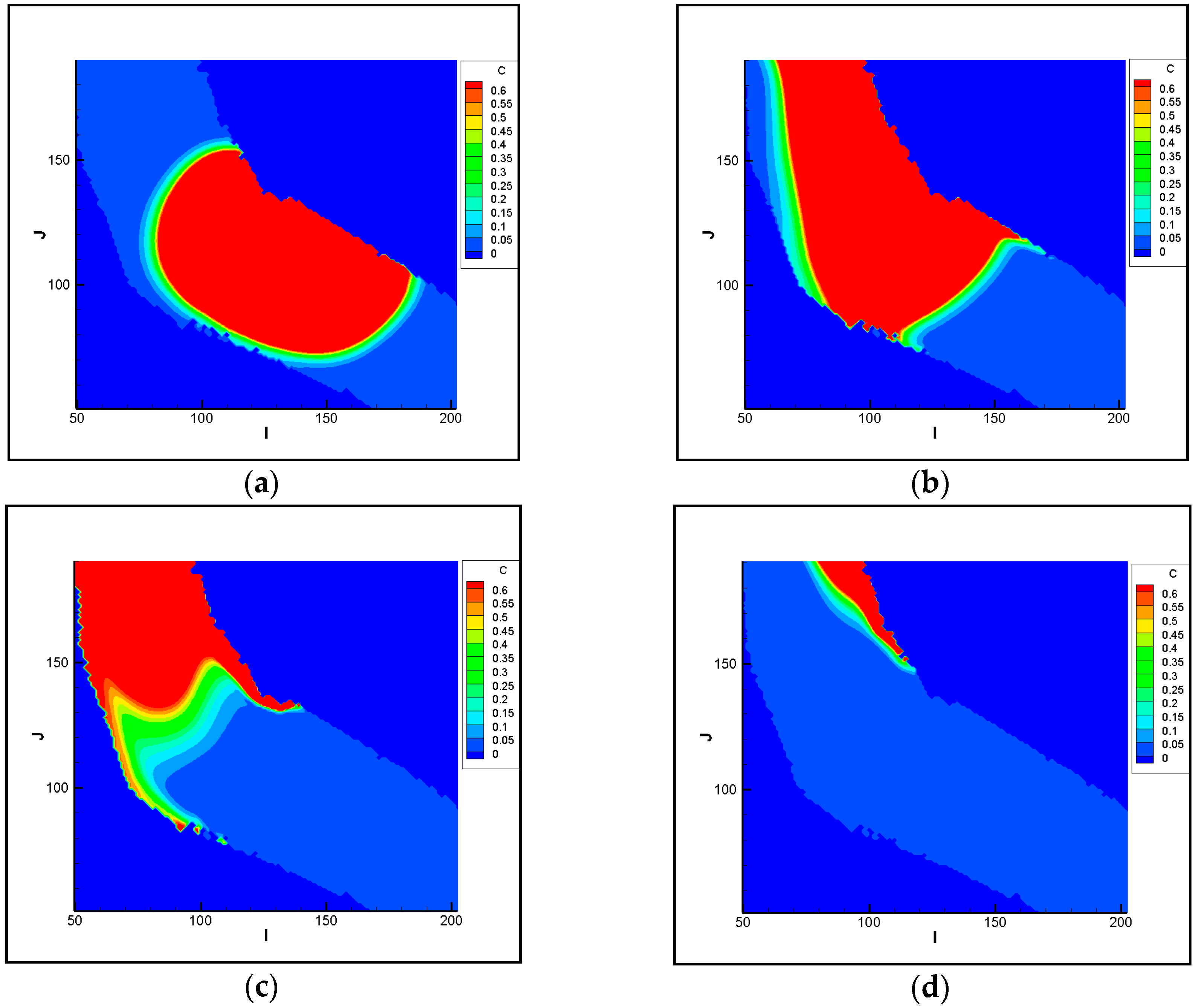
3.2.1. Analysis of Pollutant Spatial-Temporal Changes
3.2.2. Analysis of the Polluted Ranges
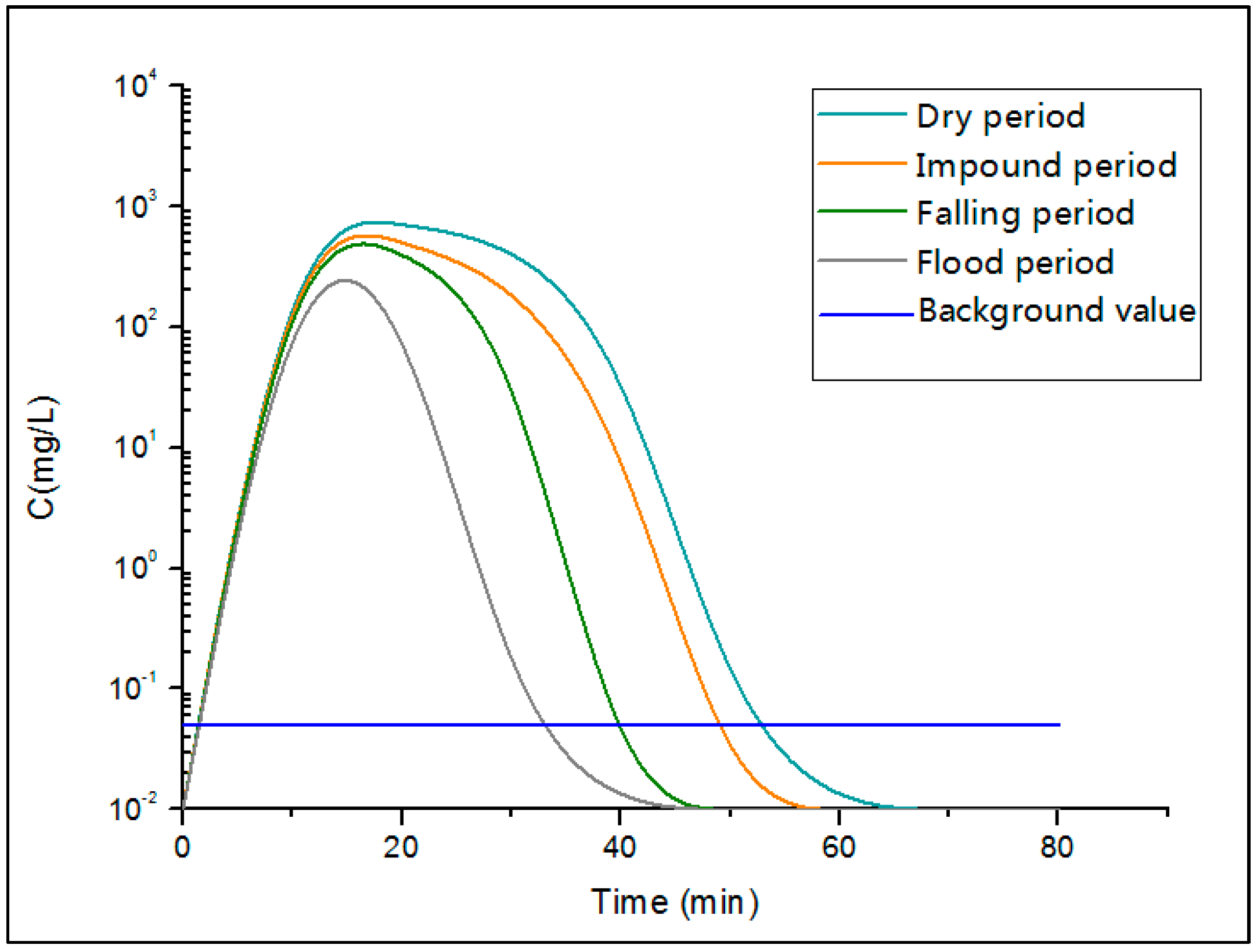
3.2.3. Analysis of the change of Maximum Pollution Concentration
3.2.4. Analysis of the Emergency Response Time
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheili, A.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Sadiq, R. Impact of human operational factors on drinking water quality in small systems: An exploratory analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 133, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeong, G.H.; Jeong, J.C. The Assessment of Water Pollution Accident on Dam watershed using GIS. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2011, 20, 489–496. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.H.; Yi, Y.J.; Yang, Z.F. Risk forecasting of pollution accidents based on an integrated Bayesian network and water quality model for the South to North Water Transfer Project. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 96, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Meng, X.L.; Ye, X.Q. Characteristic variation and original analysis of emergent water source pollution accidents in China between 1985 and 2013. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19675–19685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.J.; Borthwick, A.G.L. Water-Scale Environmental Risk Assessment of Accident Water Pollution: The Case of Laoguan River, China. J. Environ. Inform. 2018, 31, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, T. Evaluation of major polluting accidents in China—Results and perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Escriva-Bou, A. Developing a water-energy-GHG emissions modeling framework: Insights from an application to California’s water system. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, S.; Hasegawa, H.; Kakiuchi, H. Nuclear accident-derived H-3 in river water of Fukushima Prefecture during 2011–2014. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 146, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, G. Distribution and source of organic matter in surface sediment from the muddy deposit along the Zhejiang coast, East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 325–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, Y.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Song, K.W. Radioactivity release from the Fukushima accident and its consequences: A review. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2014, 74, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.G. The iconic Torrey Canyon oil spill of 1967-Marking its legacy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guideline for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvalter, V.; Rognerud, S. Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pasvik River drainage. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakan, S.M.; Đorđević, D.S.; Manojlović, D.D.; Predrag, P.S. Assessment of heavy metal pollutants accumulation in the Tisza river sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.D.; He, Y.; Hiscock, K.M. Modeling the impacts of agricultural management practices on river water quality in eastern England. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, Y.; Engel, B.A.; Peng, H.; Zhang, W. Modelling hydrology and water quality processes in the Pengxi River basin of the Three Gorges Reservoir using the soil and water assessment tool. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 182, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, Y.W.; Chung, G.J.; Ji, W.L. Evaluation of Watershed Scale Aquatic Ecosystem Health by SWAT Modeling and Random Forest Technique. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3397. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, R.; Sabater, S.; Marce, R.A. Methodolofical Framwork for Characerizing the Spatiotemporal Variability of River Water-Quality Patterns using Dynamic Factor Analysis. J. Environ. Inform. 2018, 31, 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, M.H. Modeling and assessing agro-hydrological processes and irrigation water saving in the middle Heihe River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagò, A.; Vigiak, O.; Bouraoui, F.; Pagliero, L.; Franchini, M. The Hillslope Length Impact on SWAT Streamflow Prediction in Large Basins. J. Environ. Inform. 2018, 32, 82–97. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.K.; Lu, X.X.; Ran, L.S. Geomorphometric Assessment of the Impacts of Dam Construction on River Disconnectivity and Flow Regulation in the Yangtze Basin. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J. Modeling hydrodynamics and salt transport in the Alafia River estuary, Florida during May 1999–December 2001. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.M.Y.; Wai, O.W.H.; Li, Y.S.; Li, Z.L.; Jiang, Y. Integration of a GIS and a complex three-dimensional hydrodynamic, sediment and heavy metal transport numerical model. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2009, 40, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lei, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y. Integrated assessment method of emergency plan for sudden water pollution accidents based on improved topsis, shannon entropy and a coordinated development degree model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Yi, Y.J.; Yang, Z.F. Water pollution risk simulation and prediction in the main canal of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Sun, L.; Li, C.H.; Wang, X.; Jia, X.L.; Cai, Y.P. Water Quality Risk Assessment for the Laoguanhe River of China Using a Stochastic Simulation Method. J. Environ. Inform. 2018, 31, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.S.; Rahmat, S.N.; Tan, L.W.; Rosly, N. Application of SWAT and GIS to simulate the river flow of the Sembrong River, Johor, Malaysia. Adv. Civ. Archit. Struct. Constr. Eng. 2016, 3, 393–397. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Homer, M.; Dyer, S.D.; White-Hull, C.; Du, C. A river water quality model integrated with a web-based geographic information system. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 75, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Bi, J.; Ambros, R.B. Development and application of mathematical models to support total maximum daily load for the Taihu Lake’s influent rivers, China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, S.H.; Hao, Q.T. A temporal-spatial simulation and dynamic regulation system of water quality on sudden water pollution accidents. Mechatron. Eng. Comput. Inf. Technol. 2014, 556–562, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, Y.; Shen, D.; Khalid, S. GIS-based emergency response system for sudden water pollution accidents. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 79–82, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portoghese, I.; Uricchio, V.; Vurro, M. A GIS tool for hydrogeological water balance evaluation on a regional scale in semi-arid environments. Comput. Geosci. 2005, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Gorai, A.K.; Katpatal, Y.B.; Pathak, G. Development of GIS-based fuzzy pattern recognition model (modified DRASTIC model) for groundwater vulnerability to pollution assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3161–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.C. Forecasting and warning the accidental water pollution effect based on the EFAD and WASP. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2011, 20, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Li, S. Spatio-temporal simulation of water quality based on SD-GIS accidential water pollution. Geomatics Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2009, 34, 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, F.; Valenzuela, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Choi, J. ArcGIS-SWAT: A geo-data model and GIS interface for SWAT. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 2, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.P.; Zhou, J.T. Research on visualization of pollution concentration distribution in sea water using GIS. J. DaLian Univ. Technol. 2004, 4, 506–509. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.W.; Zhu, Q.; Zai, A.F.; Liu, L. Water quality safety prediction model for drinking water source areas in Three Gorges Reservoir and its application. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Liao, W.G.; Huang, Z.L. Numerical simulation of water quality for the Three Gorges Project Reservoir. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 33, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Liao, W.G. The effect of water flow on the biodegradation of organic pollution. Res. Environ. Sci. 2002, 15, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhang, Y. 2D numerical modeling for unsteady flow and sediment transport in Chongqing reach. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2005, 24, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.T.; Hou, W.G.; Ren, N.H. 2D horizontal modeling for the movement of flow and sediment from Yichang to Yangjianao reach at the Gezhouba downstream. Adv. Water Sci. 2008, 19, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Elkady, A.A.; Sweet, S.T.; Wade, T.L.; Klein, A.G. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in the aquatic environment of Lake Manzala, Egypt. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastami, K.D.; Bagheri, H.; Kheirabadi, V.; Zaferani, G.G.; Teymori, M.B.; Hamzehpoor, A. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments along southeast coast of the Caspian Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, S.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N. Heavy metals distribution, risk assessment and water quality characterization by water quality index of the River Soan, Pakistan. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalit, K.P.; Kumar, D.; Yadav, A.; Rai, J.; Gaur, J.P. Morphological abnormalities in periphytic diatoms as a tool for biomonitoring of heavy metal pollution in a river. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 272–279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.X. A new stabilized finite volume method for the stationary Stokes equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 2009, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audusse, E.; Bouchut, F.; Bristeau, M.O.; Klein, R.; Perthame, B. A fast and stable well-balanced scheme with hydrostatic reconstruction for shallow water flows. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2004, 25, 2050–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.Z.; Duffy, C.J. A semidiscrete finite volume formulation for multiprocess watershed simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.J.R.; Cottrell, J.A.; Bazilevs, Y. Isogeometric analysis: CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2005, 194, 4135–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, L.J. Application of Emergency Water Environment Risk Area Partitioning in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 32, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Duann, Y. Development of roughness updating based on artificial neural network in a river hydraulic model for flash flood forecasting. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 125, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.B.; Song, X.X.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, H.J. An early warning and control system for urban, drinking water quality protection: China’s experience. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4496–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.M.; Vieira, D.A.; Wang, S.S.Y. One-dimensional numerical model for nonuniform sediment transport under unsteady flows in channel networks. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Natarajan, G. On the role of discrete mass conservation for non-Boussinesq flow simulations in enclosures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 104, 1283–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.G.; Tao, W.Q.; He, Y.L. Implementation of clear algorithm on collocated grid system and application examples. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B-Fundam. 2005, 50, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Yu, M.X.; Hu, B.; Wang, Z.G.; Yu, Z.Q. Analysis and assessment of the nutrients, biochemical indexes and heavy metals in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China, from 2008 to 2013. Water Res. 2016, 92, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Deng, P.X. Simulation of water quality variation in middle reaches of Yangtze River before and after operation of Three Gorges Project. Yangtze River 2018, 49, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.U.; Hua, G.U.; Lou, C.H.; Wang, G.Q. Simulation of Accidental Water Pollution in Da’ning Reservoir of Beijing South-to-North water diversion project based on MIKE21FM. South-To-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 11, 67–71. [Google Scholar]

| . | Continuity Equation | Momentum Equation | Water Quality Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| u v | c | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | - | ||
| - | - | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, X.; Fang, P. Accident Trend Prediction of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Heshangshan Drinking Water Source Area Based on Integrating a Two-Dimensional Water Quality Model and GIS. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11153998
Ding X, Fang P. Accident Trend Prediction of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Heshangshan Drinking Water Source Area Based on Integrating a Two-Dimensional Water Quality Model and GIS. Sustainability. 2019; 11(15):3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11153998
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Xiaowen, and Ping Fang. 2019. "Accident Trend Prediction of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Heshangshan Drinking Water Source Area Based on Integrating a Two-Dimensional Water Quality Model and GIS" Sustainability 11, no. 15: 3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11153998
APA StyleDing, X., & Fang, P. (2019). Accident Trend Prediction of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Heshangshan Drinking Water Source Area Based on Integrating a Two-Dimensional Water Quality Model and GIS. Sustainability, 11(15), 3998. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11153998




